1.3 Pathology of the Kidneys
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is the functional unit of the kidney?
Nephron (glomerulus & renal tubules)
What will happen if any portion of the nephron is damaged?
Reduced renal function
Potential progressive damage
What changes are often seen in early stages of kidney disease?
Specific anatomic components targeted by specific insults
(ex: glomeruli in immune-mediated disease)
In more chronic kidney disease what pathological changes are often seen?
Non-specific end-stage responses caused by multiple different insults
What are the portals of entry for renal disease?
Hematogenous (septic embolic nephritis or ischemic necrosis)
Via glomerulus (substances secreted into ultrafiltrate or preformed filtered toxins/metabolites)
Ascending from ureter (extension from lower tract)
What are ascending renal infections from the ureters typically secondary to?
GIT content contamination (diarrhea)
Genital tract contamination (pyometra)
Skin contamination (perivulval dermatitis)
What are some developmental disorders of the kidney?
Renal aplasia (failure of development), hypoplasia, or dysplasia
Ectopic kidneys
Polycystic kidney disease
Fused kidneys
Progressive juvenile nephropathy
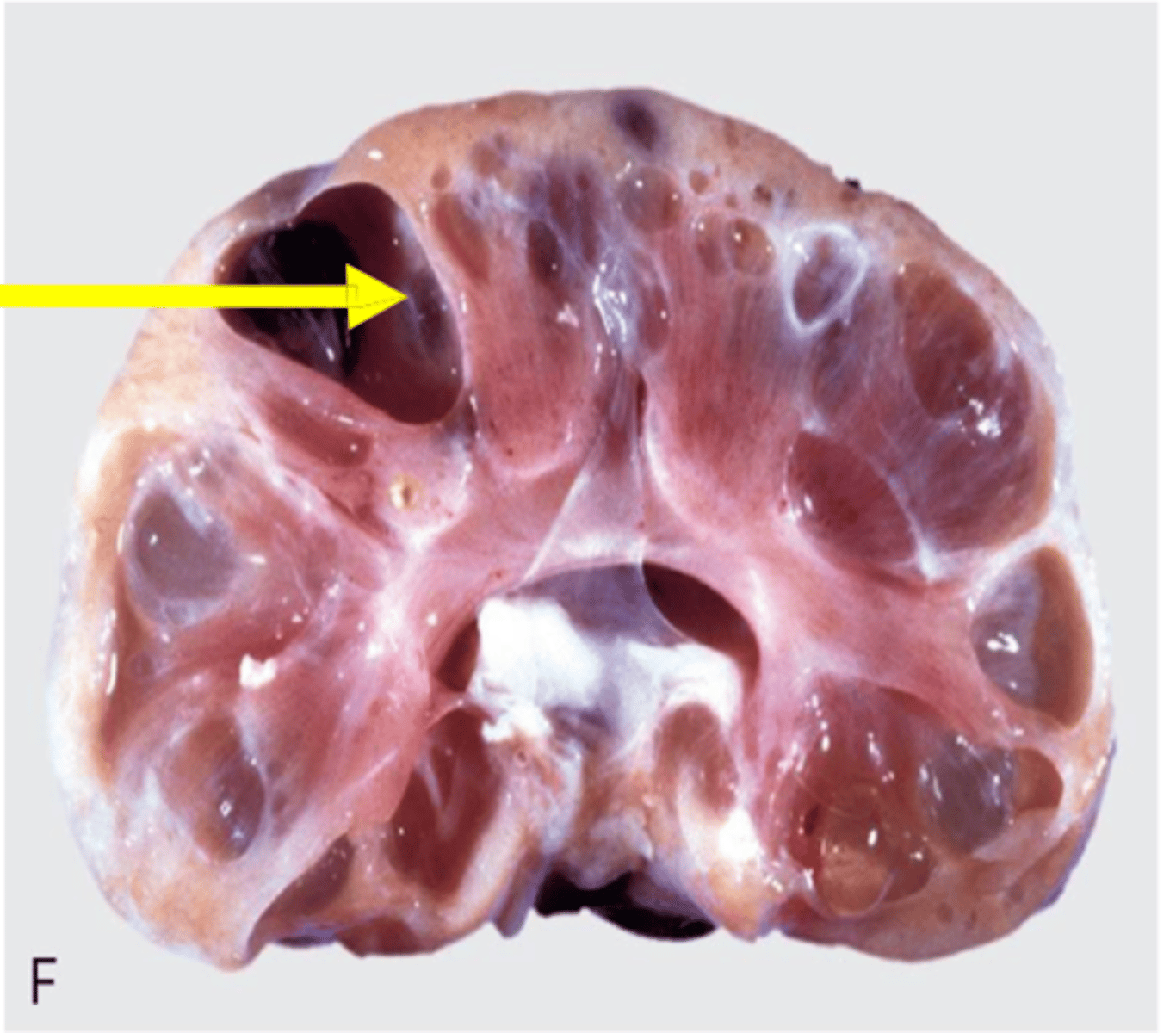
Polycystic kidney disease
Genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys
Persian cats predisposed
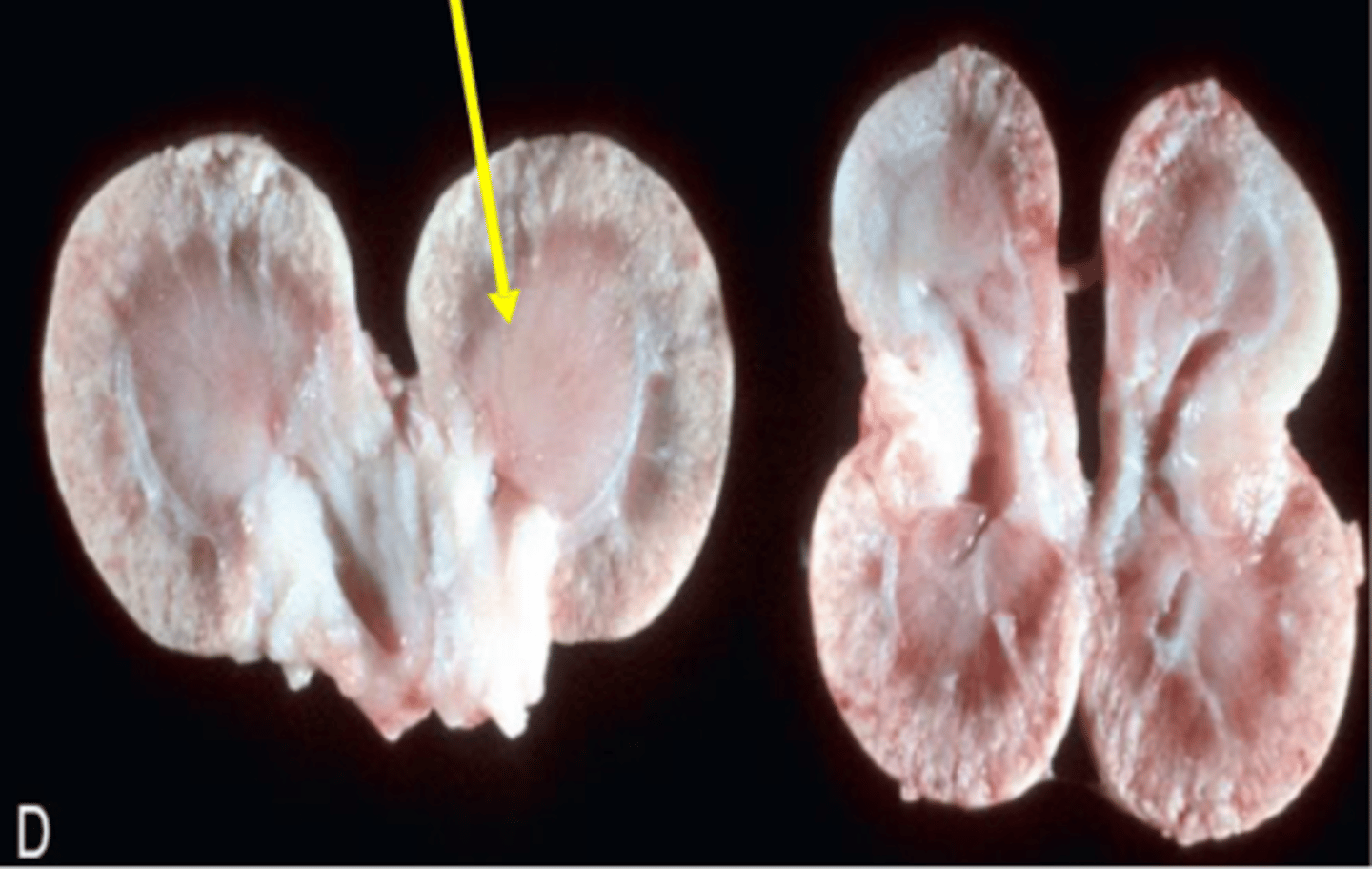
Progressive juvenile nephropathy
Failure of kidney development leading to disease in early life
Glomerulus
Convoluted tuft of fenestrated capillaries supported by a mesangial matrix within Bowman's Capsule
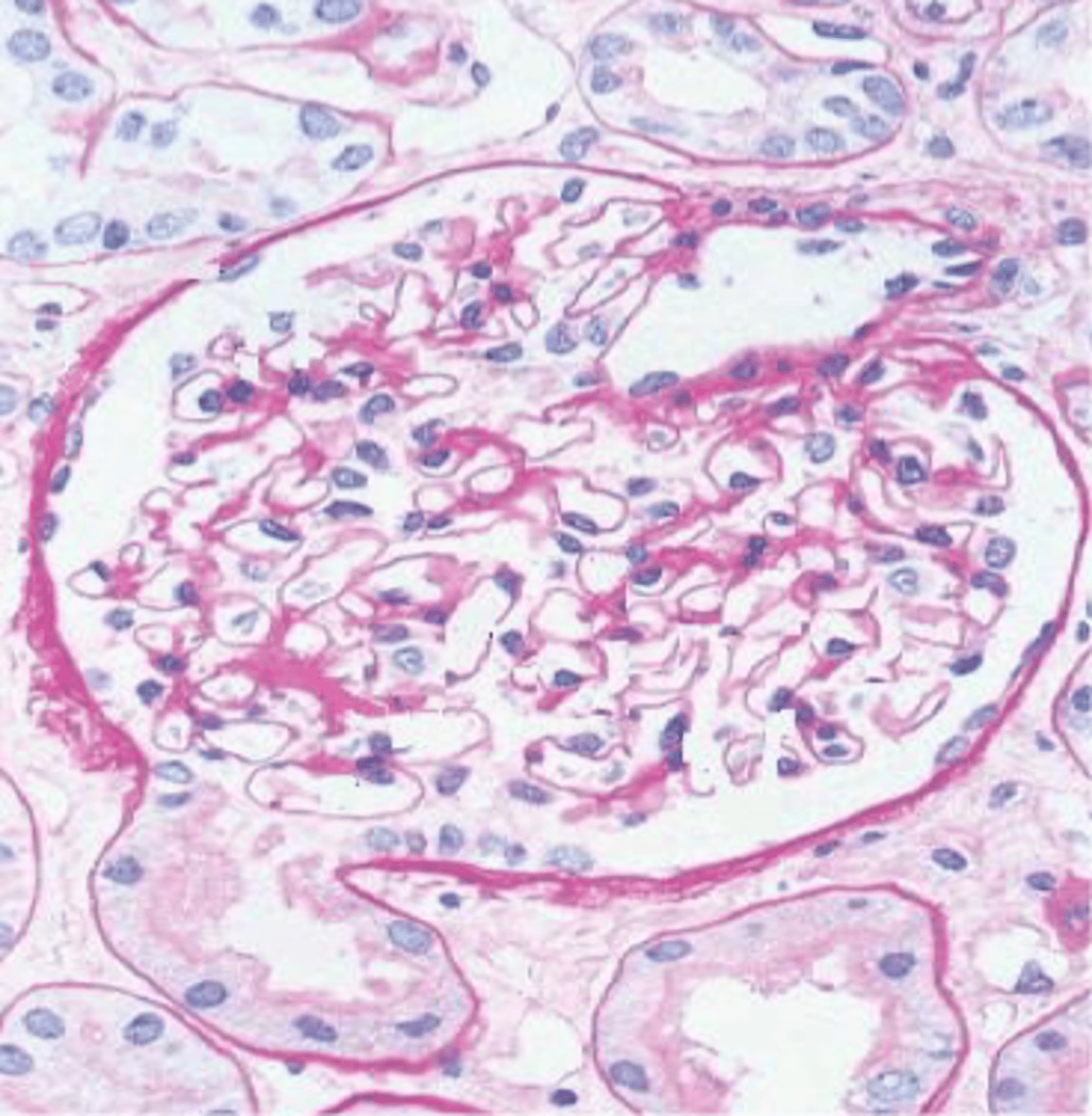
Glomerular filtration barrier
Fenestrated endothelium
Basement membrane
Pedicles of podocytes
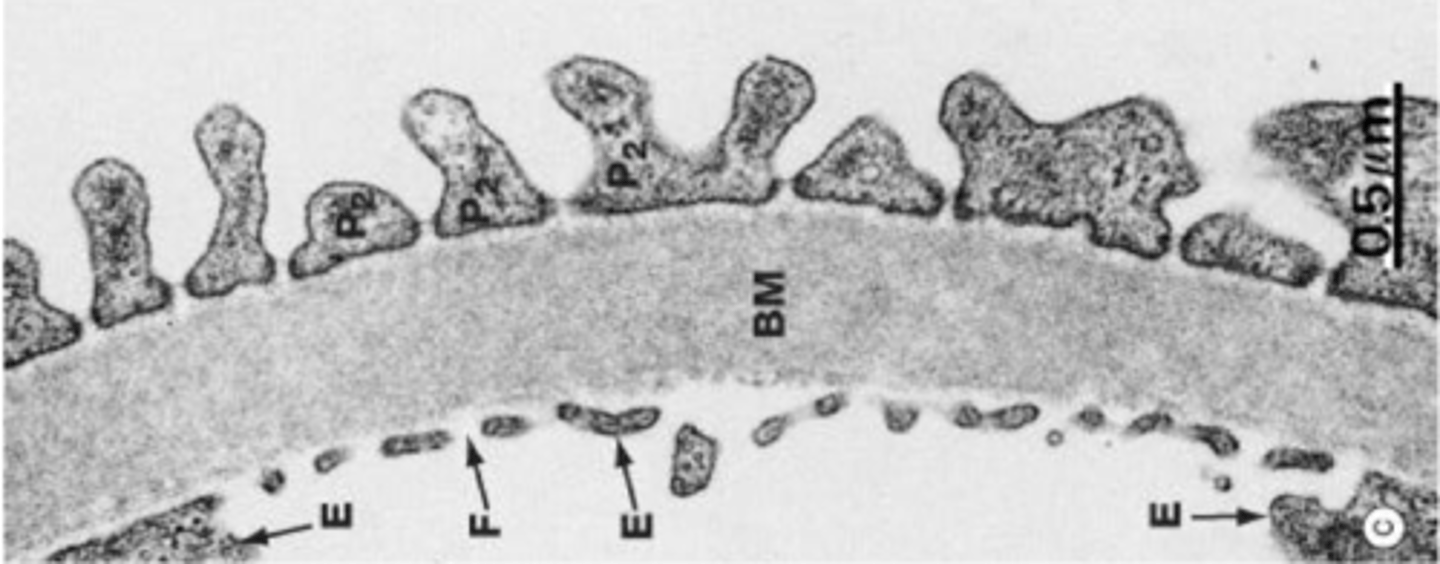
Ultrafiltrate (glomerular filtrate)
Fluid formed within the nephron after passing through the glomerulus into Bowman's Space
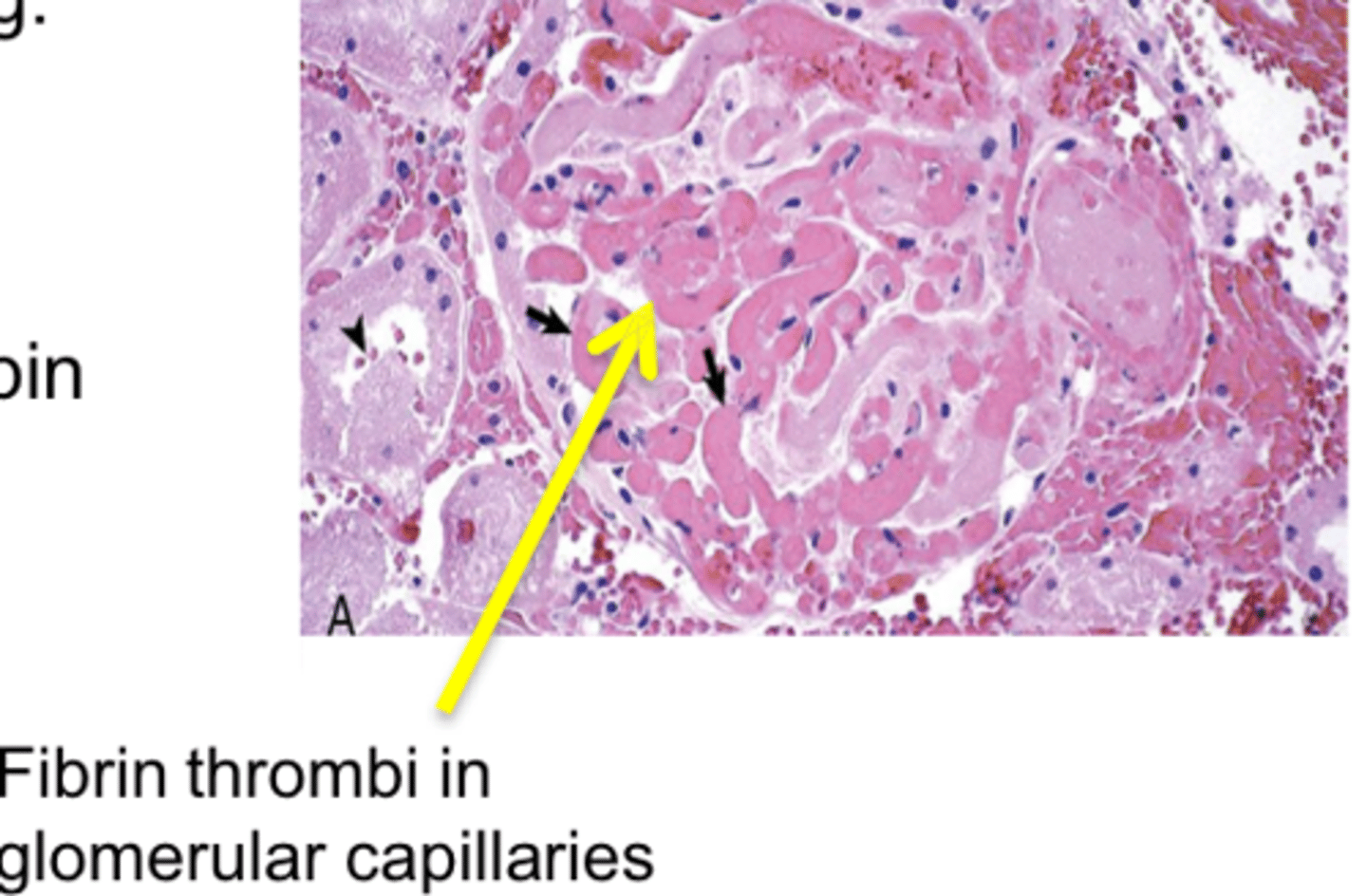
Immune-mediated glomerulonephritis
Persistent infections or prolonged antigenemia enhance the formation of soluble immune complexes
Complement fixation & associated leukocyte damage occurs
What are some diseases that can cause immune-mediated glomerulonephritis?
FeLV
FIP
Pyometra
Pyoderma
Chronic parasitism
Auto-immune disease or neoplasia
Describe the gross pathological change seen with immune-mediated glomerulonephritis
Pinpoint pale/tan foci in the renal cortex
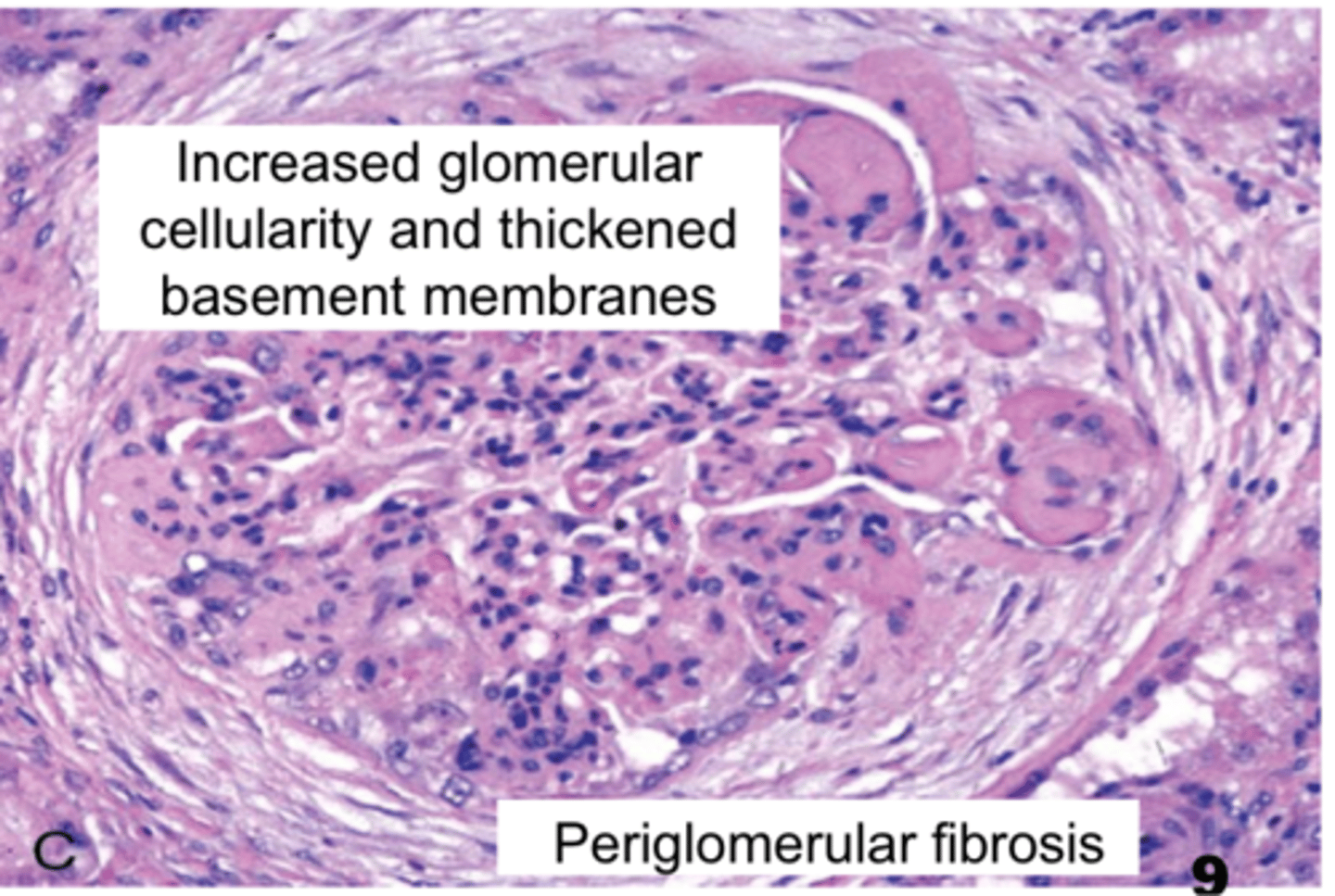
Describe the microscopic pathology associated with immune-mediated glomerulonephritis
Increased glomerular cellularity with thickened basement membranes
Periglomerular fibrosis
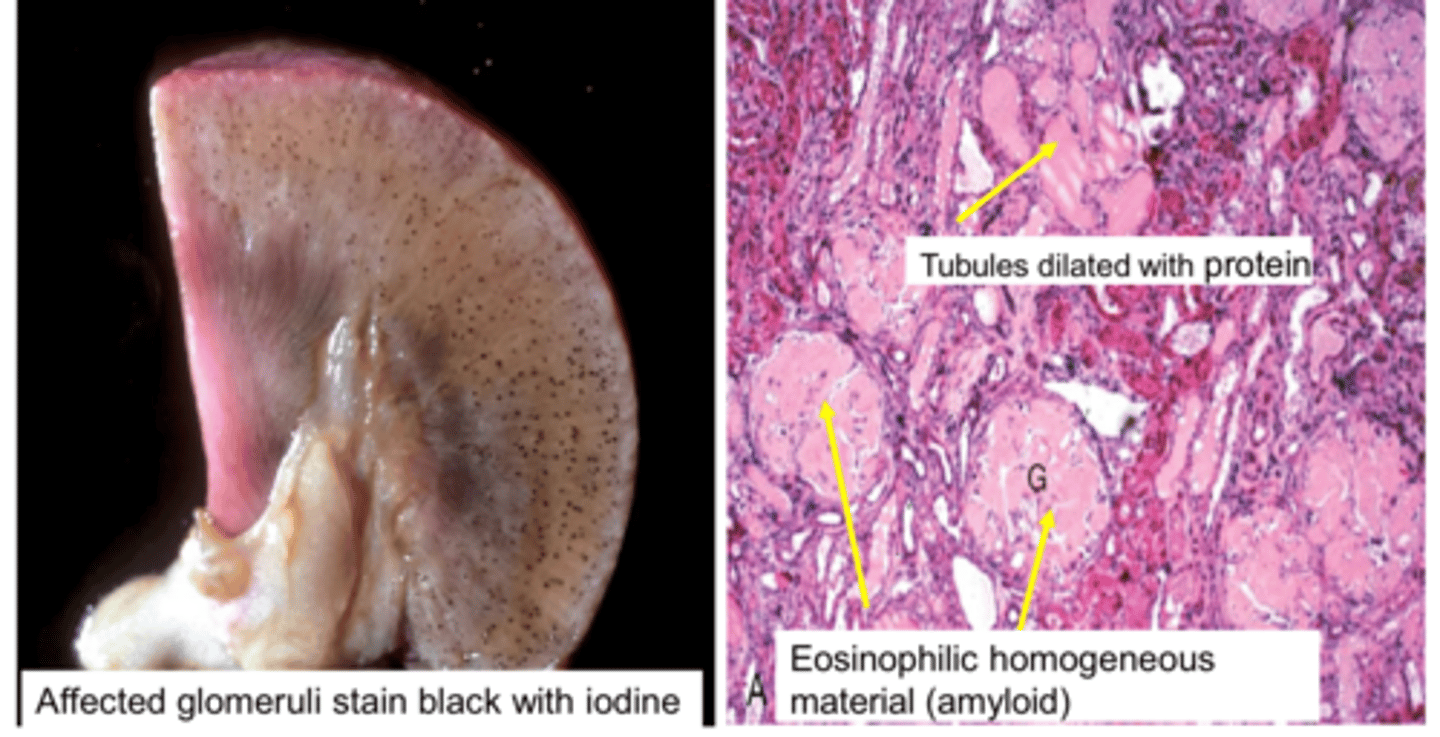
Glomerular amyloidosis
Accumulation of insoluble extracellular protein
Most cases occur secondary to chronic inflammation
Affected glomeruli stain black with iodine on gross pathology
Tubules dilated with protein & eosinophilic homogenous material show on microscopic pathology
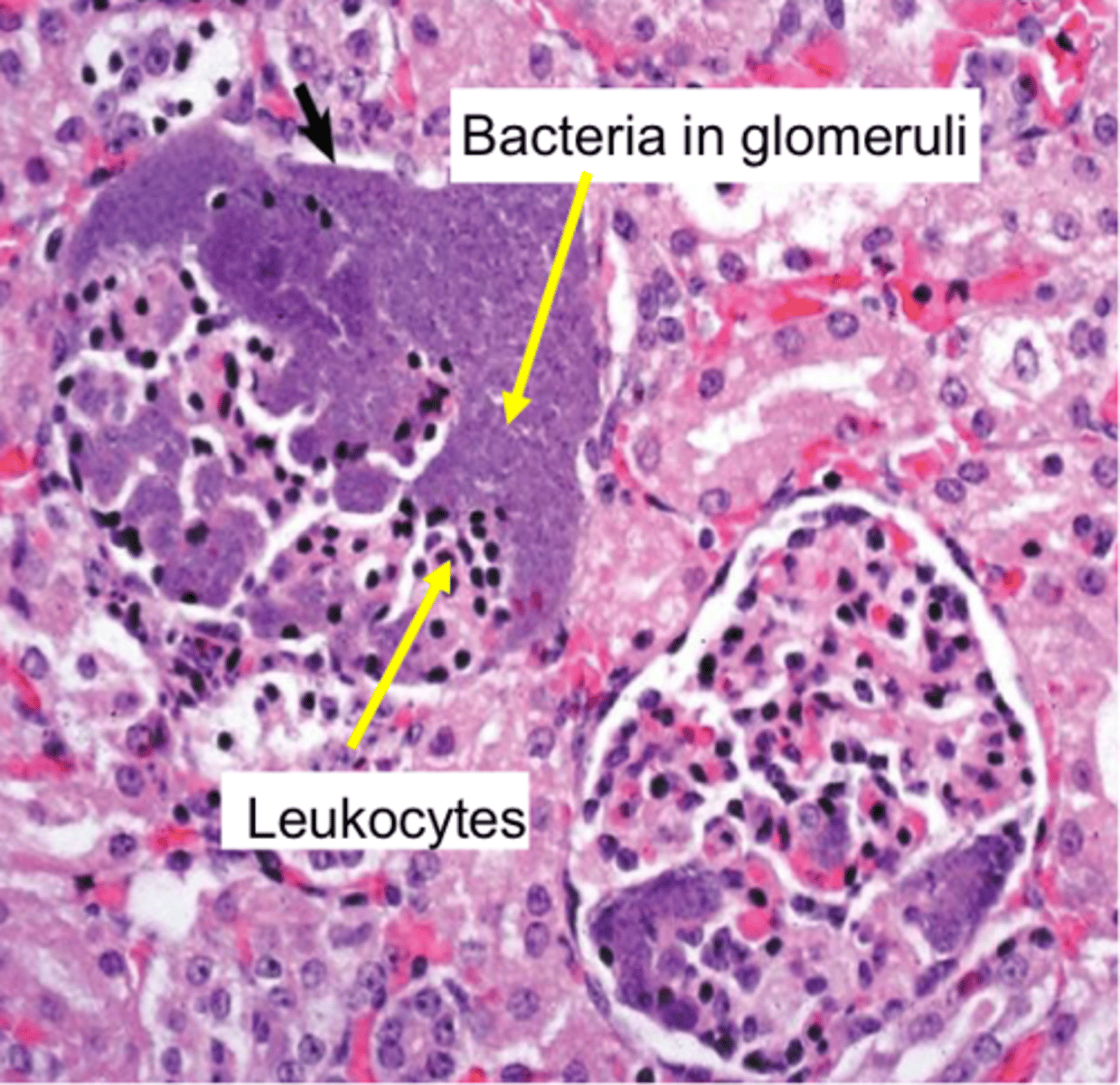
Acute suppurative glomerulitis
Bacteria lodge in glomerular & interstitial capillaries
Formation of multiple cortical microabscesses
Random tan/red, raised foci of gross pathology
Leukocytes & bacteria in glomeruli on microscopic pathology
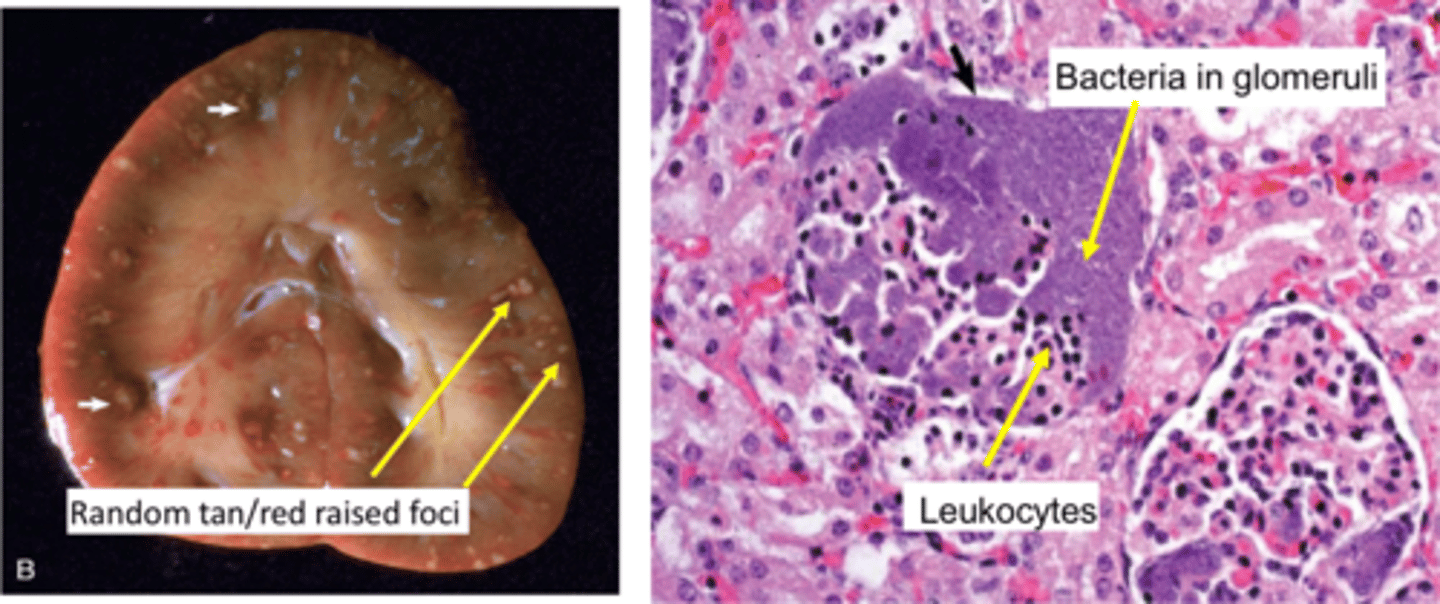
What are some diseases that cause Acute Suppurative Glomerulitis?
Actinobacillus equuli (foals)
Trueperella pyogenes (cattle)
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae (pigs)
Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis (sheep & goats)
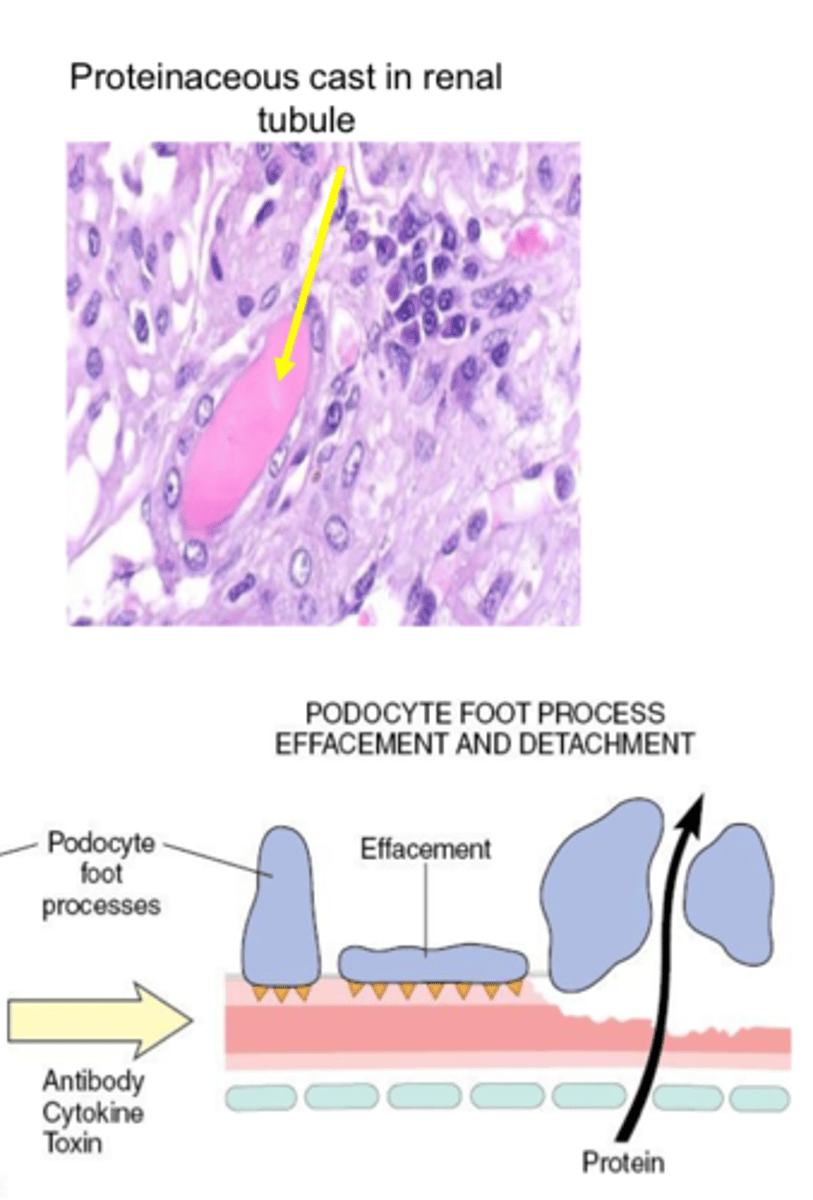
What are some consequences of glomerular damage?
Protein losing nephropathy leading to nephrotic syndrome
- loss of protein into ultrafiltrate
Protein losing nephropathy
Leakage of albumin into glomerular filtrate overwhelms resorptive ability of PCT leading to proteinuria
Leads to hypoproteinemia & reduced plasma osmotic pressure
Loss of antithrombin III (anticoagulant)
Nephrotic syndrome
Group of clinical signs and symptoms caused by excessive protein loss in urine
Low protein edema & effusions into body cavities with hypercoagulability & hypercholesterolemia
Acute tubular necrosis
Damage to the renal tubules due to presence of toxins in the urine or ischemia
Most important cause of acute kidney injury
What are the mechanisms of damage to the kidney by nephrotoxins?
Direct damage to tubular epithelium
Production of reactive metabolites that stimulate vasoconstriction (lead to toxin-associated ischemia)
What are the mechanisms of damage to the kidney by ischemia?
Reduced renal perfusion leads to reduced GFR
Results in arteriolar vasoconstriction, worsening the ischemia
*Nephrotoxic & ischemic insults can be synergistic*
How can the renal tubules respond to acute tubular necrosis?
If basement membrane remains, tubules can regenerate (remaining epithelial cells proliferate)
Loss of basement membrane leads to replacement by fibrosis (non-functional)
Regeneration is more likely with toxic damage versus ischemia
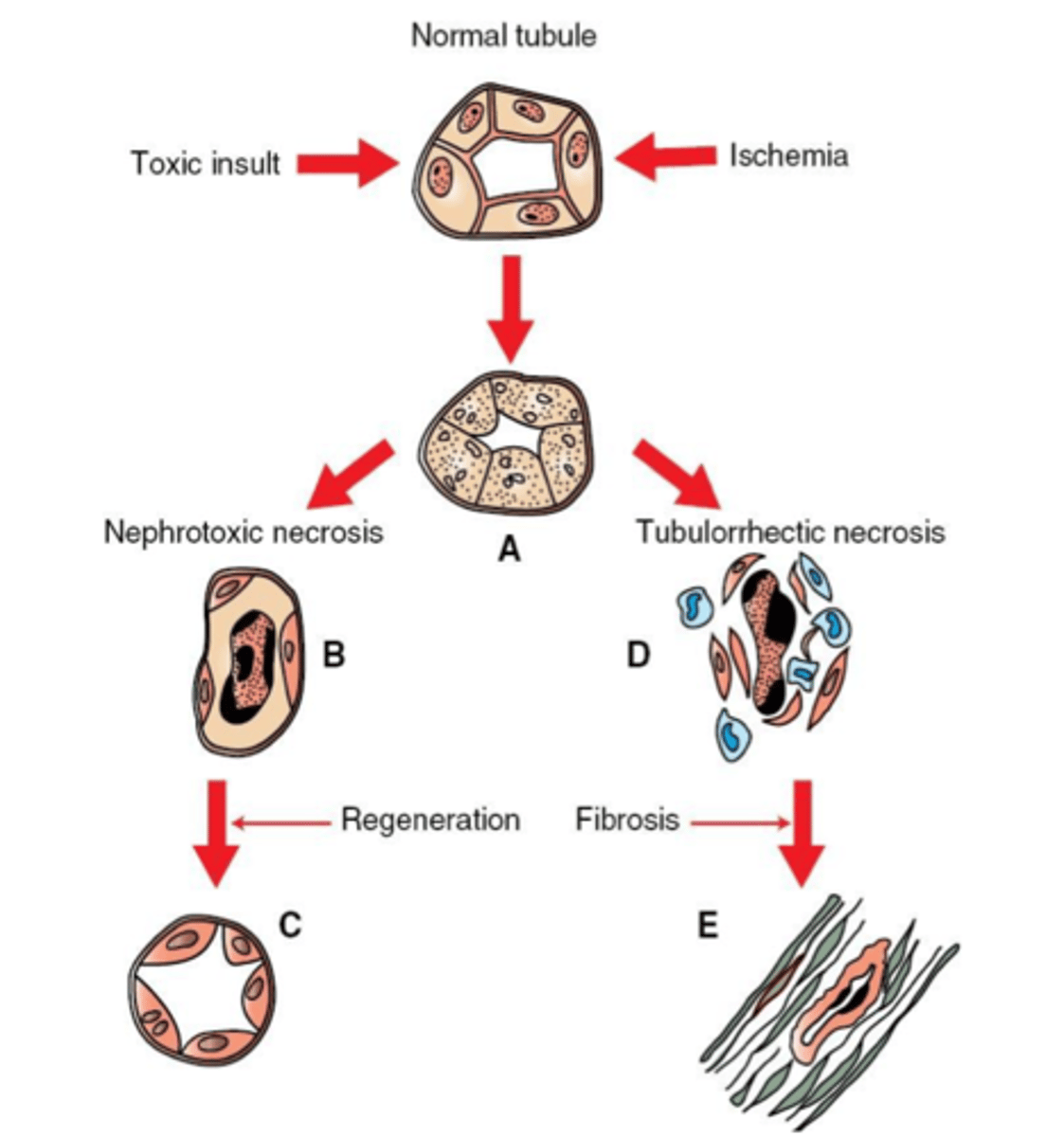
What are some causes of acute tubular necrosis?
Drugs (NSAIDs)
Fungal & plant toxins
Ethylene glycol (antifreeze)
Bacterial toxins (Pulpy Kidney Disease)
How can NSAIDs result in acute tubular necrosis?
Reduce prostaglandin synthesis leading to afferent arteriole constriction
Decreased renal perfusion leads to acute tubular & papillary necrosis
Additional risk with dehydration, CHF, or CKD
What are some examples of fungal & plant toxins that can cause acute tubular necrosis?
Mycotoxins (Aspergillus spp.)
Lily (cats)
Grapes & raisins (dogs)
Oak tannins (cattle & horses)
How does ethylene glycol cause acute tubular necrosis?
Readily absorbed from the GIT in dogs, cats & pigs
Oxidized by the liver into toxic metabolites (glycolic acid & oxalate)
Filtered by glomeruli causing direct damage to renal tubules
Antifreeze ingestion or oxalate containing plants can cause
What gross pathological change is seen in acute tubular necrosis due to ethylene glycol toxicosis?
White streaks in the renal cortex
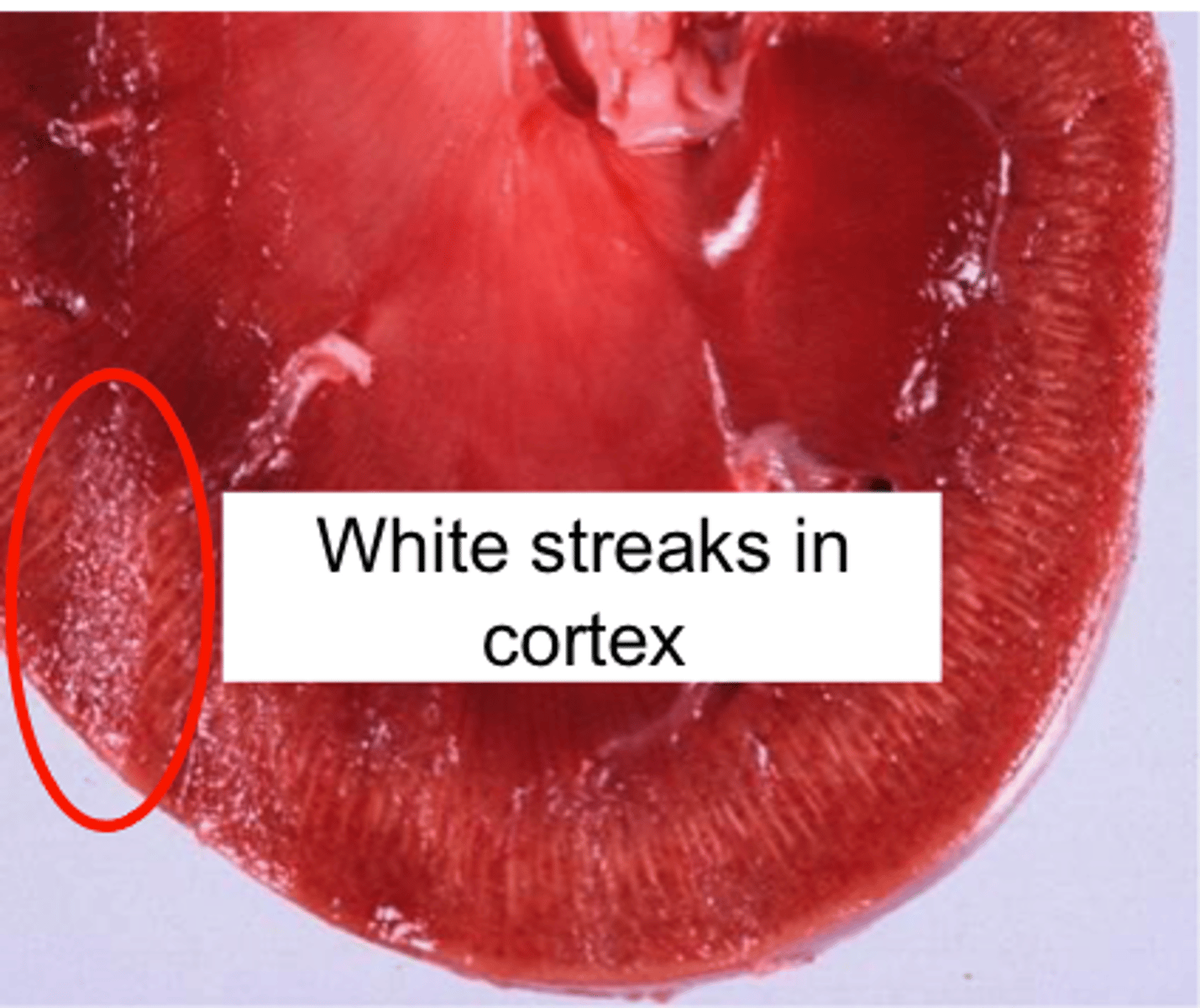
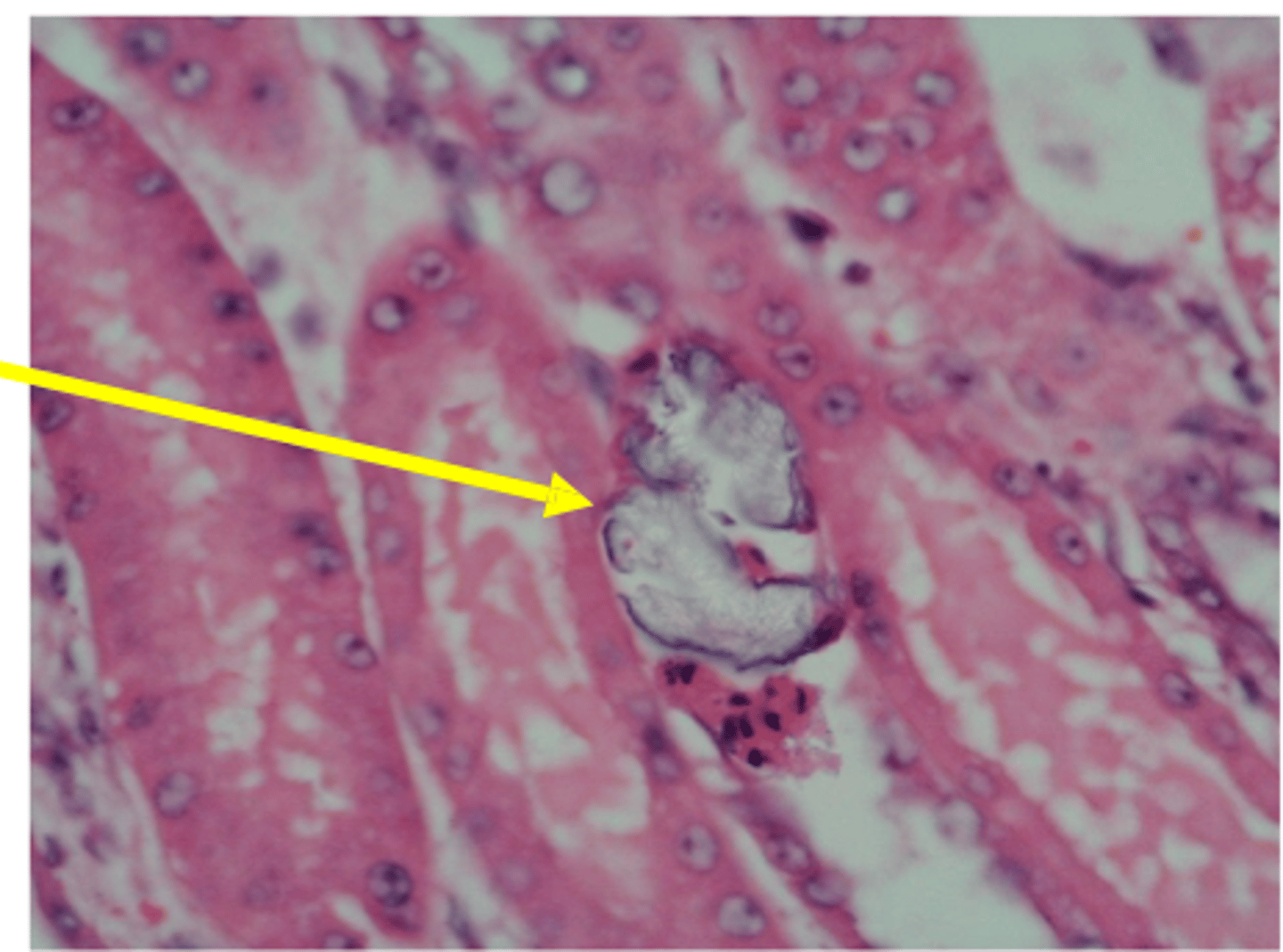
What microscopic pathological change is seen in acute tubular necrosis due to ethylene glycol toxicosis?
Calcium oxalate crystal precipitate in the tubules causing obstruction
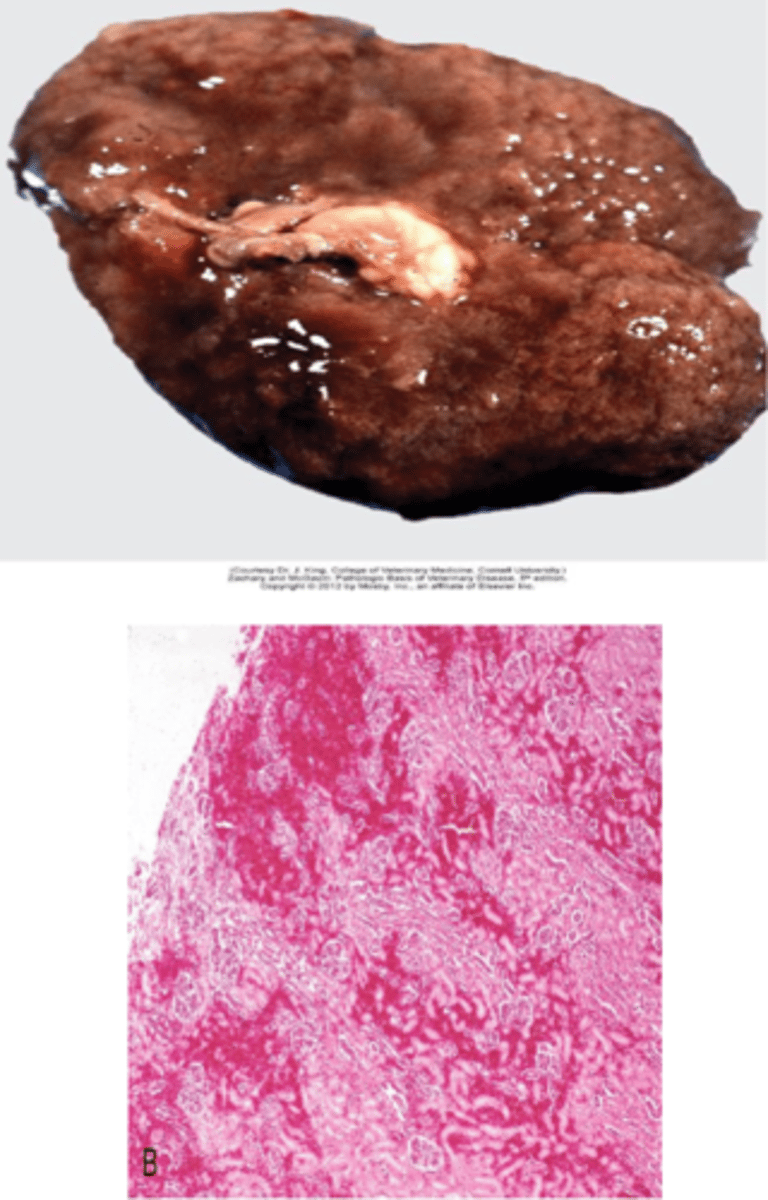
What bacteria is the cause of pulpy kidney disease (acute tubular necrosis)?
Clostridium perfringens Type D
Produces epsilon toxin in small ruminants
Toxic damage causes tubular degeneration & necrosis with interstitial edema & hemorrhage
*Need to conduct rapid post mortem (autolysis can obscure lesions)*
What are some inherited abnormalities of renal tubular function?
Primary renal glucosuria
Fanconi Syndrome
Cystinuria
Primary renal glucosuria
Inherited disorder or Norwegian Elkhounds with reduced functional capacity of tubular epithelium to reabsorb glucose
No gross or histological findings present
Predisposes to bacterial infections of lower urinary tract
Fanconi Syndrome
Hereditary defect in tubular reabsorption of protein, glucose, phosphate, & amino acids
Can develop progressive renal insufficiency & renal fibrosis
Basenji dogs are predisposed
Cystinuria
Sex linked inherited tubular defect in male dogs
Predisposes to calculi formation & obstruction of the lower urinary tract
Renal interstitium
Fibrovascular stroma that surrounds the nephron
Tubulointerstitial disease
Primary interstitial disease or interstitial disease secondary to tubular damage
What are some causes of tubulointerstitial disease?
Ascending infection (pyelonephritis)
Hematogenous (E. coli, Leptospira, Canine Adenovirus, FIP)
Secondary to tubular damage (infectious, toxic, immune-mediated)
What renal pathological change is seen with E.coli or Leptospira spp.?
White Spotted Kidney Disease
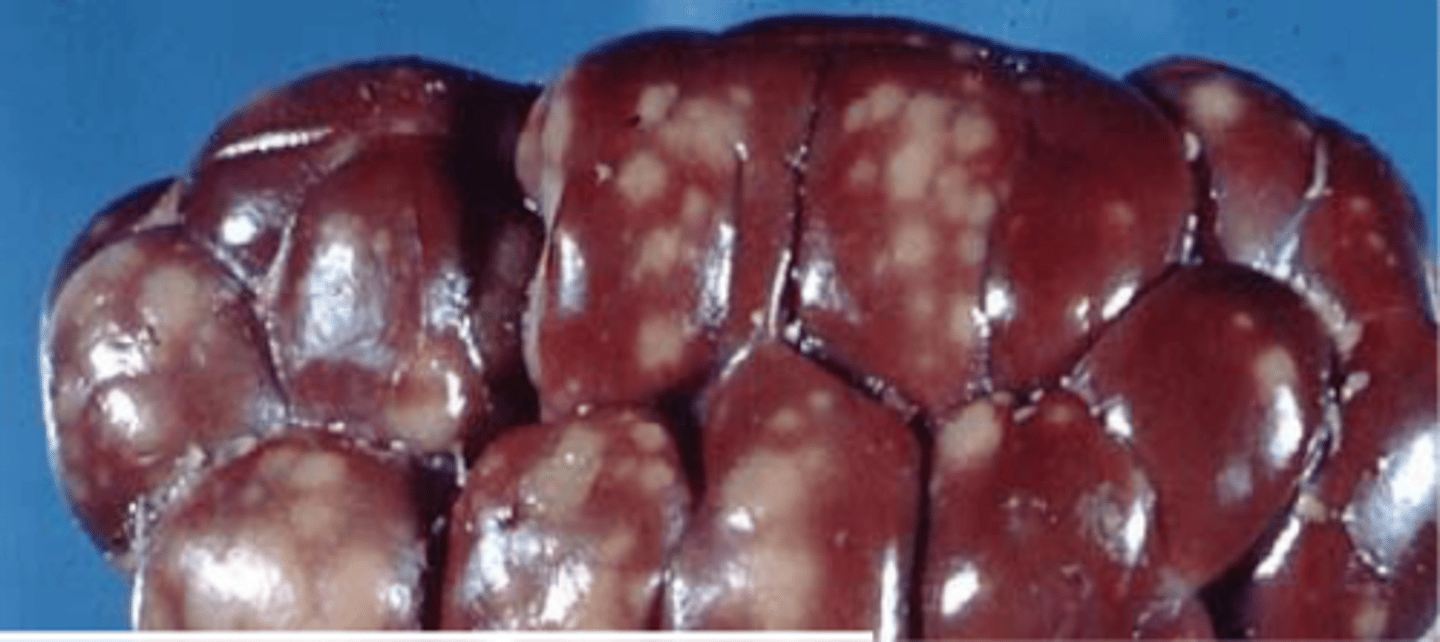
What renal pathological change is seen with feline infectious peritonitis (FIP)?
Granulomatous necrotizing vasculitis
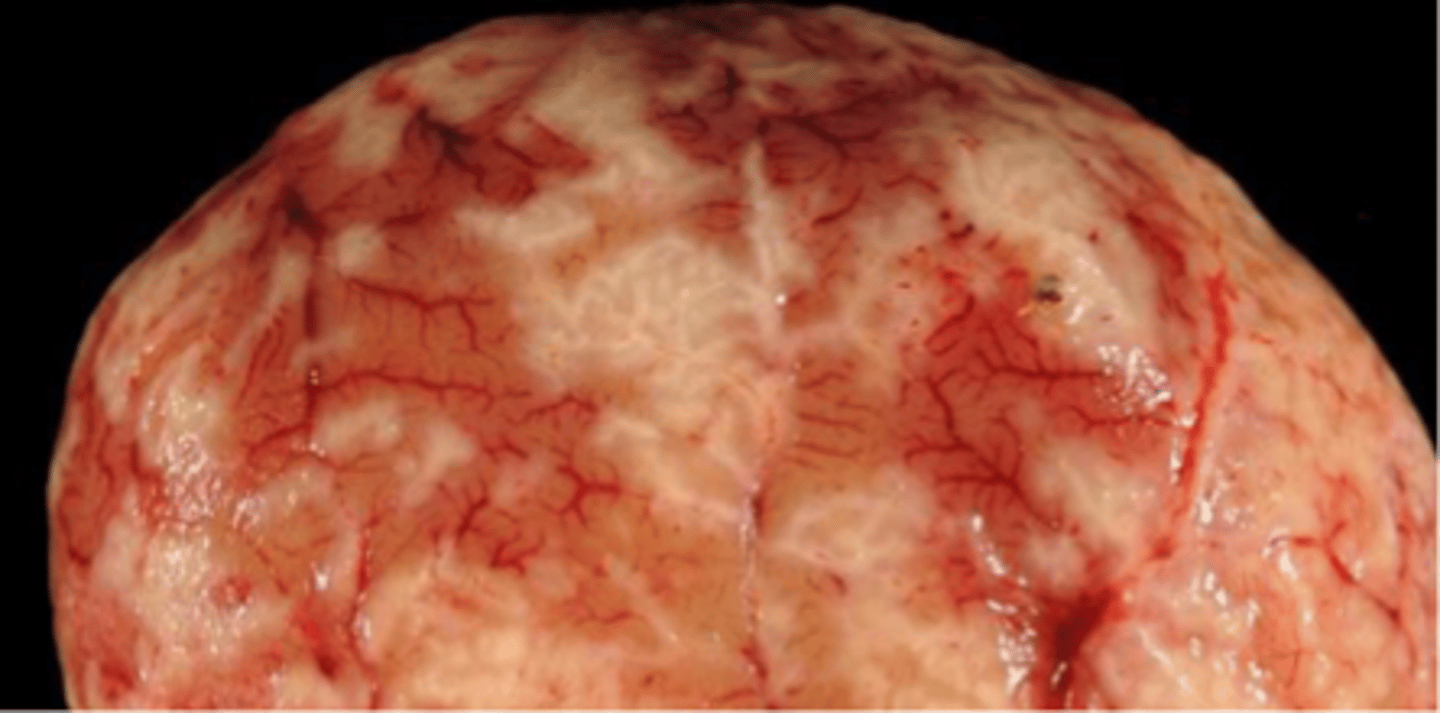
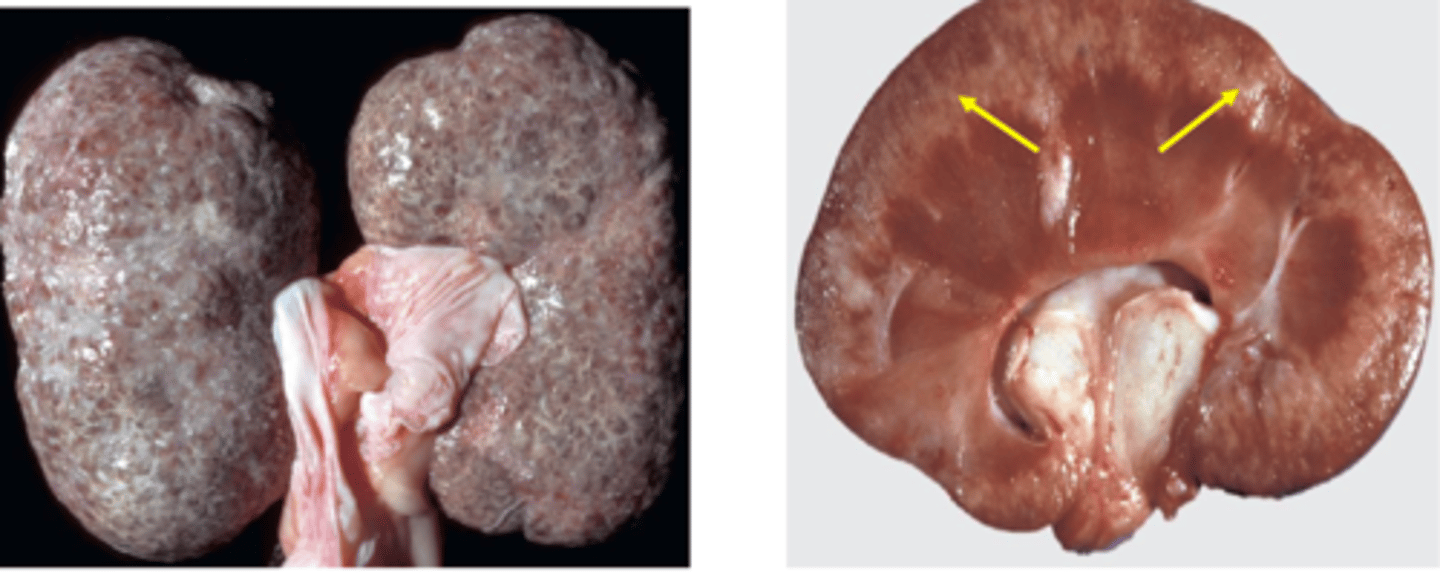
What gross renal pathology can be seen with chronic interstitial disease?
Nodularity & fine pitting on capsular surface (fibrosis)
White foci & streaks in cortex (inflammation & fibrosis)
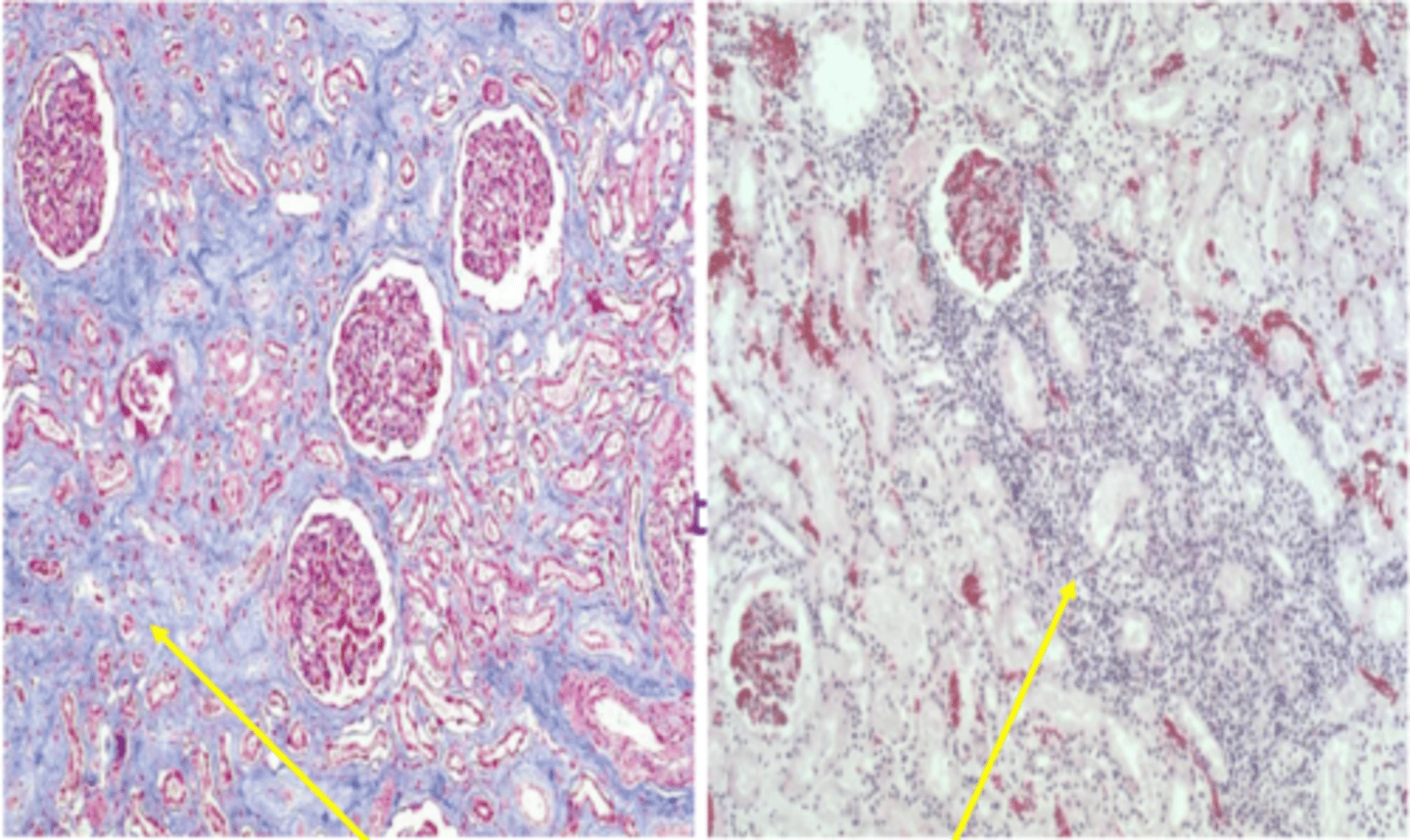
What renal histopathological change can be seen with chronic inflammation of the interstitium?
Stain for collagen (blue) showing fibrosis
Lymphocytes & plasma cells present
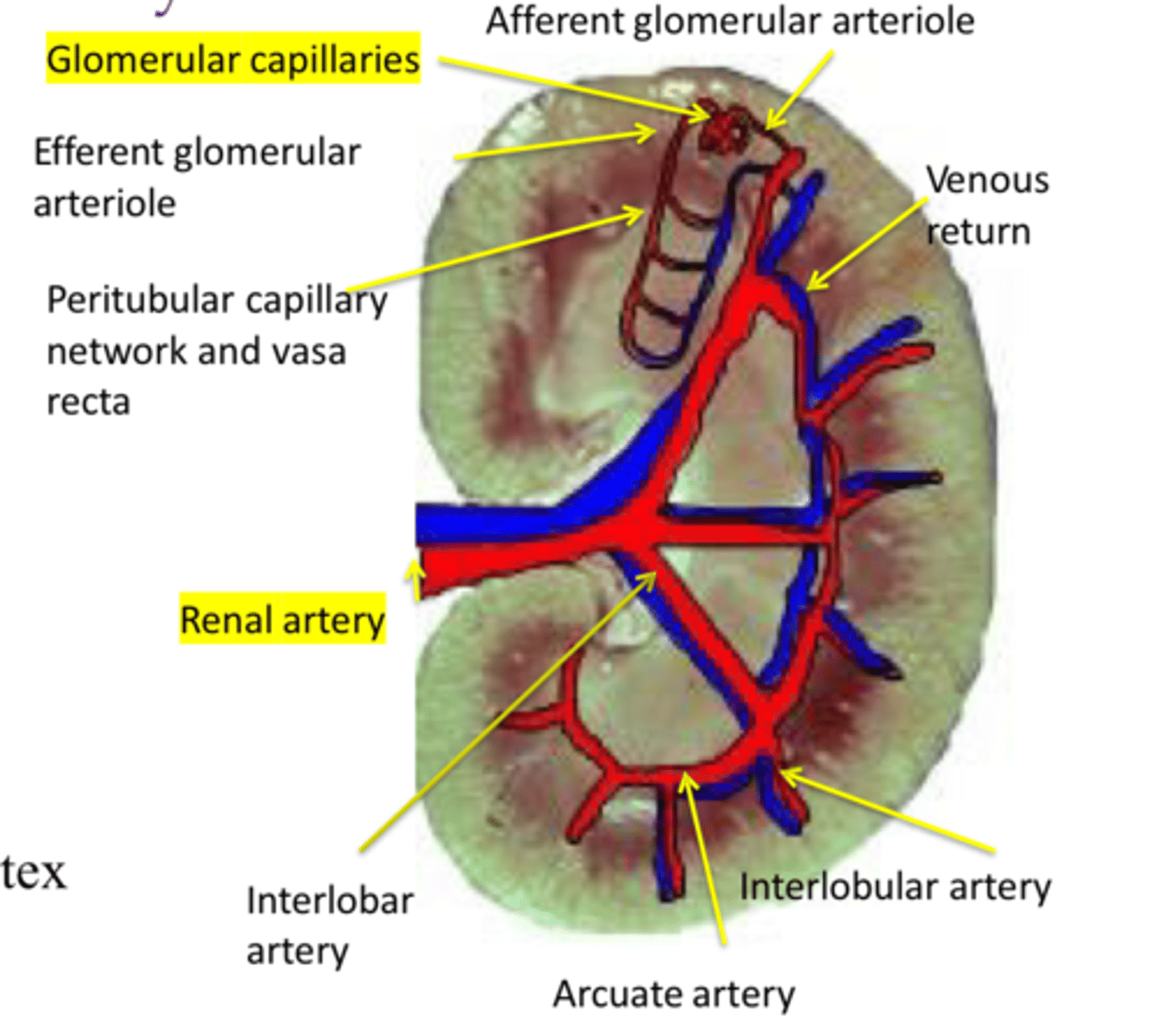
Describe the blood circulation in the kidney
Renal artery branches into interlobar (between pyramids) > arcuate (at pyramid base, corticomedullary junction) arteries > interlobular (in cortex)
Afferent arterioles branching off lobular arteries feed into glomerular capillaries
End-circulation
What effect does reduced glomerular blood flow have on the remainder of the nephron?
Reduced flow
What are some diseases of the renal vascular system?
Hyperemia & congestion
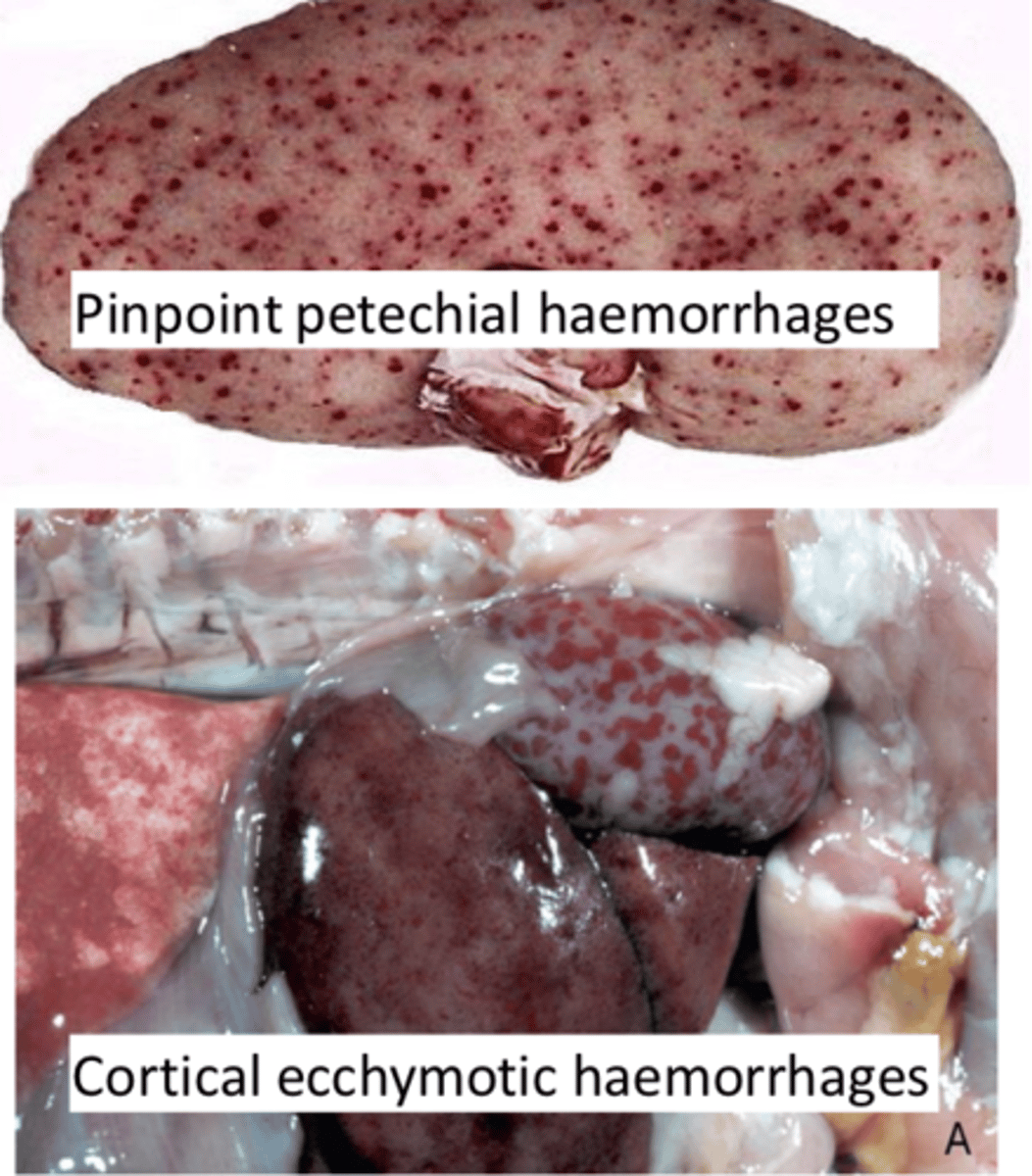
Hemorrhage
Thrombosis
Infarction
Emboli
Hyperemia
Increased arterial blood flow (acute inflammation)
Congestion
Venous blood pooling (cardiac insufficiency, hypovolemic shock)
What diseases/conditions can lead to renal vascular hemorrhage?
Trauma
Coagulopathies (factor VIII deficiency)
Septicemia (Erysipelas, Streptococcal infection)
Vasculitis (FIP, malignant catarrhal fever)
Vascular necrosis (Canine Herpesvirus)
Embolic bacterial diseases (Actinobacillus spp.)
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
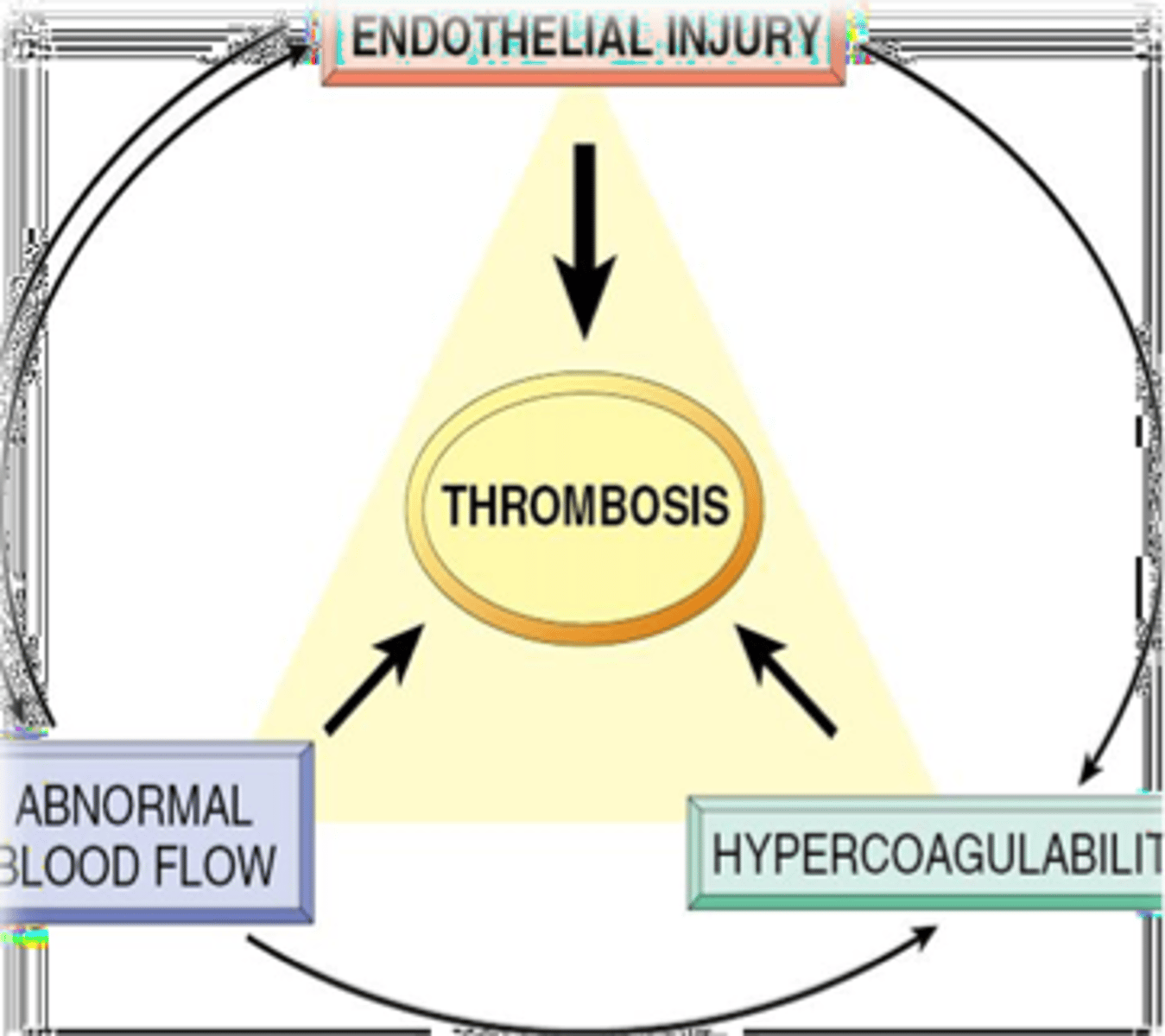
Thrombosis
Pathological blood clotting in blood vessels or lymphatics
Virchow's triad
Endothelial injury (Canine Adenovirus, FIP, renal glomerular & cutaneous vasculopathy or endotoxin)
Dynamics of blood flow (stasis or turbulence with cardiac disease or hypovolemia)
Hypercoagulability of blood (inflammation, DIC, glomerulonephritis, glomerular amyloidosis)
Major determinants of thrombosis
Renal infarction
Area of peracute ischemia that undergoes coagulative necrosis
Occlusion of arterial supply or venous drainage
What are some causes of renal infarction?
Emboli/thromboemboli
Vasospasm
Extrinsic compression of a vessel
Traumatic rupture
Endotoxemia
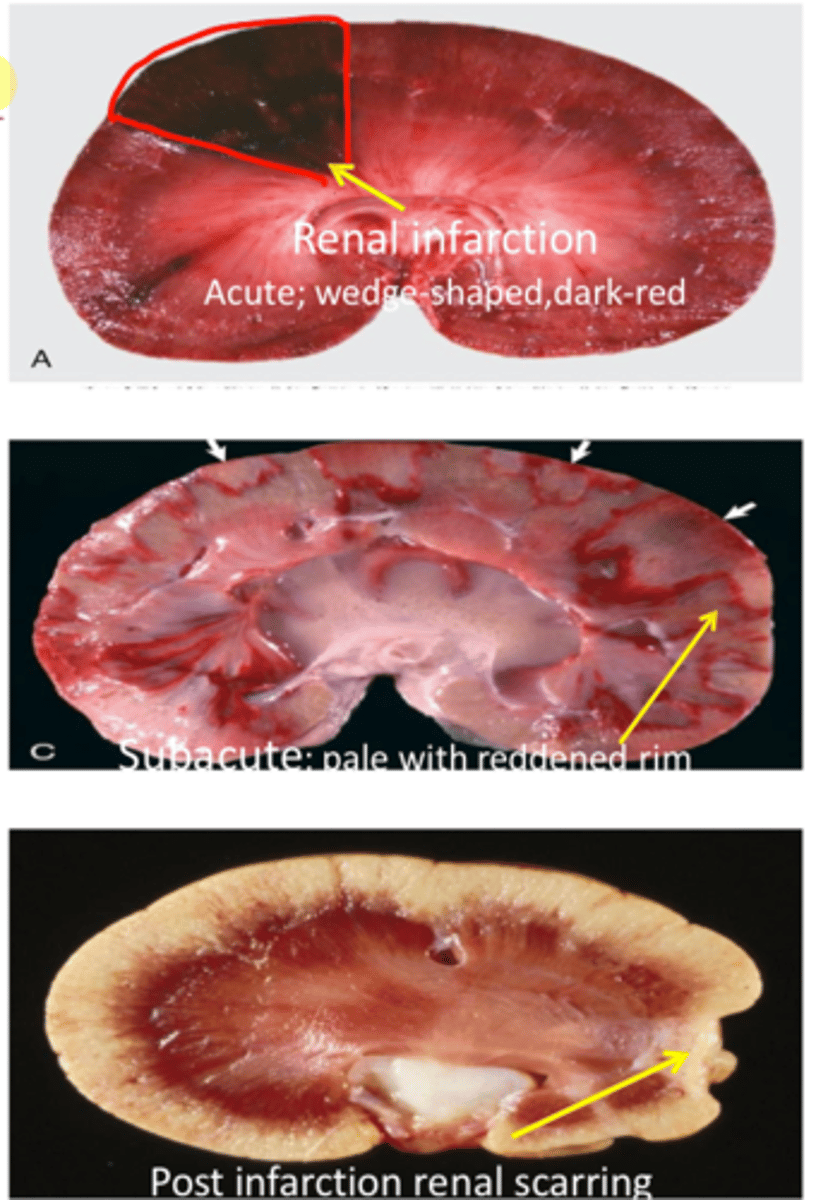
What aspect of the renal vasculature is typically affected by renal infarction?
Interlobular artery (cortex only)
What will occur if the renal or interlobar artery are blocked (renal infarction)?
Cortex & medulla are affected
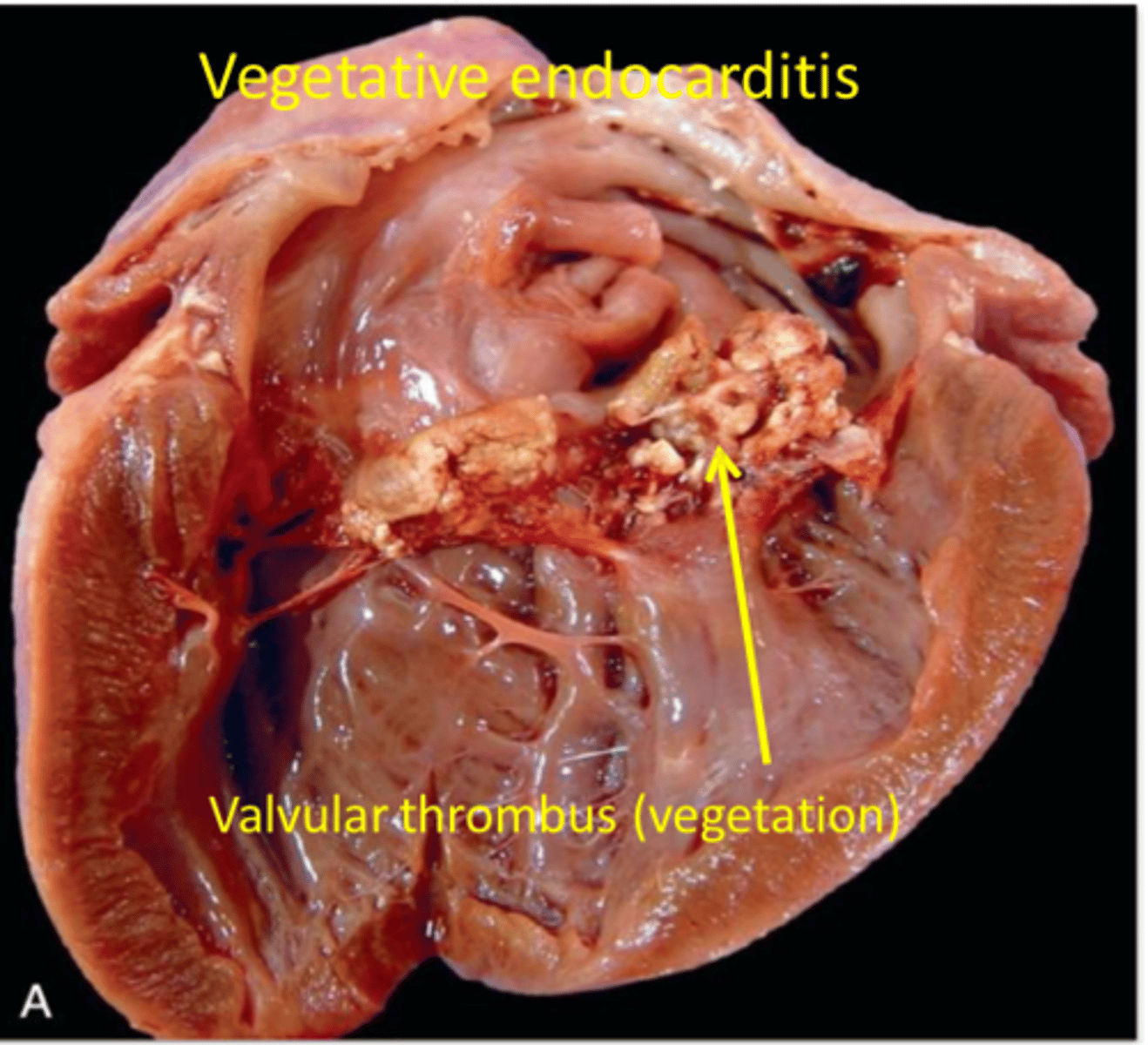
What are the common origins of renal emboli?
Cardiac mural or valvular thrombi
Endarteritis (parasitic disease)
Neoplastic cell
Bacterial or septic
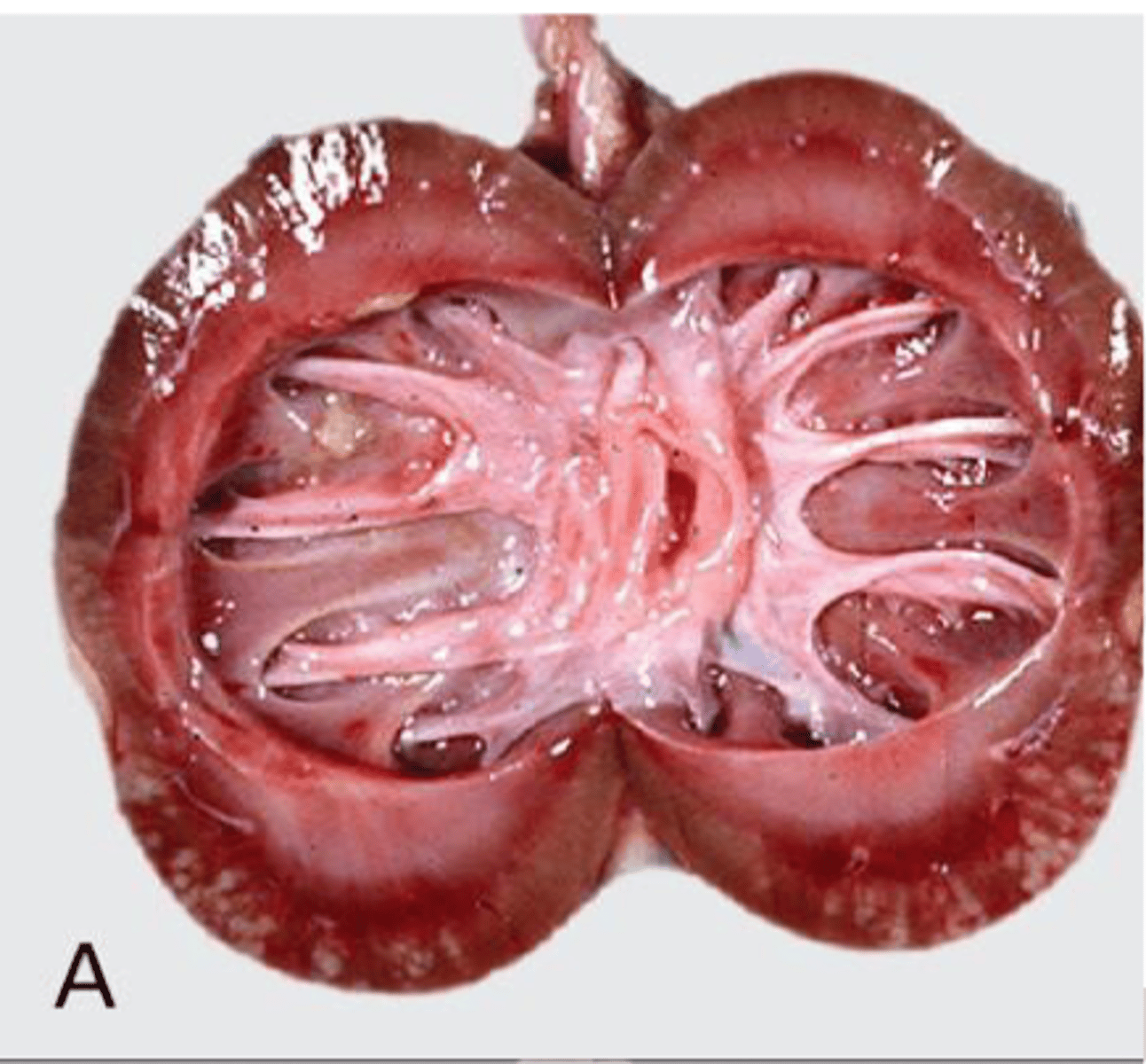
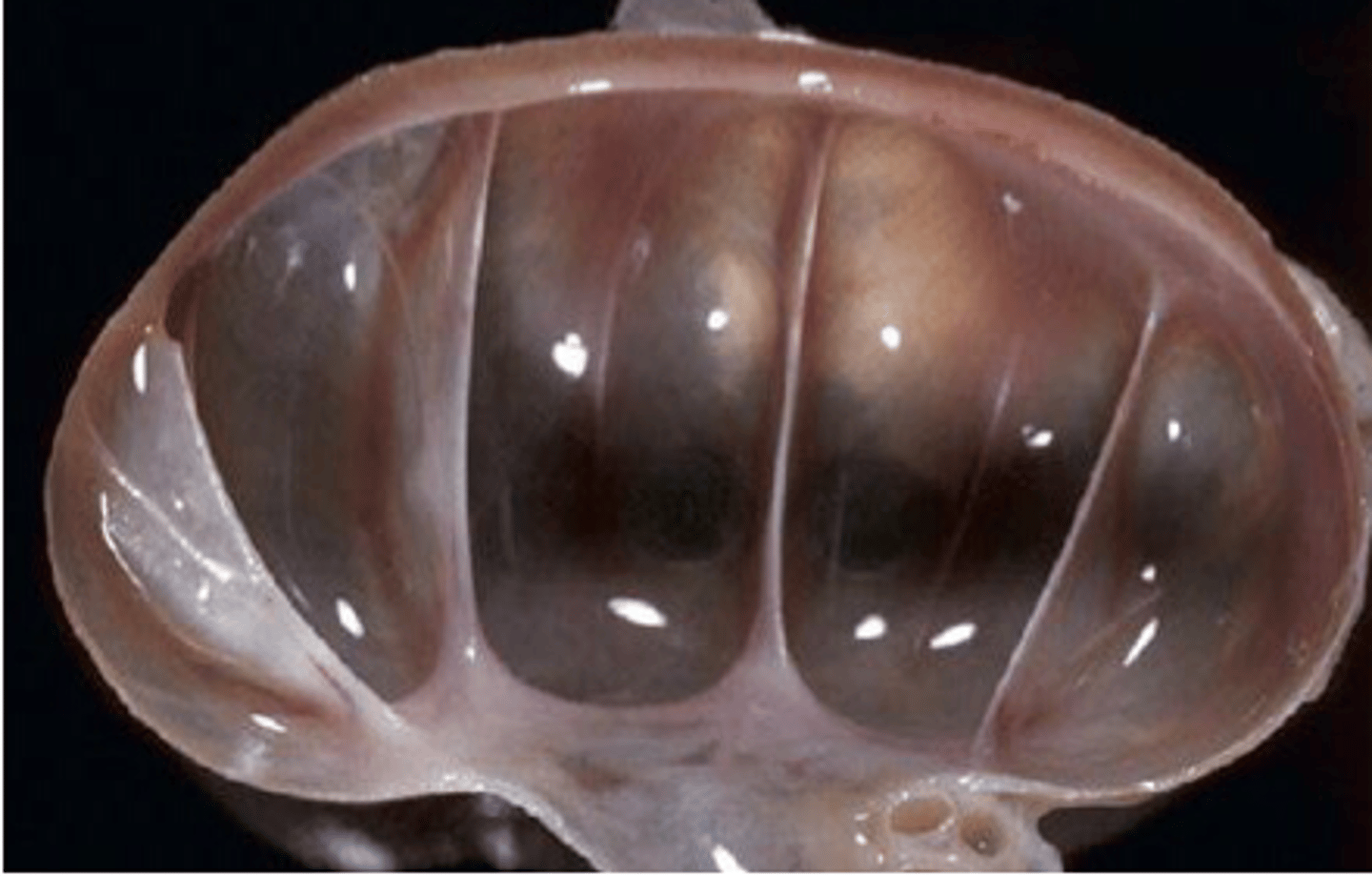
Hydronephrosis
Dilation of one or both kidneys with fluid
Dilation of the renal pelvis due to obstruction of urine outflow leads to increased pelvic pressure & atrophy of renal parenchyma
Intrapelvic pressure increases & blood vessels collapse
Reduced renal blood flow causes ischemia, tubular loss, & fibrosis
*If unilateral, other kidney may be able to compensate*
What are some predisposing factors to hydronephrosis?
Congenital malformation
Ureteral or urethral blockage
Neurogenic functional disorders
Iatrogenic
Pyelonephritis
Bacterial infection of the renal pelvis with extension into the tubules and interstitium
Most common in sows & cows
Associated with parturition, service, & catheter use
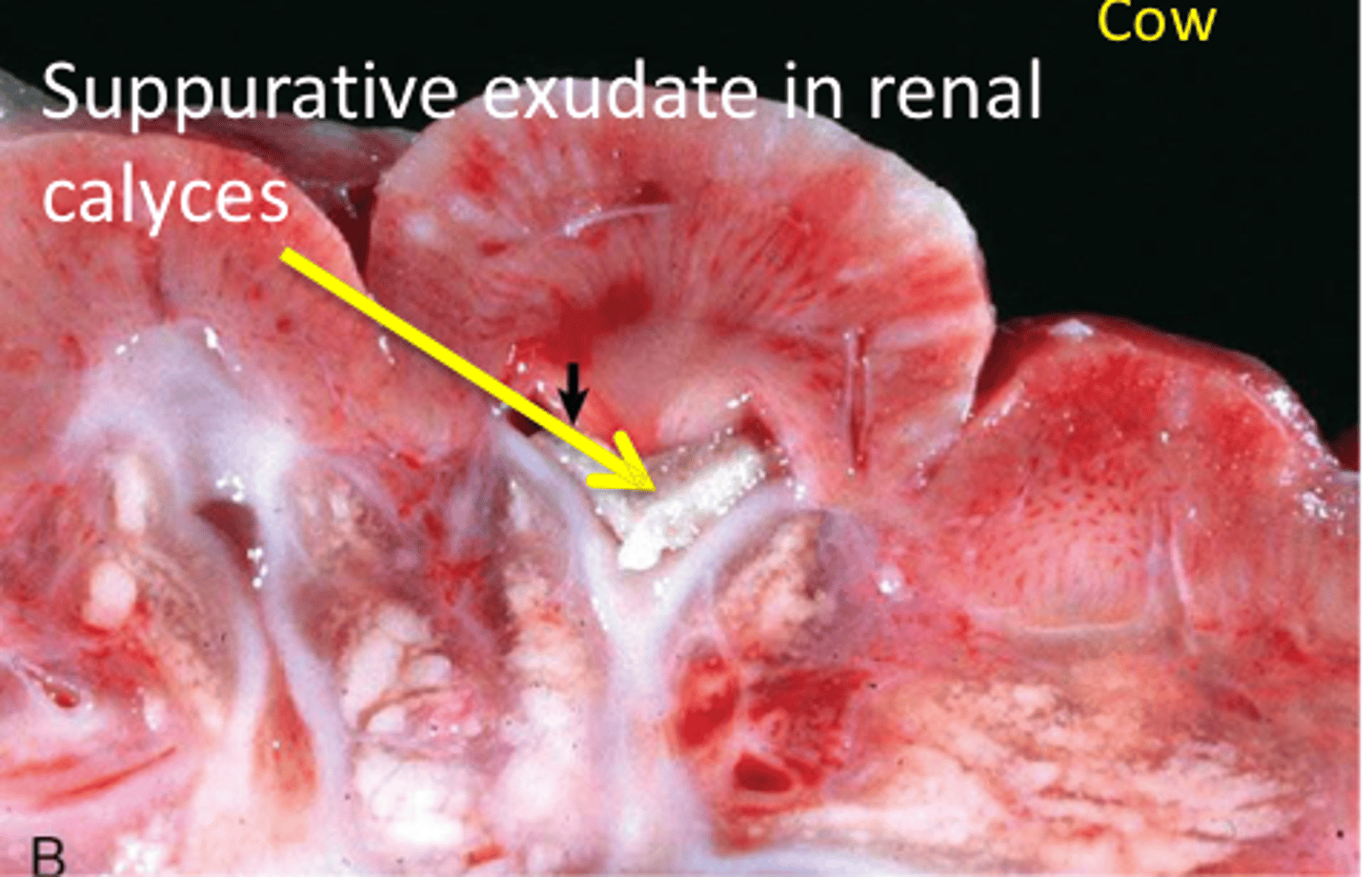
What are some causes of pyelonephritis?
Corynebacterium spp.
E. coli
Staphylococcus spp.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Trueperella pyogenes
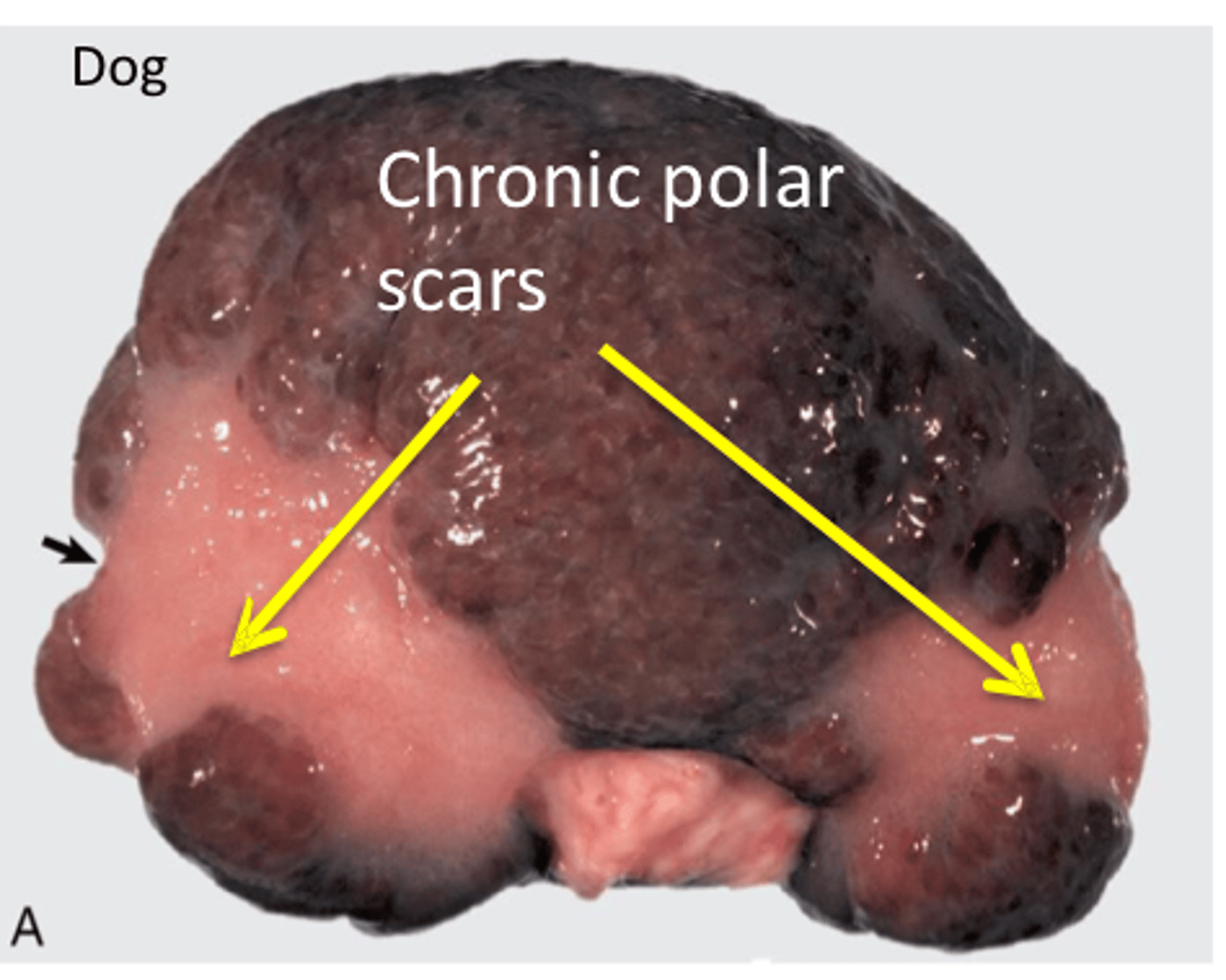
Papillary necrosis
Destructive process involving the medullary papillae and the terminal renal pyramids
Response of the inner medulla to ischemia
What can cause primary papillary necrosis?
Prolonged treatment or overdose of NSAIDs leading to reduced prostaglandin synthesis, reducing renal blood flow, causing ischemic necrosis
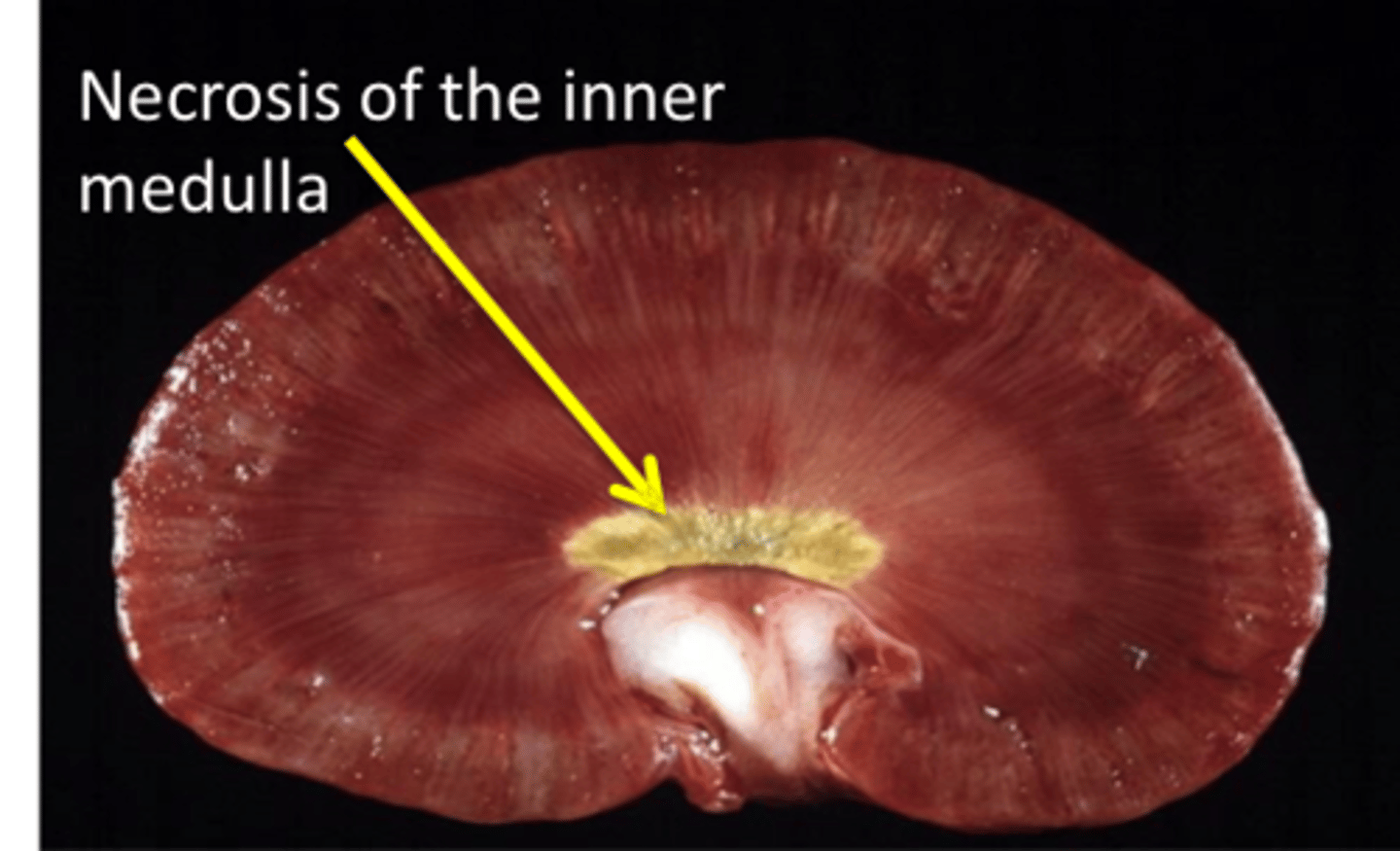
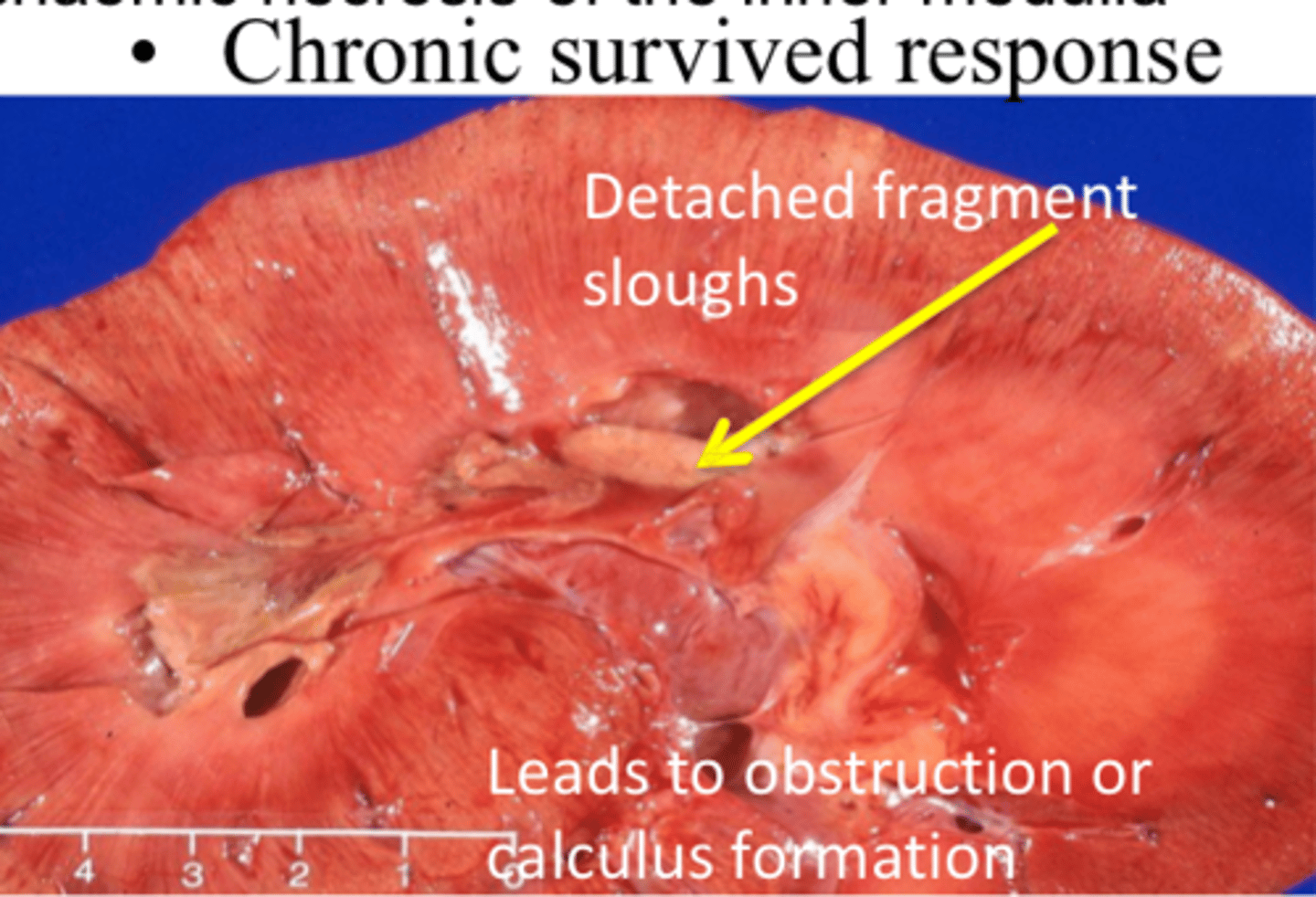
What can cause secondary papillary necrosis?
Reduced vasa recta blood flow due to glomerular disease
Compression of the vasa recta by medullary interstitial disease or compression of the renal papilla
What are some general features of renal neoplasia?
Rarely reported
Usually unilateral
Epithelial, mesenchymal, embryonal, or metastatic
Primary renal tumors are often highly malignant with high level of metastasis
Nephroblastoma
Embryonal kidney tumor with high metastatic rate in dogs <2 years
Found incidentally at slaughter in cattle, pigs, and poultry
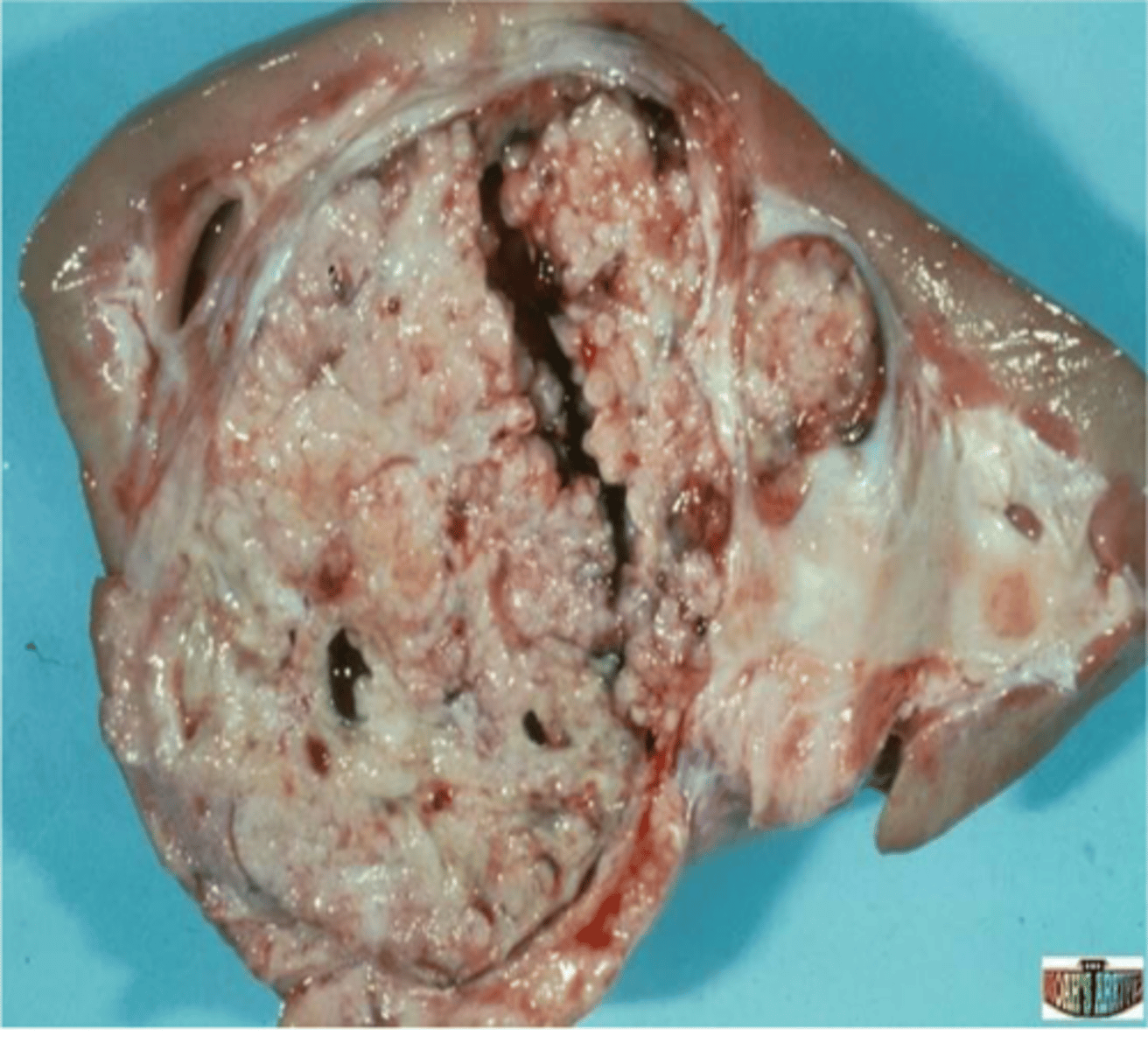
Renal Carcinoma
Most common primary renal tumor in older dogs
Large, hemorrhagic, necrotic, & cystic lesions
Over 50% metastasize
Can lead to paraneoplastic syndrome (erythropoietin)
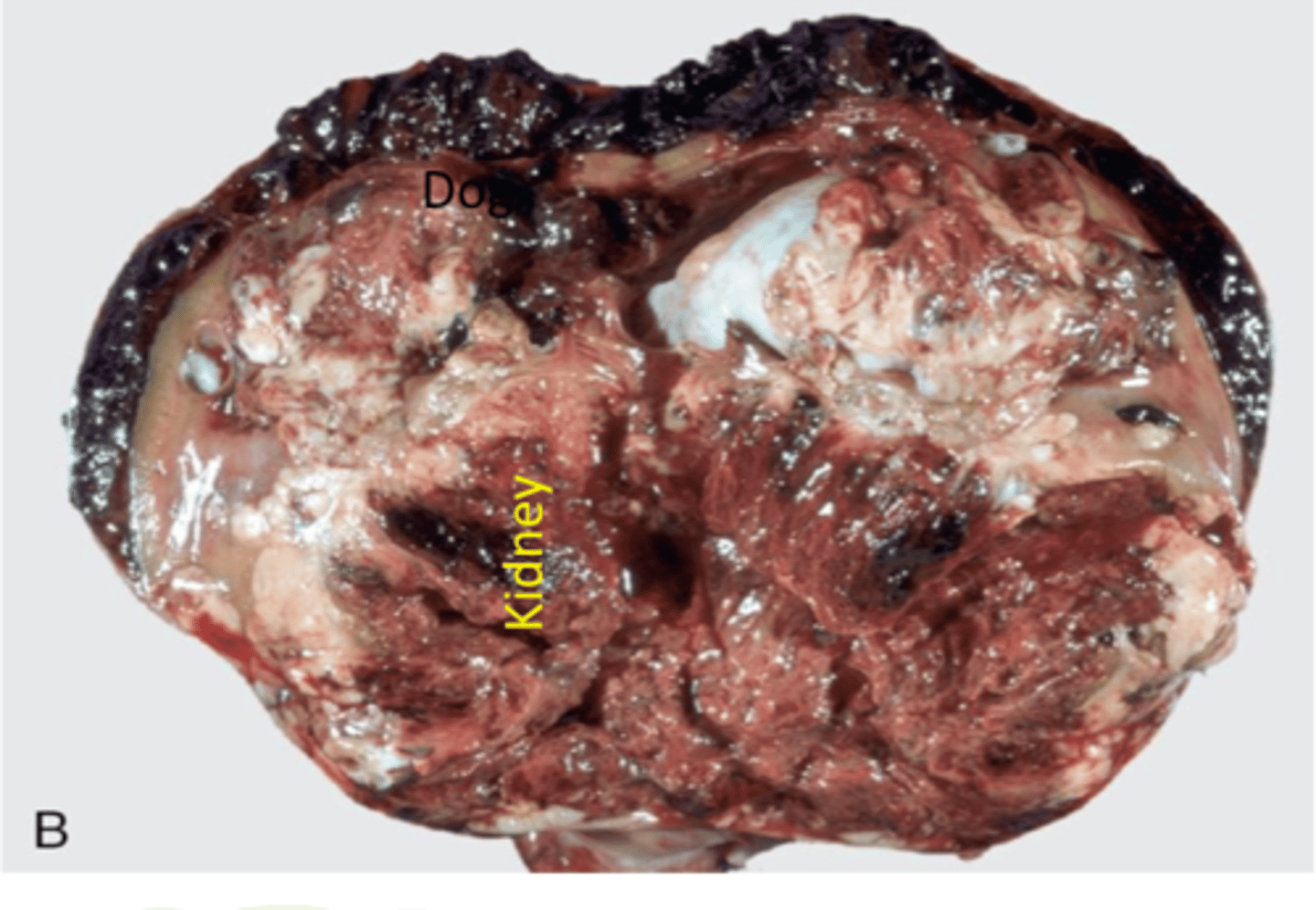
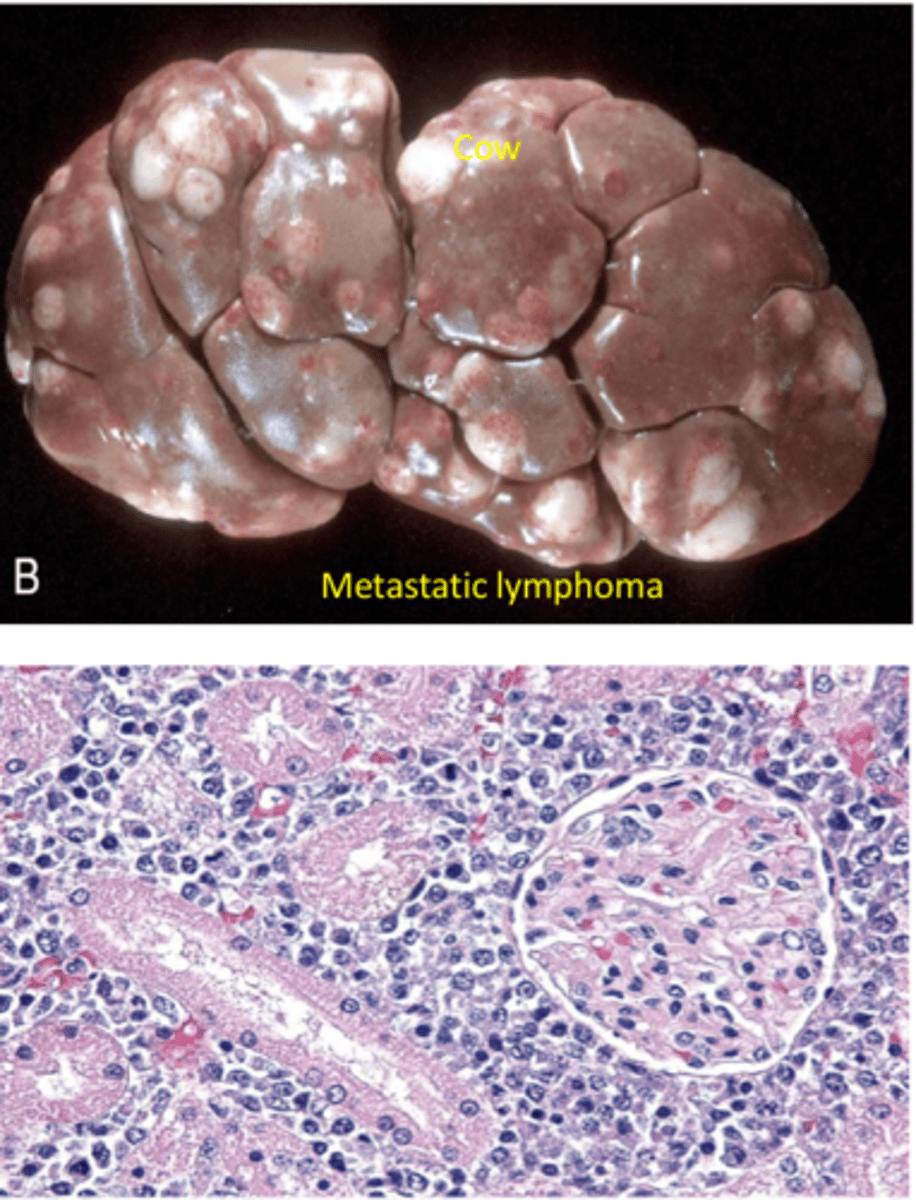
Lymphoma
Malignant tumor of lymph nodes and lymph tissue
Primary or metastatic can impact kidneys