APHG Unit 2 CED Vocabulary - Population + Migration
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
population distribution
the pattern of people scattered over an area
population density
the number of people within a given area
human factors
culture, economics, history, politics
physical factors
climate, landforms, water bodies
ecumene
the habitable parts of the world
population density
measure of total population relative to land size
arithmetic population density
measure of the number of people within a given area divided by the total land area
physiologic population density
measure of the number of people per arable (farmable) land
agricultural population density
measure of the number of farmers per arable land
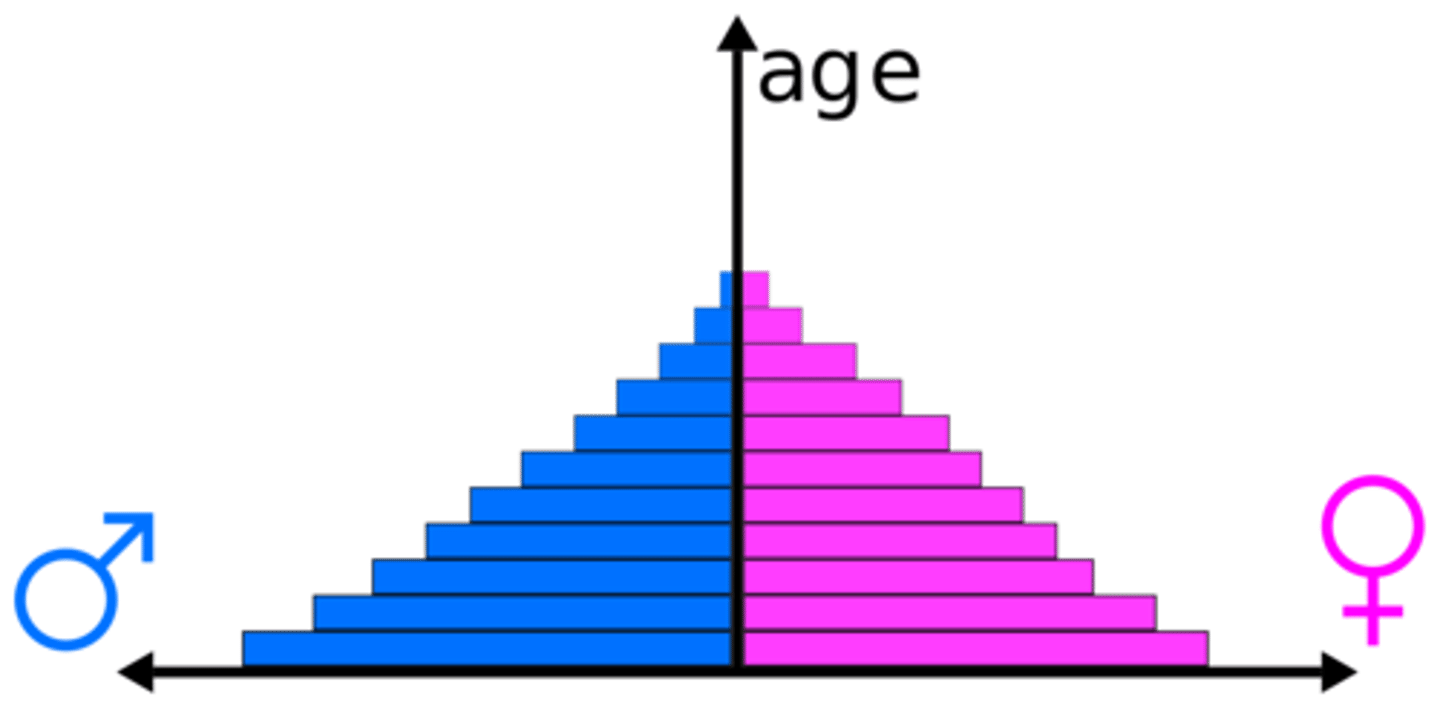
population pyramid
provides a visual representation of a population in terms of age and sex as well as a good indication of the dependency ratio within a country and is used to assess population growth and decline and to predict markets for goods/services
total fertility rate (TFR)
the average number of children a woman will have during her childbearing years (15-49)
birth rate
number of live births in a single year for every 1000 people (in a population)
replacement fertility level
2.1 (slightly higher than 2.0 to account for infant/childhood mortality/childless women)
mortality (death) rate
number of deaths in a single year for every 1000 people (in a population)
infant mortality rate
number of deaths during the 1st year of life (per 1000)
child mortality rate
number of deaths of between the ages of 1 and 5 (per 1000)
maternal mortality rate
number of deaths during or shortly after childbirth (per 100,000)
migration
involves a degree of permanence when moving to a new locale
emigration (out migration)
describes movement out of a particular place
immigration (in migration)
describes movement to a particular place
natural increase
birth rate minus death rate
population doubling time
the length of time for a population to double in size
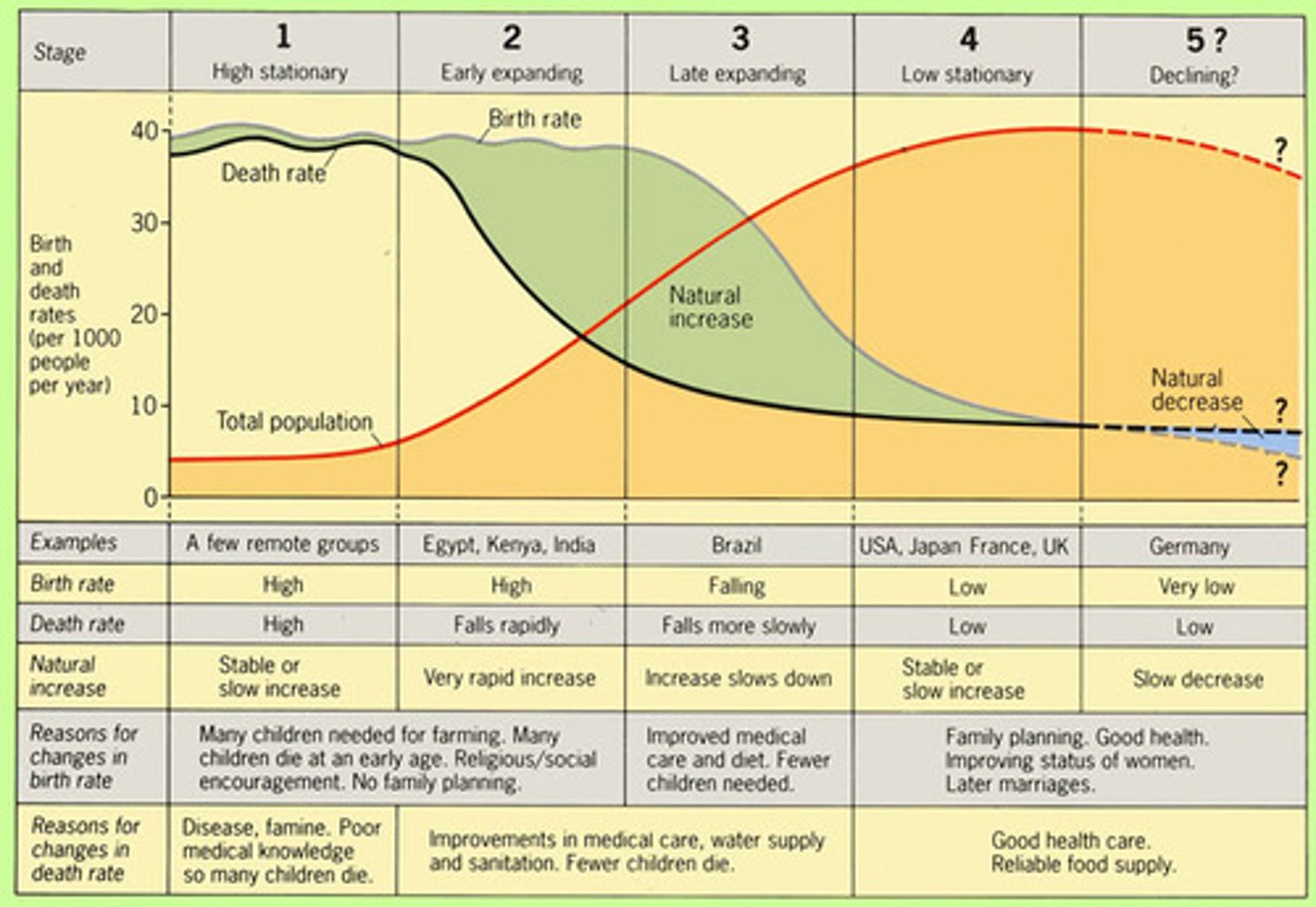
Demographic Transition Model
describes the relationship between population and the development of a country and can be used to explain population change over time
epidemiologic transition (mortality revolution)
increase in population due to medical innovation (modern medicine) causing a decrease in the death rate
population explosion
the very great and continuing increase in human population in modern times
Thomas Malthus (1798)
argued that the size and growth of a population depends on the food supply and agricultural methods AND when there is an insufficient supply of food, people die

Ester Boserup (1965)
theorized that people will find ways to increase food production and improve agricultural methods in times of pressure

pro-natalist population policies
policies that provide incentives for women to have children, typically in countries with declining populations: Japan, Singapore, Denmark, Germany, Italy
anti-natalist population policies
policies that encourage couples to limit the number of children they have
immigration policies
policies that address the movement of persons across borders
Ravenstein's laws of migration (1885)
every migration flow generates a return migration flow, most migrants move a short distance, migrants who, move longer distances tend to choose big-city destinations, most migrants are from rural areas, migration is caused mostly by economic reasons
population aging
determined by birth rates, death rates, and life expectancy
life expectancy
average number of years an infant newborn can expect to live; number varies within countries, cities, ethnicities, sexes, and between MDCs and LDCs
aging population
an increasing median age in the population due to declining fertility rates/rising life expectancy
dependency ratio
a measure of the economic impact of younger and older cohorts on the economically productive members of a population
pull factors (migration)
characteristics that attract a person to a place
push factors (migration)
characteristics that make a person want to leave a place
intervening opportunity
the presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away
intervening obstacle
an event or obstacle that discourages people from migrating
genocide
premeditated effort to destroy a national, ethnic, racial, religious group e.g. Rwanda, Holocaust, Cambodia
ethnic cleansing
the effort to rid a country/region of a particular ethnicity either through forced migration or genocide, e.g. former Yugoslavia
forced migration
an individual migrates against his/her will, including events that produce slaves, refugees, internally displaced persons, and asylum seekers
refugee
individuals, protected by law, who cross national boundaries to seek safety from armed conflict or persecution
asylum seeker
individuals who flee their home country and applies for protection, but their request for sanctuary has yet to be processed, once processed, they are either given refugee status or refused and returned to their home country
internally displaced person (internal refugee)
individuals who leave their home due to conflict, human rights abuse, war, or environmental catastrophes, but do not leave their country to seek safety
voluntary migration
an individual chooses to move, typically based on various push-pull factors
transnational migration
migration across national boundaries
internal migration
migration within national boundaries
transhumance
seasonal movement of pastoral nomads who move livestock between summer and winter pasture
chain migration
immigrants who follow family and/or friends to the same destination.
step migration
migration to a distant destination that occurs in stages (steps)
guest workers
a person with temporary permission to work in another country (e.g. migrant labor)
rural to urban migration
the movement of people from the countryside to the city which causes two things to happen; increasing proportion of people living in towns and cities and expansion of urban areas
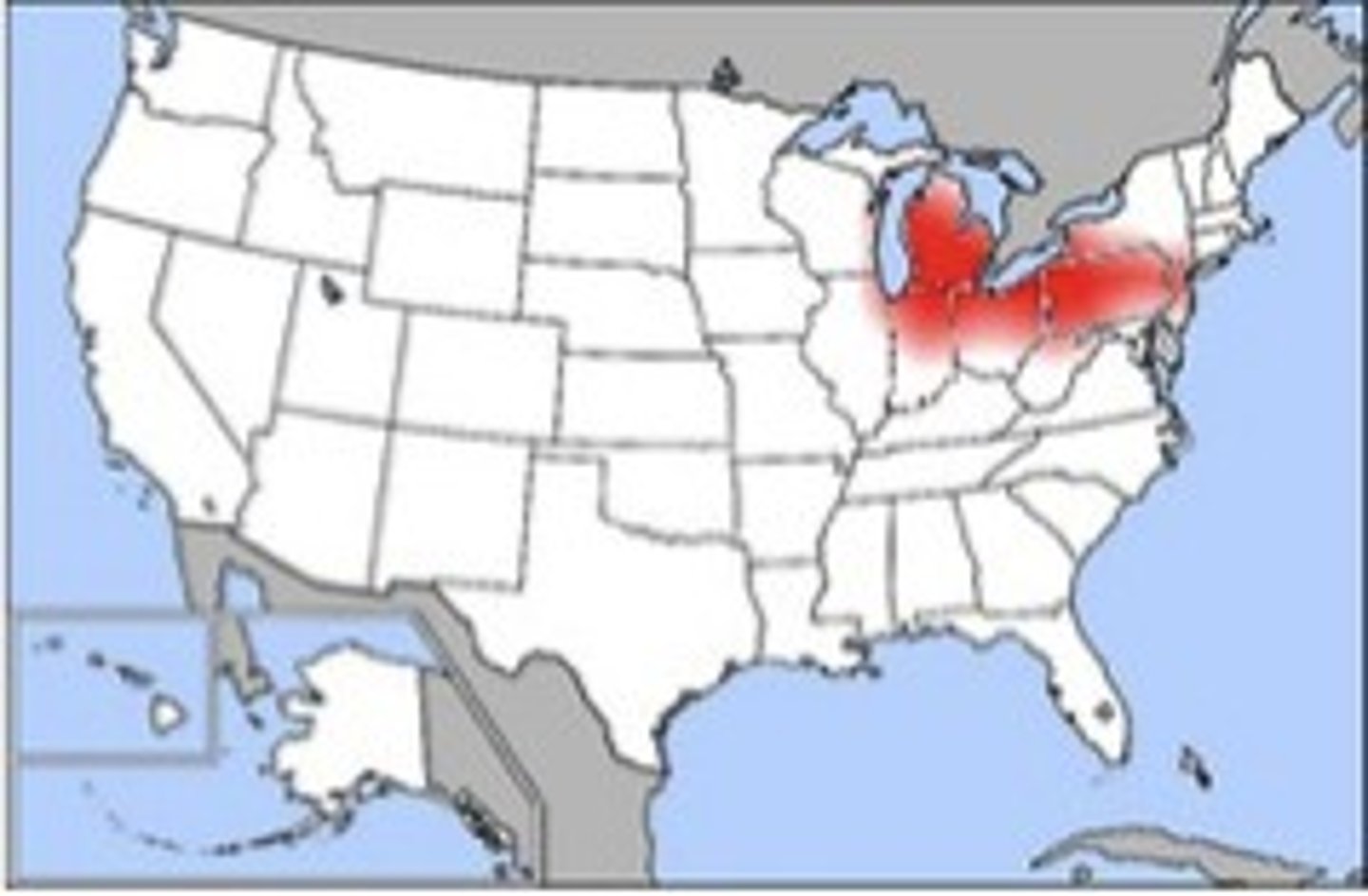
Rust Belt
area in the upper Midwest that had been an industrial powerhouse, but lost much of their economic base to other parts of the country and other parts of the world
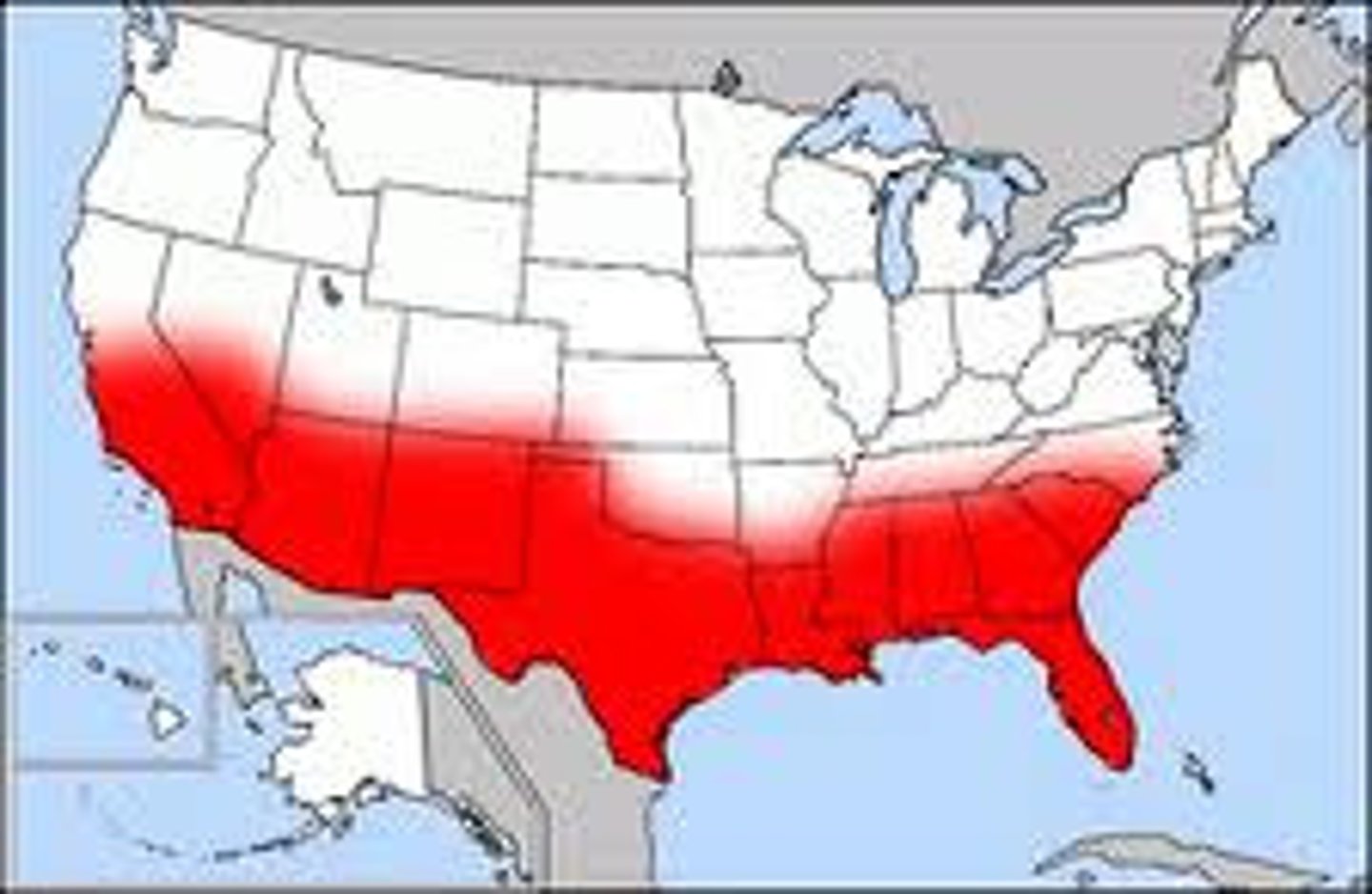
Sun Belt
the states in the South and West Coast where in the 1960s and 1970s, large numbers of white, middle-class Americans moved from older northeastern and Midwestern cities