Economics of Taxation: Deadweight Loss, Revenue, and the Laffer Curve
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the deadweight loss of taxation?
The loss in total surplus due to the tax, which reduces both consumer and producer surplus.
How does a tax affect total surplus?
Without a tax, total surplus is maximized at equilibrium; with a tax, total surplus equals consumer surplus plus producer surplus plus tax revenue.
What is the formula for tax revenue?
Tax revenue = Tax size × Quantity sold.
What happens to market participants when a tax is imposed?
The price paid by buyers increases, the price received by sellers decreases, and the quantity sold falls.
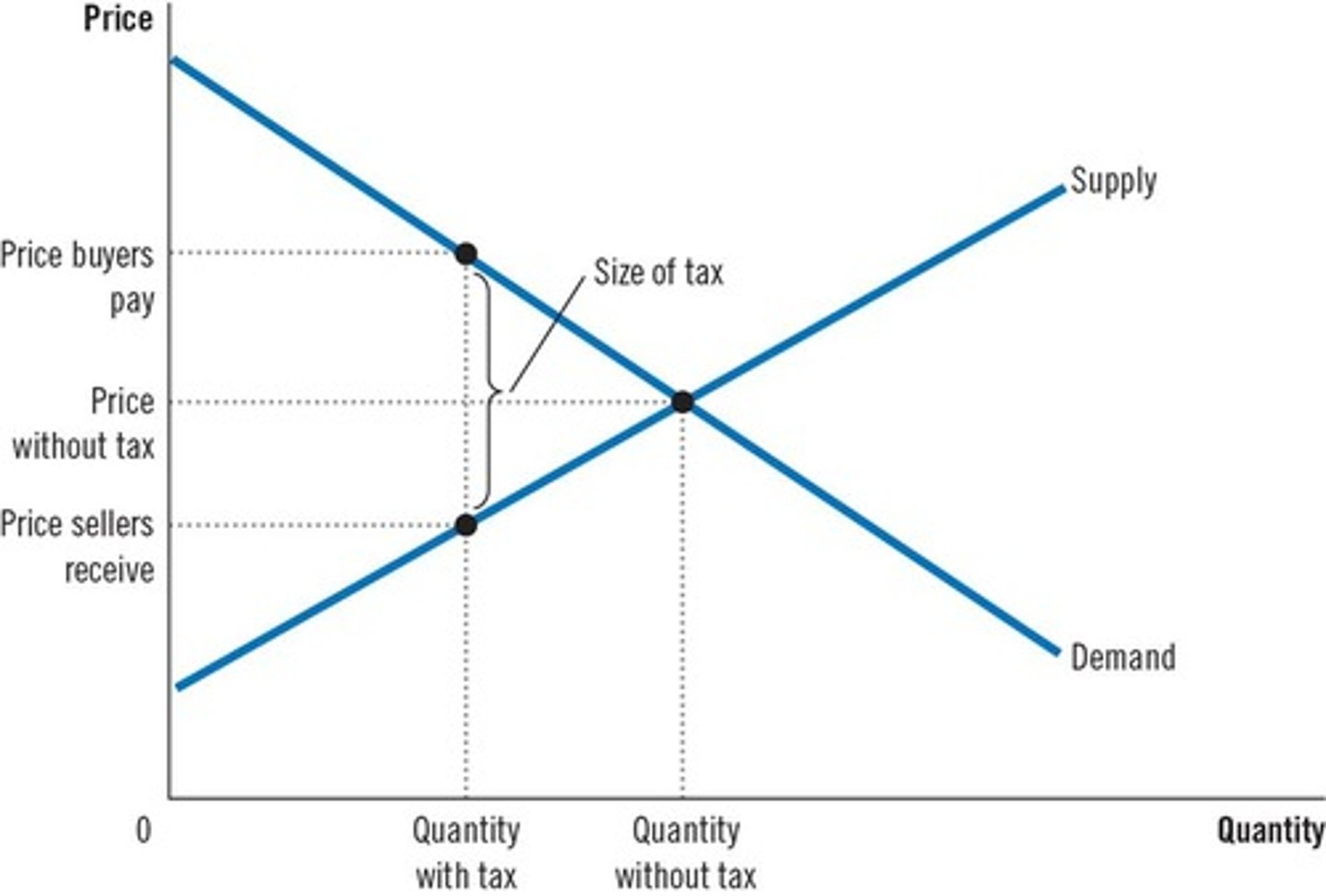
Why do taxes cause deadweight losses?
Taxes prevent buyers and sellers from realizing some gains from trade.
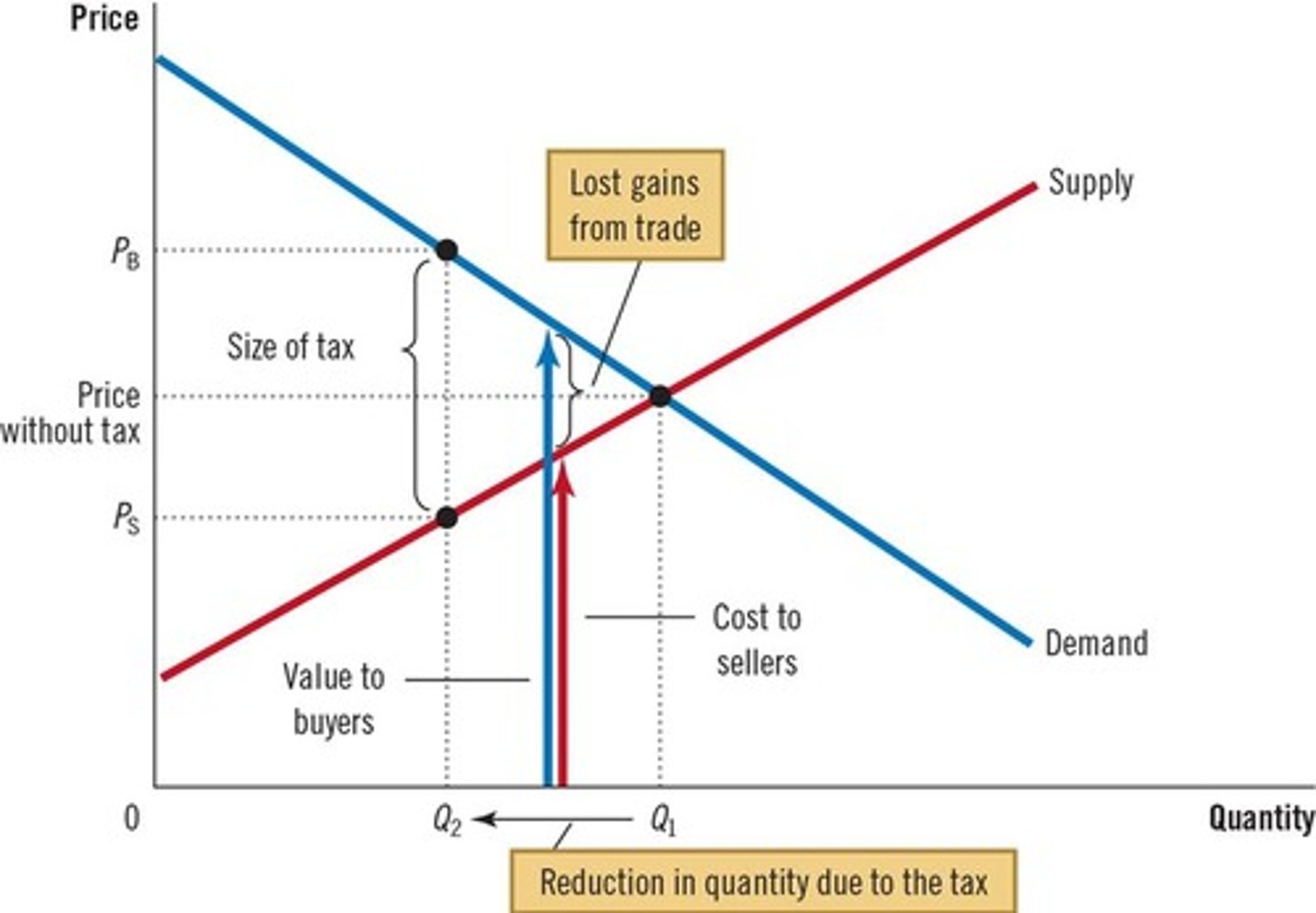
What factors increase deadweight loss?
More elastic supply or demand curves lead to larger deadweight losses.
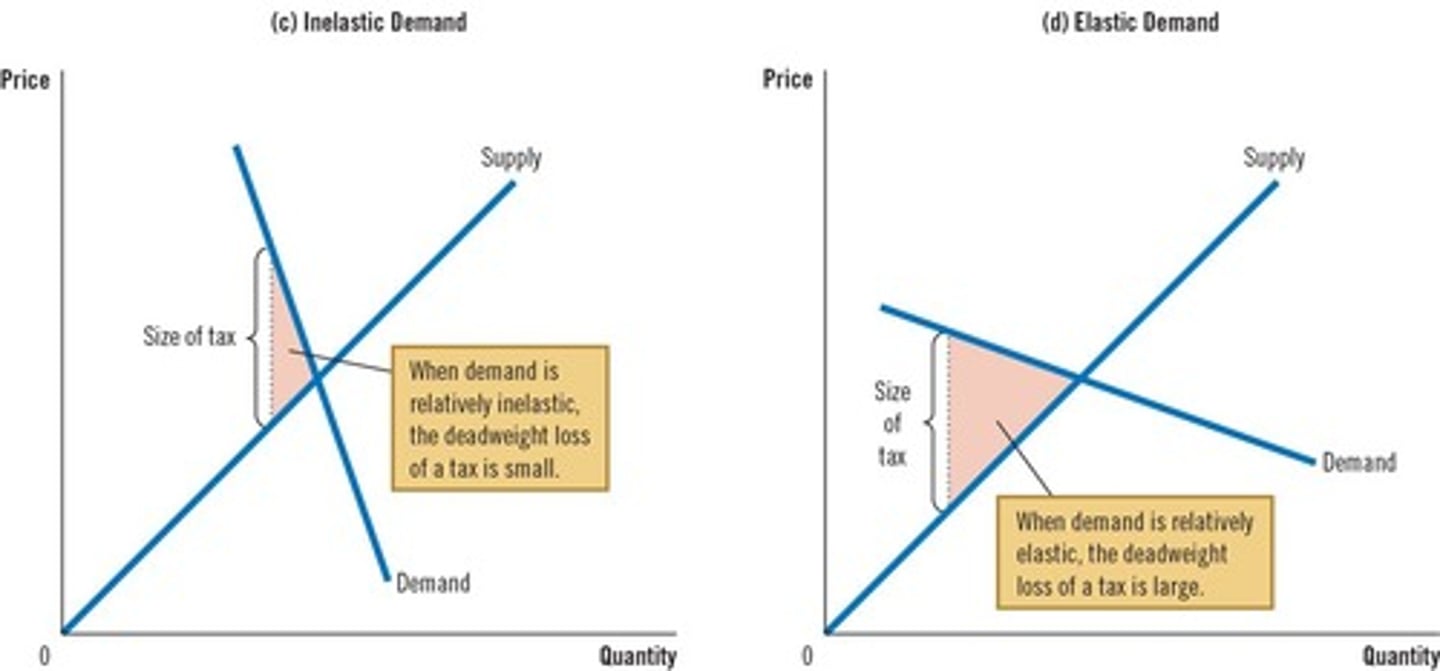
What is the relationship between tax size and deadweight loss?
Initially, a small tax raises revenue with little deadweight loss, but as the tax size increases, deadweight loss grows faster than tax revenue.
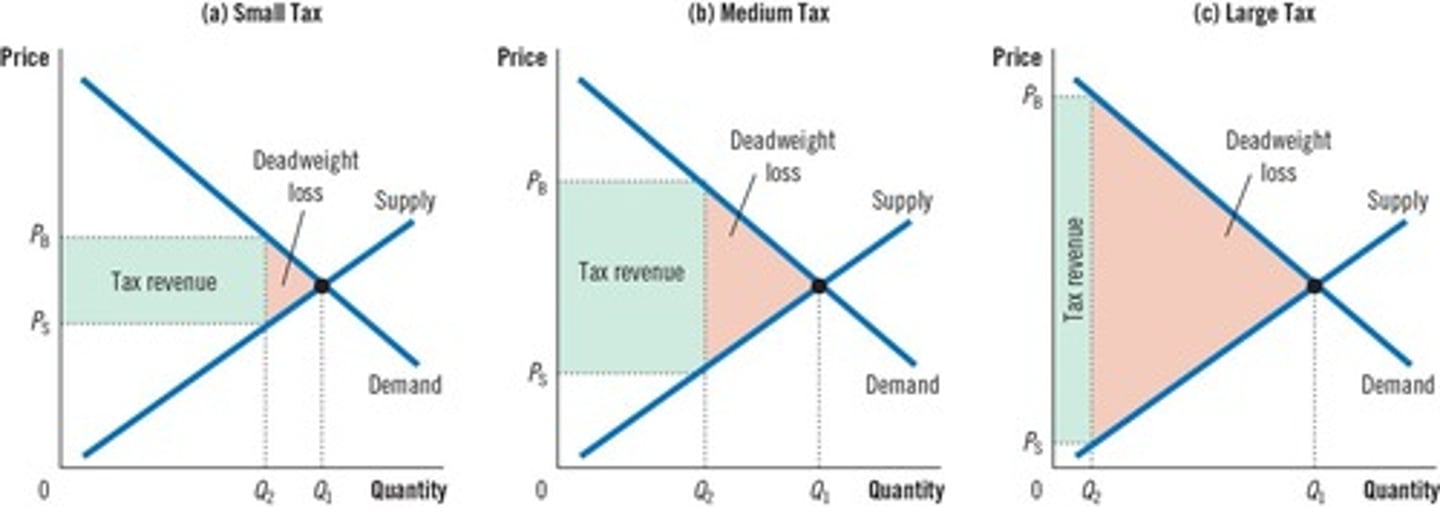
What is the Laffer Curve?
The Laffer curve shows the relationship between tax rates and tax revenue, indicating that higher tax rates initially increase revenue but can reduce it after a certain point.
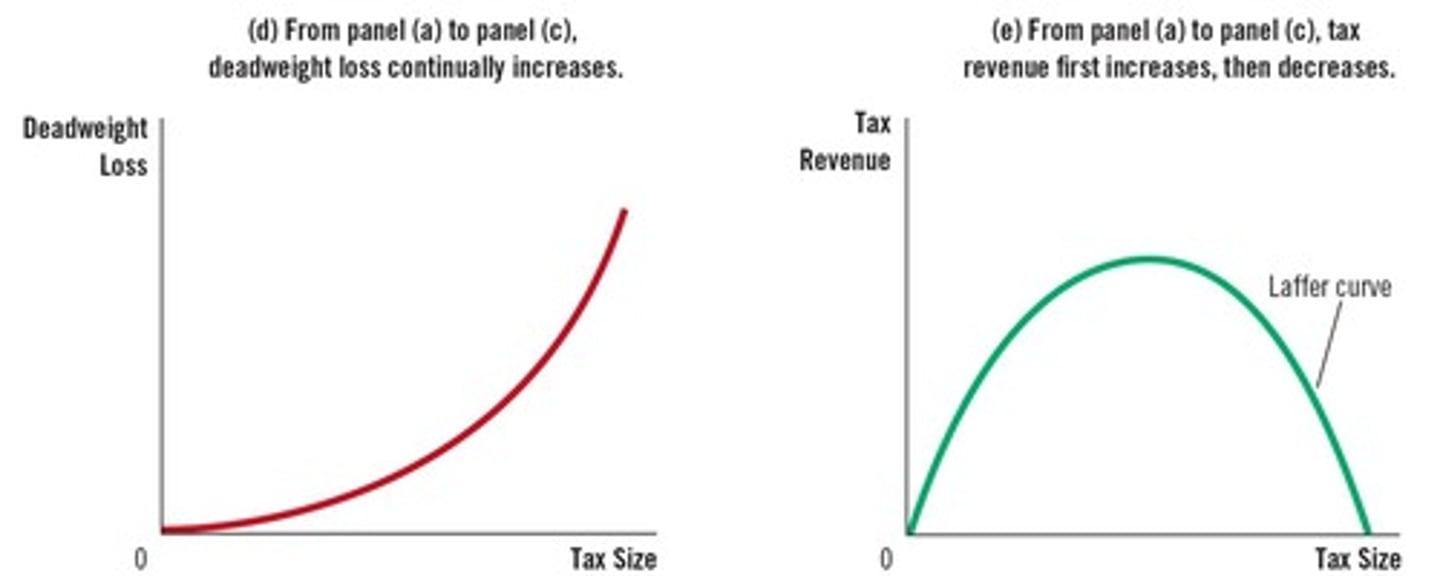
What is the effect of very high tax rates on tax revenue?
At very high tax rates, tax revenue decreases as the market size shrinks.
What is the impact of larger taxes on economic efficiency?
Larger taxes lead to larger deadweight losses, creating a trade-off between tax revenue and economic efficiency.
What is the area representing tax revenue on a graph?
The area of the rectangle between the supply and demand curves.
What occurs to the quantity sold due to taxation?
The quantity sold decreases from Q1 to Q2, resulting in lost gains from trade.
What are the components of total surplus?
Total surplus is the sum of consumer surplus, producer surplus, and tax revenue.
How do taxes distort market outcomes?
Taxes reduce the quantity sold and cause deadweight losses.
What is the effect of elasticities on market distortion due to taxes?
The larger the elasticities of supply and demand, the greater the distortion of the market.
What is consumer surplus?
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay.
What is producer surplus?
The difference between what producers are willing to accept and what they actually receive.