TEAS STUDY SCIENCE COMPLETE MASTERY, TEAS 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY , TEAS STUDY SCIENCE, TEAS 7 Life and physical sciences , CHEM TEAS REVIEW IN DEPTH , ATI TEAS HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY PRACTICE TEST QUESTIONS
1/594
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
595 Terms
antecuboidal
front of elbow
Pollex
thumb
Crural
shin
Tarsal
ankle
Coxa
hip
Dorsum
back of hand
manual
hand
Otic
ear
Mental
chin
Acromial
shoulder
Olecranal
back of elbow
Perineal
region between the anus and external genitalia (Grundle)
Sural
calf
Calcaneal
heel
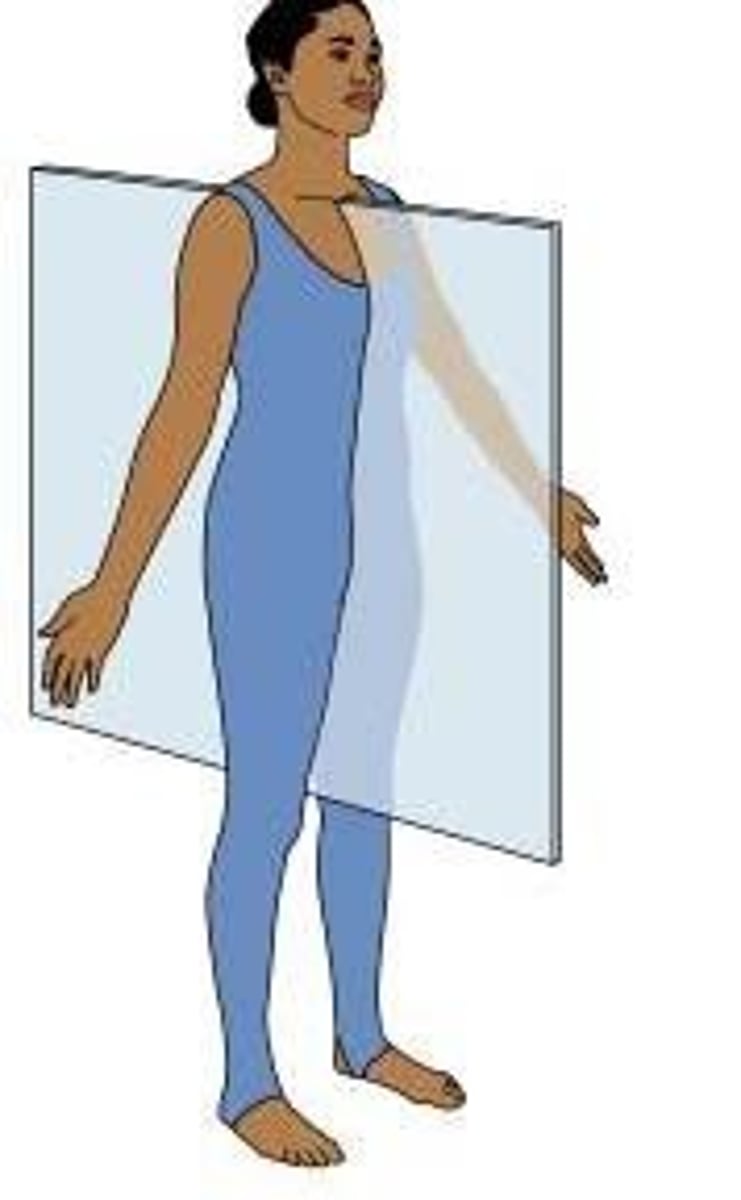
coronal plane
divides body into front and back
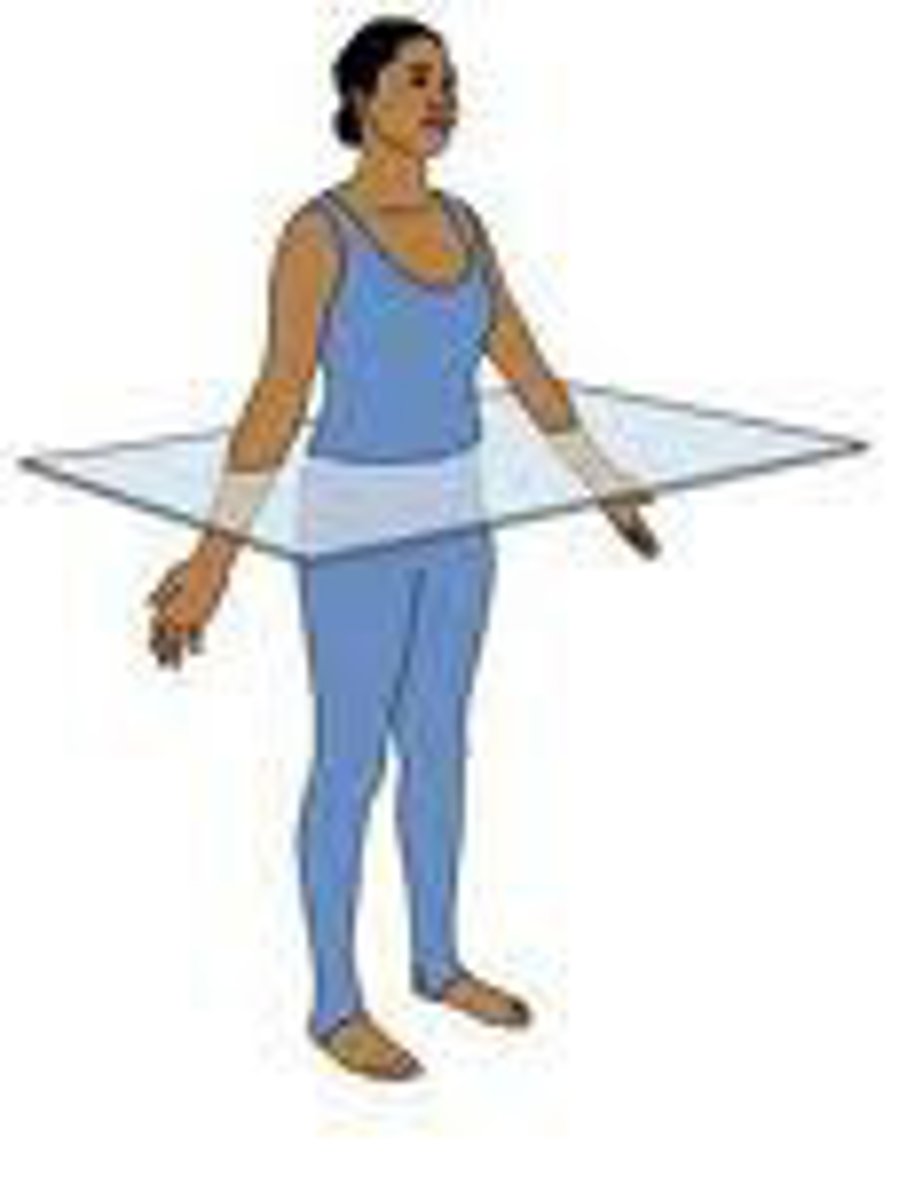
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
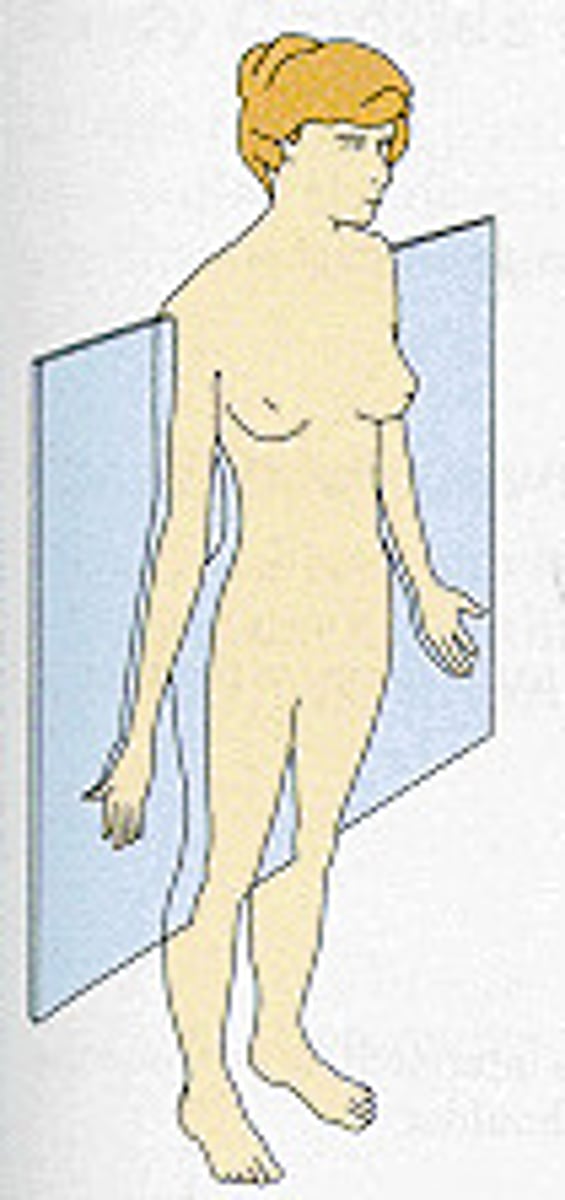
saggital or median plane
divides the body into equal right and left halves
in the human body, which of the following body parts are in superior position to the lungs? (select all that apply)
b. trachea
3 multiple choice options
In two to three sentences, describe the part of the arm that is most distal to the shoulder of the human body.
The part that is most distal to the shoulder are the phalanges. The phalanges are distal to the antecuboital and so are far more distal to the shoulder.
Which terms add clarity to anatomical position relative to the coronal plane?
C. Anterior and posterior
C. Anterior and posterior
3 multiple choice options
Which two terms are likely to appear in the same discussion related to a part of the body?
Dorsal and lumbar
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following statements below is/are accurate
The oral, nasal, buccal, and ocular region are all anterior to the occipital region
2 multiple choice options
Function of the respiratory system
supply the body with oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide
The process of exchanging the gas oxygen with the gas carbon dioxide is known as
Ventilation
pathway of respiratory system
nose/mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
Bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
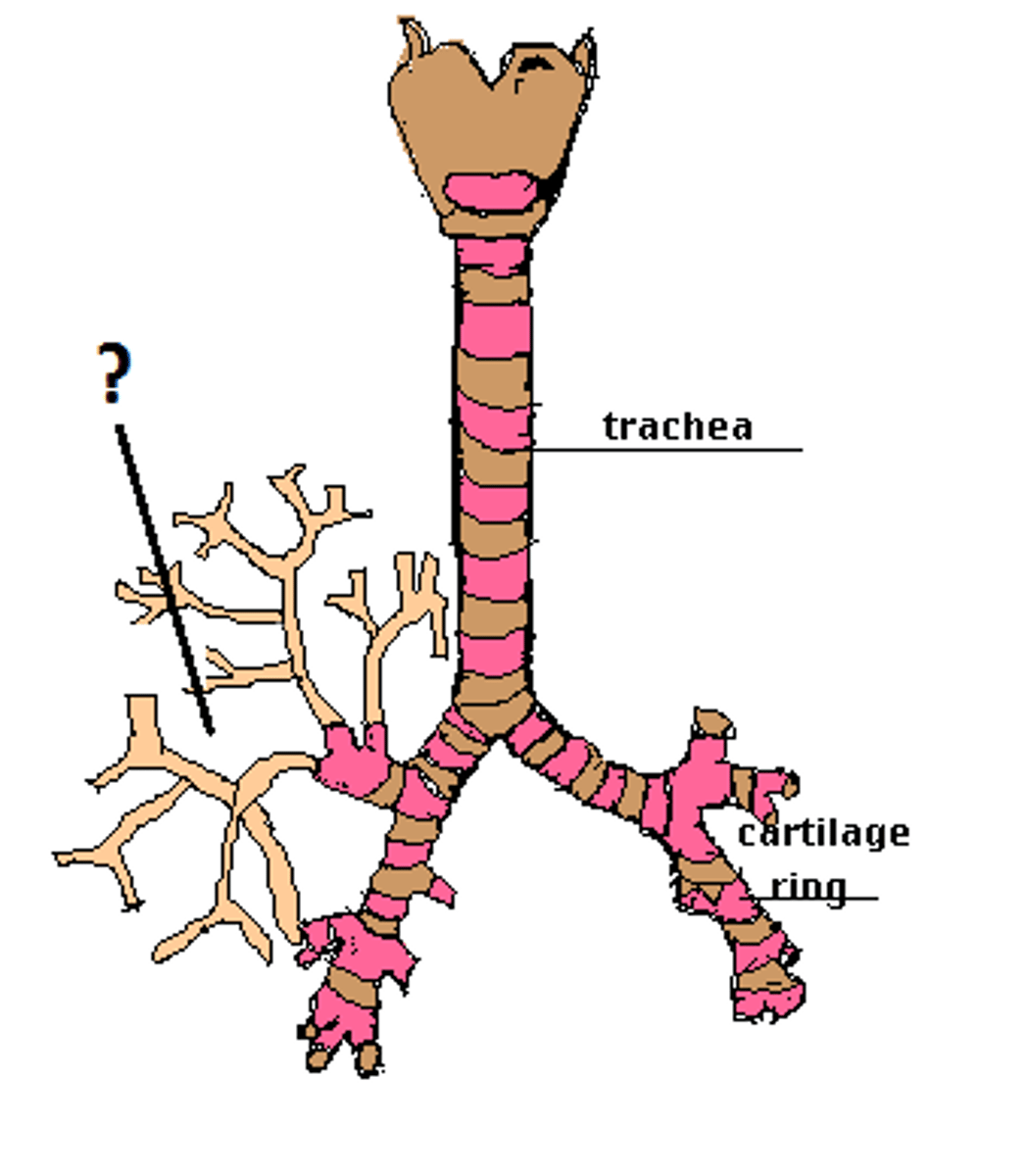
where do bronchioles terminate?
alveoli
What are alveoli?
Single celled thin walled structures that look like clusters of grape that are sites of gas exchange
What alveolar cells release the lipoprotein surfactant to reduce surface tension
Type two alveolar
Where is the heart located?
mediastinum, between lungs on the left side so the right lung has more space
What lung is larger?
right
1 multiple choice option
What is the difference between the left and right lung( excluding the size)
The right lung is split into three lobes
-Superior
-Middle
-Inferior
The left lung only has two lobes
-Superior and inferior
Do lungs share oxygen and arteries
No, they have different
1 multiple choice option
What is each lung filled with?
Pleura (contains pleural fluid)
What part of the body facilitates gas exchange in the lungs
Capillaries (They interact with with the alveoli of the lungs via diffusion)
True or false: The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the surface area involved and the concentration gradient is inversely proportional between the two solutions.
True
passive transport
Movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy from the cell
The rate of diffusion increases if
the distance between the blood cells and the alveoli is decreased
Diffusion increases if
surface area increases
pressure gradient increases
Rate of diffusion increases
while the distance between two solutions decreases
Molecules move from
high to low concentration
What allows for diffusion in the lungs
thin alvoelar epithelium
How does ventilation occur
due to the difference in pressure gradient between the interior of the lungs and the atmosphere (negative pressure)
Inhalation
the act of taking in air as the diaphragm contracts and pulls downward (Intercostals expand)
Exhalation
diaphragm relaxes (moves up)
tidal volume
Amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs during a normal breath
residual volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation
What controls breathing
medulla oblongata
how does the medulla oblongata regulate inhalation?
Through blood pH and monitoring of carbon dioxide
Respiration increases if
blood pH starts to decrease (too much co2 in blood)
Asthma
A condition in which a person's airways become inflamed, narrow and swell, and produce extra mucus, which makes it difficult to breathe.
What causes emphysema?
Repeated exposure to irritant causes repeated inflammatory response with scarring of alveolar tissue
Genetic conditions in the lungs
Lung surfactant insufficiency
Asthma
Cystic fibrosis
Disease in the lungs
Influenza
Tuberculosis
Pneumonia
Allergies
an immune response to a foreign agent that is not a pathogen
Virus
a non cellular entitiy that consist of nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA) surrounded by protein coat
Which of the following structures change the volume of the lungs?
Diaphragm
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following statements best explains how the structure of alveoli relates to its functions?
Which of the following statements best describes the primary function of the respiratory system
It exchanges gases between the blood and the air in an environment
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following correctly describes the makeup of the lungs?
Right lung, three lobes, left lung, two lobes
3 multiple choice options
Top chambers of the heart are called
Atria
Bottom chambers of the heart are called
Ventricles
What are the functions of the heart
Transporting nutrients, circulating oxygenated blood and removing CO2 via respiratory system, transporting hormones and other waste.
What are the two circuits of the heart?
Systemic and pulmonary
Function of the pulmonary loop/system
Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs where it is oxygenated and returns as oxygenated blood via the left atrium
Functions of the systemic circuit
Carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body, returning deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
What are the two cycles of contraction of the heart
Diastole and systole
Systole contraction
Indicates the contraction of the heart muscle
Diastole
Indicates the relaxation of the heart
Lub sound heart
AV valves closing (Mitral and tricuspid valve)
When are the ventricles filled with blood
When there is atrial systole
dub sound
semilunar valves closing
What controls diastole and systole of the heart?
The pace maker (AKA sinoatiral node)
What is the function of the sinoatiral node?
Sends electrical signals to start contraction of the heart chambers to pump blood
Difference between veins and arteries
Arteries are thicker than veins as they need to withstand pressure of the blood pumped by the heart
What does blood plasma contain?
nutrients, hormones, antibodies, and other immune proteins
What do red blood cells contain to transport oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body?
Hemoglobin
What percentage of carbon dioxide is used to maintain acid-base or pH balanced via the bicarbonate buffer system?
85%
Bicarbonate buffer system
most important buffer system that keeps blood pH from changing drastically
What are buffers
A solution of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa that can causes and maintain a proper pH when there is an imbalance
What are the two divisions of the white blood cells
granulocytes and agranulocytes
Granulocytes
Neutrophils
Basophils
Eusinophils
Agranulocytoses (PHILZ IS GRAND)
Monocyte and lymphocyte
What do RBC also contain?
Platelets or thrombocytes for blood clotting
Where do the capillaries drain the interstitial fluid that fills the spaces between the cells to filter it
To the lymph NODES :D
What are the lymph nodes enriched with?
Lymphocytes, Macrophages
Essentially, what is lymph?
Plasma with red blood cells removed
Function of lymph nodes
In a sense, they monitor and respond to foreign molecules washed into the system (They are the TSA of the body, they need to check in before they can get inside!!!)
Where do lymph nodes reside?
In certain areas such as oral (Tonsils), Nasal, and genital regions (Basically where foreign bacteria can enter through)
Myocardial infarctions
Also known as heart attacks. This is caused by a blockage in the arteries of the heart which can lead to loss of oxygen in the tissues and then myocardium death.
aneurysm
an excessive localized enlargement of an artery caused by a weakening of the artery wall.
Arrhythmias
abnormal heart rhythms
Hypertension
Also called high blood pressure
A condition where the force of the blood is too high against the arteries
Where is deoxygenated blood carried to the pulmonary circuit
Pulmonary artery
Blood flow through the heart
1-Superior & Inferior Vena Cava, 2-Rt Atrium, 3-Tricuspid Valve, 4- Rt Ventricle, 5-Pulmonary Valve, 6-Pulmonary Artery, 7- Lungs-pick up oxygen, 8-Pulmonary Veins, 9- Lt Atrium, 10- Mitral Valve (Bicuspid), 11-Lt Ventricle, 12- Aortic Valve, 13-Aorta, 14- Body
What chamber of the heart pumps blood towards the lungs
right ventricle (LOOK AND STUDY HEART DIAGRAM)
What statement best describes the function of the veins
Veins carry deoxygenated blood
Veins carry oxygenated
Veins carry blood away from the heart
Veins carry blood back to the heart
Where does digestion begin?
In the mouth
Order of digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
Function of digestive system
Break down food fr absorption and distribution of nutrients to the rest of the body.