Neuromuscular (EXAM #1) study guide
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
What is the common goal of scientists that study neuroscience?
to understand the structure and function of normal and abnormal brain
Hint:
Neuroscience
Neuro = Nerves, Science= study of nerve, brain
Neuroscience= Brain Science
What area of science do these researchers come from? (NAME 3)
Anatomists (uh-nah-tuh-mists)
Physiologists
Psychologists
What does a Anatomists study?
Studies the brain’s shape, cellular structure, and it’s circuitry (sir-cut-tree)
What does a Physiologists study?
They study the brain’s electrical properties
Hint:
Physio= nature/function of the body
What does a Psychologists study?
They study the organization and neural substrates of behavior and cognition
Hint:
When you think of psychology you think of behavior and cognition
Neuroscience is the study of the ______.
Nervous system
*Neuroscience stretches from _______ biology of nerve cells to ____ basis of behavior
molecular ; biological
Define Afferent pathways (neurons)
Brings information into the CNS
(carries info from body into CNS)
Hint:
Arrives at CNS
Afferent pathways
What does the Afferent pathway do? (responsible for)
*Sensory
EX: Touch, pain, temp., pressure
Define Efferent Pathways (neurons)
Take information away from CNS
(Carries info from CNS)
Hint:
Exits CNS
Efferent pathways
What does the Efferent pathway do? (responsible for)
*Motor
skeletal muscle movement, HR, digestion, and gland secretions
The nervous system has TWO different kinds of systems, what are they?
CNS
PNS
What makes up the Central Nervous System (CNS)?
Brain and Spinal cord
CNS
*The CNS is known as the “integrating” or “control” center because it…..
takes info. and makes decisions
What makes up the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Ganglia
Cranial and Spinal nerves
Clusters of nerve cell bodies located outside the CNS are called what?
Ganglia
PNS
*Carries ______ signals to and from the ______
Peripheral; CNS
*Define INNERVATION
Nerve supply to a tissue
What are the TWO (three ig) FUNCTIONAL DIVISONS for the PNS?
Somatic Division
Autonomic Division
Enteric
The Somatic Division has TWO NEURONS, sensory neurons and motor neurons. Explain what the sensory neurons are responsible for.
Somatic Division - Sensory neurons
Sensory information from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to CNS
The Somatic Division has TWO NEURONS, sensory neurons and motor neurons. Explain what the motor neurons are responsible for.
Somatic Division - Motor neurons
Motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles
The Autonomic Division has TWO NEURONS, sensory neurons and motor neurons. Explain what the sensory neurons are responsible for.
Autonomic Division - Sensory neurons
Sensory information from visceral organs to CNS
The Autonomic Division has TWO NEURONS, sensory neurons and motor neurons. Explain what the motor neurons are responsible for.
Autonomic Division - Motor neurons
Motor impulses from CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
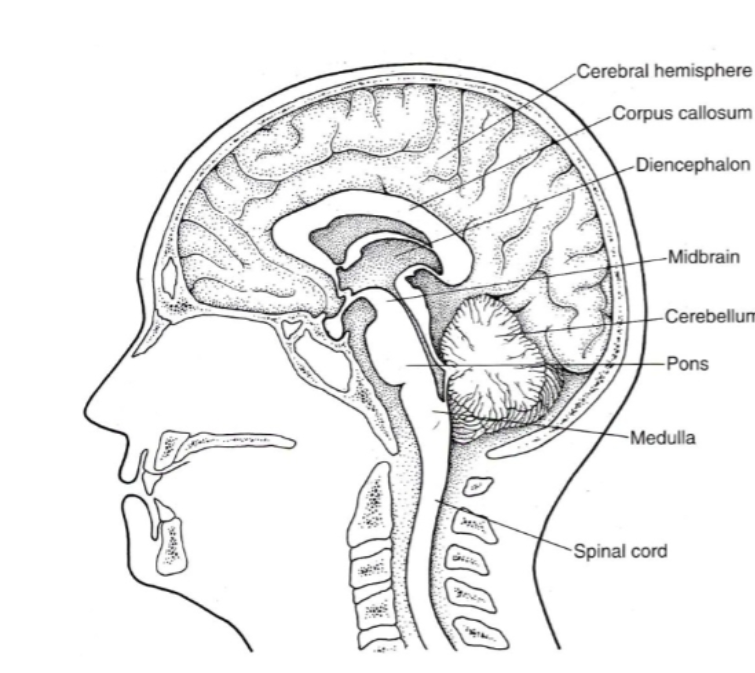
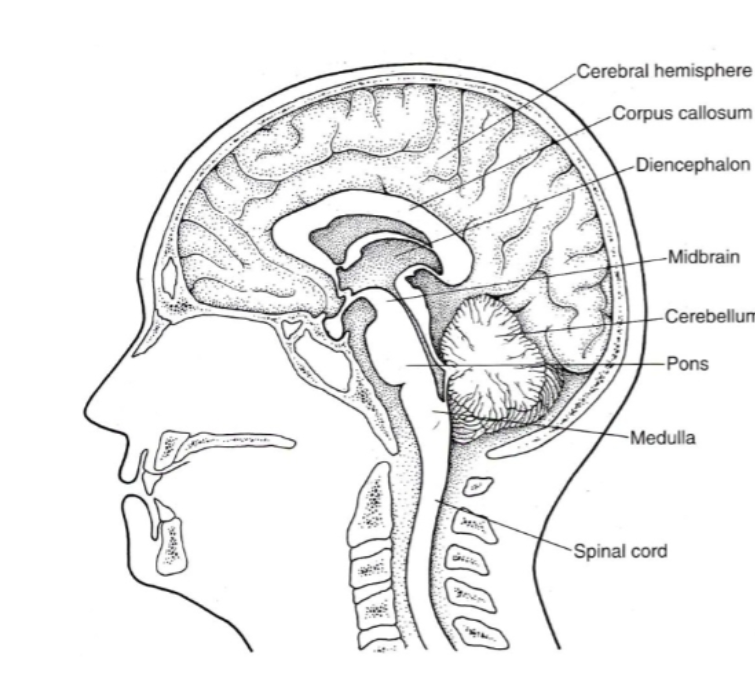
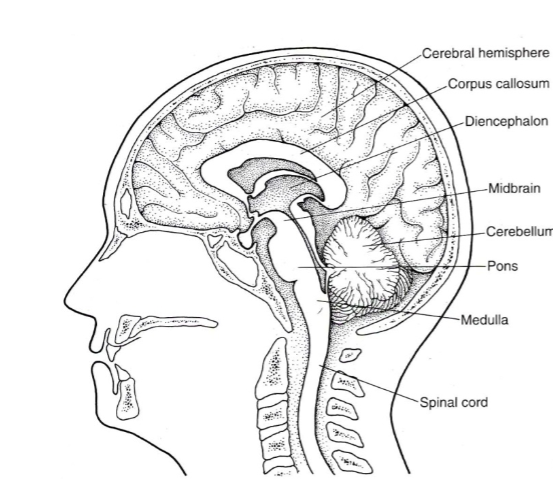
The CNS is divided into FIVE PARTS what are they?
Spinal cord
Brainstem
Cerebellum
Diencephalon (die-in-seph-uh-lawn)
Cerebral hemispheres
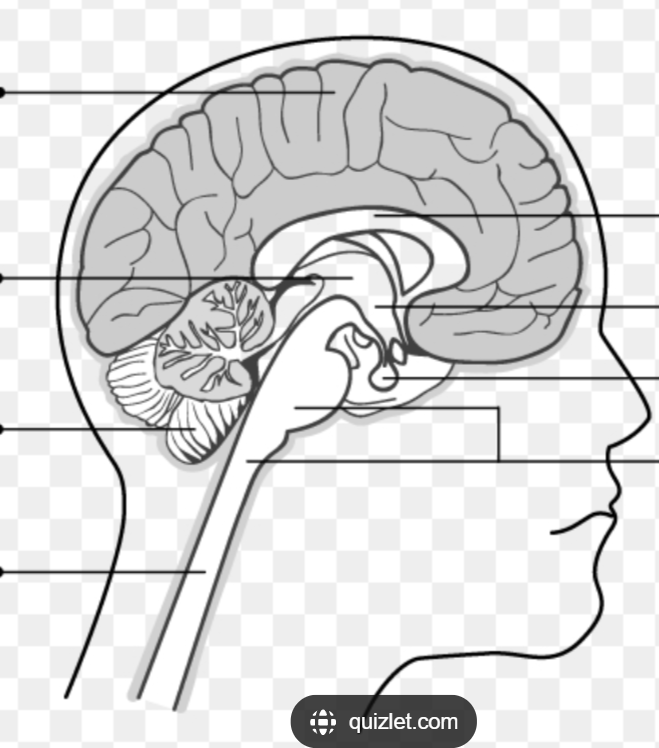
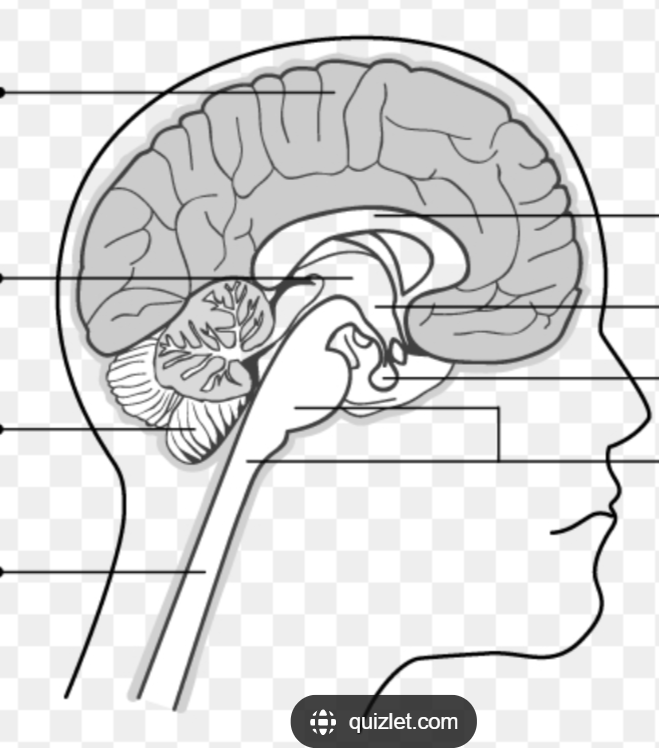
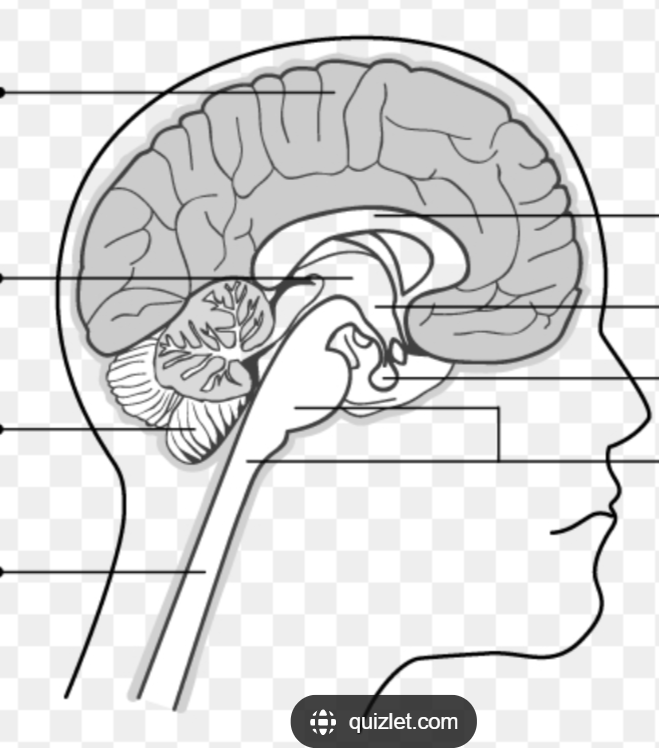
Be able to identify where each of the five parts are on a diagram:
Where is the Spinal cord located in the diagram?
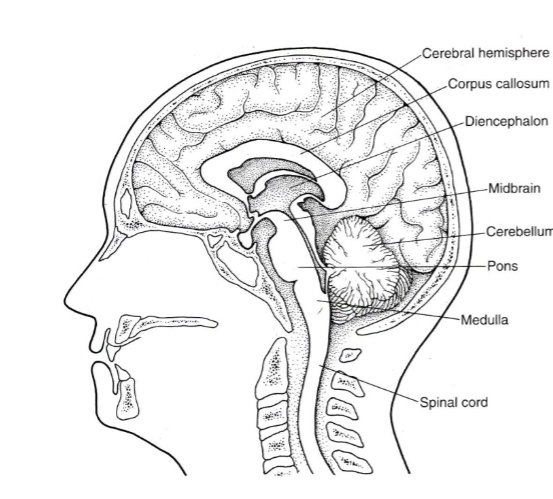
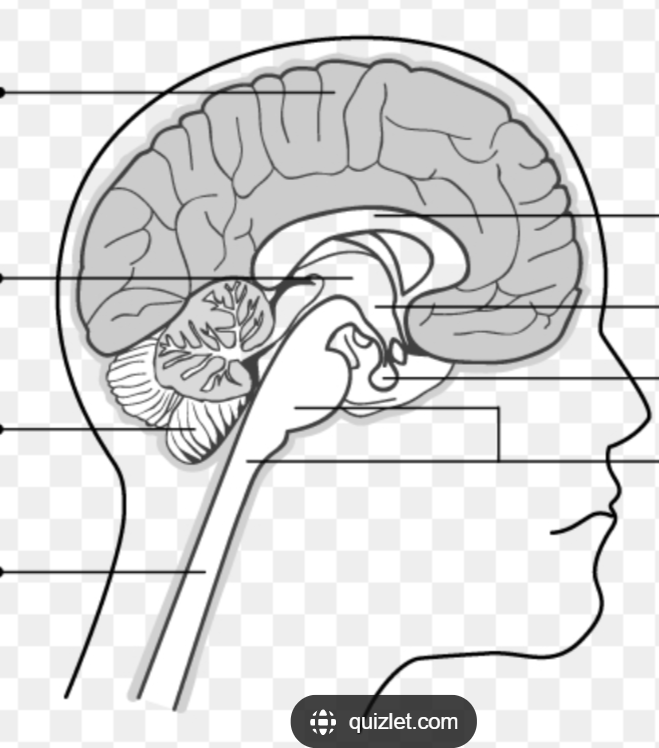
Be able to identify where each of the five parts are on a diagram:
Where is the Brainstem (medulla, pons & midbrain) located in the diagram?
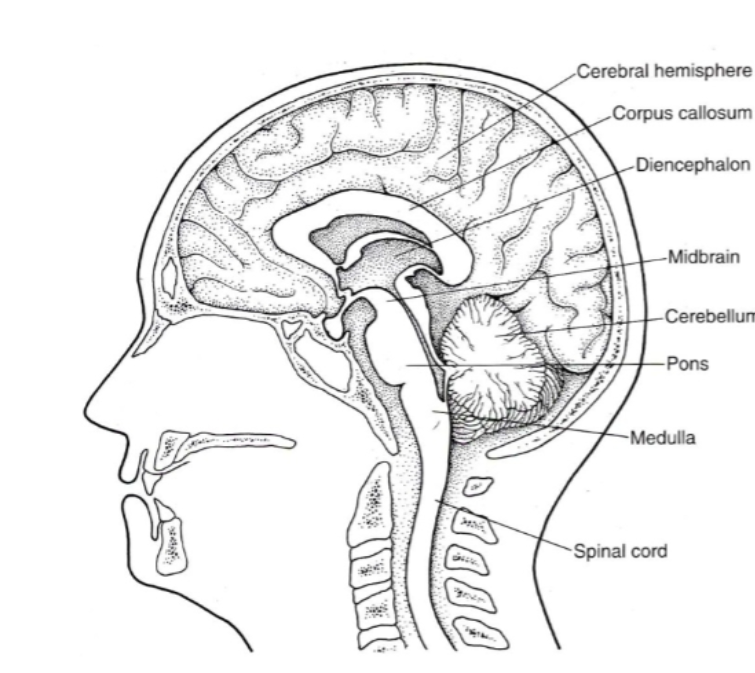
Be able to identify where each of the five parts are on a diagram:
Where is the Cerebellum located in the diagram?
Be able to identify where each of the five parts are on a diagram:
Where is the Diencephalon located in the diagram?
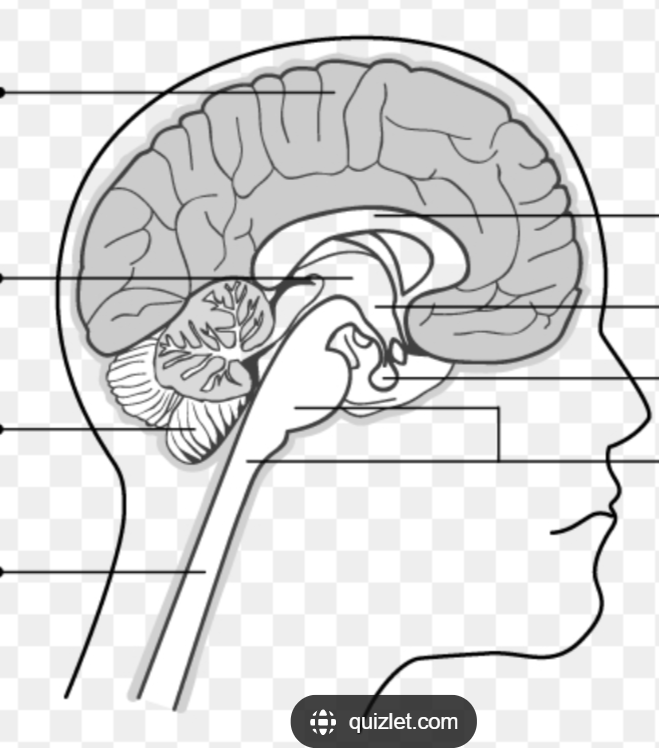
Be able to identify where each of the five parts are on a diagram:
Where is the cerebral hemispheres located in the diagram?
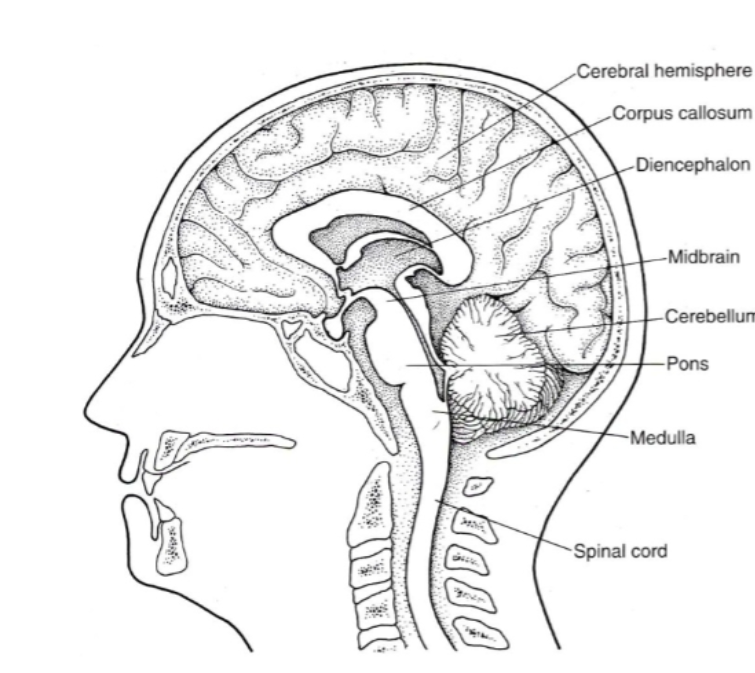
CNS
The BRAINSTEM is made up fo THREE parts, what are they?
Medulla
Pons
Midbrain
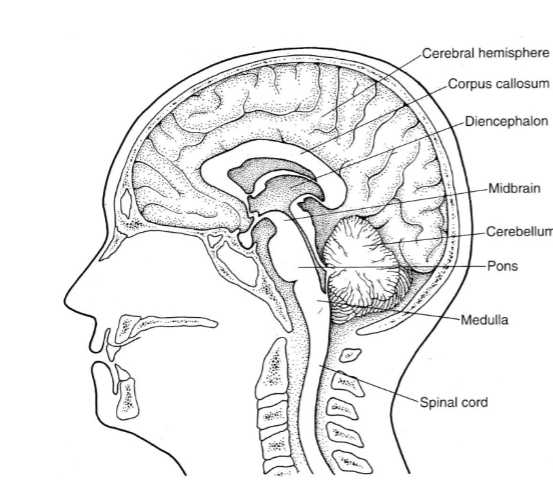
The Medulla (or medulla oblongata) is responsible for what?
Digestion, breathing, control of heart rate. Also the location of decussation for sensory and motor pathways
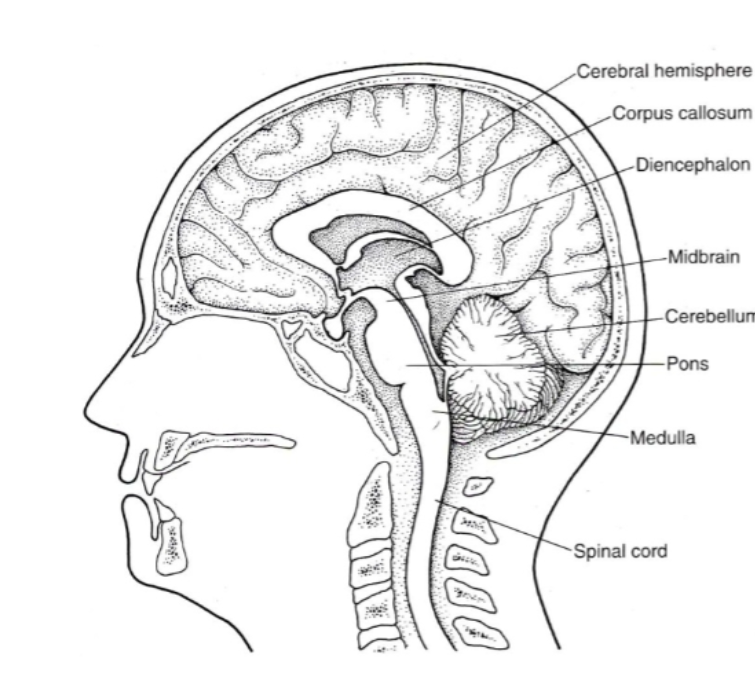
The Pons is responsible for what?
Movement of information to cerebellum
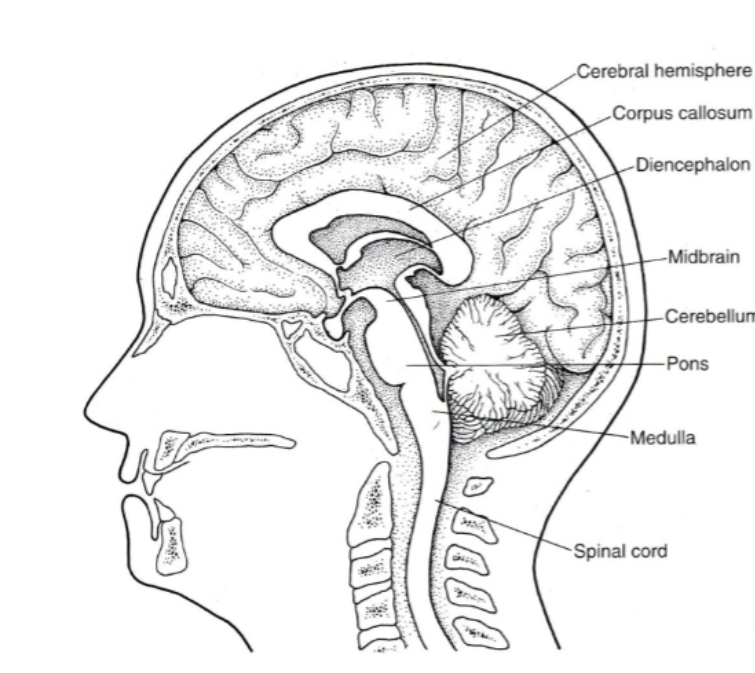
The Midbrain is responsible for what?
Vision, arousal, and temp regulation
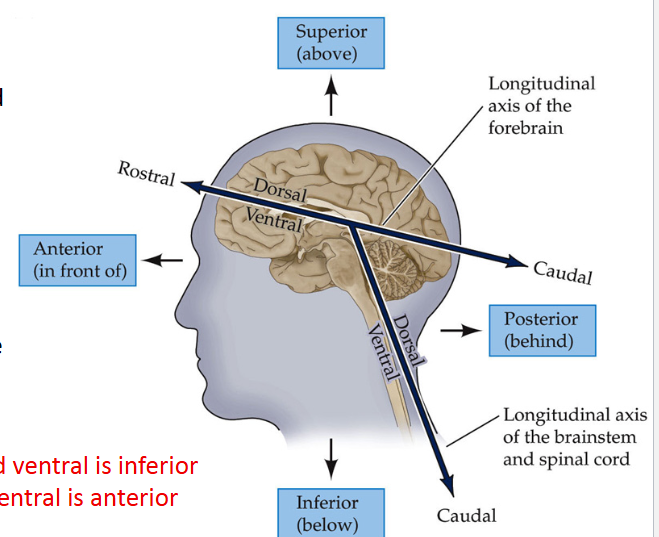
Directional terms for Brain and Spinal cord:
Define Dorsal
Refers to the back (For spinal Cord) and on top of the brain
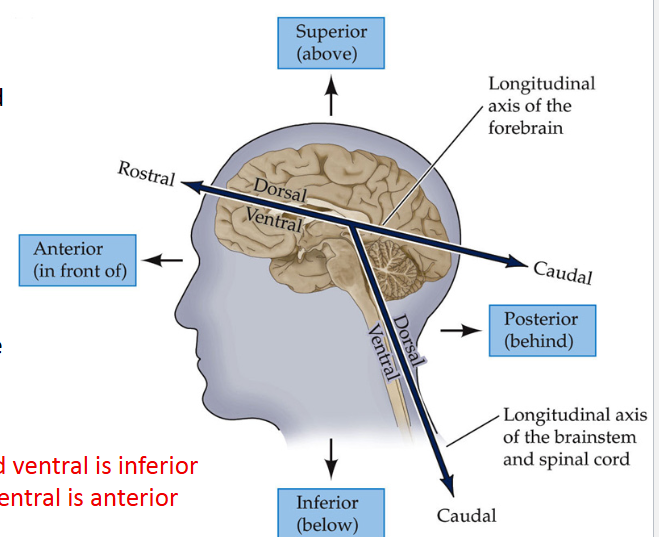
Directional terms for Brain and Spinal cord:
Define VENTRAL
Refers to the front (for spinal cord) and bottom of the brain
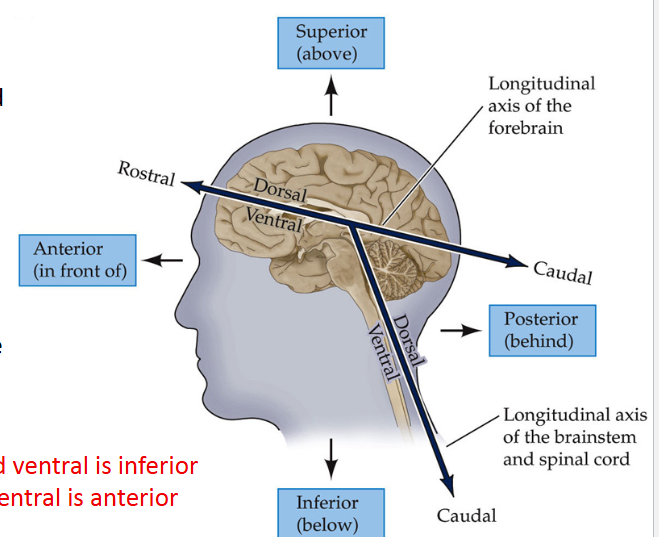
Directional terms for Brain and Spinal cord:
Define Rostral
“Toward the beak,” front of the brain and top of the spinal cord
Hint:
Rostral = Rooster = beak = Front
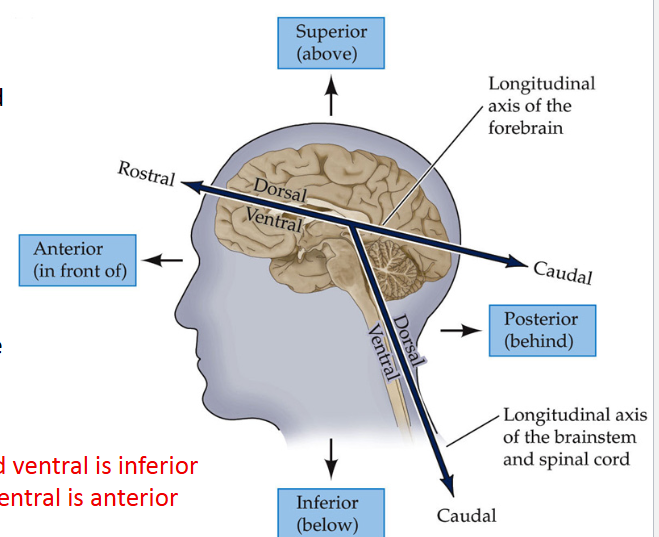
Directional terms for Brain and Spinal cord:
Define caudal
“Towards the tail,” back of the brain and bottom of the spinal cord
Hint:
Caudal = Cats have TAILS
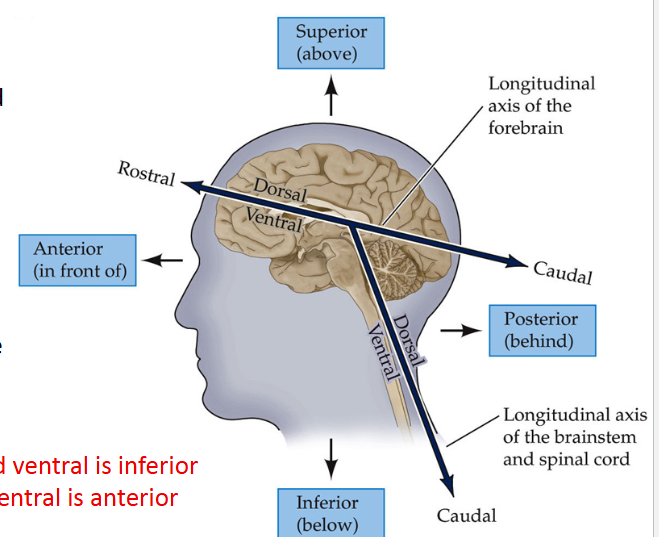
*For the brain, _____ is superior and _____ is inferior
dorsal; ventral
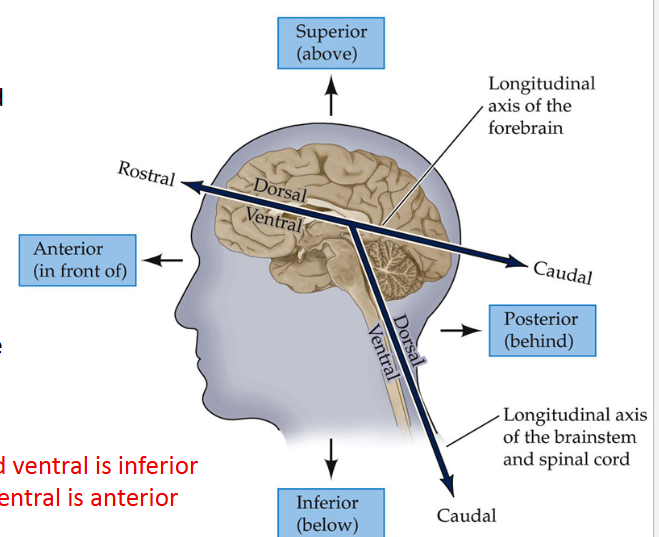
*For the spinal cord (SC), _____ is posterior and ____ is anterior
Dorsal; ventral
What are the Functions of the spinal cord (what does it do)?
Functions primarily in transmission of neural signals between the brain and body
Receives and processes sensory information from skin, joints and muscles of the limbs and trunk.
Controls movements of the limbs and trunk
How many spinal nerves are there?
There are 31 pairs of nerves (5 parts)
Name the 5 parts of the 31 spinal nerves?
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Coccygeal (cock-se-G-ul)
How many are there in each part of the Spinal Nerves?
Ex: how many cervical are in the spinal cord nerves that help add up to 31
Cervical (8)
Thoracic (12)
Lumbar (5)
Sacral (5)
Coccygeal (1)
How many are there in each part of the Vertebrae?
Cervical (7)
Thoracic (12)
Lumbar (5)
Sacral (5)
Coccygeal (4)
The first ____ pairs exit above their corresponding
vertebra, while the ______ cervical nerve exits between
____ and ___. The remaining spinal nerves exit below
their corresponding vertebrae.
Seven; Eight; C7 and T1
*Cranial nerves bypass the ____ and connect directly to the ____
Spinal Cord; Brain
The spinal cord connects the brain to nearly all parts of the body.
Which are composed of TWO different areas, what are they?
Inner H-shaped core of gray matter (composed of cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons)
Surrounding area of white matter (ascending and descending myelinated axons)
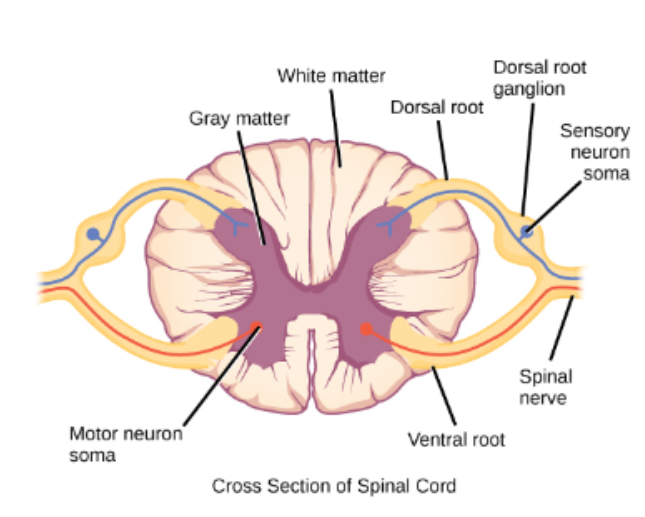
For the 1st one "the “inner H-shaped core of gray matter (composed of cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons")” what is this area composed of?
Two dorsal horns and Two Ventral horns
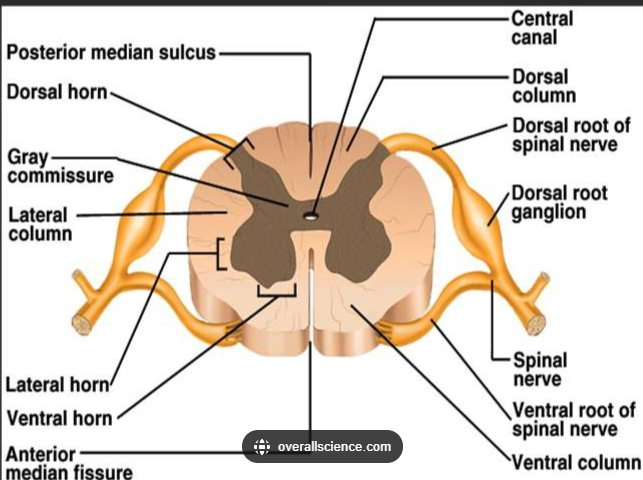
For the 2nd one “Surrounding area of white matter (ascending and descending myelinated axons)” at the level of each vertebra, the spinal cord gives off a pair of what?
At the level of each vertebrae, the spinal cord gives off a pair of dorsal and ventral roots to each side (left & right)
Dorsal _____, Ventral _____
Dorsal in, Ventral out
Hint:
Dorsal = Come in the Door
Ventral = if you want to Vent go outside
Define Decussation
Crossing of neuro pathways from one side of the brain or spinal cord to the other. Reason for the left brain controlling the right side of the body and vice versa
Define Plexus
Bundle of nerves that originates from a specific anatomical area and serves a particular region of the body
How many Plexuses are there and what are they? (Name them)
There are 3 Plexuses
Cervical Plexus, Brachial Plexus, & Lumbar Plexus
Define cervical plexus
Network of nerves in the neck that supplies innervation to the head, neck, and shoulders
Define Brachial Plexus
Network of nerves in the shoulder that carries motor signals from the spinal cord to the arms and hands
Define Lumbar plexus
Provides motor and sensory information to the lower abdominal, pelvic and thigh region
What is the largest part if the brain?
The Cerebrum (upper most region of the CNS)
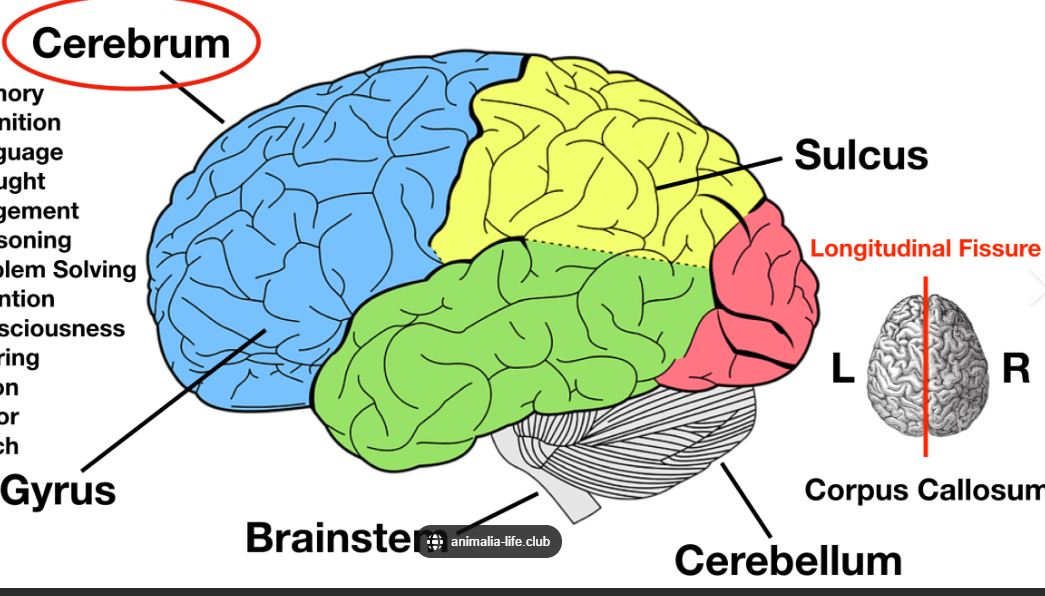
There are 2 hemispheres (left&right) that are divided into 4 or 5 lobes. What are the names of these lobes?
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Temporal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Insular Lobe
What is the frontal lobe responsible for? (3)
Executive function: attentional control, working memory, reasoning, problem solving
Personality
Movement
HINT:
Frontal lobe = Front door of the Brain
This front door leads to working memories, personality, movement, reasoning, probelm solving and attentional control
What is the Parietal Lobe responsible for? (1)
Sensory processing: touch, temperature, pressure
Hint:
Parietal Lobe = Parent
imagine a parent putting their hand on your forehead to check your temperature (touch + pressure too)
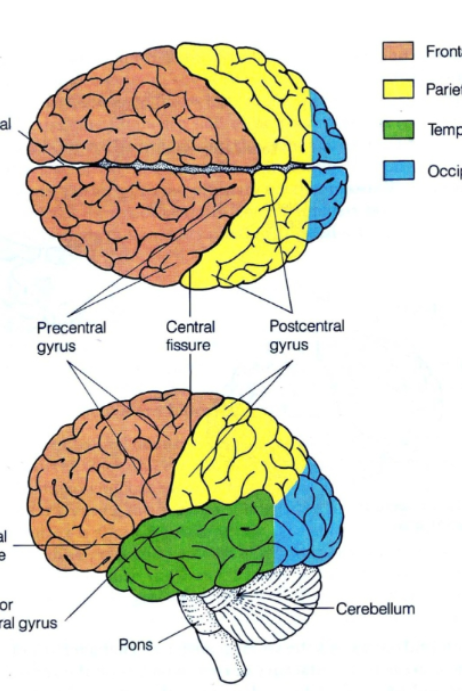
What is the temporal lobe responsible for? (1)
Memory, auditory information, and understanding language
HINT:
Temple = Telephone = listen to a phone call in your ears where your temples are. When you hear a voice, you remember who it is by memory by processing the auditory information and understanding the language being spoke to you
What is the Occipital Lobe responsible for? (1)
Visual processing
What is the Insular Lobe responsible for? (1)
Emotion, long-term memory, and behavior
The lobes are named are the skull _____ they underlie
BONES
What is the Cerebral Cortex:
Name TWO characteristics of the Cerebral Cortex
Refers to the corrugated surface (~3 mm deep) of the cerebral hemispheres
Wrinkled surface allows more cells in a limited space
(Be sure to remember what the purpose of the wrinkled surface is for!)
For the first one “Refers to the corrugated surface (~3 mm deep) of the cerebral hemispheres” what are the TWO CHARACTERISTICS of this surface?
~25 billion neurons (pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons; gray matter)
6 layers of cells (gray matter)
For the second one “Wrinkled surface allows more cells in a limited space” what is the TWO Characteristics of this surface? (2)
– Gyri (singular gyrus)
– Sulci (sulcus)
What is a gyrus and a Sulcus?
– Gyri (singular gyrus): folds, bumps or ridges
– Sulci (sulcus): grooves
TRUE or FALSE:
Majority of cortex not visible from outside but buried in sulci
true
TRUE or FALSE:
The cortex is where most neural integration happens in the CNS
TRUE
What are the TWO main sulcus?
Central sulcus
Lateral sulcus
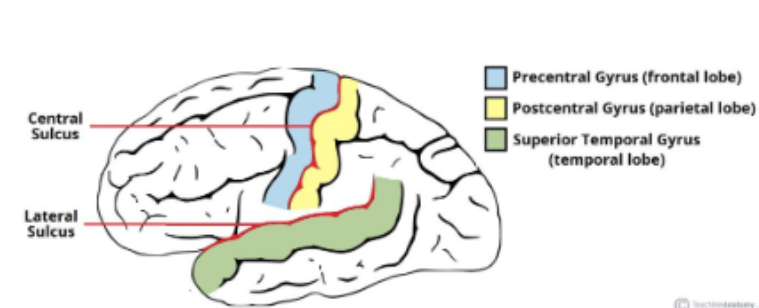
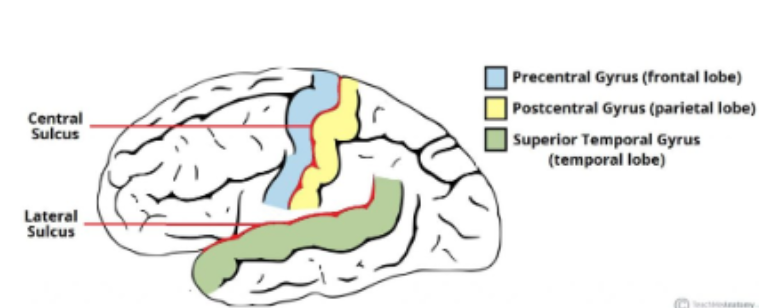
Define Central Sulcus
Groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes
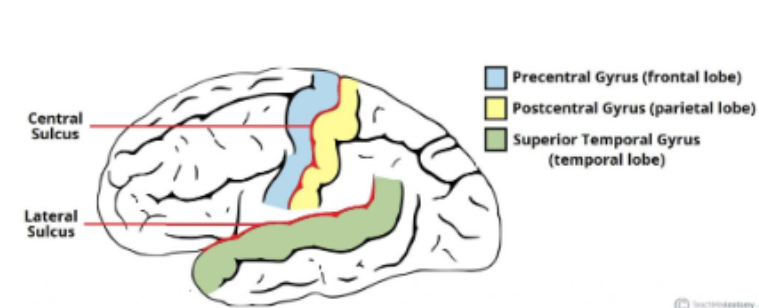
Define Lateral sulcus
Groove separating the frontal and parietal lobes from the temporal lobe
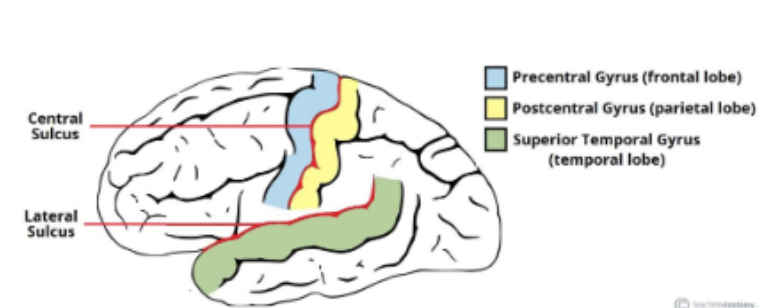
What are the TWO main gyri (gyrus)?
Precentral gyrus
Postcentral gyrus
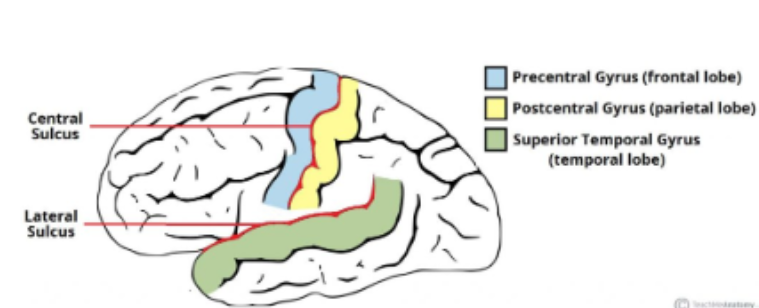
define Precentral gyrus
The ridge directly anterior to the central sulcus (primary motor cortex)
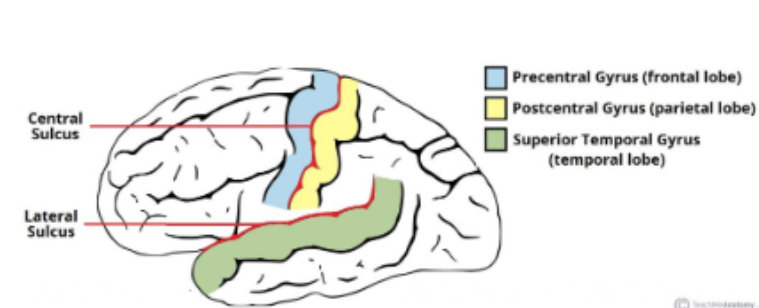
Define Postcentral gyrus
Ridge directly posterior to the central sulcus (primary somatosensory cortex)
What does Gray Matter contain?
Contains mostly neuronal cel bodies, their dendrites and associated glial cells
True or False:
The color of Gray Matter in living tissue is actually pinkish-light brown
TRUE
What does White Matter contain?
contains myelinated axons and white matter glial cells
What does the color of white matter come from, and kind of bundles does it contain?
Color comes from the lipid content of myelin sheaths
White matter contains bundles of myelinated axons that are called
tracts in the CNS
Where is the white matter most located in the brain and spinal cord?
on the inside
Where is the Gray matter most located in the brain and spinal cord?
On the outside
Define Ataxia
Having coordination issues
extra info. to help: a lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements leading to problems with balance, walking, etc…..
Define Meninges (explain what it does)
Covers, protects and nourishes the CNS
How many layers does the Meninges have, and what are they called?
3 LAYERS
Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, and Pia mater
Define Dura mater
Thick touch membrane connected to the cranium
Define Arachnoid mater
cushions the brain, CSF
Define Pia mater
thin layer that adheres to the surface and follows its contours, with many capillaries
True or False:
The brains dura mater is connected to the skull bone, whereas the spinal cords dura mater is surrounded by fluid and fat.
TRUE
Define Meningitis
infection causing inflammation of the meninges
define Subdural Hematoma
Blood pooling in the subdural space causing intra-cranial pressure
Who is Broadman? And what did he examine?
A German neuroanatomist (early 1900s) who examined structural differences in cells to identify 52 different areas
What Brodmann areas correspond to the motor function and sensory
function?
Motor- Areas 4,6
Sensory - Areas 3,1,2, and 5,7
The nervous system has two types of cells, what are they?
Nerve cells and Glial cells
Define Nerve Cells
(Neurons) the signaling units (information messengers)
Nerve Cells:
Name 3 characteristics of the Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons
carry sensory information form receptors in the periphery to the CNS for a response
Pseudo-unipolar
Afferent
Nerve cells:
What is the function of the Motor neurons cells?
Carry motor commands from the CNS to innervate target cells (i.e., other neurons, muscle and glands
True or False:
Neurons can also be classified according to their connections?
TRUE
Define Afferent neurons (sensory)
Brings information into the CNS
Define Efferent Neuron (motor)
Take information away from CNS