Lesson 5.7. Blood Agents
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Vasoconstriction
BLOOD AGENTS PROCESSES:
done to prevent blood loss and pathogen spread
Thromboxane
BLOOD AGENTS PROCESS:
participant molecule of vasoconstriction
Platelet Plug Formation
BLOOD AGENTS PROCESSES:
Platelets migrate to the site of the open wound and undergoes adhesion, activation, and aggregation
Platelet Plug Formation — Adhesion
BLOOD AGENT PROCESSES:
open wound exposes factors that will attract platelets
TXA, ADP, Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
BLOOD AGENTS PROCESS:
participant molecule of activators
Platelet Plug Formation — activation
BLOOD AGENT PROCESSES:
clump through linking glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors at their periphery
cAMP
BLOOD AGENTS PROCESS:
participant molecule of inhibitors
Coagulation cascade
Fibrin clot/ thrombus formation (Coagulation)
a. _________________________ leads to conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
b. ___________________ converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin.
c. The strands of fibrin wrap around the platelet plug, resulting in a _____________.
a = ?
Thrombin
Fibrin clot/ thrombus formation (Coagulation)
a. _________________________ leads to conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
b. ___________________ converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin.
c. The strands of fibrin wrap around the platelet plug, resulting in a _____________.
b = ?
strong fibrin clot
Fibrin clot/ thrombus formation (Coagulation)
a. _________________________ leads to conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
b. ___________________ converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin.
c. The strands of fibrin wrap around the platelet plug, resulting in a _____________.
c = ?
Clotting Factors
BLOOD AGENT PROCESSES:
coagulation activator
antithrombin
BLOOD AGENT PROCESSES:
coagulation inhibitors
Fibrinolysis
BLOOD AGENT PROCESSES:
The fibrin clot must be dissolved by an active protease called plasmin
Plasmin
must be activated from plasminogen by virtue of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA).
t-PA, Plasminogen
Fibrinolysis Participating Molecule
Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine, Prasugrel
Antiplatelet drugs (target components responsible for platelet aggregation)
MOA:
Inhibition of ADP binding on P2Y12 receptor
Aspirin
Antiplatelet drugs (target components responsible for platelet aggregation)
MOA:
Inhibition of thromboxane A2 (TXA2)
Abciximab, Eptifibatide, Tirofiban
Antiplatelet drugs (target components responsible for platelet aggregation)
MOA:
Binds to Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GP IIb/GP IIIa)
Aspirin
Antiplatelet Drugs
has anti-inflammatory activity and affects prostaglandin synthesis
COX-1
ASPIRIN MOA:
a. irreversibly inhibits _________ near active site
b. inhibits _________ synthesis
c. reduced __________________
a = ?
TXA2
ASPIRIN MOA:
a. irreversibly inhibits _________ near active site
b. inhibits _________ synthesis
c. reduced lately activation
b = ?
lately activation
ASPIRIN MOA:
a. irreversibly inhibits _________ near active site
b. inhibits _________ synthesis
c. reduced lately activation
c = ?
PDE
PDE Inhibitors MOA:
a. inhibits _________
b. leads to an ___________________
c. reduces ______________
a = ?
increased cAMP
PDE Inhibitors MOA:
a. inhibits _________
b. leads to an ___________________
c. reduces ______________
b = ?
platelet activity
PDE Inhibitors MOA:
a. inhibits _________
b. leads to an ___________________
c. reduces ______________
c = ?
Dipyridamole, Cilostazol
PDE Inhibitor Drugs
P2Y purinergic receptors
P2Y / ADP Inhibitors (thienopyridines) MOA:
a. binds to ________________________
b. leading to decreased _____________
c. decreased _______________________
a = ?
ADP binding
P2Y / ADP Inhibitors (thienopyridines) MOA:
a. binds to ________________________
b. leading to decreased _____________
c. decreased _______________________
b = ?
platelet aggregation
P2Y / ADP Inhibitors (thienopyridines) MOA:
a. binds to ________________________
b. leading to decreased _____________
c. decreased _______________________
c = ?
Clopidogrel, Ticlopidine, Prasugrelm, Ticagrelor
P2Y / ADP Inhibitors (thienopyridines) Drugs
protease-activated receptor
PAR blockers MOA:
a. inhibits ___________________________
b. leads to __________________________ for platelet aggregation
a = ?
decreased thrombin capacity
PAR blockers MOA:
a. inhibits ___________________________
b. leads to __________________________ for platelet aggregation
b = ?
Vorapaxar
PAR blockers Drugs
Heparin, Enoxaparin, Fondapirinux
Anticoagulant drugs (inhibit clotting factors before a clot is formed) MOA:
Inhibition of Factor IIa (thrombin)
Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban
Anticoagulant drugs (inhibit clotting factors before a clot is formed) MOA:
Inhibition of Factor Xa
Warfarin
Anticoagulant drugs (inhibit clotting factors before a clot is formed) MOA:
Inhibition of Vit. K-dependent Factors
sulfate glycosaminoglycan
Heparin is a ______________________
indirectly inhibit thrombin
Heparin MOA:
a. ____________________________ by activating antithrombin
b. __________________________ requires monitoring of use.
c. _______________________________________________ are more predictable w/ less monitoring.
a = ?
Unfractionated heparin (UFH)
Heparin MOA:
a. ____________________________ by activating antithrombin
b. __________________________ requires monitoring of use.
c. _______________________________________________ are more predictable w/ less monitoring.
b = ?
Low Molecular Weight heparin (LMWH) and Fondaparinux
Heparin MOA:
a. ____________________________ by activating antithrombin
b. __________________________ requires monitoring of use.
c. _______________________________________________ are more predictable w/ less monitoring.
c = ?
bleeding
ADR of Heparin
Protamine
Heparin ADR antidote
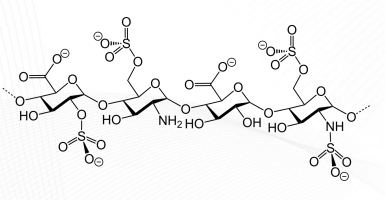
Heparin Structure
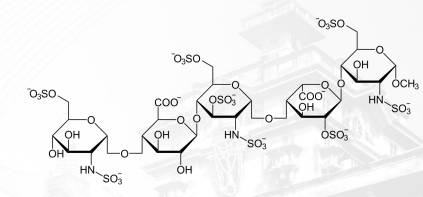
Fondaparinux Structure
Factor IIa
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (from Hirudo medicinalis, medical leech) MOA:
directly binds and inhibits _____________________
Hirudin, Lepirudin, Desirudin, Bivalirudin
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (from Hirudo medicinalis, medical leech) Drugs:
a. From leech:
b. Small molecule inhibitors:
a = ?
Argatroban, Dabigatran
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors (from Hirudo medicinalis, medical leech) Drugs:
a. From leech:
b. Small molecule inhibitors:
b = ?
Vit. K epoxide reductase complex (VKORC)
Coumarins (Warfarin) MOA:
a. inhibits ____________________________________
b. leads to reduced synthesis of ________________________________
a = ?
cofactors 10, 9, 7 and 2 (“1972”)
Coumarins (Warfarin) MOA:
a. inhibits ____________________________________
b. leads to reduced synthesis of ________________________________
b = ?
Vitamin K
antidote of Warfarin ADR
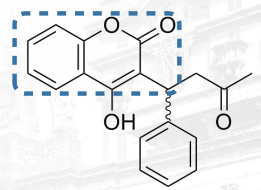
Warfarin Structure
Fibrinolytics / Thrombolytics
Dissolve fibrin clots that may be blocking blood flowinthevessels.
All Fibrinolytic agents are derivatives of ________________________.
tissue Plasminogen Activators (tPAs)
tissue Plasminogen Activators (tPAs)
Fibrinolytics MOA:
a. works like _________________________________
b. converts______________________
c. breaks _____________
a = ?
plasminogen to plasmin
Fibrinolytics MOA:
a. works like _________________________________
b. converts______________________
c. breaks _____________
b = ?
blood clots
Fibrinolytics MOA:
a. works like _________________________________
b. converts______________________
c. breaks _____________
c = ?
Streptokinase, Urokinase, Alteplase, Reteplase, Tenecteplase
Fibrinolytic Drugs
plasminogen to plasmin
Antifibrinolytics MOA:
a. inhibit conversion of ____________________
b. prevents __________________
a = ?
bleeding
Antifibrinolytics MOA:
a. inhibit conversion of ____________________
b. prevents __________________
b = ?
Tranexamic acid and Aminocaproic acid
Antifibrinolytic Drugs
Antiplatelets and anticoagulants
Prevention of thrombi that can lead to: myocardial infarction, pulmonaryembolism, and/or deep vein thrombosis.
Fibrinolytics / Thrombolytic
Dissolution of thrombi that has already been formed especiallywhenitcompletely blocks major cardiac blood vessels. Preventsvascularblockade that may lead to stroke.
Antifibrinolytics
Prevention of excessive bleeding from cases where wounds or bleedingare expected (e.g. surgery, hemophilia patients).
Novel Drugs
Improves platelet synthesis for patients with thrombocytopenicepisodesor for patients having very low blood counts.
Eltrombopag and Romiplostim
Example of Novel Drugs (thrombopoeitinagonist)