AP World History Unit 0
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
paleolithic
(Old Stone Age) a long period of human development before the development of agriculture
pastoral
nomadic animal-herding societies often known for spreading religion, culture, and technology across trade routes throughout history
conduit
a means by which something is transmitted
surplus
More of something than as needed.
metallurgy
the science of working with metals
agrarian
relating to land; relating to the management or farming of land
elite
People of wealth and power; upper class -- did not emerge until settled societies developed
egalitarian
believing in the social and economic equality of all people - existing before setting societies in hunter-gatherer groups
patriarchy
a form of social organization in which men are the supreme authority in the family, society, and political realm
Neolithic Revolution
(10,000 - 8,000 BCE) The development of agriculture and the domestication of animals as a food source. This led to the development of permanent settlements and the start of civilization.
specialization
The concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and firms on a limited number of activities; increases efficiency
social hierarchy
The division of society by rank or class.
disseminate
To scatter or spread widely
monumental architecture
Large structures, such as pyramid, temples, public spaces, and large statues, that tend to appear wherever powerful leaders emerge; a feature of all agrarian civilizations.
urban planning
The area of land use planning which explores several aspects of built and social environments of municipals and communities.
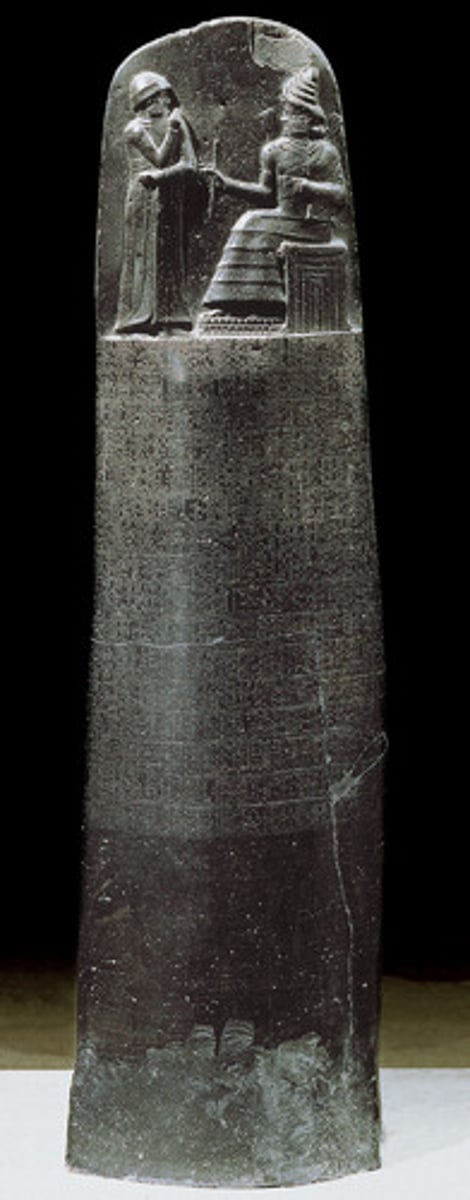
Code of Hammurabi
credited as the first written law code; written by a Babylonian king and established the basis for law codes

Zoroastrianism
One of the first monotheistic religions, particularly one with a wide following. It was central to the political and religious culture of ancient Persia.

Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. They preserved their early history in the Old Testament.

Vedic religion
The ancient religion of the Aryan peoples who entered northwestern India from Persia c. 2000-1200 B.C.E. It was the precursor of Hinduism, and its beliefs and practices are contained in the Vedas

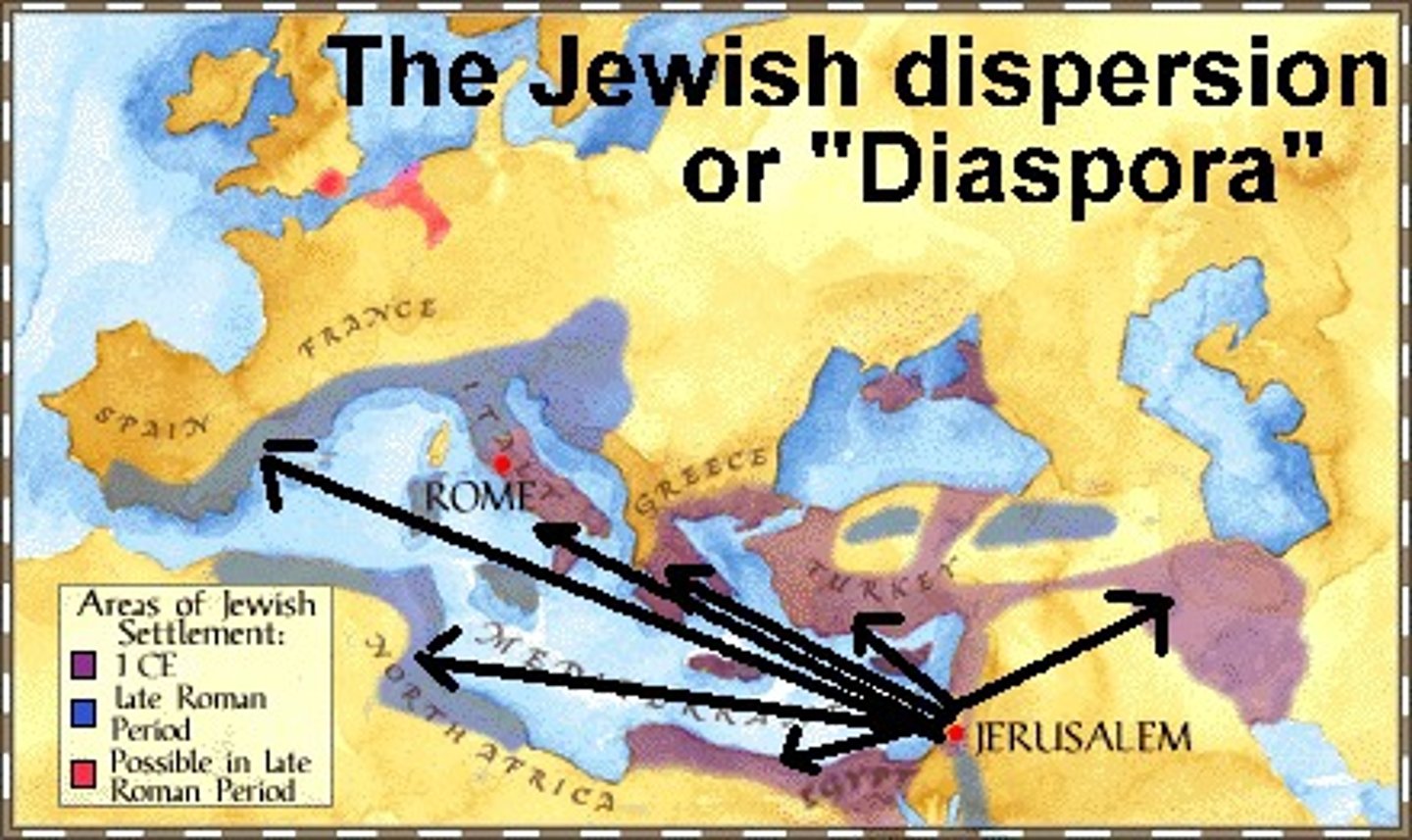
diaspora
any group migration or flight from a country or region; dispersion. Particularly used in relation to Jews scattered by Romans in 70 CE or to Africans spread to new places during the Atlantic Slave Trade.
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation, karma, the caste system, and a supreme being who takes many forms

Buddhism
A religion with origins in South Asia in which Buddha (a former prince) taught that life is suffering, which is caused by desire. Suffering ceases when desire ceases. Enlightenment (Nirvana) is obtained through following the Eightfold Path.

Confucianism
A philosophy that adheres to the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius. It shows the way to ensure a stable government and an orderly society in the present world and stresses a moral code of conduct.

five relationships
Confucian philosophy about social order where everyone has a place and respect is paid to elders, parents, and the government. The relationships are, ruler to ruled, father to son, older brother to younger brother, husband to wife, friend to friend.
filial piety
In Confucian thought, one of the virtues to be cultivated, a love and respect for one's parents and ancestors.
Mandate of Heaven
A political theory developed during the Zhou Dynasty of ancient China in which those in power were believed to have the the right to rule from divine authority.
Christianity
An Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in the New Testament. Drew on Judaism and initially rejected Roman and Hellenistic influences. Spread through the efforts of missionaries and merchants. Eventually gained support by the time of Emperor Constantine.

Greco-Roman philosophy
emphasized logic, empirical observation, and the nature of political power

monasticism
Living in a religious community apart from secular society and adhering to a rule stipulating chastity, obedience, and poverty. (Primary Centers of Learning in Medieval Europe) - occurred in Christian and Buddhist communities

shamanism
tribal religion; involves community acceptance of a shaman, religious leader, healer, and worker of magic who can intercede with the spirit world (ex: Mongols)

animism
Belief that objects, such as plants and stones, or natural events, like thunderstorms and earthquakes, have a discrete spirit and conscious life (ex: Shintoism in Japan)

ancestor veneration
Worship and respect for ancestors (occurred in African, Mediterranean, East Asia, and Andean societies during the classical time period)
Hellenistic
The spread of Greek culture, Greek history, language from the death of Alexander the Great
centralized government
A government in which power is concentrated in a central authority to which local governments are subject (ex: China, Rome, Byzantines, etc)
stirrup
device for securing a horseman's feet, enabling him to wield weapons more effectively. First evidence of the use of stirrups was among the Kushan people of northern Afghanistan in approximately the first century C.E.

lateen sail
triangular sail that made it possible to sail against the wind; used in the Indian Ocean trade
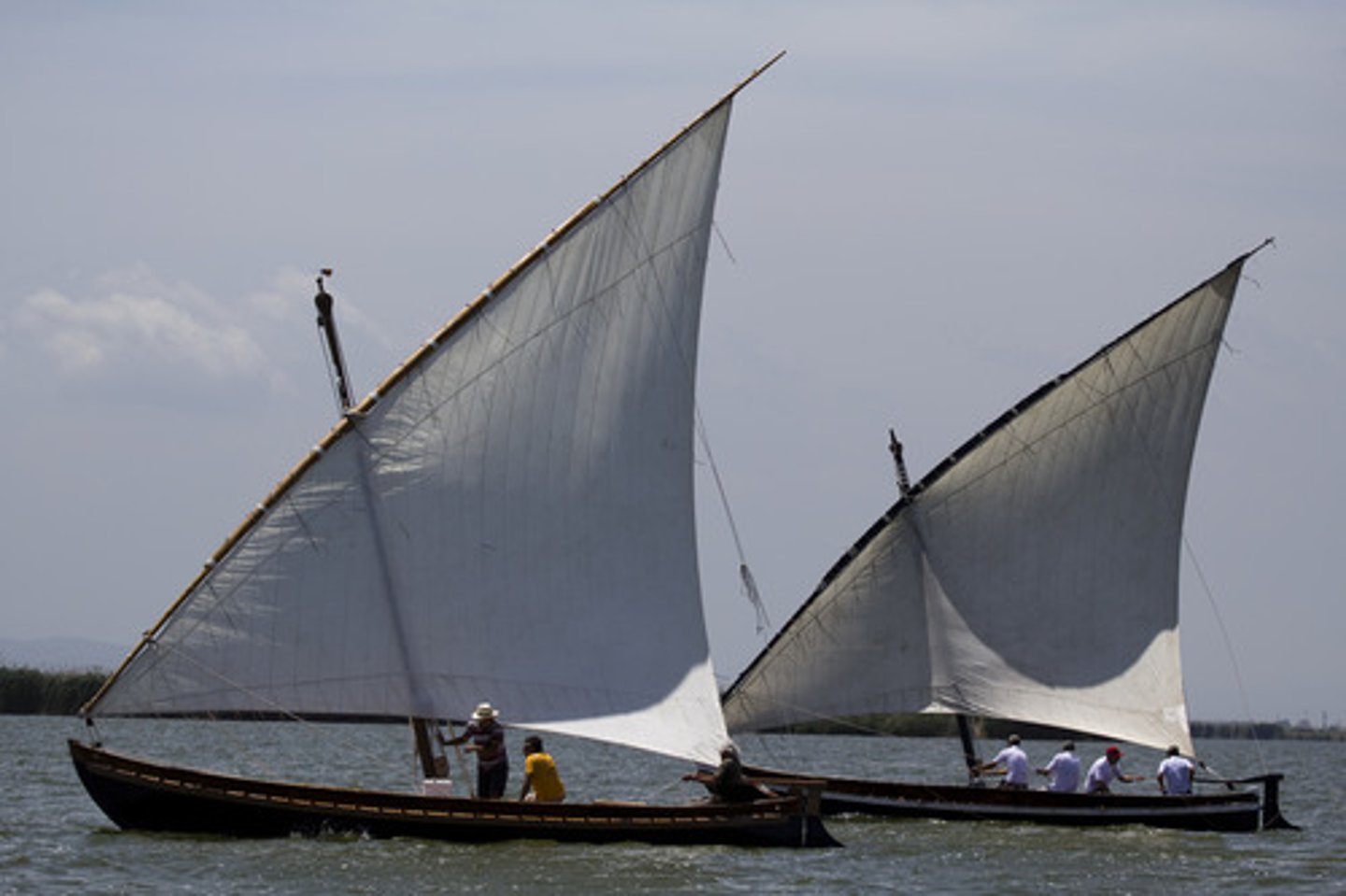

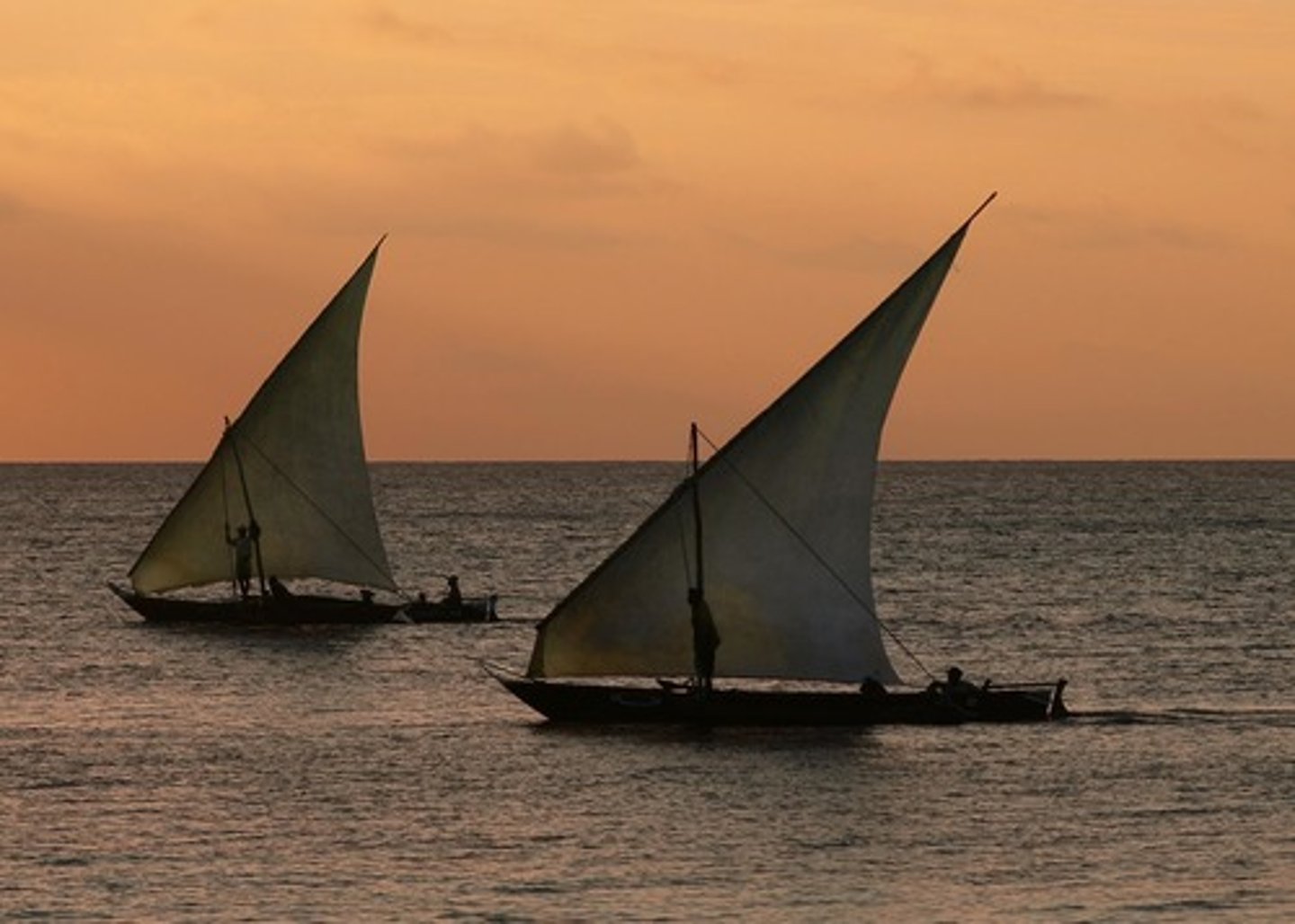
dhow ship
emerged in middle east; sturdy enough to carry a lateen sail to cross open water; vessel of commerce and used in the Indian Ocean

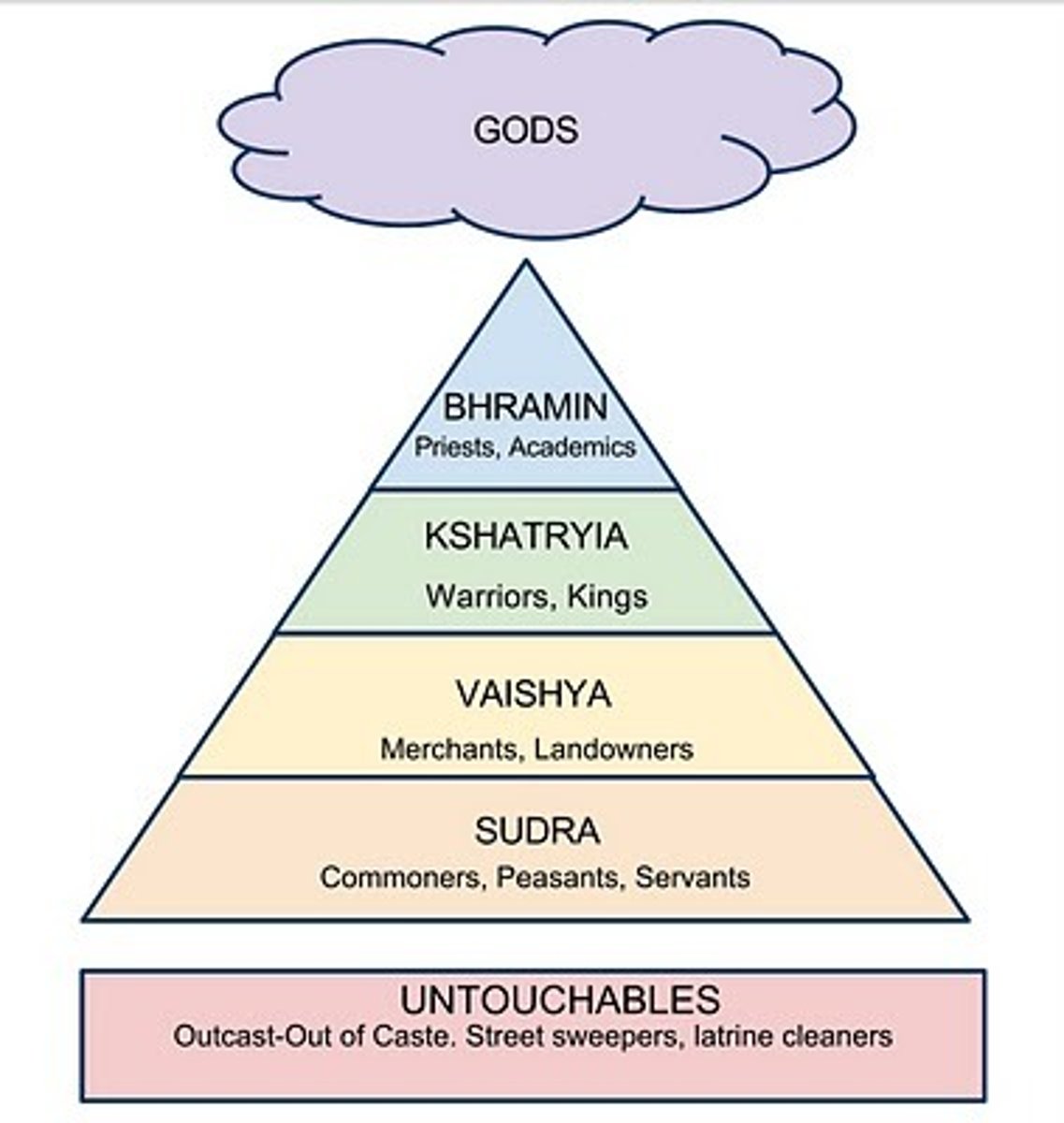
caste
(n.) any of the social or subclasses of traditional Hindu society, such as the Brahman or Sudra castes; a social class distinct from others and characterized by hereditary rank, profession or wealth; (n.) a social position conferred on someone based on a system of castes
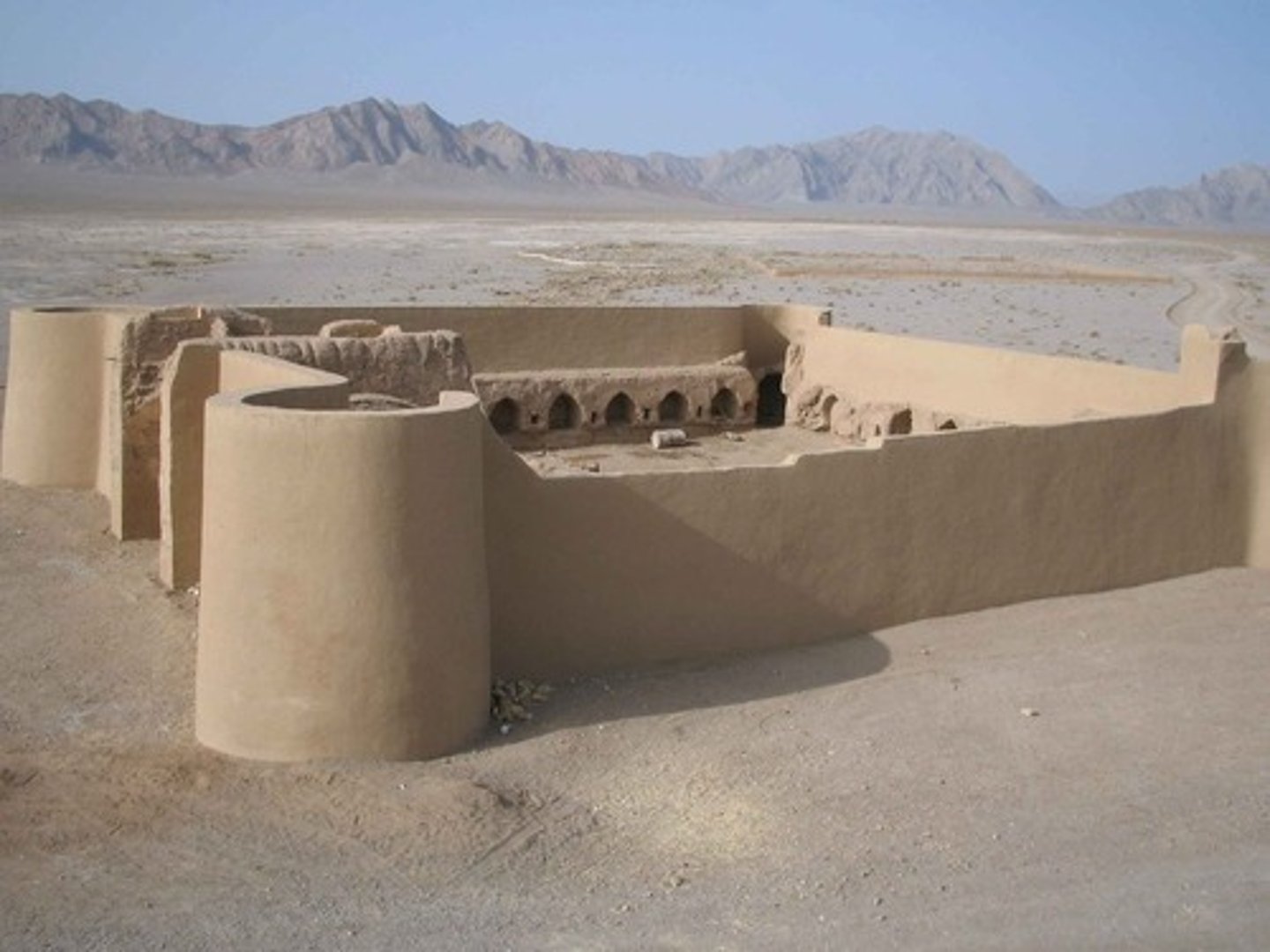
caravanserai
Fortified inns that were built along trade routes in Central and Western Asia in the twelfth century to provide food, lodging, and protection for merchants traveling with camels, donkeys, and horses.

collapse of classical empires
spread of disease, over-expansion, corrupt governments, invasions by nomadic/pastoral groups, over-taxation of peasants, food shortages
Legalism
Chinese philosophy developed by Hanfeizi; taught that humans are naturally evil and therefore need to be ruled by harsh laws; embraced by the Qin Dynasty
Daoism
Chinese religion that believes the world is always changing and is devoid of absolute morality or meaning. They accept the world as they find it, avoid futile struggles, and deviate as little as possible from "the Tao/Dao" also known as "the way" or "path" of nature; emphasized living in harmony with nature; ying and yang