Unit Three: Mangroves/ Marshes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Salt marshes are
coastal grasslands that are flooded and drained by the tides
What conditions foster the development of salt marshes?
1. protection from waves
2. gradual slope thru intertidal region (passive margin)
3. temperate. subpolar latitudes
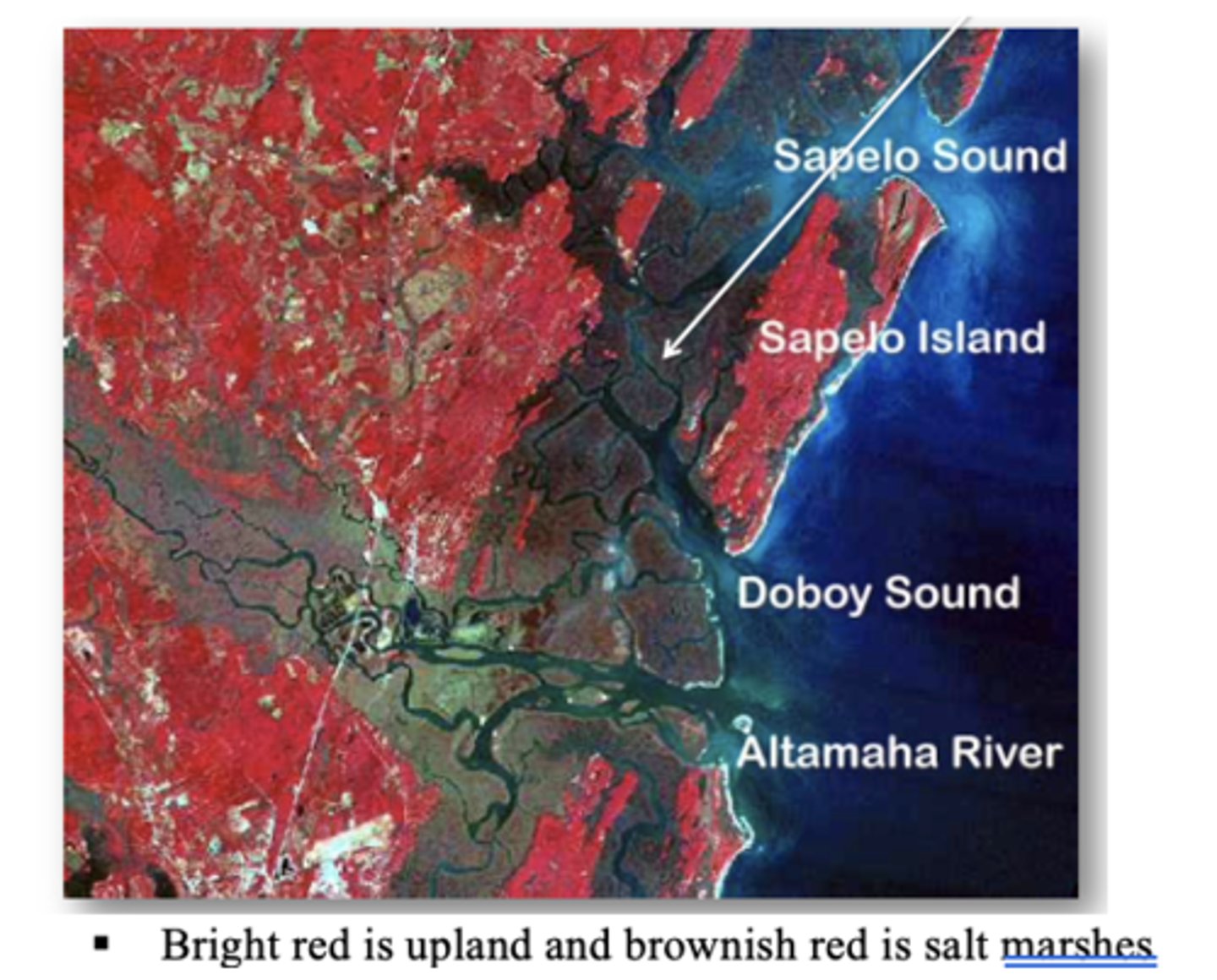
Where are the most extensive salt marshes found?
southeastern US, GA
Latitude's affect on primary production
high latitude = low PP
low latitude = high PP
Tidal drainage network
-tidal creeks
-brings water/ organisms into marsh
Coastal wetlands provide
storm protection, C sequestration, habitat, tourism, and more
What effects do salt marshes have on marine environments?
-reduced flooding (accretion)
-protection from erosion (trapping sediments)
-improved water quality (biological filters)
Three common plants found in salt marshes
1. Spartina (cord grass)
2. Juncus (black needle brush)
3. Salicornia
Challenge: osmotic uptake at roots
-Solution 1: maintain water vis osmolytes, waxy leaf coating, inc. SA, water storage tissues
-Solution 2: salt export via salt crystals, salt excretion
Challenge: O2 availability in sediments
Solution: roots grow close to surface, air passages in aerenchyma tissue that can also inc. in volume
Zonation in salt marshes
-Tall-form cordgrass: more frequent inundation, well drained sediment, lower salinity, higher O2, lower H2S
-Short-form cordgrass: less frequent inundation, poorly drained sediments, higher salinity (evaporation), lower O2, higher H2S
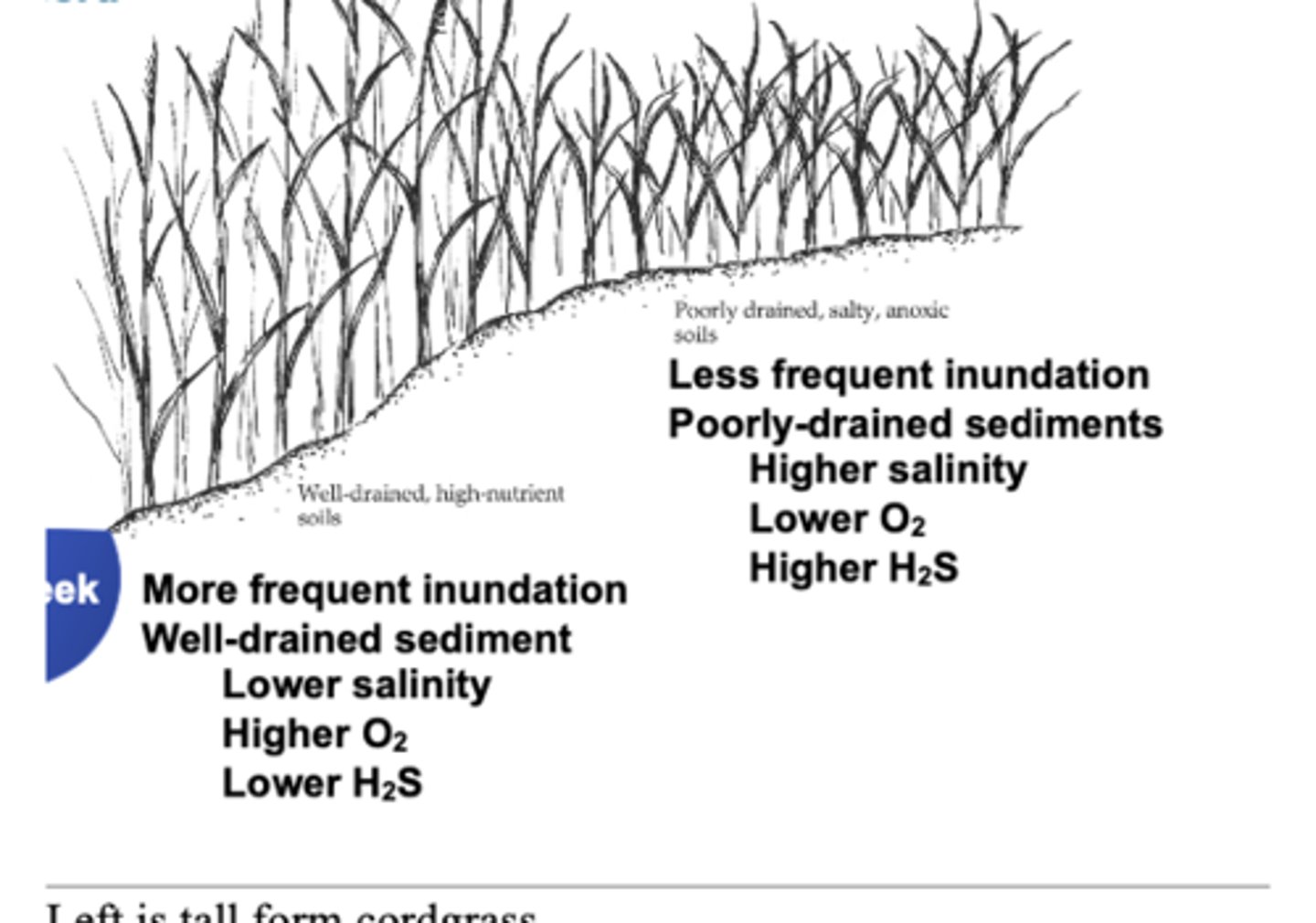
Physical factors effecting zonation
tolerance
Biological factors effecting zonation
-competition
-juncus is bad competitor once water is salty
-salicornia is bad competitor in less inundation
How is primary production processes through the food web?
-salty, high lignin content --> not great food
-detritus-based food web
What conditions foster the development of mangrove forests?
1. protection from waves
2. gradual slope thru intertidal regions
3. tropical latitudes/ no freezing temps
Salt marshes and mangroves are found in ___ environments but different ___.
environments; latitudes
Both salt marshes and mangroves act as
biological filters
Common Trees in mangrove forests
-Rhizophora (red mangrove): most inundated, aerial propogation, roots for stability/ O2
-Avicennia (black mangrove): horizontal roots for O2
-Laguncularia (white mangrove): least inundated, highest elevations
What are the challenges for plants living in a mangrove environment?
1. osmotic uptake
2. O2 availability in sediments
How does Rhizophora adapt to the challenges?
-tolerates 60-65 psu
-organic osmolytes
-aerial propogation roots
-lenticels (pore for gas exchange)
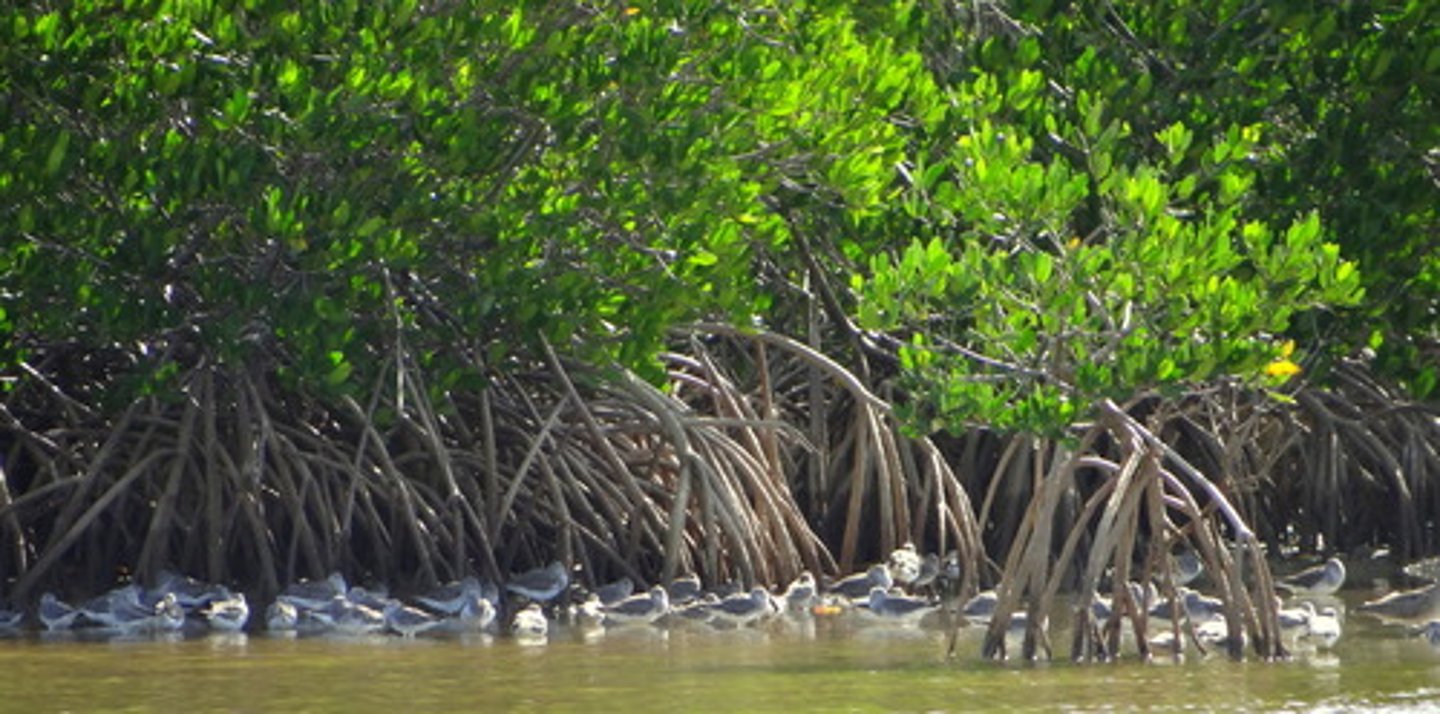

How does Avicennia adapt to the challenges?
-tolerates >90 psu
-salt-secreting glands on leaves
-lenticels
0pneumatophores (above ground roots for O2)
-organic osmolytes

Zonation in mangrove forests is affected by
physical tolerance and competitive ability
How is primary production process through the food web of a mangrove forest?
-very few herbivores bc trees hard to eat
-detritus-based food web
Blue Carbon
organic C stored as plants/ sediments in marine ecosystems
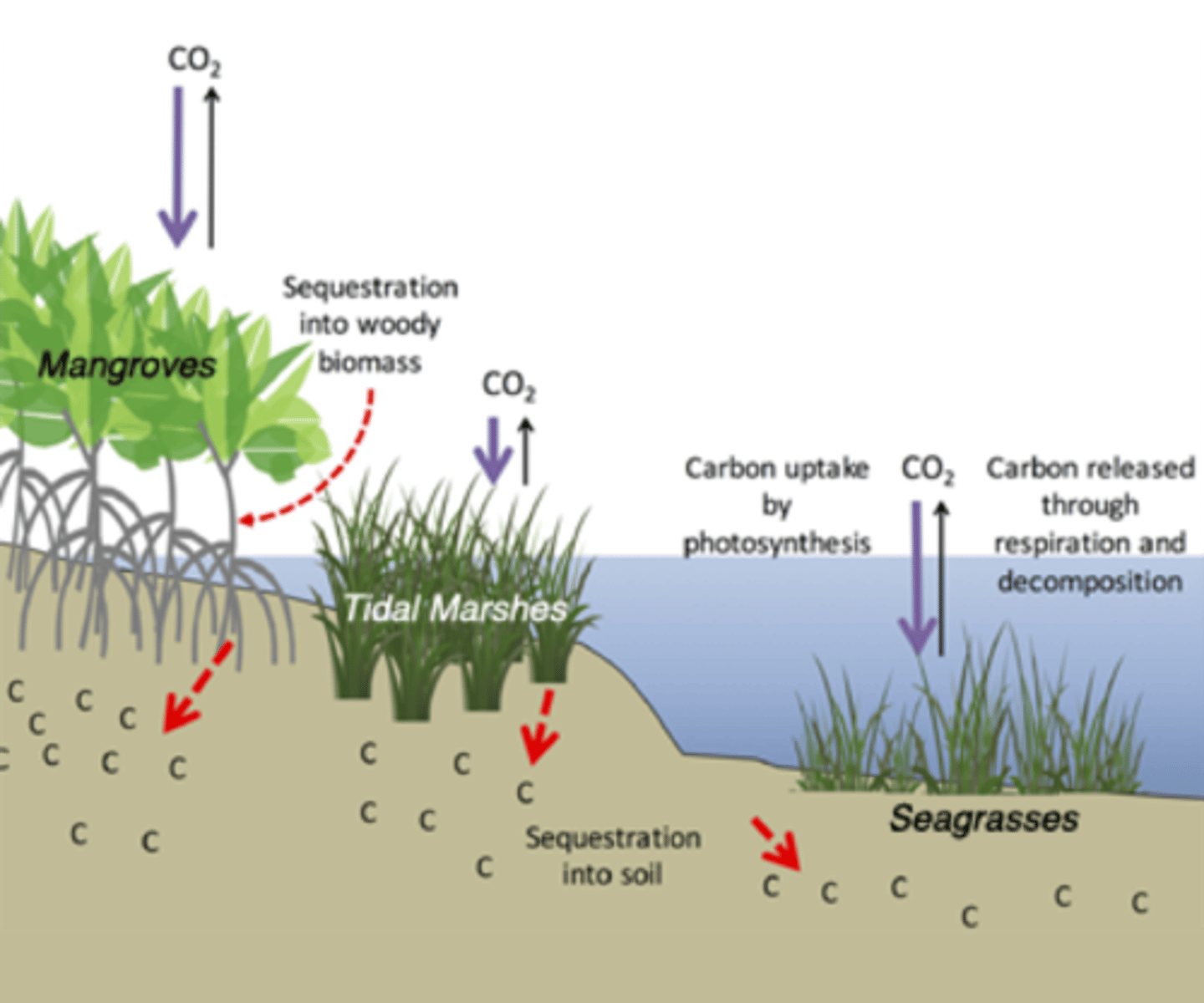
Why are salt marshes, mangroves, and seagrass meadows important?
-they are major pools of carbon storage
-sequesters CO2 from atmosphere
Loss of Blue Carbon does what?
releases CO2 into atmosphere