Unit 3 Flashcards
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
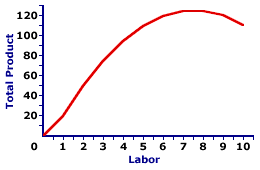
Total Product (TP)
Output made with a specific number of workers, e.g., 5 workers make 10 clocks.
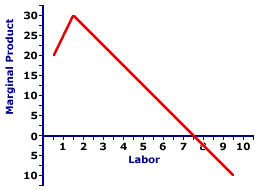
Marginal Product (MP)
Extra output obtained from adding one additional resource.
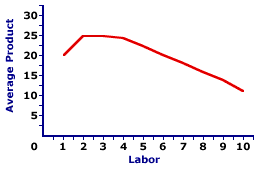
Average Product (AP)
Labor productivity calculated as Total Revenue (TR) divided by Units of Labor.
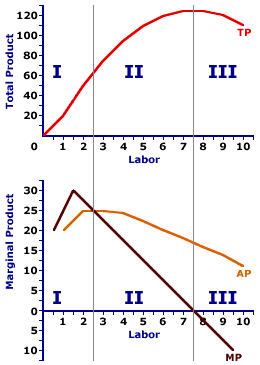
3 stages of production are what and what do they mean
Increasing - Marginal product is increasing by each unit of labor, and TP is increasing
Diminishing - MP is decreasing by each unit of labor, but TP still increasing
Negative - TP is now decreasing
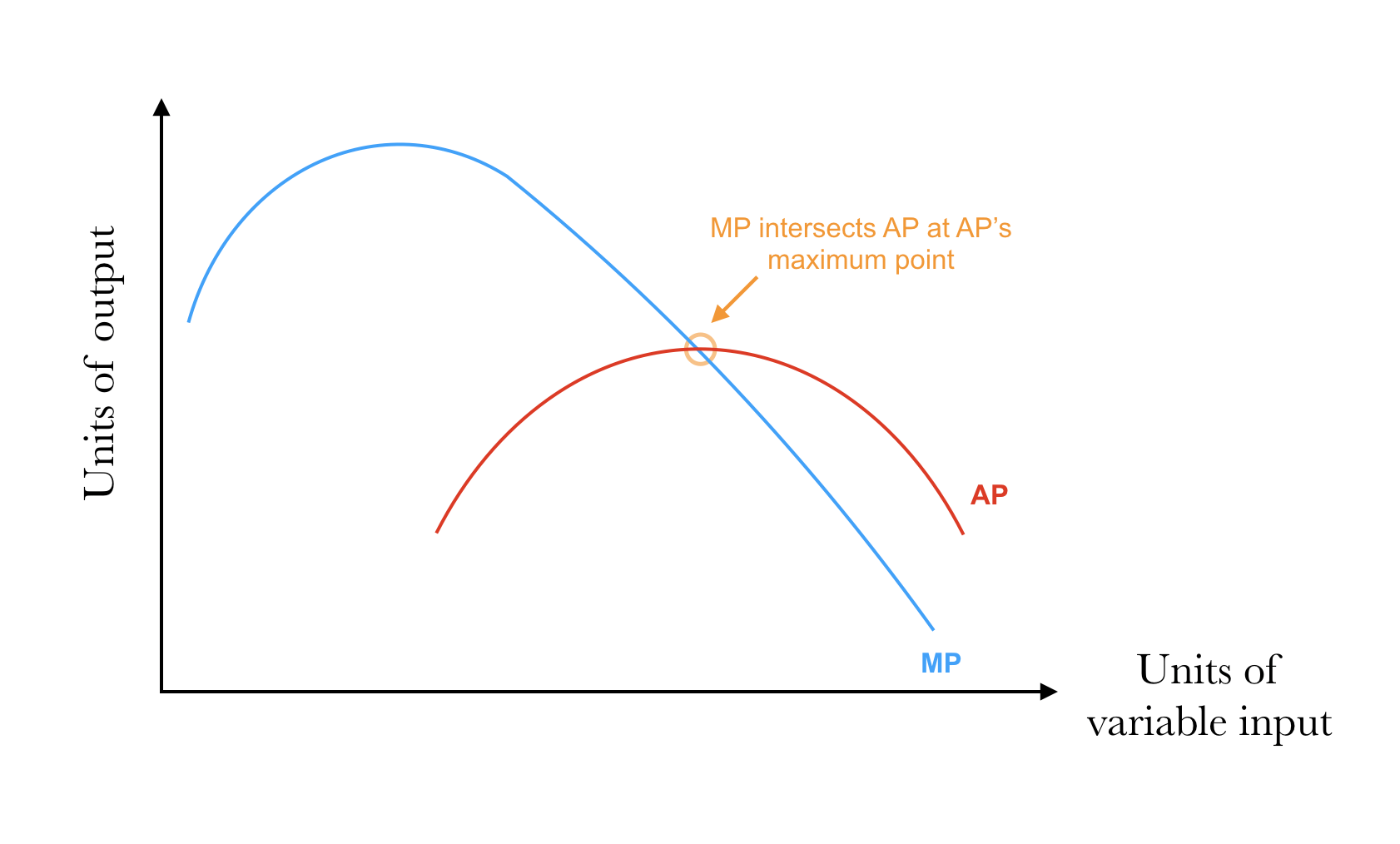
When MP > AP, what happens to AP?
When MP < AP, what happens to AP?
What occurs at the intersection of MP and AP?
AP is rising
AP is falling
AP is at its maximum.
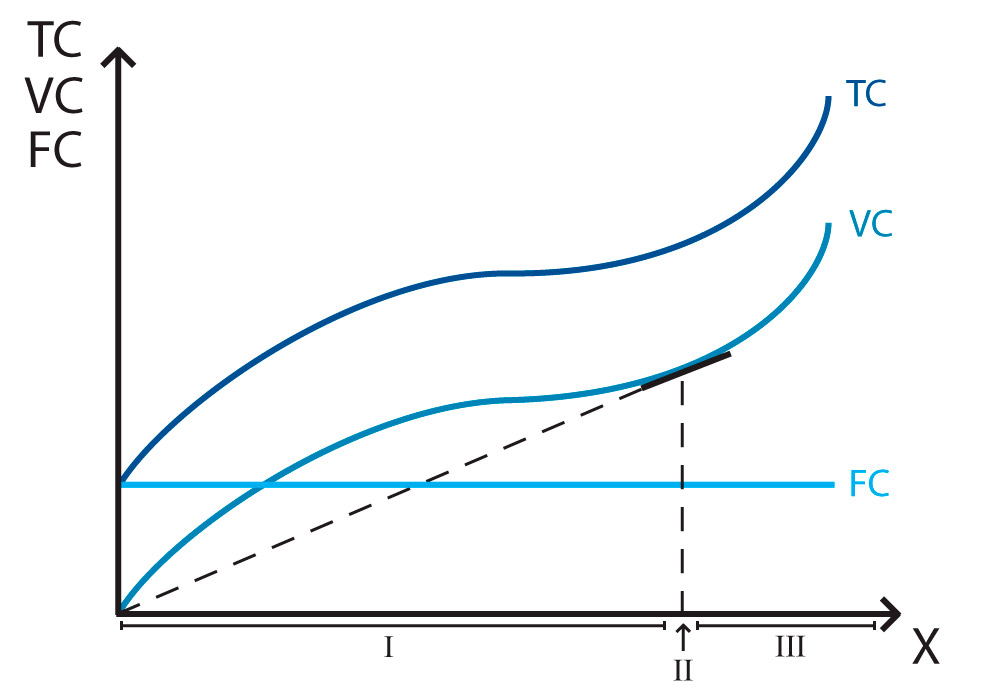
Fixed Costs (FC)
Costs that remain unchanged when quantity (Q) changes.
Variable Costs (VC)
Costs that change when quantity (Q) changes.
Total Costs (TC) formula
Total Costs (TC) equals Fixed Costs (FC) plus Variable Costs (VC).
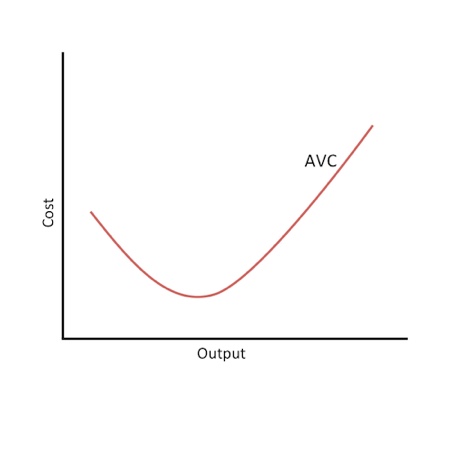
(AVC)Average Variable Costs formula
VC/Q
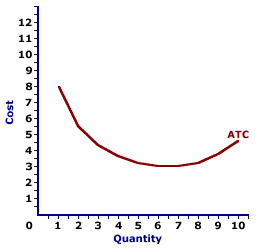
(ATC)Average Total Costs
TC/Q OR AFC + AVC
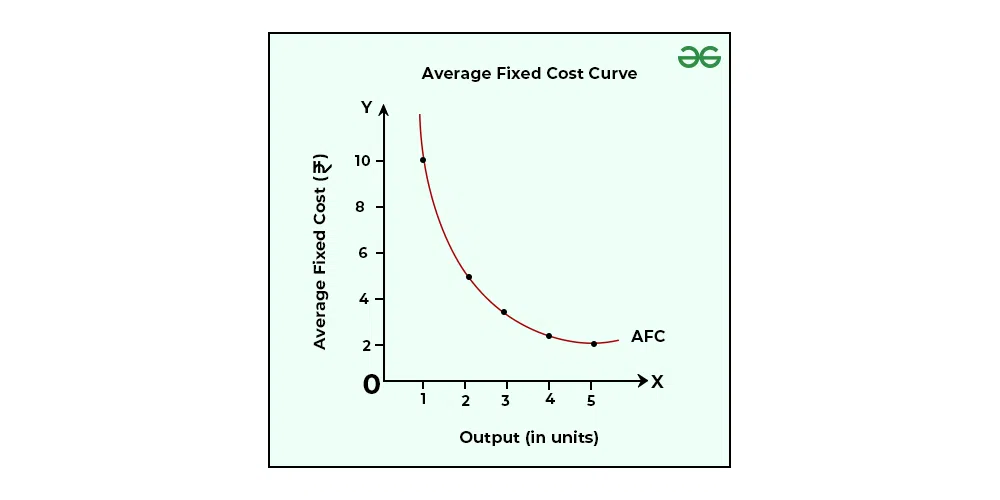
(AFC)Average Fixed Costs
FC/Q
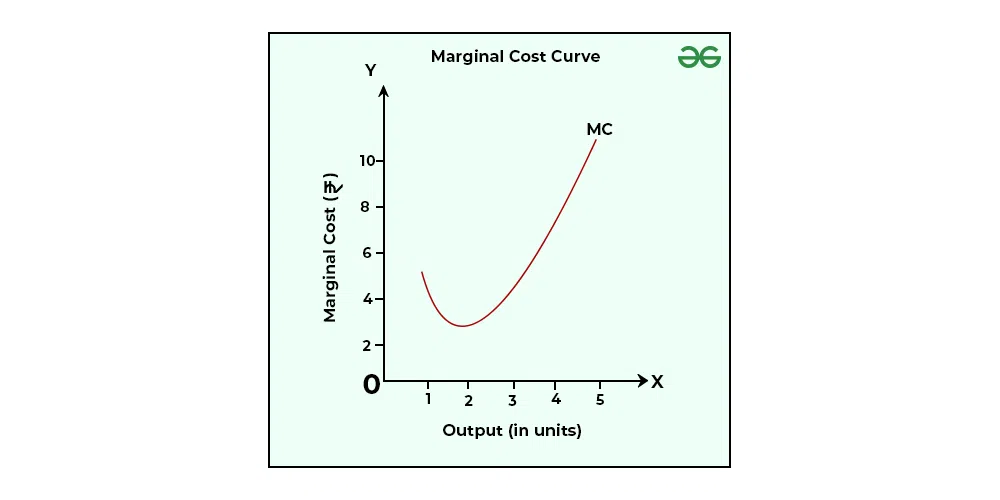
(MC)Marginal Cost
∆TC(change in TC)/∆Q(change in Q)
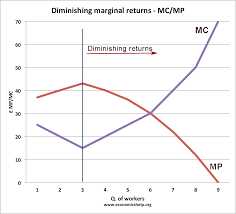
As MP increases what happens to MC?
AS MP decreases what happens to MC?
MC is minimized when?
MC decreases as MP increases
MC increases as MP decreases
MC is minimum when MP is maximum
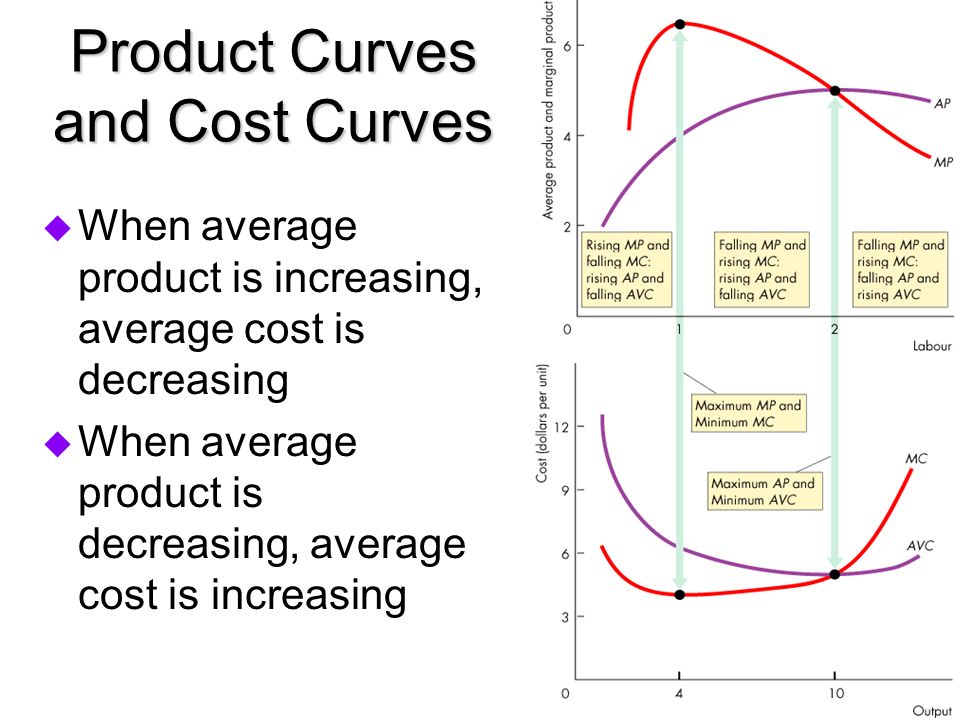
As AP increases what happems to AVC?
As AP decreases what happens to AVC?
When AP is maximized what happens to AVC?
AVC decreases as AP increases
AVC increases as AP decreases
AVC is minimized when AP is maximized
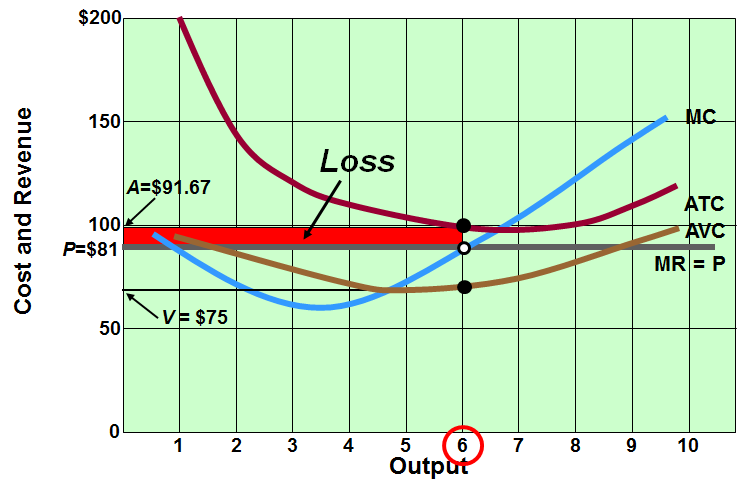
What is short run loss and how does it happen?
When MC(where MR = MC) < ATC but MC > AVC
Continue producing since FC can still be paid, and AVC can be lowered until there is profit
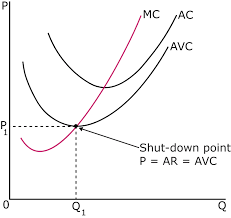
What is a short run shutdown and how does it happen
When MC(where MR = MC) < AVC
Stop producing since FC can’t be paid no matter what, since FC doesn’t change
Market and Firm Profit is maximized when?
At the quantity where the MC = MR(or sometimes the last quantity where MC < MR
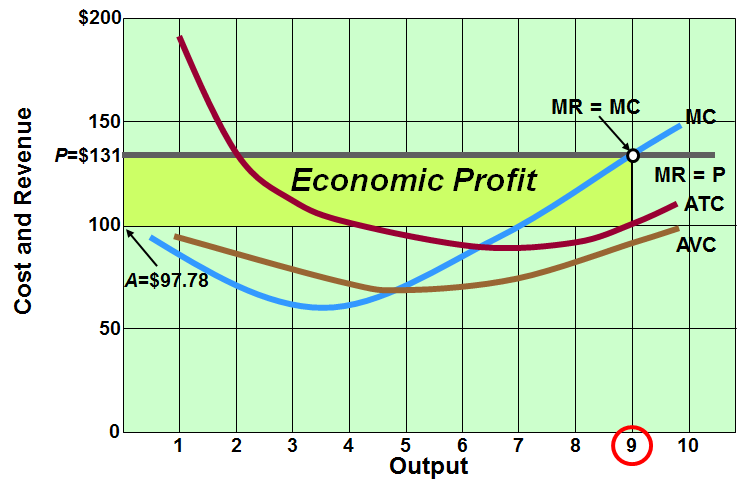
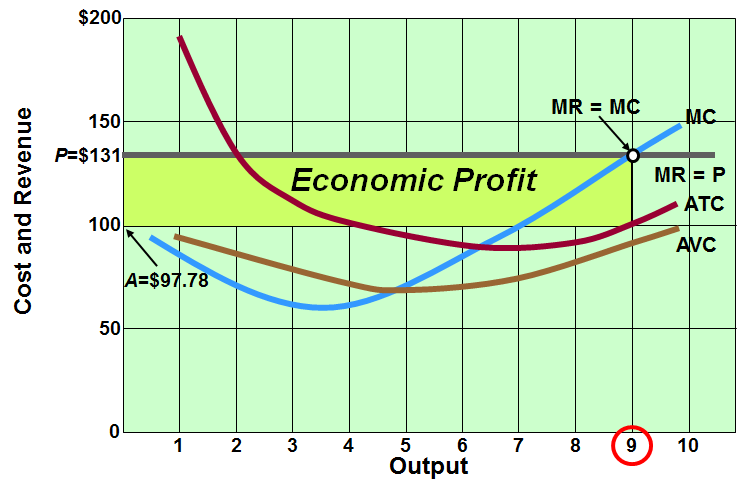
What is short run profit and how does it happen?
When MC(where MR = MC) > ATC
Keep producing as you are gaining money
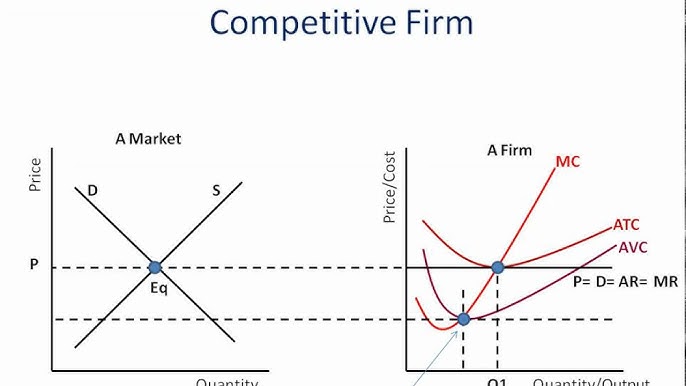
Compare a SR(short run) single firm perf comp equilibrium to an industry equilibrium
Both caused by meeting of S(MC in single firm) and D(MR in single firm) curves
But in single firm equilibrium demand can not change, in industry supply and demand can change equilibrium
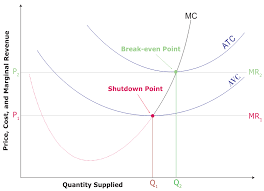
What is a break-even point?
Where MC=MR is = ATC
No profit, meaning firm can’t do any better, so it should continue to produce
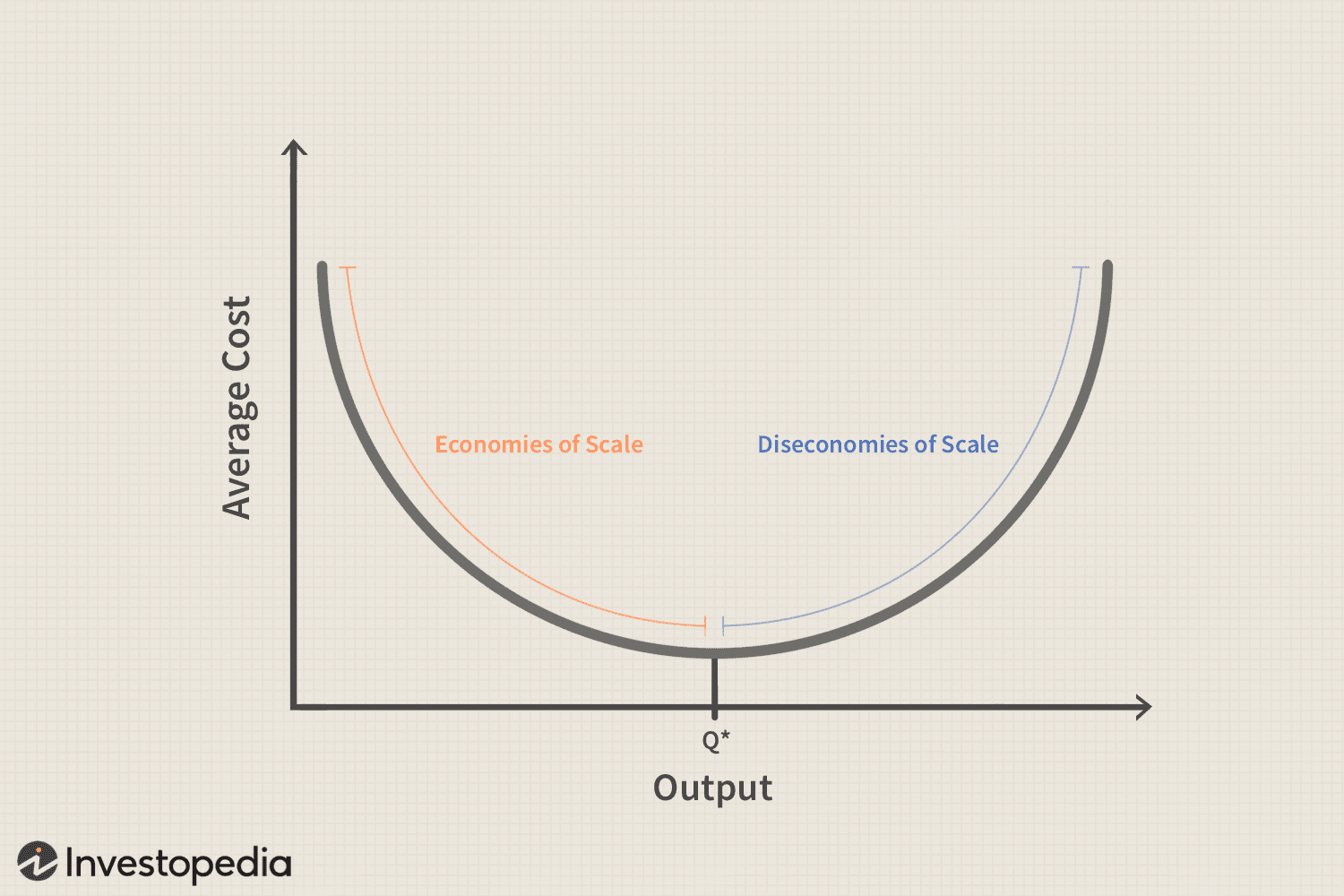
Economies of Scale(ATC decrease)
Labor Specialization » dividing jobs as workers increase
Managerial Specialists » individuals focusing on specific areas of management
Efficient (human/physical)capital use » less production = less equipment and vice-versa
Start-up costs decline overtime
Ad costs decline as selling increases
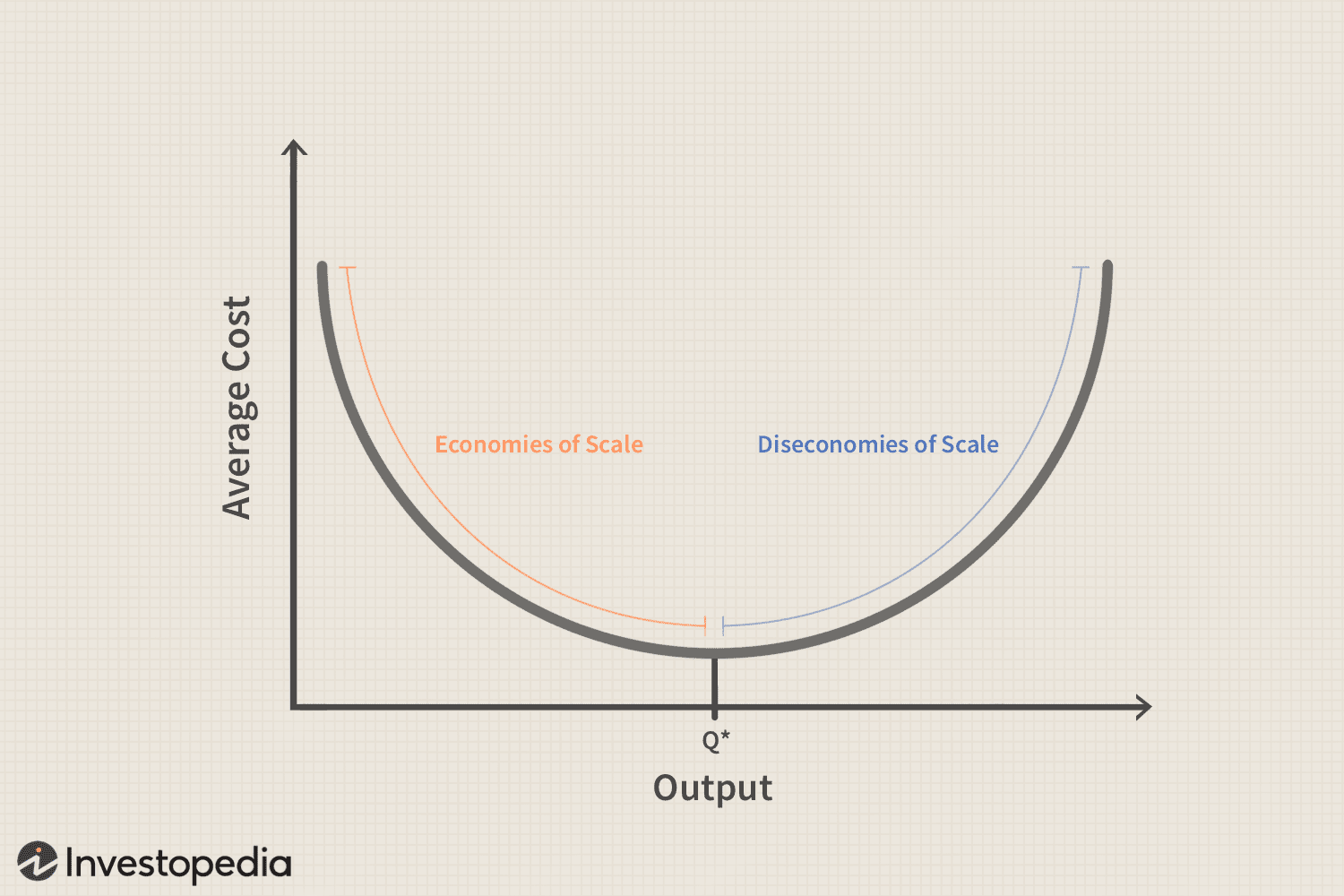
Diseconomies of scale(ATC increase)
Decrease scale/efficiency of operations as firm grows