science- year 7
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all year 7 stuff
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
cell
the basic unit that is the fundementle molecules of life and that all living things are made of
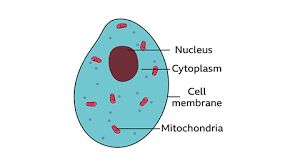
what is this a diagram of
an animal cell
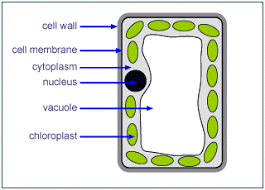
what is this a diagram of
palisade cell (plant cell)
nucleus- animal and plant
controls the cell. chromosones are found here (DNA)
cytoplasm- animal and plant
jelly like substance, where most chemical occurences take place
cell wall- plant
strengthens the cell
cell membrane- animal and plant
controls what goes in and out
ribosomes- animal and plant
where proteins are made
vacuole- plant
stores substances
chloroplasts- plant
photosynthisis
mitochondria- animal and plant
powerhouse of the cell
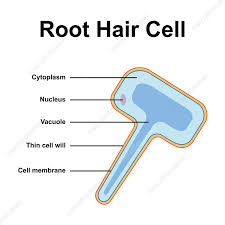
root hair cell- plant cell
takes up water and minerals from the soil
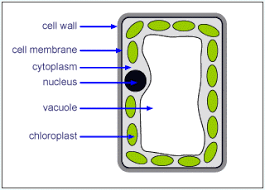
palisade cell
carries out photosynthesis
white blood cell
fights invading germs
nervous system cell
carries nerve impulses over long distances
ciliated epithelial cell
little hair like cilia beat to move mucus carrying trapped dirt towards the throat
red blood cell
carry oxygen around the body
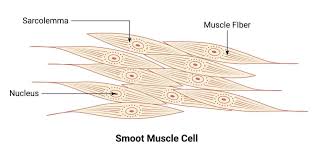
muscle cell
allows movement

look at the diagram, then cover it and try to remember all the parts
microscope
tube
holds lenses and keeps all light out
mirror/ light source
reflects the light through the specimin
stage
to hold the slide in place
objective lenses
the lens at the lower end of tube.
eyepeice
where you look through
how do you work out how many times your object is being magnefied
total magnification = power of eye peice x power of the objective lens
unicellualar organism
an organism that only has one cell
multicellular organism
an organism that has multiple cells
diffusion
when particles move from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration
variable
the characteristics of the object
value
the amount
continuous variable
the thing you measure
independent variable
the thing you change
dependent variable
the thing you measure
control variable
the thing that stays the same
when plotting a graph where does the independent variable go?
x axis
when plotting a graph where does the dependent variable go?
y axis
anomalies
the values that do not fit the pattern in results
categoric variables
they have values that are labels
kinetic energy
energy formed from movement
light energy
hot objects release this energy
sound energy
energy made from sound vibrations
thermal energy(internal energy)
energy an object stores because it is hot
electrical energy
the energy carried by and electrical current in a circuit
gravitational potential energy
the energy an object stores because it is high up
elastic potential (spring) energy
stretched/ squashed spring can store energy that can be released later
nuclear energy
stored in atoms and is released in nuclear power stations and the sun
chemical energy
the bonding between atoms. the energy inside the bond is the chemical energy
solar cells
light energy is transferred from teh sun to the solar cell which makes electrical energy.
wave
kinetic energy is transferred from the water to the generator which transforms it into electrical energy
wind
kinetic energy is transferred from the moving air to the wind turbine, which transforms it into electrical energy
hydroelectric
a change in gravitatinoal potential energy causes water to gain kinetic energy making it into electrical energy
solar heating
light energy and heat energy from sun makes water hot - thermal energy
geothermal
naturally occuring radioactive substance
tidal
a change in gravitational energy causes the water to gain kinetic energy which turns a generator making it into electricity
fossil fuels
coal, oil, gas
chemical energy stored in coal millions of years ago is released in heat energy when coal is burnt
nuclear
nuclear energy to thermal energy to kinetic energy to electrical energy converts nuclear energy to thermal energy as particles change
renewable energy sources
energy sources that will never run out. for example solar energy, wind energy
non- renewable energy sources
energy sources that will run out. for example coal, oil, gas
name 1 benifit of renewable energy sources
better for environment
name 1 benifit of non-renewable energy sources
high level of energy release per amount of source
attract
pulls together
repel
pushes apart
what is a cell
a chemical pump
what is this a diagram of?
cell
what is this a diagram of?
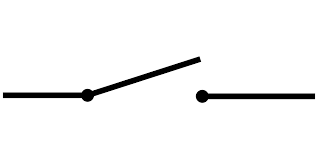
switch
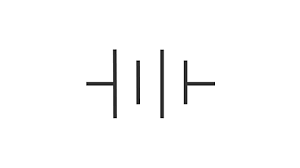
what is this a diagram of?
battery
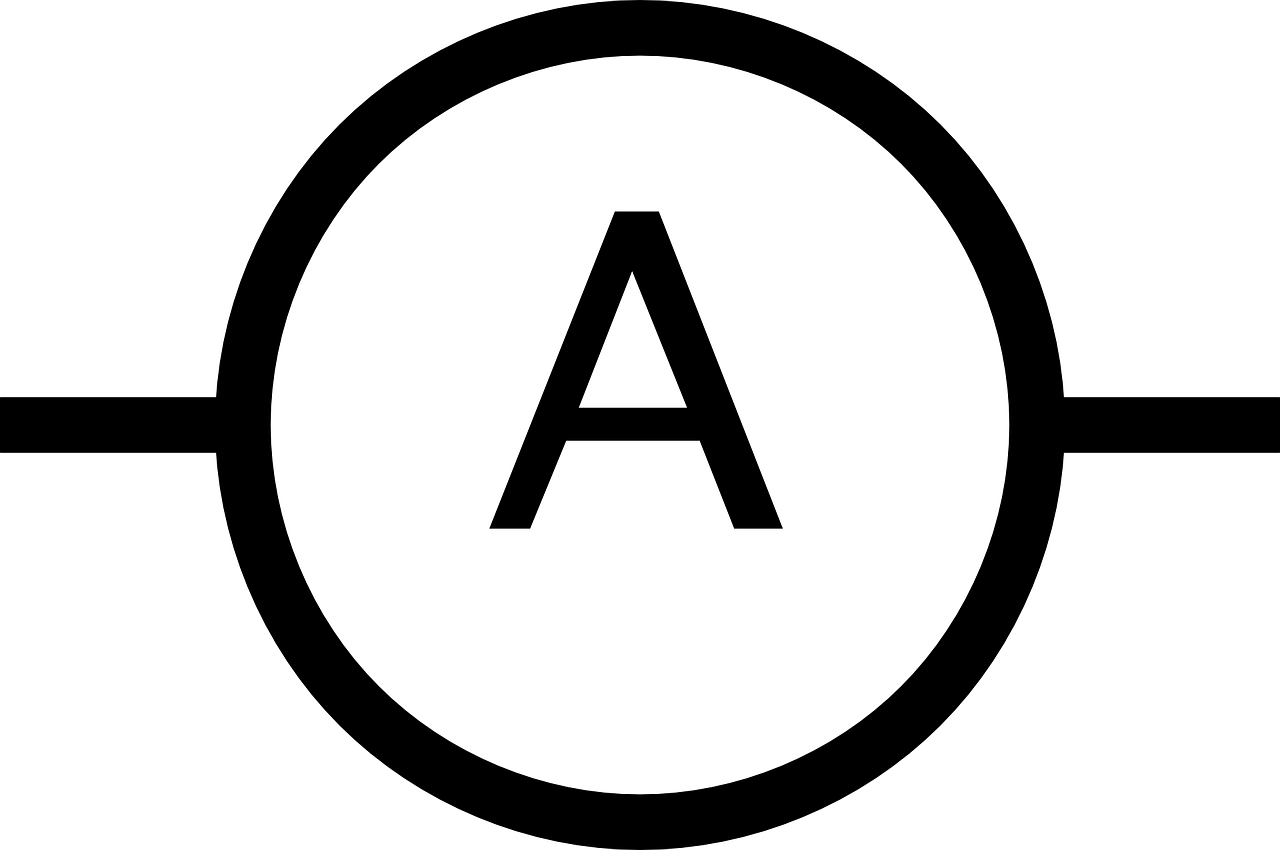
what is this a diagram of?
ammeter
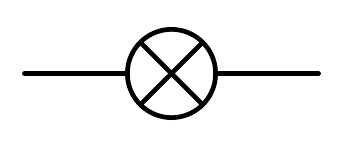
what is this a diagram of?
a lamp
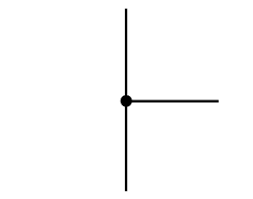
what is this a diagram of?
junction between wires
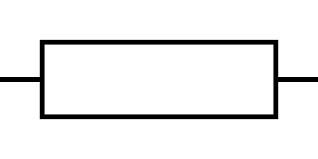
what is this a diagram of?
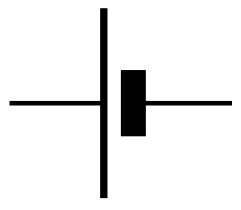
a resistor
current
speed of moving charge
charge
a property of matter that can be positive or negative and causes objects to attract or repel
electron
tiny negatively charged partciles that orbit the nucleus in the centre of a atom
force
push/ pull that acts on another object
insulator
materials that dont allow electricity through
conductor
materials that allow electricity through
circuit
loop where electricity flows
cell
power source in circuit
series circuit
where all circuit elements are arranged in one path
parallel circuits
where circuit elements have multiple pahts
resistance
measure of how difficult it is for current to flow
matter
everything in the universe
particle
what makes up matter
property
stuff that something has
substance
a pure form of matter
melt
solid> liquid
fluid
liquid, water
freeze
liquid> solid
boil
liquid> gas
solid
hard form, cannot be compressed
liquid
water, cannot be compressed
gas
can be compressed
condense
to make smaller
evaporate
when heated, makes gas
classify
put things into categories
melting point
the temperature at which a certain thing melts
boiling poing
the temperature at which a certain thing boils
volume
liquid amount
compress
make something smaller
diffusion
to make something into a gas