Terpenes, Antihyperlipoproteinemics, Alkaloids, Natural Products
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
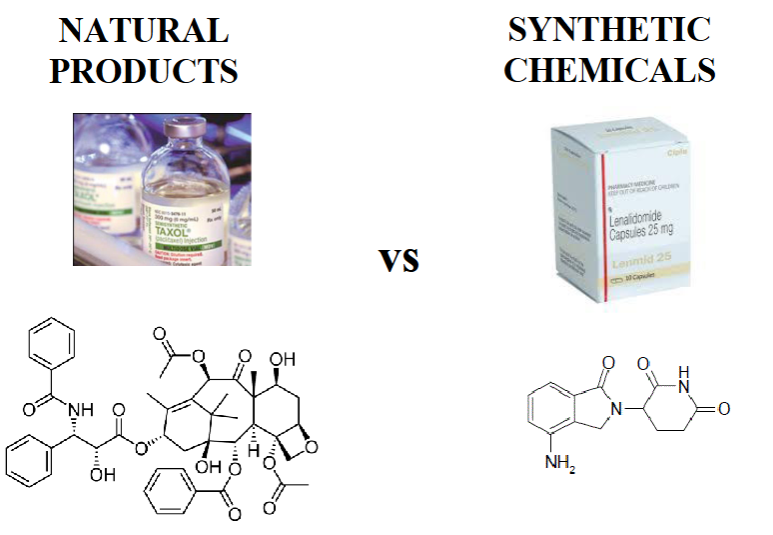
NATURAL PRODUCTS
Natural products have ______ molecular weights than synthetics
_________ oxygen content
_________ atoms of N, S, or halogen
_________ number of rings, chiral centers, and sp3-hybridized bridgehead atoms
higher
more
less
larger
Lipinsky Rules → POOR absorption/permeability when:
cLogP is _____
molecular mass is ______
# of H bond DONORS (OH + NH) is ________
# of H bond ACCEPTORS (O + N) is ________
HOWEVER, these rules DO NOT apply to ________________
>5
>500 Da
>5
>10
natural products
____________: the study of natural product molecules (typically SECONDARY metabolites → important for the survival of plant species, but not required in ALL plant species)
pharmacognosy
The natural species that are the source of the compounds under study span all biological kingdoms, MOST NOTABLY → 4
marine invertebrates
plants
fungi
bacteria
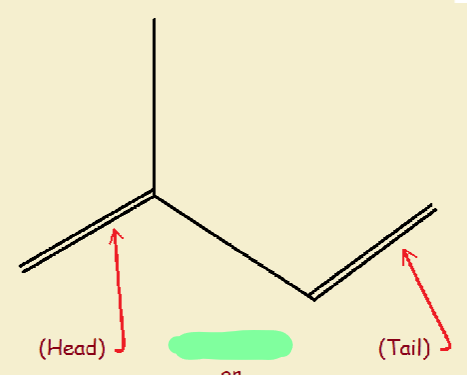
TERPENES
Many terpenes are _________, but oxygen-containing compounds (alcohols, aldehydes, ketones) are also found
Building block = _____________ linked in head → tail fashion
hydrocarbons
isoprene
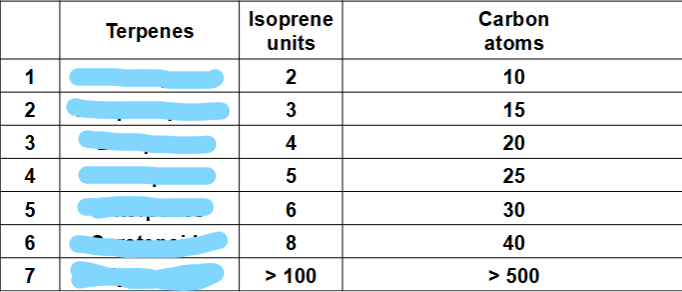
monoterpenes
sesquiterpenes
diterpenes
sesterpenes
triterpenes
carotenoids
polyterpenes
What kind of terpenes are major components of fragrant oils (perfumes, flavorings)?
monoterpenes
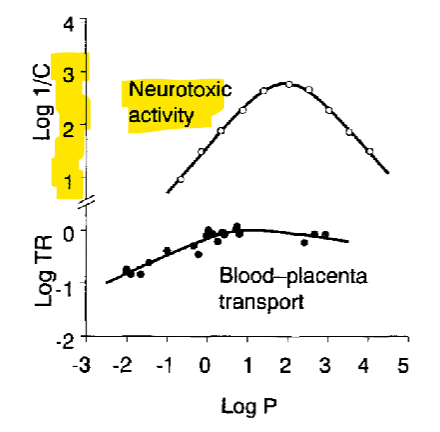
CAMPHOR’s mechanism of toxicity is unknown, but it possesses both __________ and ___________ activity
Death is secondary to _____________ or _________
Camphor LogP?
excitatory, depressant
respiratory failure, seizures
2.38
_______________: therapeutic use of aromatic substances extracted from plants (essential oils)
aromatherapy
The use of aromatherapy during pregnancy, particularly the _____________ should be AVOIDED
1st trimester
___________________: bicyclic monoterpenes, they are some if not the most bitter of all compounds, often responsible for the so-called “bitter principle” of a plant
iridoid glycosides
_____________ → _________ natural product example that has traditionally been used as a sedative, has CNS-depressant activity, and +GABA
Valerian, iridoid
SESQUITERPENES (C15)
wide distribution in nature, form the largest class of terpenes
provides plant protection as _________ and ________
__________ from cotton plant → antifertility agent in men, acts on testicular mitochondria
__________ → used for sleeplessness, anxiety, GI conditions, skin conditions + mouth ulcers resulting from cancer tx
Sesquiterpene lactone: _______________ → treatment of malaria
antimicrobial, insecticidal
Gossypol
chamomile
artemisinin
_______________ is the major component of chamomile oil, it is believed to be responsible for some of the effects of chamomile
bisabolol
The ____________ in artemisinin is essential for antimalarial activity, This compound is very _________ and well absorbed in the CNS
peroxide, lipophilic
Suffix “_______” indicates presence of a lactone group
-olide
Many members of the Asteraceae family are known to cause _________________ in humans
Sesquiterpene lactones react with _________ receptors
contact dermatitis, nucleophiles
The leaves of _________ (Tanacetum parthenium) have been used for the treatment of headaches. Originated in Europe and is a member of the sunflower family (Asteraceae)
Suspected to have antiplatelet effects and thus might cause excessive __________ if used preoperatively → *tell patients to DC at least 2 weeks before elective surgical procedures
Limitation → potential toxic effect of _________ observed in some patients e.g. mouth ulceration or hepatotoxicity
feverfew
bleeding
SL
DITERPENES (C20)
_________ (rebaudioside A) → noncaloric sweetener
_________ (Paclitaxel) → breast cancer chemotherapy → natural production too slow, now produced semi-synthetically from baccatin
_________ → potentially beneficial effects for patients w dementia, insufficient evidence in preventing dementia
Truvia
Taxol
ginko biloba
Ginkgo biloba has 2 primary active ingredients:
diterpene lactones (___________)
ginkgo flavone glycosides (__________)
What kind of terpene?
ginkgetin
bilobetin
diterpene
________ are included in the group of triterpenes (C30)
steroids
____________ → metabolic regulators, +resistance to harmful factors/stressors, typically no side effects unlike traditional stimulants (addiction, tolerance, abuse potential), NO FDA APPROVED
Example →
adaptogens → ginseng
Claims/uses of GINSENG
Support overall health and boost ___________
+sense of _________ and _________
improving both ______ and ______ performance
Treating _________
lowering _______ and controlling _______
Most common side effects → 3
immune sys
well-being, stamina
mental, physical
ED
blood glucose, BP
headaches, sleep problems, GI
Ginseng Drug Interxns
Likely → 2
Possibly → 4
anticoagulants, antidiabetics
MAOI, antipsychotics, cardiac glycosides, BP meds
Advise patients NOT to take American ginseng w __________ (-effectiveness)
warfarin
Ashwagandha → adaptogenic, sedative, tonic, mood booster
Advise patients with ____________ to AVOID/use with caution
autoimmune diseases
Cholesterol Biosynthesis + Biotransformation
_____________ reduces the CoA thioester to mevalonic acid (primary alcohol)
Cholesterol → pregnenolone by ____________
Pregnenolone is a common intermediate for biosynthesis of ________ hormones
Cholesterol also converted to ________ and _______ → difference?
Cholesterol converted to cholic acid (a bile acid) by __________ enzyme
HMG CoA reductase
20,22-desmolase
steroid
bile acids → 75% gly + 25% taurine, bile salts → anionic detergents (emulsify dietary lipids + fat-sol vitamins)
7a-hydroxylase
Name the primary function
Chylomicrons → transport ____________
Chylomicron remnants → transport ____________
VLDL → transport _____________
IDL → transport _____________
LDL (Bad) → transport _______________
HDL (Good) →
dietary triglycerides
dietary cholesterol
endogenous triglycerides
endogenous triglycerides
endogenous cholesterol
REMOVE cholesterol from extra hepatic tissues
Drugs affecting LIPOPROTEIN → 4
bile sequestrants
HMG CoA reductase inhib
fibrates
nicotinic acid (niacin)
BILE ACID SEQUESTRANTS
Cholestyramine and Colestipol are __________________ (+ charged polymer resins that BIND to - groups
Cholestyramine originally used in patients with ____________ (when flow of bile from liver is reduced)
MOA: not absorbed in GI tract, sequester bile acids in the ___________ → prevent reabsorption and +excretion → -[bile acid] in liver
______________ is indirectly lowered by these drugs by +rate that it is cleared from blood
anion exchange resins
cholestasis
intestine
plasma LDL
The total nitrogen content of COLESTIPOL per gram is ________ than that for cholestyramine, however
Its functional anion exchange capacity may be less since colestipol depends _________ of the intestine.
Bile salt adsorption capacity comparison
greater
upon pH
cholestyramine > colestipol
Colestipol and Cholestyramine
Drug class
Contraindications: → 2
Drug interxns →
BA sequestrants
hypertriglyceridemia, cholelithiasis (gallbladder stones)
may -abs of drugs = admin other meds 1h before OR 4-6h after
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors are known as ___________
The first 2 drugs =
Prodrug that is activated by in vivo ____________________
Active drug mimics ________ intermediate produced by HMG CoA reductase
Enhanced ________________ may be the primary mechanism for lowering plasma LDL levels
Unlike the others, ______________ decreases plasma LDL in pts w homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia
statins
mevastatin, lovastatin
hydrolysis of lactone ring
tetrahedral
LDL receptor expression
atorvastatin (Lipitor)
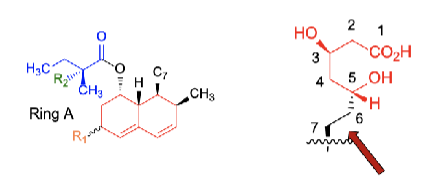
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors SAR
The _____________ is essential for inhib activity
________________ ring essential for anchoring the compound
^ Replacement w cyclohexane ring = ____________ in activity
___________ can inc/dec activity
Ester side chain → ether = _____ activity
_________ +activity 2x
3,5-dihydroxycarboxylate
unsat decalin
10,000 fold dec
double bond C7/8
dec
methyl R2
PK considerations for HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
Food does NOT affect absorption → EXCEPT ________
Should be admin at _______________ to counteract peak cholesterol synthesis that occurs in early morning
________ effective regardless when admin bc of long half-life
May be used alone OR in combination with ___________ or ___________ (1h before or 4-6h after for BA sequestrants)
*CONTRAINDICATIONS →
ADVERSE EFFECTS → 3
lovastatin
bedtime/evening
atorvastatin
BA sequestrants, niacin
pregnancy, nursing mothers
GI, +hepatic transaminase, +CPK (creatine phosphokinase)
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have a rare but serious risk of ___________
rhabdomyolysis
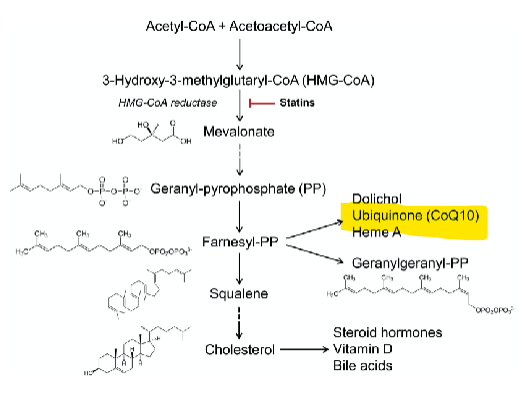
Mechanisms of Statin-associated Myotoxicity (muscle damage)
Inhibition of __________________
mitochondrial dysfunction → 2
inhibition of __________________
____________
Inhibition of ___________ pathway
protein prenylation
inhib ETC, ubiquinone deficiency
mt biogenesis
oxidative stress
Akt/mTORC
NORMAL cholesterol levels:
<200 mg/dL
FIBRATES
1st Drug =
newer and safer developed drugs = 2
MOA: decrease plasma __________ levels more dramatically than cholesterol levels
Moderately increase ________ lvls
clofibrate
gemfibrozil, fenofibrate
triglyceride
HDL
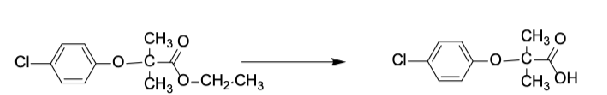
which fibrates are PRODRUGS and require ester hydrolysis?
para-substitution of aromatic ring with _________ produces compounds with significantly LONGER _________
_______________ group essential for activity
clofibrate, fenofibrate
Cl, t1/2
isobutyric acid
Nicotinic acid =
niacin = vit B3
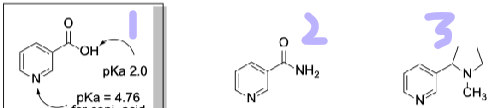
name these
*recognize that these are NOT the same compounds, even tho their names are similar
nicotinic acid
nicotinamide
nicotine
Nicotinic acid MOA
Inhibits ___________ in adipose tissue
_____________ leads to -LDL → -triglyceride within several hrs, -cholesterol takes several days
Nicotinic acid has NO effect on cholesterol __________ or ___________
Increases HDL due to -clearance of __________
lipolysis
-VLDL
catabolism, biosynth
apoA-I
Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
-
-
Peptic ulcer disease
hepatic disease
predisposed DM or gout
Friedrich Wilhelm Adam __________ discovered opium’s main narcotic principle, MORPHINE
serturner
MOST alkaloids are present forming _________ → usually ______________
Salts are (less/more) stable than free alkaloids
Basic or non basic alkaloids will be readily absorbed in stomach?
IV administered alkaloids are usually administered as ______
salts, water soluble
more
non basic
salts
Caffeine and Theobromine are CNS _________ and __________
Which one has LESS CNS activity?
stimulants, diuretics
theobromine
The LD50 of caffeine in humans is estimated to be about ________/kg of body mass
Reports of hospitalization after ingestion of about ________
150-200 mg, 2 g
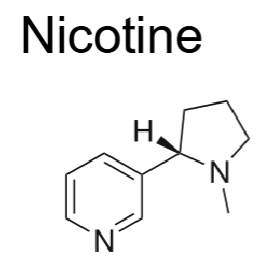
Nicotine is a _____________ ___________
2 enantiomeric forms → which form is more active?
Why does very little nicotine oral absorption occur when smoking cigarettes? (pKa = 8.02)
Chewing tobacco and oral snuff are made from air-cured tobacco, resulting in tobacco that has a ______ pH, which is ideal for oral absorption
pyridine alkaloid
S (-)
acidic smoke → ionized → -abs
basic
Phenylpropanoids Common Structure =
C6 unit + C3 unit attached to aromatic ring
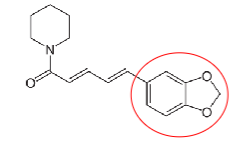
Phenylpropenes
_________: plant product example
_________: active components
Use =
Has _______ status (generally recognized as safe)
*Drug interxn:
BioPerine is standardized black pepper extract → _____ piperine minimum and also _______ status
turmeric
curcuminoids
anti-inflam
GRAS
CYP3A4 + P-gp inhibitor
95%, GRAS
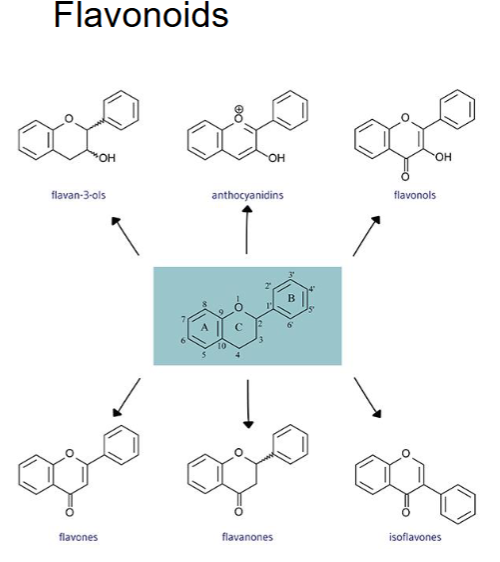
FLAVONOIDS occur as plant pigments, often yellow or orange
Likely main role in nature is as color attractants to insects and birds, or to affect the taste of plants
Their basic chemical structure is ___________ connected by _____ link
C6 - C3 - C6
2 benzene rings, 3C
MILK THISTLE / SILYMARIN
commonly used for tx of ________ and _________ disorders
Lab studies demonstrate that milk thistle: stabilizes ________ membranes
stimulates __________ pathways
stimulates __________ of liver tissue
Clinical studies do NOT show any effect against _________
Oral milk thistle for ___________ - results promising, but better research needed
Also possibly effective for ________ when used in combination with conventional treatments
liver, gallbladder
cellular
detoxification
regeneration
hep C
cirrhosis
Type 2 diabetes
FLAVONOIDS have important dietary significance because being ________ compounds, they are strongly ___________
Flavonoids occur both free (__________) and as ___________
predominant conjugated metabolites = 3
_________ are most well absorbed (then flavanones, then quercetin glucosides)
_________ and _______ LEAST well absorbed
phenolic, antioxidant
aglycone, glycosides
glucuronate, sulfate, methyl
isoflavones
anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins

Anthocyanins (ACN) been consistently shown to INCREASE endothelial-derived ___________ → vascular smooth muscle relaxation via cGMP, -BP
ACN shown to prevent ^ __________ and radical-induced conversion
ACN shown to reduce synthesis of __________ molecules such as Ang II, endothelian-1, thromboxanes
Name the 3 food with highest ACN content
Red-purple-blue-wine color → present in certain fruits, vegetables, legumes + rice, beverages
NO
oxidative damage
vasoconstricting
blackberries, elderberries, red cabbage
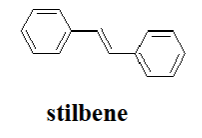
STILBENES are related to flavonoids but have the basic structure ____________
C6-C2-C6
Resveratrol is naturally occurring compound found in various plant species including _________, very strong ________ and also possess anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties
grapevines, antioxidant
Phytoestrogens may inhibit the development + progression of _______________
breast cancer
Soy isoflavones provides ____________ relief by naturally relieving hot flashes and night sweats
menopause