NPB101: Reproductive System
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is a viviparous sexual reproductive strategy, and what are its advantages and challenges?
internal fertilization and live birth (develop in oviduct/uterus; mostly in mammals, some fishes, scorpions)
Advantages: protection of the developing embryo inside the body.
Challenges: higher energy investment by the parent, fewer offspring.
Oviparous Sexual Reproduction
Egg-laying (invertebrates and some vertebrates)
Fertilization internal or external
Describe the developmental pathway of male reproductive anatomy.
XY sex chromosomes → testes develop from common gonad precursor
Fetal testosterone secretion → differentiation of internal ducts (epididymis, vas deferens), accessory glands, external genitalia (penis, scrotum)
Antimüllerian hormone causes loss of female internal structures
What hormone causes loss of female internal structures in male development?
Antimullerian hormone
Describe the developmental pathway of female reproductive anatomy.
XX sex chromosomes → ovaries develop from gonad precursor
No early hormone secretion → differentiation of oviducts, uterus, cervix, external genitalia (vagina, labia, clitoris)
Male structures lost due to absence of testosterone
What causes a loss of male structures in female development?
Absence of testosterone
What is the basic anatomy of the testes?
Seminiferous tubules → epididymis → vas deferens → urethra
Sertoli cells: support spermatogenesis
Leydig cells: secrete testosterone
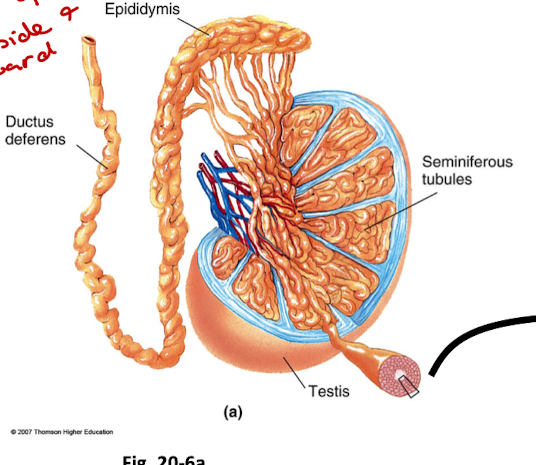
Outline Spermatogenesis and the Role of Sertoli Cells
One diploid spermatogonium → four haploid spermatozoa
Sertoli cells support maturation
form a tight barrier btwn developing sperm and blood
provide nutrients to developing sperm
phagocytose the material leftover from remodeling of spermatids
secrete fluid that washes sperm into the epididymis
secrete androgen binding protein to keep some local testosterone
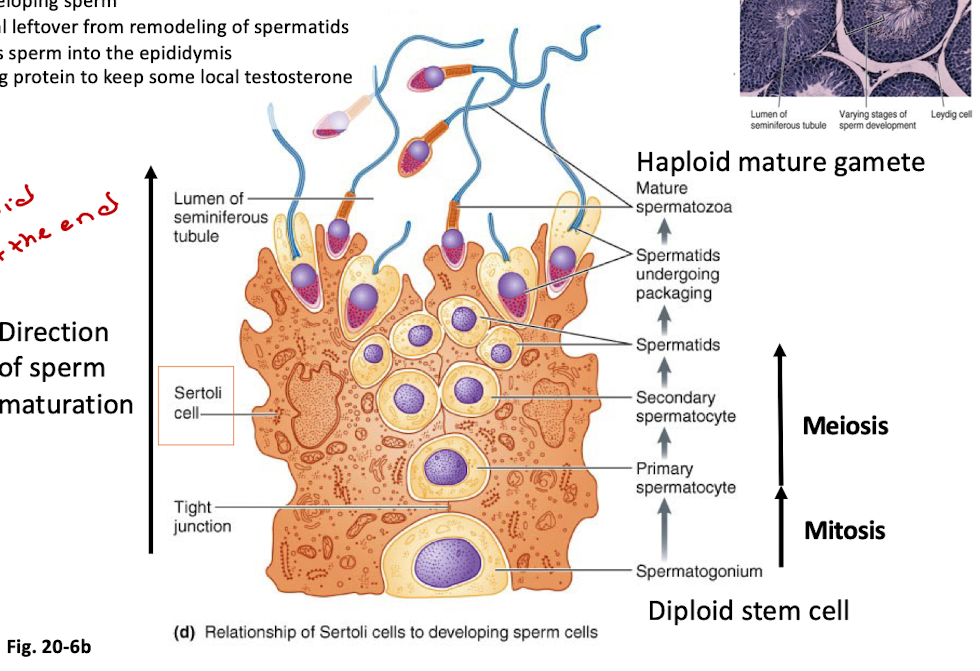
List male reproductive tract glands
Testes
Epididymis
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicles
Prostate gland
Bulbourethral glands
Urethra
Function: contribute fluids, nutrients, and enzymes to semen
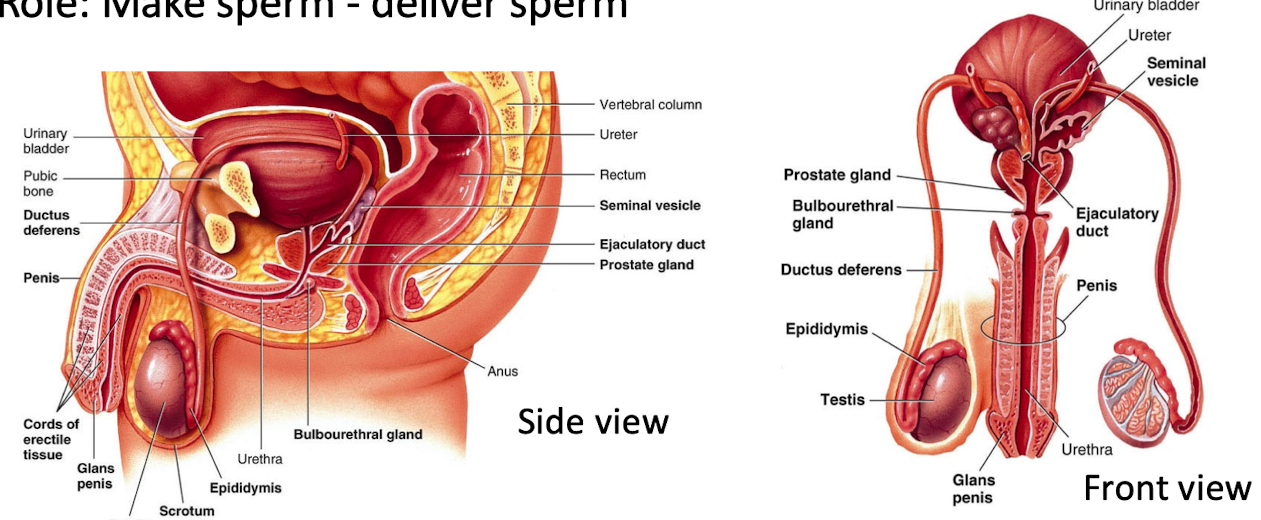
Describe the hormonal regulation of male reproduction.
GnRH (hypothalamus) → stimulates LH & FSH (anterior pituitary)
LH → Leydig cells → testosterone
FSH → Sertoli cells → support spermatogenesis
Sertoli cells → inhibin (inhibits FSH)
Testosterone → local effects (converted to estradiol), systemic effects, feedback inhibition
How does testosterone feedback work in the male brain?
Testosterone inhibits kisspeptin neurons in the hypothalamic "pulse center"
High androgens in females → disrupt pulse center → LH secretion stops → loss of cycles & masculinization
What do male brains lack that female brains have?
Functional surge center
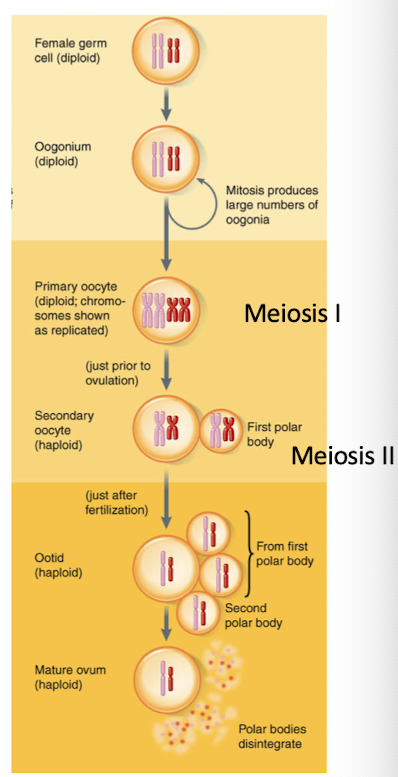
Describe the stages of oogenesis.
Oogonia → primary oocyte (at birth) → secondary oocyte (puberty) → ovum (after fertilization)
One primary oocyte → one ovum + 3 polar bodies
Meiosis starts before birth, arrested in meiosis I
Resumes and arrests in meiosis II until fertilization
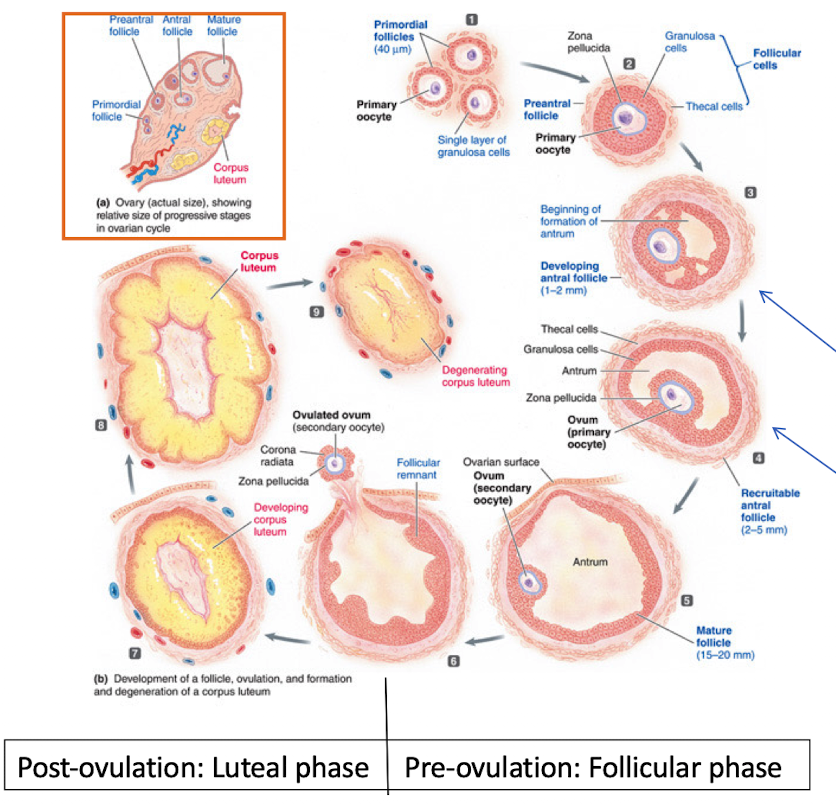
Outline the ovarian cycle.
Follicular phase (pre-ovulation) — days 1-14
Ovulation — day 14
Luteal phase (post-ovulation) — days 15-28
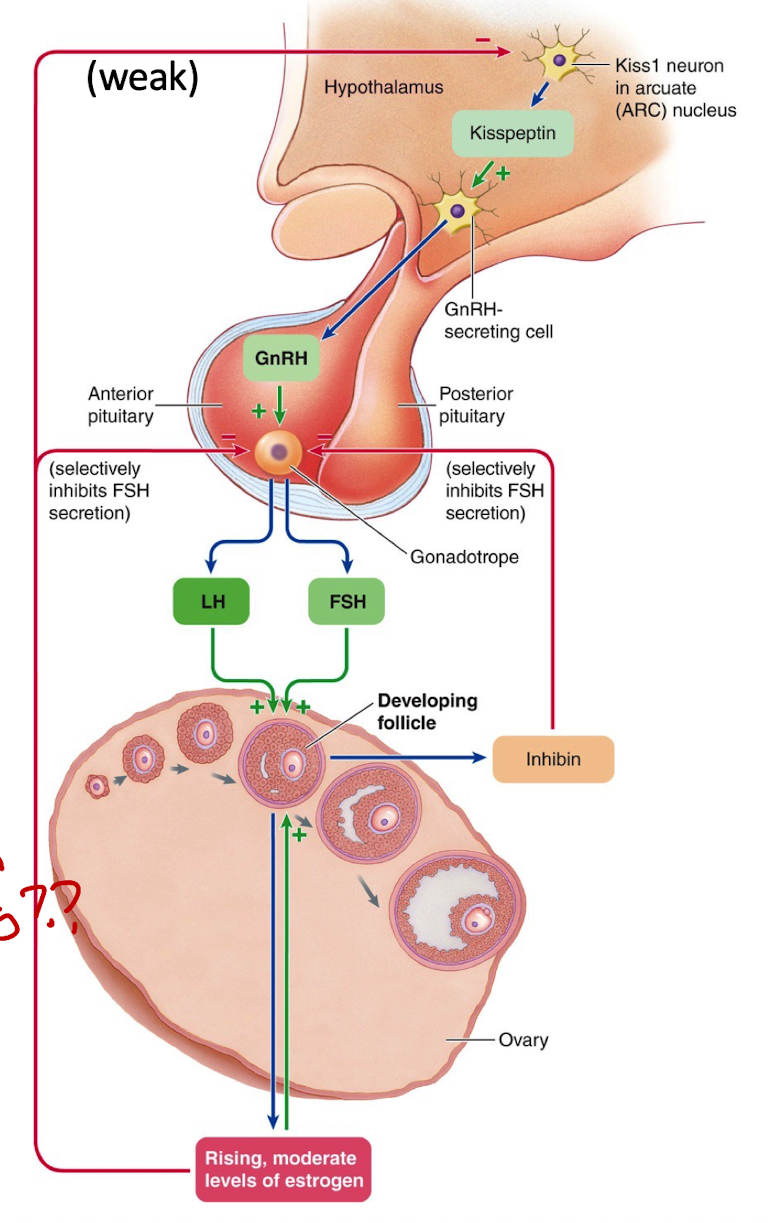
Describe early to mid-follicular hormonal regulation.
LH stimulates thecal cells → produce androgens
FSH stimulates granulosa cells → convert androgens to estradiol (via aromatase)
Granulosa cells also release inhibin, which helps suppress FSH
Estradiol + FSH together help the follicle grow and form the antrum
Low estrogen levels at this stage give weak negative feedback to the hypothalamus (through kisspeptin neurons in the pulse center)
Late follicular phase leading into ovulation
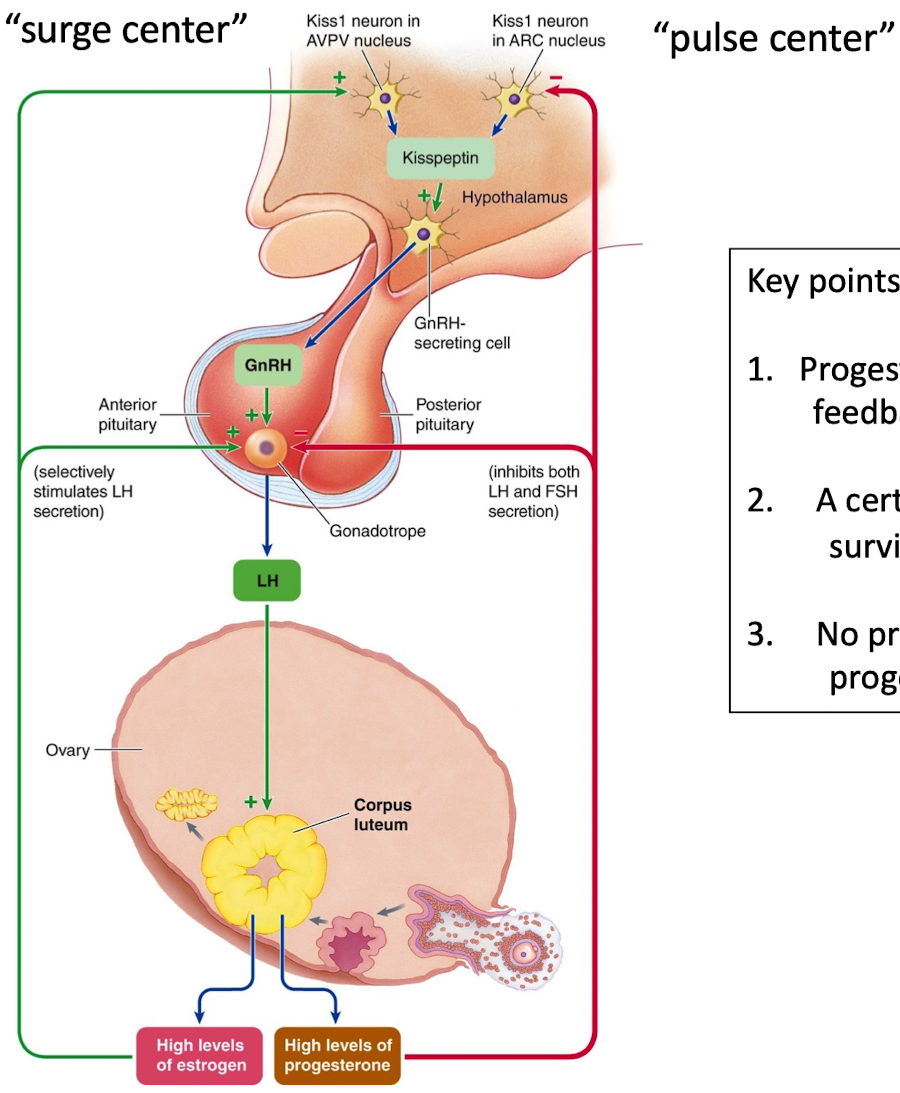
High estrogen causes positive feedback via kisspeptin “surge center” in the hypothalamus
Surge of GnRH → LH surge and smaller FSH surge from anterior pituitary → ovulation
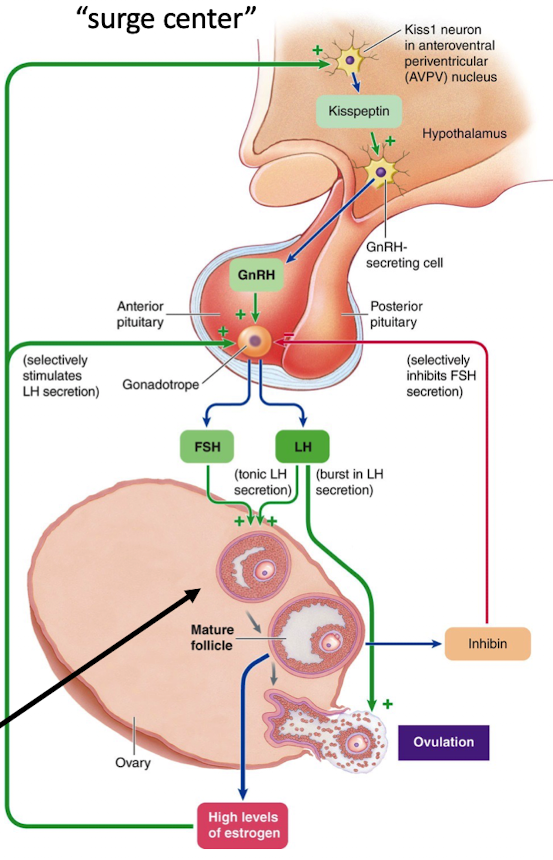
What does LH do in late follicular phase to ovulation hormonal changes?
Promotes follicle rupture
Ovum Release (ovulation)
Corpus luteum (CL) formation
What does corpus luteum (CL) do in late follicular phase to ovulation hormonal changes?
Secrete progesterone and estradiol
What occurs during the Luteal Phase?
Progesterone → inhibits GnRH, LH, FSH, and kisspeptin surge center to prevent another ovulation
Prevents second LH surge (prevents second ovulation)
CL depends on LH, dies if LH drops if no fertilization
Menstruation begins once progesterone and estradiol levels drop
Describe the phases of the uterine cycle
Proliferative phase
Secretory phase
Menstrual phase
Uterine Cycle: Proliferative Phase
Follows follicular → endometrial growth
Uterine Cycle: Secretory Phase
Luteal → nutrient/gland development
Uterine Cycle: Menstrual Phase
Hormone drop → shedding
What are systemic effects of estrogen (estradiol)?
Endometrium growth
Mammary gland growth
Growth plate fusion and bone density maintenance
Permissive for actions of progesterone (estrogen stimulates transcription receptor gene to make more progesterone)
What are systemic effects of high levels of progesterone?
Uterus: Inhibits estrogen induced growth
Induces endometrial environment secretion to implantation (glycogen)
Inhibits uterine contractions
Forms cervical mucus plug to oppose sperm entry
Maintains endometrium for pregnancy
endometrial lining collapses and is lost
Ovulation inhibited due to negative feedback of GnRH and LH secretion
What happens if fertilization and implantation occur?
Embryo secretes hCG → maintains corpus luteum (CL)
corpus luteum (CL) continues progesterone and estradiol production
Placenta later takes over hormone production (independent of LH/hCG)
LH (luteinizing hormone) remains low during pregnancy
When is the peak function of CL post ovulation?
6-7 days
When is the presence of healthy enough CL post-ovulation?
10-12 days
What happens to CL in the absence of fertilization?
accelerated decline after 10 days, lost by 13-14 days.
What secretes testosterone in males, and what hormone stimulates its secretion?
Leydig cells in the testes
Stimulated by luteinizing hormone (LH)
What does testosterone, secreted by Leydig cells in males, inhibit through negative feedback?
GnRH from the hypothalamus/pulse center
LH from the anterior pituitary
→ This reduces further testosterone production
What secretes inhibin in males, and what stimulates it?
Secreted by Sertoli cells in the testes
Stimulated by FSH
What does inhibin, secreted by Sertoli cells in males, inhibit?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary
→ Selectively reduces FSH without affecting LH or GnRH
What secretes estradiol in females, and what stimulates it?
Secreted by granulosa cells in ovarian follicles
Stimulated by FSH and conversion of androgens (from thecal cells via aromatase)
What do low levels of estradiol (estrogen) in females inhibit through negative feedback?
GnRH pulses (via kisspeptin neurons in pulse center)
FSH, especially in combination with inhibin
→ This helps limit recruitment of additional follicles
What do high levels of estradiol in females trigger, and how is this feedback different?
Triggers positive feedback on:
GnRH pulse frequency
LH secretion → leads to LH surge
→ This induces ovulation
What secretes progesterone and under what conditions?
Secreted by the corpus luteum in the ovary
After ovulation, in response to LH
What does progesterone secreted by the corpus luteum inhibit?
GnRH, LH, and FSH secretion
Kisspeptin neurons in both pulse and surge centers
→ Prevents another LH surge and ovulation during the luteal phase.
What does inhibin, secreted by granulosa cells in females, inhibit?
FSH from the anterior pituitary
→ Helps limit recruitment of new follicles during the late follicular phase.
What do high levels of androgens in females inhibit?
GnRH and LH secretion
Via inhibition of kisspeptin neurons in the hypothalamic pulse center
→ Can stop cycling and promote male secondary sex characteristics.
What’s a common feature Leydig cells of the testes and thecal cells of the ovaries?
They synthesize testosterone under the control of LH
Where does fertilization of the embryo occur?
Ampulla region of the oviduct/Fallopian tube
After fertilization, where does implantation of the embryo occur?
Endometrium of the uterus
How long does it usually take for an embryo to travel and implant in the endometrium after fertilization?
6-7 days
Effects of Testosterone before birth
Differentiation of the reproductive tract and external genitalia
Promotes descent of the testes into the scrotum
Effects of Testosterone on Sex-Specific Tissues after Birth
Promotes growth and maturation of the reproductive system at puberty
Is essential for spermatogenesis (conversion to estradiol)
Maintains the reproductive tract throughout adulthood
Other Reproduction-Related Effects of Testosterone
Develops the sex drive at puberty
controls gonadotropin hormone secretion
Effects of Testosterone on Secondary Sexual Characteristics
Induces the male pattern of hair growth
Deepens voice
Promotes muscle growth responsible for the male body configuration
Non-reproduction actions of testosterone
Exerts a protein anabolic effect
promotes bone growth at puberty
closes epiphyseal plates
induces aggressive behavior
Hormone Secretion Patterns during Pregnancy
Increased prolactin secretion at end of pregnancy
caused by decrease in hypothalamic dopamine and estrogen stimulation of prolactin synthesis
Increased oxytocin receptors in uterus and mammary glands
caused by positive feedback with estrogen