immunology exam 3 Ab based vaccination against bacteria
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all done
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
microorganisms definition
all life we canot see with the naked eye
number of bacteria on earth
10 ^ 30
bacterial variation
is substantial- from micrometers to cm! most around 1 micrometer though
pathogenicity def
ability to cause disease
pyramid of pathogens bottom to top
non-pathogenic, potential pathogen (opportunistic pathogens, are always in our body but have the potential to become pathogenic), true pathogen (primary pathogen, eg TB, will cause disease if come into contact)
how to prove a causal relationship between a microbe and disease (4 steps - Kochs postulates)
Microorganism is present in sick, but not healthy individuals/animals; our organism must be grown to pure culture; cultural microorganism must cause the same disease in healthy individuals; same microorganism must be culturable from sick individuals
who developed the germ theory of disease
John Snow
exceptions to Kochs postulates (5)
Microorganisms cannot be cultured with available methods or required additional factors for in vitro growth (eg viruses need host cells), microorganisms only cause the disease in humans (no proof of disease from animal models), long incubation period (eg AIDS, prions), microbes that also asymptomatically colonize (commensals turning pathogens), microbe associated/triggered but non-infectious diseases (eg periodontitis)
how many microorganisms in the microbiome?
4 × 10 ^ 13, 500-1,000 species, diff in diff parts of the body
The positive role of our microbiome in health (3)
nutrition and metabolism of food (eg vit B production), maturation and instruction of the immune system, colonization resistance: protection against infiltration by new and harmful microorganisms
The negative role of our microbiome in health (2)
Disease association with disturbances in (intestinal) microbiome, source of infection (presence of opportunistic pathogens, immunocompromised host)
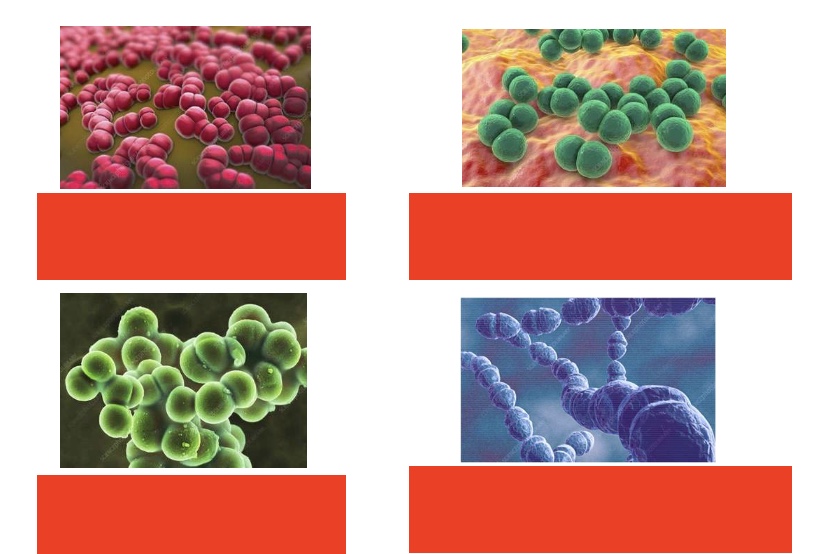
potentially “bad bacteria” in microbiome- label names & colonization rate (left to right, starting top row)
neisseria menigitidis (colonization rate - 10%), streptococcus pneumoniae (colonization rate - 15%), staphylococcus aureus (colonization rate - 25%), Group A streptococcus (colonization rate - 10%)
what is the continuous balancing act with your microbes?
between host immune defense and pathogen virulence factors
Virulence factors definition
Pathogen associated molecules that are required for a pathogen to establish an infection and cause disease
four functions of virulence factors
Colonization and adhesion, invasion (& dissemination), immune evasion, nutrient acquisition
In what way can you see an acute infection
Failure of immune system and/or bacterial virulence
Main infection routes for pathogens (3)
mucosal membranes: airway (droplets, aerosols), gut (infected food ingestion)
skin: wounds, IV lines
what can symptoms of bacterial infection vary depending on?
The route of infection, type of bacteria causing the infection
two types of symptoms of bacterial infections and 5 examples each
Local: skin redness, local pain, cough, diarrhea, vomiting
(More) disseminated/widespread: fever, headache, confusion, petechiae, stiff neck (meningitis)
Host defenses upon primary bacterial infection- eg in skin, 1
invading bacteria detected by local tissue cells: APCs (DC & macrophages through PRRs), non-immune cells (epithelial cells, keratinocyes, fibroblasts)
Host defenses upon primary bacterial infection- eg skin, 1: non-immune cells more depth (2 points)
activated by bacteria but also in response to tissue damage, can produce antimicrobial proteins and peptides for local non-specific killing)
Host defenses upon primary bacterial infection- eg skin, 2
Local cells activate and coordinate downstream immune response: in lymph nodes- activated specific T and B cells/production of specific antibodies, memory formation: prevent re-infection
Host defenses upon primary bacterial infection- eg skin, 3
local cells activate and coordinate downstream immune responses: attract phagocytes from the bloodstream (eg neutrophil-mediated killing)
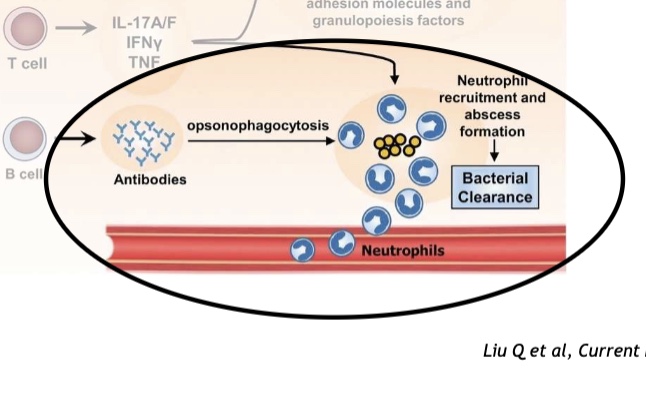
What does this image show?
Convergence of innate and adaptive immunity, neutrophils are like the cavalry
antibody-mediated defense against bacteria pathogens
Direct killing through complement activation (only gram negative bacteria though), enhancing bacterial phagocytosis and killing (both gram positive and negative)
Why does complement mediated killing only work for gram-negative bacteria?
Because the thick peptidoglycan layer protects gram positive bacteria from MACs
Another function of antibodies
Boost neutrophil recruitment and pathogen recognition
What do bacteria specific antibodies do?
Complement activation (IgM, IgG)- pathogen opsonization, neutrophil recruitment → more affect cells
what does interaction with Ig receptors (IgG, IgA) do?
Receptor mediated phagocytosis
What can restore maintain the balance between immune defence and virulence factors in favor of the host?
Antibiotics and vaccines
what do vaccines do (basic)
Induce immunological memory
first vaccine
smallpox- infection with cowpox helped
types of vaccines (7)
Subunit vaccine, nucleic acid vaccine, inactivated vaccine, live vector vaccine, virus like particles vaccine, gene deleted vaccine, live attenuated vaccine
Vaccine effector mechanisms (2)
Antibodies that neutralize bacterial toxins (eg tetanus), induction of bactericidal antibodies that enhance bacterial phagocytosis and killing (eg meningococcal vaccines)
what is an issue for vaccination with bacteria?
Many bacterial pathogens are encapsulated with a thick capsule - cannot make antigens for what's inside of it
Solution to finding antigens of encapsulated bacteria, one drawback
Using capsular polysaccharides (CPS) as virulence factors- CPS composition varies between bacterial species but even within species (eg s. pneumoniae)
Examples of encapsulated bacteria that can cause invasive disease
Streptococcus pneumoniae, haemophilus inluenzae b, Group B streptococcus, neisseria meningitidis
Why is CPS an important virulence factor?
Resistance to phagocytosis and killing by immune cells, resistance to serum killing (gram negative bacteria)
Neisseria menigitidis: general info (5 points)
commensal and pathogen, gram-negative, human-specific, natural habitat is the human nasopharynx, can cause invasive meningococcal disease (IMD)- deadly
why is there a low incidence of IMD in newborns?
They get some antibodies from their mother, but then afterwards it takes time to build up their own antibodies so infants are the most vulnerable

What does the graph show?
Bactericidal antibodies against capsular polysaccharide and IMD incident have an inverse correlation
what was the first vaccine against IMD?
Plain polysaccharide vaccine
drawbacks of the plain polysaccharide vaccine for IMD (3)
Insufficient for population wide application- not immunogenic in young children (most at risk group), no immunological memory (have to be repeated immunizations), ineffective against carriage- only individual protection
why did the plain polysaccharide vaccine for IMD have the restrictions?
Because the vaccine is recognizing directly by the BCR and it causes a T cell independent immune response- only low affinity antibodies and no memory formation
what was a game changer for vaccination with polysaccharides
Protein conjugation- works by growing the bacterium in large quantities, extracting the CPS and then conjugating it to a protein carrier, then that protein carrier is in the B cells and is presented on MHC to T cells activating them
Why is protein conjugation a game changer for vaccination with polysaccharides? Its benefits vs plain polysaccharide vaccine
It allows for a T cell dependent response: allows for immunological memory, high affinity antibodies, effective in infants, herd immunity- reduces carriage and protects non vaccinated individuals
Drawback of protein conjugated vaccine against MenC?
only serogroup specific protection BUT still it very much brought down the numbers of that one serogroup
how do menigococcal serogroups work? (4 points)
same species, different “faces”; determined by capsule structure; 13 in total; most common: A, B, C, X, Y, W
what vaccine gives an even broader protection against MenC?
Multivalent glycoconjugate vaccines- for multiple serotypes at once in one vaccine and still conjugated to a protein
other successful examples of polysaccharide conjugate vaccines
vaccine for haemophilus influenzae b. streptococcus pneumoniae (reduction in disease also in non-vaccinated age groups! now for 17 serotypes already)
Are there vaccines available for staphylococcus aureus and Group A streptococcus?
not yet :(
limitations for vaccines based on CPS (4)
limited vaccine coverage in case of wide range in CPS diversity (eg s pneumoniae has 90 serotypes), glycan antigen is not immunogenic, glycan structures are similar to human structures- mimicry (can risk inducing autoreactive Ab), doesnt work on disease caused by low/non-encapsulated species/strains
take home messages of lecture (5)
not all bacteria capable of causing disease, infections can start at different sites of the body resulting in a local and/or widespread symptoms, Koch’s postulates: four criteria to establish cause a relationship between a bacterium and a disease but they are clear limitations, antibody mediated effector functions are often critical for the protective effect of antibacterial vaccines, conjugation of polysaccharides to a protein carrier has enabled their community wide application