Business Law 3
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
2 required elements in a Crime
Criminal Intent
Criminal Act
Criminal Intent
Intentional and knowing, willful act
Felonies vs. Misdemeanors
Felonies are crimes punished by more than a year; Misdemeanor is punished by less than a year
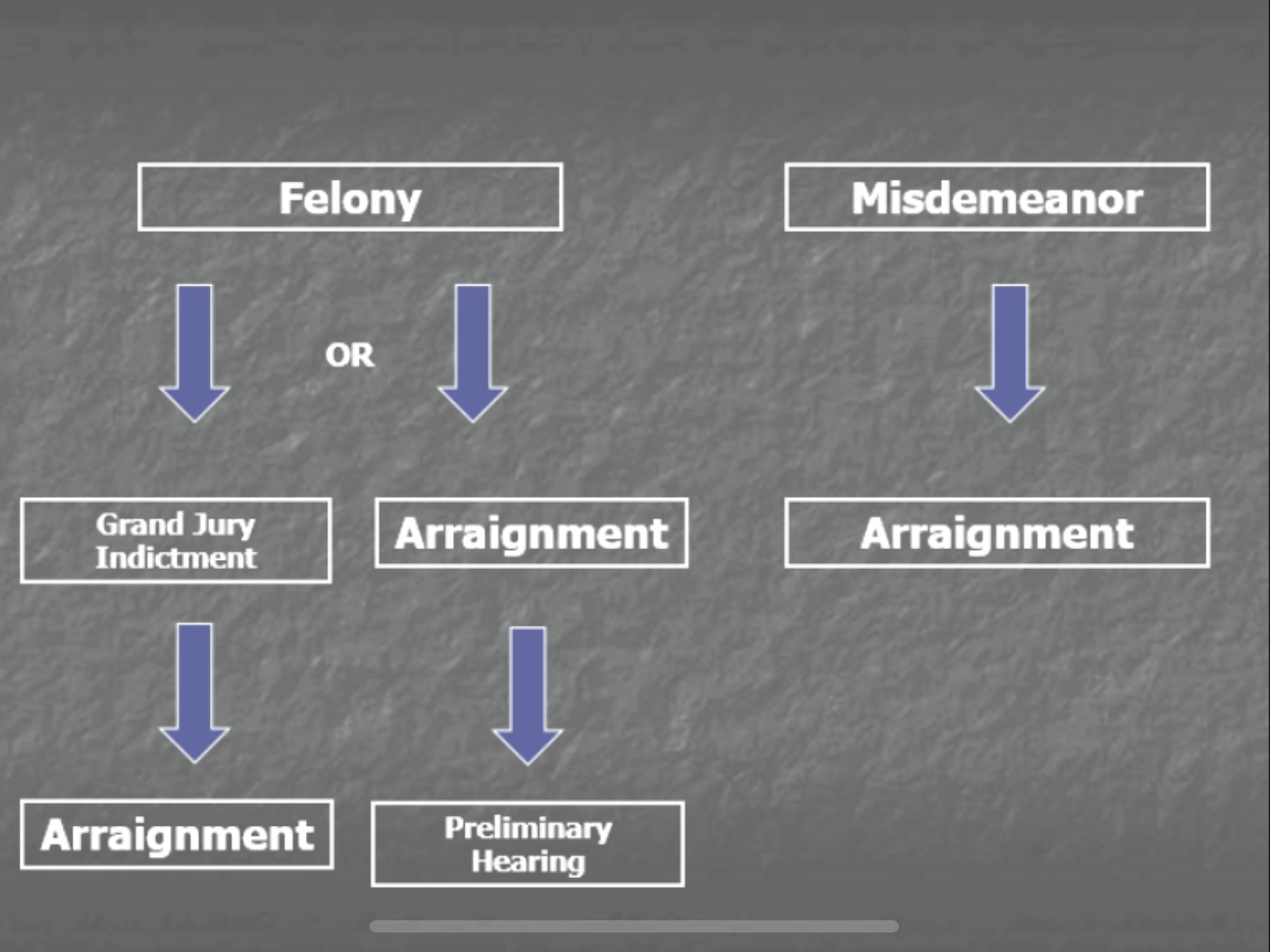
Felony and Misdemeanor Procedure
Guilty vs. Not Guilty vs. No Contest
Guilty: Admitting you did and all charges come, not defending self
Not Guilty: defending self
No Contest: Not defending self, but not admitting it; usually for defending self later in civil court
4th Amendment
Need Probable Cause for a warrant and a search
Exceptions where police do not need a warrant
Consent to a search
Evidence likely to be destroyed
No actual reasonable expectation of privacy
Car w/ Probable Cause
Person following arrest
Two protections under the 5th amendment
Self Incrimination; don’t have to answer polices questions
Double Jeopardy; cannot be tried for the same crime twice
6th Amendment’s 6 protections
right to a speedy and public trial
right to a trial by jury'
right to be informed of the charges against you
right to confront your accuser
right to subpoena witnesses in your favor'
right to counsel
Business related crimes
Fraud
Obstruction of Justice
Insider trading
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (RICO)
Endangering Workers
3 requirements for fraud
A false statement
Made regarding a material fact; important
With intent to defraud
non-employees cannot trade if?
they learn the information from someone with a duty to keep it confidential, AND
They provide a benefit for exchange of the information
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)
It is illegal to offer or give anything of value to foreign officials to influence official government action
Racketeer Influence and Corrupt Organizations Act (RICO)
Allow government to seize property belonging to an organization in a pattern of racketeering
Pattern: two or more predicate acts in a 10 year period
Associated Crimes
Conspiracy
Aiding and Abetting/Accessory
4 requirements of a conspiracy
plan or agreement
the defendant willfully joined the conspiracy
one of the co-conspirators knowingly committed an overt act
the overt act was committed in order to accomplish an objective of the conspiracy
Intentional Torts
Assault
Battery
Intention Infliction of Emotional Distress (IIED)
Invasion of Privacy
False Imprisonment
Fraud
Defamation
Injurious Falsehood
Intentional Interference with Contractual Relations
eggshell skull rule
If there is an intent to an action but an unintended outcome that results from that action, they are responsible for that outcome
Assault
Placing another in immediate apprehension for his/her physical safety
Battery
Touching another without justification or consent
Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress (IIED)
Outrageous, intentional conduct carrying a strong likelihood of causing mental distress
3 types of Invasions of Privacy
Misappropriation of a persons name or likeness
Intrusion upon a persons physical solitude
Public disclosure of highly objectionable, private information
False Imprisonment
Intentional, unjustified confinement of a nonconsenting person
Fraud
Intentional misrepresentation of a material fact that is justifiably relied on by someone, causing an injury
Defamation
Publication of untrue statements about another, leading to damage the persons character or reputation
2 defenses for Defamation
Truth
Public Figure/Public Official
Injurious Falsehood
Untrue statements disparaging the quality or safety of a competing businesses products or services
Intentional Interference with Contractual Relations
Wrongfully inducing someone to break a valid contract with a 3rd party
Negligence requirements
Duty of Care: have a responsibility to something; Business customer or employee, doctor, landowner, driver
Breach of Duty: failed to use reasonable care
Causation in Fact: injury was because of the negligence
Proximate Causation: Reasonable Forseeablility
Injury: some harm has to happen
Defenses for Negligence
Contributory/Comparative Negligence
Assumption of Risk
Strict Products Liability
the seller, manufacturer, or supplier is automatically legally responsible for any injury caused by a defective product
Types of Defects
Production Defect
Design Defect
Marketing Defect, Failure to warm
Defenses for Strict Products Liability
Assumption of Risk
Misuse
Contributory Negligence
3 Requirements for Abnormally Dangerous Activities
Activity involves high degree of risk of serious harm
the risk cannot be completely guarded against through the exercise of reasonable care
the activity is not one commonly performed in that area
2 ways one can Assume Risk
Implied by the circumstance
By agreement
Contributory vs Comparative Negligence
Contributory: The plaintiff is also to blame for acting negligent
Comparative: What % of the blame falls on the victim and what % falls on the defendant; each side is responsible for their share of the blame
Types of Tort Damages
Compensatory
Punitive
Compensatory vs. Punitive Damages
Compensatory: Compensate the plaintiff monetarily for the injuries they received
Punitive Damages: Punish the defendant to deter future wrongdoing of similar nature
Typically applies to intentional torts or willful and wanton negligence
5 Factors to consider for Business Organizations
Ease of Creation
Managerial Control
Continuity
Liability
Taxation
What to file when asserting managerial control in a partnership
Partnership Agreement
What to file and where to create a corp
Articles of incorporation; state government
3 levels of descending management for a corp
Shareholders
Board of Directors
Officers
Fiduciary Duty 2 requirements
Duty of Care; Duty of Loyalty
Requirements for defense of violation of Fiduciary Duty
Decision was made in good faith
Reasonable care
With the corporations best interest in mind
Requirements for “piercing the corp veil”
Some sort of unity of interest; using corp assets as own
Some type of fraud
2 difference between limited and traditional partnership
register with the gov
has to have two types of partners
General: manage business
Limited: provide capital