Chem Midterm Pt 2.
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
An isotope is an atom of the ____ element with a different number of _____.
same; neutrons
What is the mass of this isotope? U-236
236g/mol
One atom has 40 protons and a mass of 92, the second atom has 40 protons but a mass of 87. What is this atom’s identity and why are the mass’ different?
They are isotopes of Zr, xzirconium
What is the average atomic mass of hydrogen if Hydrogen-1 is 99% abundant, Hydrogen 2 is 0.5%, and Hydrogen-3 is 0.5%.
1.01 g/mol
(1×99%)+(2×0.5%)+(3×0.5%)
What is the average atomic mass of Lithium if Lithium-7 is 92.5% abundant and Lithium 6 is 7.5% abundant?
6.93 g/mol
(7×92.5%)+(6×7.5%)
who was known for the thinking substances were composed of different portions of what the earth was made of?
Aristotle/Plato
Who though the world was made of indivisible particles called “atomos” (cutting rock)
Democratus
Who studied the weight of element and compound, noticed that matter always combined to form a whole number ratio based on weight/ volume (proposed first atomic theory?
John Dalton
Who discovered electron with his Cathode Ray Tube Experiment, found positive and negative charges with his model Plum Pudding?
JJ Thomson
Who discovered the nucleus of an atom and atoms were mostly empty space, Gold Foil experiment (atoms were small and dense) + inside/- outside
Ernest Rutherford
Who thought that e- moves in fixed energy orbits (Bohr model like planets)
Niehls Bohr
where are protons located?
in the nucleus
where is the neutrons located?
in the nucleus
where are electrons located?
Anywhere outside of the nucleus (electron cloud)
Who created the mathematocal equation to find the position of e- and quantum mechanics?
Erwin Schrodinger
What does Rutherford find out with the Gold Foil experiment?
atoms are mostly empty space/nuclei is super small/ if particles hit + they will repel
Why is the Bohr model inaccurate?
NOT ACCURATE, does not spin around the orbitals
What is the atomic number of Vanadium?
23
What is the element symbol for sodium?
Na
what is the name of the element Sn?
Tin
what is the atomic mass of Pt?
195.08 g/mol
What changes the identity of the element?
the # of protons
How many protons and electrons are in Na?
11 p+ 11e-
How do you find how many neutrons are in a element
atomic mass- # of protons/atomic number = # of neutrons
How many neutrons are in Mn?
30 n
How many neutrons are in Y?
50 n
What are the rules to drawing Bohr models?
write the element symbol in the middle
find the # of rings/energy levels
follow 2, 8, 8 rule (1st ring:2; 2-infinite:8)
What does the Bohr model help us find?
the number of valence electrons a element has
What are isotopes?
atoms of the same element with a different # of neutrons
Who is the biggest atomic radius? (sulfur, strontium, oxygen)
Strontium, Sulfur, Oxygen
Who has the biggest electronegativity?(sulfur, strontium, oxygen)
Oxygen, Sulfur, Strontium
Which one is the “periods”
the horizontal rows
Which are “groups”?
vertical columns
Properties of metal?
good conductors of heat/electricity, lustrous, malleable, ductile, solid at room temp
Properties of nonmetals
poor conductors of heat/electricity, brittle, dull
Properties of Metalloids
Fair conductor of heat and electricity, looks metallic but brittle, mostly forms anions (more closely related to nonmetals)
What is the name of Family 1 A and some of its properties?
Alkalai Metals; 1 ve-, explosive with water to form hydroxides, extremely soft, can cut with a knife; more reactive as you move down; needs to be in oil
What is the name of Family 2A and its properties?
Alkalai Earth Metals; 2ve-, reacts with water to form hydroxide; soft (not as much as Family 1A)more
What is the name of Family 7A and properties?
Halogens; 7 ve-, react with hydrogen to form halide; reacts readily; more reactive as they move up
What is the name of Family 8A and properties?
Noble Gases; 8ve-, already stable, do NOT bond; more dense moving down, extremely useful in nature.
Lowest to highest atomic radius (H, Fr, He)
He, H, Fr
What is electronegativity?
a measure of how much an atom attracts e- to itself (homeless wanting money)
What is ionized energy?
the energy required to remove na e- from an atom
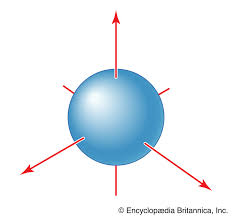
What orbital is this
S orbital
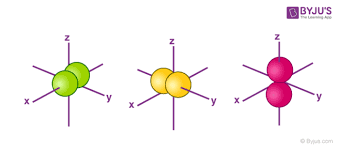
What orbital is this?
p orbital
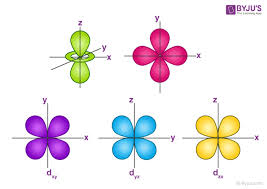
what orbital is this?
d orbital
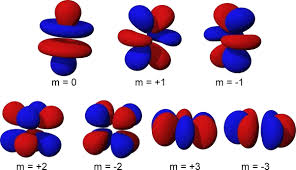
what orbital is this?
f orbital
What are the 3 rules for electron configuration?
Aufbau, Pauli, Hund’s
What is Aufbau principle?
electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy (start with 1s)
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
no 2 e- in the same atom can have the same spin, 2 opposite parrallel spins
What is Hund’s rule?
When filling orbitals within a subshell, electrons will occupy each orbital before pairing up
How many orbitals and electrons are in subshell s?
1, 2e-
How many orbitals and electrons are in subshell p?
3, 6e-
How many orbitals and electrons are in subshell d?
5, 10e-
How many orbitals and electrons are in subshell f?
7,14 e-
How to write Oxygen’s electron configuration?
1s22s22p4
How does electronegativity, atomic radius, and ionized energy related?
The more electronegativity the element is, the more ionized energy it needs to remove the electron. The elements with higher electronegativity have a smaller radius
Is magnesium a cation or anion and oxidation state?
cation, Mg2+
Lewis dot structures show what?
lone pairs, bonds, and lone e-
What does a compound contain?
nonmetal and metal
How are Ionic Compounds stuck together?
electrostatic force
Is there a tangible bond between atoms
no, held together by electrostatic force
Does the dots get drawn on the metal or nonmetal when doing bracket notation?
Nonmetal
When do you need to write a Roman numeral?
when the metal is a transition metal
Properties of Ionic compounds
strong/stable, dissolves in water, HIGH melting and boiling point, conducts electricity and heat
Name of K2S
Potassium Sulfide
Name of CoAs2
Colbalt VI Arsenide