BIO 1201 PRACTICAL 2
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
photosynthesis equation
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂.
cellular respiration equation
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP.
What are the two processes of photosynthesis
Light reaction and Calvin cycle
Where do light reactions take place?
thylakoid membrane
Light reaction process
pigments in membranes absorb solar energy, releasing electrons down an electron transport chain → produces ATP by chemiosmosis → energy stored in NADPH→ photolysis splits water into e- and O2
Calvin cycle process
ATP and NADPH generated in light reactions build CARBS, carbon fixation
How is light absorbed in plants?
Carotenoids and Chlorophyll
Where is light absorbed in plants?
thylakoid membranes
What light is absorbed?
blue and red
why are leaves green?
the light spectrum is reflected by leaves
blue/violet light
400 -450 nm
red light
650-700 nm
green to yellow light
500 -600 nm
Where do we measure oxygen release from?
photolysis, fixation of carbon dioxide to form carbohydrates, reducing power generated from ETC
Spectrophotometry
device that measures how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam of light passes through the sample solution
Transmittance (t) formula
l(t) / l(o)
l(t) = light intensity before cuvette
l(o) = light intensity after cuvette
Absorbance (A) formula
-log (l(t)/l(o))
Absorbance
amount of photons absorbed
beer lambert law
A = E * c * l
A = absorbance
E = molar coefficient/molar absorption
I = path length
c = concentration
Spectrophotometer range
UV :185-400 nm
Visible light: 400 -700 nm
True or False
Absorbance and O.D are the same units
True
Net photosynthesis
Gross photosynthesis and respiration
after 10 minutes, you record where the solution fell/rose on the pipette level
Gross photosynthesis equation
(net + cellular respiration)
convert to hour
When is phenol red acidic and why?
it is yellow due to carbonic acid
When is phenol red basic and why?
when it is red, CO2 is used up
What is DPIP?
What does it mean when DPIP is blue?
oxidized
What does it mean when DPIP is clear?
reduced
gains electrons, gets lighter in color
DCMU
blocks electron flow from photosynthesis ll
Ammonia
eliminates H ion gradient, speeds up electron transport chain
Positive controls for photosynthesis lab
Tube 3
Negative controls for photosynthesis lab
tube 1 (dependent on chloroplasts)
tube 2 (needs light)
meiosis
How to find % of cells in each stage (cell divison)
Count the number of cells in each stage of meiosis and divide by the total number of cells examined, then multiply by 100 to get the percentage
multiply by 1440 minutes (24 hours)
What phase is the whitefish in?
anaphase
Sperm
ovary
crossing over frequency
nonrecombinant type ratio
4: 4
recombinant type ratio
2:2:2:2 or 2:4:2
relative distance (units)
½ * number of recombinant asci (%)
genome/plasmid
certain number of base pairs long
restriction endonucleases
characterize and manipulate DNA molecules
enzymes that recognize an specific sequence and cut the DNA at/near this site
Palindromes
the sequence of the complementary strands read the same nucleotide sequence forward and backwards
sticky ends
overhanging single strand DNAresulting from the staggered cut made by restriction enzymes
mapping
characterizing the position of restriction endonuclease sites in a particular DNA molecule
plasmid
small, circular DNA molecule found in bacteria and yeast
agarose gel electrophoresis
charged DNA molecules migrate through a gel because they are placed in a powerful electricak field
PCR steps (D1S80 LOCUS)
set up the gel electrophoresis unit with 1% agarose gel
load 20 microliters of marker in one well
load 20 microliters of PCR sample in wells next to marker
fill all empty wells with 20 microliters water
run the unit for 10 minutes
Central Dogma
What are the x-values in a log graph?
distance in cm
what are the y-values in a log graph?
base pairs
What does detergent do to cells?
destroys cell plasma membrane and nuclear envelope
what does NaCl do cells/DNA?
blocks negative charges of DNA → pellets
What should DNA purification look like?
white and stringy
What should DNA purification look like in water?
turn back into solution
(polar H20 molecules interact with various charges of the DNA)
mendelian genetics
Gregor Mendel - 1866
Alleles
Gene governing an INHERITABLE CHARACTERISTICS occur in pairs/2’s
law of segregation
Alleles segregate in the production of Male and Female Gametes
law of independent assortment
Alleles governing 1 inheritable characteristic segregate independently of alleles governing another characteristic
homozygous dominant
AA
heterozygous dominant
Aa
homozygous recessive
aa
genotype
refers to an individual’s allele composition
phenotype
refers to an individual’s PHYSICAL CHARACTERTISTIC
monohybrid cross
allows to cross a single pair of genes (1 trait crosses): between dominant and recessive phenotypes: RATIO of 3:1
dihybrid cross
allows two pairs of genes (2 trait crosses): between dominant and recessive phenotypes: RATIO of 9:3:3:1
homologous pairs
1 paternal and 1 maternal (meiosis (sex cells) vs mitosis (autosomal cells))
When do alleles separate in meiosis?
Anaphase l
sex linked traits
inheritance of a trait that is LOCATED ON A SEX CHROMOSOME
sex chromosome for male
XY
sex chromosome for female
XX
Drosophila flies
easy to maintain
female = 800 eggs
9-11 generation cycle in 11 days
8 chromosomes
easily observable traits
Chi squared formula
x2 = E (observed value - expected value)2/expected value
E = sum
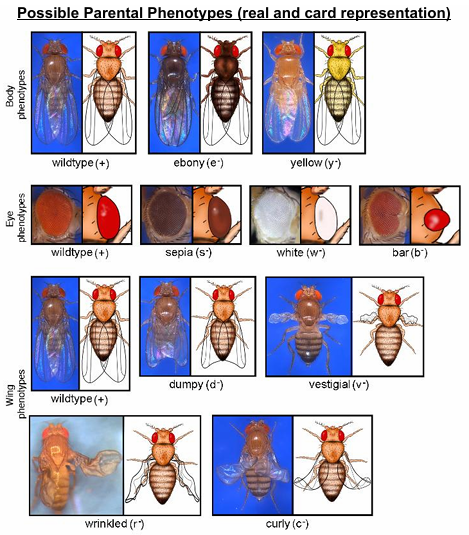
Phenotypes of drosophila fly
body
wildtype (+)
ebony (e-)
yellow (y-)
Eye
wildtype (+)
sepia (s-)
white (w-)
bar (b-)
wing
wildtype (+)
dumpy (d-)
vestigial (v-)
wrinkled (r-)
curly (c-)
central dogma
= DNA (replication) → Transcription into mRNA → Translated into Proteins
how are genes controlled?
epigenetic efforts, chemical modifications in the DNA, no changes in the DNA sequence
identifying an individuals unique DNA sequence fingerprint
0.1% difference between all humans, 3 billion genome letters → DNA fingerprinting → identification of individuals → ancestry, diseases, paternity, etc.
polymorphic loci
sites of variation
polymerase chain reaction
amplification of DNA
DNA primers
short pieces of single-stranded DNA that are complementary to the template
forward and reverse
three steps to PCR reaction
Denaturation: the samples are heated to 94-98 C for one minute to separate the template DNA into single strands
Annealing: the samples are heated to 55-70 C for one minute to allow the primers to bind (anneal) to the template with their specific complementary sequences
Extension: the samples are heated to 65-72 C for one minute to allow the DNA polymerase to build complementary DNA extending from each primer 3’OH
DNA fingerprinting using region VNTR D1S80
Chromosome 1 = D1S80 → variability caused by VNTR’s —> size of repeat of this D1S80 locus is around 16 bases pairs in length.
29 different alleles of D1S80 in humans, so there are 14-41 possible different repeats.
86% of the population is Heterozygous for this locus.
how to calculate number of repeats
(PCR products size - base pairs)/ base pairs
genotype frequency for a heterozygote
(allele frequency 1 x allele frequency 2 ) * 2
genotype frequency for a homozygote
(allele frequency)2
green genes
upregulated in NORMAL CELLS (downregulated in cancer cells)
red genes
upregulated for CANCER cells (not in normal cells)
yellow genes
exhibit similar regulation in CANCER and NORMAL CELLS (=)
black genes
exhibit NO ACTIVITY/INACTIVE in both cell types