Nose & Paranasal Sinuses
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Paranasal sinus
an air-filled cavity within a bone connected to the nasal cavity
Functions of the nasal cavity:
- adjusts temp (mols collide = friction & heat)
- adjusts humidity (high = olfaction can occur, regulated by rich vascular supply)
- traps & removes particulate matter (hair, mucous)
- drains paranasal air sinuses (lined by respiratory epithelium)
- olfaction
Path of the olfactory nerve from the nasal cavity to the brain:
small branches of olfactory nerve (neurones) will be embedded in superior part of NC
pass through multiple, small foramina in ethmoid
travels into ant CF
travels on the base/inferior surface of brain
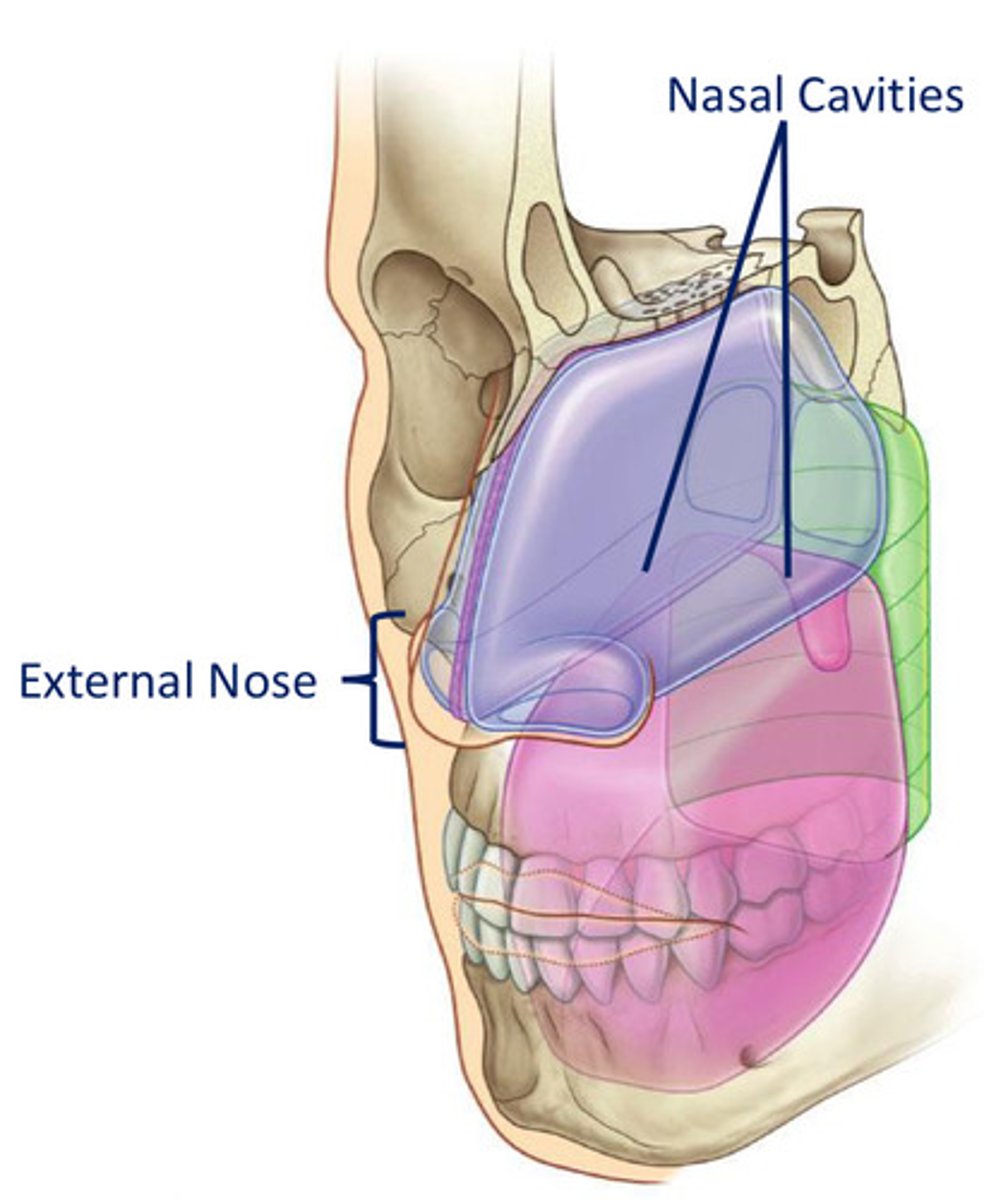
The nose can be subdivided into:
1. external nose - located at the centre of the midface
2. internal chamber - located centrally within the cranium
What is the external nose supported by?
bone
fibroelastic tissue
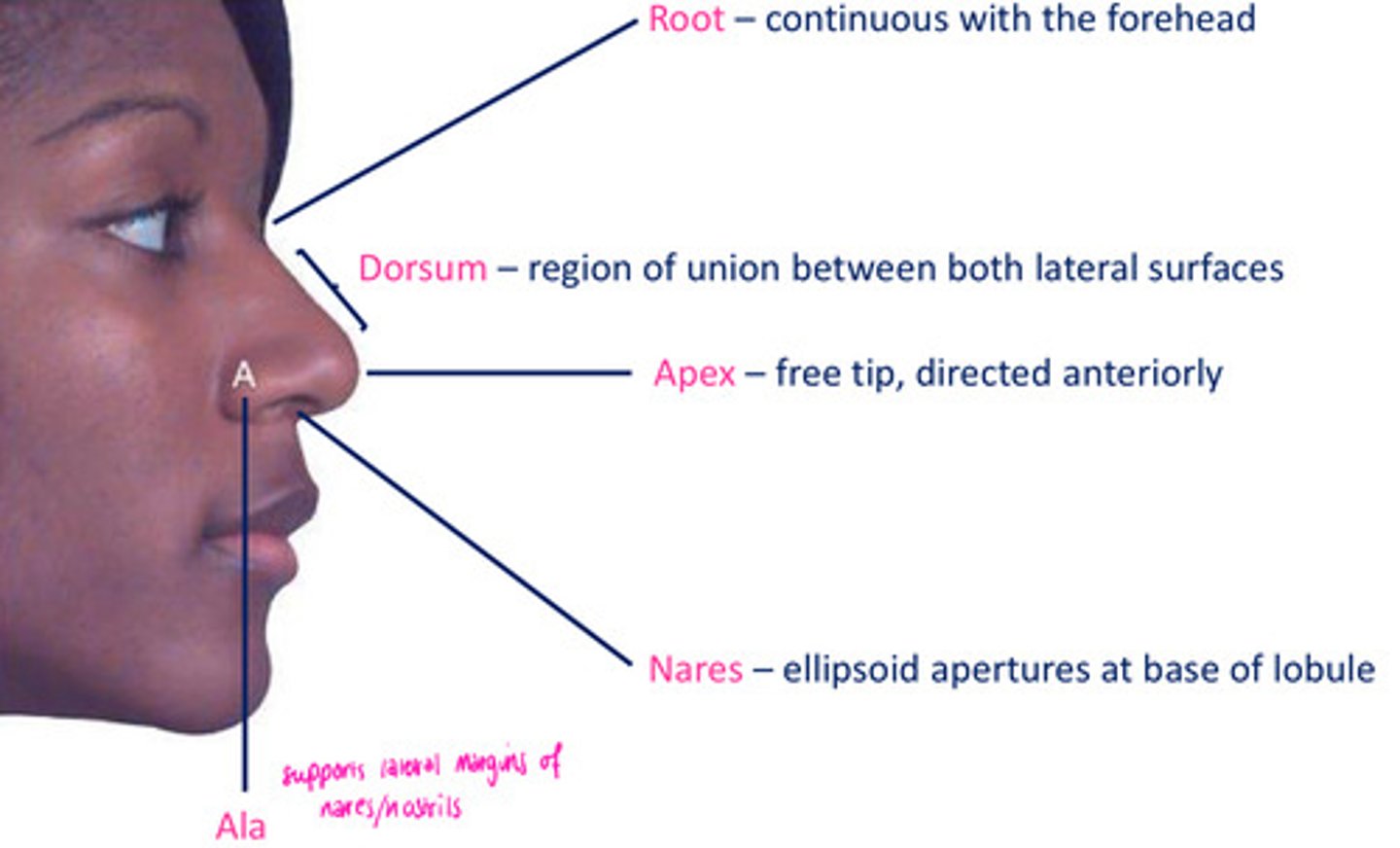
Features of the external nose
root
dorsum
apex
nares
ala
Anterior apertures of nasal cavity supported by skeletal framework composed of __________ & ___________.
cartilage
bone
Cartilaginous support for the external nose:
midline septal cartilage
minor alar cartilage
lateral process of septal cartilage
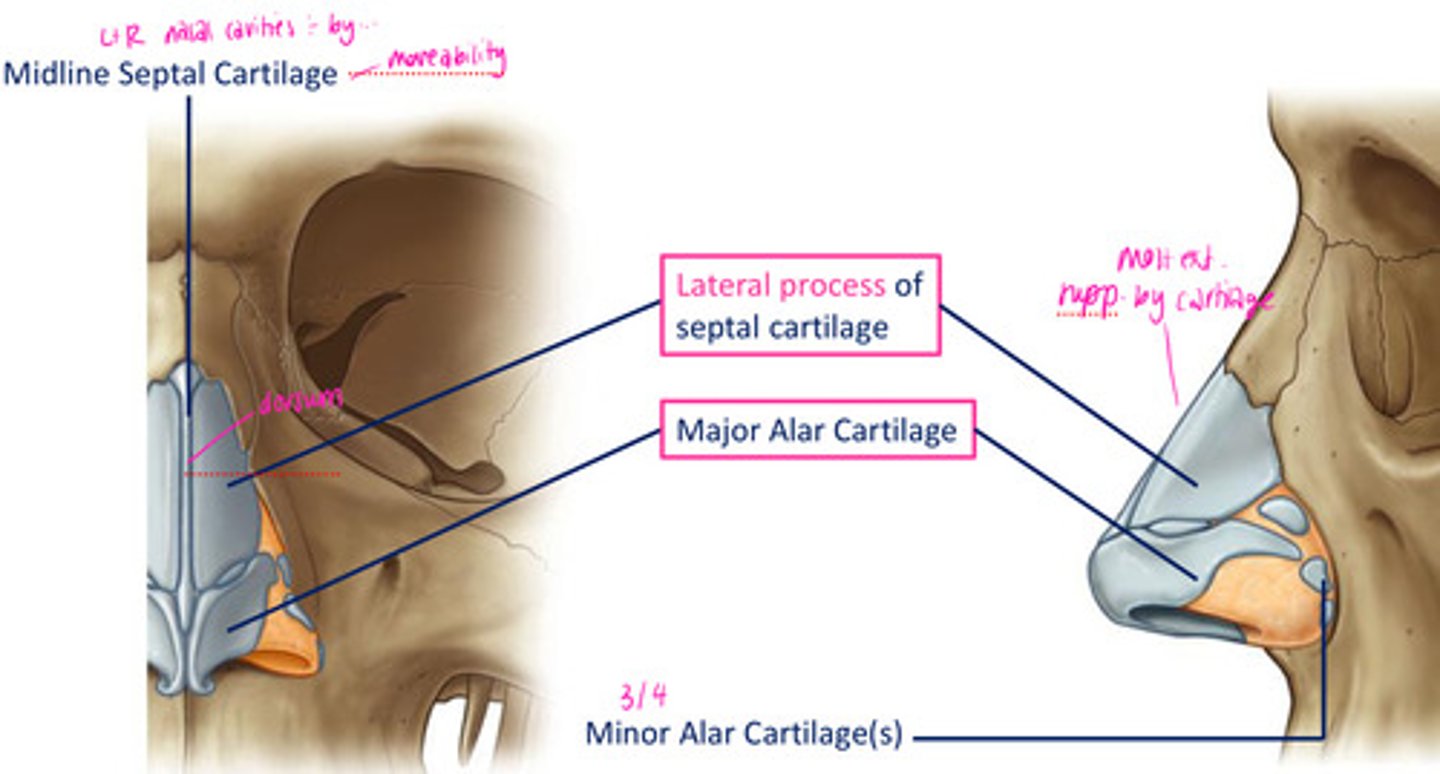
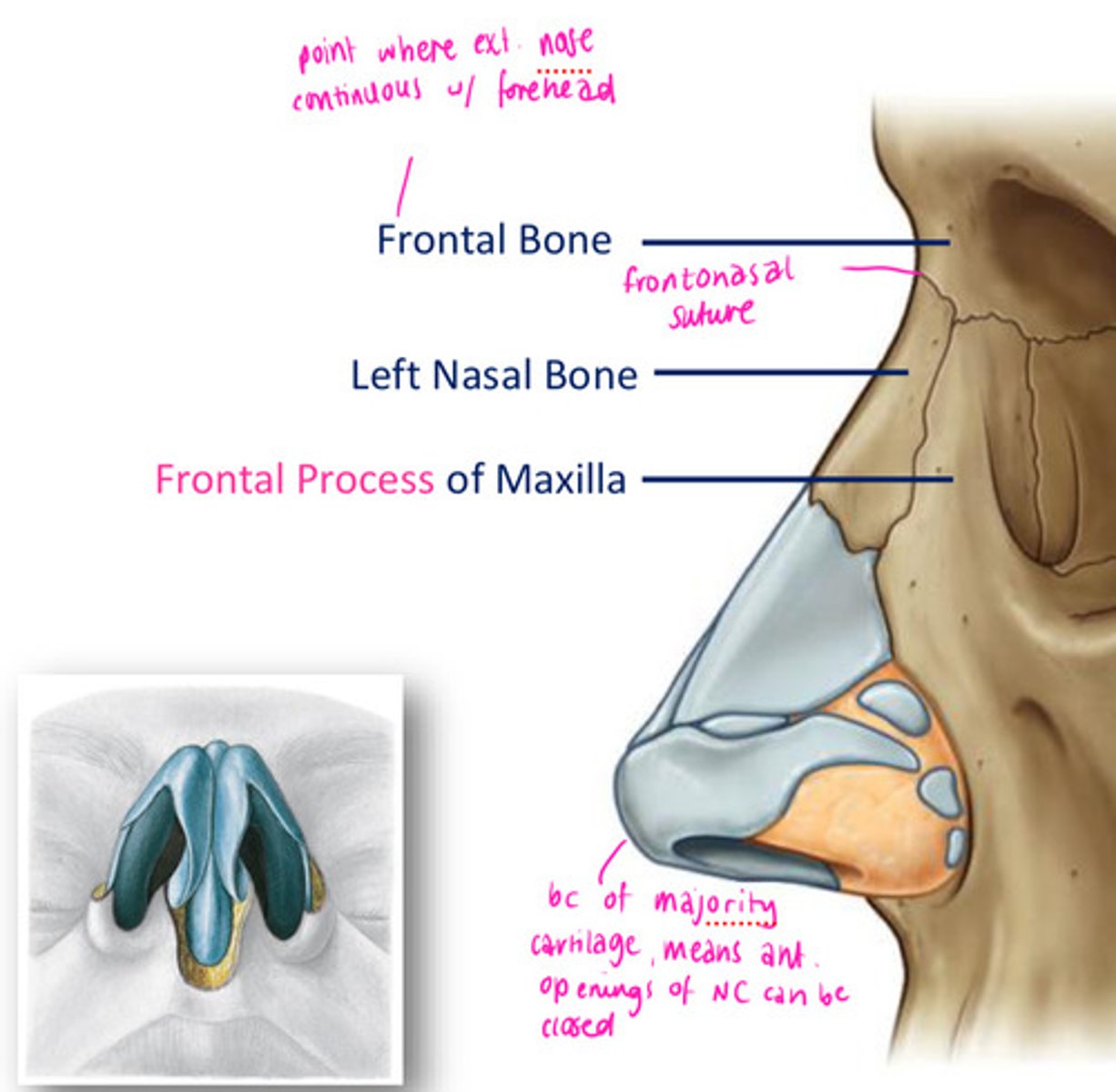
Bony support for the external nose:
Frontal bone
Left & right nasal bone
Frontal process of the maxilla
Which cranial nerve is responsible for the muscles of facial expression?
facial
Muscles of facial expression: Nose
Nasalis
Depressor septi nasi
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
Procerus
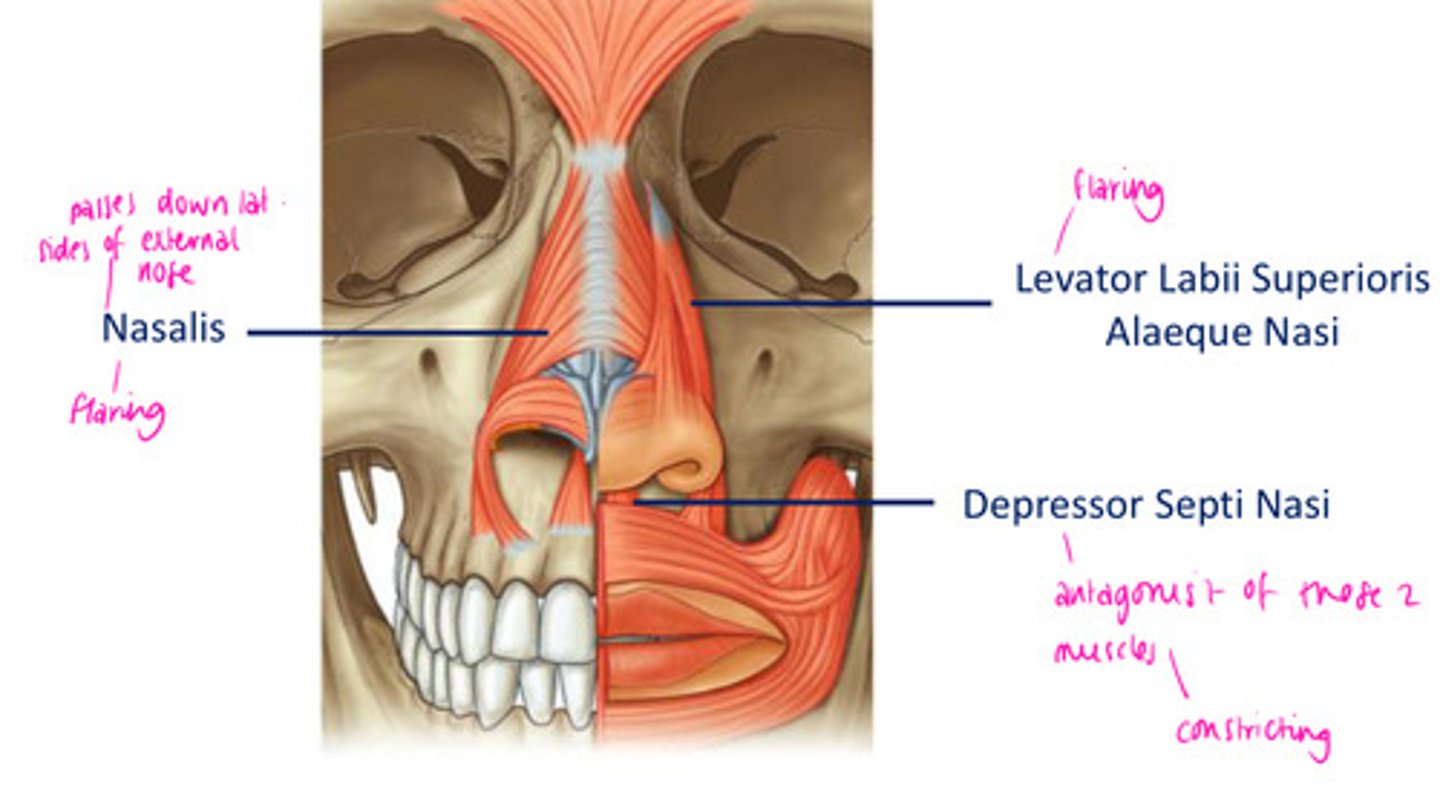
Nasalis
flares nostrils
Depressor septi nasi
a muscle that constricts the nostrils (closes)
Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
raises upper lip and flares nostril
Procerus
moves and wrinkles nose
Each nasal cavity is an elongated, wedge-shaped space held open by a skeletal framework of ______ & ________ cartilage.
bone
fibroelastic
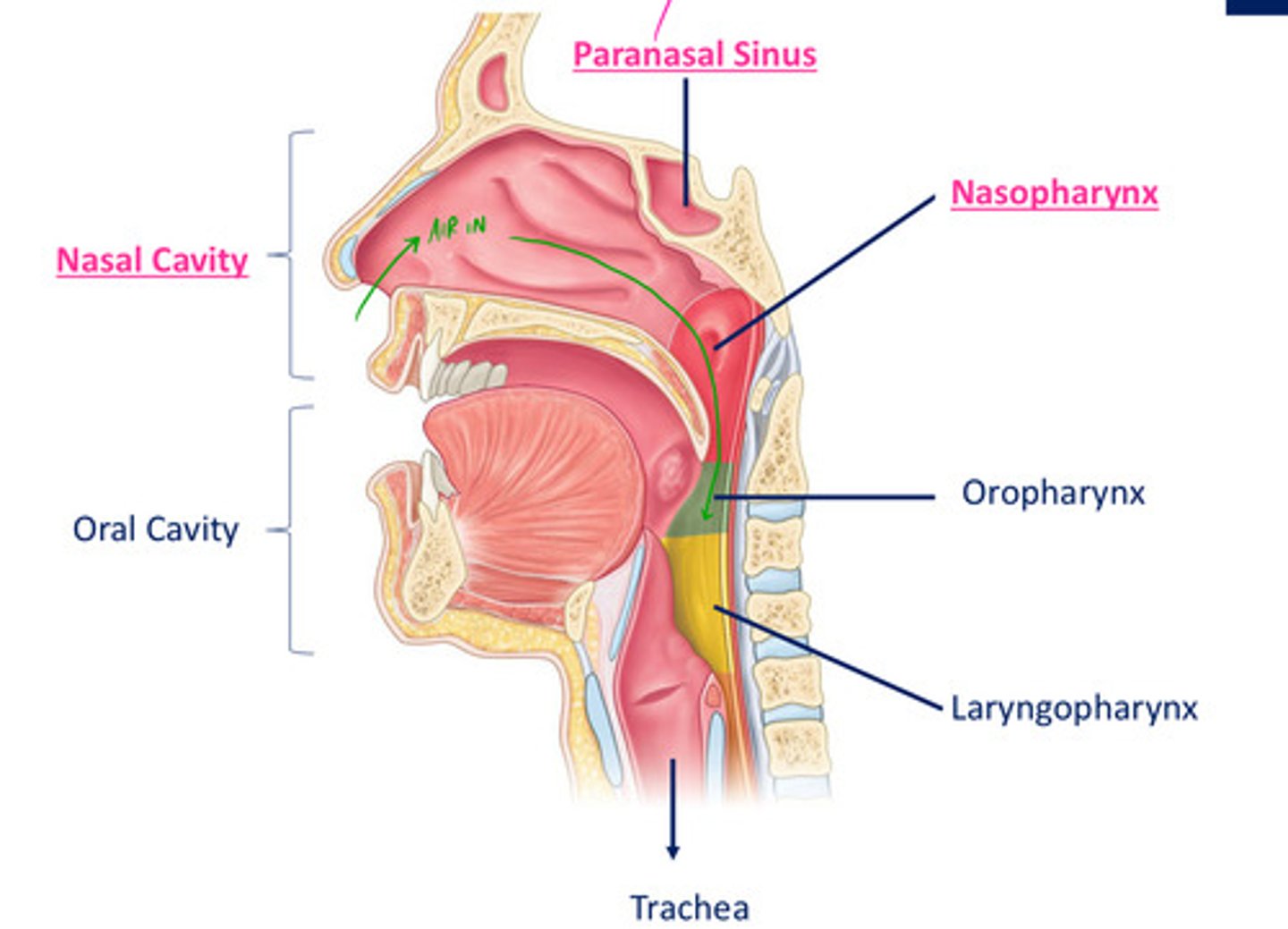
Nasal cavity openings
choanae - posterior nasal apetures
nares - anterior nasal apetures
hard palate - NC divides into OC
divided from cranial cavity above by frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid bones
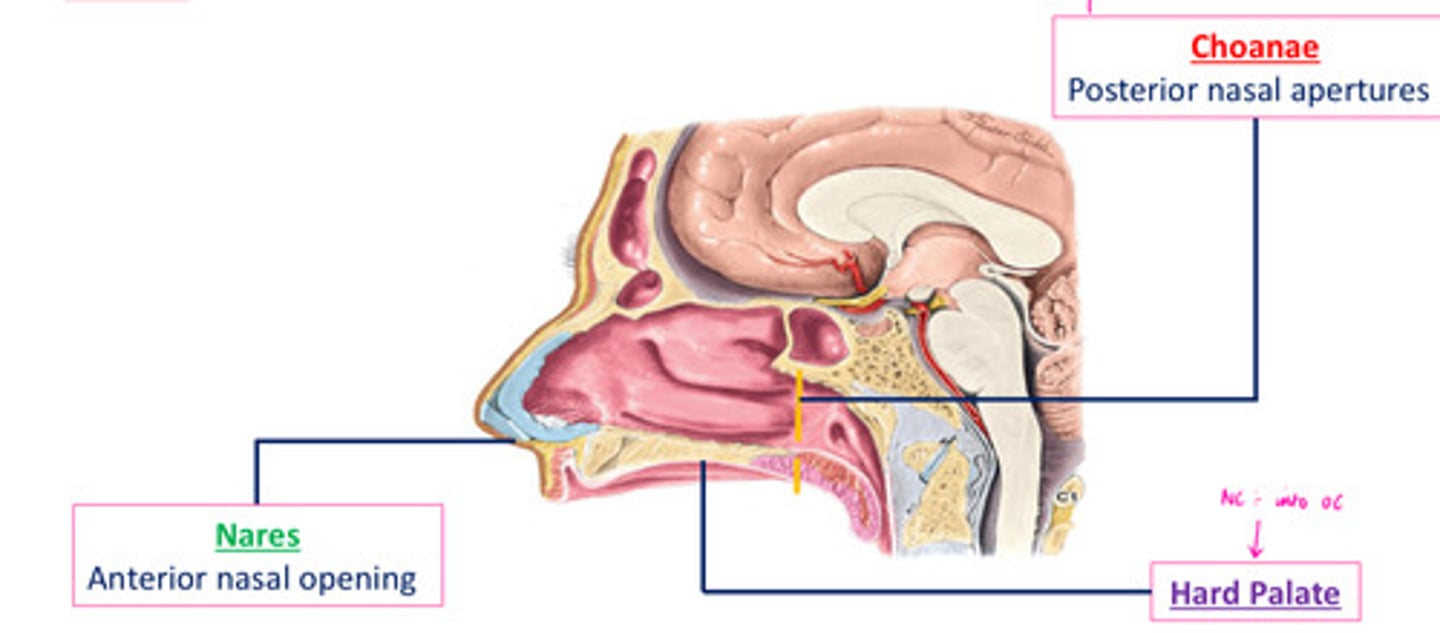
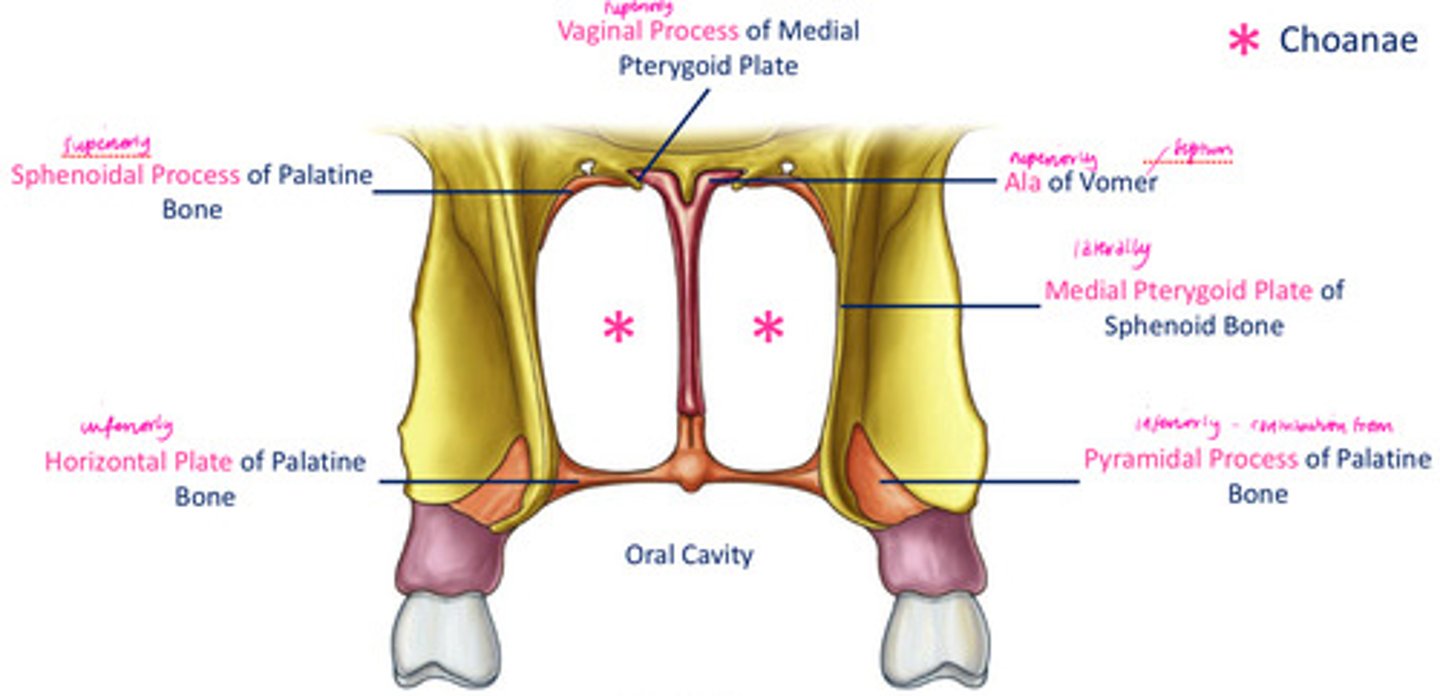
Choanae
- funnel shaped openings, especially of the posterior nares
- 1 of the comm passageways b/t nasal fossae & pharynx
- supported & completely surrounded by bone, inability to be closed off
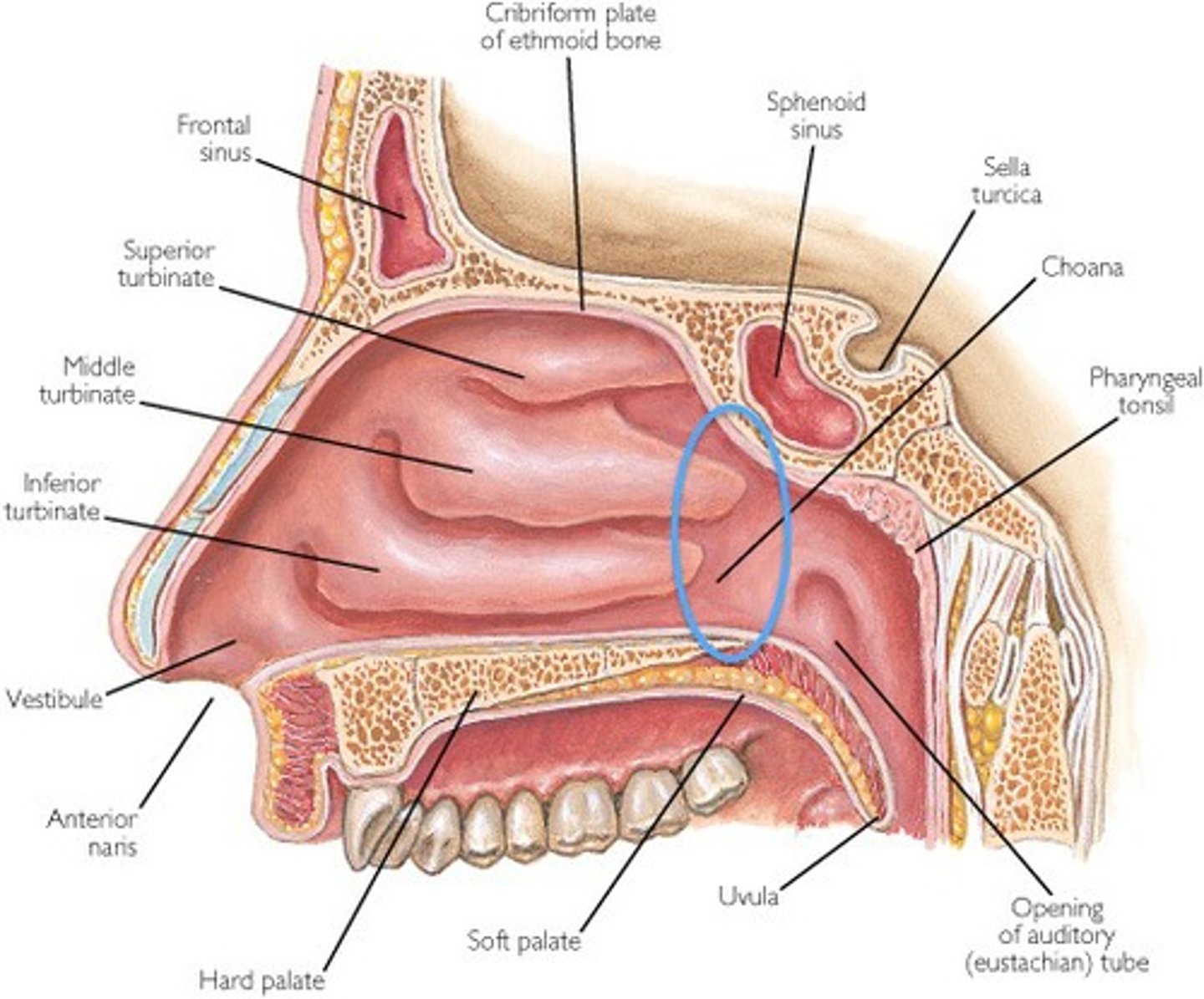
DIAGRAM: Posterior nasal apeture
Superiorly - vaginal process of medial pterygoid plate, sphenoidal process of palatine bone, ala of vomer
Laterally - medial pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone
Inferiorly - horizontal plate of palatine bone, pyramidal process of palatine bone
oral cavity
choanae
Regions of the nasal cavity: Respiratory
largest part of NC
rich neurovascular supply
lined by respiratory epithelium, composed mainly of ciliated & mucous cells
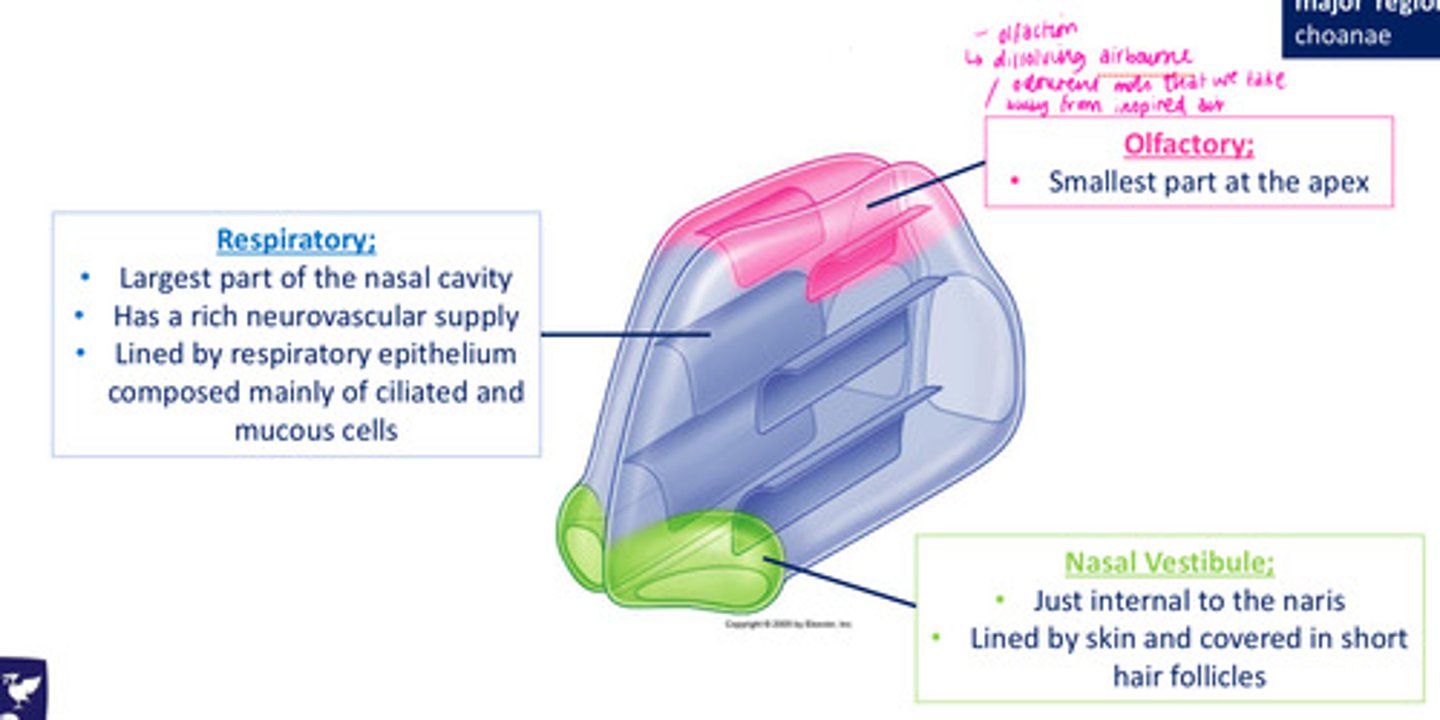
Regions of the nasal cavity: Olfactory
smallest part at the apex
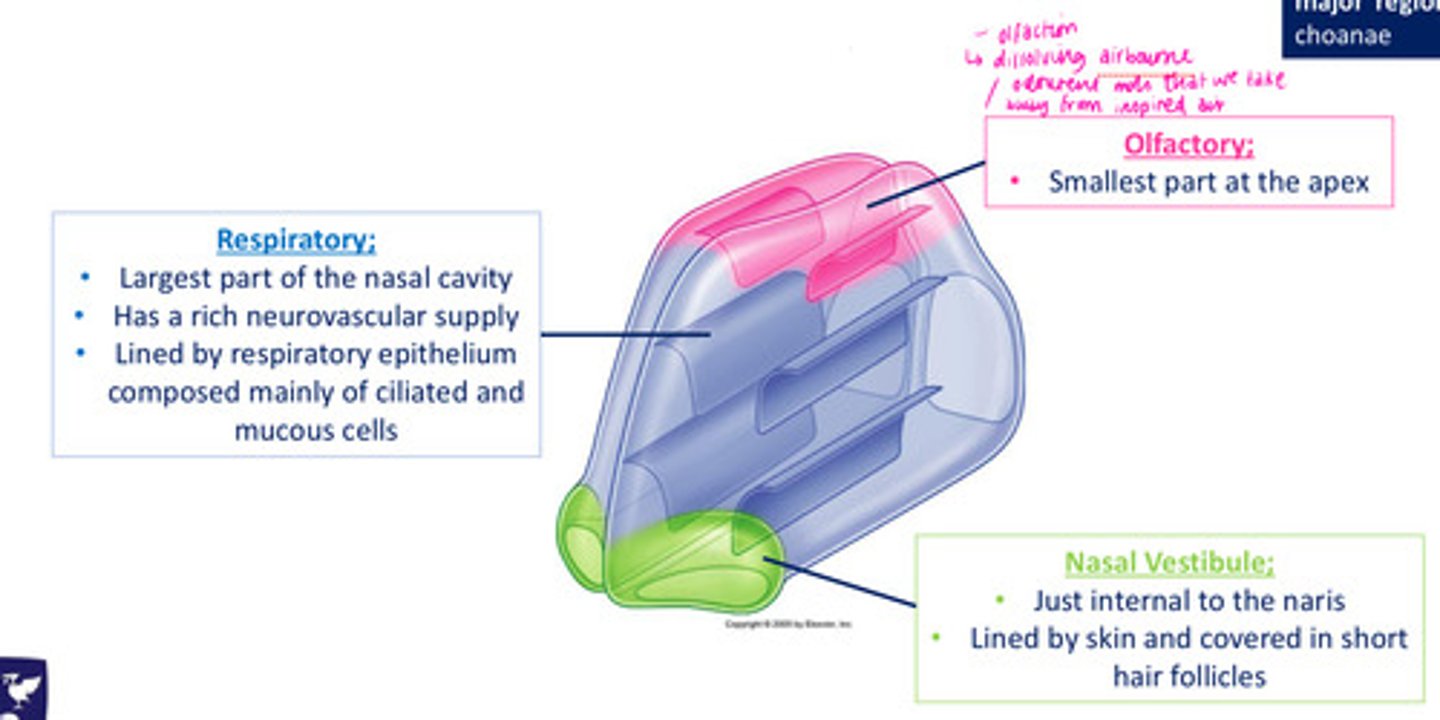
Regions of the nasal cavity: Nasal Vestibule
just internal to naris
lined by skin & covered in short hair follicles
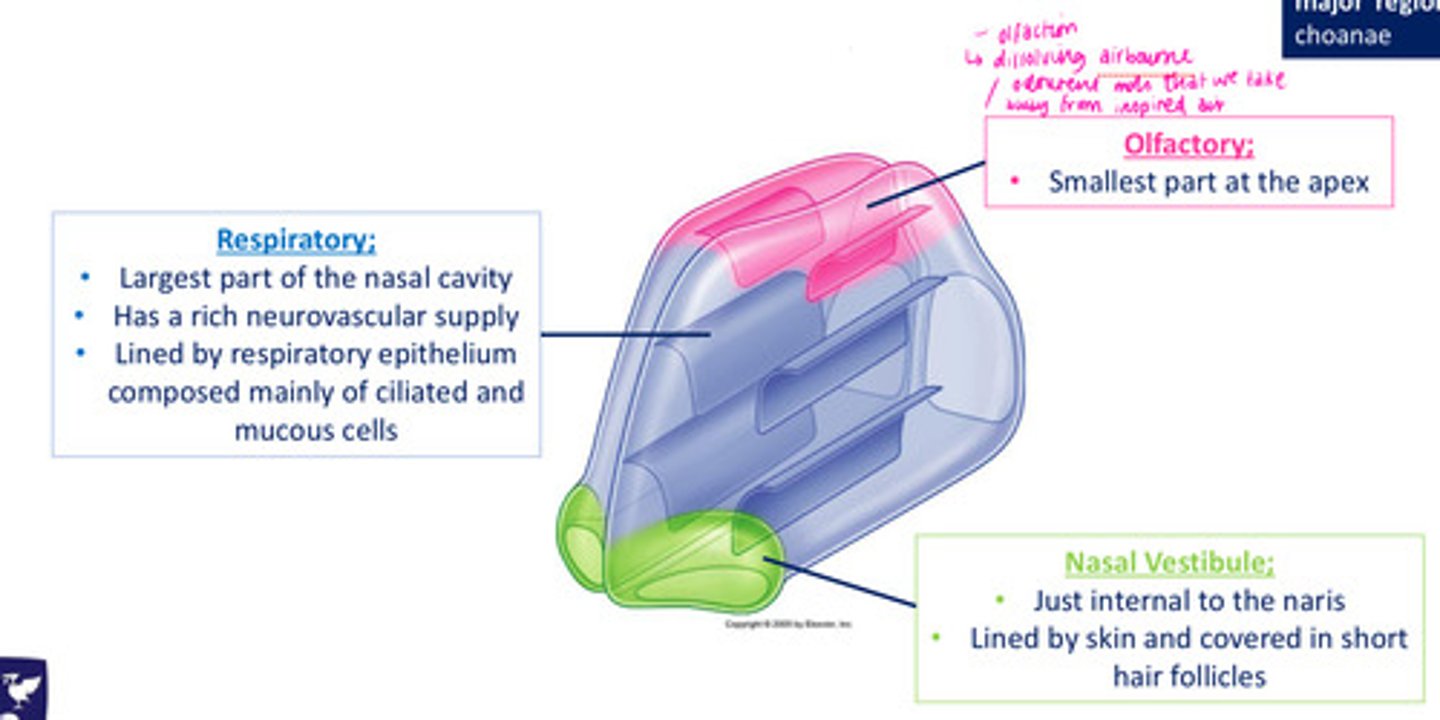
Role of olfaction
dissolving airbourne odourent mols that we take away from inspired air
DIAGRAM: Medial wall of the nasal cavity
supported posteriorly by bone & anteriorly by a sheet/plate of cartilage
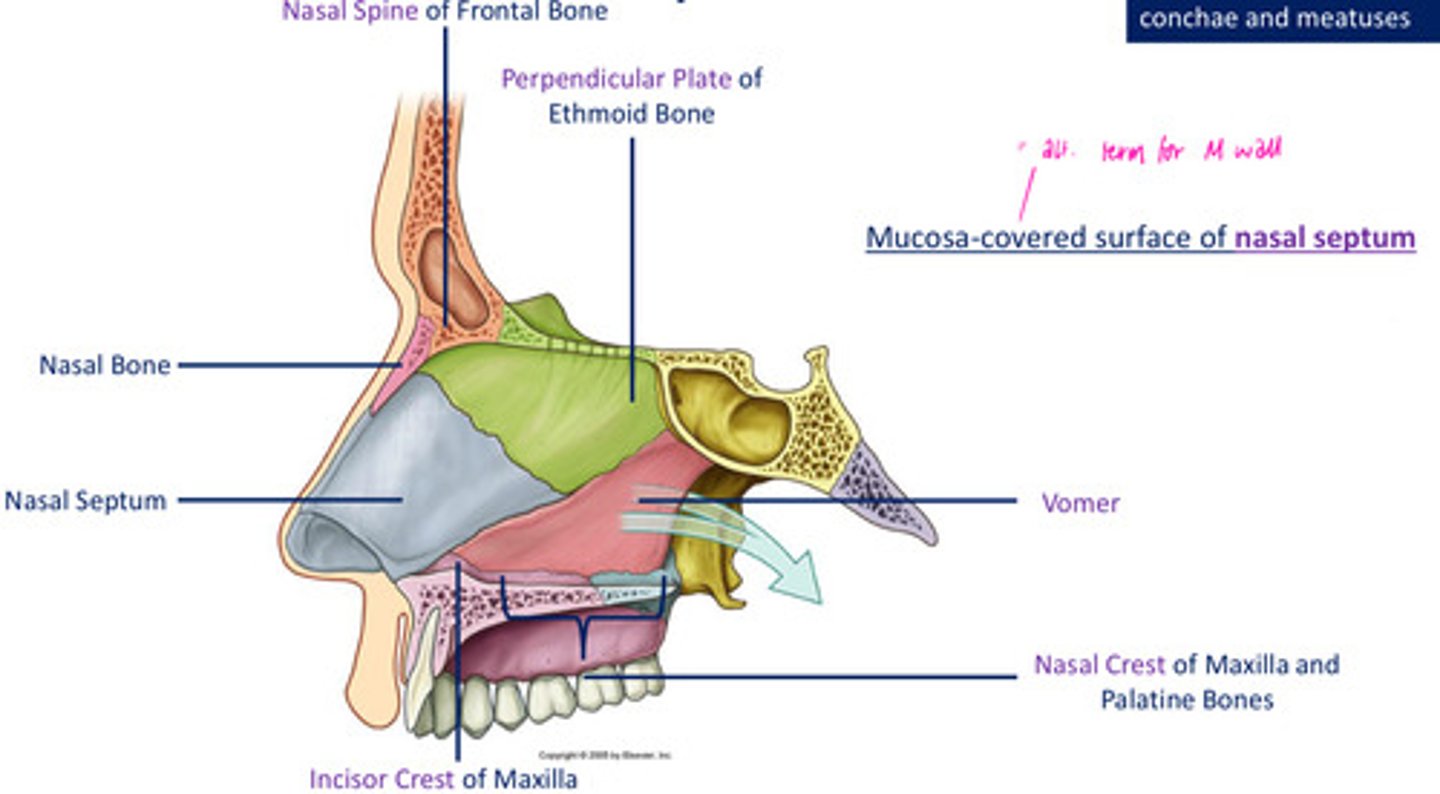
Roof of the nasal cavity: Anterior to cribiform plate
- nasal spine of frontal bone
- nasal bone
- lateral process of septal cartilage
- major alar cartilage
Roof of the nasal cavity: Posterior to cribiform plate
- anterior surface of sphenoid bone
- ala of vomer
- sphenoidal process of palatine bone (adj to ala)
- vaginal process of medial pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone
What is the role of the small formina in the cribiform plate of the ethmoid?
convey olfactory neurones from the roof of NC onto the base of the brain & conveys meningeal layers
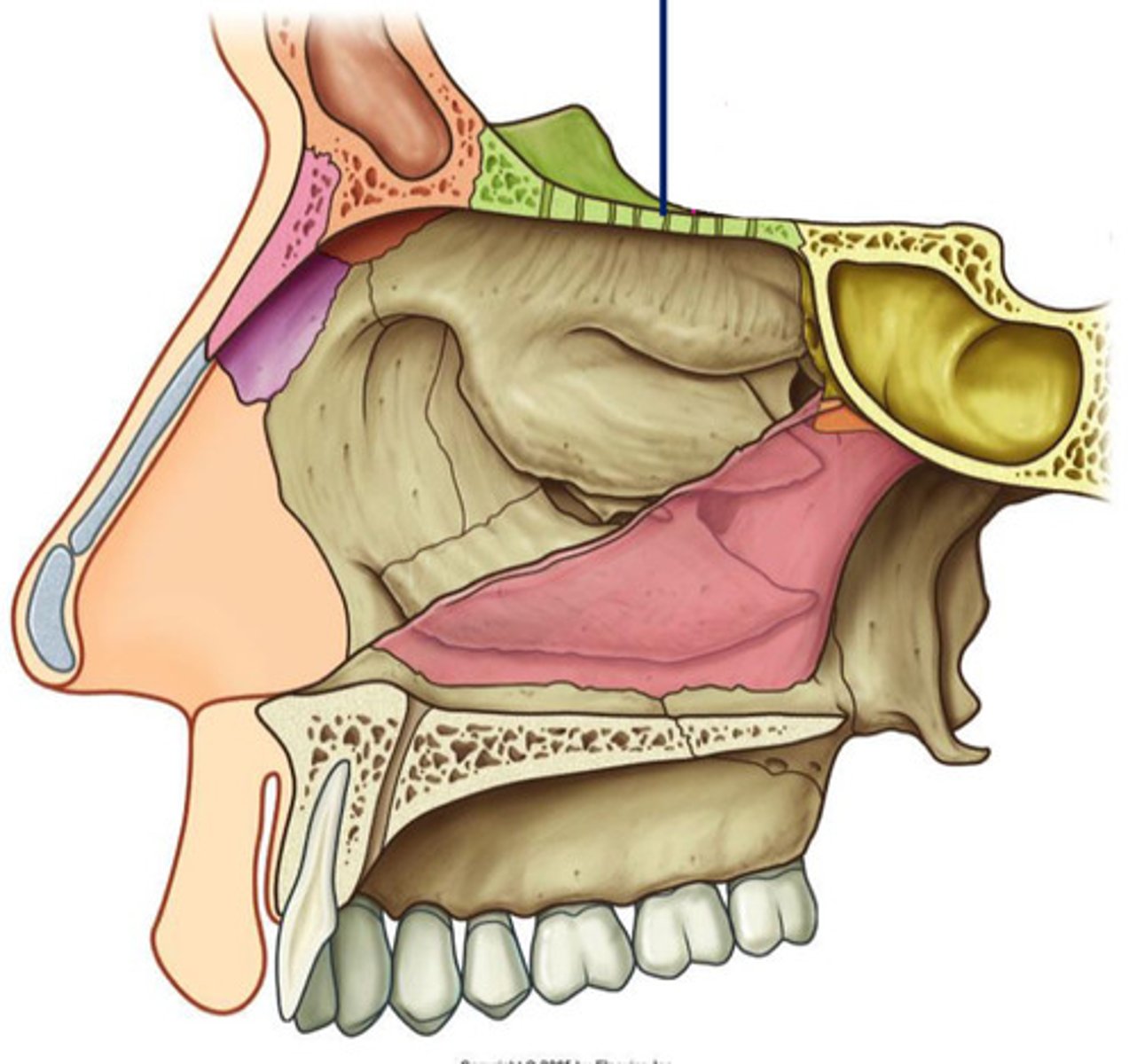
DIAGRAM: Floor of the nasal cavity
smooth& concave - floor caves inwards
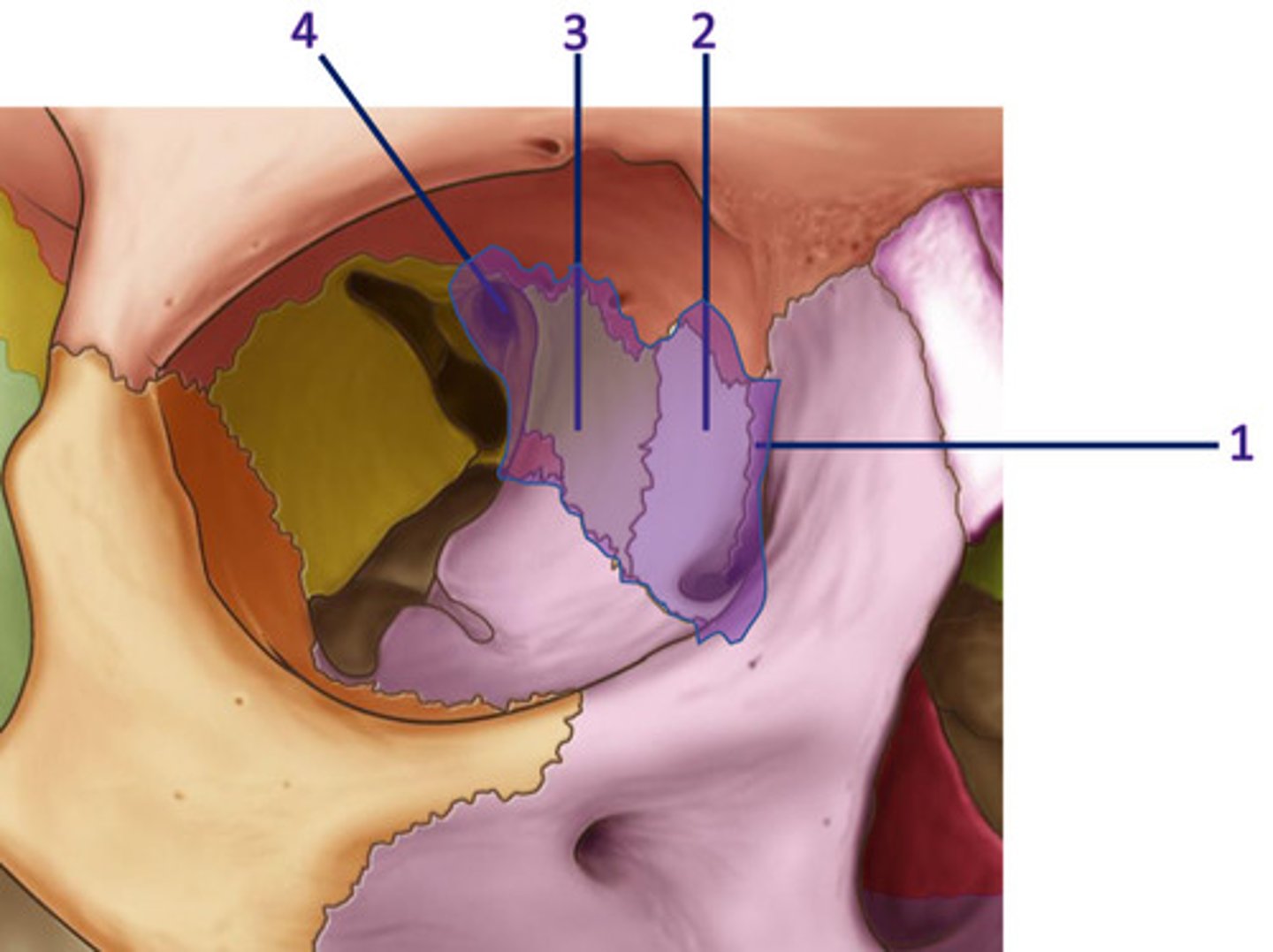
What bones are present on the medial wall of the orbit?
1 - frontal process of maxilla
2 - lacrimal (nasolacrimal duct - drains lacrimal fluid into lateral wall of NC)
3 - orbital plate of ethmoid
4 - body of sphenoid
What structures provides bony support for the lateral wall of the nasal cavity?
1. ethmoid labyrinth, superior concha, middle concha & uncinate process
2. inferior concha
3. perpendicular plate of palatine
4. medial pterygoid of sphenoid
5. medial surface of lacrimal & maxilla
Concha of the lateral wall
3 curved shelves of bone - conchae/turbines
Superior, middle concha - ethmoid
inferior concha - sep
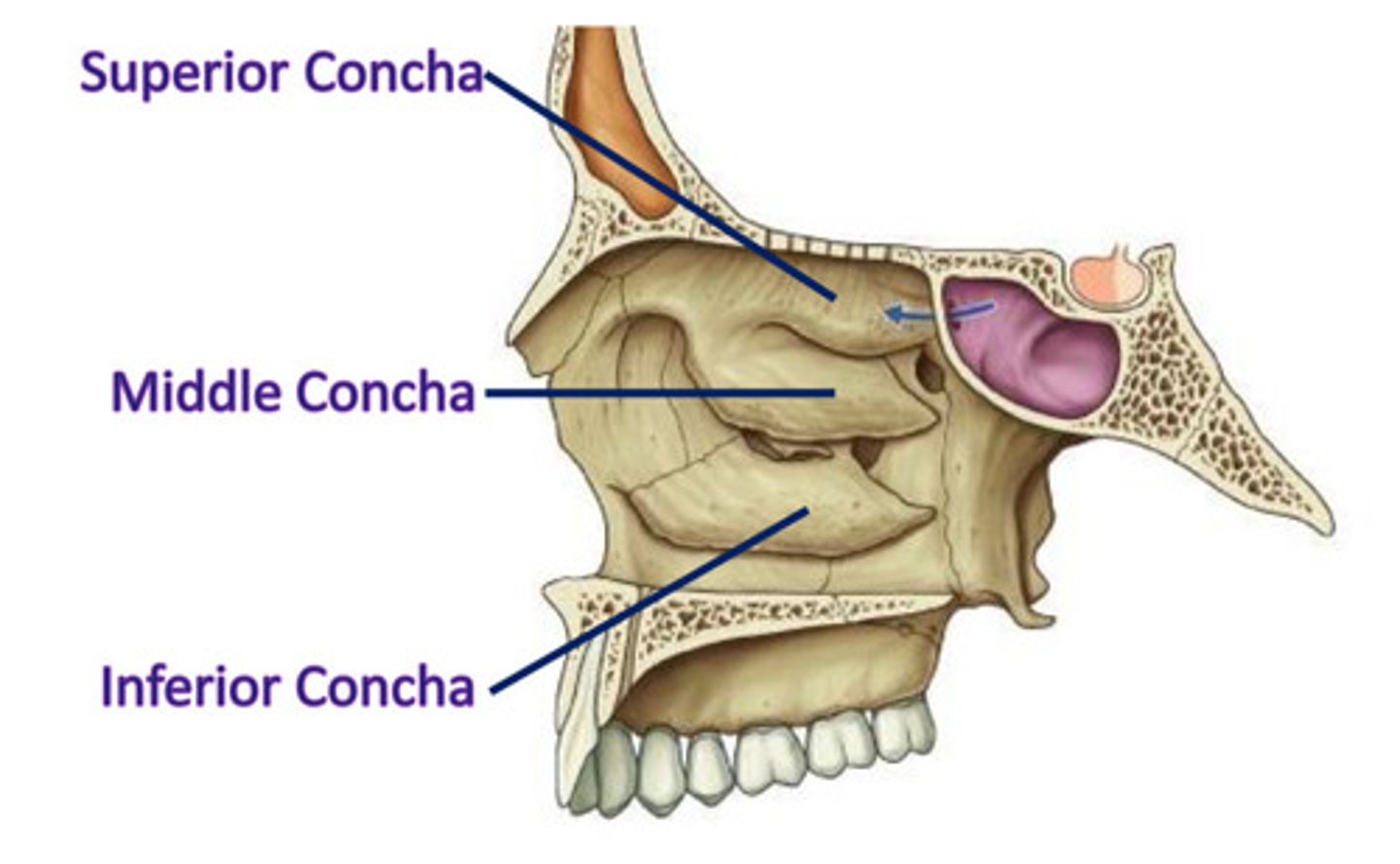
Purpose of a concha
4 air channels are created within each cavity, increasing SA for contact w/ inspired air & SA to receive odourant mols (creating olfactory stimulus)
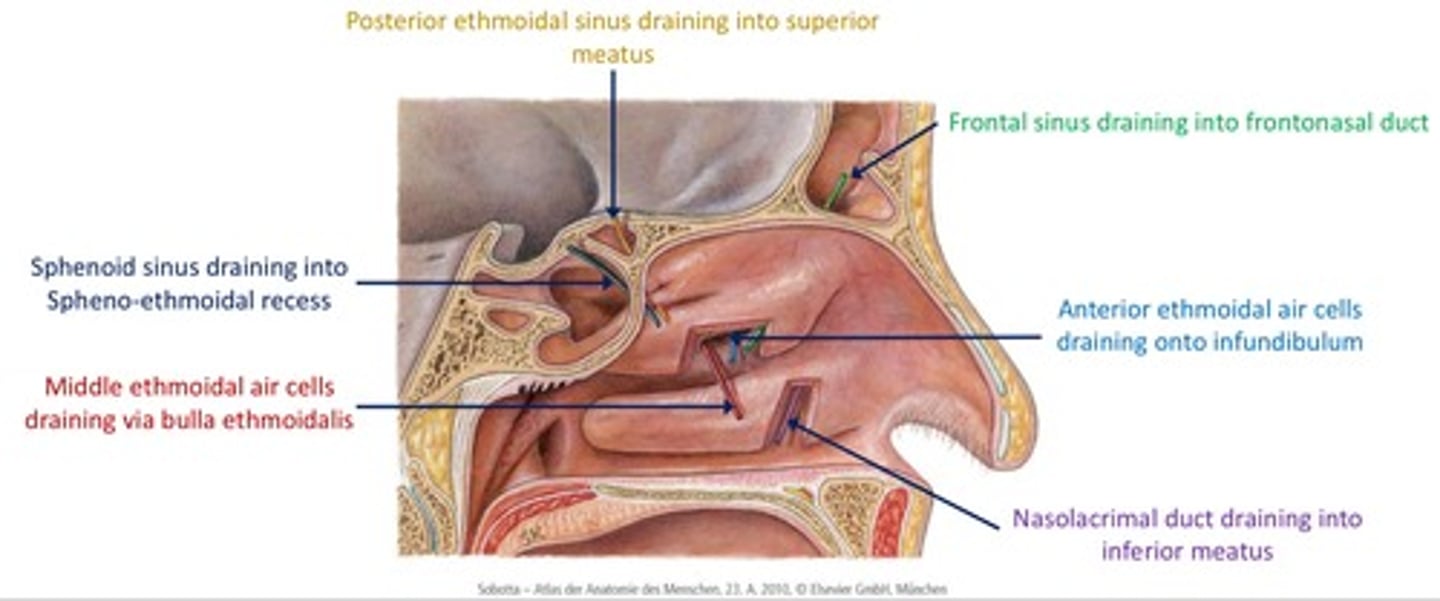
Meatuses of the nasal cavity
sphenoethmoidal recess
inferior meatus
middle meatus
superior meatus
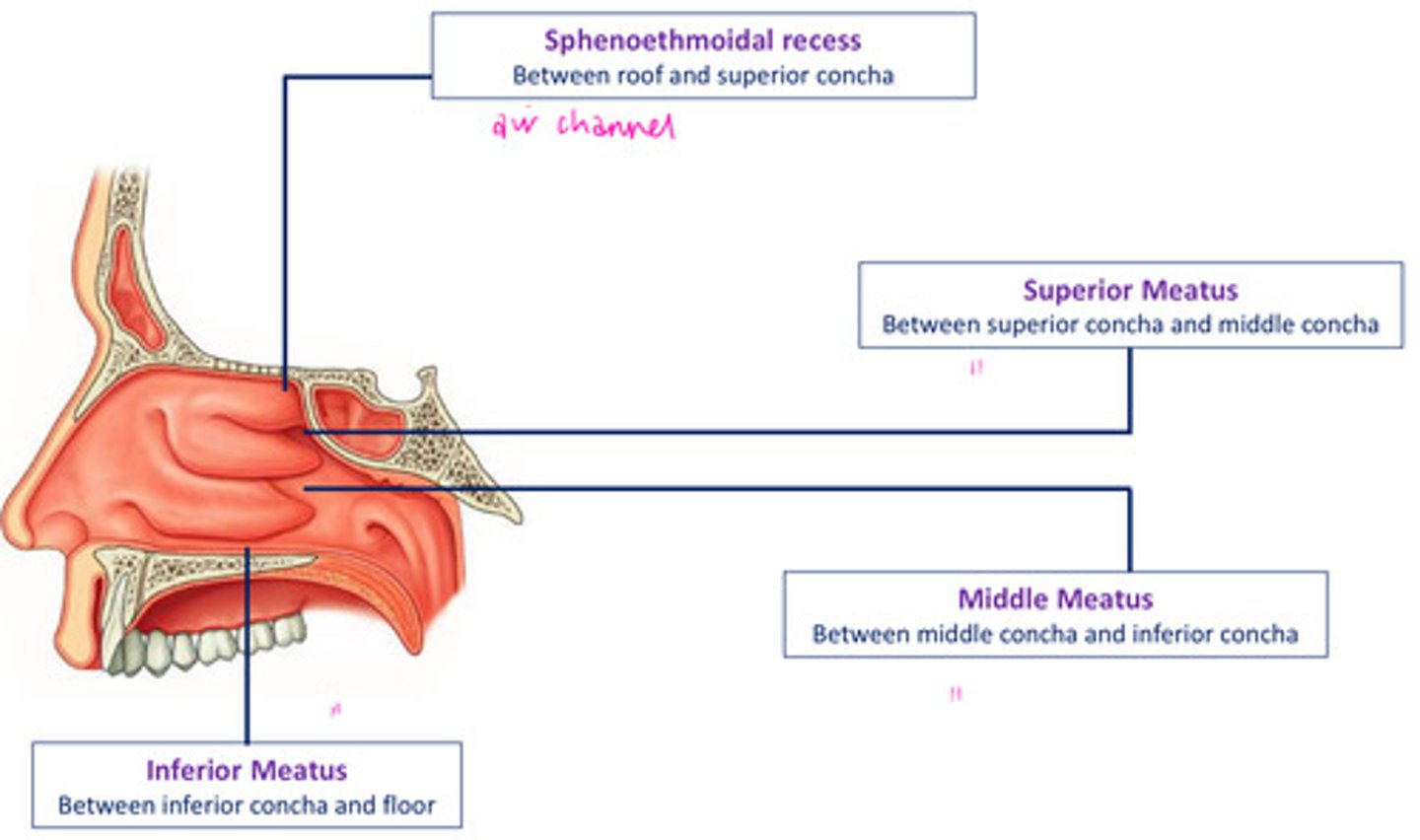
Meatuses of the nasal cavity provide...
a position through which the paranasal air sinuses drain into the NC
Features of the ethmoid bone:
Perpendicular Plate
Ethmoidal labyrinths
Cribiform Plate
Crista Galli
Superior & Middle Nasal Concha
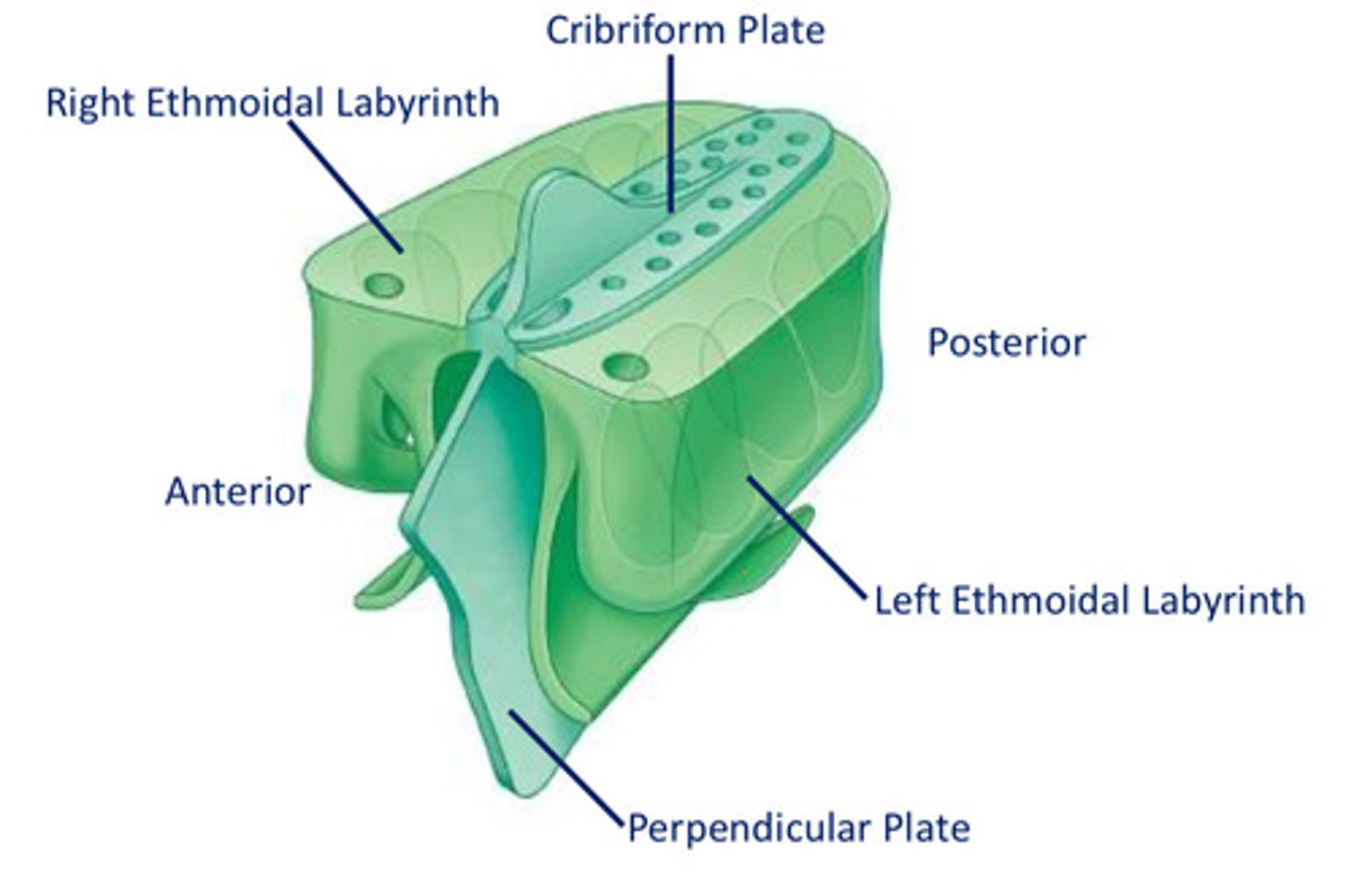
What type of cells form the ethmoid paranasal sinus?
ethmoid air cells
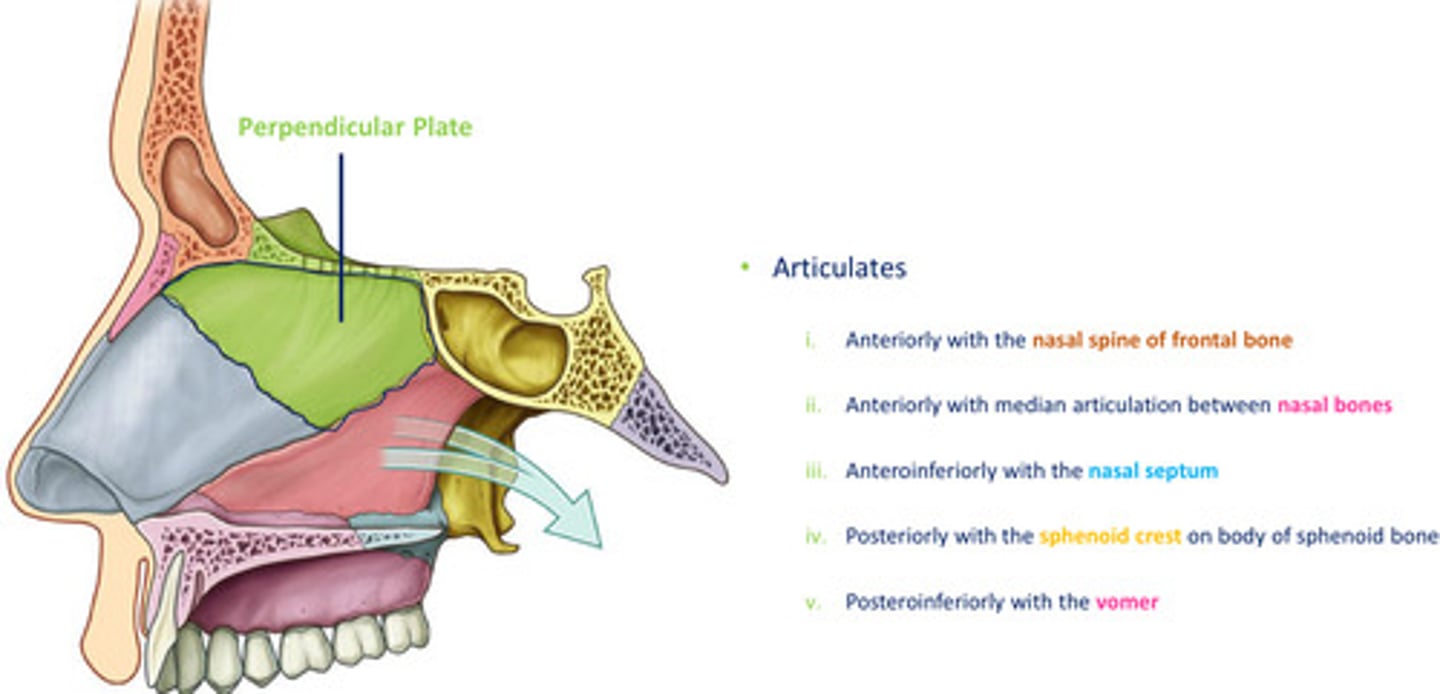
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
quadrangular in shape
forms U part of median nasal septum
articulates...(see diagram)
Ethmoidal labyrinth
R & L
each composed of 2 delicate sheets of bone
- orbital plate: contributes to formation of M wall of orbit
- medial sheet: forms U part of lateral wall of NC
(superior concha, bulla ethmoidalis, middle concha, infundibulum, uncinate process, maxillary hiatus)
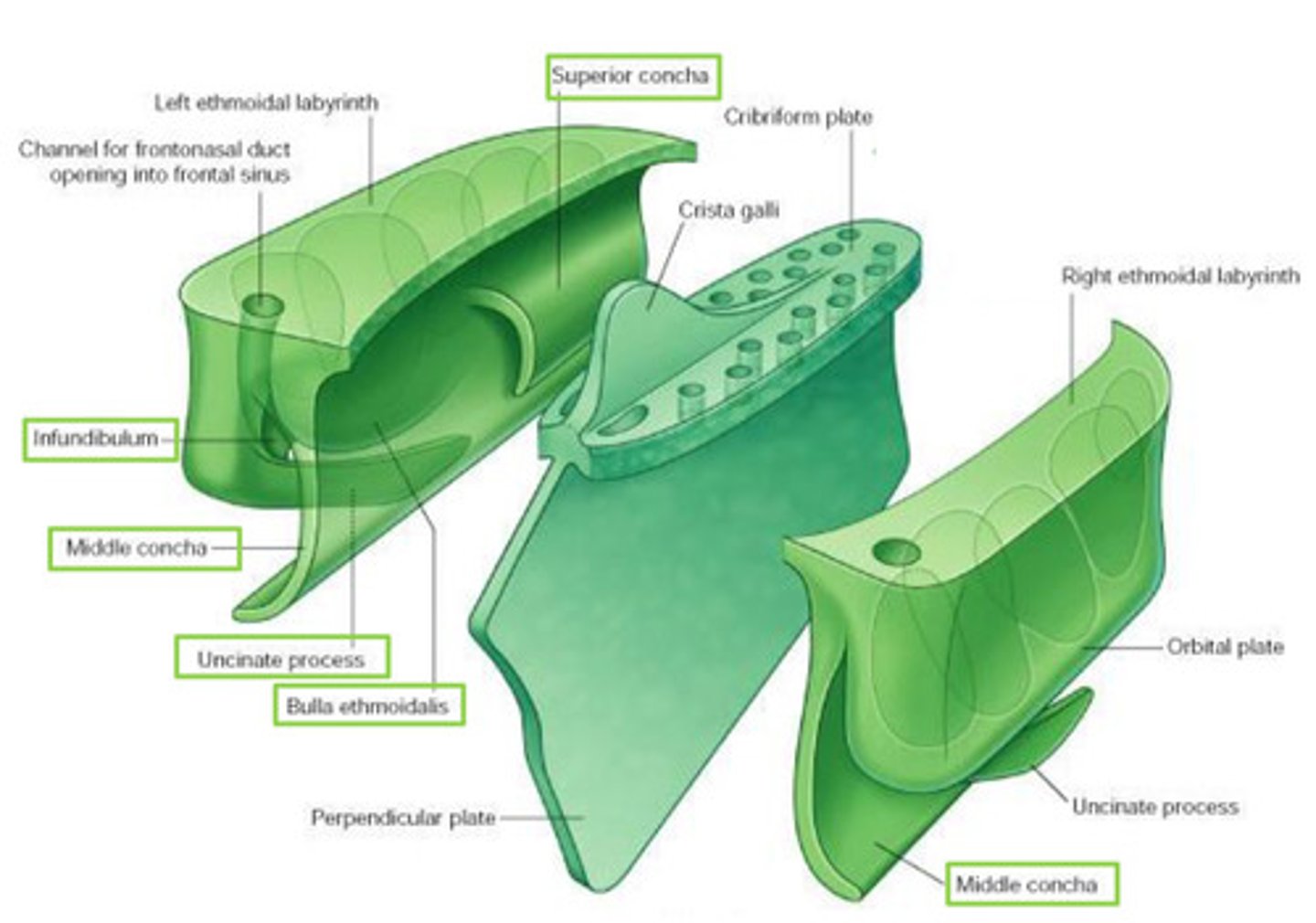
Bulla ethmoidalis
swelling on superior border of hiatus semilunaris
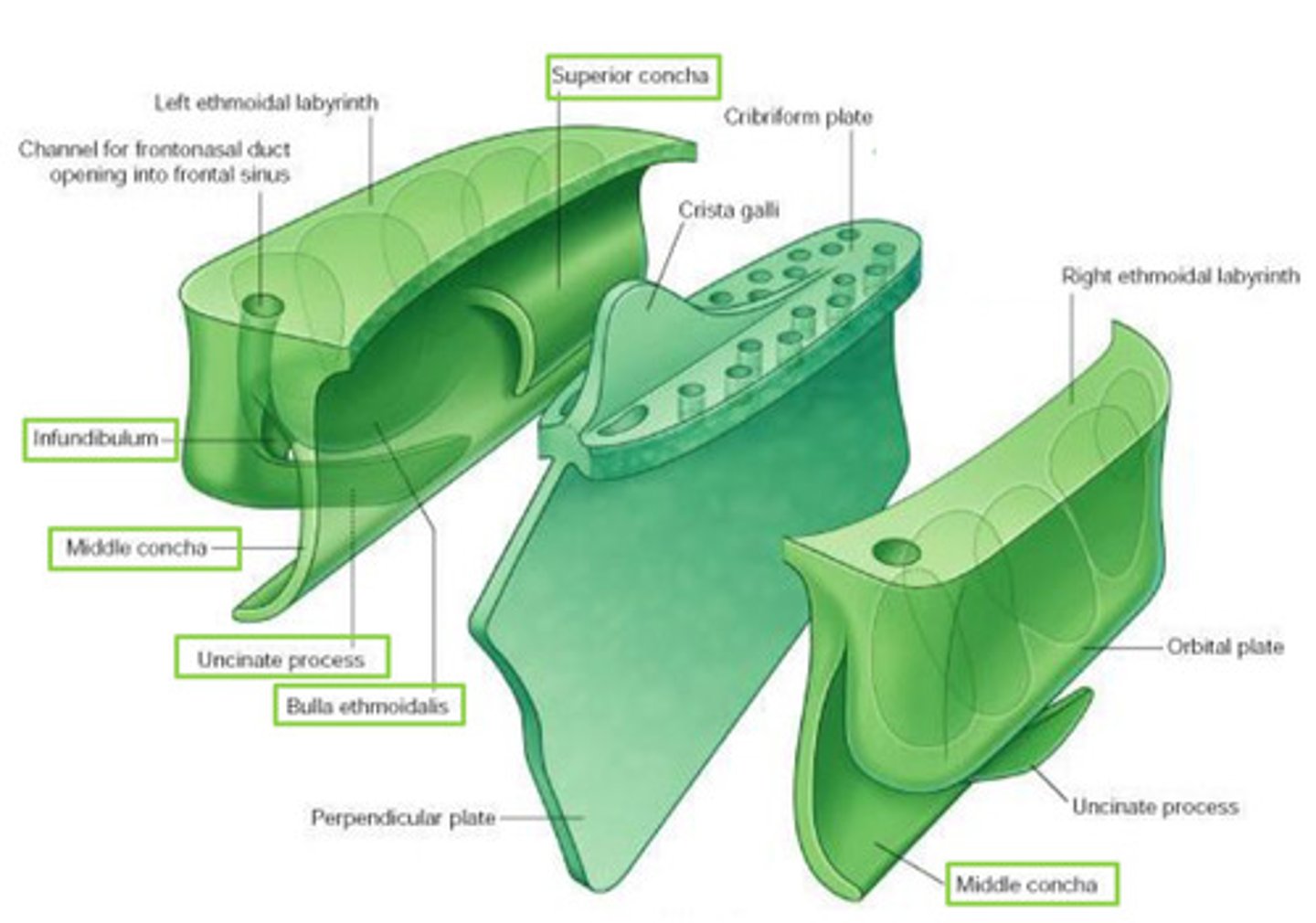
Infundibulum (ethmoid bone) opens into...
opens into frontal sinus - frontonasal duct (drains)
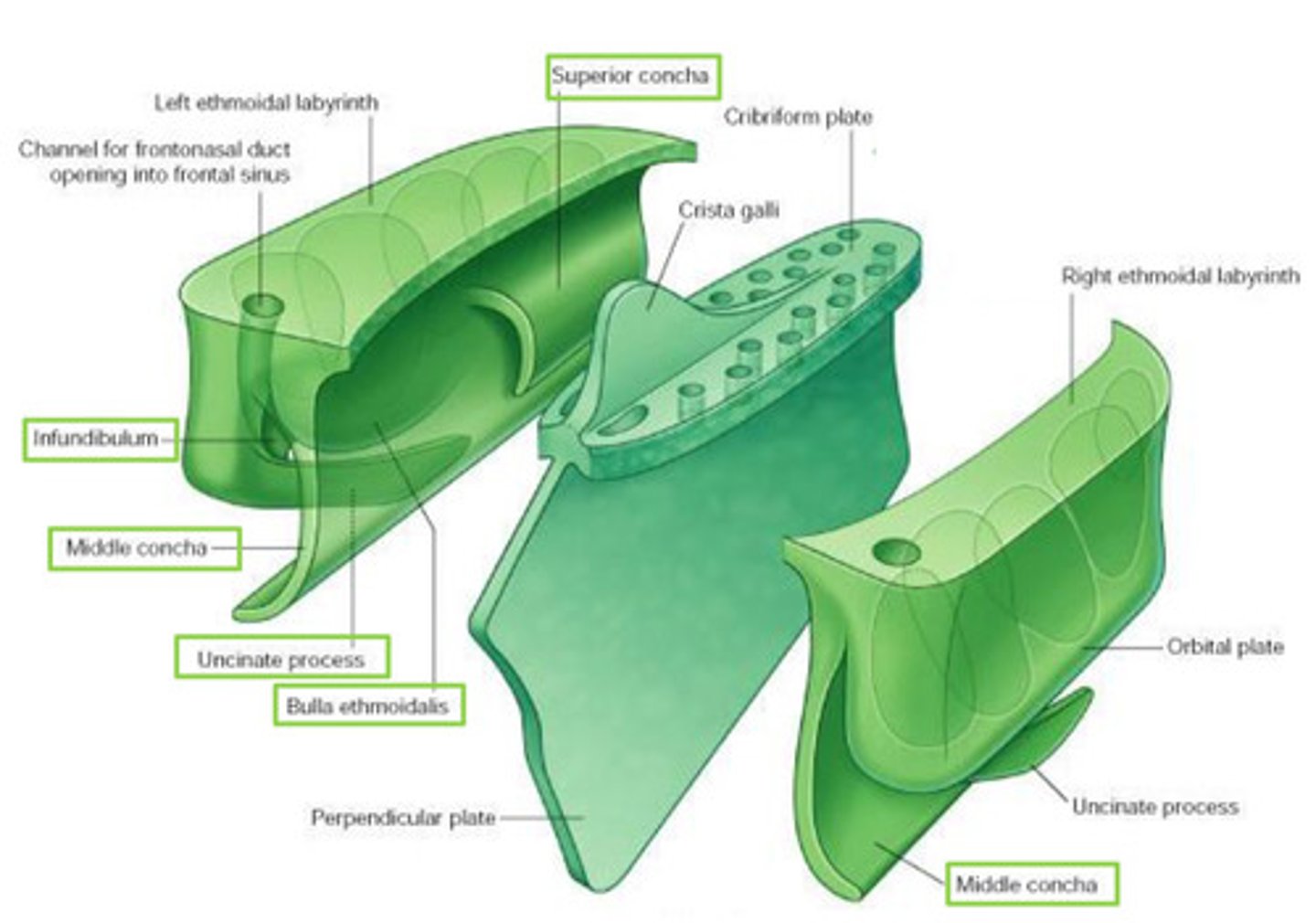
Maxillary hiatus
in M wall of maxilla - articulates w/ middle concha
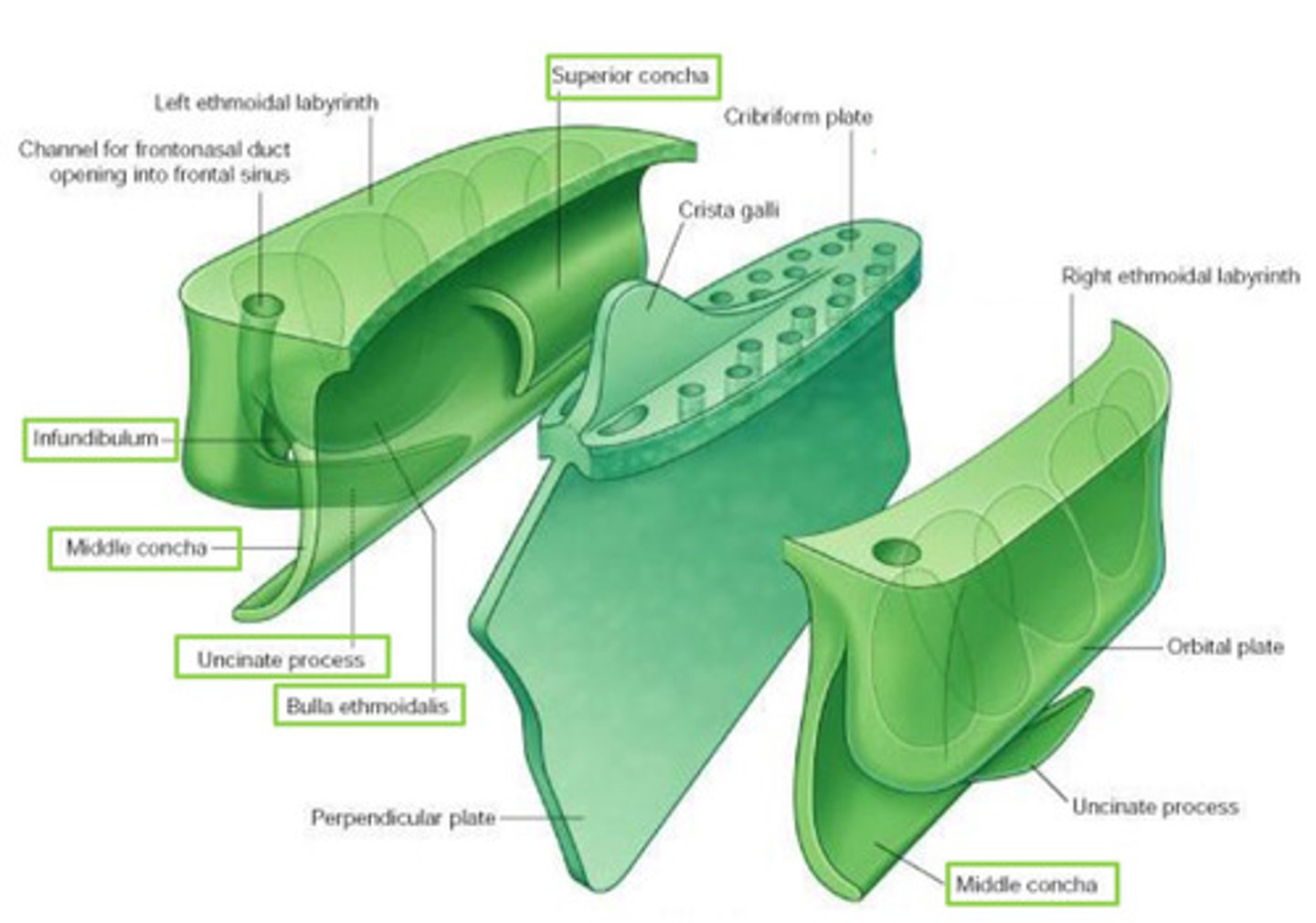
Crista galli
attachment for falx cerebri
triangular process of bone
projects superiorly from ethmoid
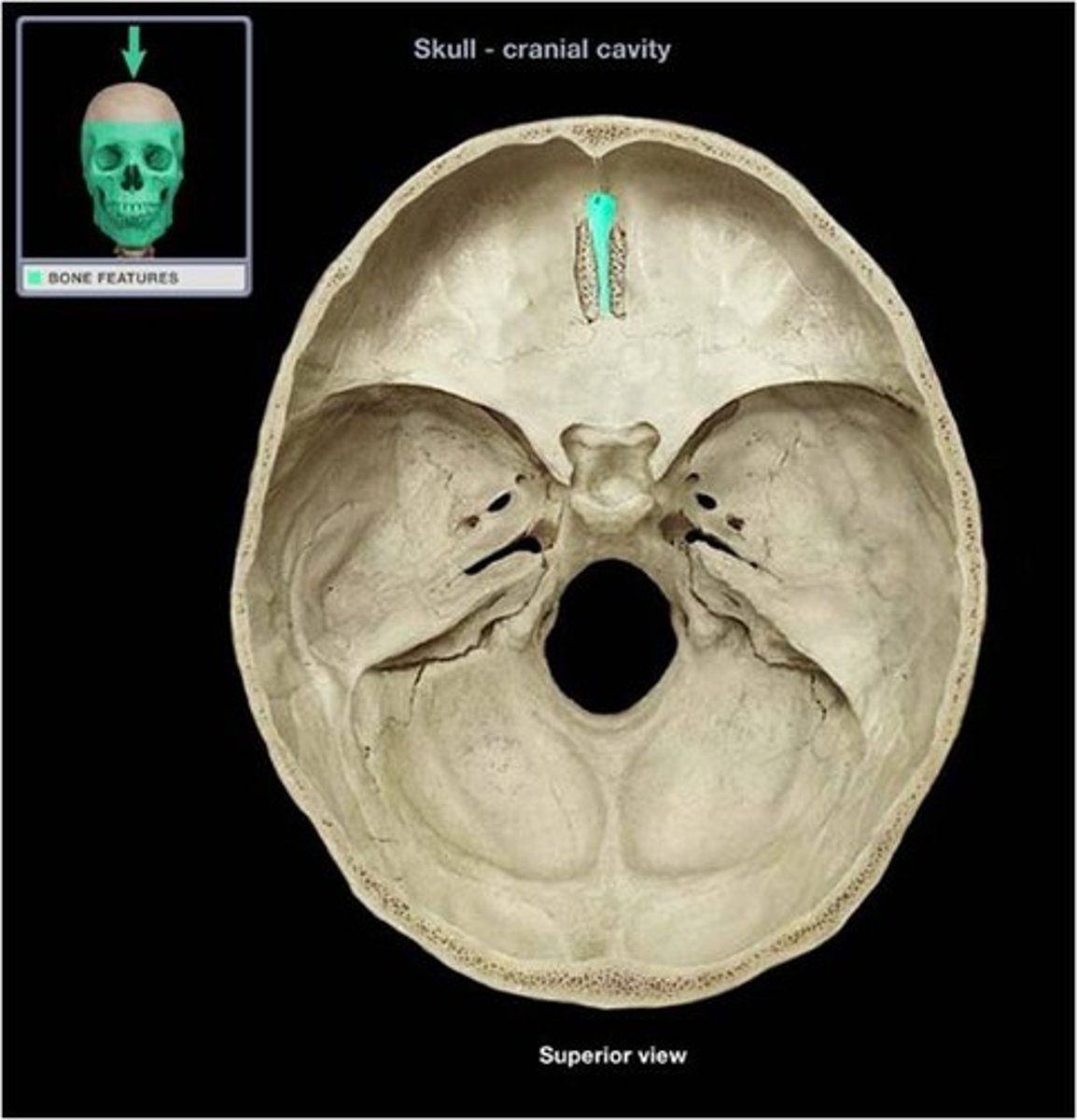
Cribiform plate
perforated sheet of bone transmitting olfactory nerve fibres via its foramina
fills ethmoid notch in frontal bone
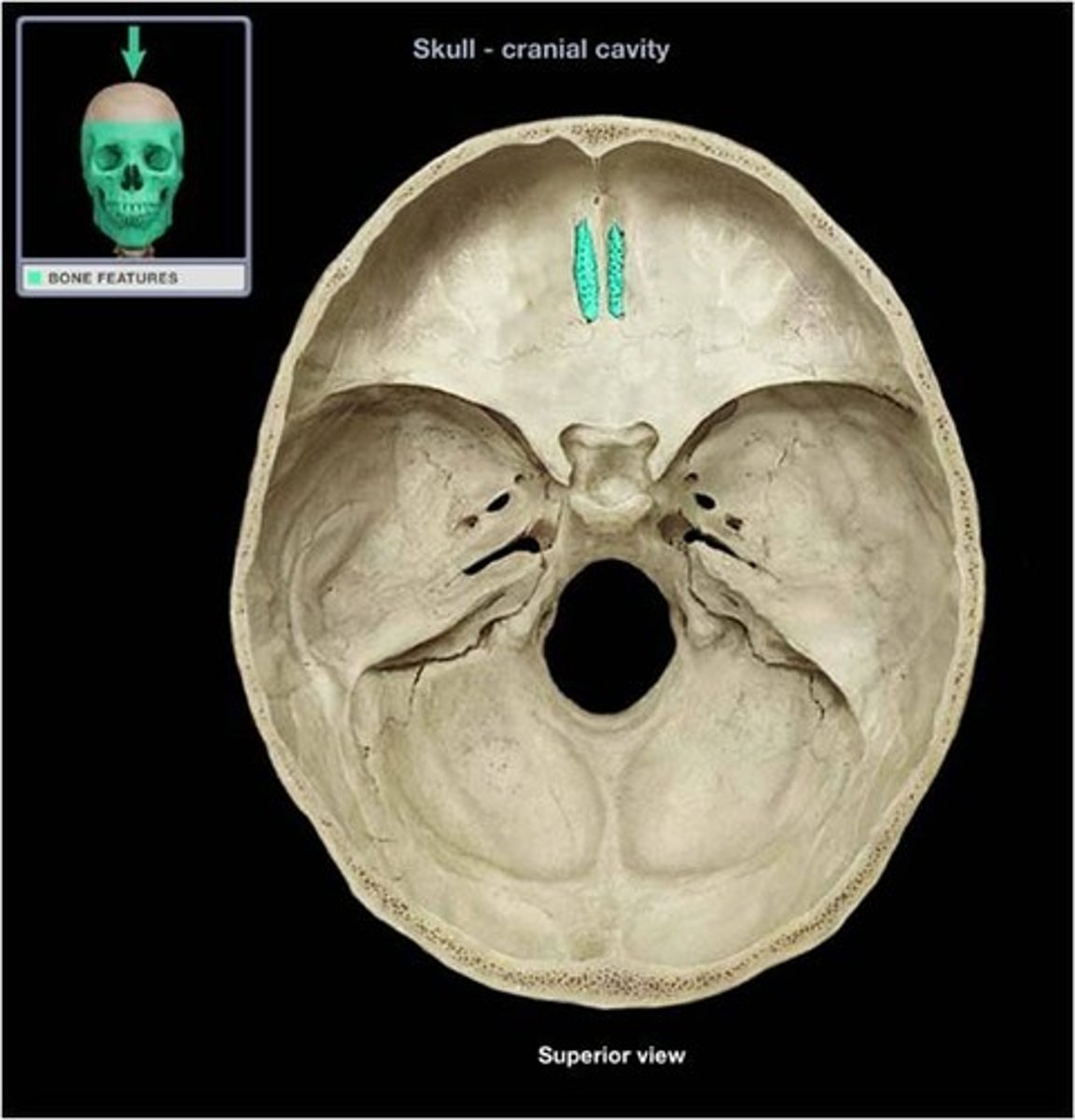
Line DIAGRAM: Coronal view of ethmoid bone
1 - superior concha: divides superior meatus from sphenoethmoidal recess
2 - superior meatus: b/t superior & middle concha
3 - middle concha: divides superior meatus & middle meatus
4 - middle meatus: between middle & inferior concha
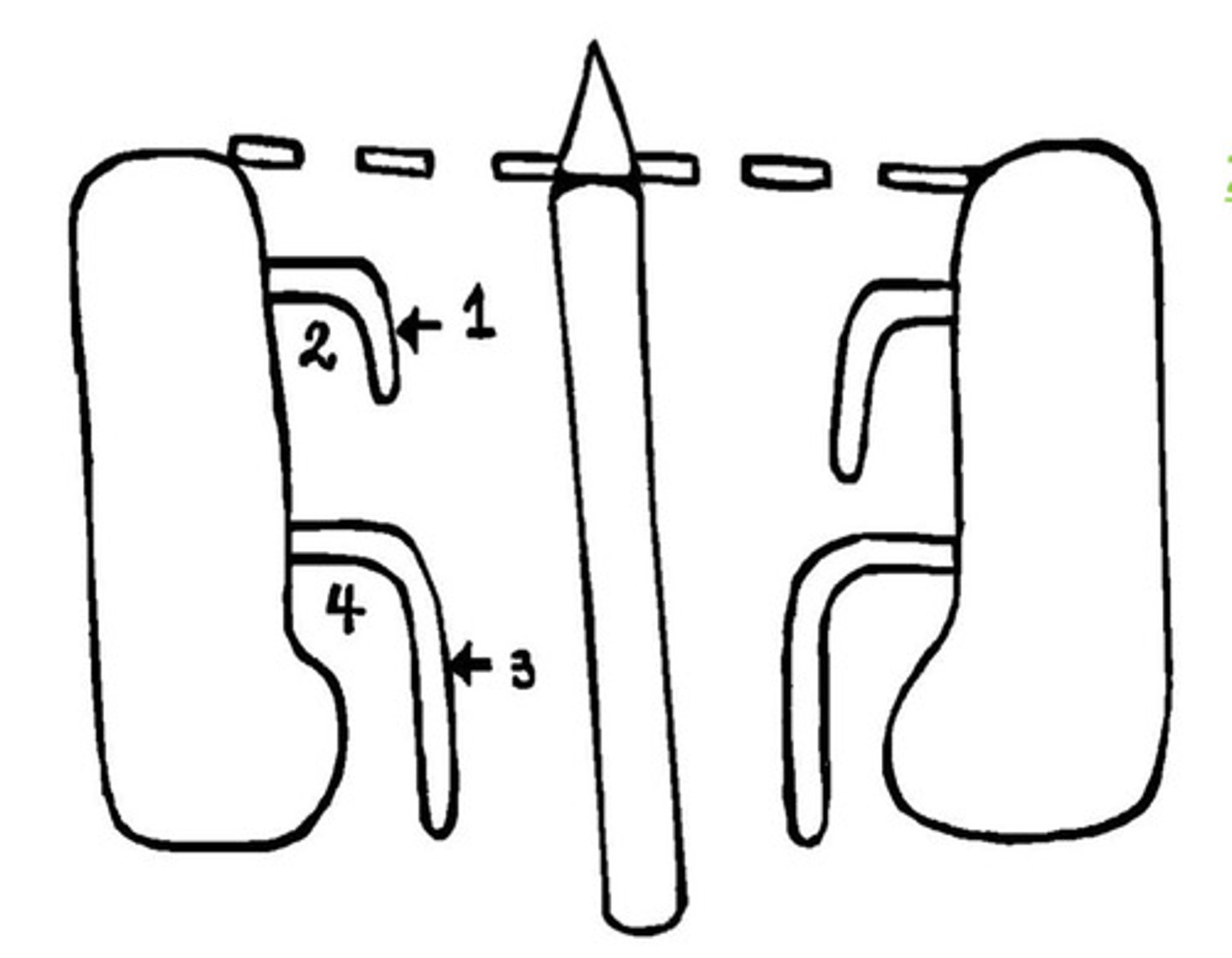
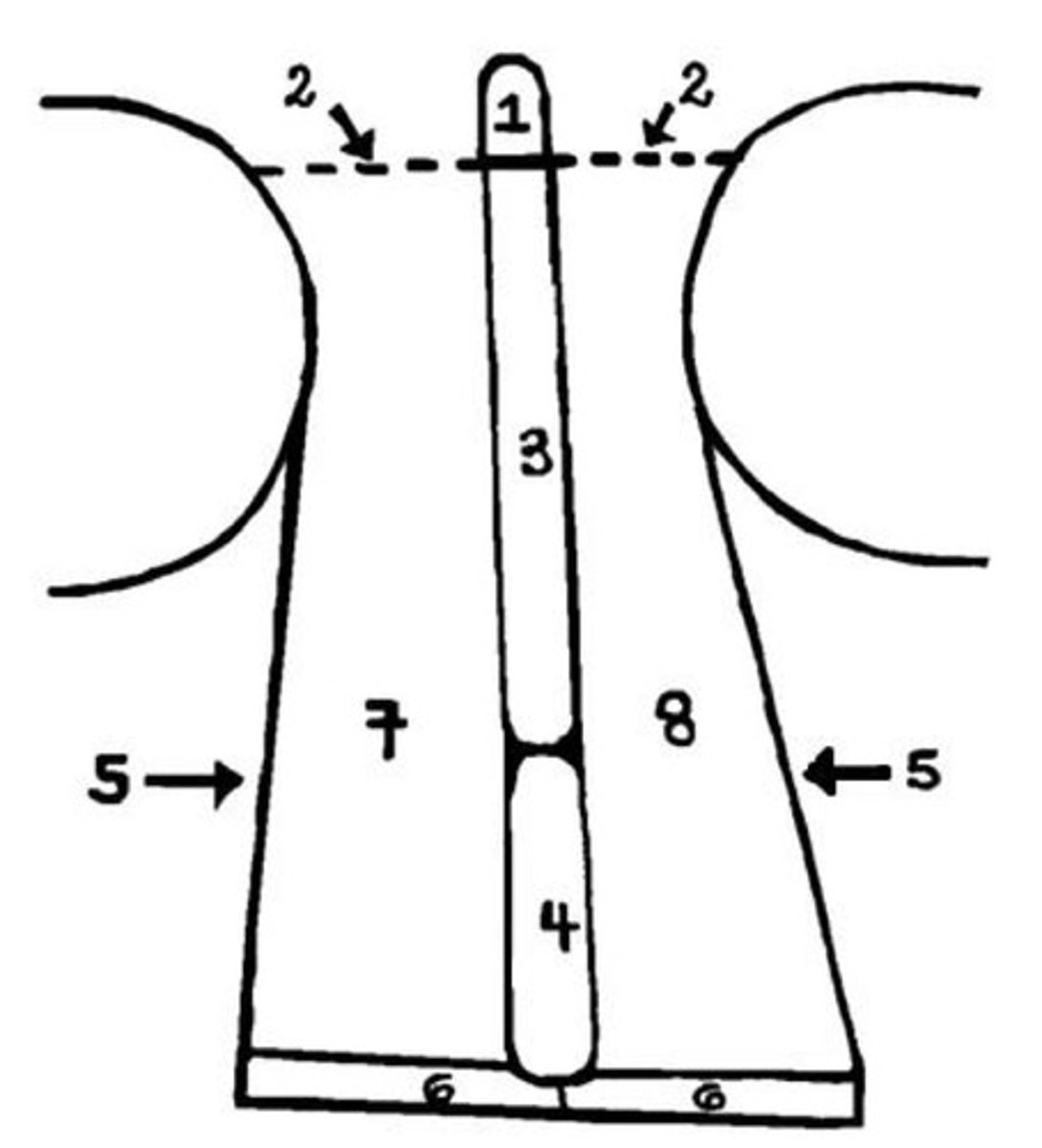
DIAGRAM: Coronal view of the head (orbit, ethmoid, maxillary sinus)
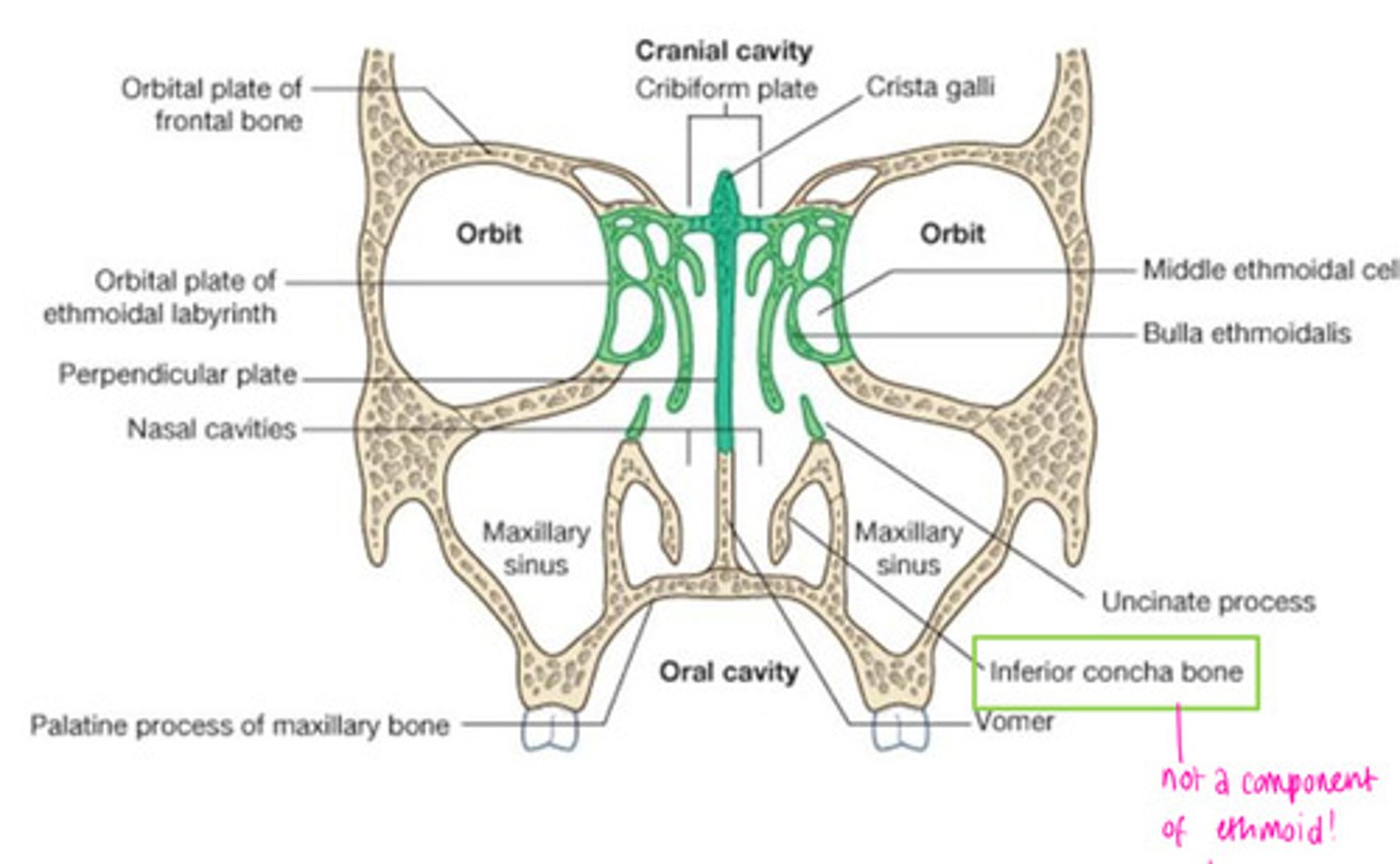
Label this coronal view of the nasal cavity
1 - crista galli of ethmoid
2 - cribiform plate of ethmoid
3 - perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
4 - vomer
5 - lateral wall (containing superior, middle, inferior conchae)
6 - hard palate
7 - right NC
8 - left NC
What are the four paranasal air sinuses?
frontal
ethmoid
maxillary
sphenoid
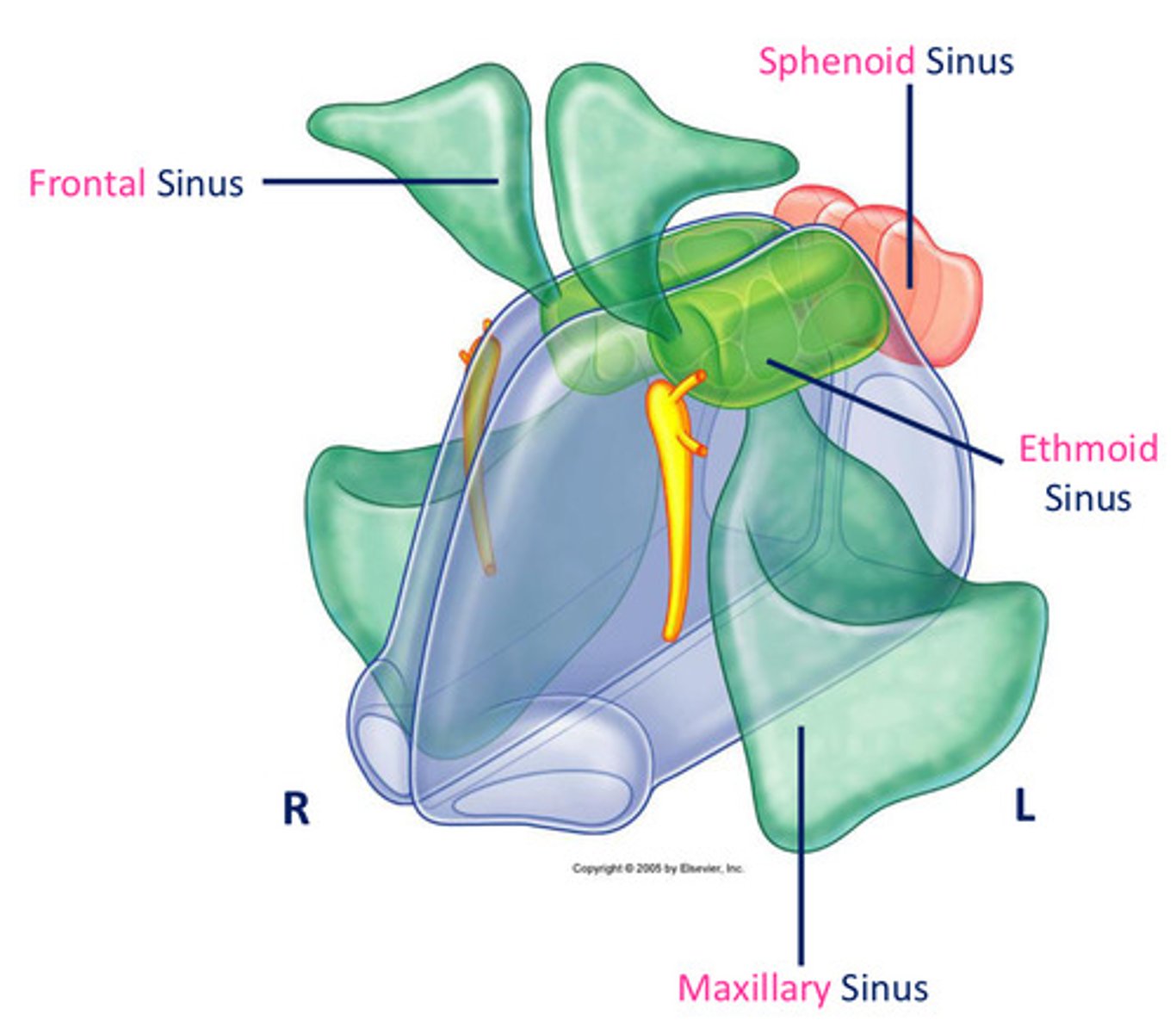
Features of the parasal air sinuses?
develop as outgrowths from NC eroding into surrounding bone
lined by cilisted, mucous-secreting respiratory mucosa
What are the possible functions of the paranasal air sinuses?
lighten skull
resonance
shock absorption
Frontal sinus
- shape
- base
- apex
- triangular in shape
- base of triangle situated vertically in the midline superior to bridge of nose
- apex situated laterally, extending 1/3rd across the superior boarder of the orbit
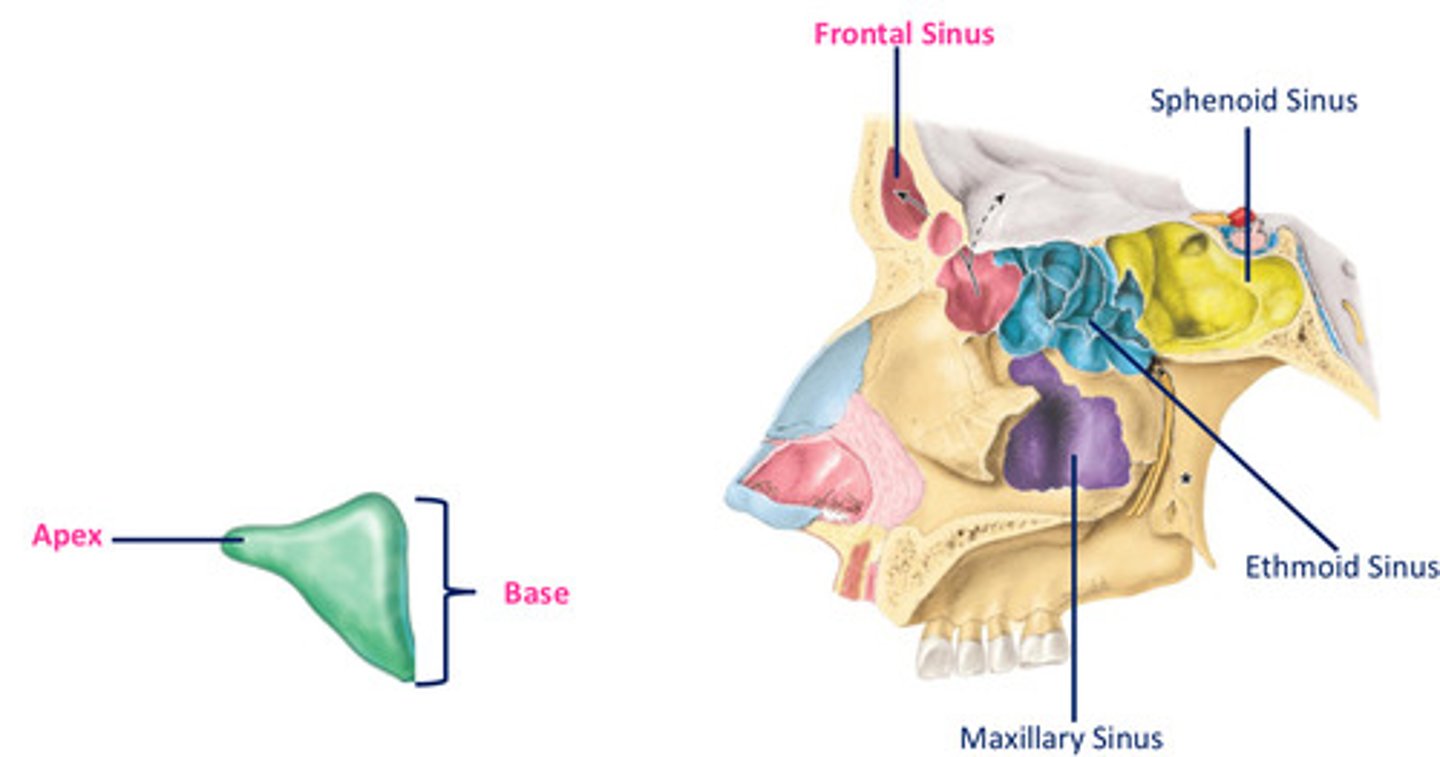
Sphenoid sinus location
- located within body of sphenoid
- cranial cavity located superiorly (pituitary gland, optic chiasm) & laterally (cavernous sinuses)
- related anteroinferiorly w/ the nasal cavity
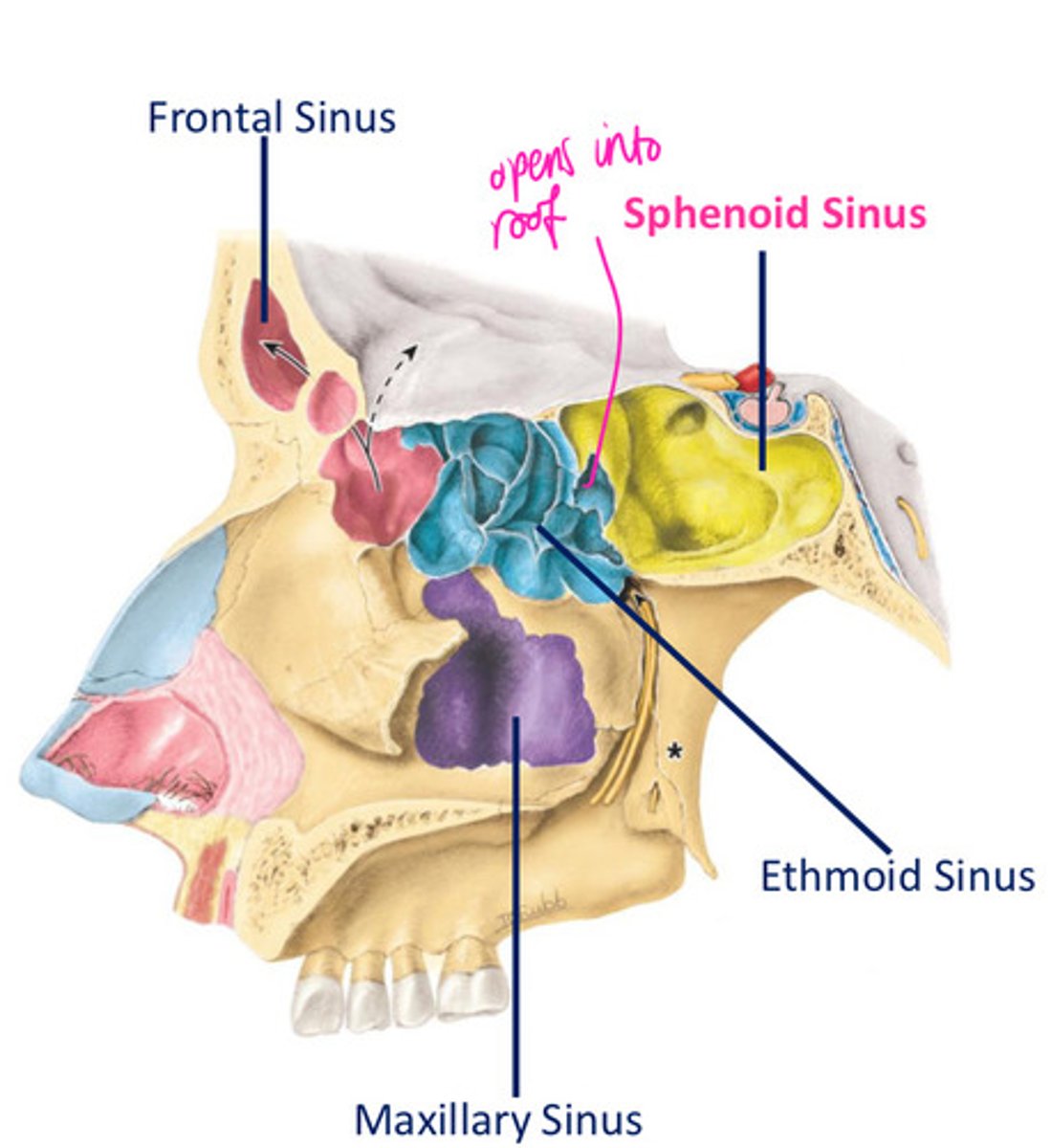
Ethmoid sinus
- formed by variable no of air chambers, clustered into anterior, middle & posterior ethmoidal air cells (3-18)
- each chamber divided from NC by the medial wall of ethmoidal labyrinth, & the orbit by a thin orbital plate of ethmoidal labyrinth
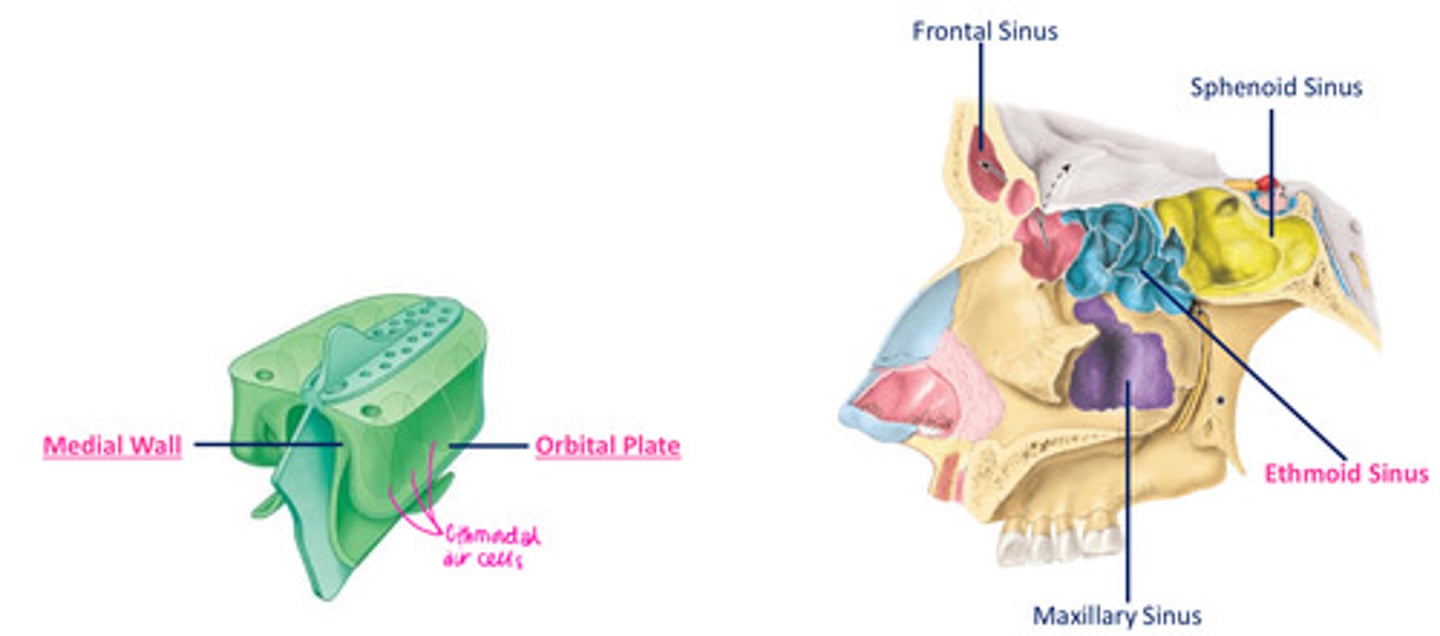
Where are ethmoidal air cells contained within?
ethmoidal labyrinth
Maxillary sinus
- shape
- base
- largest sinus, located within body of maxillae
- pyramidal in shape
- base directed towards lateral wall of NC
> superolateral surface related to orbit
> anterolateral surface related to roots of U molar & premolar
> posterior wall related to infratemporal fossa

DIAGRAM: Radiographical view of the sinuses
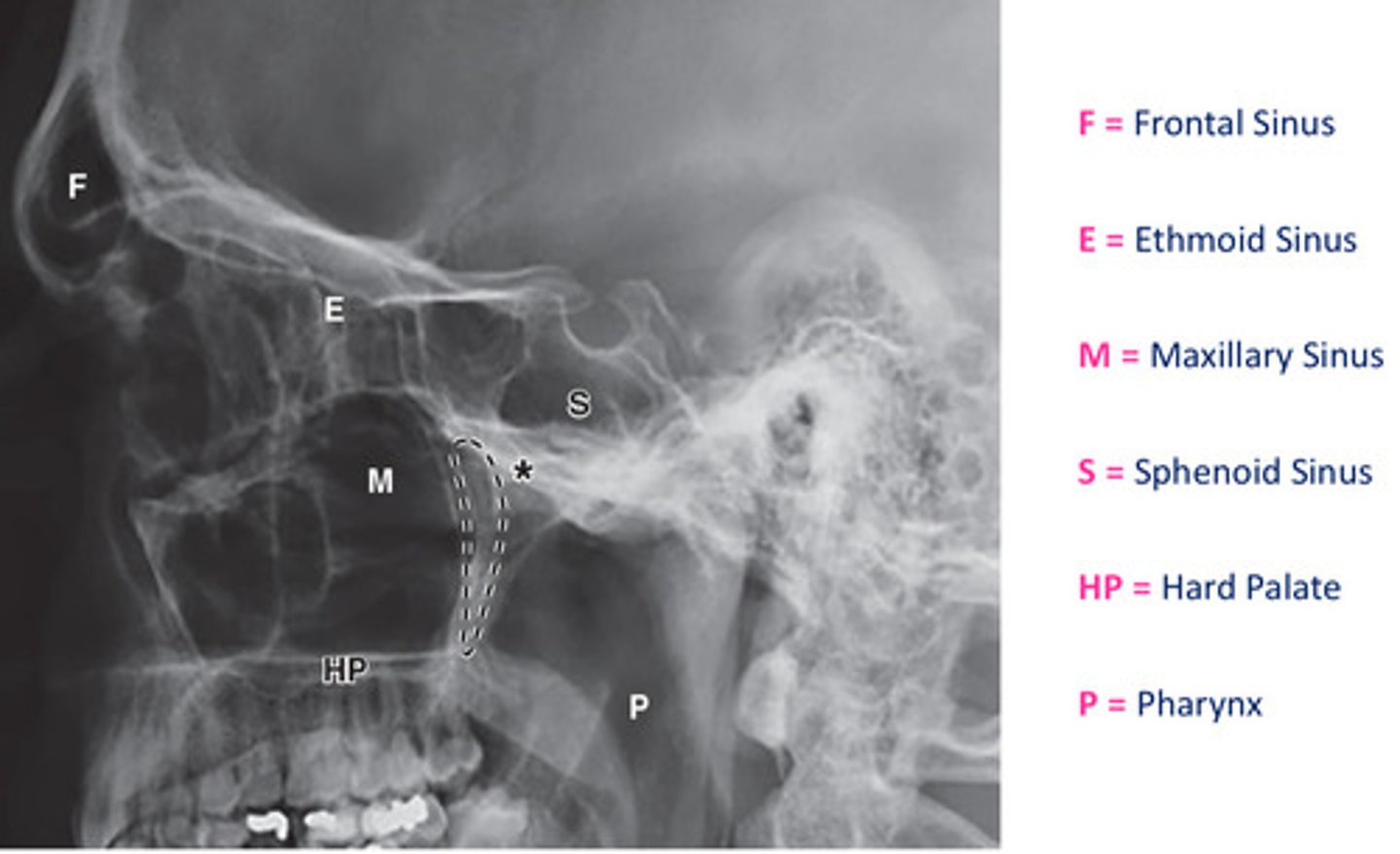
Mucous produced by mucous membrane moved by _________ action & by __________ action created during blowing of your nose.
ciliary
siphon
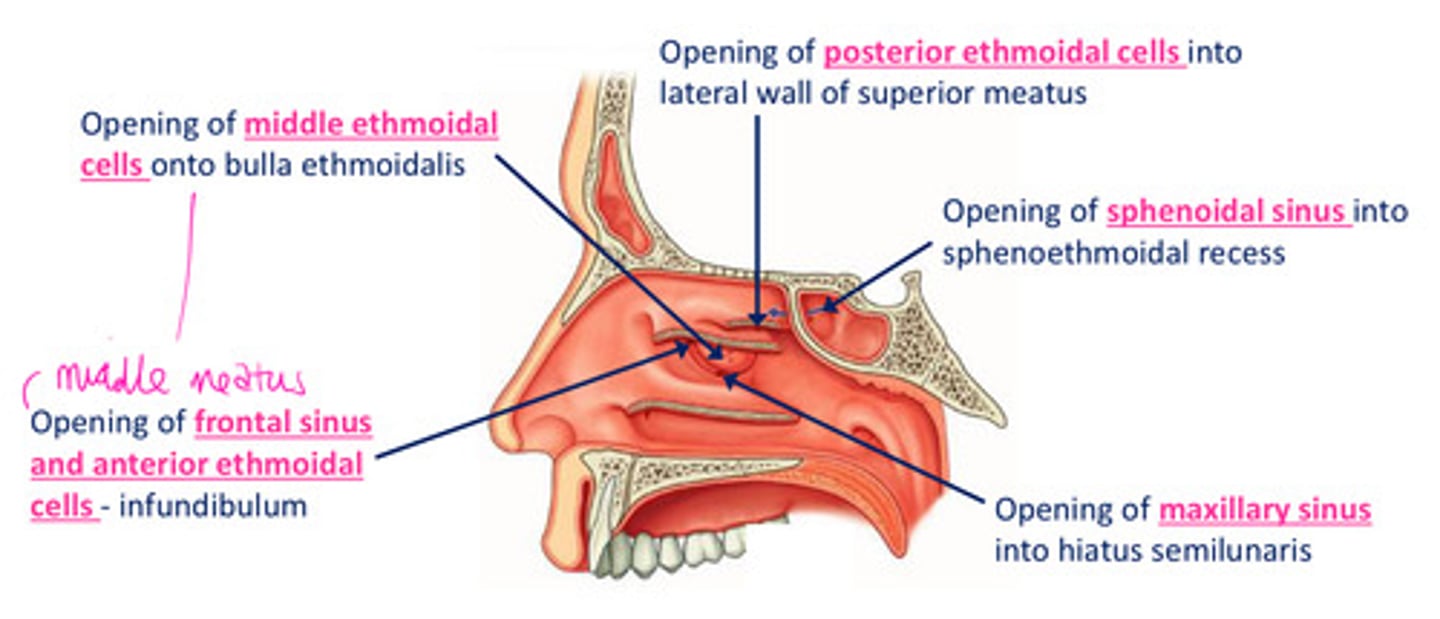
DIAGRAM: Drainage of paranasal sinuses
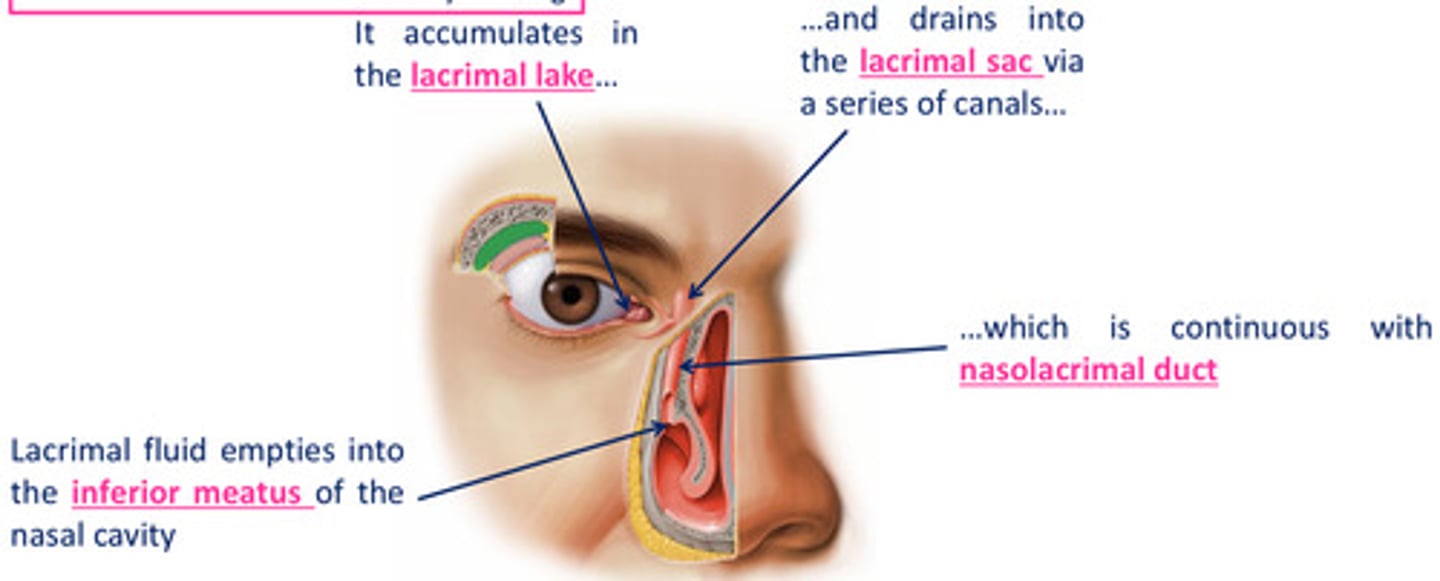
Drainage of lacrimal fluid...
1. fluid is moved over the cornea by blinking, accumulates in lacrimal lake
2. drainks into lacrimal sac via a series of canals which is continuous with nasolacrimal duct
3. lacrimal fluid empties into the inferior meatus of the nasal cavity
The sphenoid sinus opens onto...
1
sloping posterior roof of nasal cavity
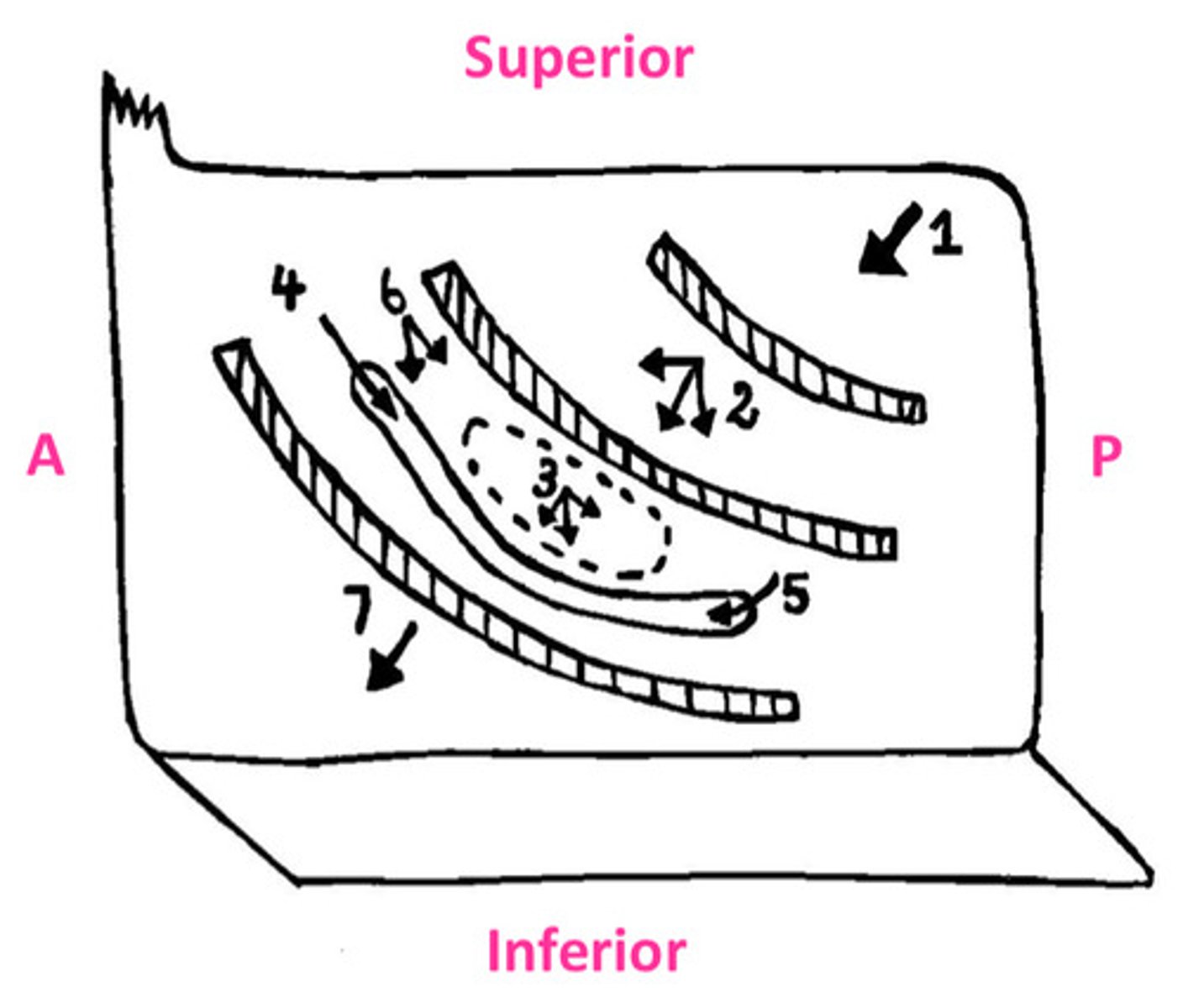
The posterior ethmoidal cells opens into...
2
lateral wall of superior meatus
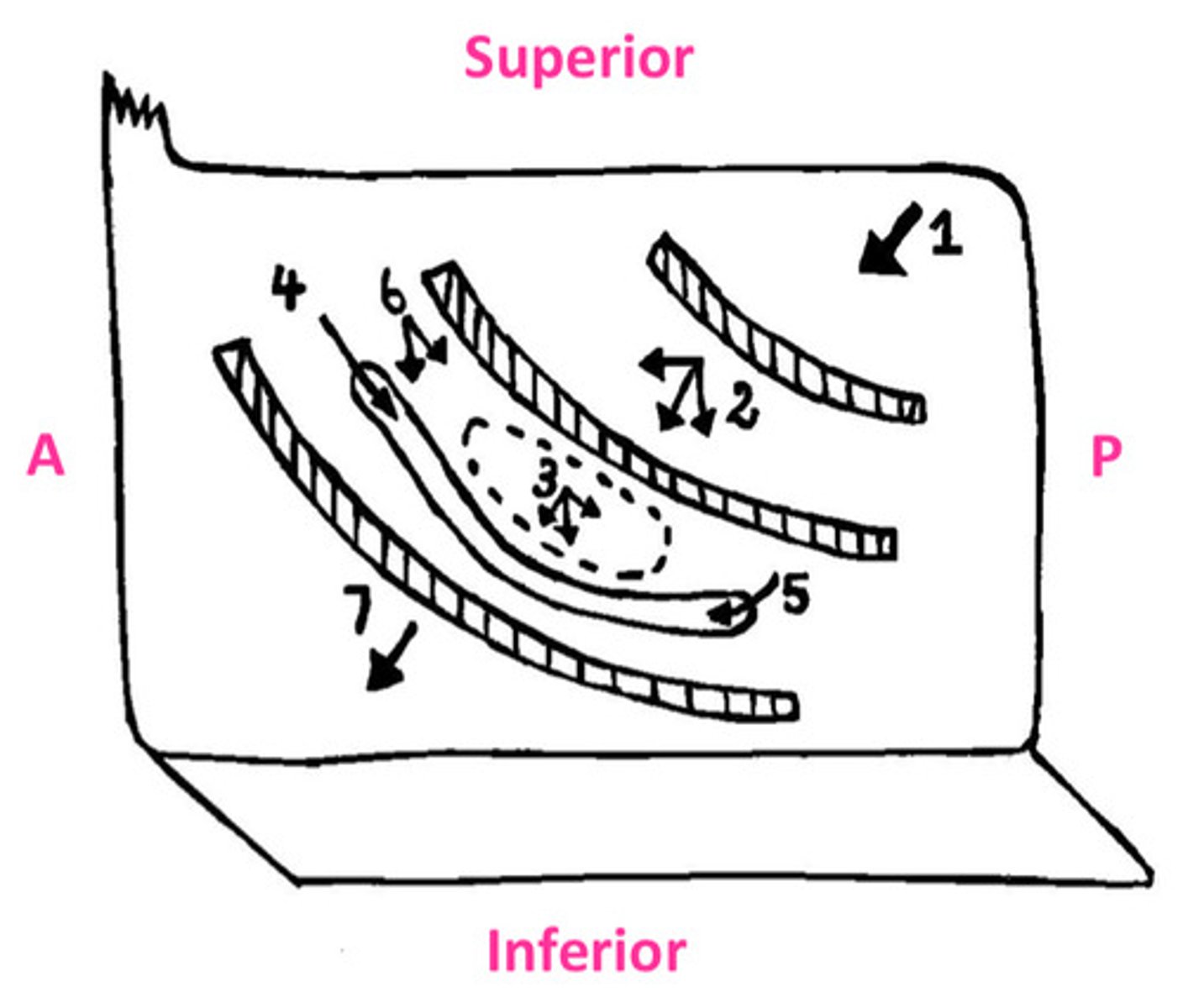
The middle ethmoidal cells opens on or just superior to...
3
the bulla ethmoidalis
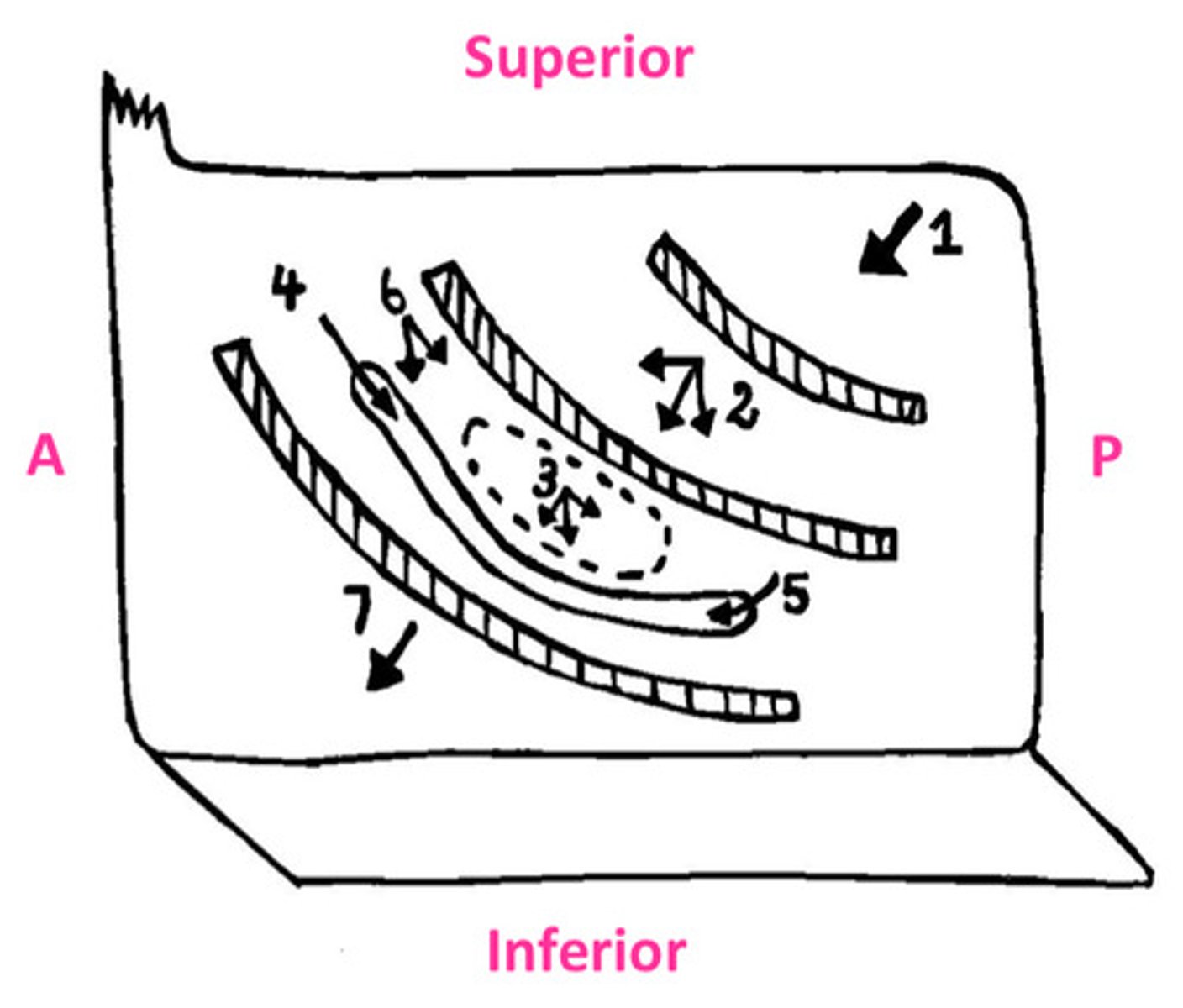
The frontonasal duct drains the...into...
4
frontal sinus into anterior end of semilunar hiatus (middle meatus)
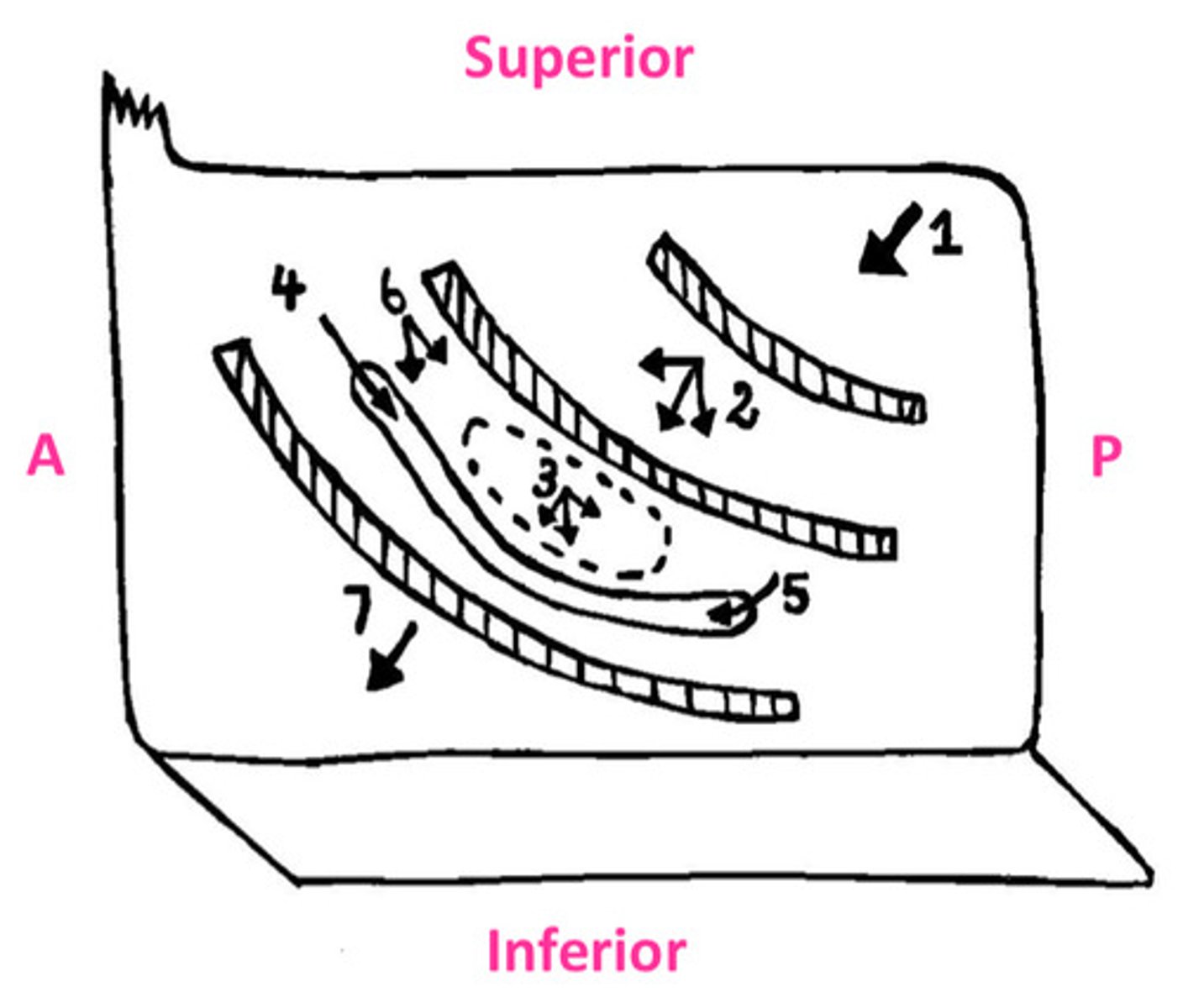
The maxillary sinus opens into...
5
the floor of semilunar hiatus
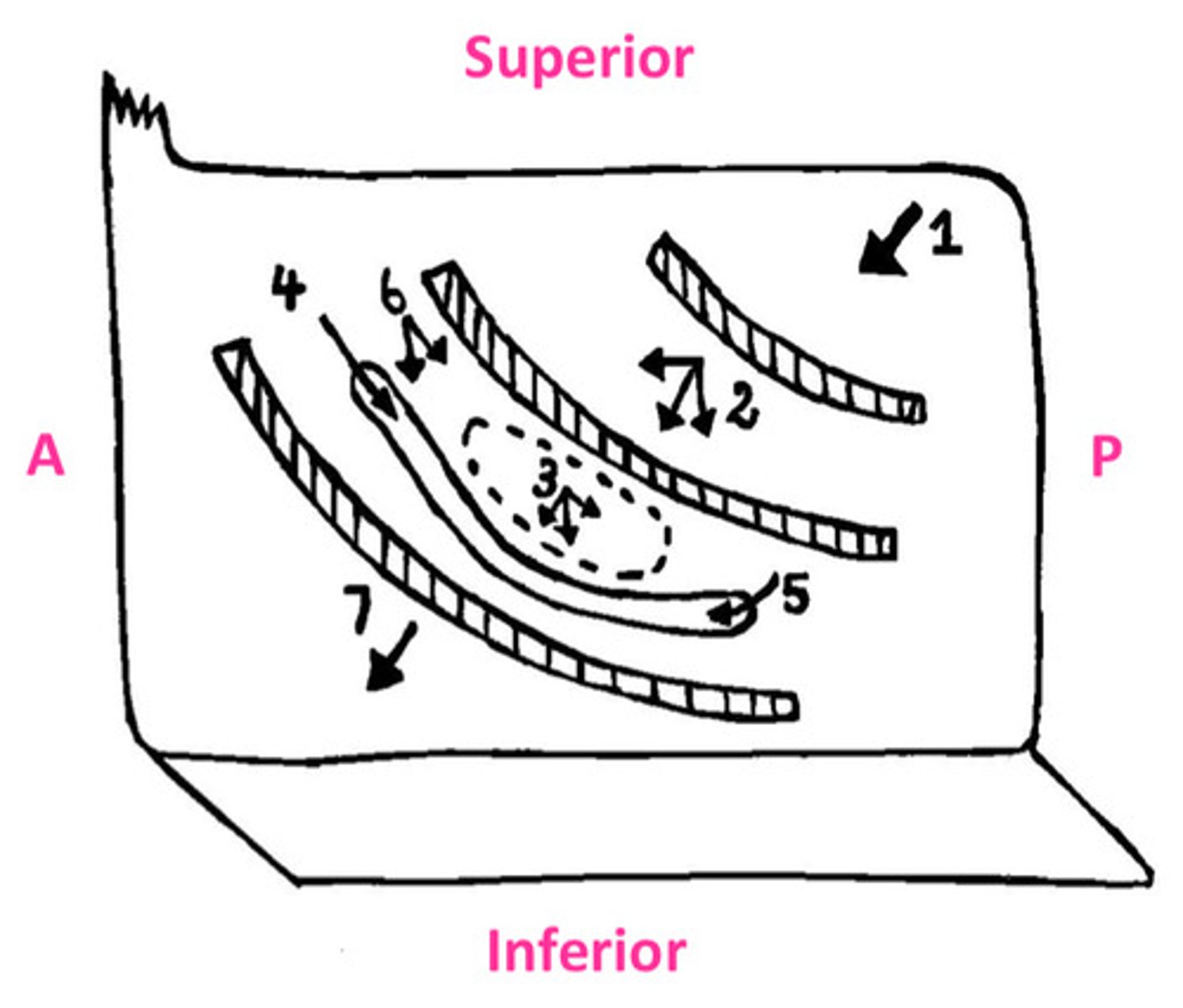
The anterior ethmoidal cells drain into...
6
ethmoidal infundibulum
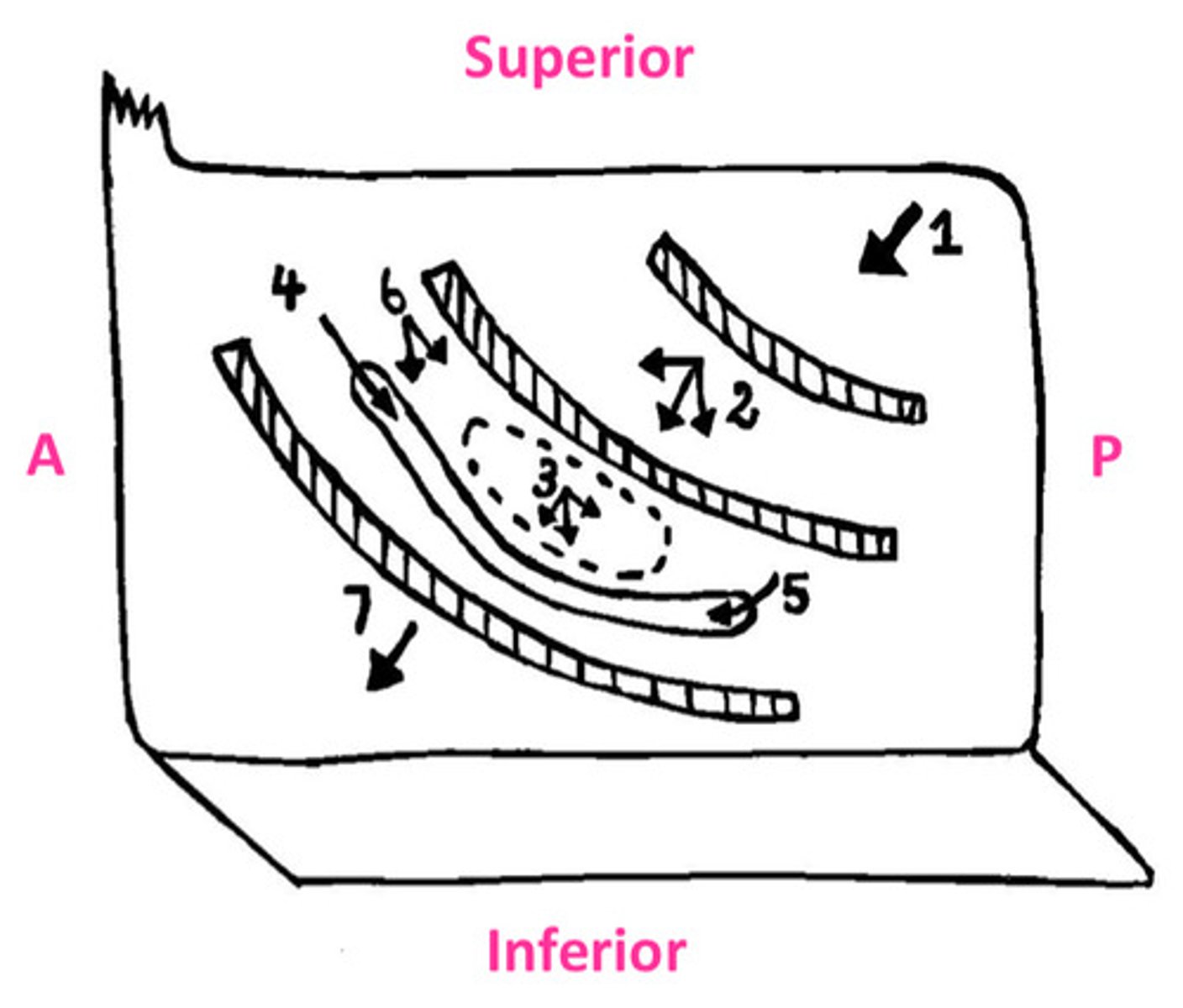
The nasolacrimal duct opens into the...
7
lateral wall of the inferior meatus underneath anterior lip of inferior concha
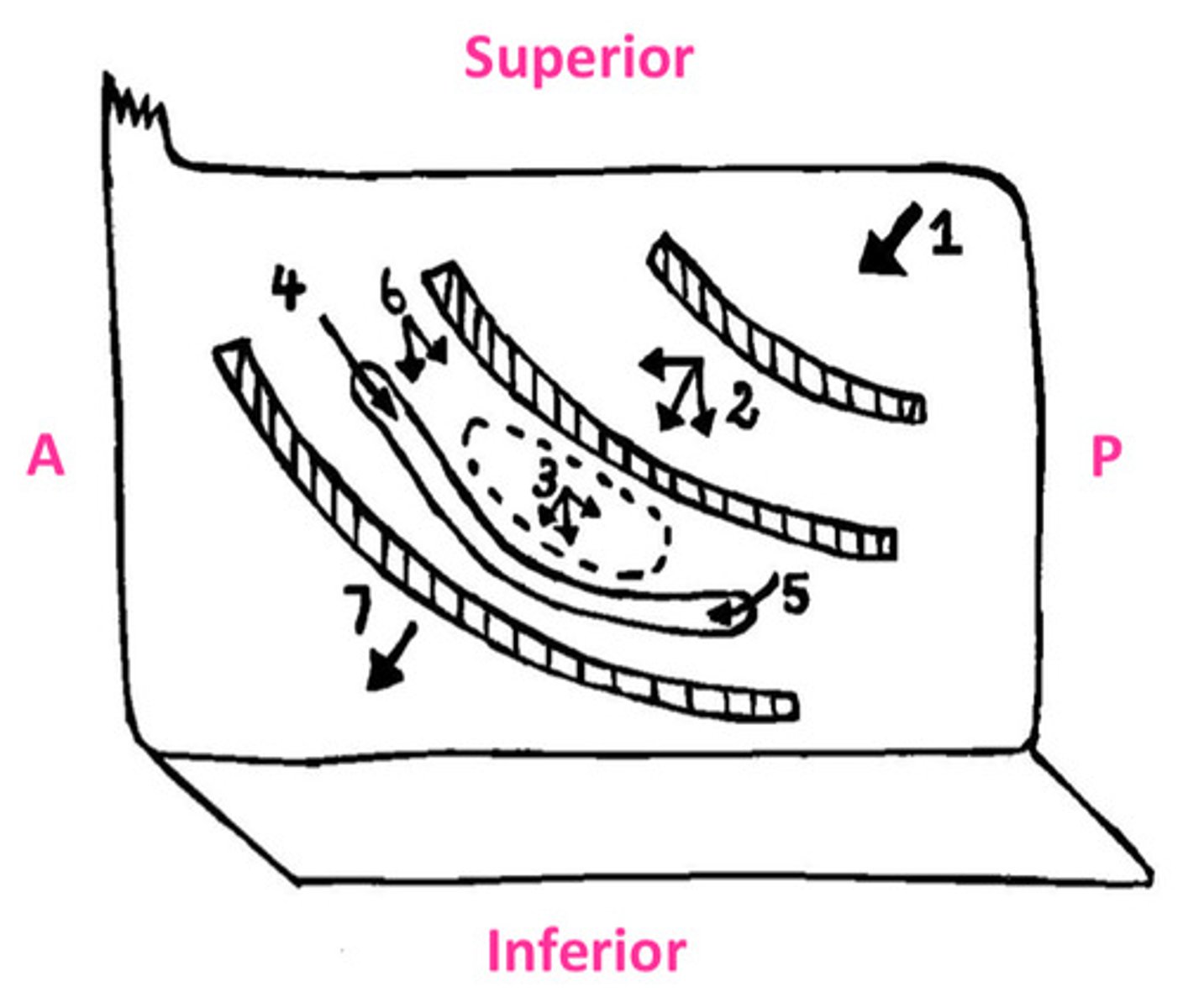
DIAGRAM: Drainage of the Paranasal Sinuses Summary
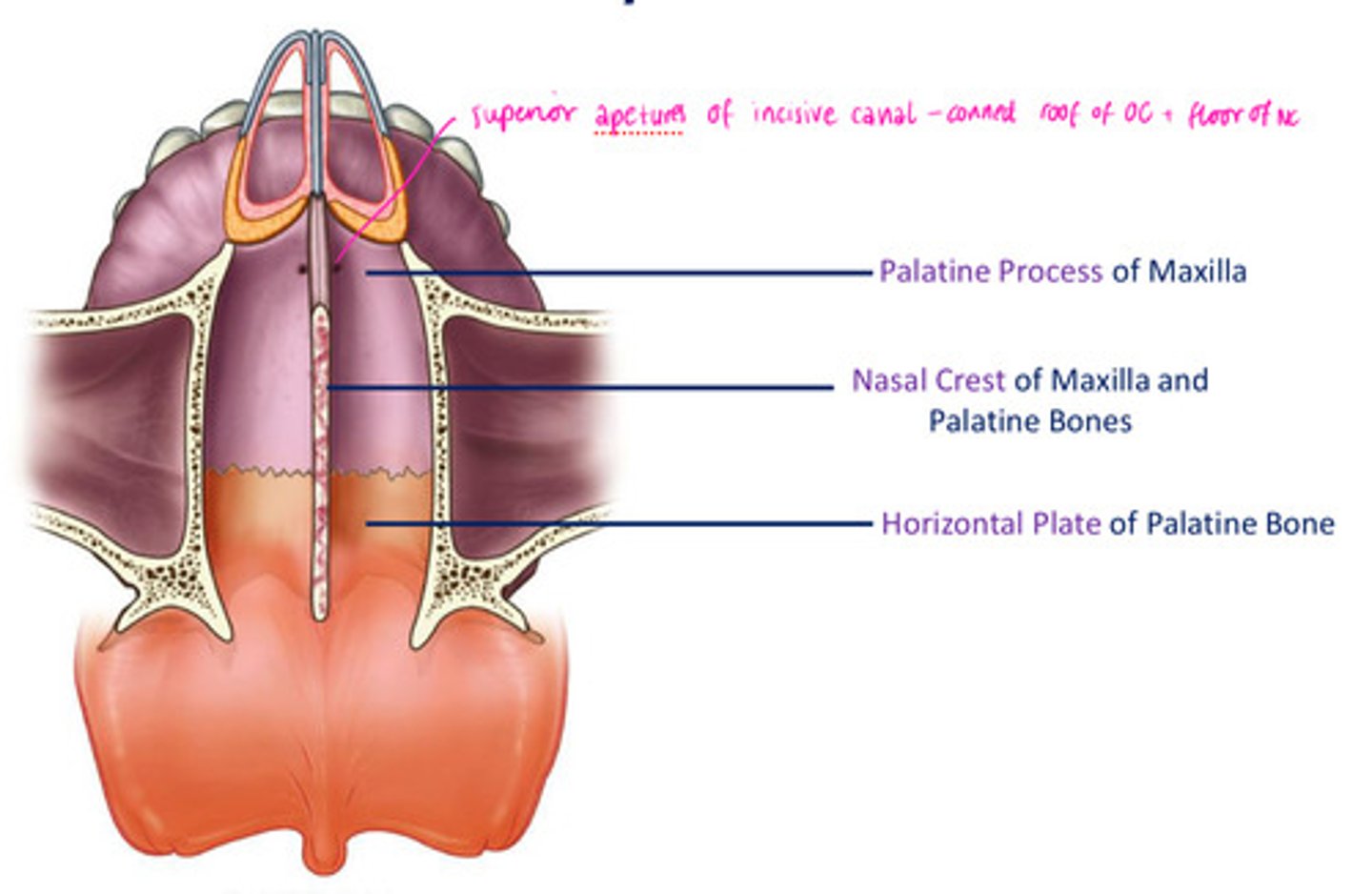
What foramina is related to the oral cavity?
- naris
- incisive canal
- foramina on lateral wall
- sphenopalatine foramen
- cribiform plate
- foramen cecum
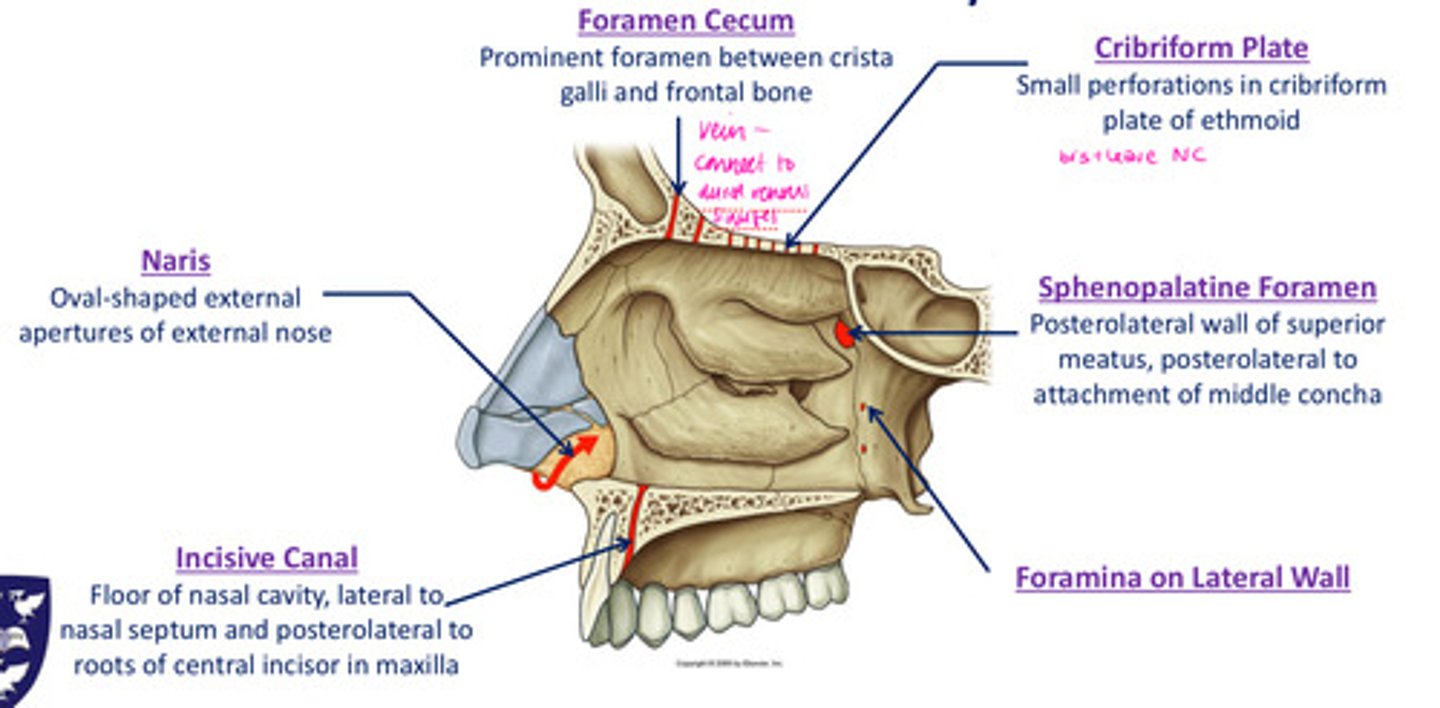
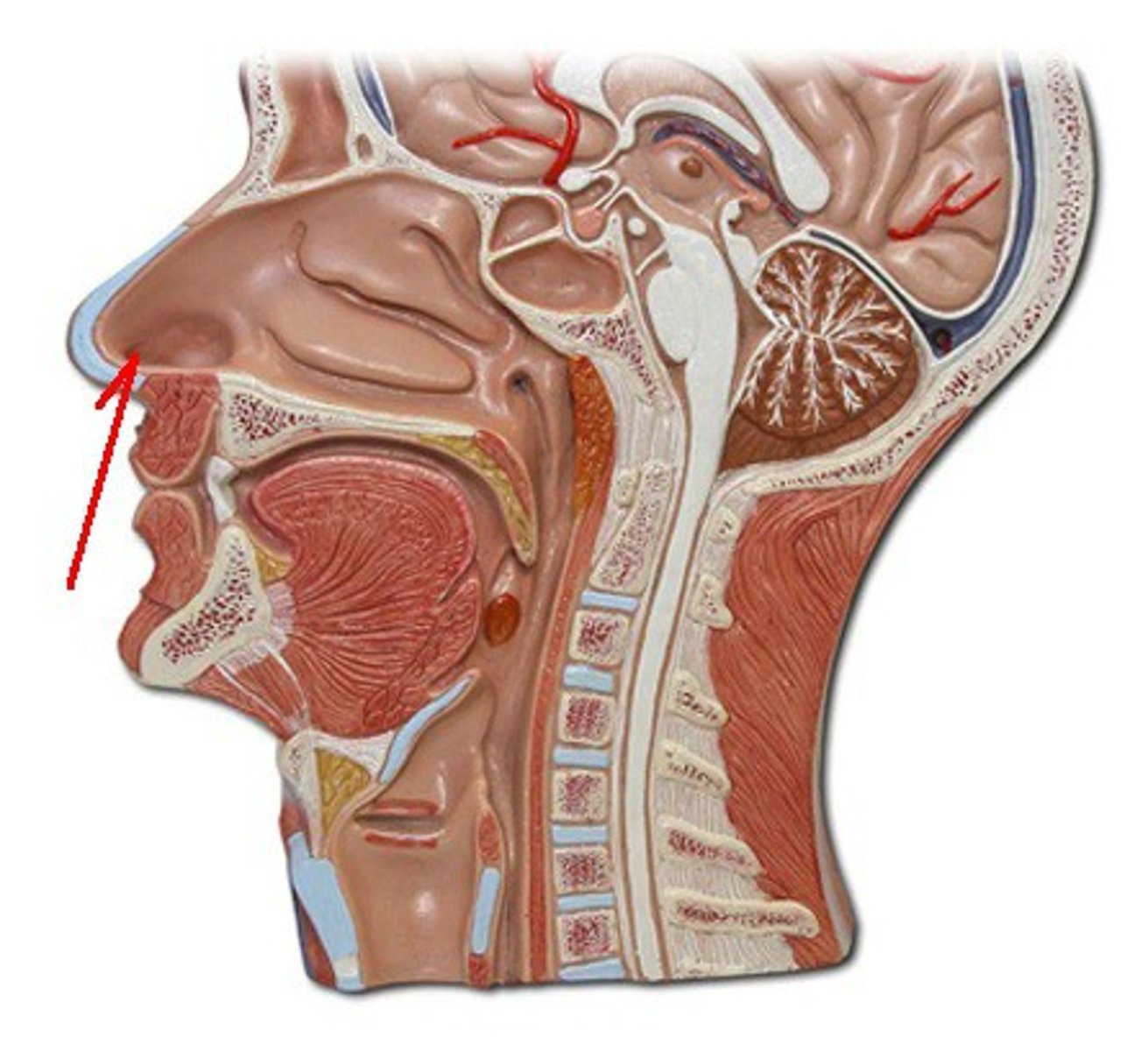
Naris
oval-shaped external apertures of external nose
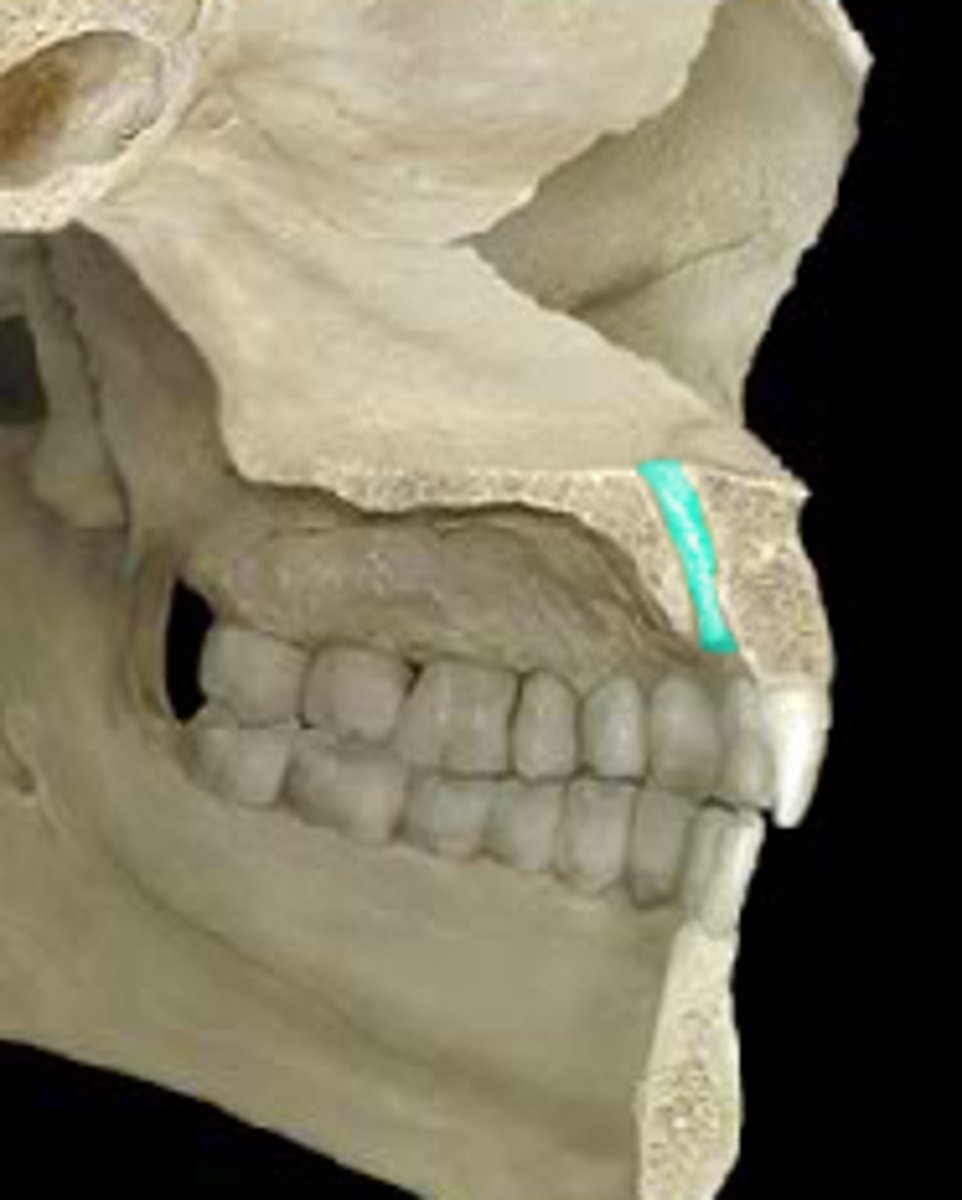
Incisive canal
floor of nasal cavity, lateral to nasal septum & posterolateral to roots of central incisor in maxilla
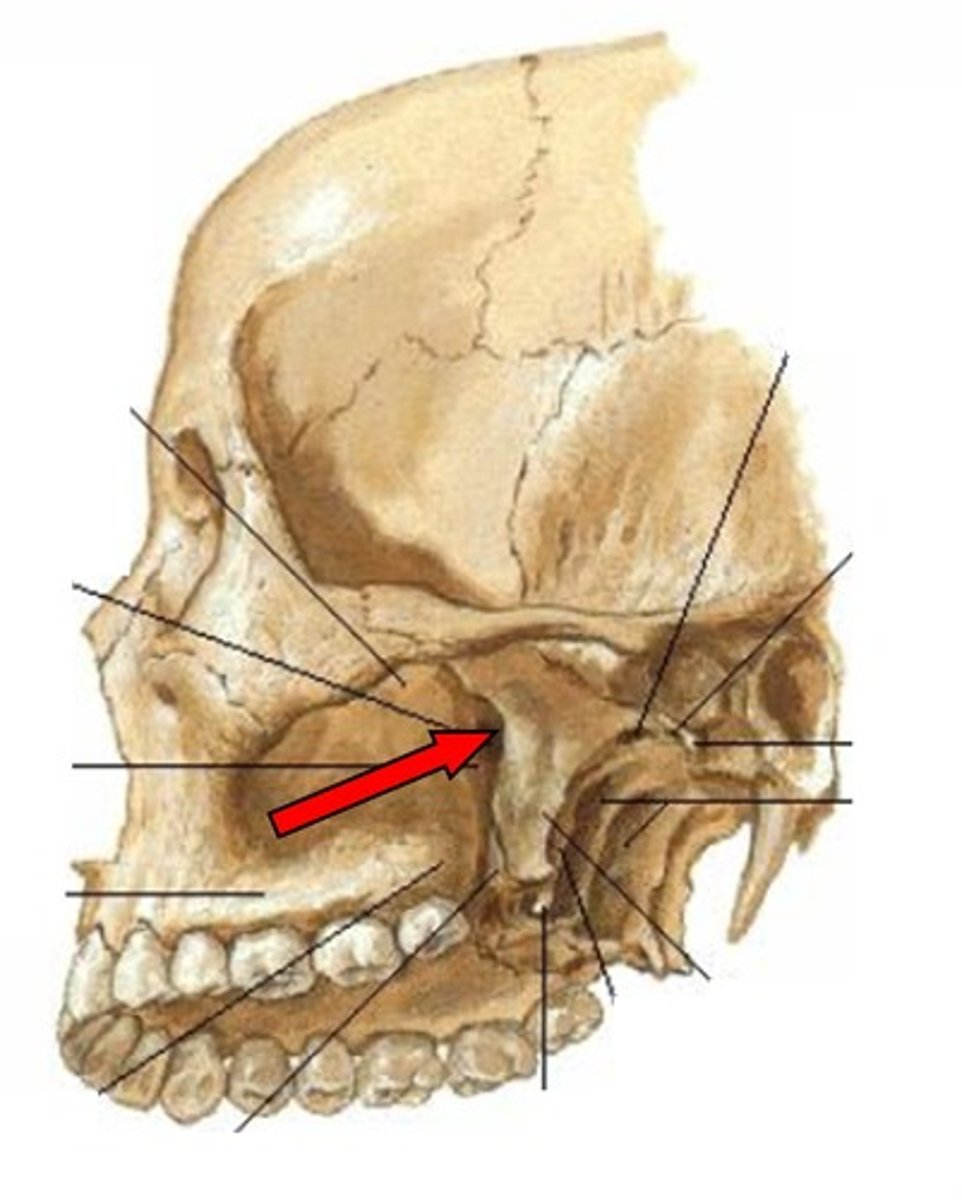
Sphenopalatine foramen
posterolateral wall of superior meatus, posterolateral to attachment of middle meatus
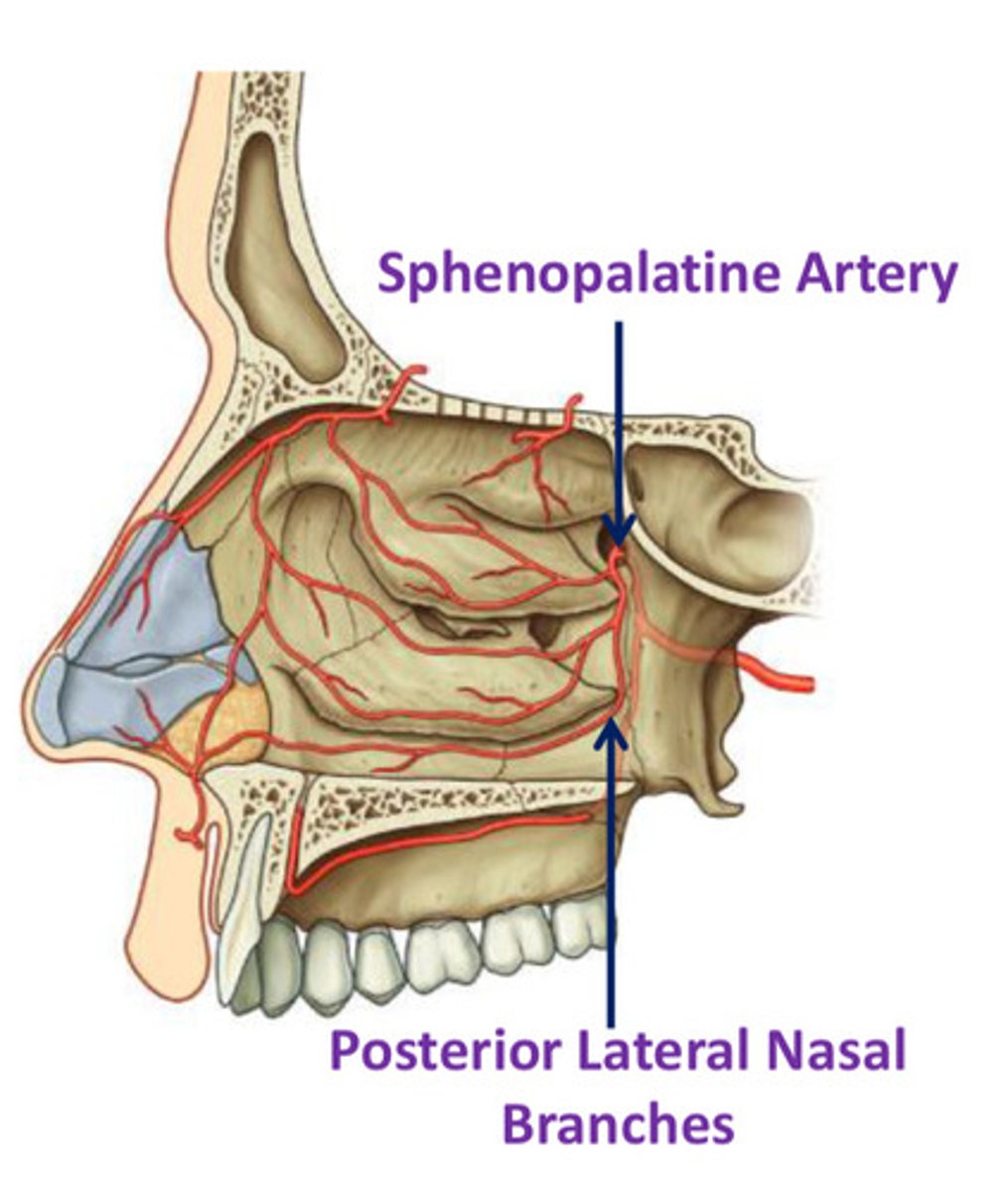
Sphenopalatine artery
Largest vessel suppliyng NC
- terminal branch of maxillary artery (ECA)
- enter NC medially from pterygopalatine fossa via sphenopalatine foramen
- additional branches include: posterior lateral nasal branches, posterior septal branches
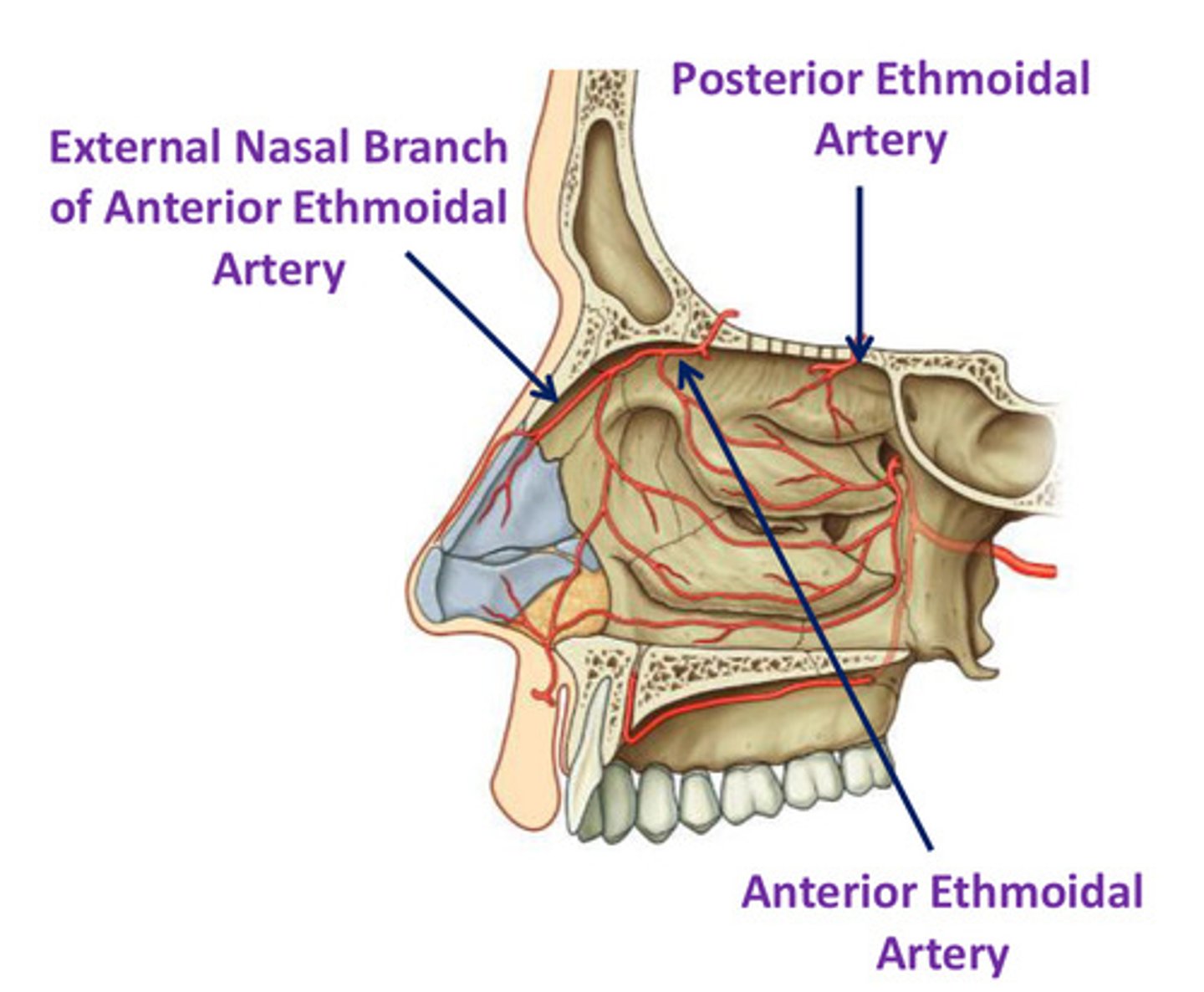
Anterior & Posterior ethmoidal arteries
- branches of opthalmic artery (ICA)
- enter NC via slit-like foramen lateral to crista galli & cribiform plate
- small branches supply medial & lateral wall
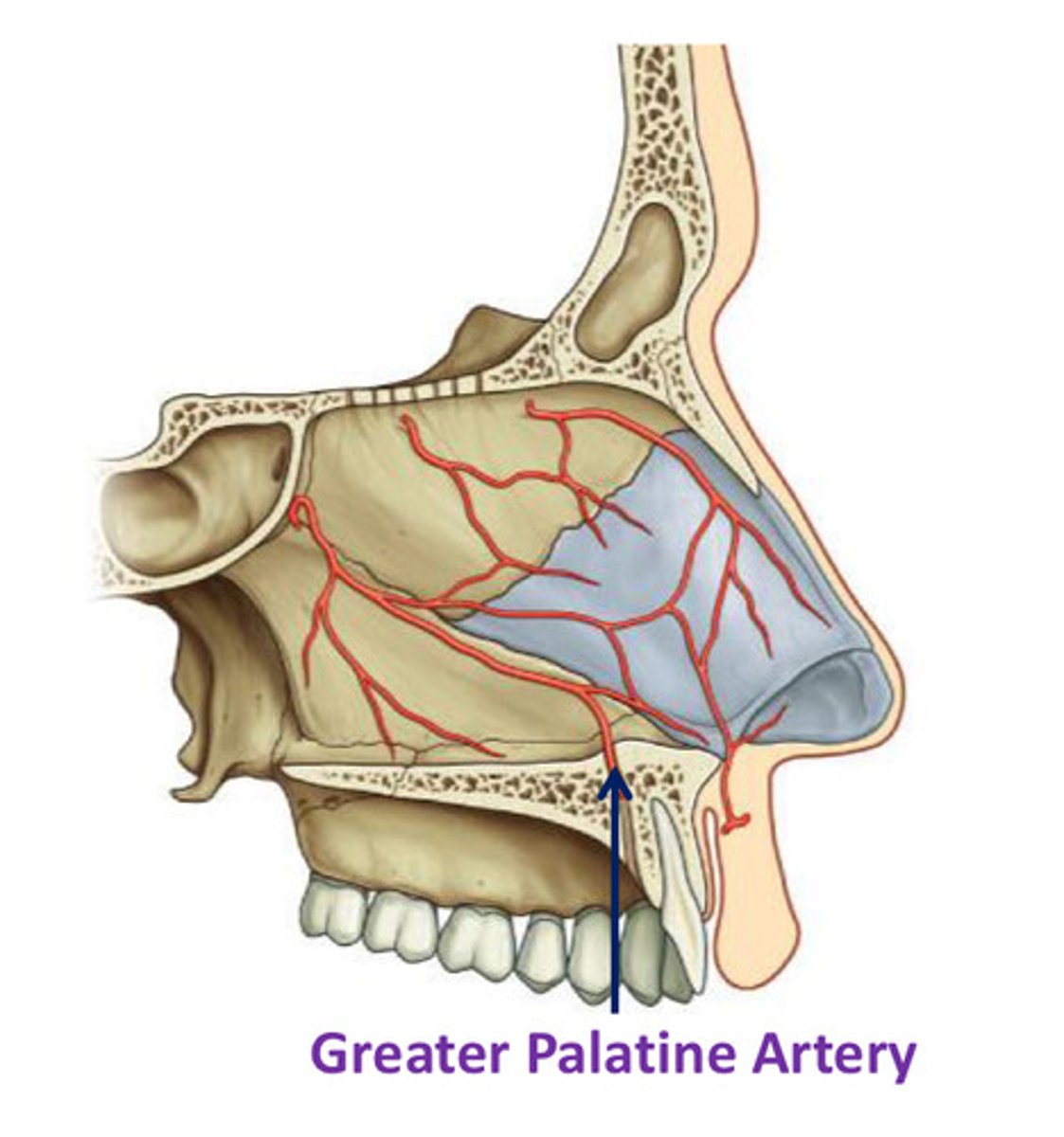
Greater palatine artery
- branch of maxillary artery in pterygopalatine fossa
- enters oral cavity by passing through greater palatine foramen
- enters floor of NC by passing through incisive fossa & canal
- supplies ant regions of medial wall & the associated floor
Lateral nasal artery
Branch of facial artery
Supplies blood to skin and muscles in area of nose - blood supply of external nose
Gives off an alar branch, supplies vestibule
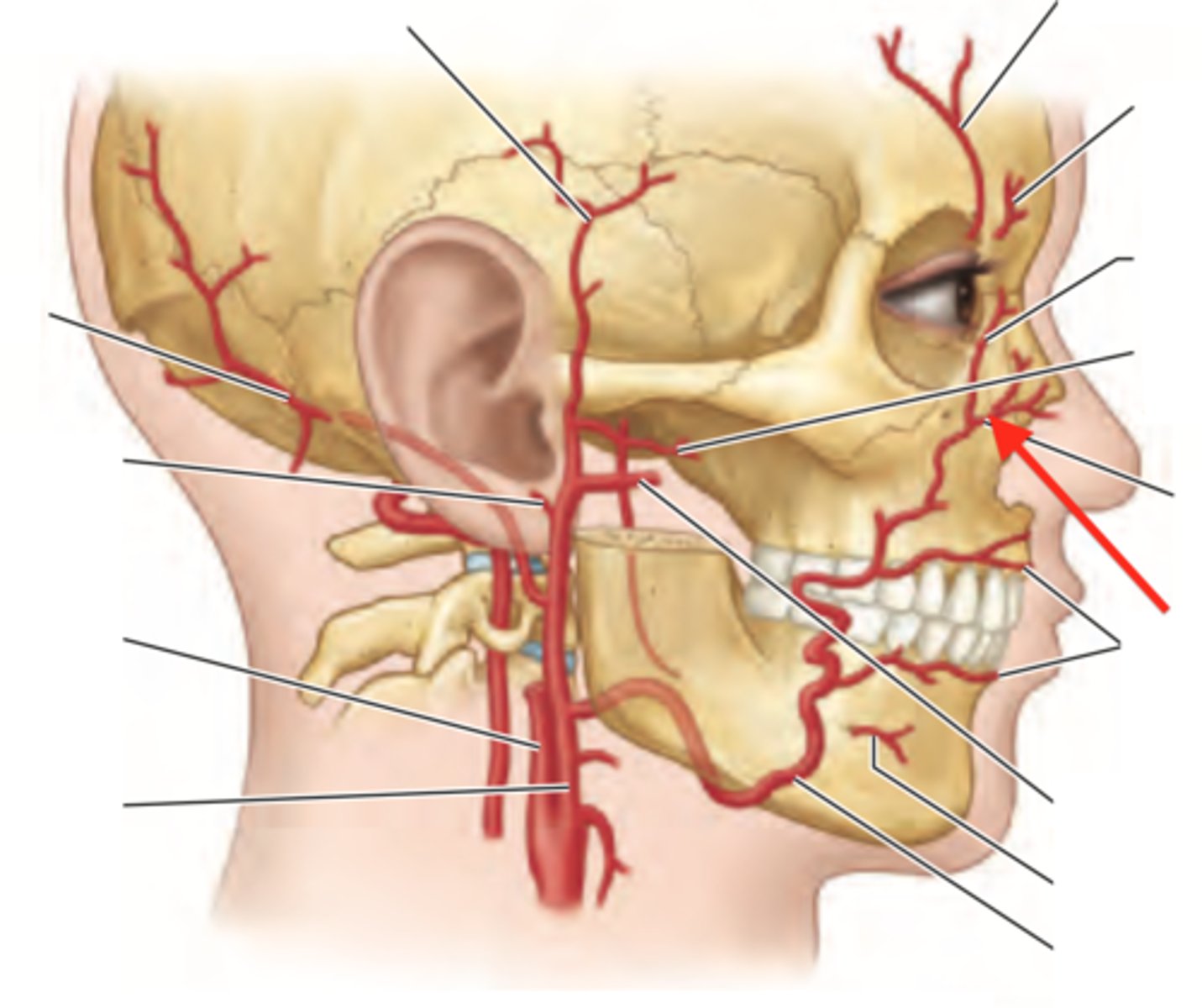
Superior labial artery
branch of facial artery
septal branch supplies anterior regions of septum
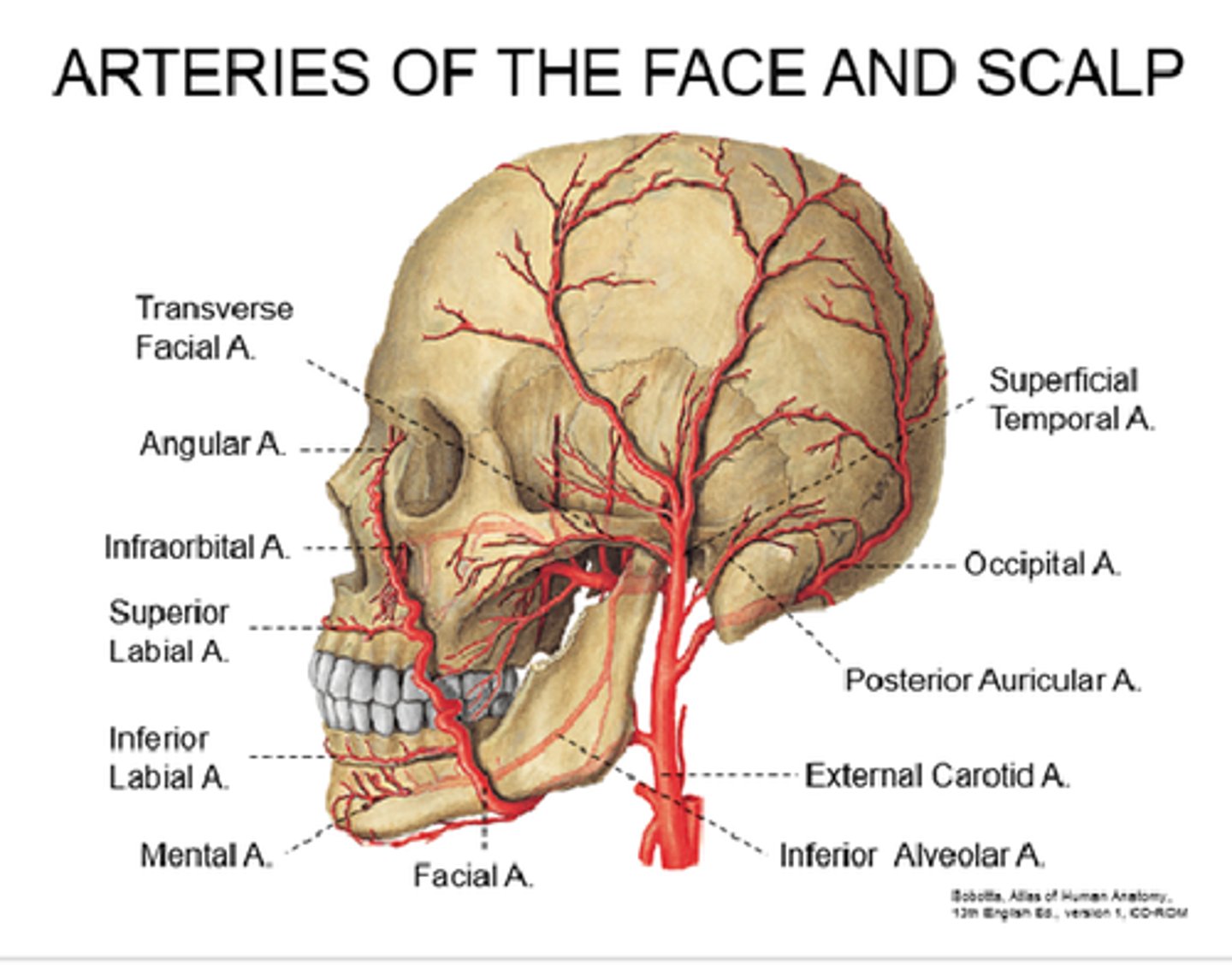
DIAGRAM: Venous drainage
Nasal vein in foramen caecum
Venous drainage to facial vein
Venous drainage to pterygoid plexus in infratemporal fossa
Venous drainage to superior opthalmic vein
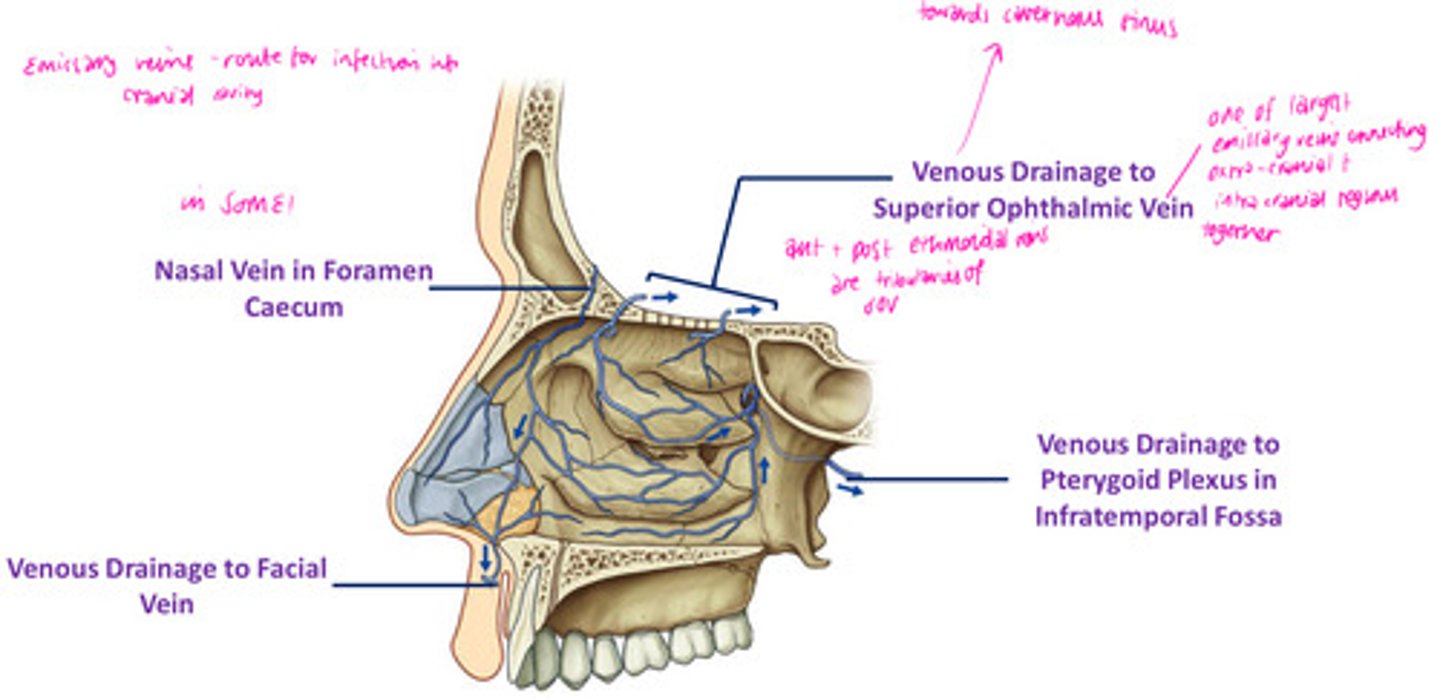
Emissary veins
Connect dural venous sinuses with veins outside the skull
Route for infection into cranial cavity
DIAGRAM: Arterial supply summary
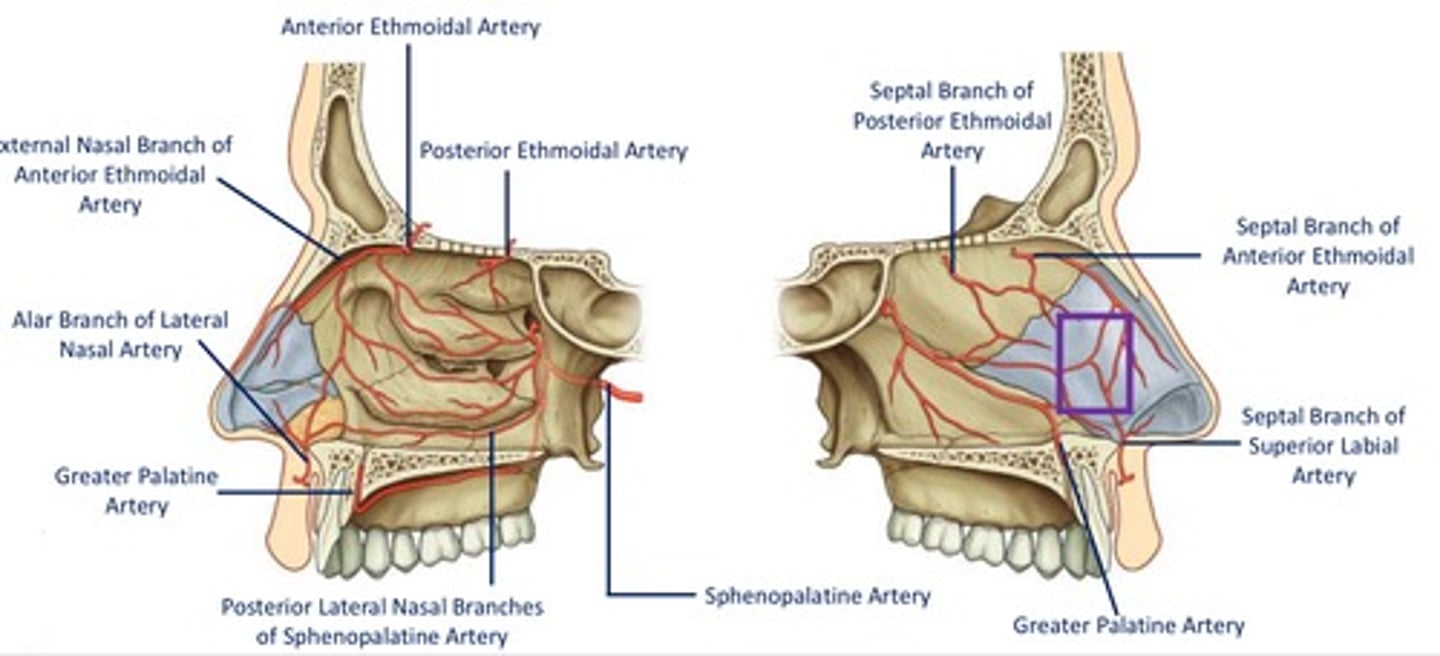
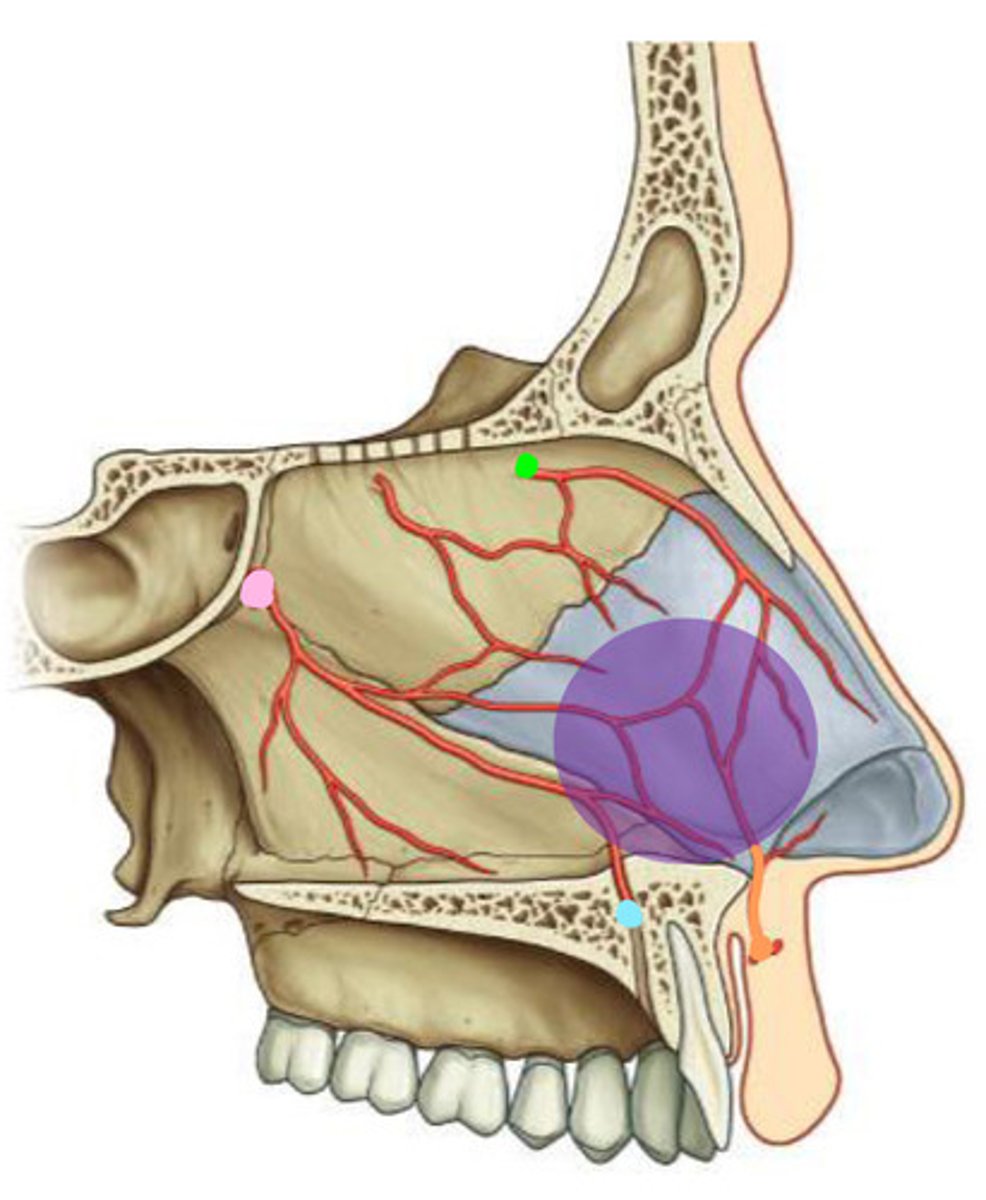
Little's Area
Another name for Kisselbach's plexus
Imp site of extensive anastomosis on nasal septum
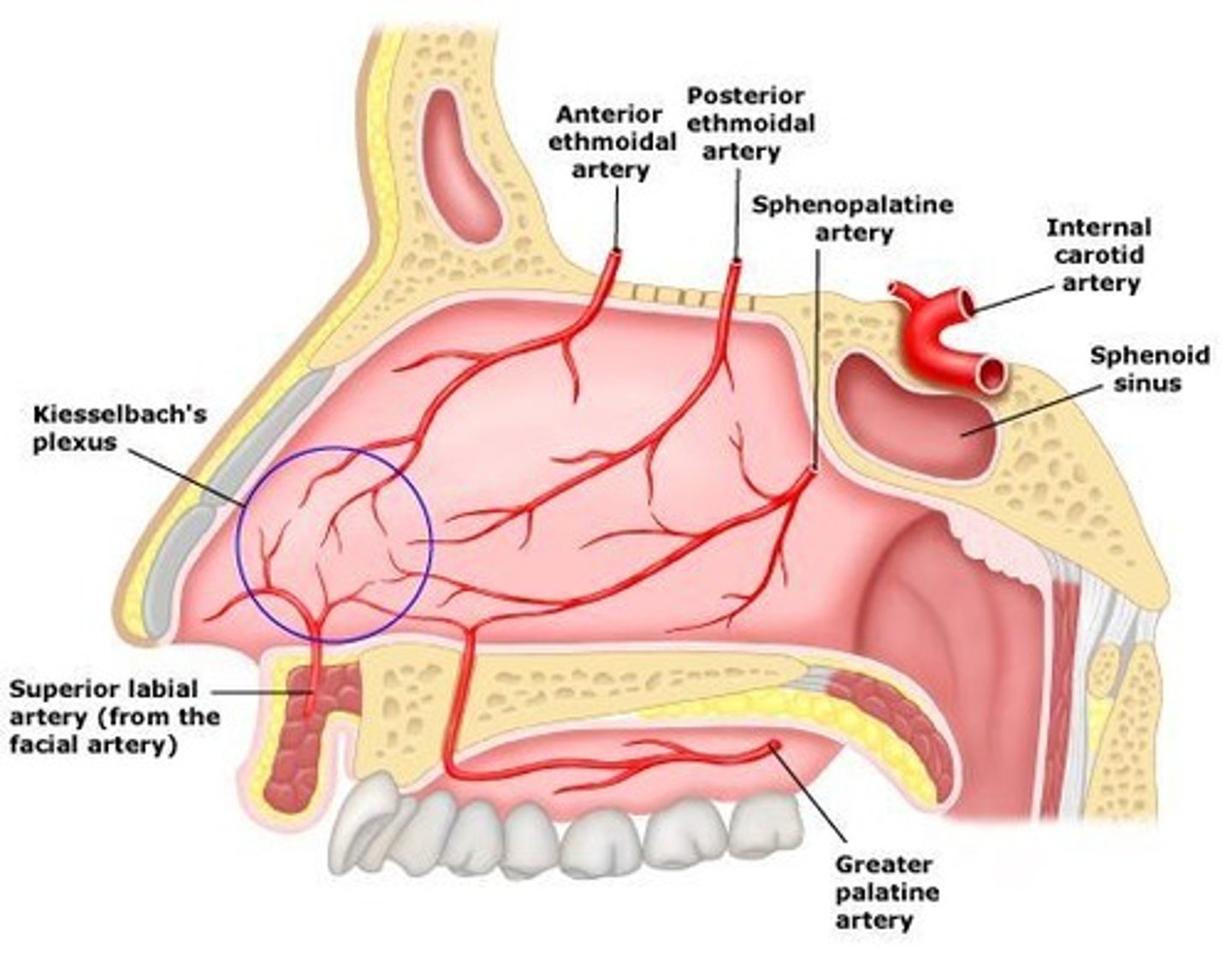
Which blood vessels are involved in Little's Area?
- anterior ethmoidal artery (green)
- greater palatine artery
- sphenopalatine artery (septal branches)
- superior labial artery (septal branches)
Epistaxis
nosebleed - rupture of thin-walled arterioles
common <10 YO & >65 YO
spontaneous (primary)/ hypertensive (secondary)
multiple causes incl anatomical predisposition i.e. deviated septum, trauma, or use of internasal drugs
Where are olfactory receptors embedded within?
olfactory epithelium at the apex of each NC
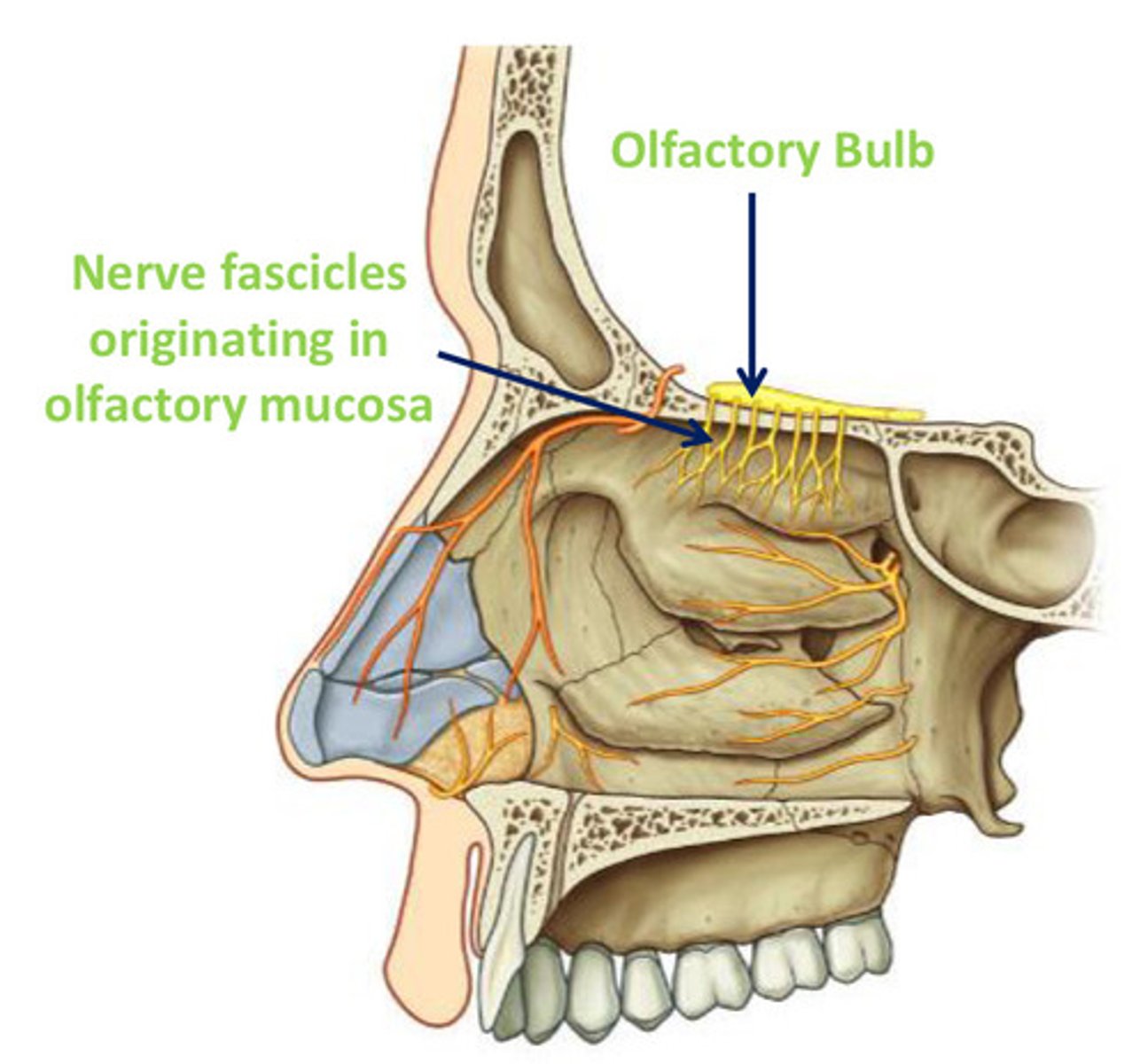
Olfactory nerve receptors
- peripheral process of bipolar (1st order) sensory neurones, w/ cell bodies deeper in epithelium
- axons of 1st order bipolar neurone pass through the cribiform plate to synapse w/ 2nd order neurones in the olfactory bulb
1st order neuron
from receptor to spinal cord
2nd order neuron
from spinal cord to thalamus
DIAGRAM: Olfactory bulb
mitral cell layer
olfactory tract
synaptic glomeruli
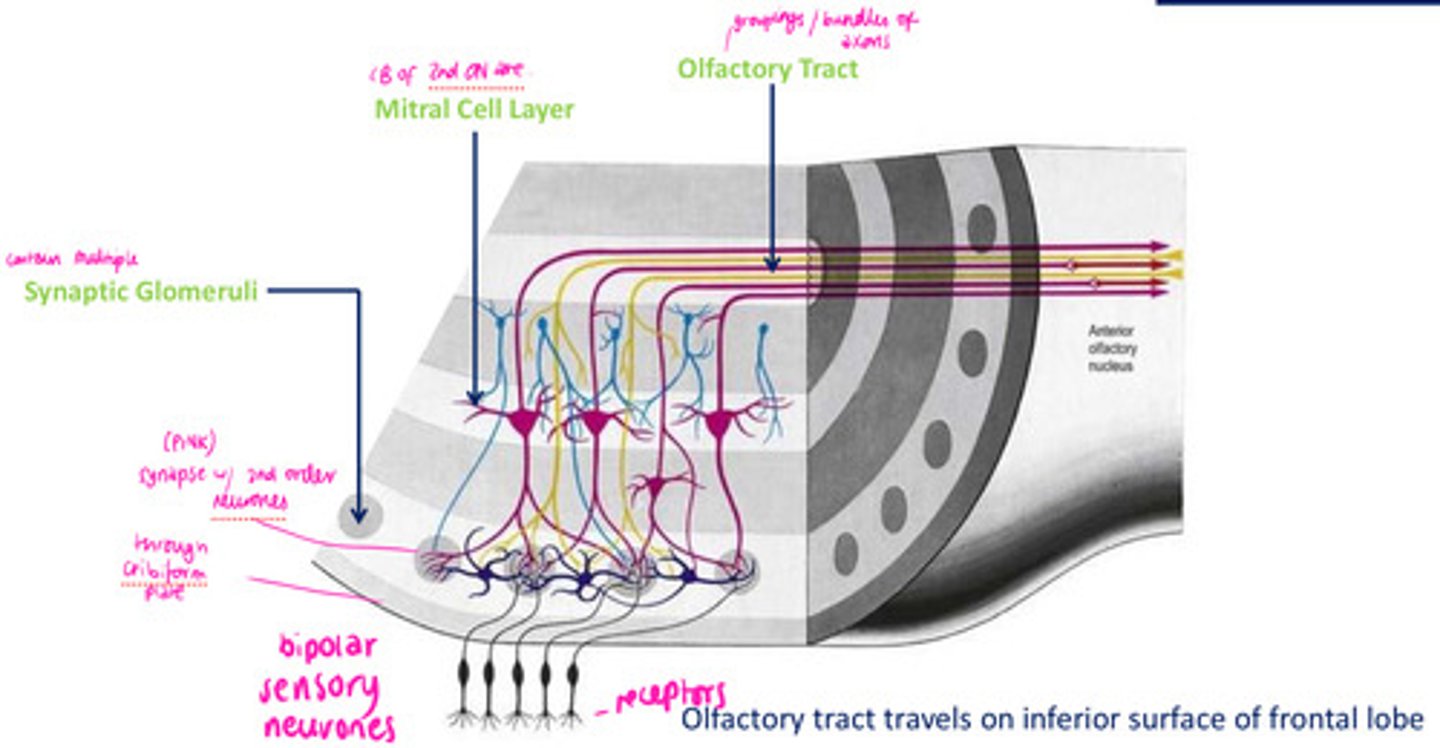
Olfactory tract
the path along which the olfactory receptors send their electrical messages to the brain
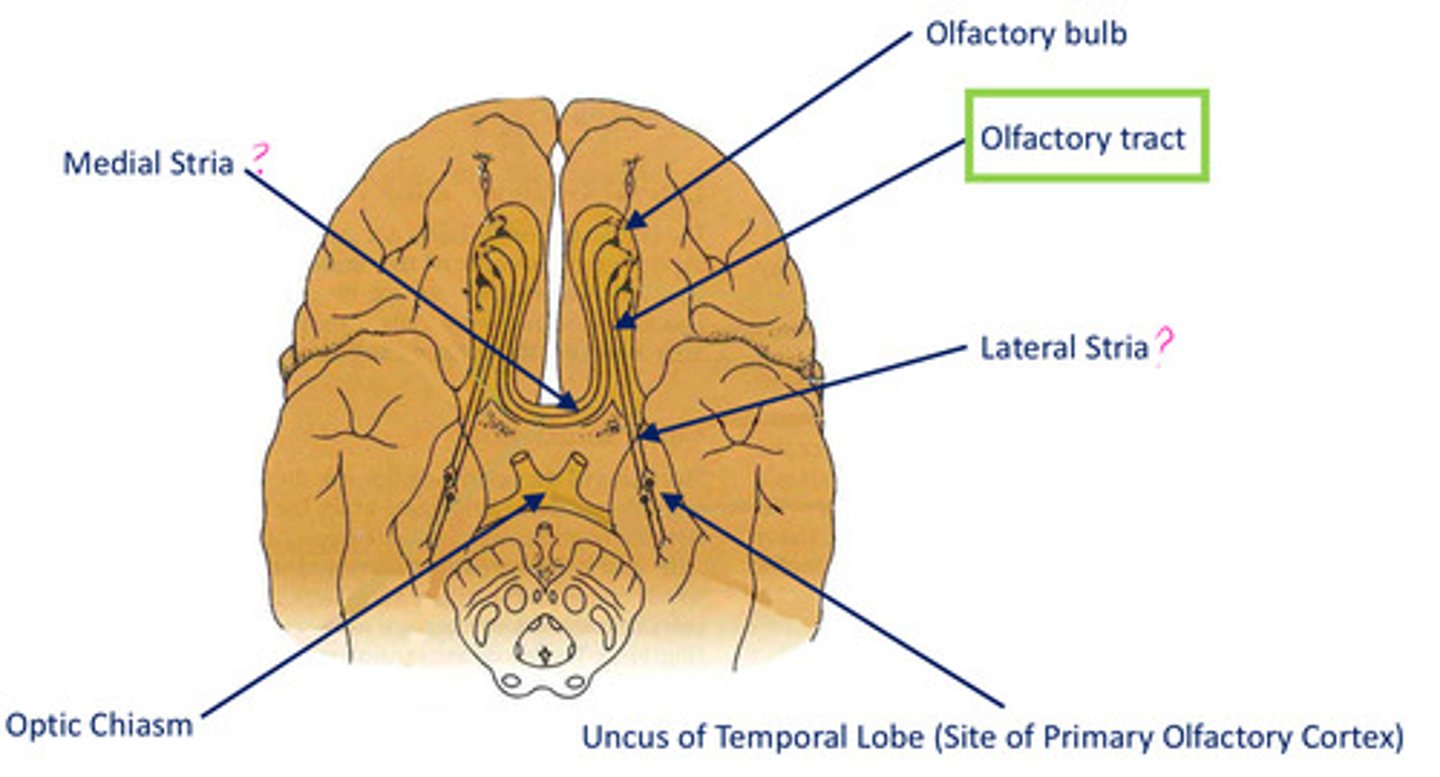
The olfactory tract forms connection with the ________ lobe and _______ system (amygalda & hippocampus). ________ can therefore evoke powerful memories and emotions.
temporal
limbic
smell
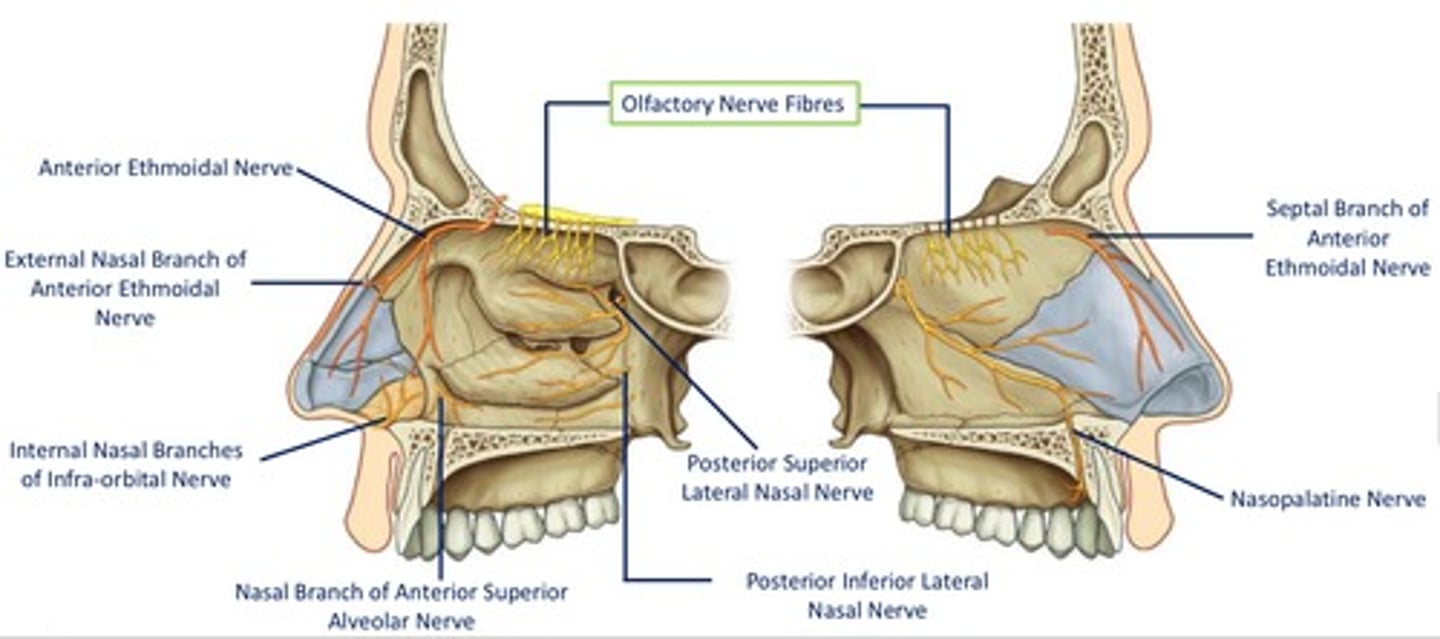
Path of the anterior ethmoidal nerve:
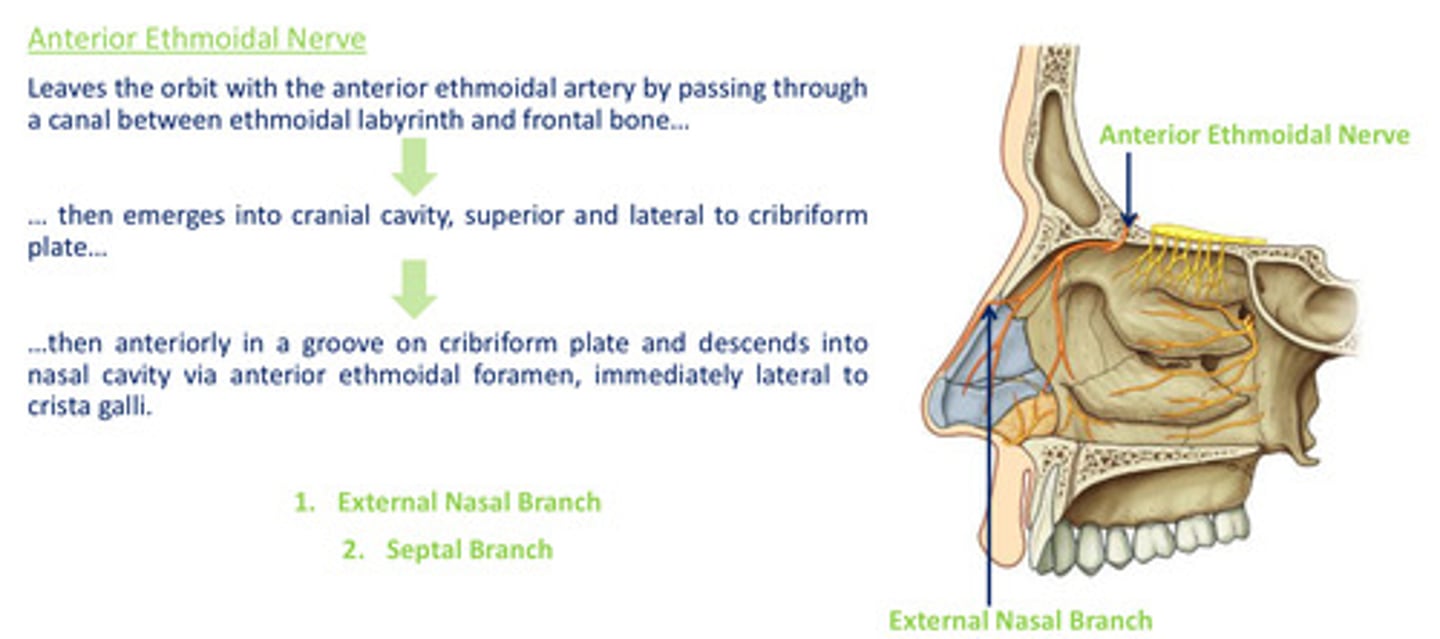
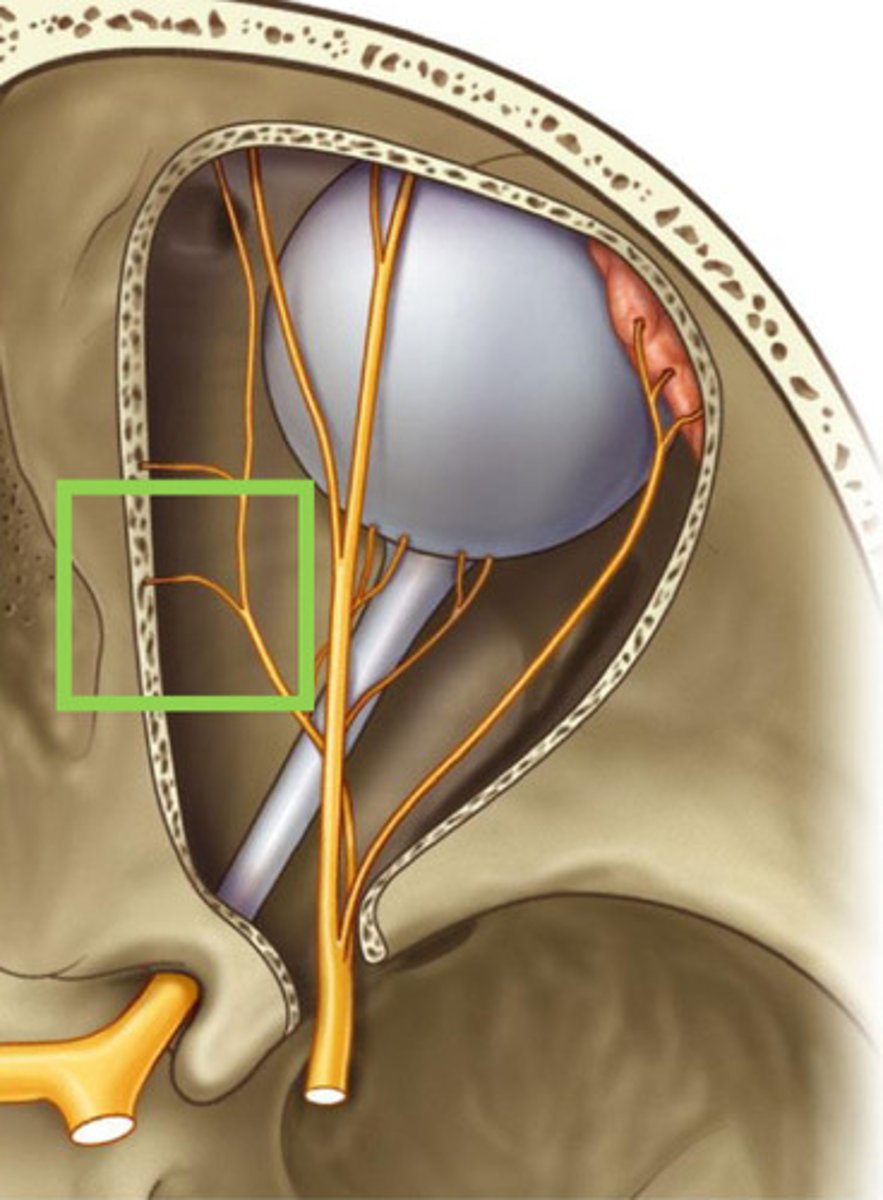
Path of the posterior ethmoidal nerve:
leaves orbit accompanied by posterior ethmoid artery, supplying mucosa of ethmoidal & sphenoidal sinuses
no branches to nasal cavity
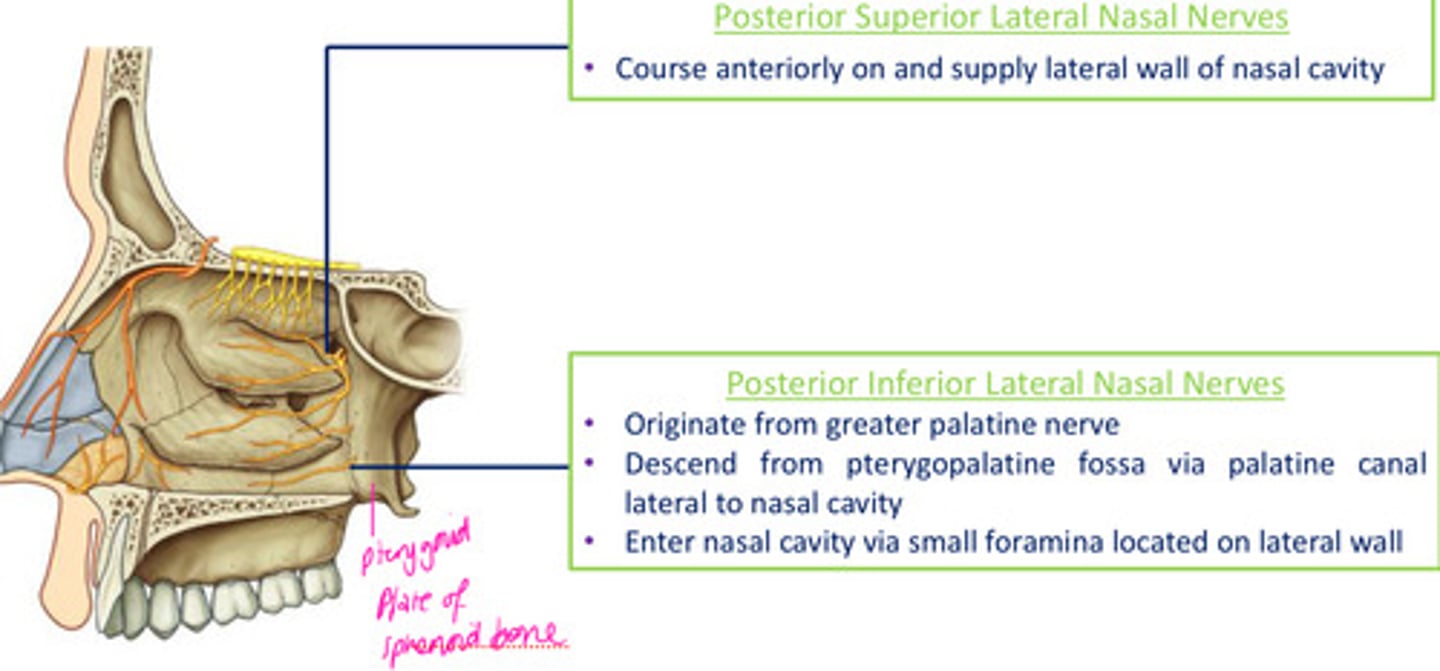
Lateral nasal branches of maxillary nerve (V2): Posterior superior lateral nasal nerves
course anteriorly on & supply lateral wall of nasal cavity
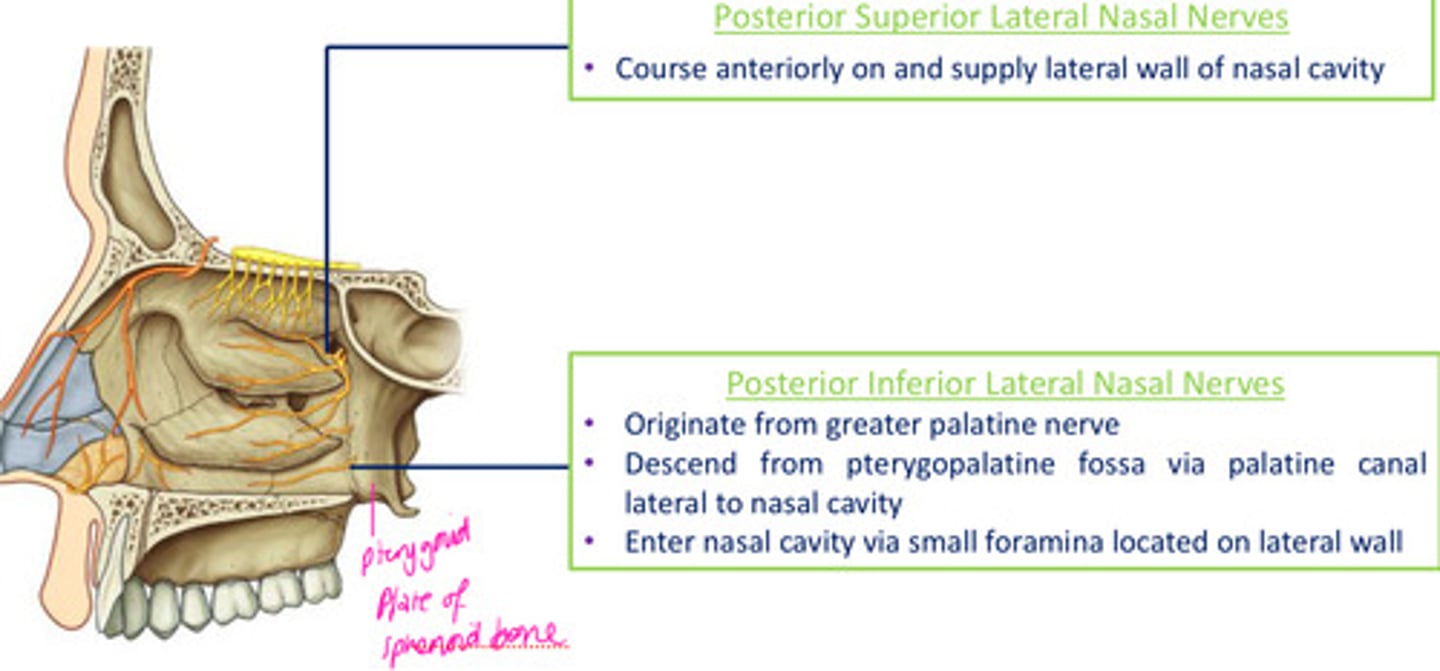
Lateral nasal branches of maxillary nerve (V2): Posterior inferior lateral nasal nerves
- originate from > palatine
- descend from pterygopalatine fosa via palatine canal lateral to nasal cavity
- enter nasal cavity via small foramina located on lateral wall
Medial nasal branches of maxillary nerve (V2): Nasopalatine nerve
- descends on medial wall of nasal cavity, passing anteriorly towards incisive canal
- passes through incisive canal and into oral cavity
- terminates supplying oral mucosa immediately posterior to incisors
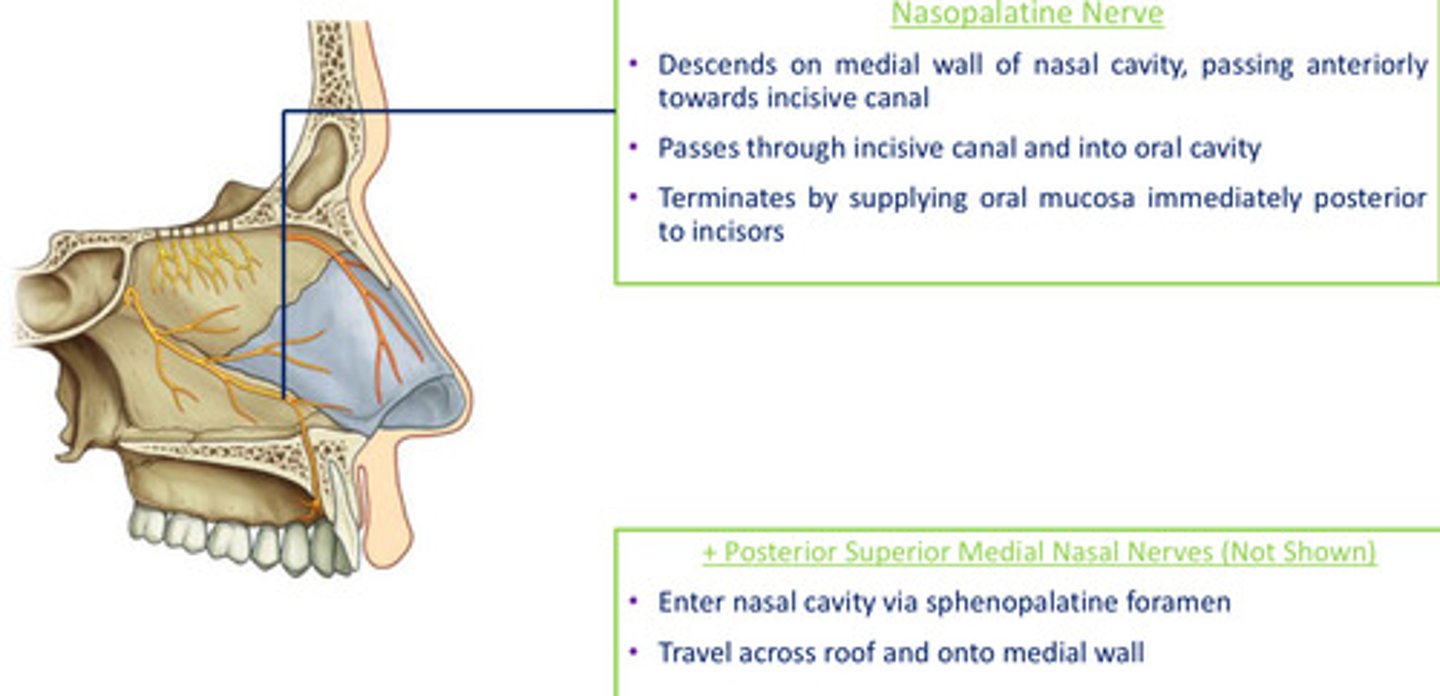
Medial nasal branches of maxillary nerve (V2): Posterior superior medial nasal nerves
- enter nasal cavity via sphenopalatine foramen
- travel across roof and onto medial wall
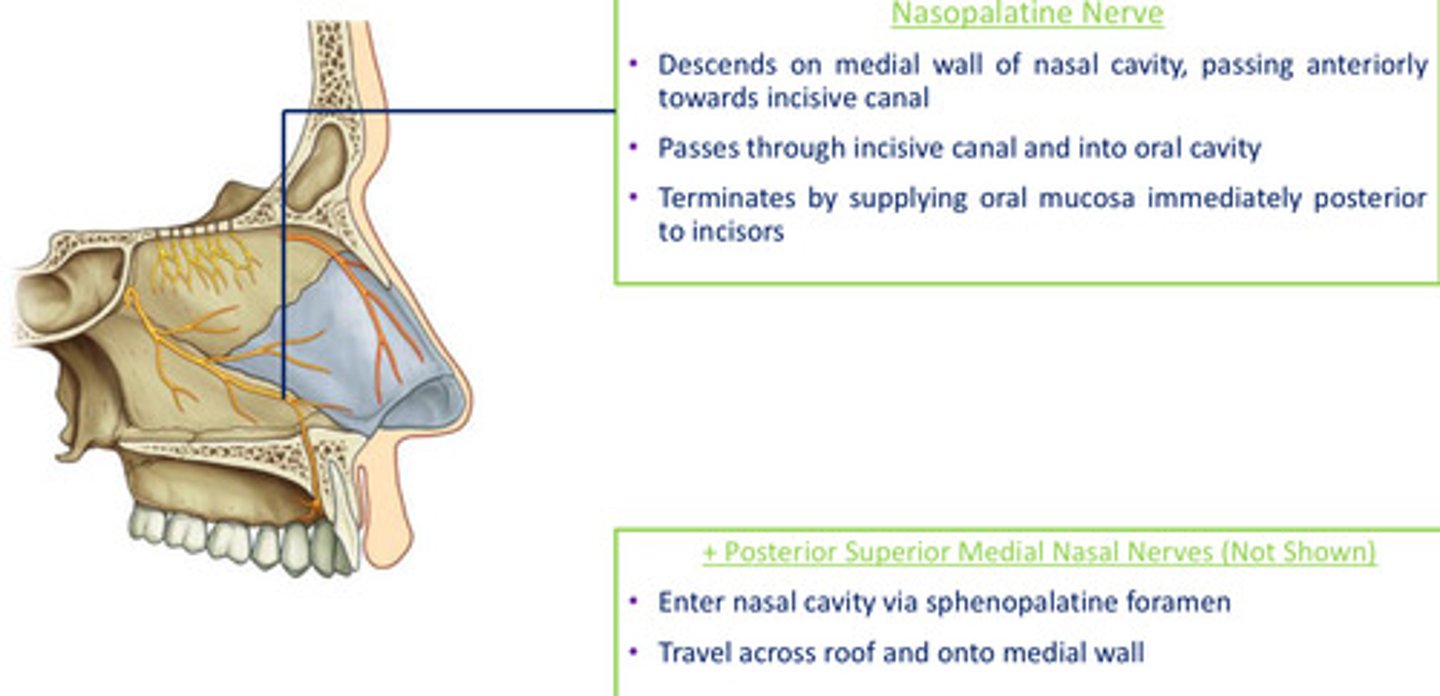
DIAGRAM: Nerve supply summary
Autonomic supply to the nasal cavity: Parasympathetic nervous system
long pre, short post
synapse in parasympathetic ganglia of head & neck - pterygopalatine fossa
control secretion of mucous glands in nasal cavity, controls humidity
Autonomic supply to the nasal cavity: Sympathetic nervous system
short pre, long post
synapse in sympathetic ganglia in head & neck - superior cervical ganglion
vasoconstriction of blood vessels, blood supply to NC
Sympathetic innervation to the nasal cavity: Preganglionic & Postganglionic fibres
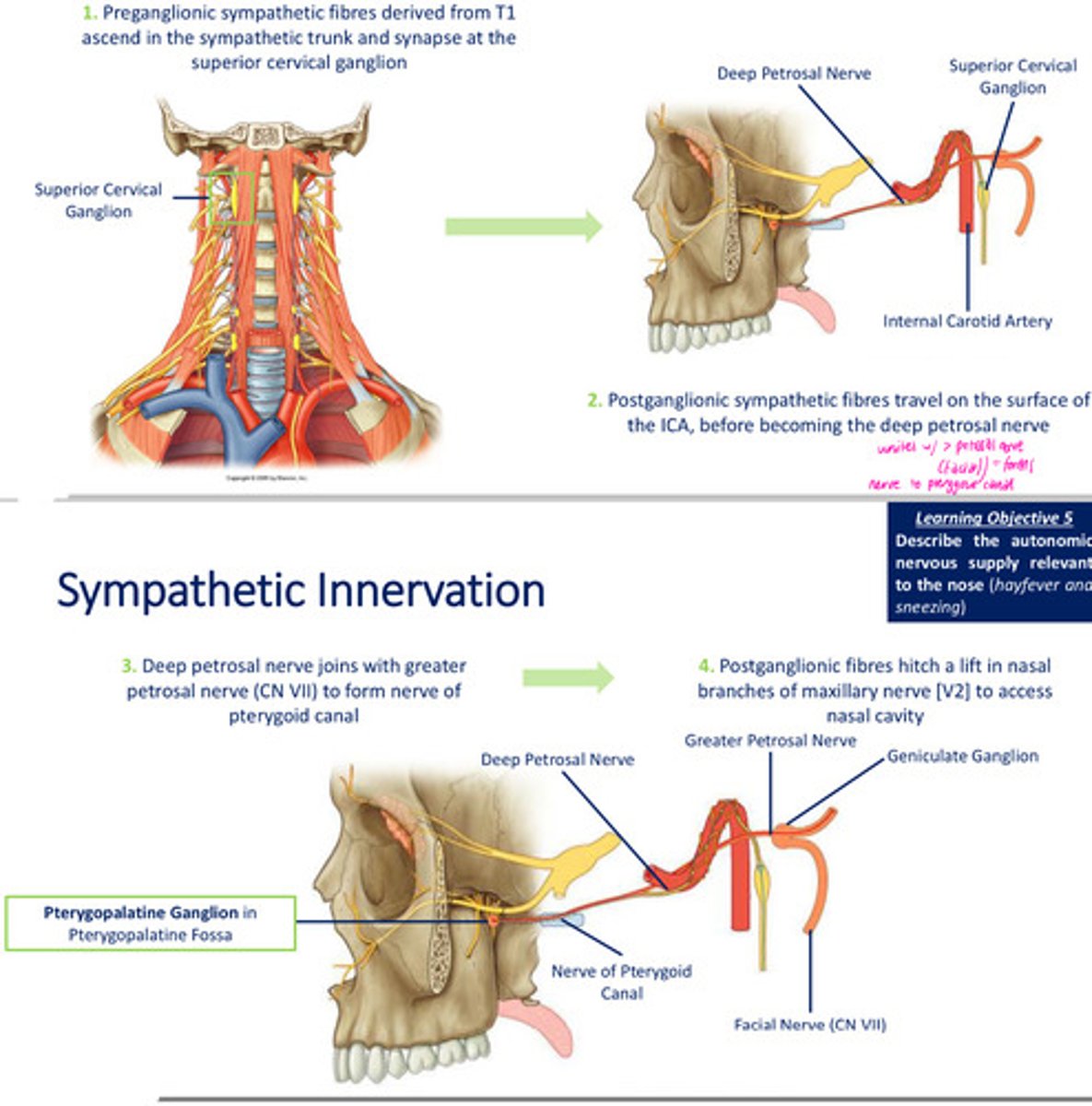
Parasympathetic innervation to the nasal cavity:
1. presynaptic parasympathetic fibres conveyed via > petrosal nerve
2. fibres pass via nerve of pterygoid canal to pterygopalatine ganglion where synapsing occurs
3. postganglionic, secretomotor fibres distributed with nasal branches (V2)