Chemistry - Unit 3: Electrons in Atoms
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Scientific notation
way of expressing very large or very small numbers
to convert an ordinary number to scientific notation
Move the decimal until you have a number between 1 and 9.9999
Place a x10 and an exponent equal to the number of times you’ve moved the decimal
Exponent is negative if the decimal is moved to the right
Exponent is positive if the decimal is moved to the left
standard notation
to convert scientific notation to standard notation:
move the decimal as many times as the exponent
move the decimal to the right if the exponent is positive
Move the decimal to the left if the exponent is negative
Light
light is a kind of electromagnetic radiation
electromagnetic radiation includes many types
ie. gamma rays, x-rays, radio waves
all electromagnetic radiation travels at the same rate (speed of light) when measured in a vacuum
electromagnetic radiation propagates through space as a wave moving at the speed of light
Speed of Light
c = 2.998 × 108 m/s
λ
lambda, wavelength in meters
ν
nu, frequency in units of seconds or hertz
wavelength and frequency
wavelength and frequency are inversely related
As one increases the other decreases
Different frequencies of light are different colors of light
the whole range is called a spectrum
J
Joules, unit of energy of a quantum of radiation
Important light equations
c = λv
E = hv
Planck’s constant
h = 6.626 × 10-34 JS
excited state (atomic state)
atom with excess energy
atoms absorb energy and become excited
ground state (atomic state)
atom in the lowest possible state
excited atoms emit photons of light and return to the ground state
atomic orbitals (sublevels)
within each energy level, the complex math of Schrodinger’s equation describes several shapes
These are called atomic orbitals
Regions where there is a high probability of finding electrons
Orbitals are s, p, d, and f
S —> 1 shape
P —> 3 shapes
D —> 5 shapes
F —> 7 shapes
Aufbau’s principle
electrons enter the lowest energy level first
Pauli Exclusion Principle
at most 2 electrons per orbital
Hund’s Rule
When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, they don’t pair up until they have to
Electron Configuration filling order
s → holds 2 electrons max
p → holds 6 electrons max
d→ holds 10 electrons max
f → holds 14 electrons max
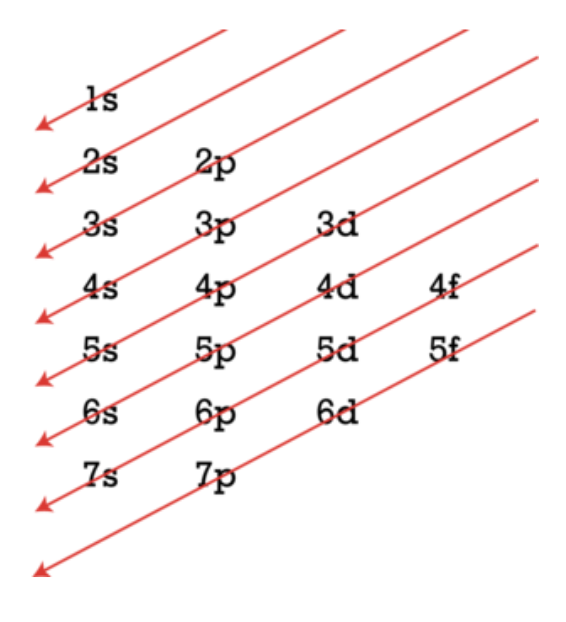
Electron Configuration exceptions
Cr and other elements in its group
s1d5
Cu and other elements in its group
s1d10
Half filled orbitals slightly lowers energy
makes the elements more stable
Ground and Excited electron configuration states
excited→orbitals are not filled fully in order]
ground→orbitals are filled in order
Periods
horizontal rows
groups
AKA family
Vertical columns
similar physical and chemical properties
Metals
one of three classes of elements
electrical conductors, have luster, ductile, malleable
Non-metals
one of three classes of elements
generally brittle and non-lustrous, poor conductors of heat and electricity
some non-metals are gases, brittle solids, and one is a fuming dark liquid
Metalloids
one of three classes of elements
properties are intermediate between metals and nonmetals
Alkali Metals
group 1
forms a “base” (or alkali) when reacting with water
excluding hydrogen
Alkaline earth Metals
group 2
Also forms bases with water
do not dissolve well
Halogens
group 17
means “salt forming”
Noble gases
group 18
previously called “inert gases” because they rarely take part in a reaction
Very stable → do not react
Transition metals
block d
groups 3 to 12
Inner transition metals
block f
Lanthanide Series and Actinide Series
Short Hand Electron configuration
start electron configuration from the previous noble gas