Abnormal Psych 3230 Test 1 - UGA Miller (Maymester)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/136
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:09 PM on 9/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
5 ways Wakefield explained how mental disorders cannot be defined as
1. value concept
2. what professionals treat
3. statistical deviance
4. biological disadvantage
5. causes distress or suffering
2. what professionals treat
3. statistical deviance
4. biological disadvantage
5. causes distress or suffering

2
New cards
Wakefield's Harmful Dysfunction
disorders must have a mechanism that fails to function normally & cause impairment - hybrid of "value judgement" and "biological disadvantage"
3
New cards
DSM-5 definition of mental disorder
- breakdown in functioning
- personal distress or disability (functional impairment)
- atypical or unexpected in terms of culture
- personal distress or disability (functional impairment)
- atypical or unexpected in terms of culture

4
New cards
Widiger definition of mental disorder
1. dyscontrol - cannot control choices
2. maladaptivity - life suffers due to lack of control
2. maladaptivity - life suffers due to lack of control
5
New cards
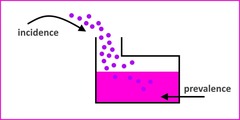
Prevalence
The number or proportion of cases of a particular disease or condition present in a population at a given time.

6
New cards
Incidence
The number or rate of new cases of a particular condition during a specific time.
7
New cards
For treatment, keep in mind
1. Prevalence
2. Incidence
3. Course
4. Onset of disorder
5. Prognosis
2. Incidence
3. Course
4. Onset of disorder
5. Prognosis

8
New cards
Etiology
the study of the causes of diseases
9
New cards
Galenic-Hippocratic Tradition (biological)
- linked abnormality with brain chemical imbalances
- foreshadowed modern views of neurotransmitters
- foreshadowed modern views of neurotransmitters
10
New cards
Psychological tradition - Plato & Aristotle believed
social & cultural influences & early learning impacted psychopathology
11
New cards
Psychoanalytic theory
A theory developed by Freud & Breuer that attempts to explain personality, motivation, and mental disorders by focusing on unconscious determinants of behavior
12
New cards
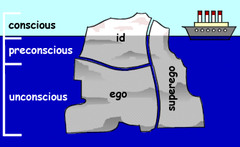
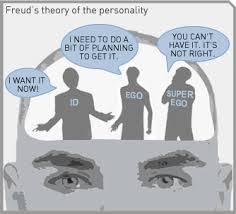
Id
a reservoir of unconscious psychic energy that, according to Freud, strives to satisfy basic sexual and aggressive drives (primary process).
The id operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification (toddler thinking)
The id operates on the pleasure principle, demanding immediate gratification (toddler thinking)
13
New cards
Ego
the largely conscious, "executive" part of personality that, according to Freud, mediates among the demands of the id & superego. The ego operates on the reality principle
14
New cards
Superego
conscious part of mind that represents moral ideals learned from society from rewards and punishments (adult thinking)
15
New cards
Affiliation (Defense Mechanism)
turning to other for support when presented with conflict - affiliate with others
16
New cards
Humor (Defense Mechanism)
the focus of amusing or ironic aspects of conflict/stressor
17
New cards
Sublimation (Defense Mechanism)
channeling threatening devices into acceptable outlets (e.g. working out)
18
New cards
Displacement (Defense Mechanism)
the transfer of feelings from one target to another that is considered less threatening

19
New cards
Intellectualization (Defense Mechanism)
use of excessive reasoning or logic to deal with situations rather than feeling their emotions
20
New cards
Reaction Formation (Defense Mechanism)
preventing unacceptable thoughts or behaviors from being expressed by exaggerating opposite thoughts or types of behaviors (e.g. gay conservatives)

21
New cards
Repression (Defense Mechanism)
involuntary blocking of unpleasant feelings and experiences from ones conscious awareness
22
New cards
Projection (Defense Mechanisms)
falsely attributing one's own thoughts, feelings, or motives to another

23
New cards
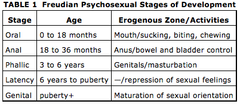
5 stages of psychosexual development (Freud)
1. Oral Stage - focus on food, mouth pleasure
2. Anal Stage - expulsion or retention of feces
3. Phallic Stage - notice genitals & differences, oedipus/electra complex
4. Latency Stage - nonsexual interest
5. Genital Stage - sexual interest
2. Anal Stage - expulsion or retention of feces
3. Phallic Stage - notice genitals & differences, oedipus/electra complex
4. Latency Stage - nonsexual interest
5. Genital Stage - sexual interest
24
New cards
Psychoanalysis therapy goals (Freud)
analyze & resolve conflict cause through catharsis, dream analysis, & free association, restructure personality - less focus on reducing symptoms but finding their cause
25
New cards
Transference and Countertransference
- patient talks to therapist as if they are something from their past experience (good)
- therapist transferring own experience onto their patient (bad)
- therapist transferring own experience onto their patient (bad)
26
New cards
Psychodynamic theory
focus on affect, patient avoidance of topics/behaviors, patterns in behavior & thoughts, past experience, interpersonal experience. large therapeutic alliance
some exploration of fantasies/dreams
some exploration of fantasies/dreams
27
New cards
Humanistic theory (Maslow & Rodgers)
people are inherently good and continue to strive to make themselves better to reach self-actualization

28
New cards
Client-centered therapy (Carl Rodgers)
- minimal therapist intervention
- therapist conveys empathy
- belief that patients have the resources within themselves to solve their own problems with support
- therapist conveys empathy
- belief that patients have the resources within themselves to solve their own problems with support
29
New cards
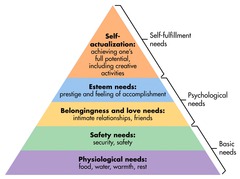
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
1. physiological - food & water
2. safety - safe home
3. social - sense of belonging
4. esteem - sense of achievement
5. self-actualization
2. safety - safe home
3. social - sense of belonging
4. esteem - sense of achievement
5. self-actualization
30
New cards
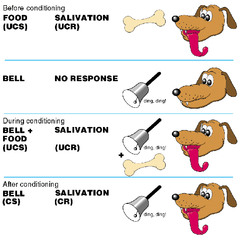
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov & Watson)
pairing neutral stimuli with unconditioned response
31
New cards
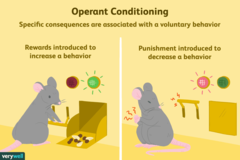
Operant Conditioning (Thorndike & Skinner)
behaviors shaped by rewards and punishments (Thorndike's Law of Effect)
32
New cards
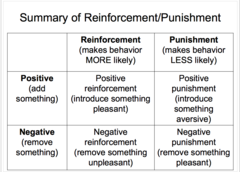
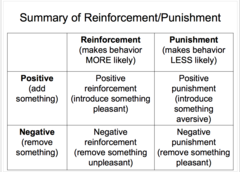
Positive & Negative Reinforcement
+ the addition of positive experience
- the removal of a negative experience
- the removal of a negative experience
33
New cards
Positive & Negative Punishment
+ the addition of a negative experience
- the removal of a positive experience
- the removal of a positive experience
34
New cards
Shaping behavior
reinforcing successive approximations of desired behaviors
35
New cards
Wolpe
systematic desensitization (exposure therapy)

36
New cards
Beck
cognitive therapy

37
New cards
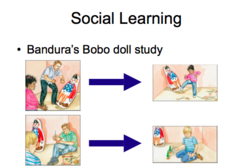
Bandura
social learning, cognitive behavior therapy, vicarious learning
38
New cards
Perl's Gestalt Therapy
emphasis on body language, questioning patient, pushes to find root of problem
39
New cards
Ellis' Rational-Emotive Therapy
high therapist involvement & interpretation of client's words
40
New cards
Aspects of Multidimensional Approach to Psychopathology
1. biological factors
2. behavioral & cognitive factors
3. emotional factors
4. social factors
5. developmental factors
2. behavioral & cognitive factors
3. emotional factors
4. social factors
5. developmental factors
41
New cards
Diathesis-stress Model
a diagnostic model that suggests a disorder may develop when an underlying genetic vulnerability (diathesis) is coupled with a particular environment (stress)
42
New cards
Gene-environment Correlation
genes can increase probability that an individual will experience certain environmental events
43
New cards
Passive Gene-environment Correlation
genes are correlated to the environment raised in
44
New cards
Evocative Gene-environment Correlation
genes may lead to behaviors that evoke a certain response from the environment
45
New cards
Proactive Gene-environment Correlation
genes make the selection of a certain environment more likely

46
New cards
Non-Genomic Inheritance of Behavior
genes are not the whole story, environmental influences may override genetics
47
New cards
Agonist neurotransmitter
increase activity by mimicking effects
48
New cards
Antagonist neurotransmitter
decrease or block a neurotransmitter
49
New cards
Inverse Agonist neurotransmitter
produce effects opposite to those produced by neurotransmitter
50
New cards
Serotonin
affects behavior, mood, & cognition
- treated with SSRIs (prozac)
- treated with SSRIs (prozac)
51
New cards
Glutamate
excitatory neurotransmitter (exciting)
52
New cards
GABA
inhibitory neurotransmitter (calming)
- increase GABA w/ benzodiazepines (valium, xanax)
- increase GABA w/ benzodiazepines (valium, xanax)
53
New cards
Norepinephrine
increase heart rate, blood pressure (fight or flight reaction)
- beta-blockers reduce anxiety response
- beta-blockers reduce anxiety response
54
New cards
Dopamine
switch that impacts the effects of other neurotransmitters
- implicated w/ schizophrenia & Parkinson's (low)
- implicated w/ schizophrenia & Parkinson's (low)
55
New cards
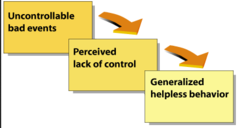
Learned helplessness
a condition that occurs after a period of negative consequences where the person begins to believe they have no control
56
New cards
Social learning
learning through observing others (modeling)
57
New cards
Prepared learning
learning that occurs without extensive training because of an evolved predisposition to the behavior
58
New cards
Cognitive science & unconscious in psychopathology
behavior may be impacted without direct knowledge, implicit beliefs
59
New cards
Emotional Dysregulation
an inability to control negative emotions in response to stressful life events or feeling too much of an emotion without cause
60
New cards
Emotion
short lived state of mind
61
New cards
Mood
persistent, enduring state of mind
62
New cards
Affect
non-verbal behavior that goes with mood (or mismatches mood)
63
New cards
Principal of Equifinality
psychological disorders can take many paths that lead up to the same outcome (the disorder)
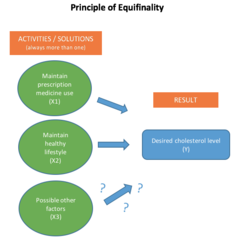
64
New cards
Multi-finality
the same experience can lead to many different outcomes
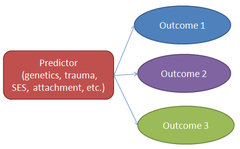
65
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
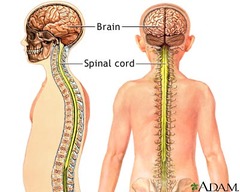
66
New cards
Soma
cell body of a neuron

67
New cards
Dendrites
receive messages from other neurons
68
New cards
Axon
part of neuron that sends chemical messages
69
New cards
Synapses
small gaps that separate neurons
70
New cards
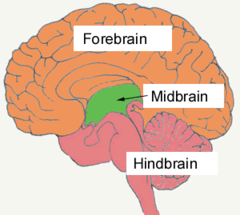
3 divisions of brain
hindbrain, midbrain, forebrain
71
New cards
3 parts of the hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum
72
New cards
Medulla
controls heart-rate, blood pressure, and breathing
73
New cards
Pons
sleep stages
74
New cards
Cerebellum
physical coordination
75
New cards
Midbrain
sensory information, reticular activating system (RAS- sleep cycles)
76
New cards
Forebrain (cerebral cortex)
sensory, emotional, and cognitive processing
77
New cards
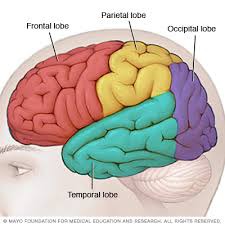
4 lobes of cerebral cortex
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal
78
New cards
Frontal Lobe
thinking, reasoning, & memory
79
New cards
Parietal Lobe
touch recognition
80
New cards
Occipital Lobe
visual input
81
New cards
Temporal Lobe
recognition of sights, smells, & sounds - long term memory & complex stimuli
82
New cards
Limbic System
emotion, motivation, & memory
83
New cards
Thalamus (Limbic System)
conveys sensory information to cortex
84
New cards
Hypothalamus (Limbic System)
eating, drinking, aggression, sex
85
New cards
The somatic branch of the peripheral nervous system
controls voluntary muscle movement
86
New cards
The autonomic branch of peripheral nervous system
regulates cardiovascular system & temp, endocrine system & digestion
87
New cards
Sympathetic nervous system (autonomic branch)
mobilizes body during stress (fight or flight)
88
New cards
Parasympathetic nervous system (autonomic branch)
restore equilibrium & energy when not stressed
89
New cards
Clinical Assessment
Systematic evaluation and measurement of psychological, biological, and social factors in a person presenting with a possible psychological disorder
90
New cards
Diagnosis
process of determining whether a presenting problem meets the established criteria for a specific psychological disorder
91
New cards
Reliability
the degree to which a measure is stable and consistent over time

92
New cards
Test-restest Reliability
the consistency in results every time a measure is used (across time)
93
New cards
Inter-rater Reliability
a measure of how similarly two different test scorers (raters) would score a test.
94
New cards
Internal Consistency Reliability
items are consistent with measuring one construct
95
New cards
Validity
the extent to which a test captures the construct

96
New cards
Content Validity
the extent to which a test measures full conceptualization of a construct
97
New cards
Convergent Validity
scores on the measure are related to other measures of the same construct
98
New cards
Criterion & Discriminant Validity
is the measure related to other constructs that are thought to be related and not related to those thought to be not related
99
New cards
Face Validity
extent to which respondents can tell what the items are measuring, does it appear to test what it is testing
100
New cards
Predictive Validity
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict