Basic Principles of Biomechanics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
________ is the study of movement.
Kinesiology
_____ branch of mechanics describes the motion of objects.
Kinematics
_____ is the study of forces that cause movement, including statics and dynamics.
Kinetics
_____ is a type of kinematics describes the movement of bony segments that make up a joint.
Osteokinematics
Forces acting on a stationary object
Statics
Forces acting on a moving object
Dynamics
_______ is the movement of a segment in a straight line where each point moves through the same distance.
Linear motion
______ is the combination of Rotary and Translatory displacement.
Curvilinear motion
______: motion refers to occurs around a 1.________ axis, where each point moves through the 2._____ angle at a 3.________ distance from the axis.
Angular, fixed, same, constant
Motion occurs in a circle around a(n) _______; every point on the object attached to the axis follows the arc of a circle.
Axis
5 Qualitative Variables of Osteokinematics:
Types of Displacement/ Motion
Location in Space of the Displacement
Direction of the Displacement of the Segment
Magnitude of the Displacement
Rate of Change in Displacement (Velocity) / Rate of Change of Velocity (Acceleration)
Type 1
1
True or False: For the Qualitative Variables of Osteokinematics, the Magnitude of Displacement can be also applied to arthrokinematics
True
__________: movement of articulating surfaces between two opposing ____ that make up the ____ (palpation)
Arthrokinematics, bones, joint
_______ is the most common type of motion in the body.
Curvilinear motion
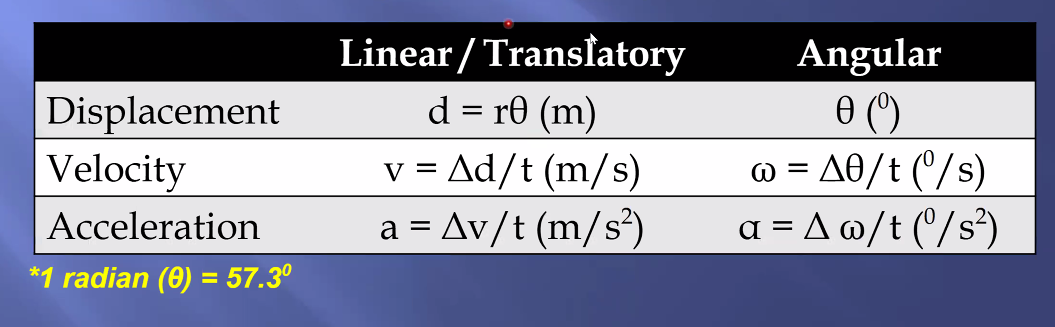
Displacement, Velocity & Acceleration formulas (Type 1)
1
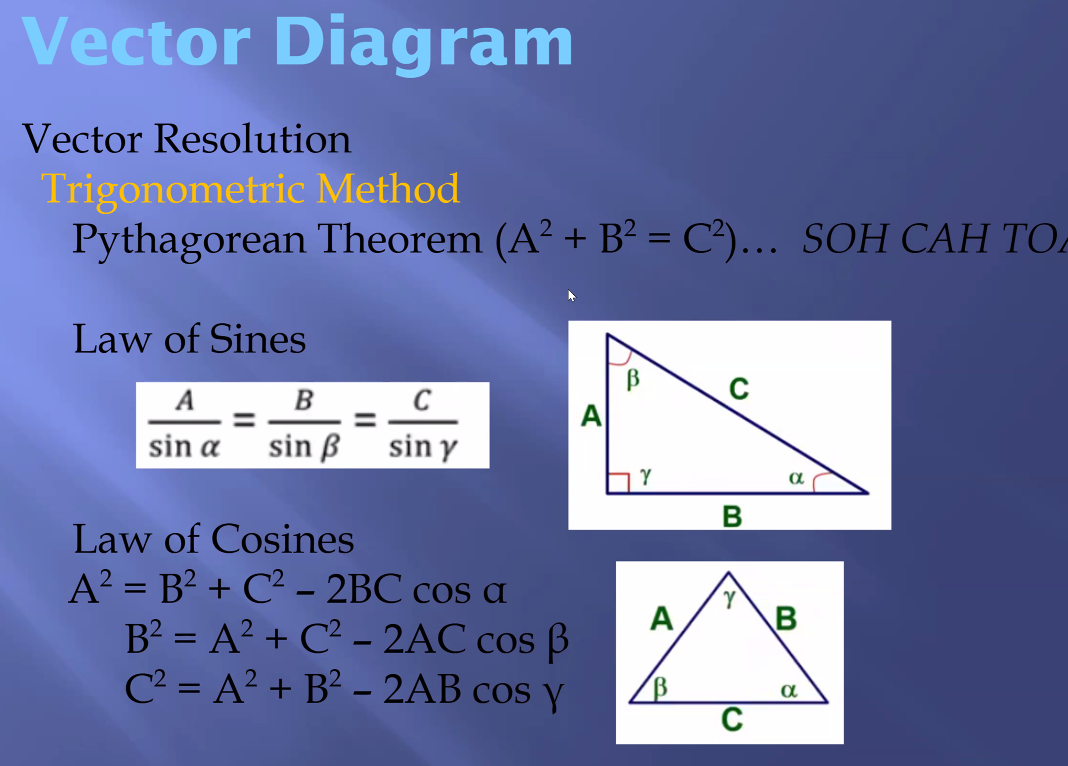
Trigonometric Method (Type 1)
1

Example 3 (Type 1)
1
Axis of the following planes:
Sagittal
Frontal
Transverse
X, Z, Y
Give 2 movements of the Sagittal Plane.
Flexion, Extension
Give 2 movements of the Frontal Plane.
Abduction, Adduction
Give 2 movements of the a Transverse Plane.
Lateral, Medial rotation
What is the pivot point for angular or rotary motion called?
Axis of Rotation
What are the three types of arthrokinematic motion?
Roll, Slide, Spin
Which type of joint focuses more on stability and has limited or no mobility?
Synarthroses
Which type of joint has a cavity that permits movements between two opposing bones?
Diarthroses
Which joint type allows movement in three planes?
Multiaxial
There are _ degrees of freedom in a human body.
3
Type of Motion: (Answer/Answer)
______ when new points on one bony segments that meet the new points in the opposing bony segment
Roll/Rock
Type of Joint: (Answer/Answer)
A single point in one articulating surface would meet new point on the opposing articulating surface
Slide/Glide
_____ is when a single point on the two opposing segments that are fixed and the bony segment would rotate over that fixed point.
Spin
True or False: In the Convex/cave rule, If the CONVEX surface is moving, gliding will occur opposite to the movement of the long bone…
True
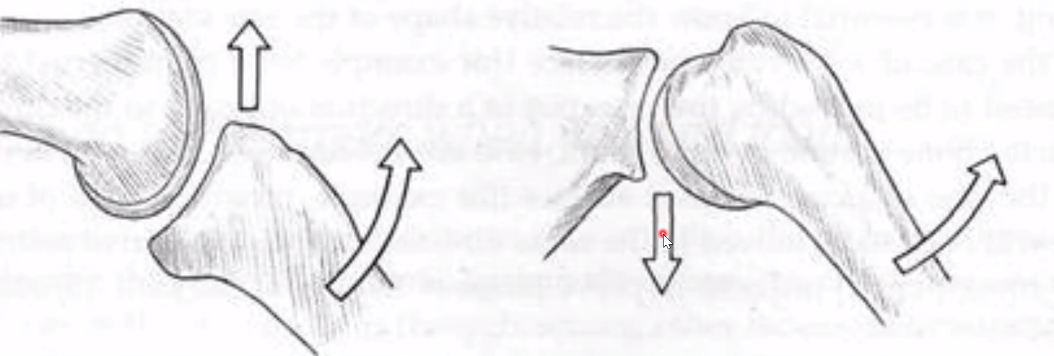
Convex moving: Roll opposite to concave, Glide opposite of shaft of long bone…
Concave: Roll & Glide same direction as the long bone…
(Type 1)
1
"When a ________ surface moves on a convex surface, the roll and glide occur in the ________ direction."
concave, same
During Knee extension, which occurs in the sagittal plane, the concave tibia rolls and glides ________.
anteriorly
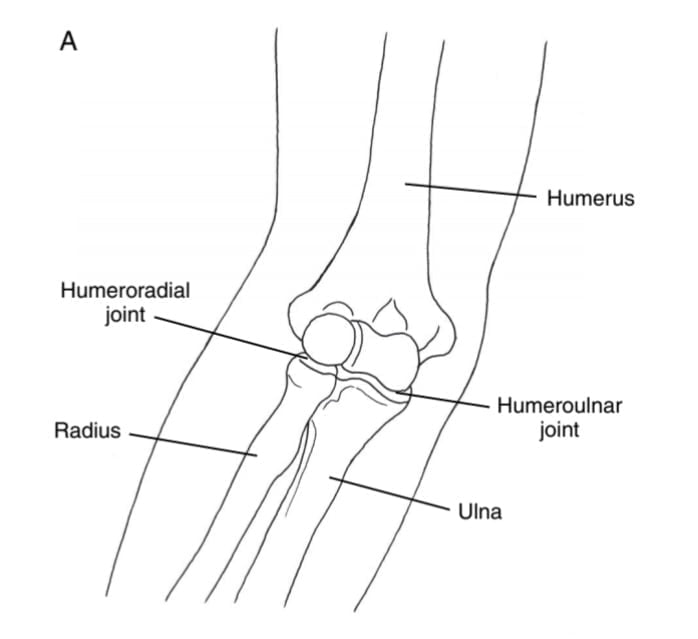
In the humeroulnar joint, during elbow flexion, the _____ ulna rolls and glides in the ________ direction."
Concave, same
During Hip internal rotation, which occurs in the transverse plane, the convex femoral head rolls ________ and glides ________.
anteriorly, posteriorly
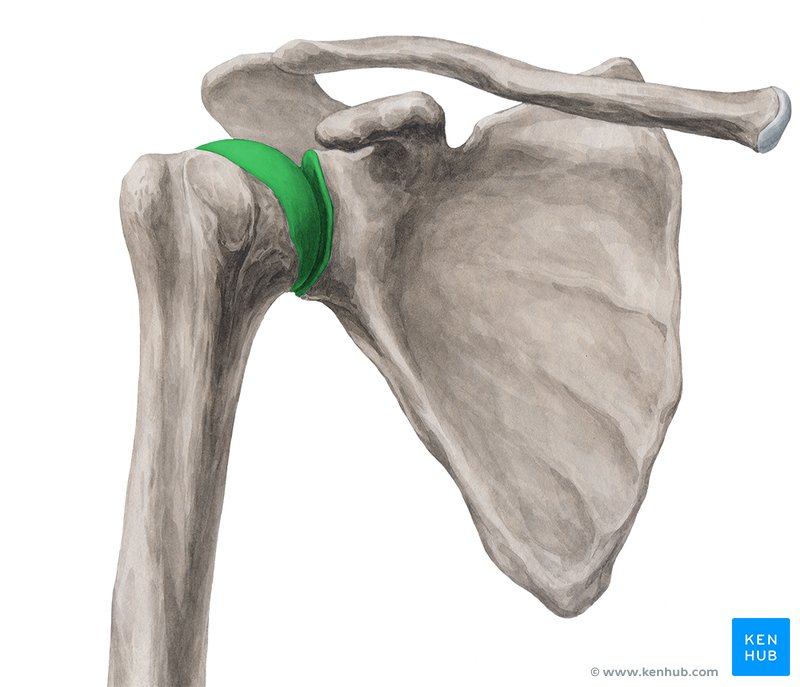
In the Glenohumeral joint, when the convex humeral head moves on the concave glenoid cavity, the roll and glide occur in ________ directions.
opposite
Same or Opposite: Glide of tibial surface on knee extension
same
Same or Opposite: Roll of talus during ankle dorsiflexion
Same
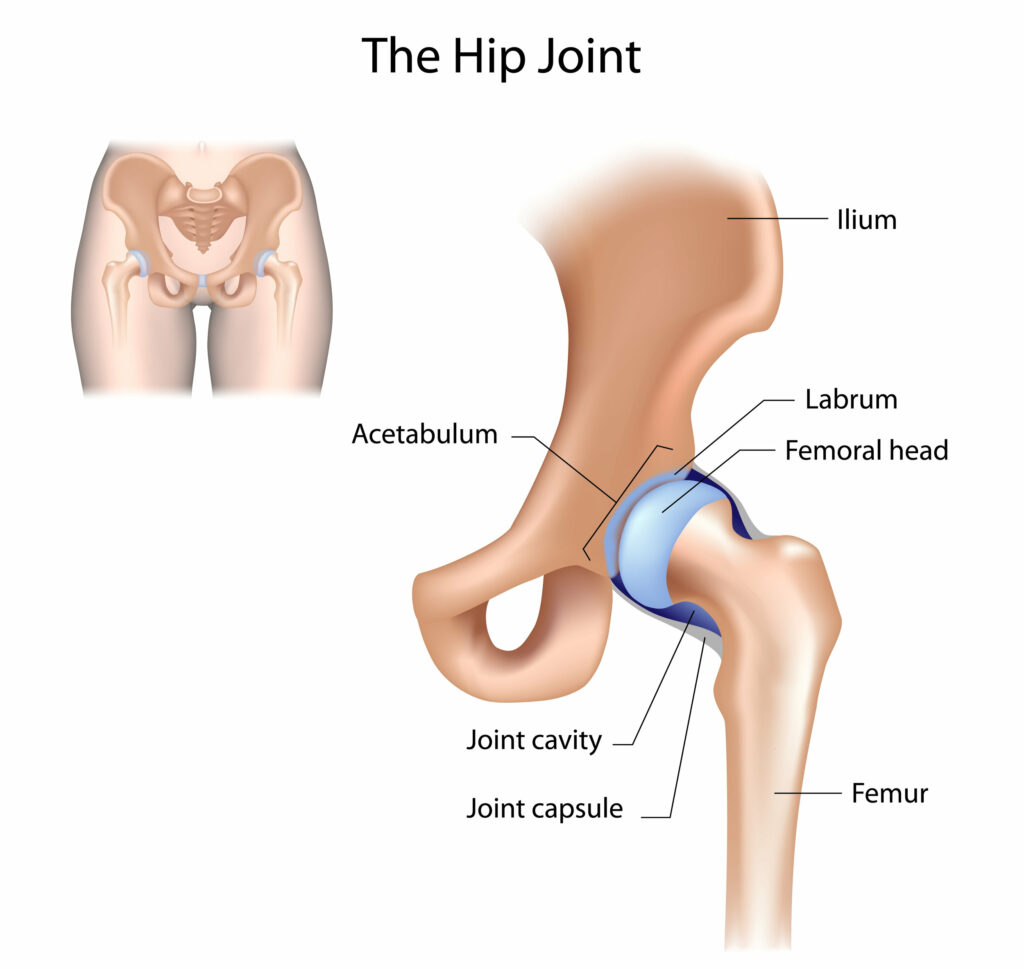
In the Hip joint, the convex femoral head moves on the concave acetabulum, the roll and glide occur in ________ directions.
opposite
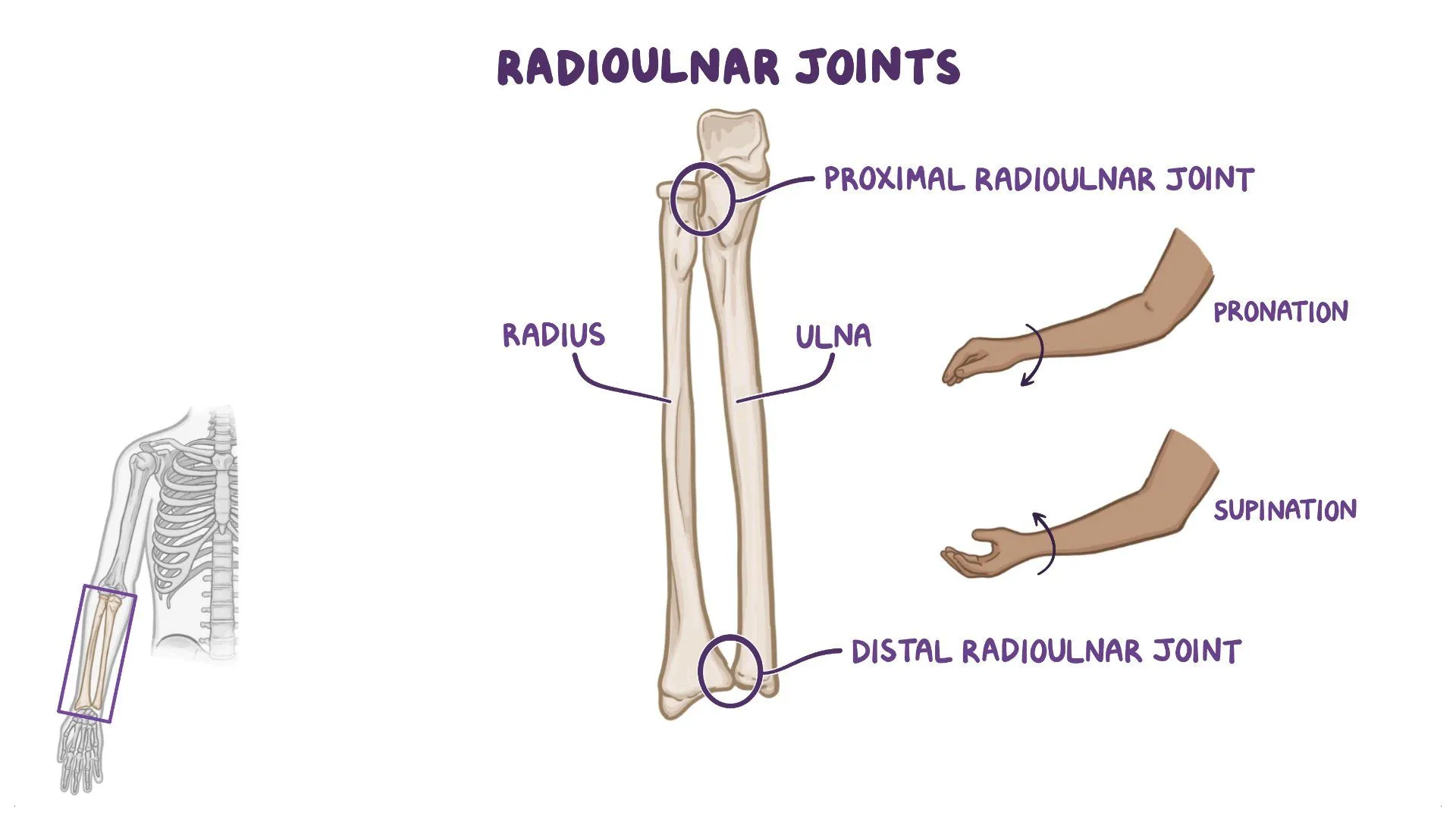
In the Radioulnar joint, during pronation, the concave radial head glides in the ________ direction as the roll on the convex ulna.
same
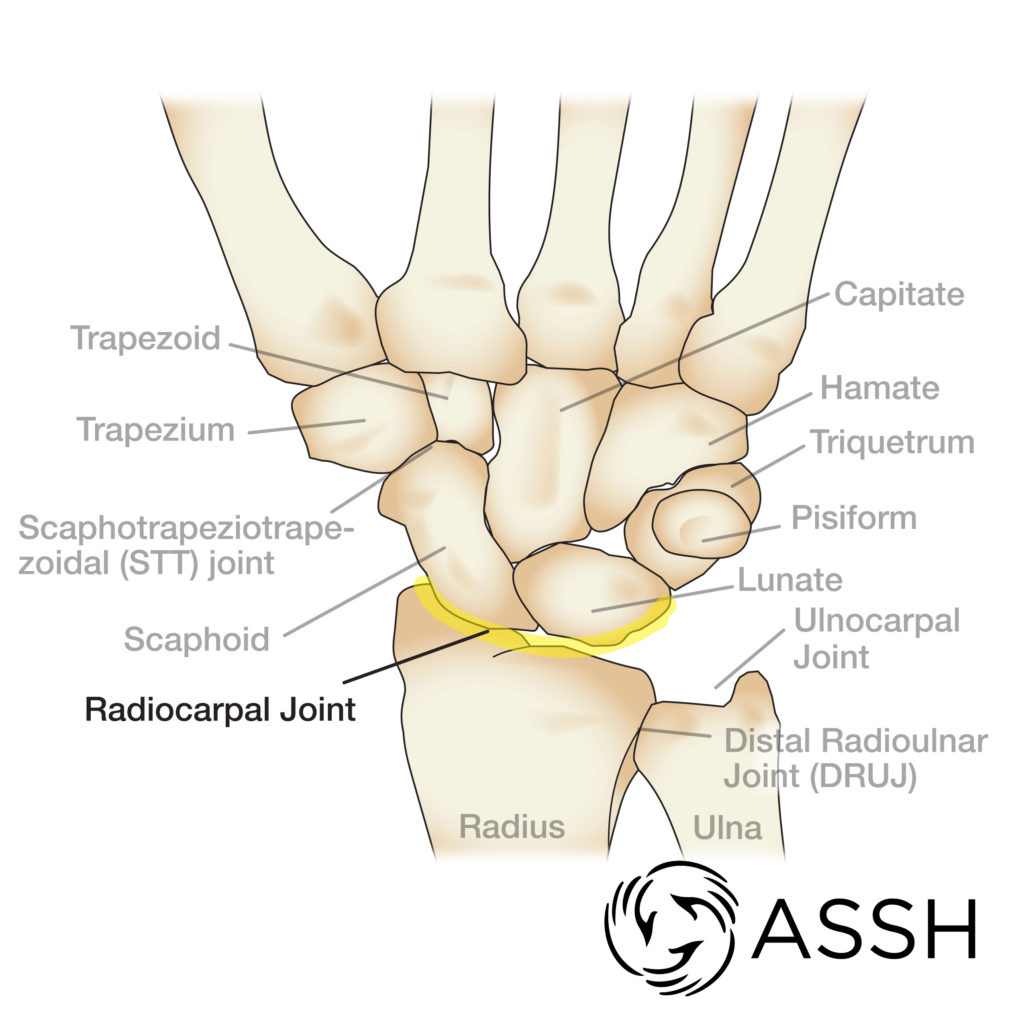
In the Radiocarpal joint during radial deviation, the carpal bones are _____ , and the radius is _______, the carpal bones move ______.
convex, concave, laterally
In the Ankle joint, during dorsiflexion of the convex talus on the concave tibia, the roll and glide occur in ________ directions.
opposite
_____ is the axis about the segment moves is not fixed
Instantaneous Axis of Rotation
In an open kinematic chain, the terminal segment is ________ to move in space, and the movements are -on- segment kinematics.
free
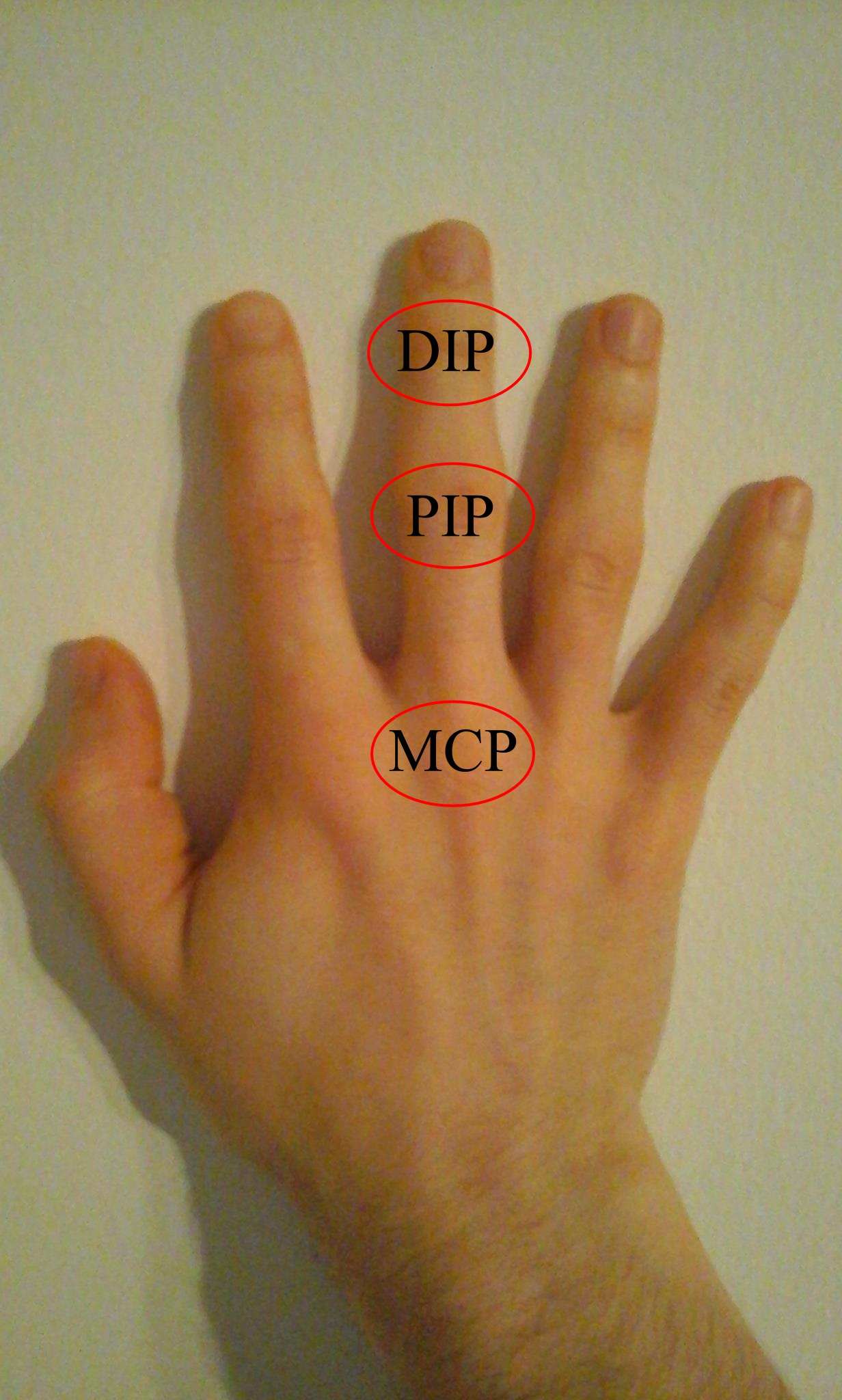
_______/Ginglymus joint - ex. Finger DIP/PIP joints (flexion, extension in sagittal plane).
Hinge
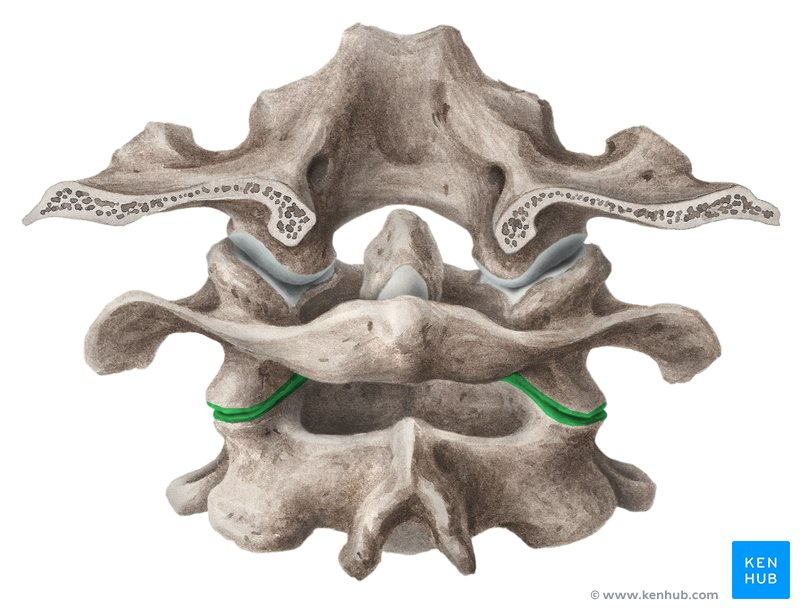
____/_______ Joint - eg. atlantoaxial joint (“no” joint; in the transverse plane).
Pivot/trochoid
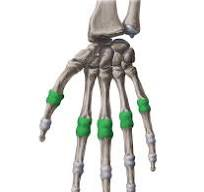
_______/_______ joint - ex. MCP joint ( flexion, extension in sagittal plane and abduction, adduction in frontal plane).
Condyloid/ellipsoid
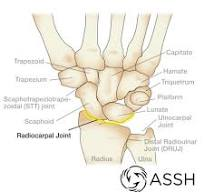
Radiocarpal joint (_________; wrist flexion, extension in sagittal plane and wrist abduction, adduction in frontal plane).
ellipsoid
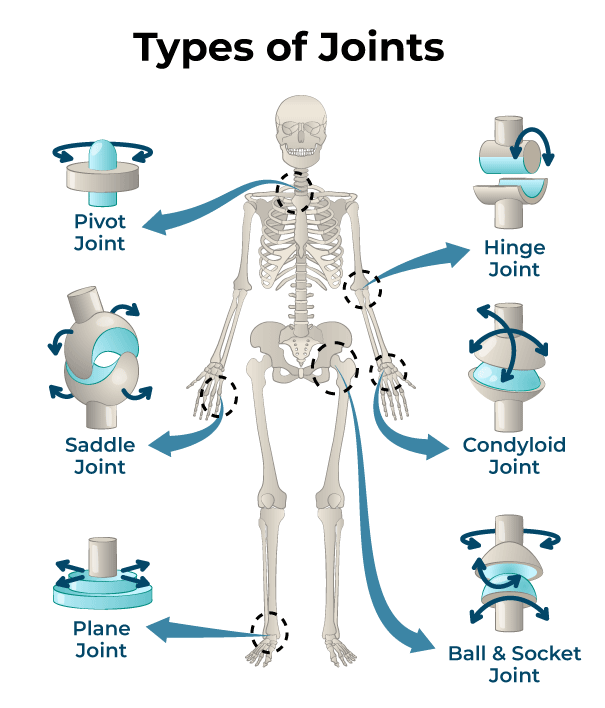
________ joint - spherical convex surface partnered with an opposing concave surface.
Condyloid
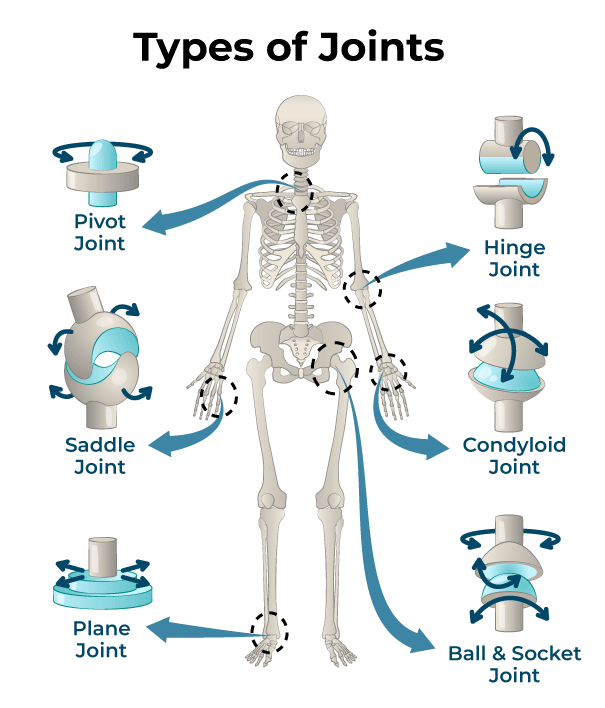
_______ joint - has a spindle-like shape in which one somewhat flattened convex surface articulates with a fairly deep concave surface.
Ellipsoid
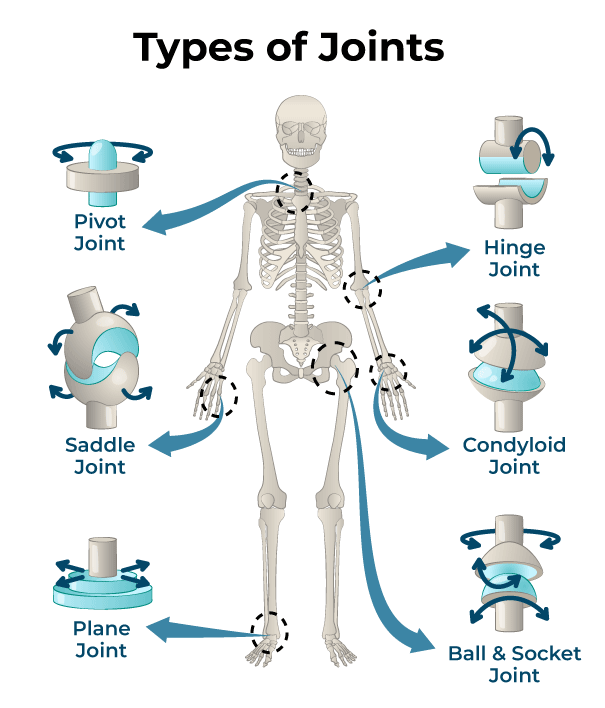
______ /_______ Joint ( reciprocal reception joint) - ex. 1st CMC joint (thumb; flexion, extension in sagittal plane; abduction, adduction in frontal plane; opposition of the thumb).
Saddle/Double plane
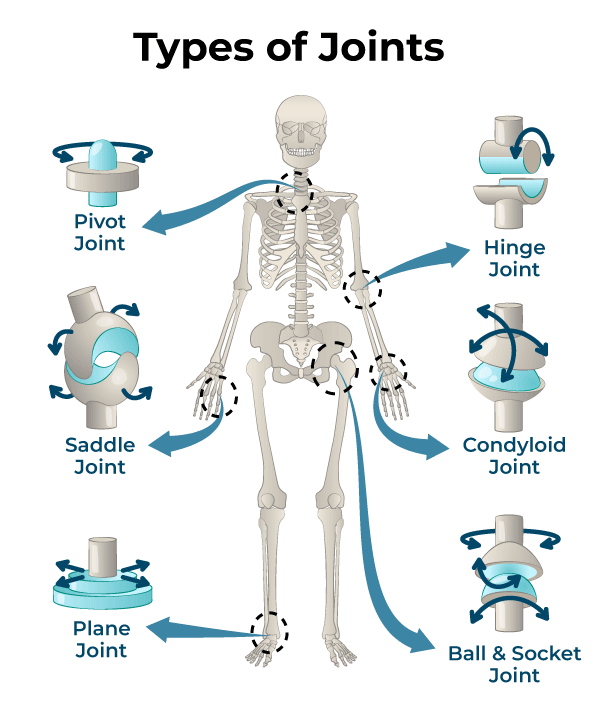
_______ Joint - ex. Joints between carpal bones; sternoclavicular joint.
Plane
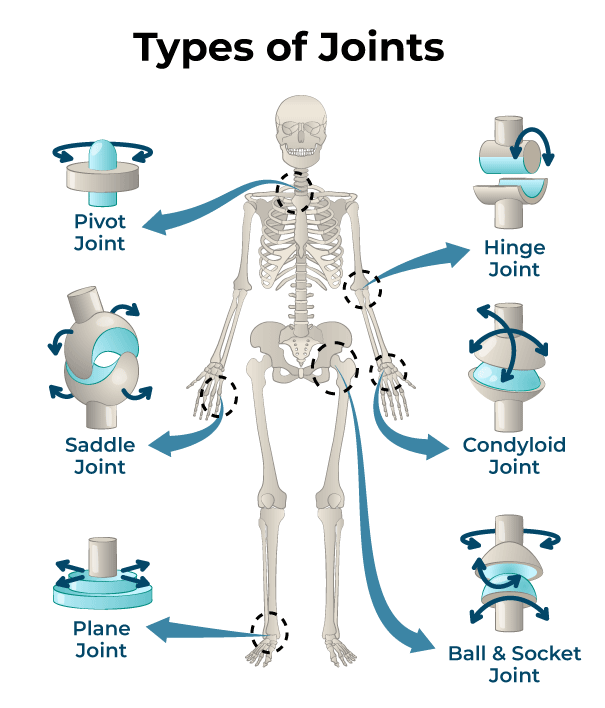
____ _ ______/_______ Joint - ex. Glenohumeral joint; coxofemoral joint.
Ball and socket/ enarthrosis
_______ of the displacement: Full ROM, limited ROM, excessive ROM.
Magnitude
For osteo - _______/gonio (common).
linear
For arthro - x-rays/musculoskeletal _______.
ultrasound
Rate of change in displacement: Velocity (_______); acceleration (_____).
Constant, change