Stage 2 Biology - Topic 2 Cells
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
cell theory
idea that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
extracellular space
space outside the cell
cell lumen
space inside the cell
cell adhesion
membrane proteins cause adjacent animal cells to stick to each other within tissues
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes.
integral proteins
Integral proteins that span the membrane and are fixed in the bilayer
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; and move in and out of the membrane
cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and influences membrane fluidity
glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
glycolipids
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to lipids.
phospholipid
a molecule containing a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
hydrophilic
Attracted to water
hydrophobic
Water fearing
polar
Molecule with partial charges. Mixes with water.
non-polar
a molecule with no overall charge and does not mix with water
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane
prokaryotes
Simple, unspecialised cells that are very small.
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Nucleus
It is surrounded by a double membrane. Its role is to protect and confine the genetic information (DNA) of the cell
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
A membranous chain of connected and flattened sacs which are coated with ribosomes on their outer surface. This allows them to synthesise and modify proteins. It typically surrounds, or is close to, the nucleus.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
A membranous chain of connected and flattened sacs which are not coated with ribosomes. They are responsible for the production of lipids in a cell.
Ribosomes
tiny structures made of ribosomal RNA and proteins that fold into a large and small subunit. They assemble polypeptide chains to create proteins.
Golgi Body (Apparatus)
Stacked flattened sacs that are the site of protein sorting, packaging, and modifying. Protein-filled vesicles often fuse with or bud off this organelle.
Lysosome
A membrane-bound vesicle that contains digestive enzymes. Is responsible for breaking down cell waste, acting like a garbage disposal.
Mitochondria
An organelle with a highly folded inner membrane surrounded by a second outer membrane. Site of aerobic cellular respiration producing ATP.
Chloroplast
A double membrane-bound organelle that contains flattened, fluid-filled sacs that allow the process of photosynthesis to take place
Vacuoles
A membrane-bound sac that is used for water and solute storage. It can also play a role in maintaining plant cell structure.
plasma membrane
a selectively permeable barrier between the intracellular and the extracellular environment. It is made of a phospholipid bilayer which is studded with many molecules
cell wall
A sturdy border outside the plasma membrane that provides strength and structure to plant, bacterial, and fungal cells.
Vescicles
A small membrane-bound sac that transports substances into or out of a cell, or stores substances within a cell
Cytoskeleton
A dynamic linkage of many protein filaments that start at the nucleus and reach out to the plasma membrane. It is critical for maintaining shape and transporting vesicles around the cell.
Flagellum
Small hair-like structures on the outside of the plasma membrane that perform a rhythmic waving to help move substances through tubes, such as clearing mucus and dirt from airways.
autotrophs
Obtain energy from inorganic sources, such as light trapped by chlorophyll.
heterotrophs
Obtain energy from other organisms, their products, or remains.
photosynthesis
the process of capturing sunlight energy to power the production of glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. This is the only biological process that can capture energy from the sun and convert it into chemical compounds for metabolism.
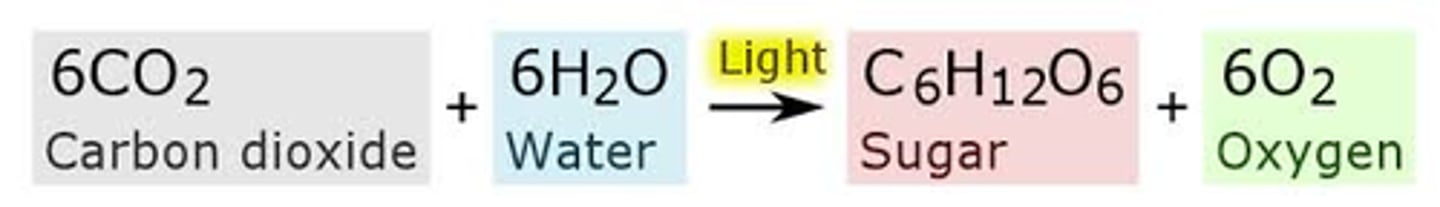
thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
granum
stack of thylakoids
stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
respiration
a process that breaks down high energy compounds (such as glucose) to produce the molecule ATP, which is a more usable form of energy.
cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electron transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.
aerobic respiration equation
glucose + 6 oxygen --> 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water + 30-32 ATP

lactic acid fermentation
occurs in animals in the cytoplasm in the absence of oxygen
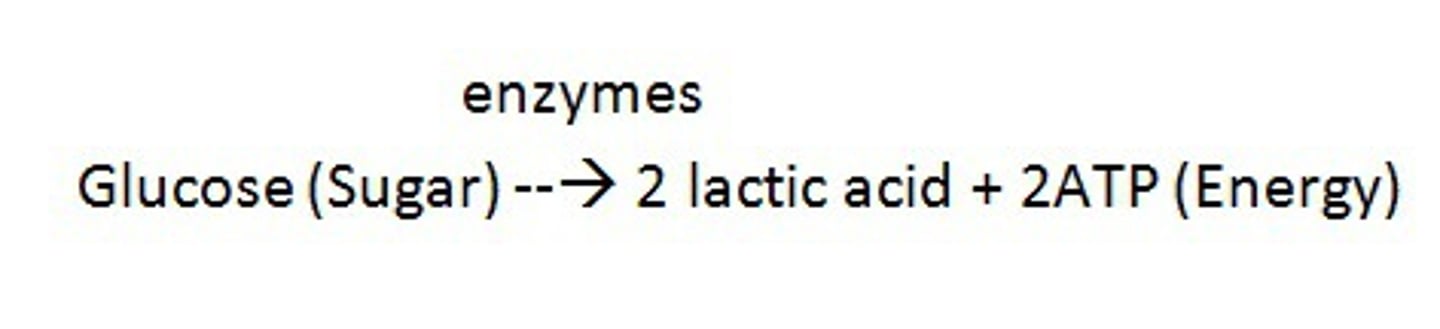
alcohol fermentation
occurs in plants and yeast, in the absence of oxygen
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
compound used by cells to store and release energy
intracellular
within the cell
extracellular
outside the cell
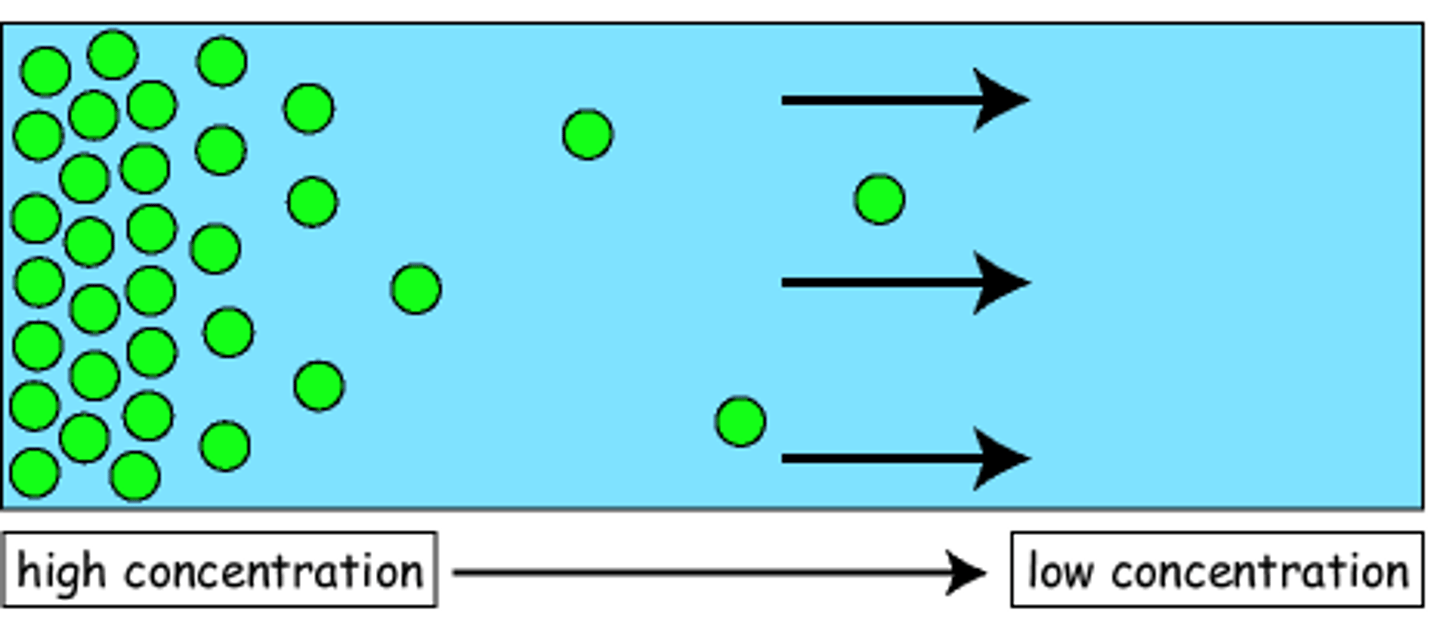
simple diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
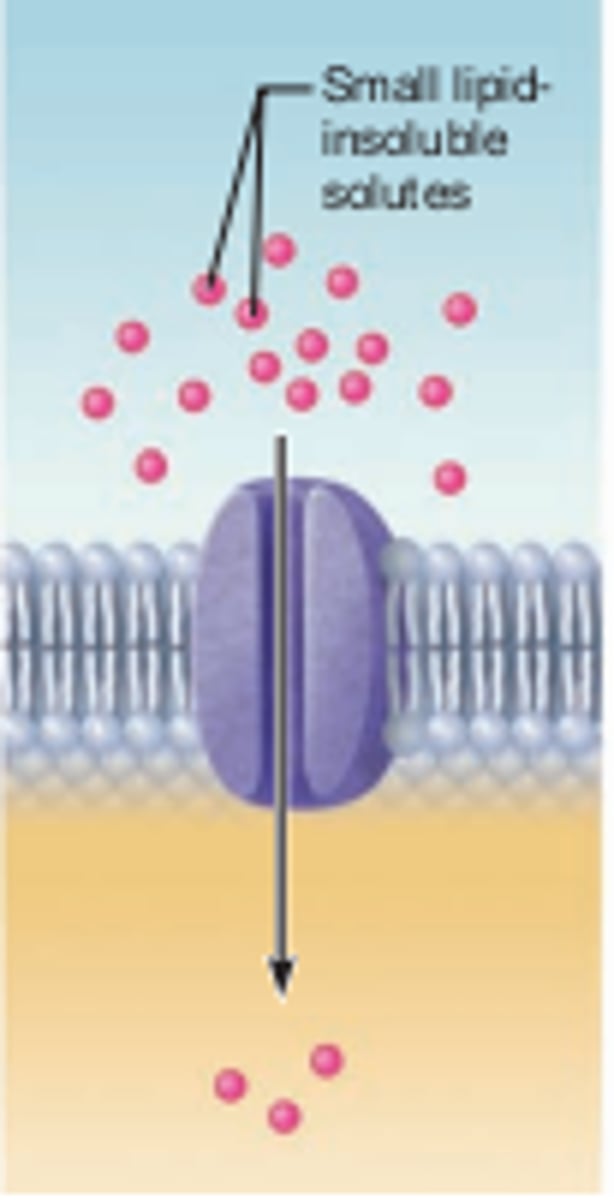
facilitated diffusion
process of diffusion in which molecules pass across the membrane through cell membrane channels
osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane to areas of high solute concentration
tonicity
a measure of the osmotic pressure gradient of two solutions separated by a semi-permeable membrane
isotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
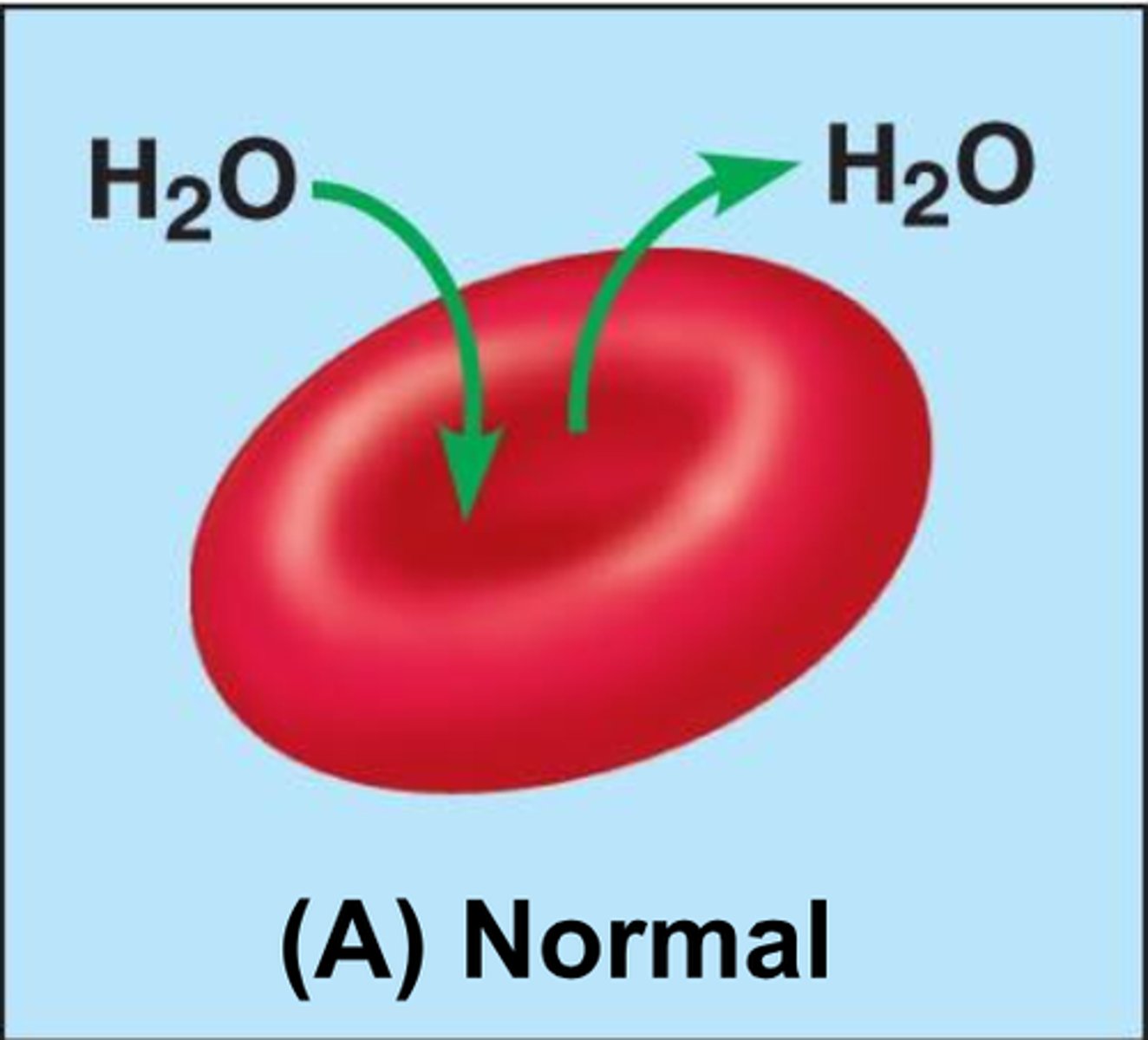
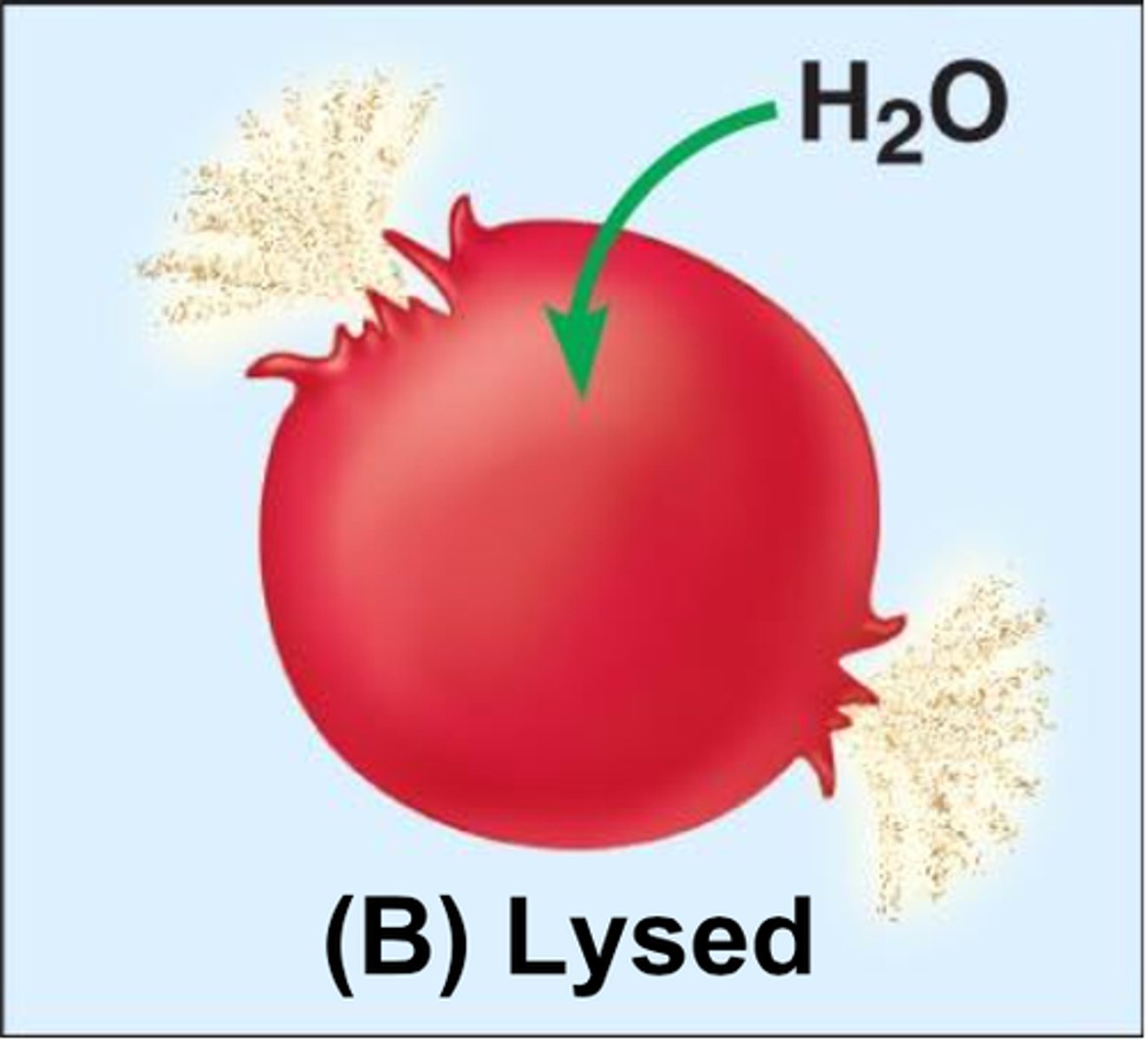
hypertonic
higher solute concentration (on the outside of the membrane).
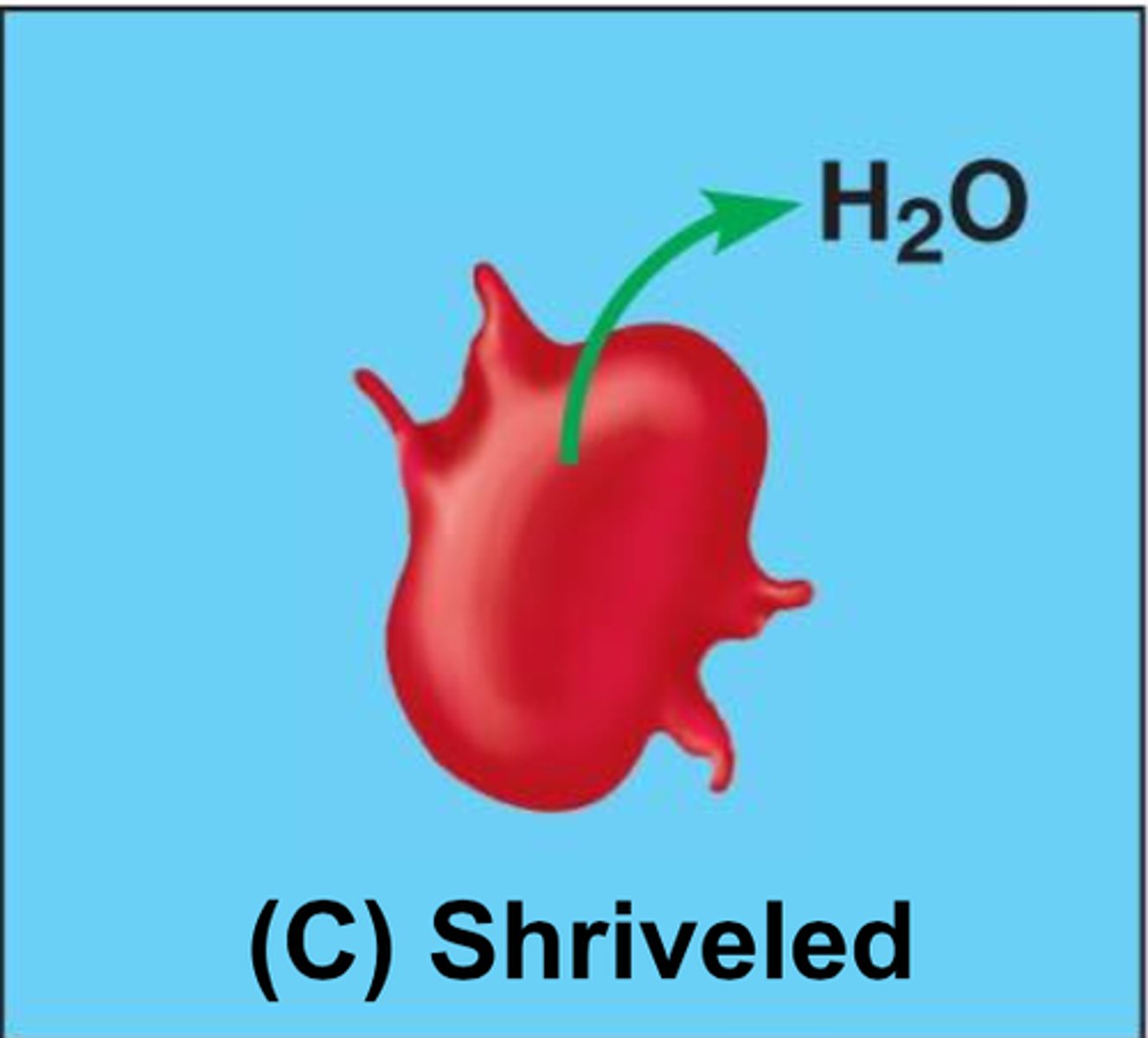
hypotonic
lower solute concentration (on the outside of the membrane).
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient
endocytosis
A process in which a cell engulfs extracellular material through an inward folding of its plasma membrane.
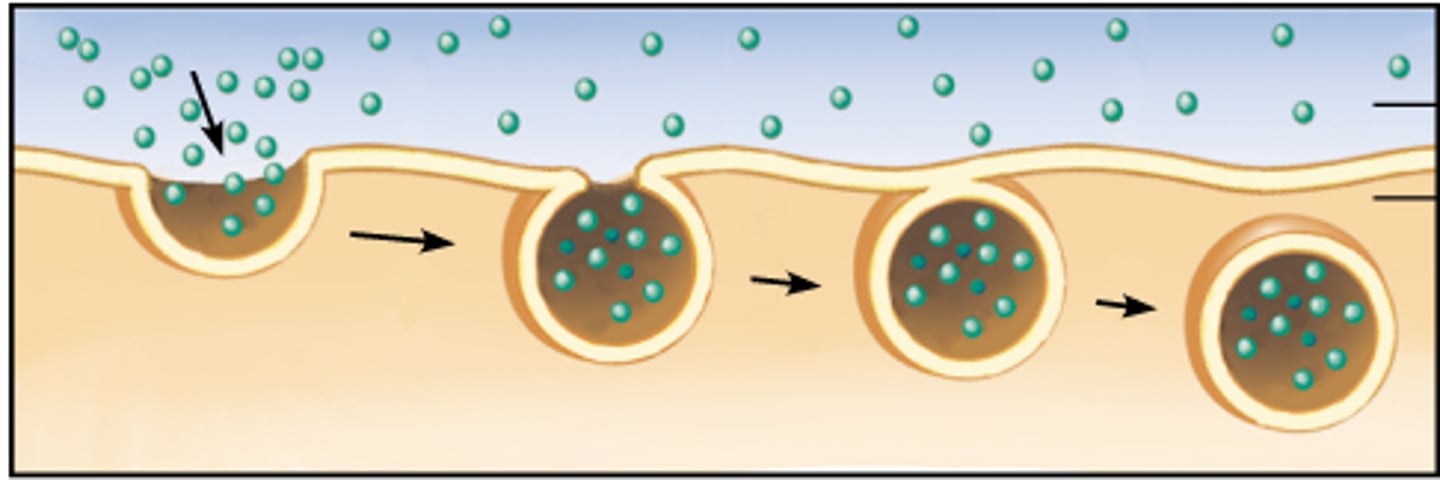
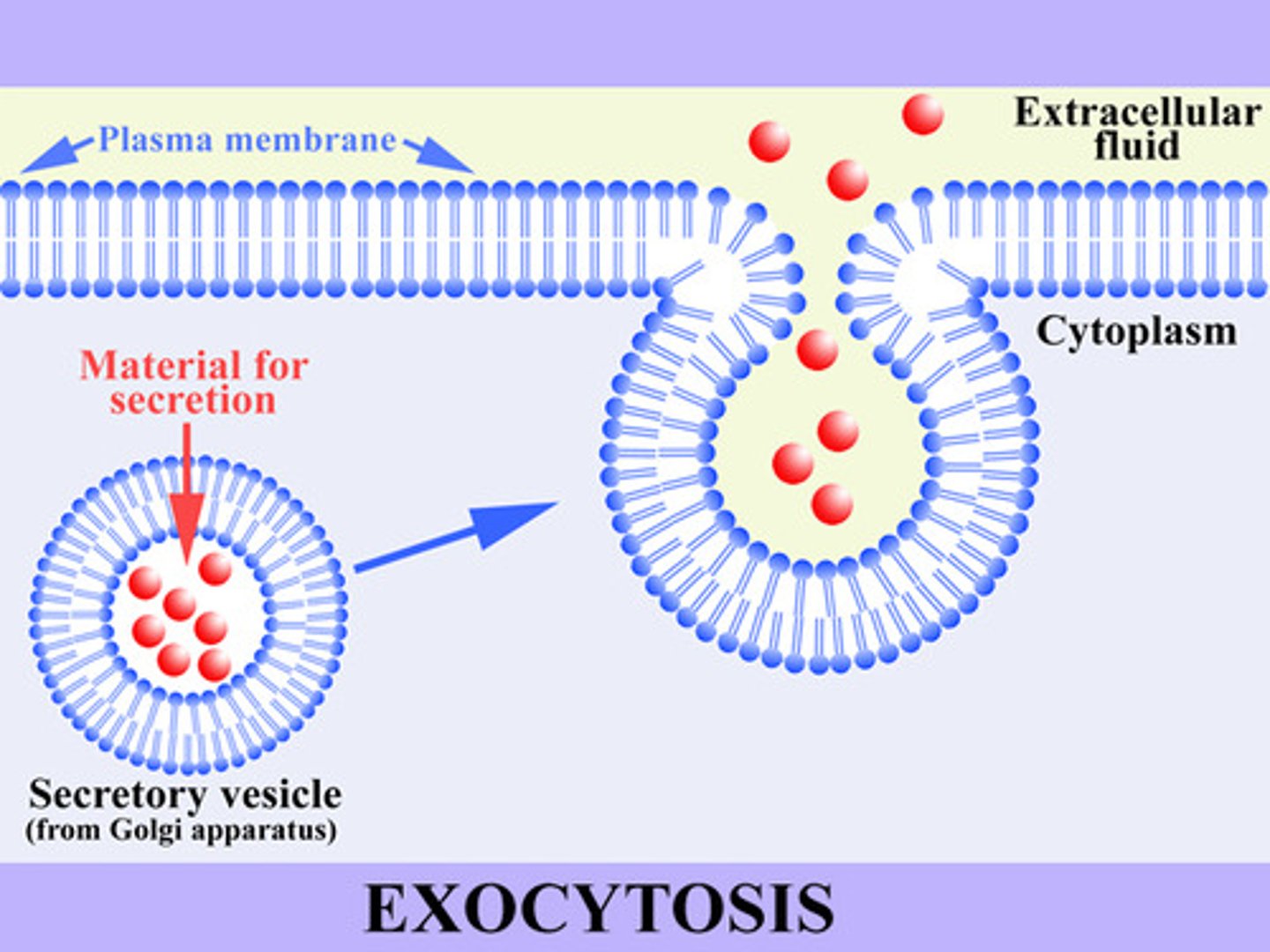
exocytosis
a process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
biochemical process
chemical process that occurs in living organisms such as protein synthesis, cellular respiration, photosynthesis, etc.
metabolic pathway
Begins with a specific molecule, which is then altered in a series of defined steps, resulting in a certain product.
germline cells
cells that produce gametes
somatic cells
body cells
gametes
sex cells
asexual reproduction
only occurs in unicellular and simple multicellular organisms. These organisms do not require a mate to reproduce and the offspring or daughter cells are clones (genetically identical) of each other and of the parent.
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction that occurs in prokaryotes such as bacteria, in which one cell divides to form two identical cells.
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
centrosome
is an organelle that organises the cell's microtubules and consists of microtubules and centrioles (these are the components of the cell's cytoskeleton)
mitosis
somatic cell division producing two identical daughter cells
prophase (mitosis)
In the nucleus, chromatid fibres condense (coil up around histones) and the chromosomes become visible
In the cytoplasm, the mitotic spindle starts to form and the centrioles move to opposite poles of the cell.
The nuclear membrane breaks down and disappears.
metaphase (mitosis)
Spindle fibres radiate from the poles to cell's equator
Each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fibre at the centromere
Chromosomes align along the metaphase plate (an imaginary line midway through the cell)
anaphase (mitosis)
Begins when the pairs of centromeres of the chromosomes divide and sister chromatids are drawn apart.
Each chromatid is now considered to be a daughter chromosome.
These chromosomes are drawn towards opposite poles of the cell by the microtubules, which are attached to the centromeres.
telophase (mitosis)
Chromosomes decondense to form chromatin (uncoiled version of DNA)
Nuclear envelope reforms
haploid
a cell having only one copy of each chromosome.
diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that look similar in length, the centromere is located in a similar position and they contain genes that code for the same characteristics.
sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents
meiosis
a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells)
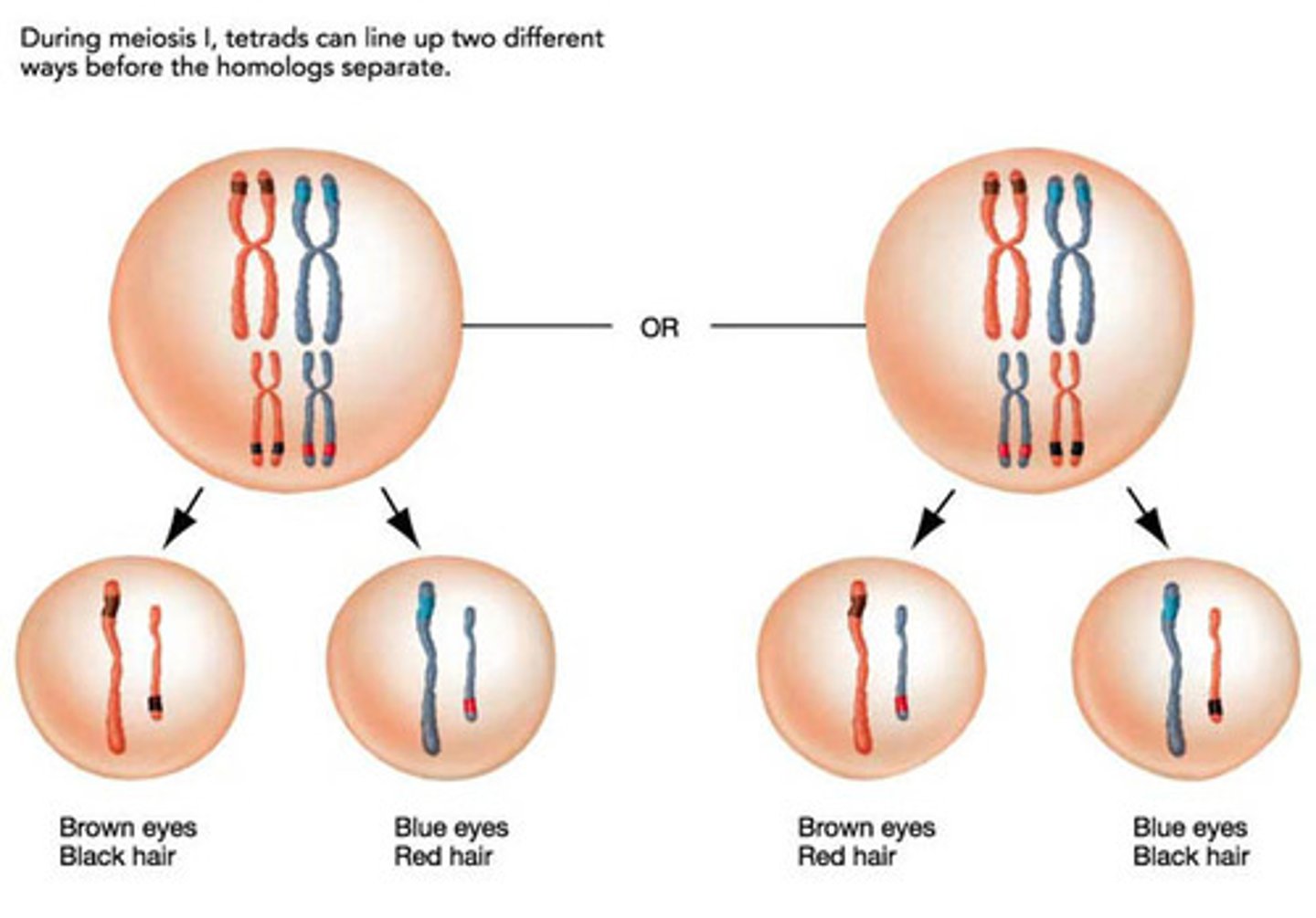
independent assortment
the random distribution of the pairs of genes on different chromosomes to the gametes
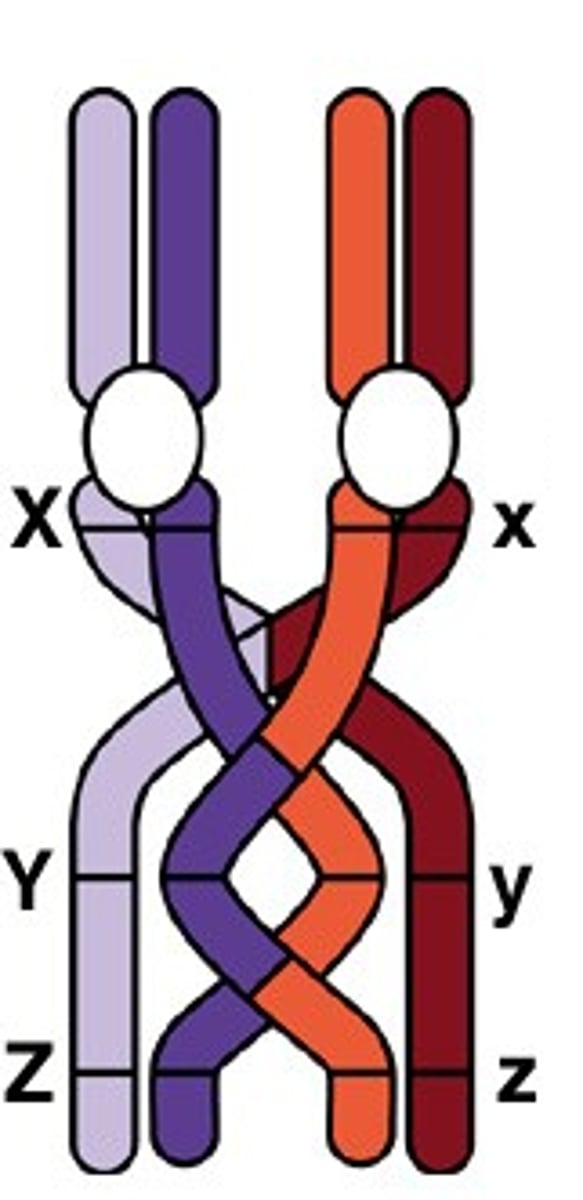
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
prophase I (meiosis)
The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. crossing-over occurs.
metaphase I (meiosis)
homologous chromosomes line up randomly on opposite sides of the metaphase plate. Microtubules attach and chromosomes are ready to be moved to opposite poles.
anaphase I (meiosis)
homologous chromosomes separate (sister chromatid stay together)
telophase I (meiosis)
nuclear membrane is cleaved. A cleavage furrow forms in preparation for cytokinesis.
prophase II (meiosis)
Nuclear membrane disapperars and chromosomes coil; centrioles replicate and move to opposite poles
metaphase II (meiosis)
Sister chromatids align at the middle plate
anaphase II (meiosis)
sister chromatids separate
telophase II (meiosis)
The sister chromatids are now in two separate regions and haploid daughter cells are formed by cytokinesis. In animals this would be called gametes.
cell cycle
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide - contains interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis
cell cycle G0 phase
cells are removed from the cycle and are not dividing though functioning
cell cycle G1 phase
cell growth, ribosome synthesis, protein sythesis
cell cycle s phase
DNA replication, histone synthesis and phospholipid synthesis
cell cycle G2 phase
developing and preparing organelles for division
cell cycle m phase
mitosis, division of the nucleus
cell cycle checkpoint G1
cell checks on its DNA to ensure its ready to proceed into DNA replication (s phase)
cell cycle checkpoint G2
ensures DNA replicated accurately and there is no damage. Checks the cell is suitable to enter mitosis.
cell cycle m checkpoint
during metaphase, it will check the spindle apparatus is in place and the chromosomes are lined up correctly, ready to separate the chromatids.
mitosis promoting factor (MPF)
A complex of a cyclin and cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk) that phosphorylates a number of specific proteins needed to initiate mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
carcinogen
physical or chemical factors that increase the rate of cancer in an organism. They do this by increasing the rate of mutation, thus leading to uncontrolled cell growth or cancer
mutagen
factors that increase the rate of mutation