Plant Reproduction and Seed Development in Angiosperms
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the four whorls of parts in a complete flower?
Calyx, Corolla, Androecium, Gynoecium
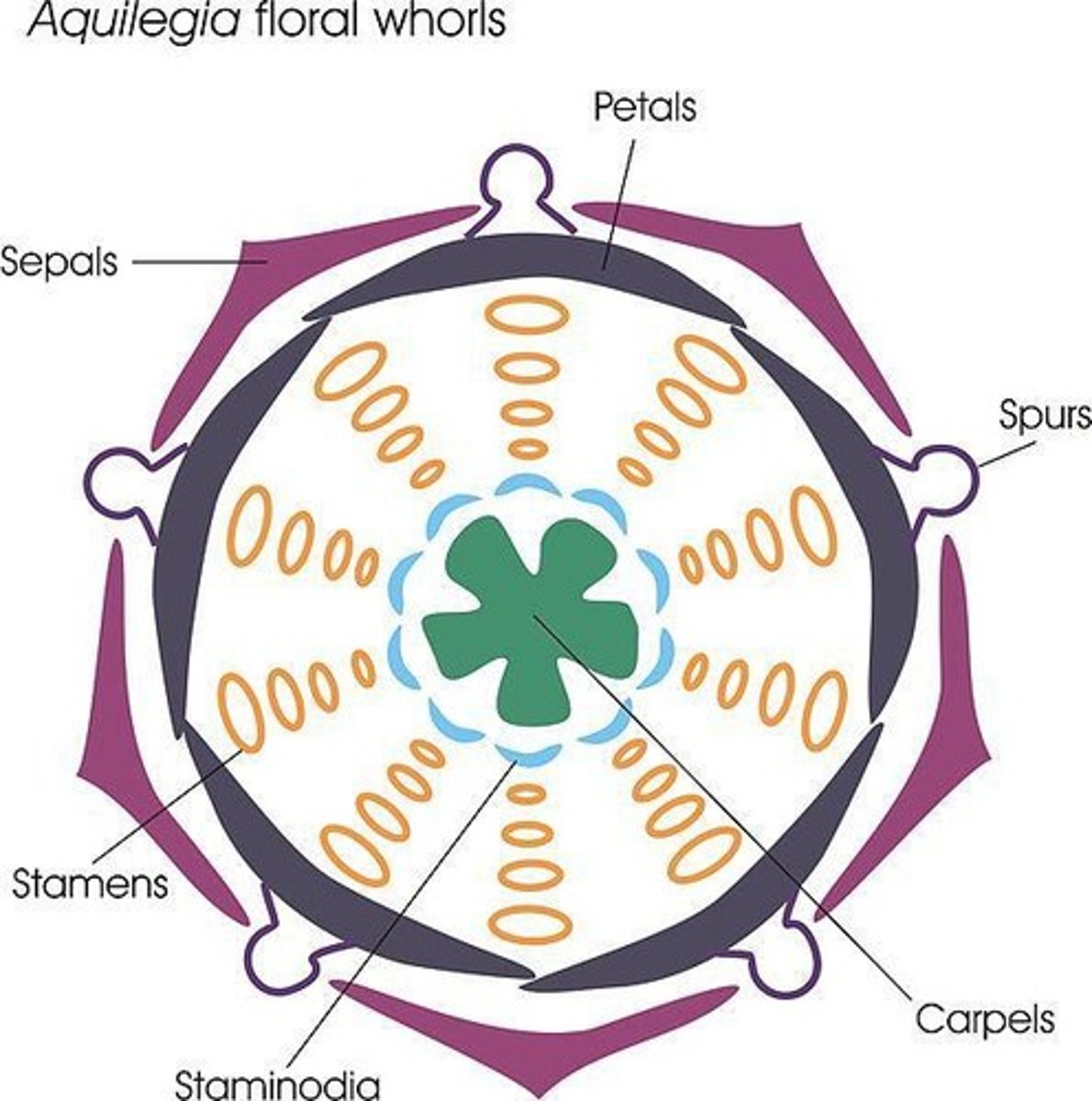
What is the function of the calyx in a flower?
The calyx is the outermost whorl, made up of sepals.
What does the corolla consist of?
The corolla consists of petals.
What is the androecium in flowering plants?
The androecium is the male part of the flower, consisting of stamens.
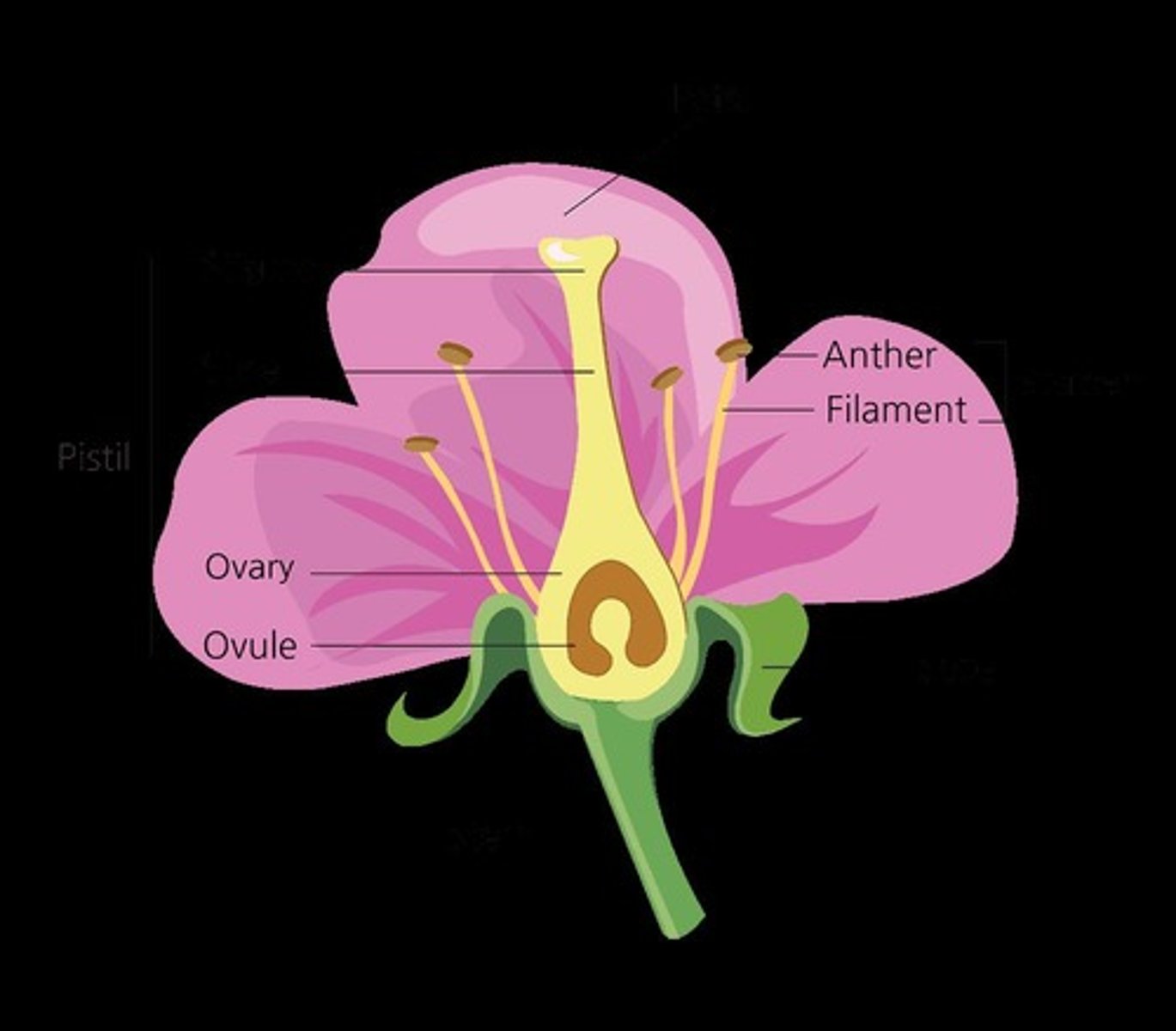
What is the gynoecium in flowering plants?
The gynoecium is the female part of the flower, consisting of carpels.
What percentage of angiosperms are hermaphroditic?
Approximately 87% of angiosperms are hermaphroditic.
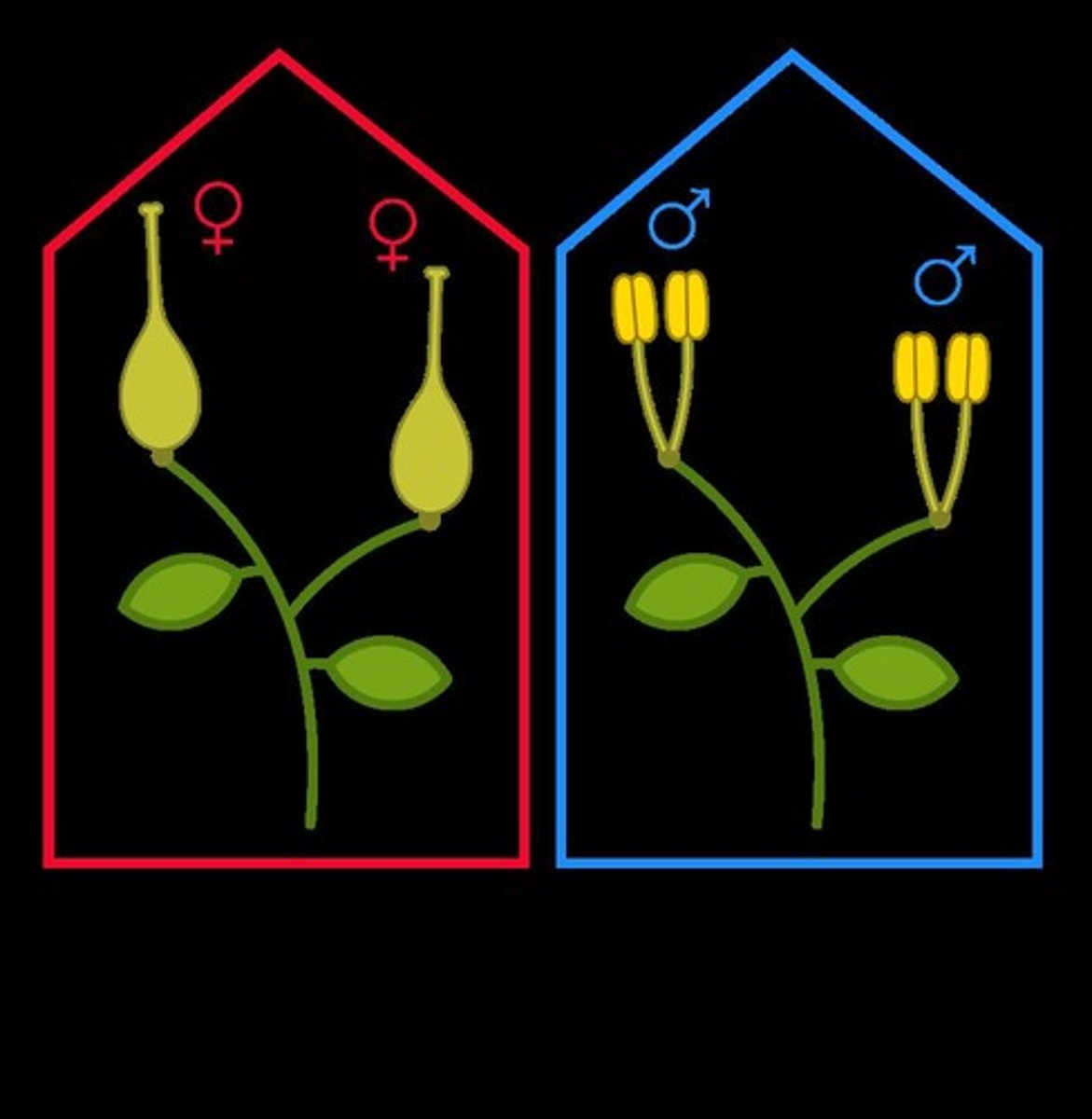
What are monoecious plants?
Monoecious plants have separate female and male flowers on the same plant.
Provide an example of a monoecious plant.
Corn (Zea mays) is an example of a monoecious plant.

What are dioecious plants?
Dioecious plants have separate female and male plants.
Provide an example of a dioecious plant.
Cannabis spp. is an example of a dioecious plant.
What is pollination?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from the stamen to the stigma for sexual reproduction.
What are the two primary pollination systems?
Wind pollination and animal pollination.
What is anemophily?
Anemophily is wind pollination, where pollen is carried by the wind.
What is entomophily?
Entomophily is animal pollination primarily by insects.
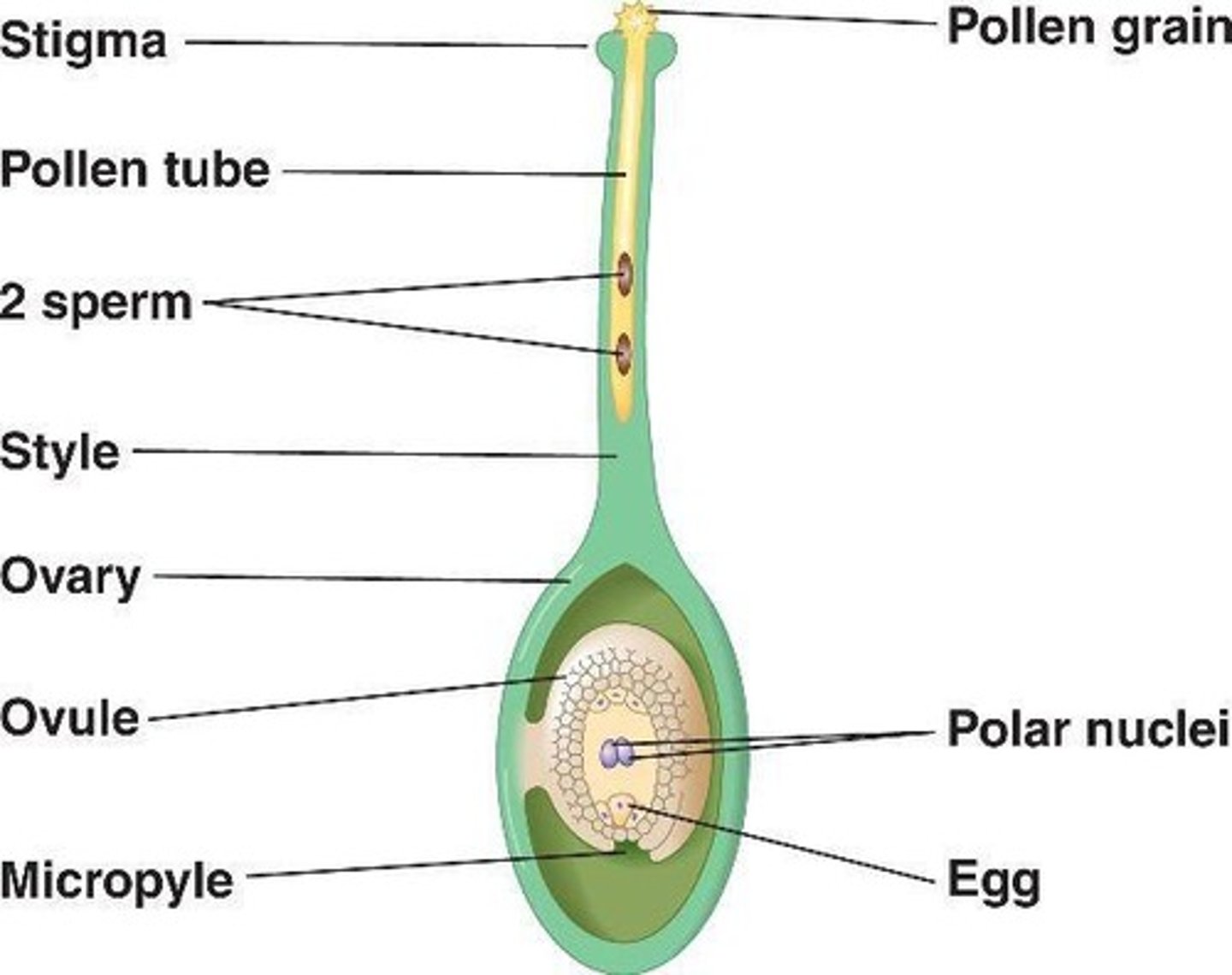
What happens when pollen reaches the stigma?
The pollen tube begins to form, and the generative cell divides into two sperm cells.
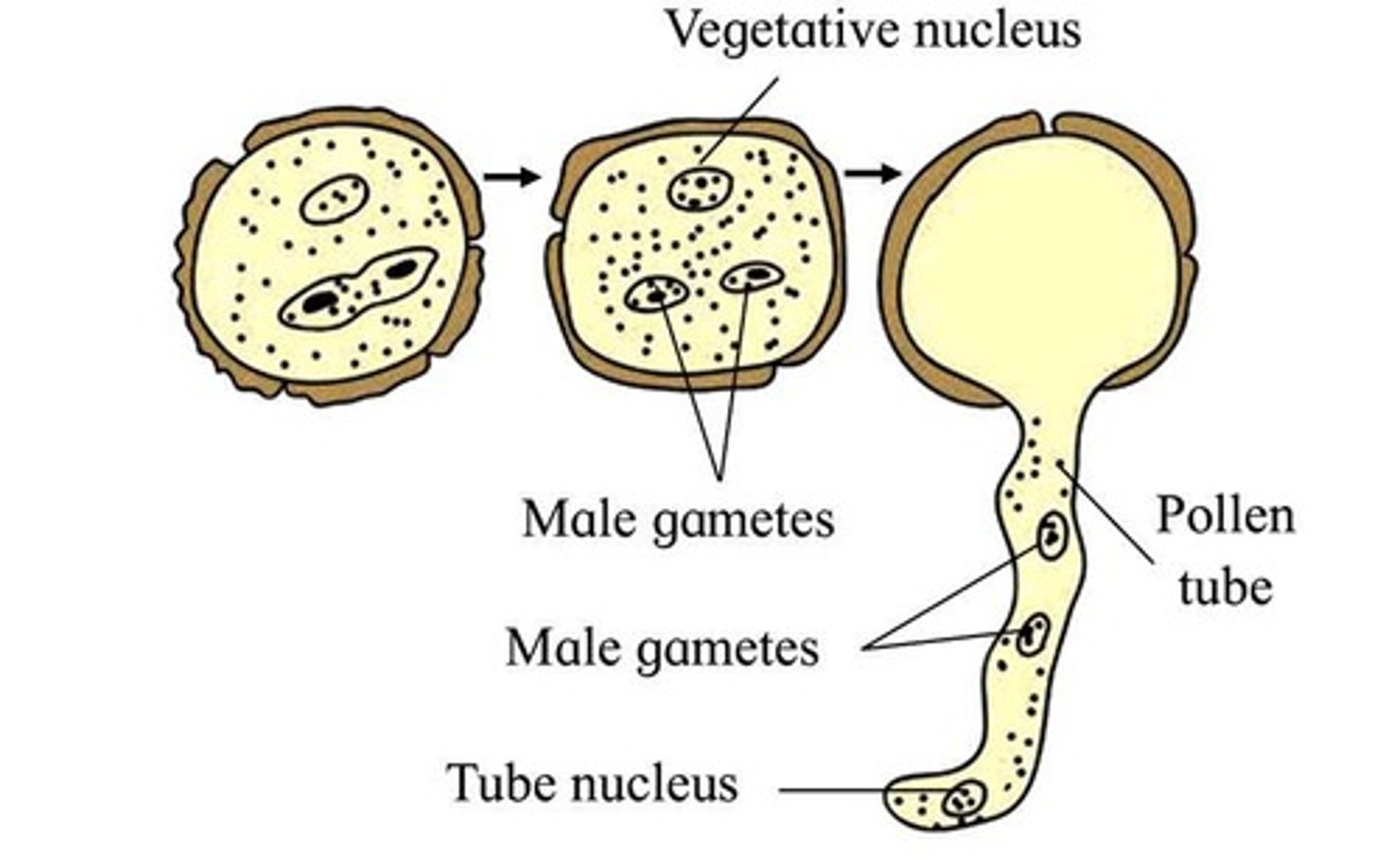
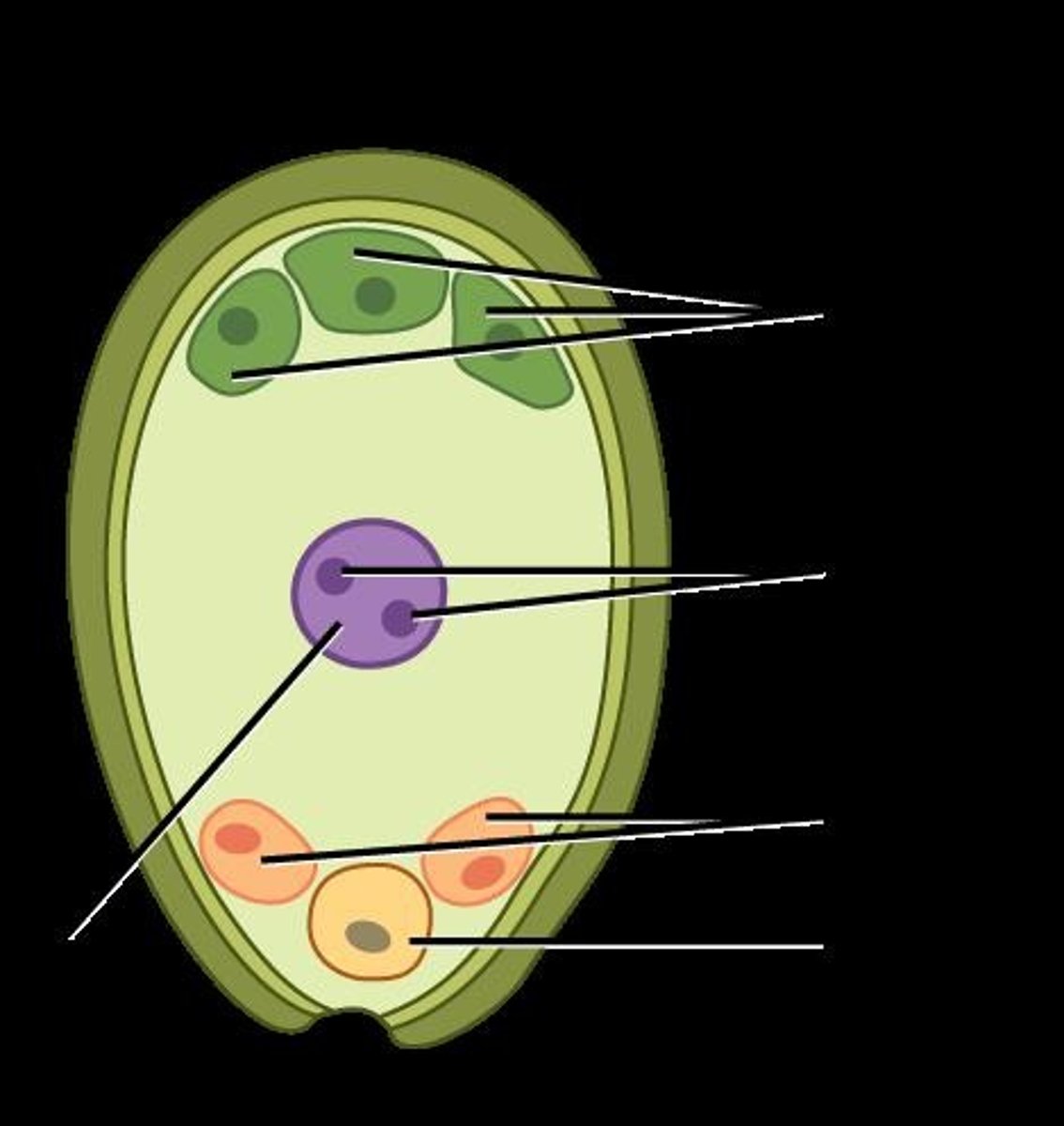
What is the structure of the female gametophyte in angiosperms?
The female gametophyte is a megagametophyte containing 8 nuclei and 7 cells.
What is the role of the first sperm cell during fertilization?
The first sperm cell fuses with the egg cell to form a diploid zygote.
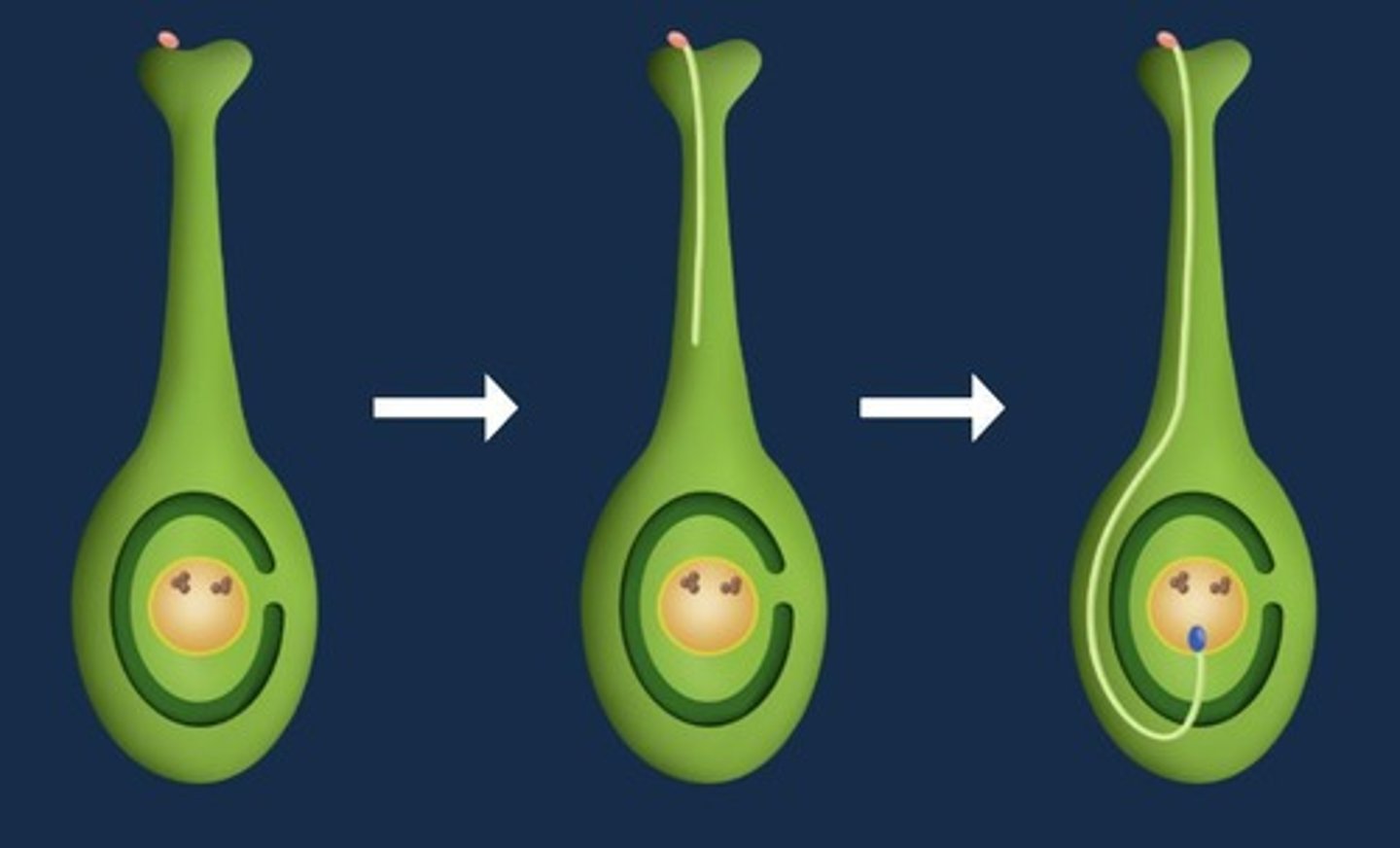
What does the second sperm cell fuse with during fertilization?
The second sperm cell fuses with the polar nuclei to form a triploid endosperm.
What develops from the zygote?
The zygote develops into an embryo, which includes the embryonic root, cotyledon(s), and first true leaves.
What is the pericarp of a fruit?
The pericarp is the part of a fruit that consists of the endocarp, mesocarp, and exocarp.
What are the three types of fruit?
Simple, aggregate, and multiple fruits.
What is a simple fruit?
A simple fruit is one fruit per flower from a single ovary.
What is an aggregate fruit?
An aggregate fruit is one fruit per flower from multiple ovaries.
What is a multiple fruit?
A multiple fruit is one fruit from multiple flowers that fuse together during development.
What are some factors that can control seed germination?
Freezing (cold stratification), fire, light, and time.
Why might seeds have specific germination requirements?
To facilitate dispersal, ensure good conditions, and reduce competition.