C1- Investigating the reactions of acids, including temperature changes that occur
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
metal + acid →
salt + hydrogen
acid + base →
salt + water
acid + metal carbonate →
salt + water + carbon dioxide
whats base is this
base is a substance that will neutralise an acid; an alkali is a soluble base
most metal oxides are:
insoluble
soluble
insoluble
sodium hydrogen and potassium dissolve in water (alkalis)
Acids are very specific chemicals:
They are soluble
They release H+ ions when dissolved in water
They all have a pH less than 7
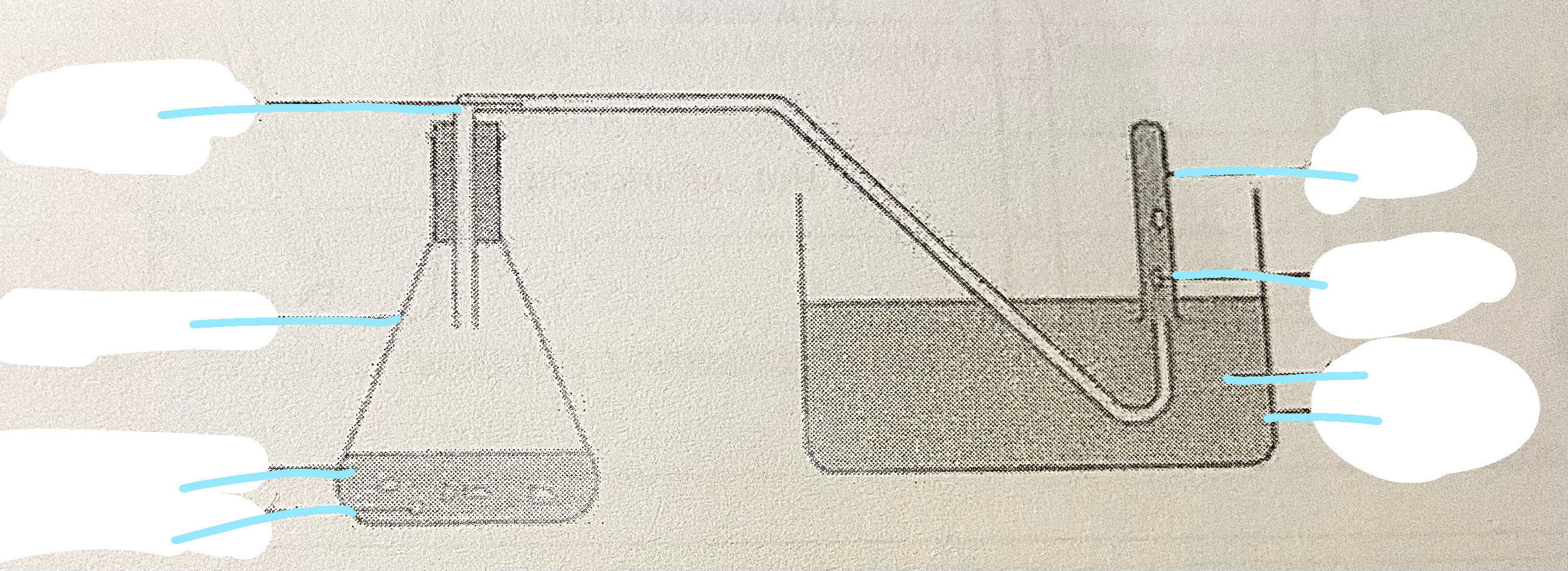
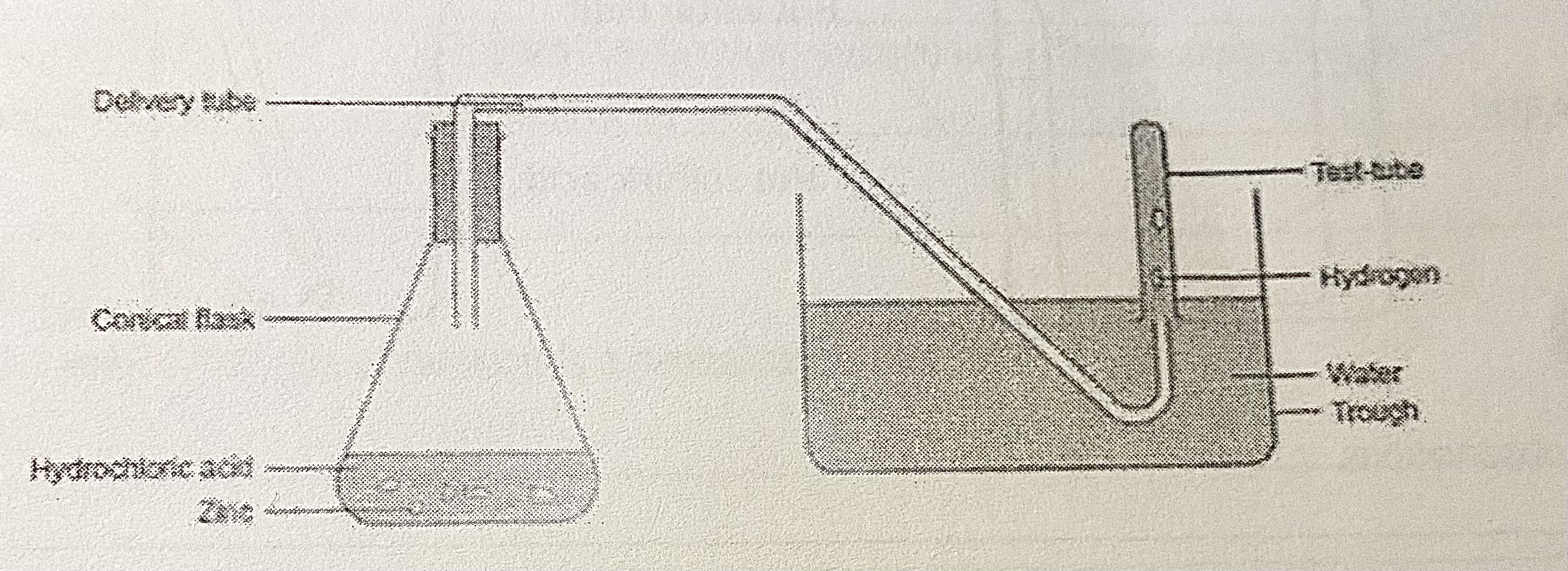
Method
Method
Fill the basin and test-tube with water, let the test tube rest on the bottom of the basin
Measure 15 cm° of hydrochloric acid using the measuring cylinder and add to the boiling tube
Add the magnesium strip to the boiling tube - ensuring that the magnesium is fully immersed in the acid by swirling and allow the reaction to proceed for 10s
After 10s, place the delivery tube onto the boiling tube and place the end of the glass tube underneath the test-tube.
Hold the test-tube upright and collect the gas produced. Once the test-tube is full, stopper the tube and place it in the test-tube rack.Light a splint. Remove the stopper of the test-tube and hold the lit splint at the top of the test tube.
Observatios
fizzing in boiling tube
magnesium disappears
boiling
lig tube becomes warm and heat is given off
gas rises to the to the test tube as hydrogen is less dense than air and insoluble in water
lit split over test tube squeaky pop