Sexual reproduction in plants
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
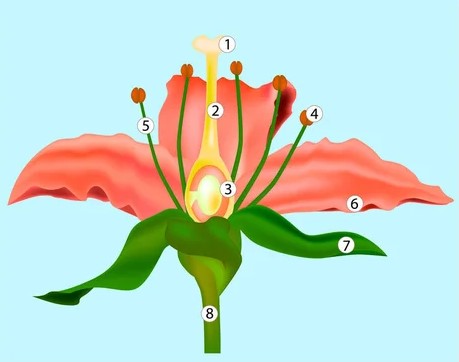
Label this diagram
1. stigma
2. style
3. ovary
4. anther
5. filament
6. petal
7. sepal
8. peduncle
2
New cards

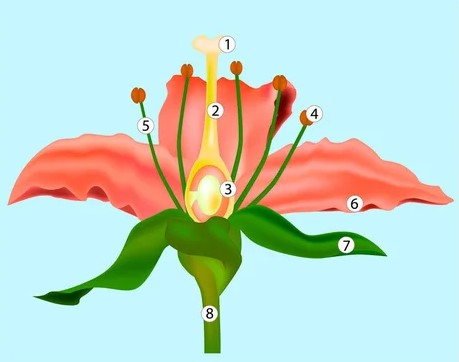
Label this diagram
1. stigma
2. style
3. anther
4. filament
5. petal

3
New cards
Which structures make up the stamen?
* anther
* filament
* filament
4
New cards
Which structures make up the carpel?
* ovary
* ovule
* style
* stigma
* ovule
* style
* stigma
5
New cards
What is the receptacle?
top of flower stalk from which different parts of the flower develop
6
New cards
Which structure makes up the calyx?
sepals
7
New cards
Which structure makes up the corolla?
petals
8
New cards
What is the calyx?
* first set of modified leaves → sepals
* protect flower while it’s still forming and before flower bud opens
* protect flower while it’s still forming and before flower bud opens
9
New cards
What is the corolla?
* layer of modified leaves → petals
* often large, coloured and patterned → attracts insects
* some colours (e.g. UV) only visible to insects
* often large, coloured and patterned → attracts insects
* some colours (e.g. UV) only visible to insects
10
New cards
What is the stamen?
* made of filament and anther
* filament carries water and nutrients to anther in vascular bundle
* male reproductive organ
* site of mitosis and meiosis to produce male gametes
* filament carries water and nutrients to anther in vascular bundle
* male reproductive organ
* site of mitosis and meiosis to produce male gametes
11
New cards
What is the carpel?
* composed of ovary, style and stigma
* ovary is site of meiosis to produce female gametes → contained in ovules
* following fertilisation, ovules becomes seeds
* style supports stigma
* stigma is sticky surface that pollen grain land on
* female reproductive organ
* ovary is site of meiosis to produce female gametes → contained in ovules
* following fertilisation, ovules becomes seeds
* style supports stigma
* stigma is sticky surface that pollen grain land on
* female reproductive organ
12
New cards
What is the nectary?
* may also be present at base of stamens
* secrete sweet substance (nectar) that attracts insects → carry pollen from one flower to another
* secrete sweet substance (nectar) that attracts insects → carry pollen from one flower to another
13
New cards
Define solitary flowers
only one flower on a stem
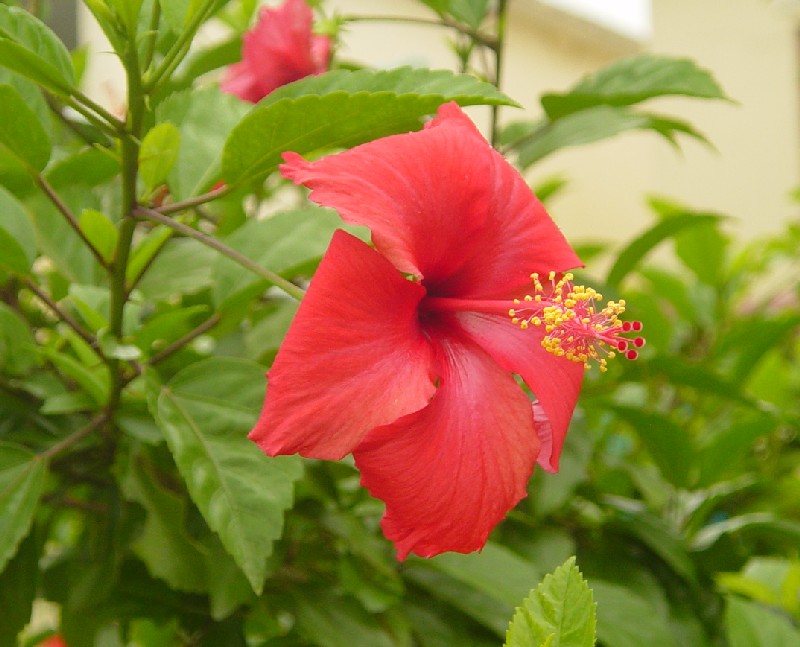

14
New cards
Define inflorescence
many flowers on one stem
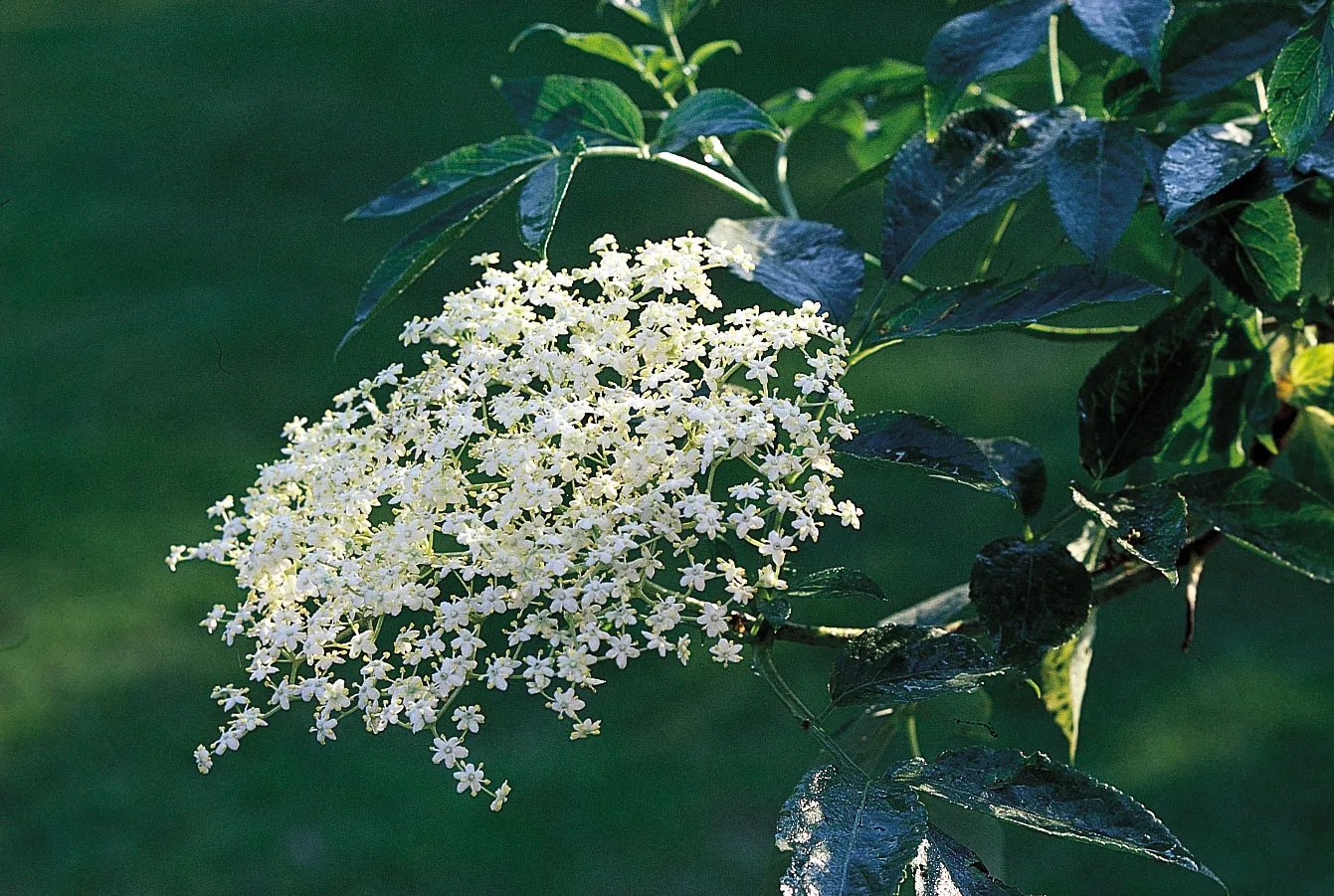

15
New cards
Define hermaphrodite
flowers with both female and male parts
16
New cards
Define monoecious
separate male and female flowers on plants
17
New cards
Define dioecious
separate male and female plants
18
New cards
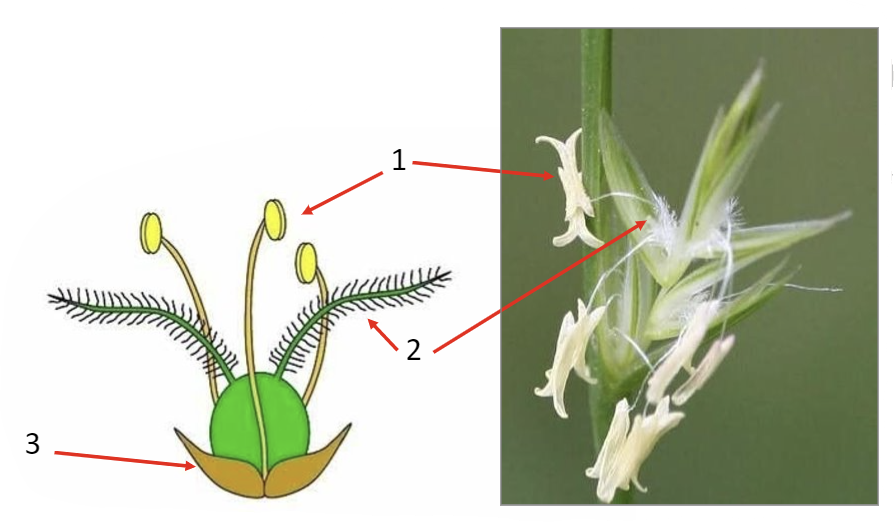
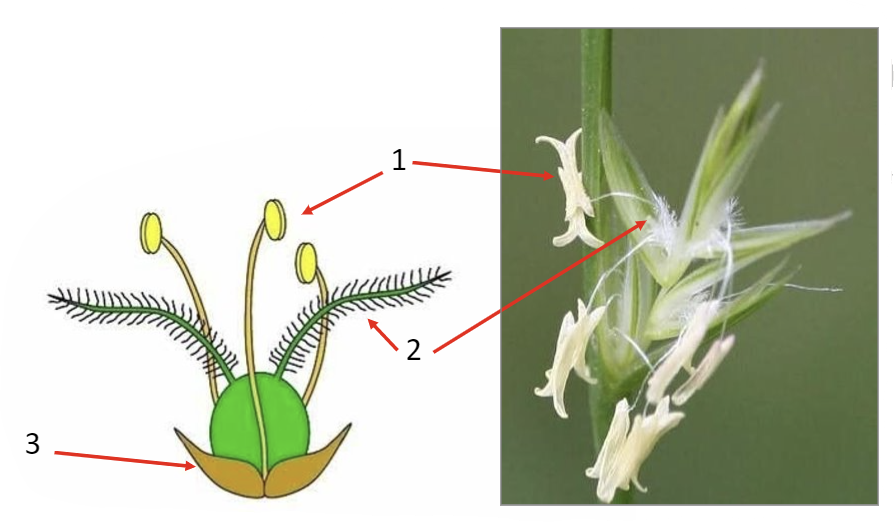
Identify the kind of plant shown and label the diagram
wind pollinated plant
1. anther
2. stigma
3. petals
1. anther
2. stigma
3. petals
19
New cards
How does the size and colour of petals in wind pollinated plants and insect pollinated plants differ?
* wind pollinated:
* small, dull-coloured
* less attractive flower
* insect pollinated
* big, visible and scented flower
* brightly coloured → attracts insects
* small, dull-coloured
* less attractive flower
* insect pollinated
* big, visible and scented flower
* brightly coloured → attracts insects
20
New cards
How does the appearance of stamens in wind pollinated plants and insect pollinated plants differ?
* wind pollinated
* long stamen
* usually sticks out of petals
* insect pollinated
* short stamen
* hidden within the petals
* long stamen
* usually sticks out of petals
* insect pollinated
* short stamen
* hidden within the petals
21
New cards
How does the appearance of anthers in wind pollinated plants and insect pollinated plants differ?
* wind pollinated
* big and sticks loosely at tip of filament
* insect pollinated
* small and sticks firmly at tip of filament
* big and sticks loosely at tip of filament
* insect pollinated
* small and sticks firmly at tip of filament
22
New cards
How does the appearance and texture of pollen in wind pollinated plants and insect pollinated plants differ?
* wind pollinated
* tiny, smooth and light
* numerous
* insect pollinated
* big, coarse and spiky
* few in number
* tiny, smooth and light
* numerous
* insect pollinated
* big, coarse and spiky
* few in number
23
New cards
How does the appearance of styles in wind pollinated plants and insect pollinated plants differ?
* wind pollinated
* long and hairy
* insect pollinated
* short and sticky
* even stigma
* long and hairy
* insect pollinated
* short and sticky
* even stigma
24
New cards
How does the nectar in wind pollinated plants and insect pollinated plants differ?
* wind pollinated
* doesn’t produce nectar
* insect pollinated
* sweet nectar
* doesn’t produce nectar
* insect pollinated
* sweet nectar
25
New cards
What are some examples of wind pollinated plants?
maize, grass, paddy and wild grass
26
New cards
What are some examples of insect pollinated plants?
rose, hibiscus, orchid, durian
27
New cards
Define self-pollination
pollen from anther of a flower is transferred to mature stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant
28
New cards
Define dichogamy
when the stamen and stigma ripen at different times
29
New cards
What are the 2 types of dichogamy?
* protandry → stamen ripens before stigma
* protogyny → stigma ripens before stamen (rarer)
* protogyny → stigma ripens before stamen (rarer)
30
New cards
How is self pollination prevented?
* anther below stigma so pollen can’t fall onto it
* genetic incompatibility → pollen can’t germinate on stigma of flower from which it was produced
* separate male and female flowers on plants (maize) → monoecious
* separate male and female plants (holly) → dioecious
* dichogamy → anther and stigma develop at different times
* genetic incompatibility → pollen can’t germinate on stigma of flower from which it was produced
* separate male and female flowers on plants (maize) → monoecious
* separate male and female plants (holly) → dioecious
* dichogamy → anther and stigma develop at different times
31
New cards
Why should self-pollination be avoided?
* prevent inbreeding
* cross-pollination leads to an increase in genetic variation
* prevent homozygosity → could result in recessive traits
* cross pollination results in larger gene pool
* increases chance of survival/selective advantage
* cross-pollination leads to an increase in genetic variation
* prevent homozygosity → could result in recessive traits
* cross pollination results in larger gene pool
* increases chance of survival/selective advantage
32
New cards
Why could self-pollination be advantageous?
preserves successful genomes that are suited to relatively stable environment
33
New cards
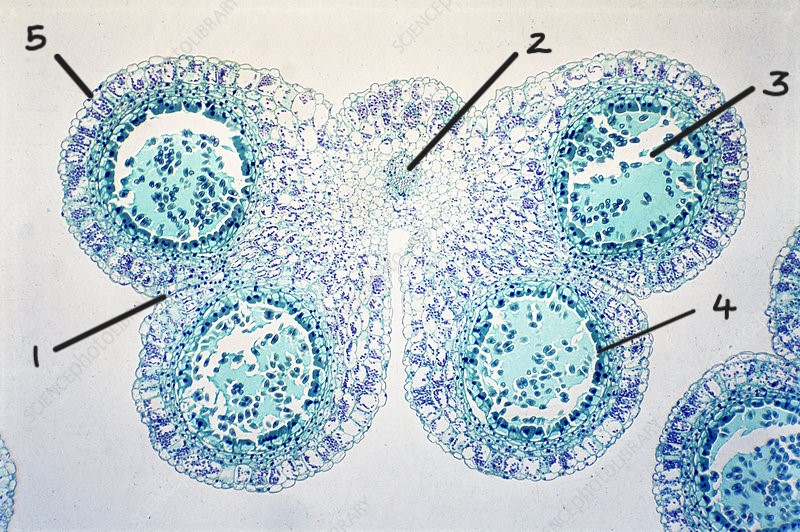
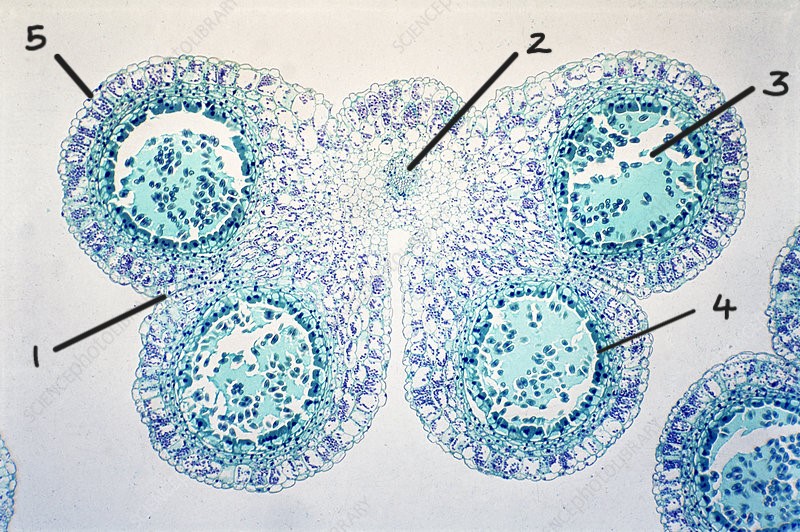
Identify this structure and label the diagram
anther
1. line of dehiscence
2. vascular bundle
3. pollen sac
4. tapetum
5. epidermis
1. line of dehiscence
2. vascular bundle
3. pollen sac
4. tapetum
5. epidermis
34
New cards
Where are the male sex cells found?
* anther
* inside pollen sacs surrounded by tapetum
* inside pollen sacs surrounded by tapetum
35
New cards
What is the function of the tapetum?
inner cell walls that provide nutrients to the developing pollen grains
36
New cards
What is dehiscence?
the opening of the anther, releasing pollen grains
37
New cards
What is the first stage in the development of the male gamete?
* diploid mother cells in pollen sacs undergo meiosis
* each forms a tetrad → contains 4 haploid cells which become 4 pollen grains
* each forms a tetrad → contains 4 haploid cells which become 4 pollen grains
38
New cards
What is the second stage in the development of the male gamete?
* haploid cells undergo mitosis
* each form a pollen grain with 2 haploid nuclei
* tube nucleus
* generative nucleus
* each form a pollen grain with 2 haploid nuclei
* tube nucleus
* generative nucleus
39
New cards
What is the third stage in the development of the male gamete?
* cell wall thickens → mature pollen grain formed
40
New cards
What is the function of the cell wall in male gamete and what are the 2 layers of this cell wall called?
* prevents desiccation (drying out) of the pollen grain
* intine (inner layer) and exine (outer layer)
* intine (inner layer) and exine (outer layer)
41
New cards
What is the function of the generative nucleus?
divides by mitosis to form 2 male nuclei during pollination
42
New cards
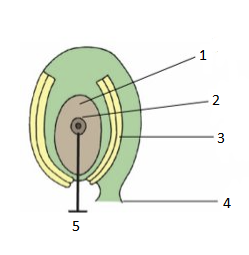
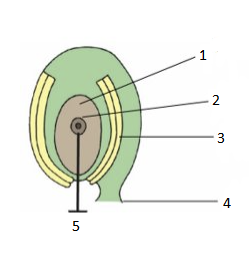
Identify this structure and label the diagram
immature plant ovule
1. nucellus
2. mother cell (2n)
3. integuments
4. funicle
5. megaspore mother cell
1. nucellus
2. mother cell (2n)
3. integuments
4. funicle
5. megaspore mother cell
43
New cards
What is the function of the nucellus?
to provide nutrition to the developing embryo
44
New cards
What is the first stage in the development of the female gamete?
megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis making 4 haploid cells → 3 degenerate
45
New cards
What is the second stage in the development of the female gamete?
remaining cell undergoes 3 rounds of mitosis → produces 8 haploid nuclei (one of these is the female gamete)
46
New cards
What is the third stage in the development of the female gamete?
* 2 of haploid nucleus fuse to form polar nuclei
* remaining nuclei develop cytoplasm around themselves and become separated by cell walls
* remaining nuclei develop cytoplasm around themselves and become separated by cell walls
47
New cards
What is the final structure of the ovule once the female gamete has been developed and the polar nucleus has been formed?
* 3 antipodal cells → top of ovule
* 2 polar nuclei → middle
* 2 synergids → on either side of female gamete
* female gamete → bottom of ovule
* 2 polar nuclei → middle
* 2 synergids → on either side of female gamete
* female gamete → bottom of ovule
48
New cards
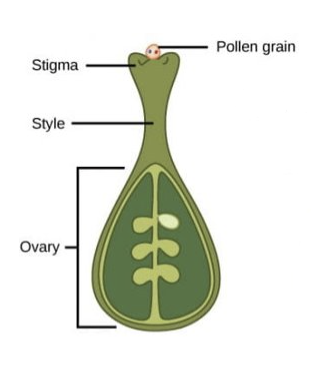
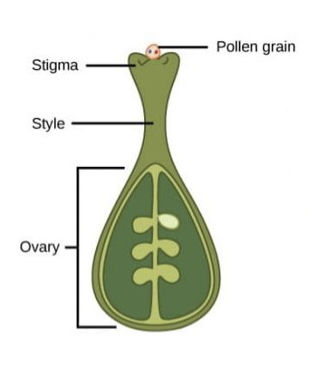
What happens in the 1st stage of double fertilisation?
* pollen grain adheres to stigma
* contains 2 cells → generative nucleus and tube nucleus
* contains 2 cells → generative nucleus and tube nucleus
49
New cards
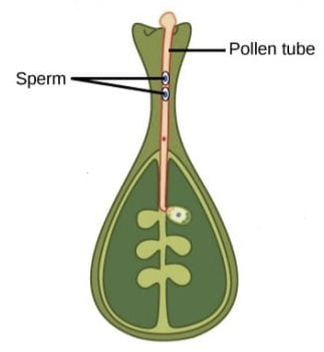
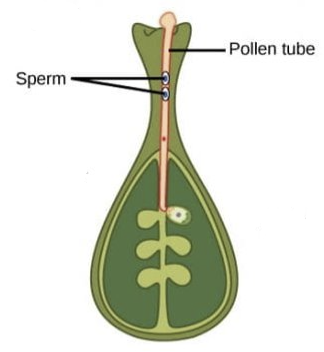
What happens in the 2nd stage of double fertilisation?
* pollen tube cell grows into style
* generative cell travels inside pollen tube
* divides to form 2 male gametes
* generative cell travels inside pollen tube
* divides to form 2 male gametes
50
New cards
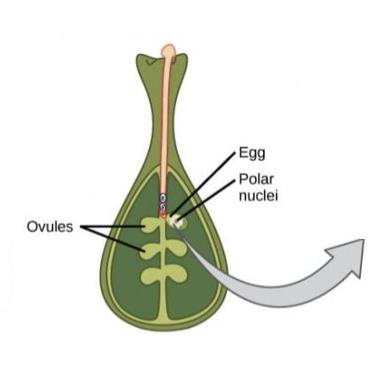
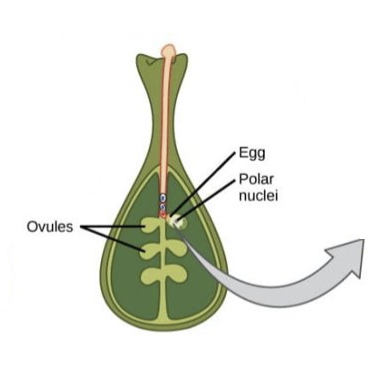
What happens in the 3rd stage of double fertilisation?
pollen tube penetrates opening in ovule → micropyle
51
New cards
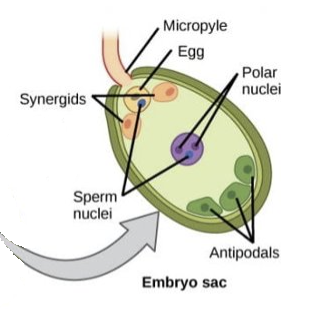
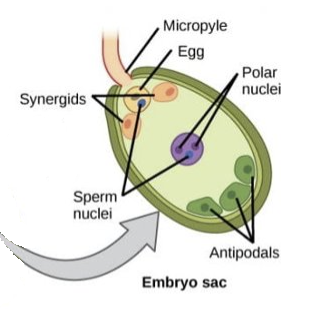
What happens in the 4th stage of double fertilisation?
* one male gamete fertilises female gamete → forms diploid zygote
* other male gamete fertilises 2 polar nuclei → forms triploid endosperm
* other male gamete fertilises 2 polar nuclei → forms triploid endosperm
52
New cards
What is the function of the endosperm?
to provide nutrition for developing embryo
53
New cards
What happens to the diploid zygote after fertilisation?
divides by mitosis to form an embryo
54
New cards
Which structures are contained in the embryo?
* plumule (developing shoot)
* radicle (developing root)
* one or two cotyledons
* radicle (developing root)
* one or two cotyledons
55
New cards
What is the micropyle?
pore in the seed
56
New cards
What do the integuments become after fertilisation?
become seed coat/testa (dried out with lignin)
57
New cards
What does the ovule contain and what does it become after fertilisation?
* contains endosperm, embryo and testa
* becomes seed
* becomes seed
58
New cards
What happens to the funicle after fertilisation?
attaches to hilum
59
New cards
What does the ovary become after fertilisation?
fruit
60
New cards
What is a dicotyledon?
* 2 seed leaves (cotyledons)
* endosperm absorbed into cotyledons so non-endospermic
* endosperm absorbed into cotyledons so non-endospermic
61
New cards
What is a monocotyledon?
* 1 seed leaf (cotyledon)
* endosperm remains as food source
* ovary wall and testa fuses
* endosperm remains as food source
* ovary wall and testa fuses
62
New cards
What does hypogeal mean?
below ground germination
63
New cards
What does epigeal mean?
above ground germination
64
New cards
What is the plumule?
shoot
65
New cards
What is the radicle?
root
66
New cards
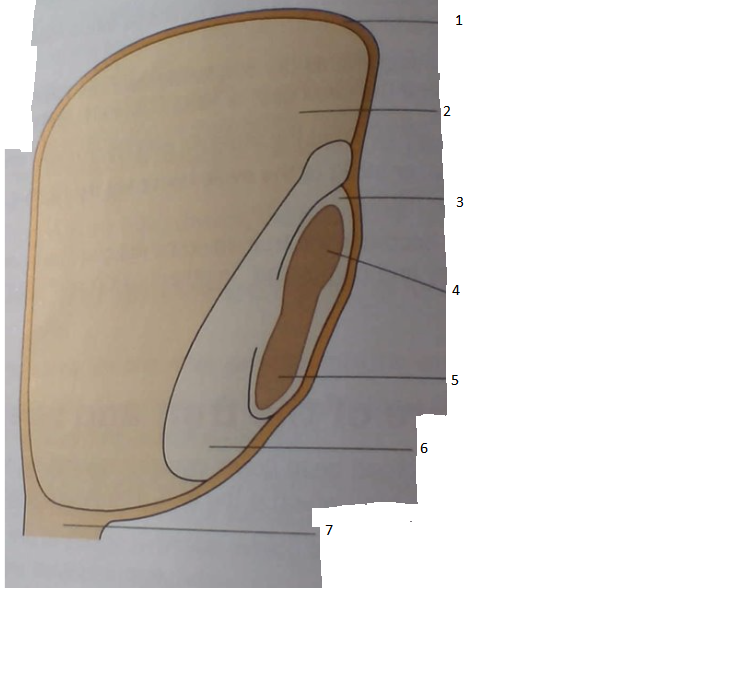

Identify the type of seed and label the diagram (beautiful ik)
monocotyledon
1. testa and ovary wall fused
2. endosperm
3. coleoptile (plumule sheath)
4. plumule
5. radicle
6. cotyledon
7. funicle
1. testa and ovary wall fused
2. endosperm
3. coleoptile (plumule sheath)
4. plumule
5. radicle
6. cotyledon
7. funicle

67
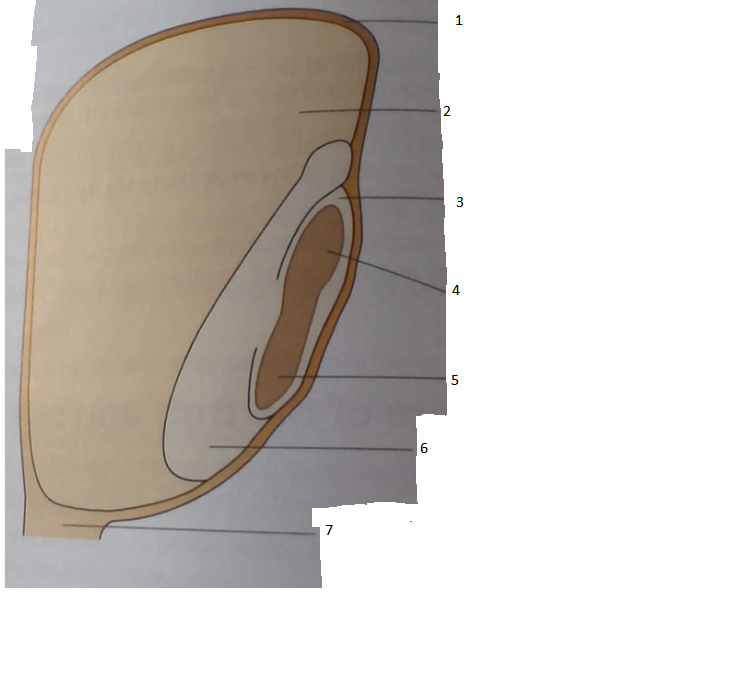
New cards
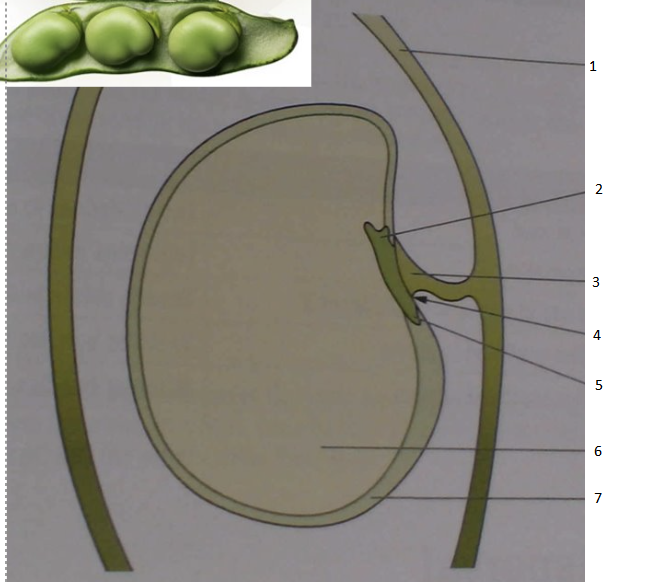
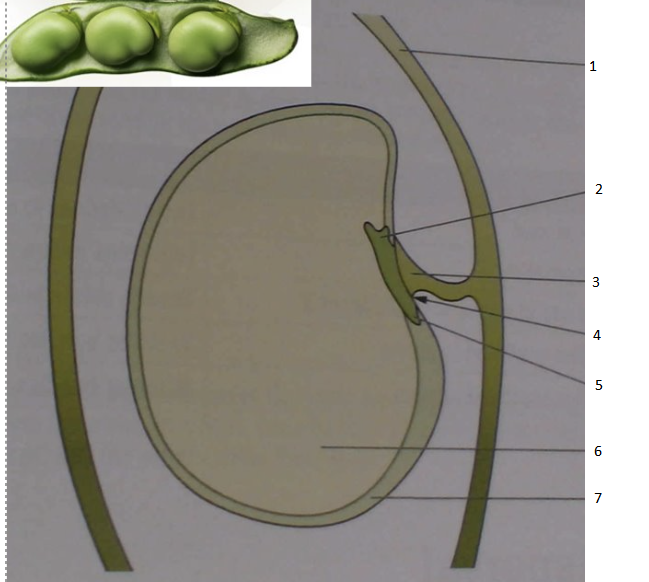
Identify the type of seed and label the diagram
dicotyledon
1. ovary wall
2. plumule
3. funicle
4. position of micropyle
5. radicle
6. cotyledon
7. testa
1. ovary wall
2. plumule
3. funicle
4. position of micropyle
5. radicle
6. cotyledon
7. testa
68
New cards
What happens during epigeous germination?
* radicle emerges from seed, raising cotyledons and remains of seed coat above ground
* cotyledons expand → may function as normal photosynthetic leaves but can transfer remaining nutrients to seedling and degenerate instead
* cotyledons expand → may function as normal photosynthetic leaves but can transfer remaining nutrients to seedling and degenerate instead
69
New cards
What happens during hypogeous germination?
* cotyledons don’t emerge from seed
* force radicle and plumule out of seed
* cotyledons remain underground and transfer nutrients to developing root and shoot
* force radicle and plumule out of seed
* cotyledons remain underground and transfer nutrients to developing root and shoot
70
New cards
What are the differences between monocotyledons and dicotyledons?
* monocotyledons
* sprout with 1 leaf
* parts with multiples of 3
* veins parallel to leaves
* vessels scattered
* pollen has single pore
* grasses, lilies, palms
* dicotyledons
* sprout with 2 leaves
* parts with multiples of 4/5
* veins branch out
* concentric rings of vessels
* pollen has 3 pores
* apples, sunflowers, strawberries
* sprout with 1 leaf
* parts with multiples of 3
* veins parallel to leaves
* vessels scattered
* pollen has single pore
* grasses, lilies, palms
* dicotyledons
* sprout with 2 leaves
* parts with multiples of 4/5
* veins branch out
* concentric rings of vessels
* pollen has 3 pores
* apples, sunflowers, strawberries
71
New cards
How has the evolutionary development of seeds aided the survival of angiosperms?
* low metabolic rate in dormant seeds → survive very cold weather
* testa chemically resistant → seeds survive adverse chemical conditions
* water content of dormant seeds reduced below 10% → can survive very dry conditions
* testa physically protects embryo
* endosperm or cotyledons provide nutrients → lasts until seed can photosynthesise
* seeds dispersed great distances from parent → no competition
* dispersal allows colonisation of new habitats
* testa chemically resistant → seeds survive adverse chemical conditions
* water content of dormant seeds reduced below 10% → can survive very dry conditions
* testa physically protects embryo
* endosperm or cotyledons provide nutrients → lasts until seed can photosynthesise
* seeds dispersed great distances from parent → no competition
* dispersal allows colonisation of new habitats
72
New cards
What conditions are necessary for germination?
* suitable temperature
* optimum for enzymes involved → between 5°C - 30°C
* light
* only some species
* water
* to make cells turgid → testa bursts
* to mobilise enzymes
* to hydrolyse food reserves
* to transport dissolved substances to embryo
* oxygen
* anaerobic respiration to release energy
* optimum for enzymes involved → between 5°C - 30°C
* light
* only some species
* water
* to make cells turgid → testa bursts
* to mobilise enzymes
* to hydrolyse food reserves
* to transport dissolved substances to embryo
* oxygen
* anaerobic respiration to release energy
73
New cards
Why does stored food need to be hydrolysed?
insoluble so can only be used by embryo for protein synthesis and respiration if hydrolysed
74
New cards
What are the food reserves of the seed?
* endosperm/cotyledons
* starch → main reserve
* oils
* protein
* starch → main reserve
* oils
* protein
75
New cards
What is the process of germination in monocotyledons?
* ==water enters== seed through micropyle
* @@Gibberellic acid@@ (plant growth regulator) @@diffuses@@ from embryo to @@Aleurone layer@@ → has high protein content
* Gibberellic acid triggers the transcription of genes
* %%translation%% of mRNA results in %%production of enzymes (incl. protease and amylase)%%
* ^^protease hydrolyses protein stores^^, releasing ^^amino acids^^ that are used in ^^amylase^^ production
* amylase ==hydrolyses starch== in ==endosperm==
* @@Maltose and glucose@@ diffuse to embryo plant where they’re used in @@respiration@@ → produce ATP needed for @@cell division and synthesis of organic molecules@@
* @@Gibberellic acid@@ (plant growth regulator) @@diffuses@@ from embryo to @@Aleurone layer@@ → has high protein content
* Gibberellic acid triggers the transcription of genes
* %%translation%% of mRNA results in %%production of enzymes (incl. protease and amylase)%%
* ^^protease hydrolyses protein stores^^, releasing ^^amino acids^^ that are used in ^^amylase^^ production
* amylase ==hydrolyses starch== in ==endosperm==
* @@Maltose and glucose@@ diffuse to embryo plant where they’re used in @@respiration@@ → produce ATP needed for @@cell division and synthesis of organic molecules@@
76
New cards
What is the process of germination in dicotyledons?
* water imbibed through micropyle
* tissues swell and enzymes become more active
* food reserves hydrolysed
* amylase digests starch in cotyledons into maltose
* maltose → glucose by maltase
* proteins → amino acids by protease
* transported to embryo
* glucose used for aerobic respiration and converted to cellulose for cell wall synthesis
* amino acids used for synthesis of proteins
* proteins used for mitosis/growth of plumule and radicle
* tissues swell and enzymes become more active
* food reserves hydrolysed
* amylase digests starch in cotyledons into maltose
* maltose → glucose by maltase
* proteins → amino acids by protease
* transported to embryo
* glucose used for aerobic respiration and converted to cellulose for cell wall synthesis
* amino acids used for synthesis of proteins
* proteins used for mitosis/growth of plumule and radicle
77
New cards