Intro to pro-comms - Part 1: Communication foundations
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Reflection question examples
How’d you learn to write, and who influenced you?
Why do you think you’re a good writer?
What frustrates you about writing?
The effects of unhelped beliefs
They can set us up for failure before we even start
e.g. Jack and Sam are good writers, but may not enjoy doing it in academic settings due to past negative experiences
How can unhelped beliefs be challenged?
By talking about our reading and writing beliefs and figuring our where they came from
What’s a benefit of thinking about our reading and writing beliefs?
It can be a great way to acknowledge the communication strengths one already has
e.g. The ability to ability to play music or sing can help write sentences that people will enjoy reading
Why’s it important to believe you can become a good writer?
Studies found that students who believe that they can become good writers improve faster than those who don’t
Examples of business-related documents
Letters, reports, business proposals, and business plans
Where can business-related documents be found?
Workplaces, school libraries, writing centre, business department
What’s a business of reading outside your niche?
Reading outside your niche can enhance your versatility and help you learn how other people express similar concepts
How else can communication be boosted?
By simply carrying out the lifelong habit of reading
What must be taken into account while reading assignment instructions?
Differentiate between what the directions say and what you think they say.
Communication
Purposefully & actively exchanging information between 2 or more people to convey or receive the intended meanings through a shared system of signs/symbols”
The communication process
The steps taken in order to make sure we’re successful in communicating.
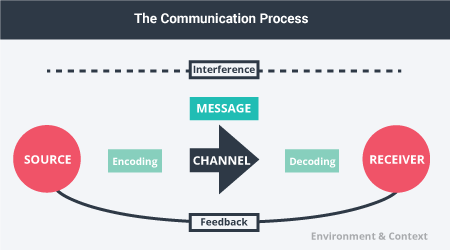
Source
The place where ideas are birthed and messages are sent; it can be in the form of one or more persons.
e.g. A friend sharing a funny story
Message
The info (opinion, feelings, instructions) that the source intends to share
e.g. Key aspects of the funny story the source is sharing.
Channels
How info’s encoded, whether it may be through words, images, sounds, body language, etc, and may be used to emphasize bits and pieces of info
e.g. One may use hand gestures when describing the climax of a story.
Receiver
The person who’s supposed to get the message, and must decode the message in order to get its meaning
Environment
The physical and psychological space in which the communication is happening, as well as its formality
Context
The setting, scene, psychological and psychosocial expectations of the source and the receiver(s); it’s connected to expectations of those who are sending the message and those who are receiving the message
Interference
Things which block effective communication
e.g. Too much noise in a given space
Reading skeptically
To not take everything as true at face value, and wonder why the author made the argument in the first place
Critical thinking
Self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective thinking
Critical thinking (con’t)
Needs established standards and attention to use, effective communication, problem solving, and a willingness to acknowledge and address our own tendency for confirmation bias
Reading skeptically (con’t)
Not only to understand the meaning of the text, but also to question and analyze the text (i.e why it says what it says)
What two basic questions does a basic reader aim to understand?
What’s the author doing?
How well is the author doing it?
How to answer “What’s the author doing?”
Carefully examine:
The author’s claims
The evidence and its legitimacy
Are there any assumptions?
How to answer “What’s the author doing?” (con’t)
Seeing the argument from different angles:
How else could the author have written this piece?
What other kinds of evidence could have been used?
What difference would that other evidence make?
How has the author constructed his or her argument?
How to answer “How well is the author doing it?”
How strong is the info
Are the ideas supported by good evidence?
What evidence is used?
Is the author biased or objective?
Does the conclusion effectively tie everything together?
What can asking questions about a text do?
Predict what a text will be about
Identify confusing parts of the reading
Clarify what confused them
Develop a response to the text
Understand the author’s purpose for writing a text
Ways to be aware to be aware of your thinking process before, during, and after reading
What did you wonder about before you started reading?
What did you think the text might be about?
What questions did the text raise in your mind as you read?
What seemed important or surprising?
Conformation bias
Only paying attention to info which aligns with one’s beliefs and/or ignoring info which contradicts one’s beliefs