World War I and the End of Empires
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
German Economy
German industrial revolution was marked by a marriage of convenience between large-scale agriculture and heavy industry
Promoted the expansion of the latter without threatening the socioeconomic position of the former
Called the marriage of iron and rye
Concentration and centralization
sectors of heavy industry (iron, steel, coal, armaments, chemicals, and electrical products) were dominated by a handful of gigantic firms
Ex. the Krupp company
Trade Deficit of Germany
At this point German prosperity was very dependent on foreign sources of industrial raw materials and foodstuff
Germany needed to expand her exports of finished industrial products to cover her mounting trade deficit
What made it difficult for Germany to expand her markets?
global markets were being penetrated, dominated and increasingly monopolized by the three global powers: the United States in Latin America, Great Britain in East and South Africa and in South Asia, and France in West Africa, the Balkans, and Russia
This meant that when Germany tried they encountered stiff competition from British and French firms
This raised further their concerns about their ability to grow their economy
German military
German Empire was losing its power in Europe due to the combined armed forces of France and Russia which outnumbered them
This led to the creation of the Schlieffen Plan
Schlieffen Plan
Born out of the desire to have a concentration of German military power in the west in the expectation that the numerically inferior French army could be defeated within a sex-week period
Afterwards, Germany would transfer their attention to the eastern front to meet the Russian army
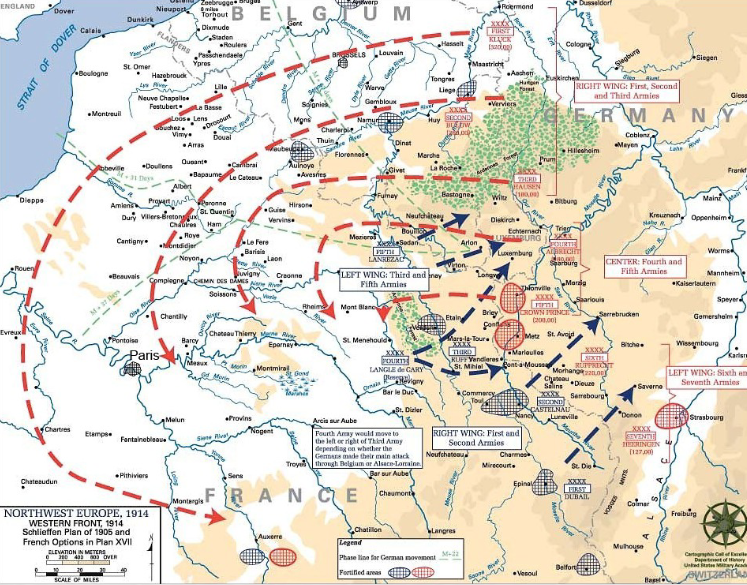
What were the assumptions the Schlieffen Plan was based on?
overwhelming German numerical superiority against France
Inability of Russian Empire to fight back strongly
What was the result of the Schlieffen plan and why?
It failed
1913 - France extended the period of national military service from two to three years which resulted in a much larger amount of soldiers in the French army, making it equal to the size of the German army by 1915 to 1916
Russian government had launched a program of strategic railway construction which gave them a better connection to the western frontier
Military Alliances 1914
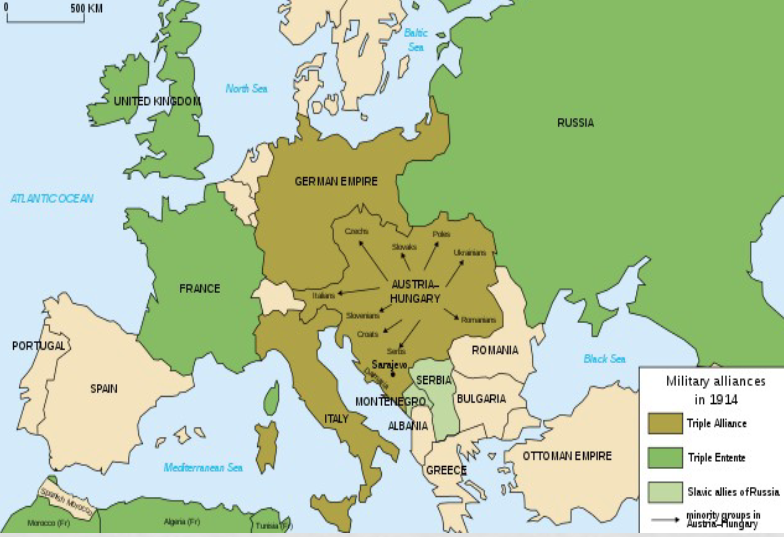
What was the result of the dispute between Austria-Hungary and Siberia in 1914?
June 28th Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated
All that was known for sure at the time was that the assassins were ethnic Serbs (part of the Black Hand) and had committed the crime with Pan-Slavist sentiments
How did Germany respond to the Ferdinand assassination and what did this lead to?
Government assured the Austrian government of its support in the event of hostilities
Austria declared war against Serbia on July 28th, 1914
This lead to Russia fully mobilizing on July 30th as a precaution to protect Russia’s frontier with Germany
What were Germany’s goals for the war?
Permanent destruction of French military power by annexing the territory where France’s principal fortresses were (near the German frontier)
Occupation of France’s major ports on English Channel
Imposition of a crushing financial indemnity that would prevent France from reconstructing their armed forces
Wanted to thrust Russia back as far as possible from Germany’s eastern frontier and her domination over non-Russian peoples
Ultimately: establish imperial Germany as the hegemonic power of Europe
Who was Basil Zaharoff?
Was one of the most notorious arms dealers of his time
Became a representative for Vickers, Maxim & Co. which was a British armaments company that made machine guns, warships, and submarines
He would sell them to Greece, but then also turn around and sell them to the Ottoman Empire and Russia
Suppression of Domestic Criticism
Russia: Tsar suspended the Duma (Parliament) during the war
Germany: Political Bureau of the General Staff created a virtual military dictatorship
England and France: Prime Minister David Lloyd George and Premier Georges Clemenceau acquired emergency powers in parliamentary regimes
Propaganda behind the enemy lines examples
Military alliance between Germany and Turkey resulted in the proclamation by the Ottoman sultan of a jihad (holy war) which enjoined the Muslims to rise in rebellion against their Christian European masters
Great Britain concentrated on inciting an Arab-Moslem revolution within the Turkish Empire
France directed their political warfare campaign at the national groups under Austro-Hungarian rule
Ottoman entry into first world war
Began 29 October 1914 when it launched the Black Sea Raid against Russian ports
Following the attack, Russia and its allies (Britain and France) declared war on the Ottomans in November 1914
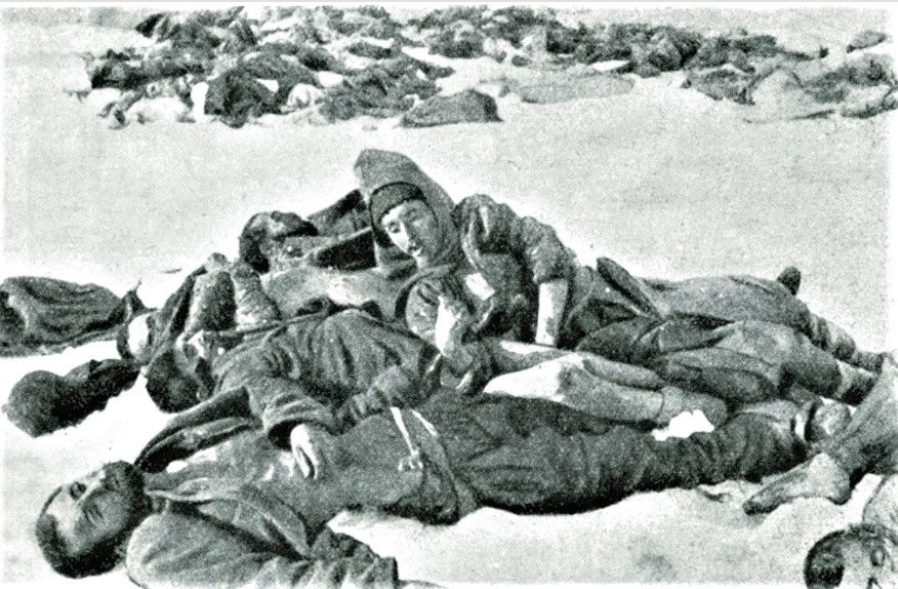
Battle of Sarikamish
Sent 1/3 of army to fight on the eastern front, most of them died in the battle
Died because of the cold
No actual war, died in two days

Gallipoli Campaign
Attempt by the Allied fleet to force the Dardanelles in February 1915 that failed and was followed by an amphibious landing on the Gallipoli peninsula in April of 1915
Britian and france offered this to help russia with their famine if they helped them to take the Dardanelles which was ottoman land
Ottoman public opinion on defending the land
Britian and france couldn’t get past the defence, it was the strongest defence
britain employed australian and new zealand colonies as well as canadian, etc. to aid in the campaign - shows how imperialism combined with nationalism works together to control people
A lot of people died just because of british pride
Allies were unsuccessful due to ottoman defense
Arab revolt was indirectly started* will come back to this
Bolshevik revolution was an indirect result of this
Ultimately the Allied attempt at securing a passage through the Dardanelles proved unsuccessful
Arab revolt
British officials sought out a Muslim dignity who might be persuaded to ally with the Entente powers and to serve as a counterweight to the prestige of Ottoman Sultan/Caliph
they found amir of Mecca Sharif Husayn Ibn Ali. His office was the most prestigious Arab-Islamic position within the Ottoman Empire
Agreement was reached, Husayn’s ambitions were secured by a Great Power guarantee, and Britain acquired a well-placed Muslim ally
The revolt started in June 1916 - Arabs joined British forces in the region and defeated the Ottomans
Sharif Husayn
Was an individual responsible for maintaining the two holy cities (Macca and Medinah) and ensuring that the annual pilgrimage was safely conducted
Amir of Mecca was selected from among families who were direct descendants of Prophet Mohammad
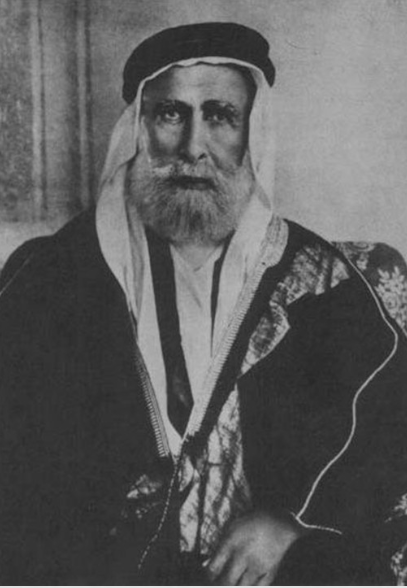

Letters Between Sharif Husayn and McMahon
Sharif Husayn exchanged 10 letters with Henry McMahon (British High Commissioner in Egypt) setting forth the conditions that might persuade him to enter in a war against the Ottomans
What Husayn requested:
Independent Arab state in Arabian peninsula, Greater Syria (including Lebanon and Palestine) and the provinces of Iraq
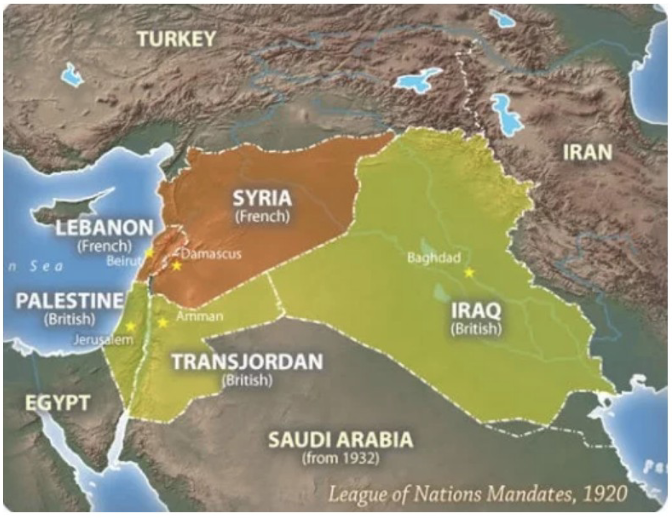
Skyes-Picot Agreement
Negotiators from Britain and France drew up a secret treaty in May 1916
They divided the Arab Middle East between them
Agreement recognized the long-standing French claims to Syria by awarding France a direct control along the Syrian coast from southern Lebanon into Anatolia
British position in Iraq was guaranteed. Britain gained the right of direct control over the southern portion of Mesopotamia
Independent Arab State promised to Husayn was designated as a confederation of states lying in the two zones of British and French indirect influence
This led to the formation of modern middle east as we know it
Balfour Declaration
“Advance booking” of a new state
British made this declaration in order to appeal to the Jewish people and to secure control over the territory adjacent to Suez Canal
Britain agreed to favor the establishment of a Jewish national home in Palestine in order to do so, and made this declaration in November 1019 in a letter from British Foreign Secretary Balfour to Rothschild, who was a prominent British Zionist
Nationalist Rebellions in Austria-Hungary
Principle of national self-determination
Liberation of the Italian, Romanian, southern Slav, Czechoslovak, and Polish subject nationalities of the Habsburg Empire
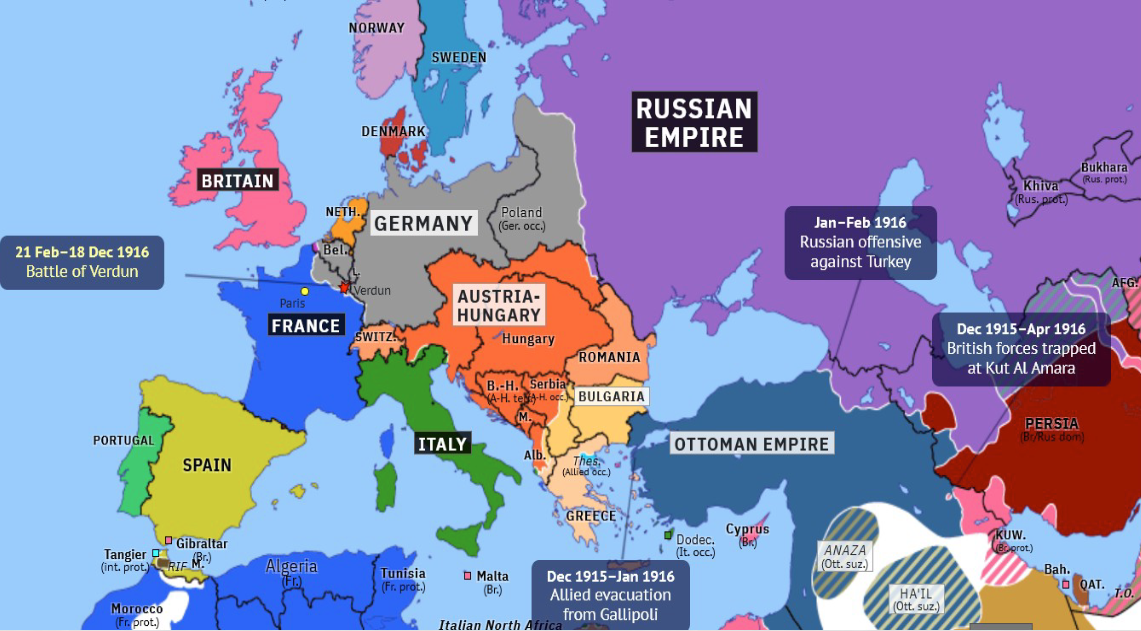
Western Front of the Battle of Verdun (February-December 1916)
France prepared to hold Verdun at all costs
General Philippe Petain (1856-1951) the new commander. became a hero in France
the French lost 315, 000 men killed or wounded. the Germans suffered 281, 000 casualties
Battle of the Somme (July-November 1916)
British Offensive against the Germans
Ended in mid-November 1916, Britain had lost 420, 000 men killed and wounded
The French lost 200, 000 men in what was primarily a British offensive
It cost the Germans 650, 000 soldier to hold on
Bolshevik Revolution in Russia
November 7, 1917
The Bolshevik leader V. I. Lenin had been granted safe transit by railway across German territory from his haven in neutral Switzerland to the Russian capital
Lenin’s publicly announced program included the immediate cessation of the war, if necessary by a separate peace with the Central Powers
Soviet Government
They opened separate peace negotiations with the Central Powers in the city of Brest-Litovsk on December 3, 1917
March 3, 1918 - Peace Treaty between Germany and Russia
New states
The Bolshevik regime was forced to cede virtually the entirety of its non-Russian territories in Europe: Poland, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, and Finland in the north, Ukraine and the provinces of Transcaucasia (Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan) in the south
Independent states of Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, and Estonia under German military protection
The creation of German client states in Ukraine, the Crimea, Georgia, and Armenia, coupled with Turkish control of the Moslem state of Azerbaijan
Poland was established in the center of Europe
German attack to France 1918
On March 21 1918, 62 divisions of German military forces launched what was expected to be the long-awaited breakthrough that would drive France out of the war and Anglo-American forces out of the continent
The German offensive ground to a halt on July 15, and three days later the Allied armies mounted a counteroffensive that by August 8 began to take on characteristics of a rout
German Revolution
Units of the German Navy refused to set sail for a last, large-scale operation in a war they believed to be as good as lost, initiating the uprising
The sailors’ revolt, which then ensued in the naval ports of Wilhelmshaven and Kiel, spread across the whole country within days and led to the proclamation of a republic on 9 November 1918, shortly thereafter to the abdication of Kaiser Wilhelm II, and to German surrender

Armistice
On November 11 the German delegates who had been negotiating with Allied military representatives in a forest north of Paris signed an armistice
it provided for the immediate evacuation of all French and Belgian territory as well as all German territory west of the Rhine River
Why did the USA Intervene?
By the spring of 1915 the British navy succeeded in driving German warships and merchantmen from the high seas
This forced Germany into total reliance on neutral shipping for its foreign trade
But Great Britain proceeded to impose a blockade on Germany that effectively severed its access to neutral sources of supply and precluded its use of neutral means of transport
Decrease in Trade
Germany’s foreign trade with neutral countries such as the United States slowed to a trickle, while the nations in the anti-German coalition took up the slack by importing huge quantities of munitions, food, and other necessities from Germany’s traditional foreign suppliers
Submarines
Germany was driven to reply on the use of submarines, which could not be easily detected beneath the surface of the sea, to harass British merchant shipping in retaliation against the blockade
German government issues on February 4 1915 the definition of a war zone around the British Isles, within which all enemy ships would be liable to destruction without warning
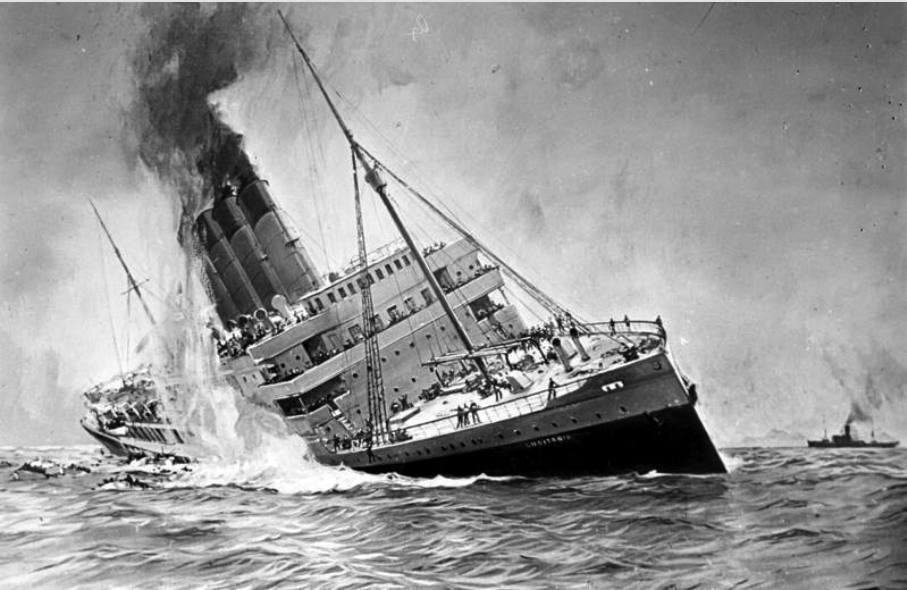
Lusitania
Between February and May 1915, 90 ships went to the bottom in this newly defined zone
On May 7 the British passenger liner Lusitania, laden with ammunition and other contraband material purchased in the United States was sunk by a german submarine off the coast of Ireland
128 American citizens died

US Entente Rapprochement
Strong sense of kinship with British traditions and institutions felt by key members of the American government, beginning with the president himself
American economic prosperity and corporate profits had become increasingly dependent on orders from Germany’s enemies for munitions, machinery, textiles, grain, oil, copper, steel, and other products
Unrestricted submarine warfare
Germany announced the unrestricted submarine warfare on January 31, 1917
Many of those American trade vessels that risked the Atlantic crossing were sent to the bottom by German U-boats as they entered the war zone
US declaration of war against Germany April 6 1917
US Army
April 1917 the American regular army of 130, 000 officers and men was smaller than the Belgian army and poorly trained
In the early summer of 1918, after the introduction of conscription and the advent of a military training program, the American military and naval forces (which by the end of the war had swollen to 4.8 million persons) began to make a critical contribution to the Anglo-French effort on the western front.