Portage Learning Anatomy & Physiology II: Module 7 Exam
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
True or False: The bladder drains into the ureters.
False
True or False: The kidneys are long, thin muscular tubes
False
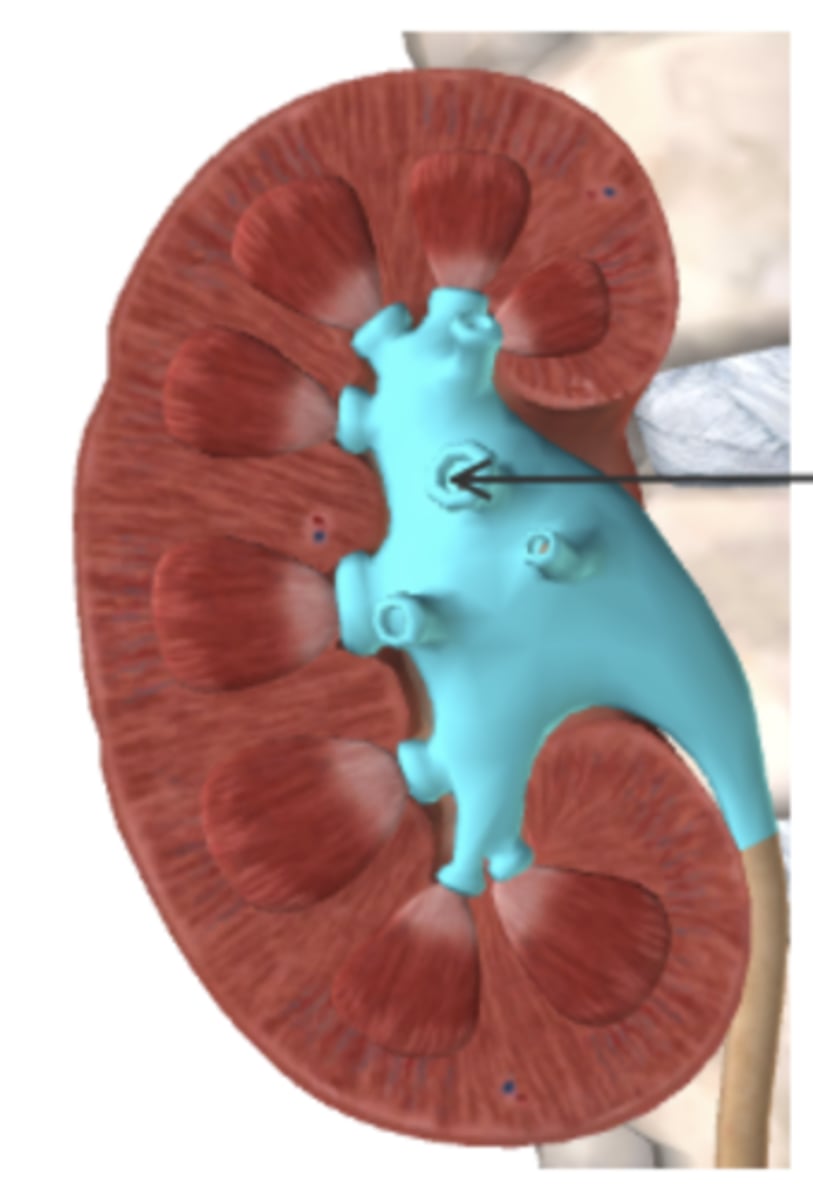
Name the layer and discuss the purpose of its extensions in the the region highlighted in blue, below.
Calyces collect and transport urine to the bladder.
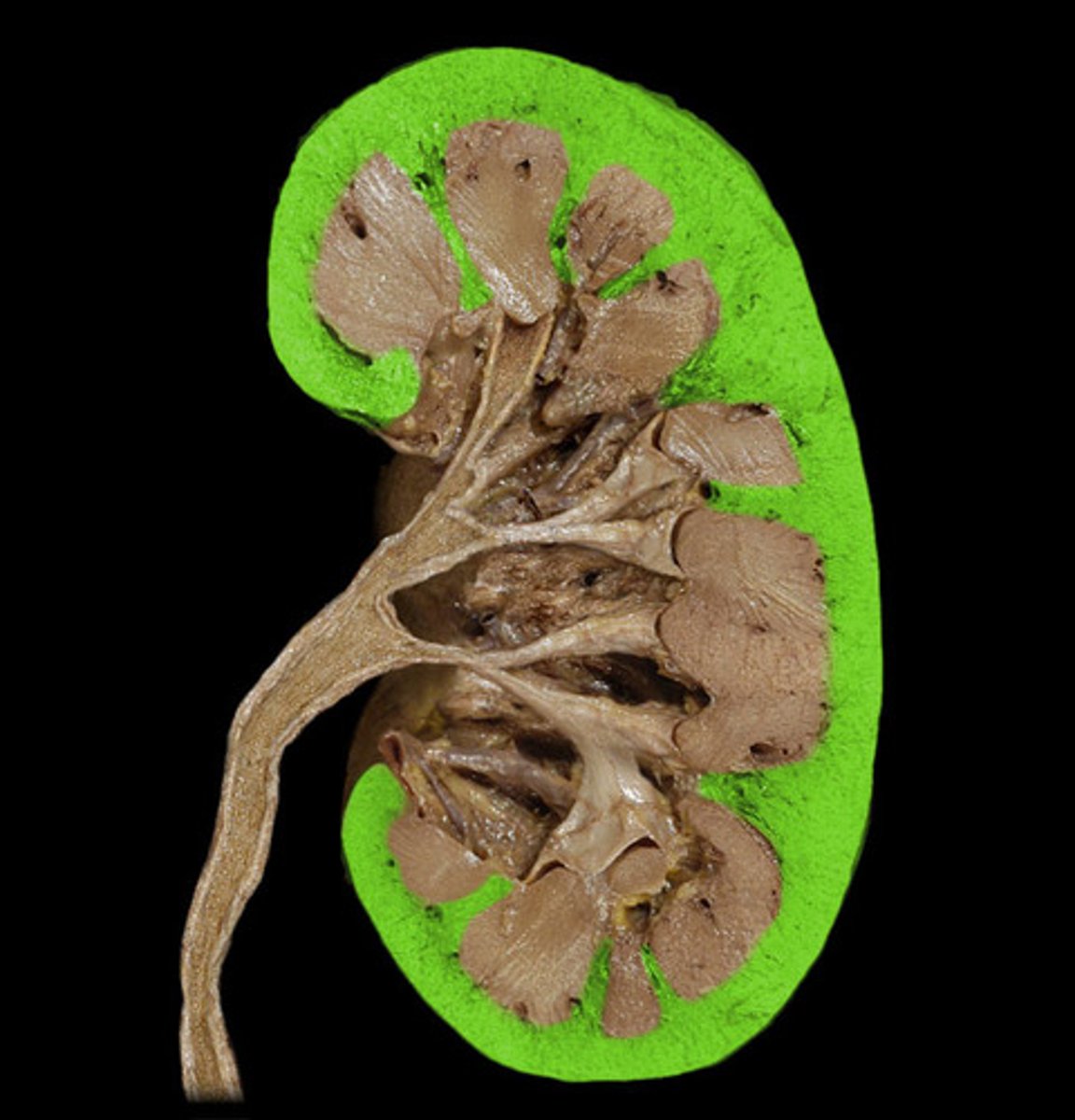
Name the layer and the parts of the nephrons located in the region highlighted in green, below.
Glomerular capsule
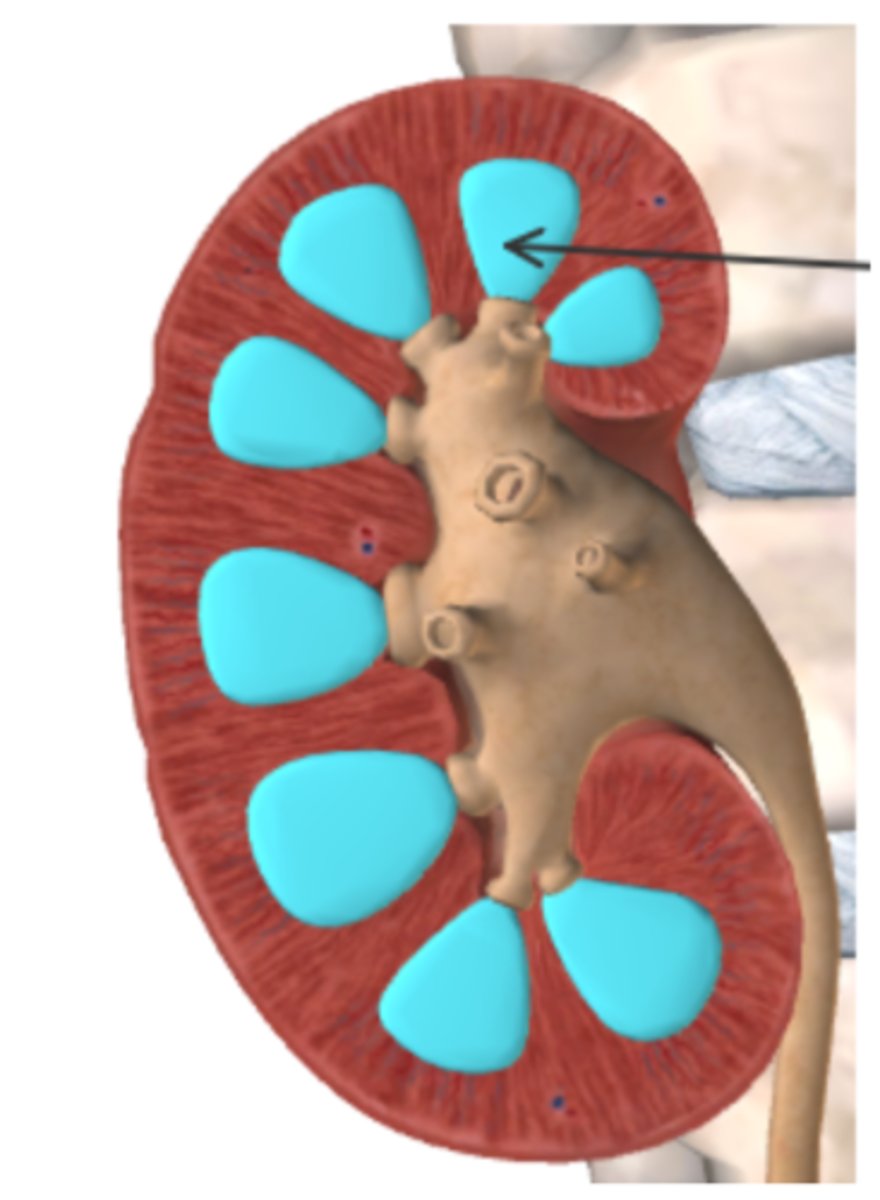
Name the layer and the parts of the nephrons located in the region highlighted in blue, below.
Renal medula located towards center of kidney
These arteries flow in between the renal pyramids.
A. Afferent
B. Lobar
C. Interlobular
D.Arcuate
E. Interlobar
F. Renal
E. Interlobar
These arteries feed the afferent arterioles.
A. Efferent
B. Lobar
C. Interlobular
D. Arcuate
E. Interlobar
F. Renal
C. Interlobular
Interlobar veins converge to form the _____.
A. Efferent arteriole
B. Renal vein
C. Interlobular vein
D.Arcuate artery
E. Arcuate vein
F. Peritubular capillaries
B. Renal vein
Interlobular veins converge to form the _____.
A. Efferent arterioles
B. Renal veins
C. Interlobular veins
D. Arcuate arteries
E. Arcuate veins
F. Peritubular capillaries
E. Arcuate veins
After filtration occurs, next blood travels into these vessels.
A. Efferent arteriole
B. Lobar veins
C. Interlobular veins
D. Arcuate artery
E. Interlobar vein
F. Vasa recta
A. Efferent arteriole
These arteries divide into the segmental arteries as they flow into the kidney.
A. Afferent
B. Lobar
C. Interlobular
D.Arcuate
E. Interlobar
F. Renal
F. Renal
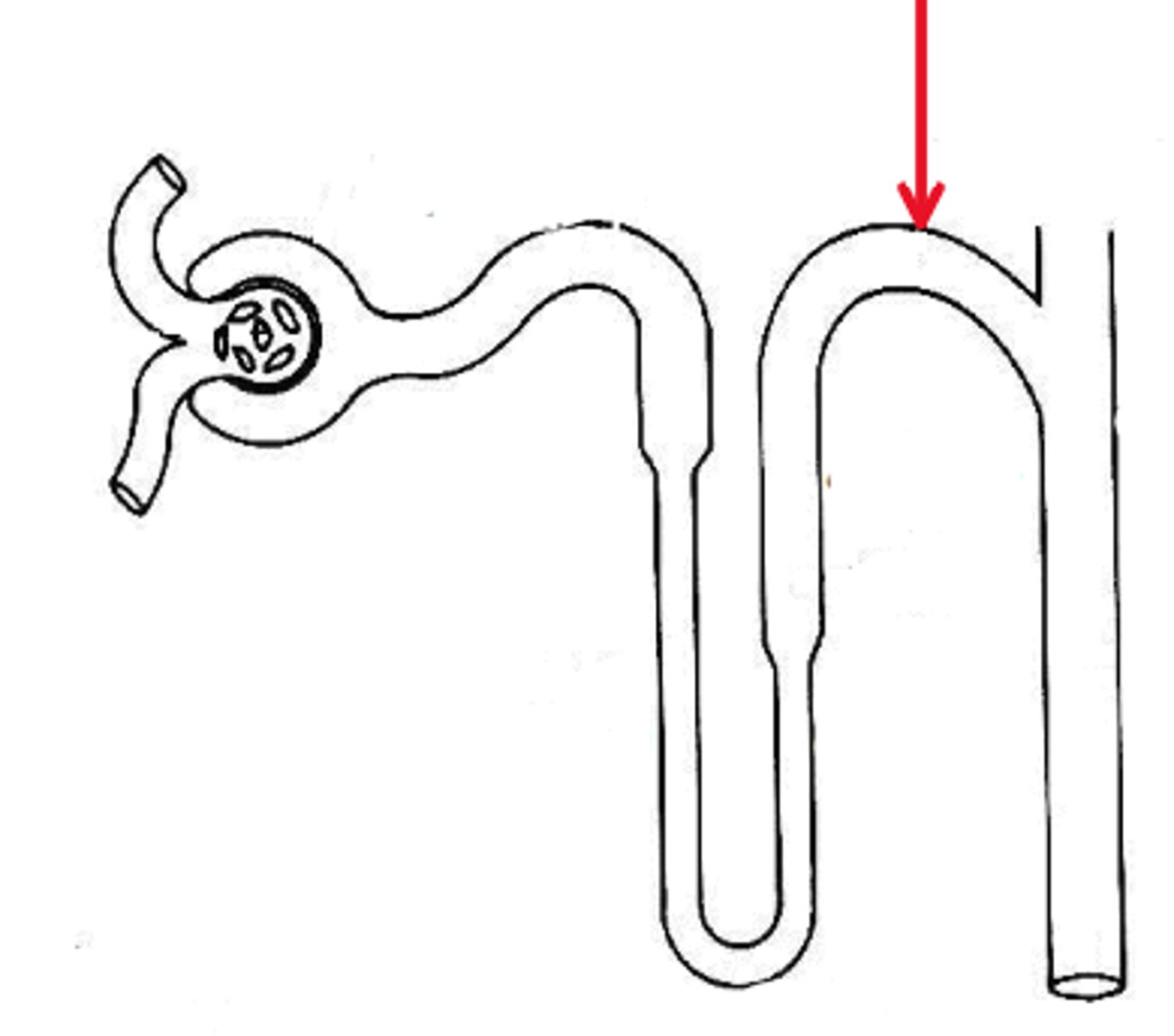
Name the region in the diagram below, indicated by the red arrow.
DCT
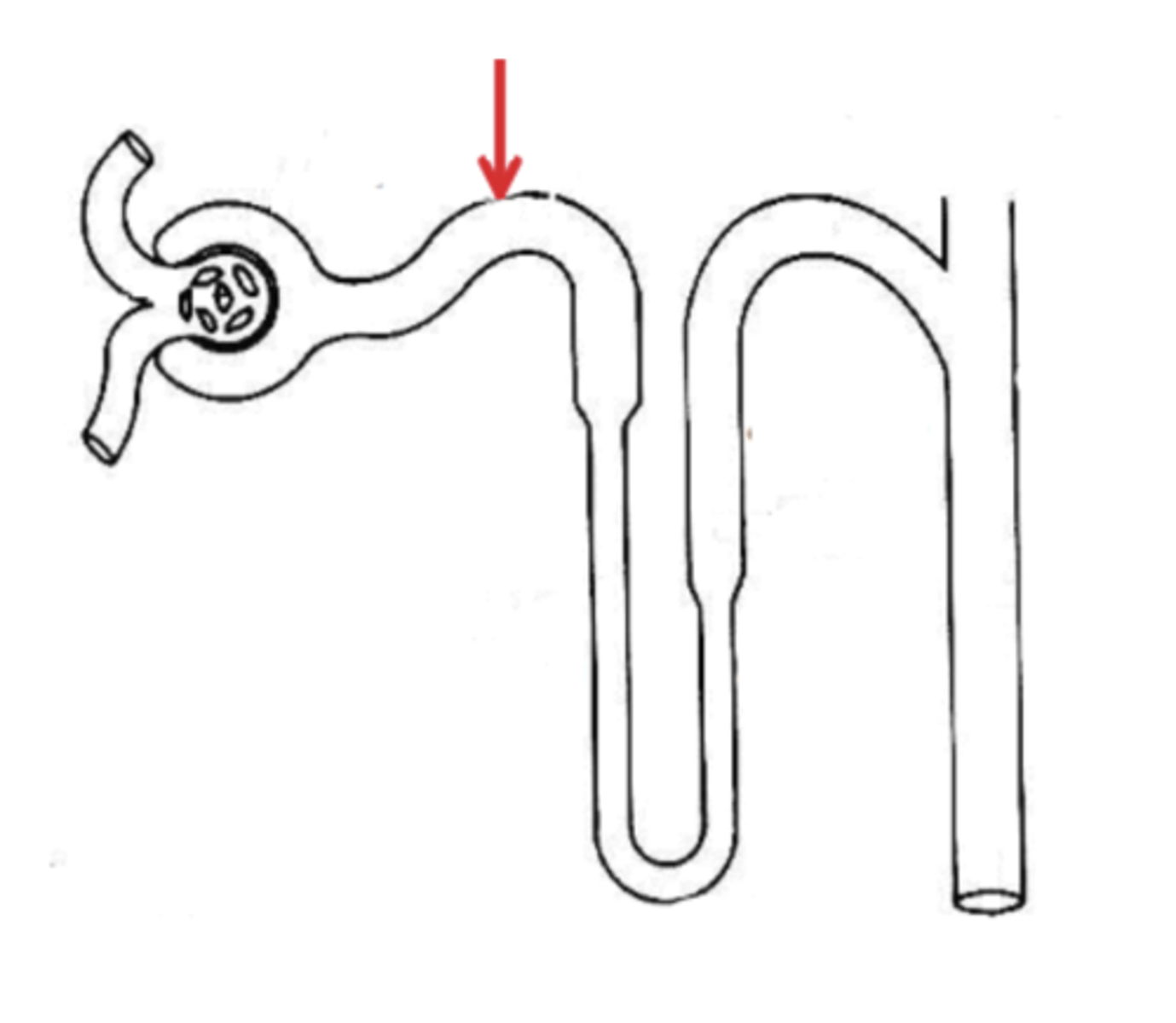
Name the region in the diagram below, indicated by the red arrow.
PCT
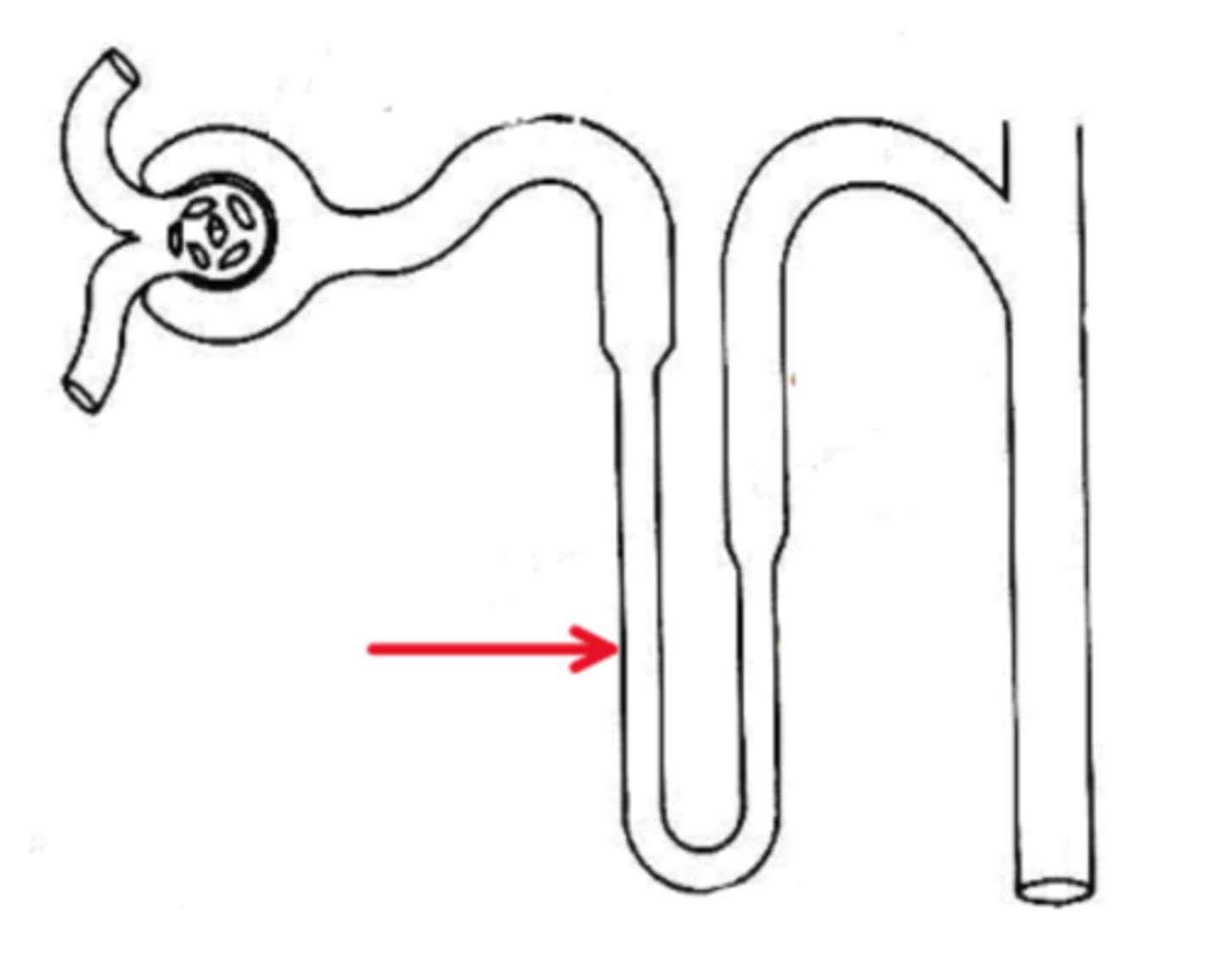
Name the region in the diagram below, indicated by the red arrow.
Loop of Henle
Which of the following is false about the location of the bladder?
A. In males, the bladder is anterior to the rectum.
B. In females, the bladder is posterior to the uterus.
C. In females, the bladder is in between the rectum and the uterus.
D. In males, the bladder is above the prostate gland.
E. B&C are false
F. A&D are false
E. B&C are false
Which of the following is true about the location of the bladder?
A. In males, rectum is anterior to the bladder
B. In females, the vagina is behind the bladder
C. In females, the bladder sits above the uterus
D. In males, the bladder is below the prostate gland
E. B&C are true
F. A&D are true
B. In females, the vagina is behind the bladder
Which of the following is true about the location of the bladder?
A. In males, the bladder is posterior to the rectum.
B. In females, the bladder is posterior to the uterus.
C. In females, the bladder is in between the rectum and the uterus.
D. In females, the bladder is anterior to the vagina.
E. A&B are true
D. In females, the bladder is anterior to the vagina.
A patient was just placed under general anesthesia. He is now awake and telling you he is having a hard time excreting urine. What is most likely causing the difficulty?
A. Incontinence due to stroke
B. Incontinence due to dementia
C. Urinary retention due to spinal cord injury
D. Bladder outlet obstruction
E. Urinary retention due to slowed detrusor muscle
E. Urinary retention due to slowed detrusor muscle
An elderly male with dementia frequently micturates at inappropriate times (during meals, not in the toilet). What is mostly likely causing the difficulty?
A. Incontinence due to end stage dementia
B. Incontinence due to swollen seminal vesicle
C. Urinary retention due to not enjoying meals
D. Urinary retention due to enlarged prostate
E. Hematuria due to diabetes
A. Incontinence due to end stage dementia
An elderly male is unable to micturate. What is mostly likely causing the difficulty?
A. Incontinence due to end stage dementia
B. Incontinence due to swollen seminal vesicle
C. Urinary retention due to spinal cord injury
D. Urinary retention due to enlarged prostate
E. Hematuria due to diabetes
D. Urinary retention due to enlarged prostate
This region of the male urethra exits the body.
A. Spongy
B. Prostatic
C. Membranous
D. Ejaculatory duct
E. Ureters
A. Spongy
This region of the male urethra exits the bladder.
A. Spongy
B. Prostatic
C. Membranous
D. Ejaculatory duct
E. Ureters
B. Prostatic
This is the smallest region of the male urethra
A. Spongy
B. Prostatic
C. Membranous
D. Ejaculatory duct
E. Ureters
C. Membranous
Micturition can be controlled consciously because of:
A. Voluntary control over the internal sphincter
B. Involuntary control over the internal sphincter
C. Voluntary control over the external sphincter
D. Involuntary control over the external sphincter
E. Voluntary control over the visceral reflex arc
F. None of the above: micturition cannot be voluntarily controlled
C. Voluntary control over the external sphincter
For micturition to occur, the _____ sphincter _____.
A. internal ; contracts
B. internal ; relaxes
C. extterm-26ernal ; contracts
D. external ; relaxes
E. A & C
F. B & D
F. B & D
This is the pressure that depends upon a person's blood pressure from the heart and vessels:
A. Colloid osmotic pressure
B. Capsular pressure
C. Net filtration pressure
D. Glomerular filtration rate
E. Hydrostatic pressure
E. Hydrostatic pressure
This is the blood pressure driving fluid out of the capillaries:
A. Colloid osmotic pressure
B. Capsular pressure
C. Net filtration pressure
D. Glomerular filtration rate
E. Hydrostatic pressure
E. Hydrostatic pressure
This is the blood pressure that depends upon the amount of proteins in the filtrate:
A. Colloid osmotic pressure
B. Capsular pressure
C. Net filtration pressure
D. Glomerular filtration rate
E. Hydrostatic pressure
A. Colloid osmotic pressure
Which of the following statements is false concerning the RAA system?
A. Aldosterone causes the retention of sodium ions.
B. It responds when blood pressure becomes too high.
C. Angiotensin II acts to cause vasoconstriction in blood vessels.
D. Renin is released by the cells inside the nephron.
E. Renin converts angiotensinogen to angiotensin I.
B. It responds when blood pressure becomes too high.
Which of the following statements is true concerning the RAA system?
A. It responds when blood pressure becomes too high.
B. Angiotensinogen is a pre-enzyme produced by the adrenal glands.
C. Renin is released by the cells inside the nephron.
D. Renin causes dilation of the afferent and efferent arterioles.
E. Angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II in the liver.
C. Renin is released by the cells inside the nephron.
The greatest amount of _______ occurs in the cells of the PCT.
A. Reabsorption
B. Excretion
C. Secretion
D. Countercurrent flow
E. Osmolarity
A. Reabsorption
True or False: Na+ can leave the ascending limb but not the descending limb.
True
True or False: In the loop of Henle, water can leave the descending limb but not the ascending limb.
True
Which of the following is not reabsorbed in the PCT?
A. Sodium ions
B. Hydrogen ions
C. Glucose
D. Bicarbonate ions
E. Calcium ions
B. Hydrogen ions
The greatest amount of reabsorption occurs in the:
A. Glomerular capsule
B. DCT
C. Descending loop
D. Ascending loop
E. PCT
E. PCT
Which of the following is true concerning ADH?
A. It is produced by the adrenal glands.
B. It is produced in response to increased water in the blood.
C. t retains up to 99% of water in the filtrate.
D. It is unable to respond during severe blood loss.
C. It retains up to 99% of water in the filtrate.
Which of the following is false concerning ADH?
A. It respond during excessive sweating conditions
B. When ADH is in circulation dilute urine is excreted
C. ADH acts by increasing channels in the collecting ducts.
D. In inhibits urine output.
B. When ADH is in circulation dilute urine is excreted
Which of the following is true concerning cardiovascular baroreceptors?
A. They are mechanoreceptors found in the aortic arch and carotid sinus.
B. They are in the lungs and the kidneys.
C. These are chemoreceptors found in the hypothalamus.
D. They are regulated by the hypoglossal and spinal accessory cranial nerves.
A. They are mechanoreceptors found in the aortic arch and carotid sinus.
Pus is an indication of:
A. Infection
B. High protein content
C. Low protein content
D. Blood in urine
E. Bile pigments
A. Infection
Which of the following is an abnormal solute in urine?
A. Urea
B. Nitrogenous wastes
C. Ammonia
D. Magnesium
E. Bile pigment
E. Bile pigment
Water in the body is primarily found in what body compartment?
A. Extracellular
B. Intracellular
C. Interstitial
D. Plasma
E. Synovial joints
B. Intracellular
Yellow color in urine is due to the presence of:
A. Pus
B. Rhubarb
C. Asparagus
D. Urochrome
E. Fruit
D. Urochrome
Urine with a pH of 5.0 is:
A. within normal range; acidic
B. within normal range; alkaline
C. outside normal range; acidic
D. outside normal range; alkaline
E. within normal range; neutral
A. within normal range; acidic
The protein buffer system:
A. generally takes several hours to respond.
B. causes hyperventilation in the respiratory system.
C. is the main buffer system of the interstitial fluid.
D. is the main buffer system of the intracellular fluid
E. all the above are true of the protein buffer system
D. Is the main buffer system of the intracellular fluid
Urine with a pH of 9.0 is:
A. within normal range; acidic
B. within normal range; alkaline
C. outside normal range; acidic
D. outside normal range; alkaline
E. within normal range; neutral
D. outside normal range; alkaline
The bicarbonate buffer system:
A. generally takes several hours to respond.
B. is the main buffer system of the urine
C. is the main buffer system of the interstitial fluid
D. causes hyperventilation in the respiratory system.
E. all the above are true of the bicarbonate buffer system
C. is the main buffer system of the interstitial fluid
The chemical buffer systems:
A. are slow acting, generally taking several hours to respond
B. includes the bicarbonate, phosphate and protein systems
C. can remove acids and bases from the body
D. remove CO2 from the body
E. all the above are true of the chemical buffer systems
B. includes the bicarbonate, phosphate and protein systems
What control mechanism can remove acids and bases from the body?
Renal control (Kidneys)