Enzyme Inhibition Models
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
uncompetitive inhibition
inhibitor binds only to enzyme-substrate complex
noncompetitive inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
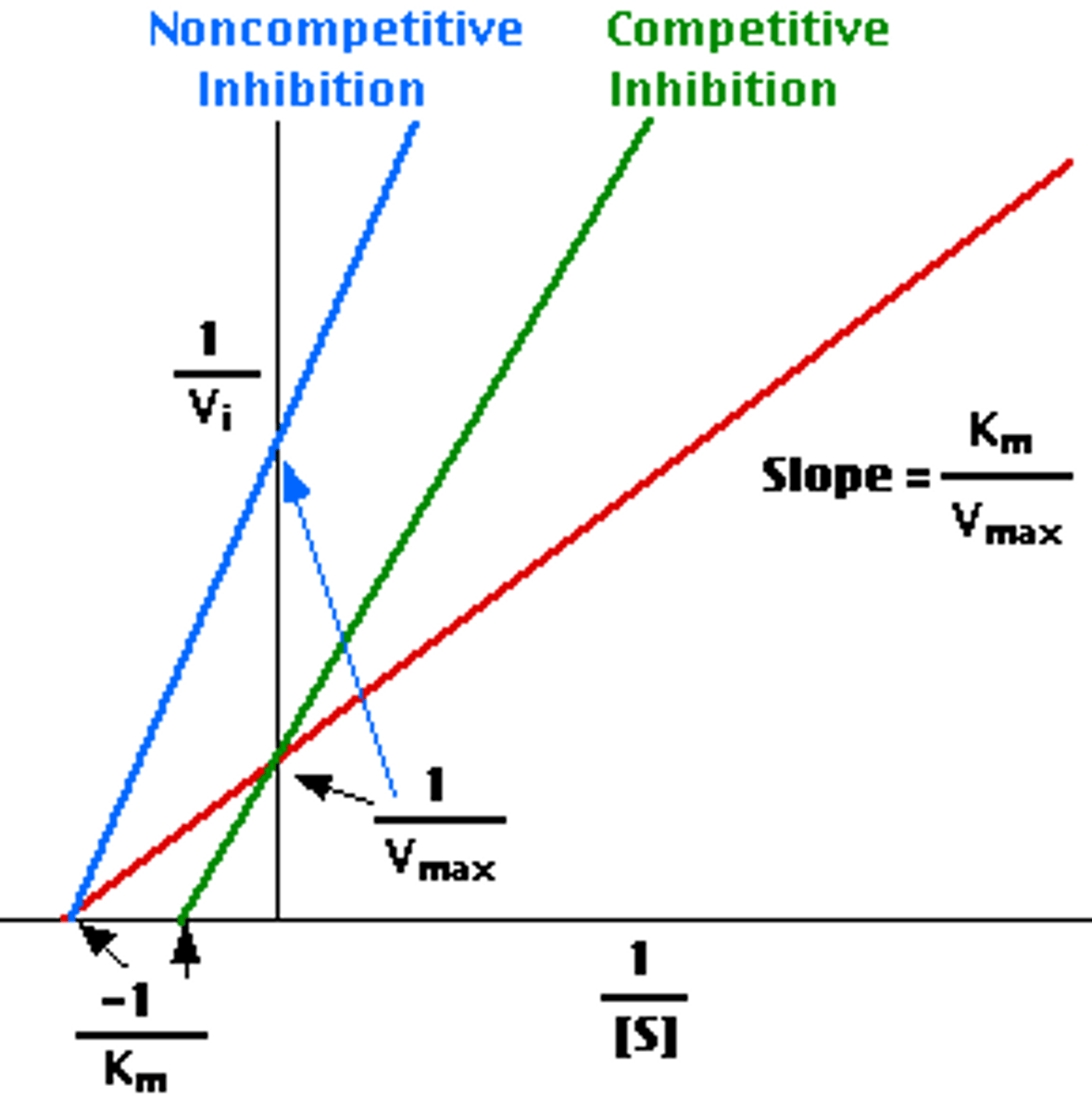
competitive inhibition graph
Cross at y-axis
Same Vmax
Different Km
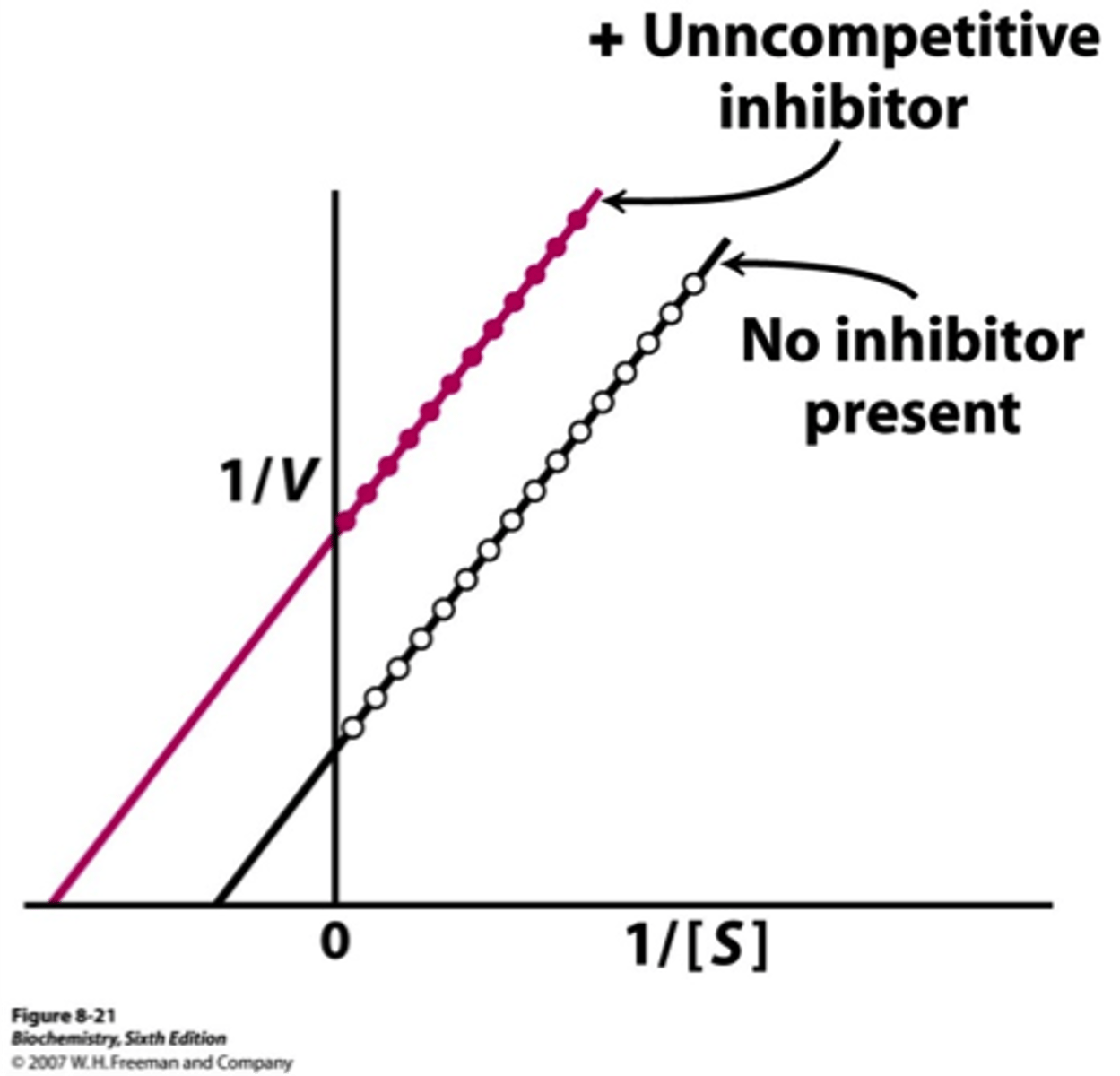
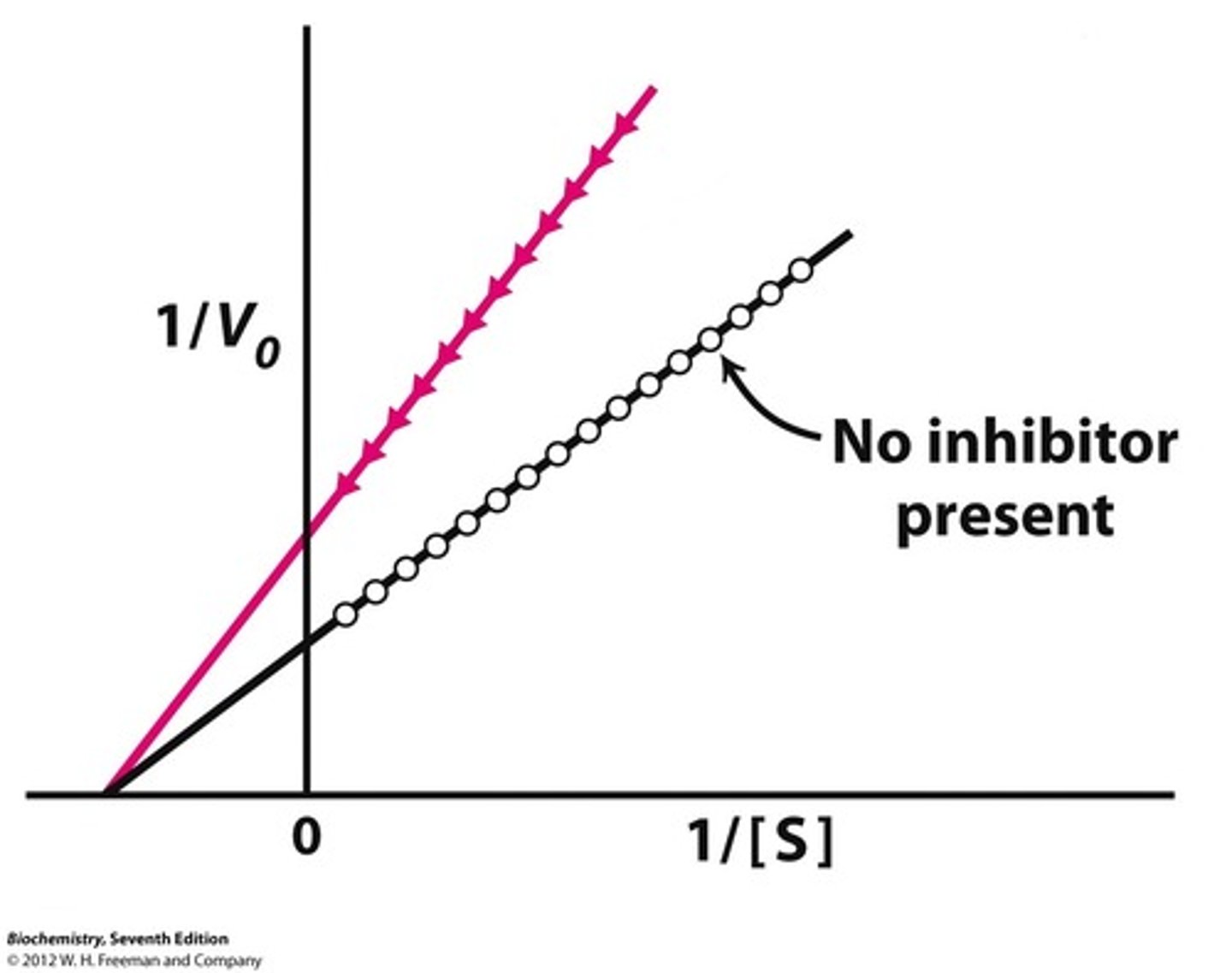
Uncompetitive Inhibition Graph
Does not change slope.
Changes Km and Vmax.
Results in vertical shift up and down.
noncompetitive inhibition graph
Cross at x-axis
Changes Vmax
Same Km
Enzyme saturation
occurs when substrate levels are so high that all enzyme molecules are actively engaged in the chemical reaction, and so further increases in substrate concentration do not increase reaction rate.
Vmax
maximum rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
saturation graph
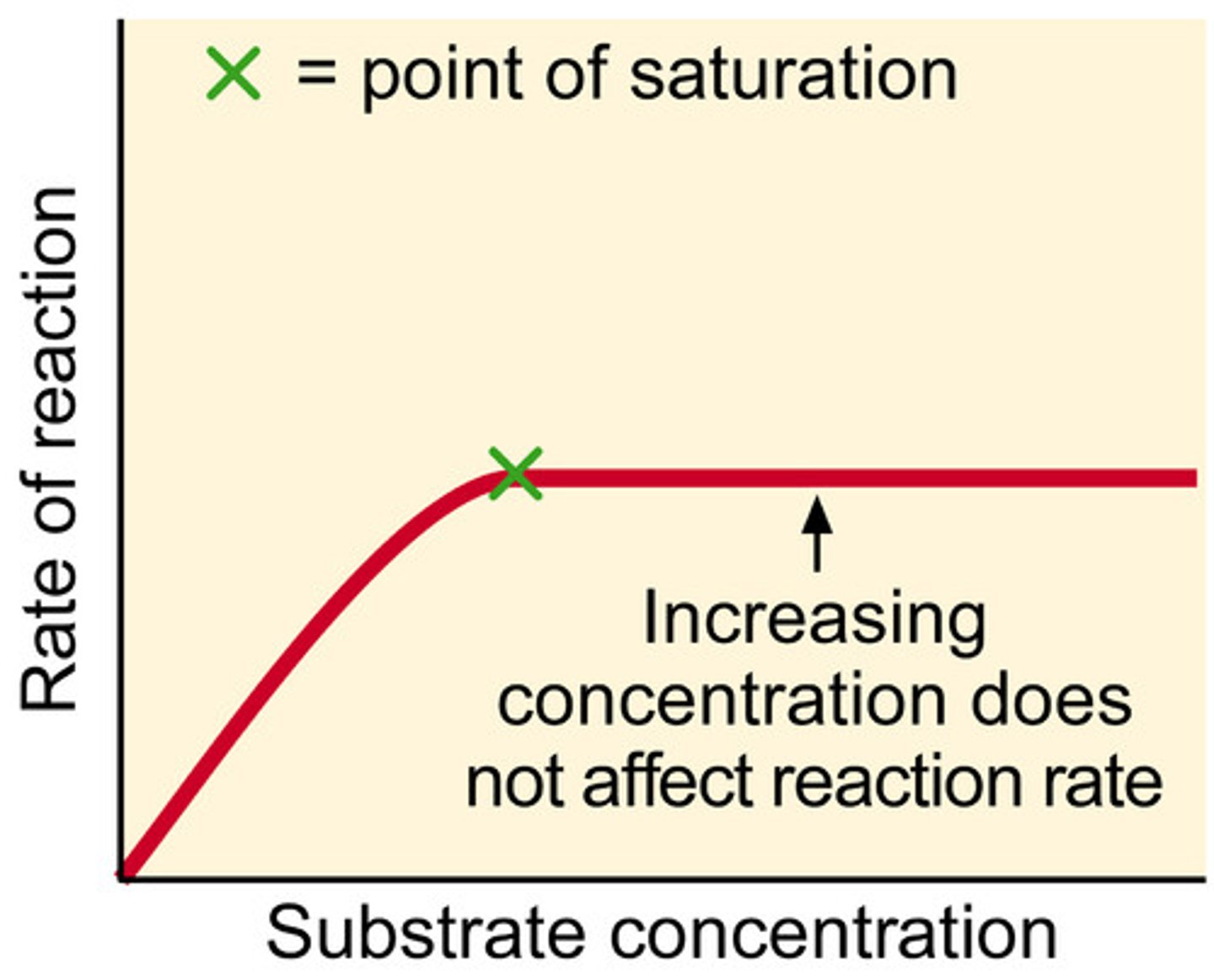
Vmax on a graph
Vmax is the horizontal asymptote that the Michaelis-Menten curve approaches at high substrate concentration.
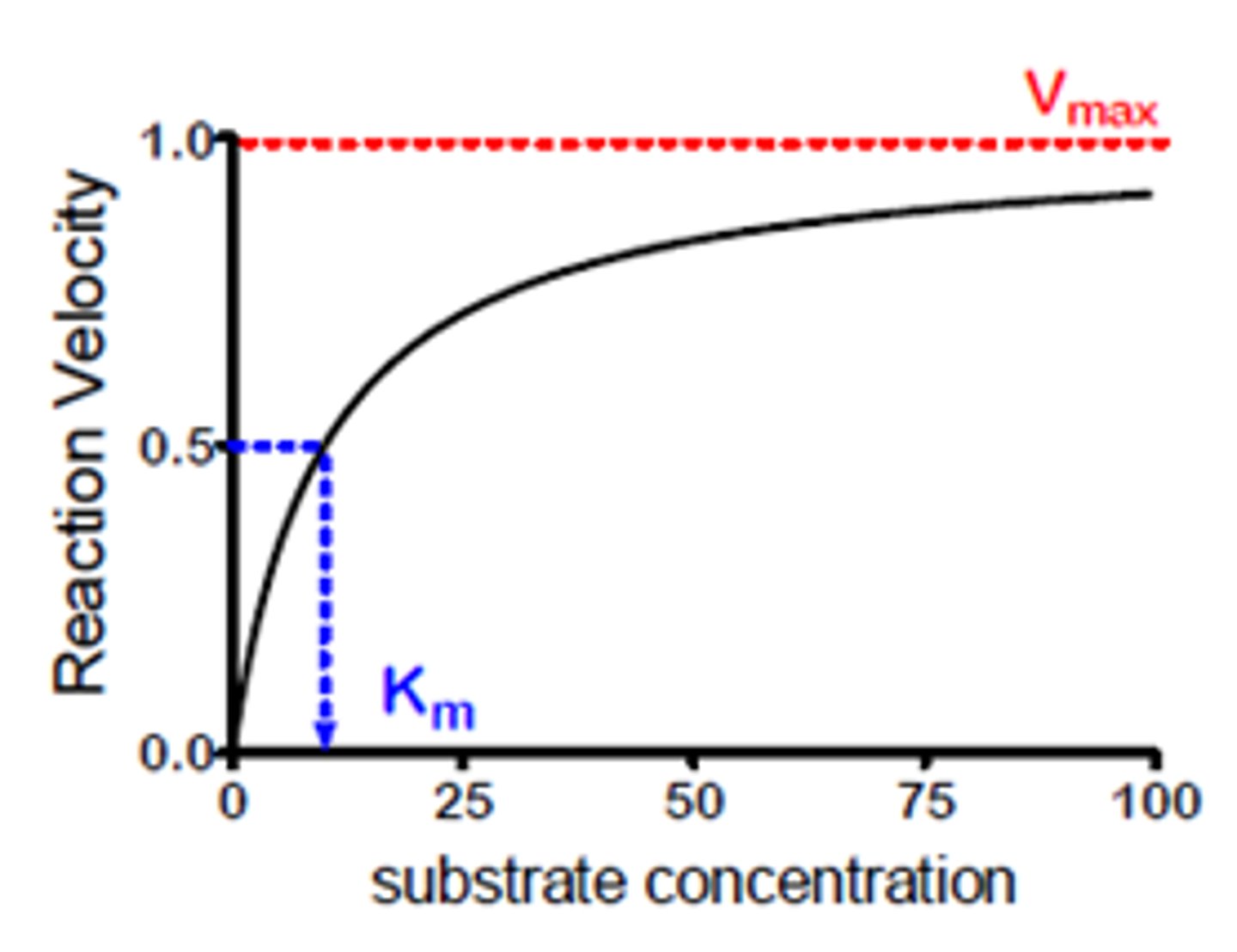
Km
Substrate concentration at 1/2 Vmax
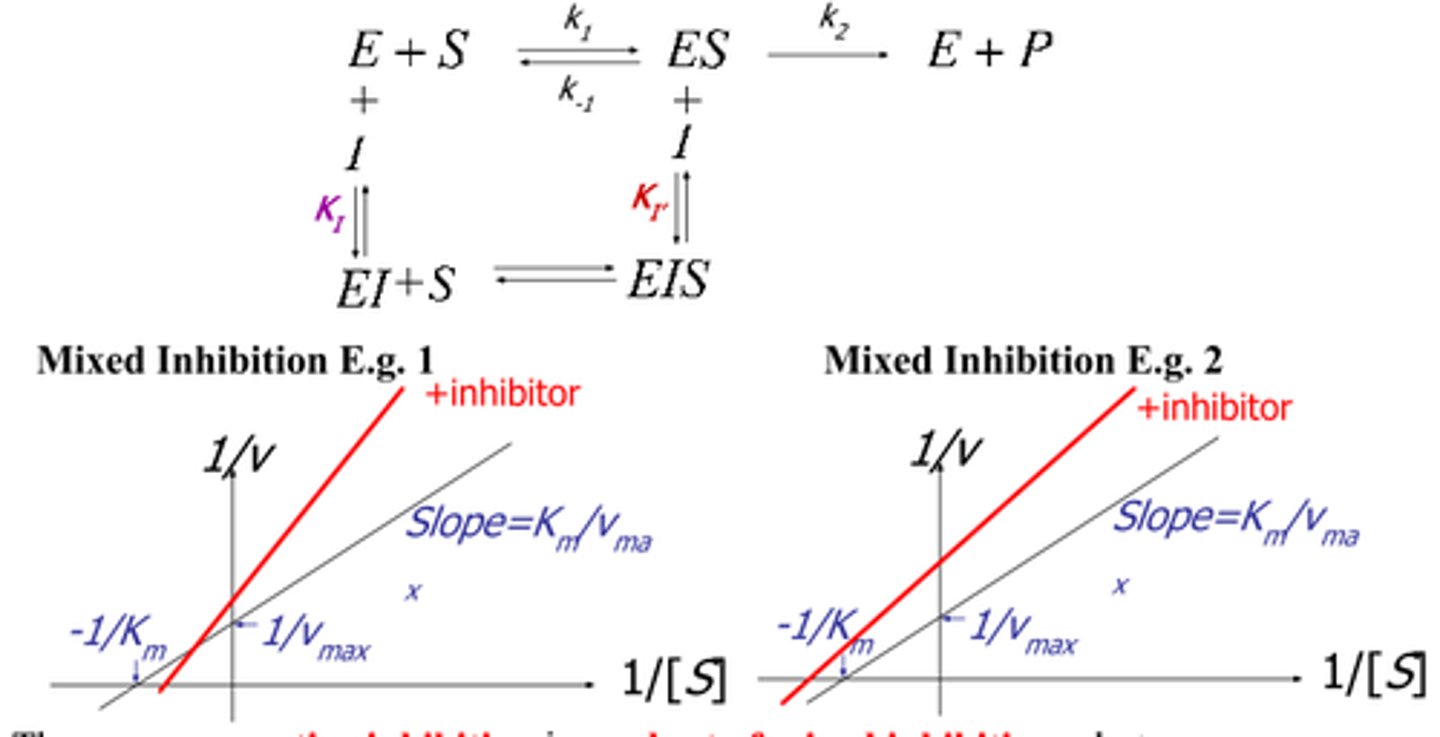
Mixed Inhibition Graph
Difference of enzymes with high vs low Km
An enzyme with a high Km is not normally saturated with substrate and its activity will vary as the concentration of substrate varies, so that the rate of formation of product will depend on the availability of substrate.
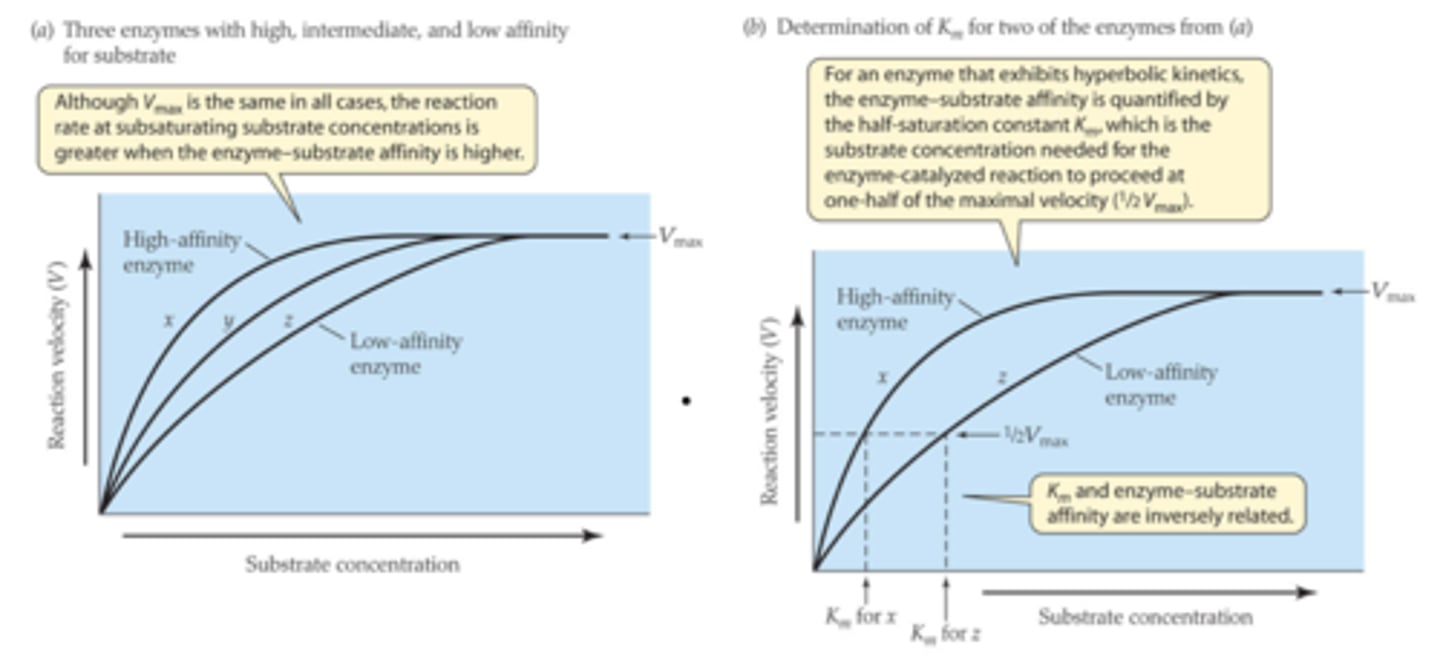
Km
Michaelis constant
Binding affinity
Pharmacophore
the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms or groups of atoms responsible for the biological activity of a drug molecule
Still learning (16)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!