post atd
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Atificial Ventilation
Ventilation that requires energy
Active Ventilation
another term for artificial ventilation
2.4 meters
minimum ceiling height for atificially ventilated spaces
For faster process of cooling a space. (Lesser volume, faster cooling)
Why are standard ceiling heights lower in artificially ventilated spaces?
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
HVAC
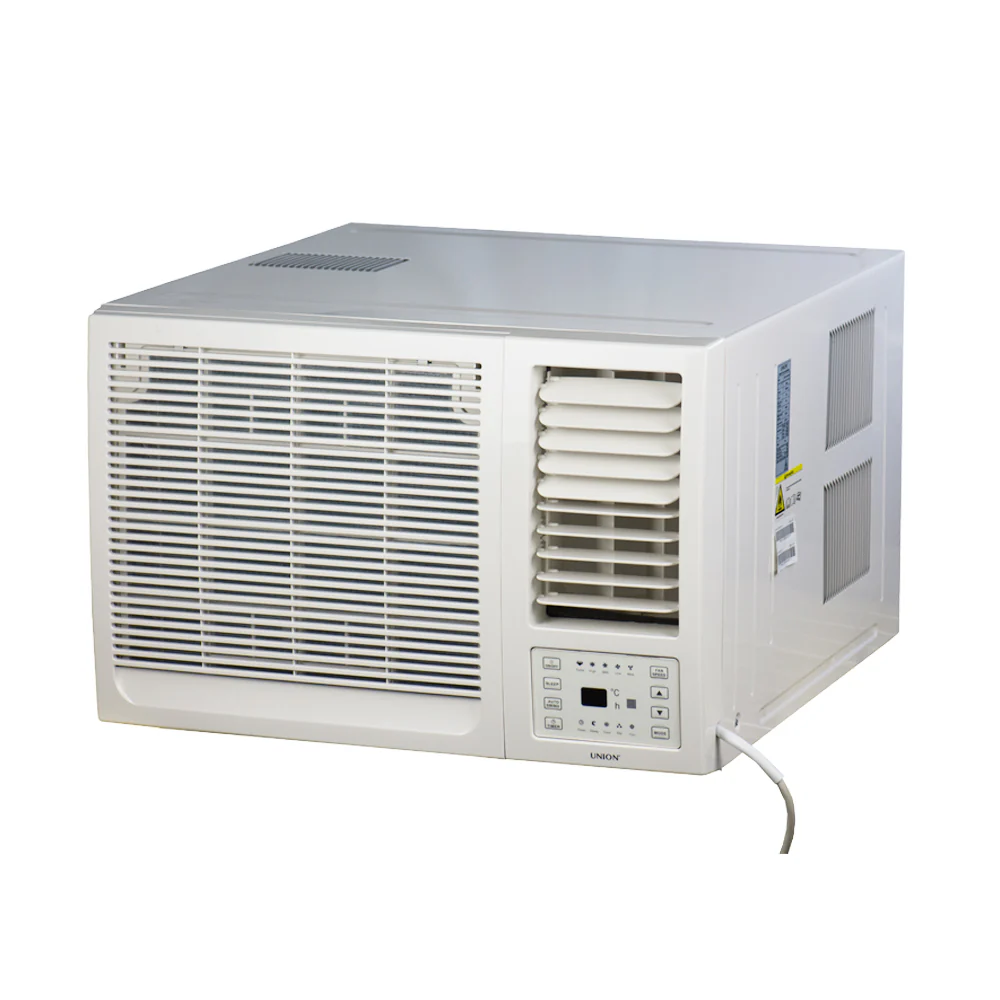
Window-type aircon

Cabinet-type aircon

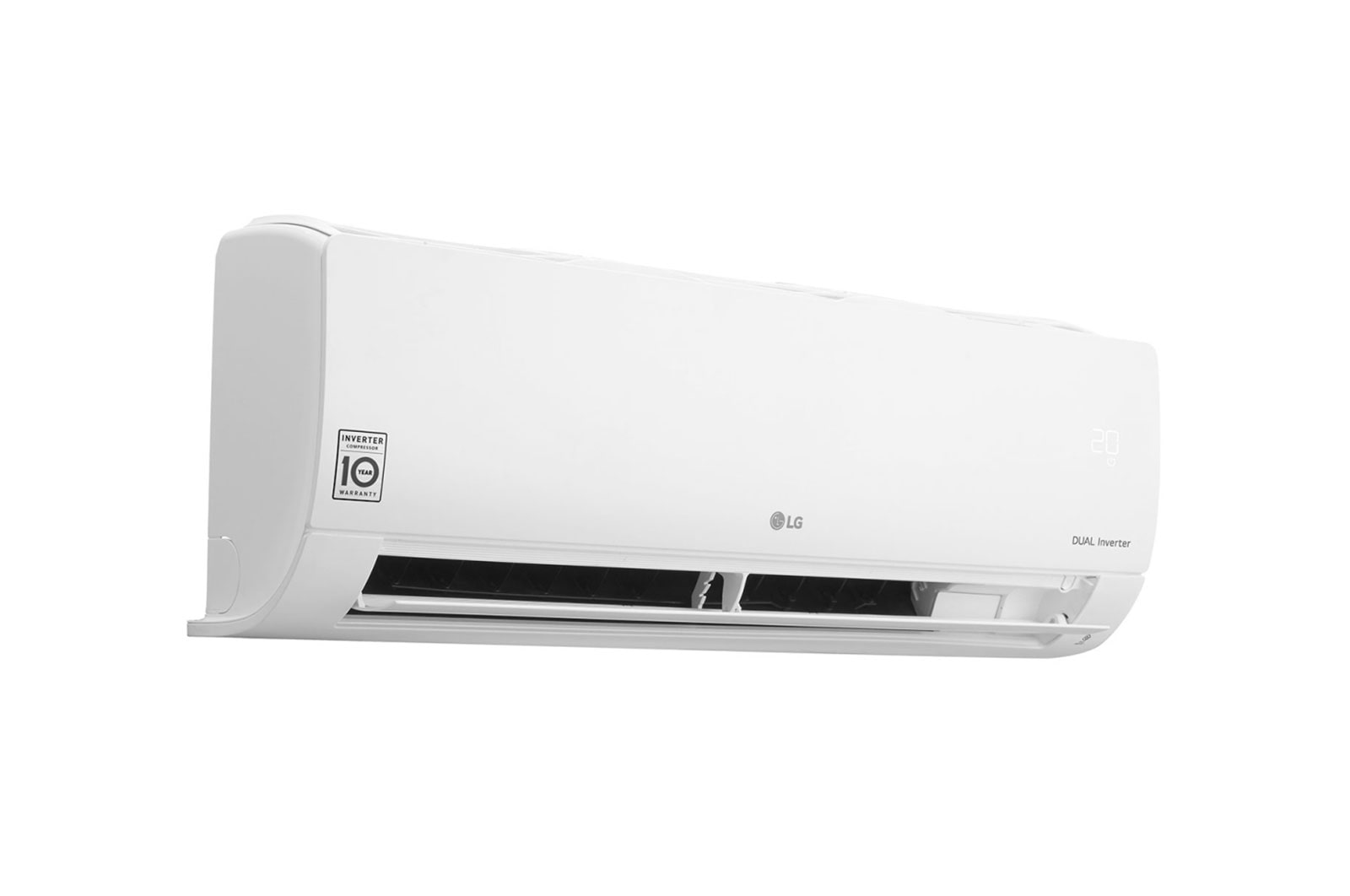
Split-type aircon

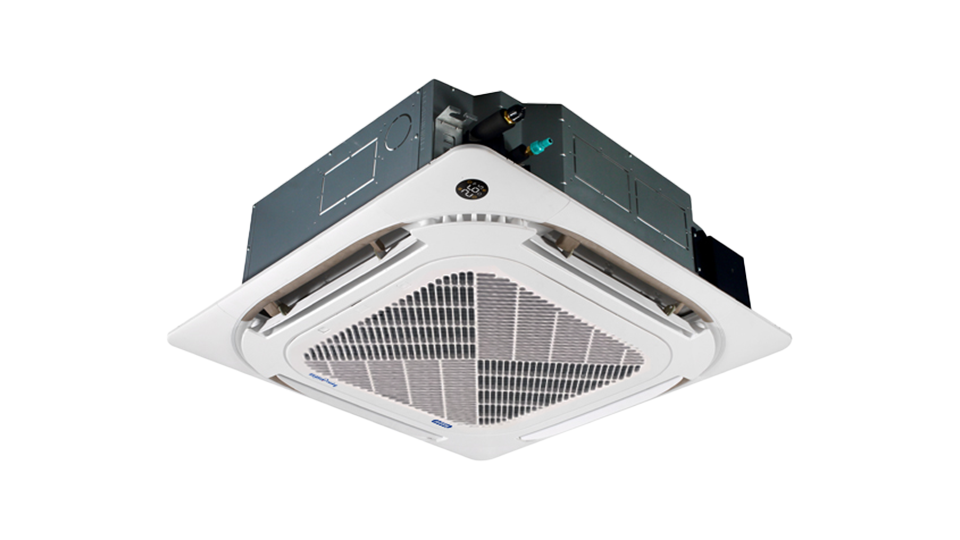
Cassette-type aircon

Energy Efficiency Ratio (ERR)
Identifies an aircon’s rating of energy consumption (Higher rating = Lesser energy consumption)
Naatural Ventilation
Ventilation that does not require energy to work
Passive Ventilation
Another term for natural ventilation
2.7 meters
minimum ceiling height for naturally ventilated spaces
Primarily to separate hot air from spaces that are accessible to users (hot air circulates upwards). Also, for better air circulation.
Why are standard ceiling heights higher in naturally ventilated spaces?
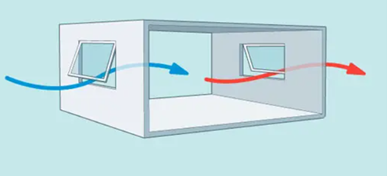
Cross-ventilation
2-opposite windows in a single space
Single-sided ventilation
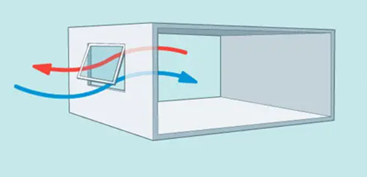
2 separate
Wind Catcher (Concrete Ledge)
an exterior element that helps redirect wind into the windows.

Stack effect Ventilation
Use of hot air pressure to suction heat from the building outside through a space in the middle called the atrium.
Mostly used in high-rise buildings
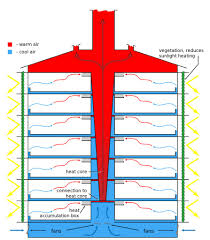
Chimney Effect ventilation
Another term for Stack effect Ventilation
Courtyard Ventiltion
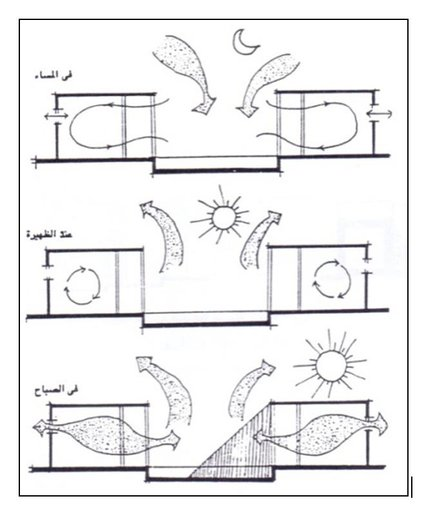
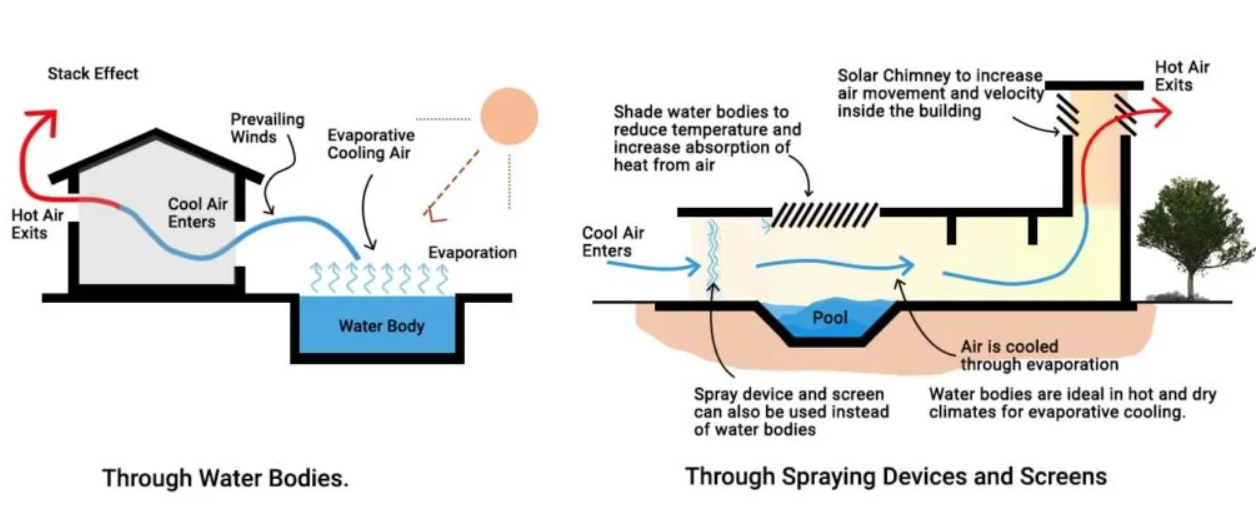
Evporative Cooling
Use of any forms of water through evaporation to cool the building
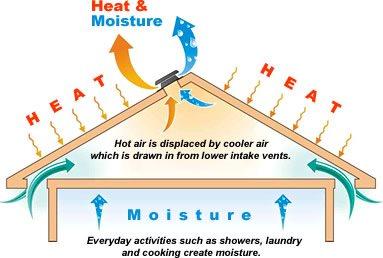
Roof Ventilation
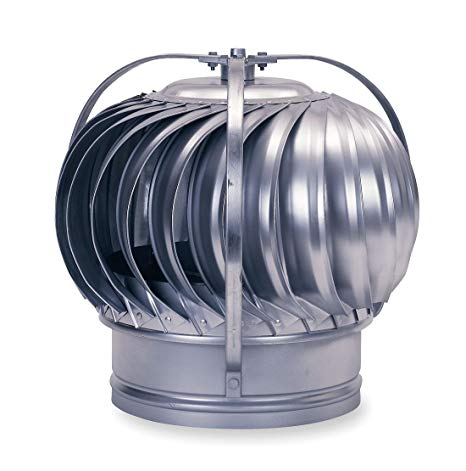
Turbine Ventilator
A device spins by using the force of the wind and utilizing that spinning motion to act on a fan that suctions hot air from the roof outside to the air.
Not recommended by Sir Sotto
