(4) Principles of Quantum Mechanics / Atomic Orbitals
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
quantum numbers.
The allowed energy states of atoms and molecules can be described by sets of numbers called __________
Schrodinger, Heisenberg & Dirac
Quantum numbers are the solutions of the _______, ____ & _________equations.
Four quantum numbers
___________ are necessary to describe energy states of electrons in atoms.
Principal quantum number (n)
__________________– size and energy of the orbital.
Angular momentum quantum number (l)
_____________________- shape of atomic orbitals (sometimes called a subshell).
Magnetic quantum number (ml)
________________- orientation of the orbital in space relative to the other orbitals in the atom.
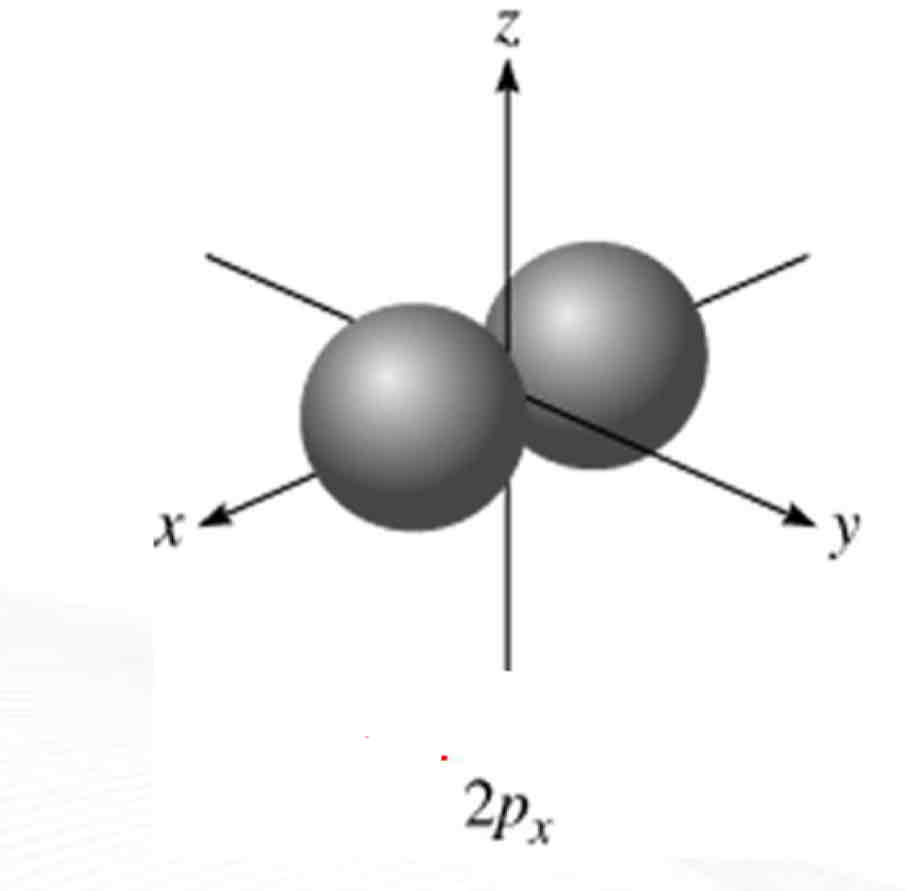
Px
What atomic orbital is being shown?
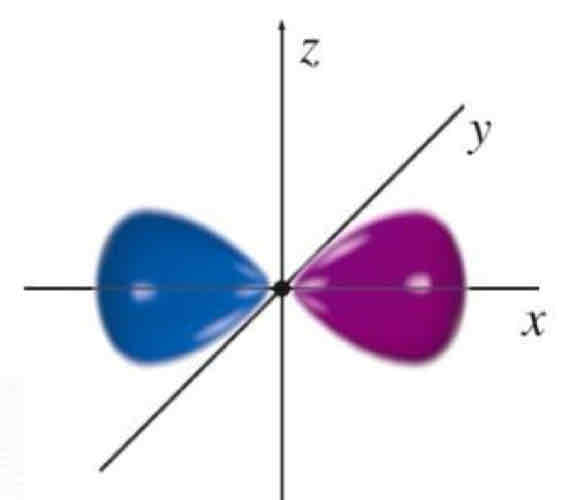
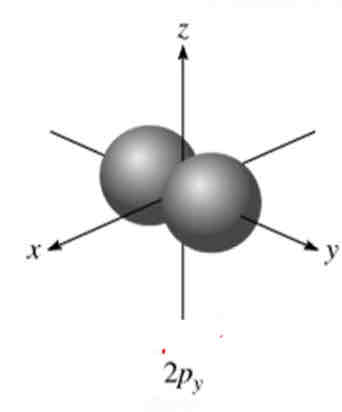
Py
What atomic orbital is being shown?
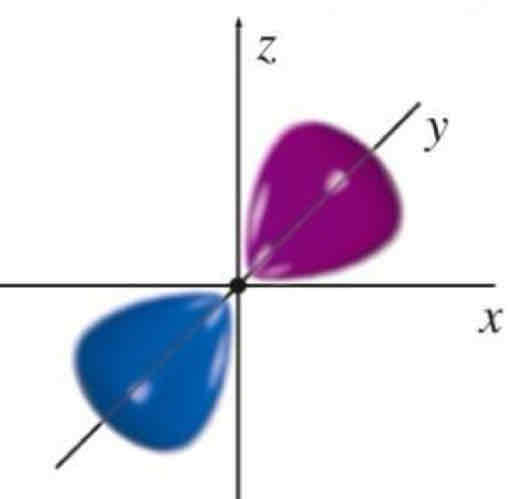
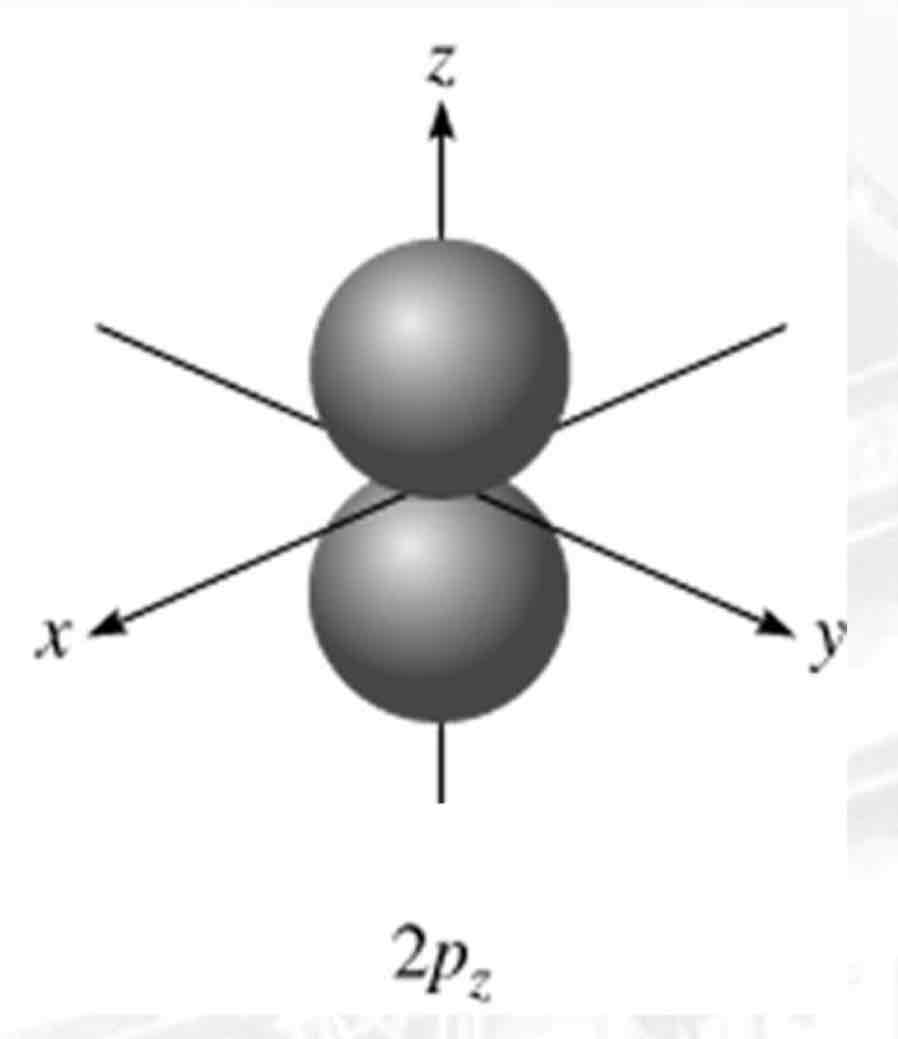
Pz
What atomic orbital is being shown?
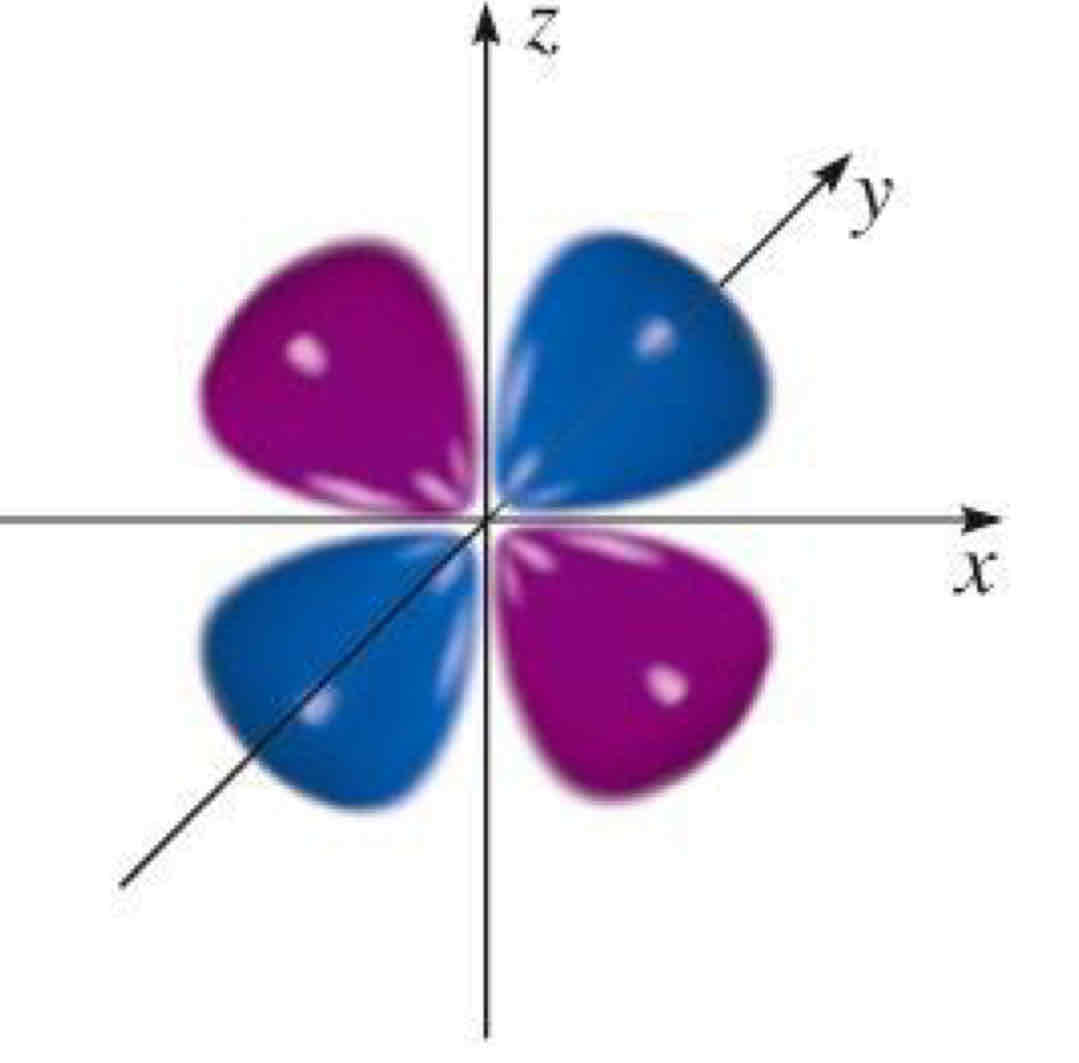
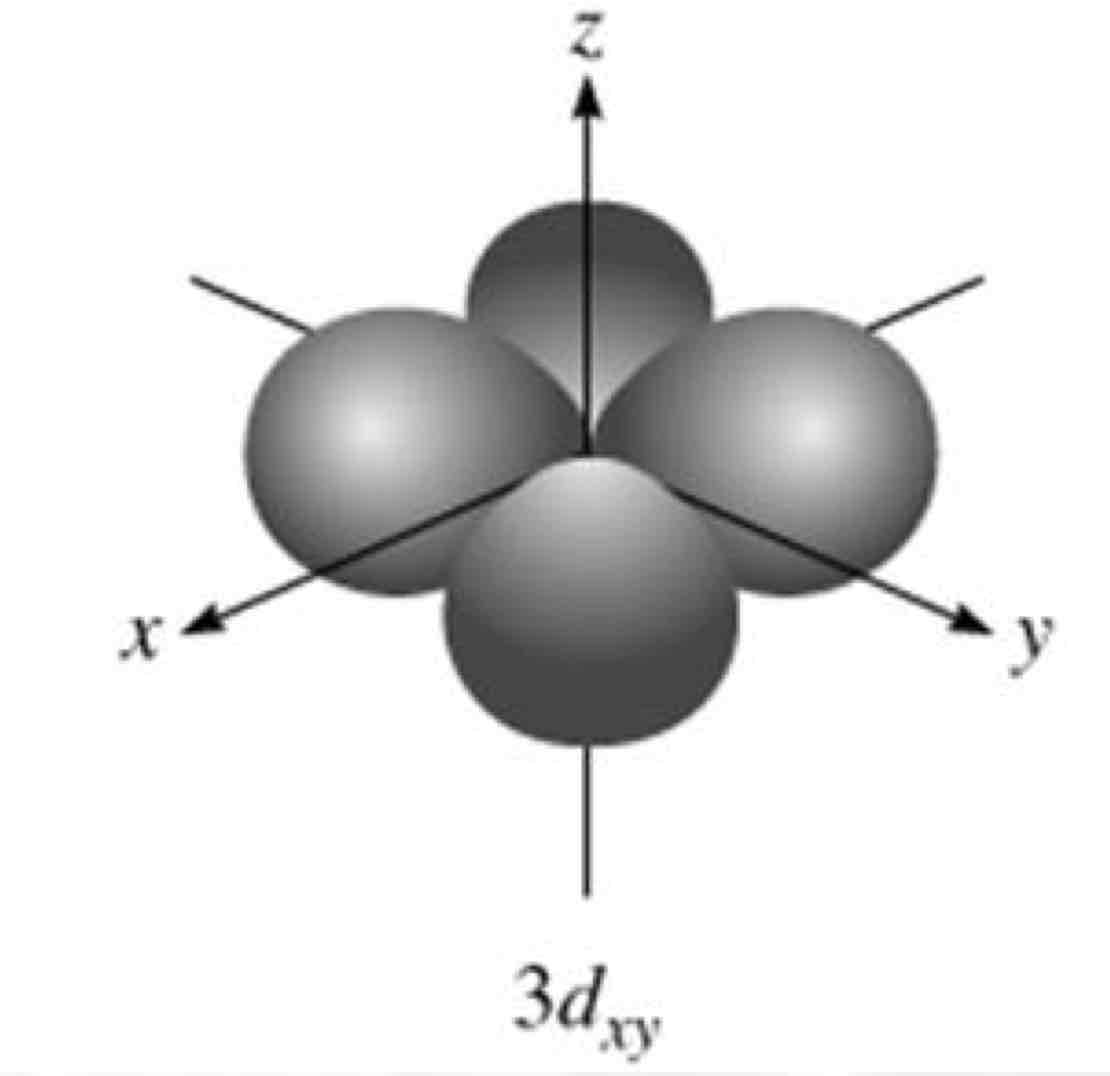
dxy
What atomic orbital is being shown?
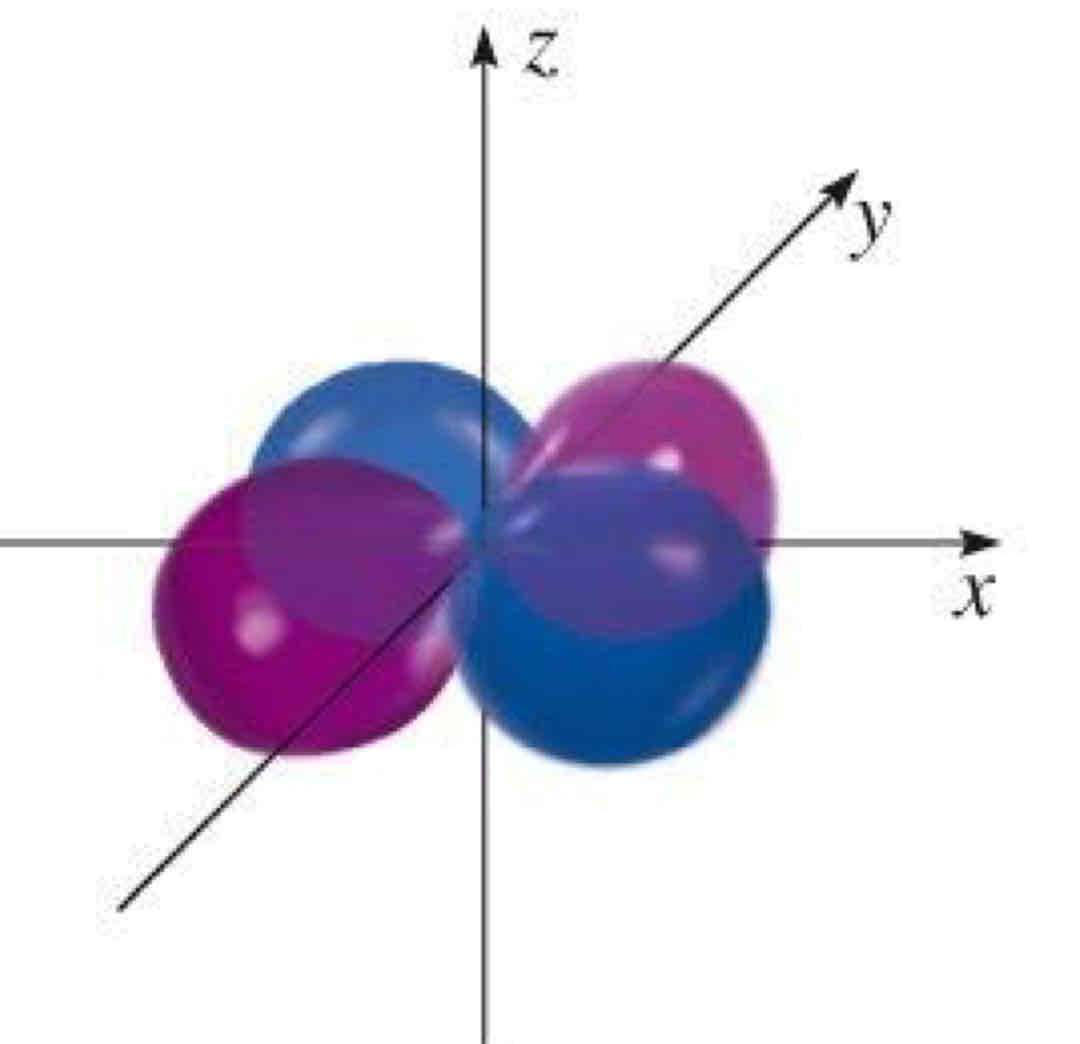
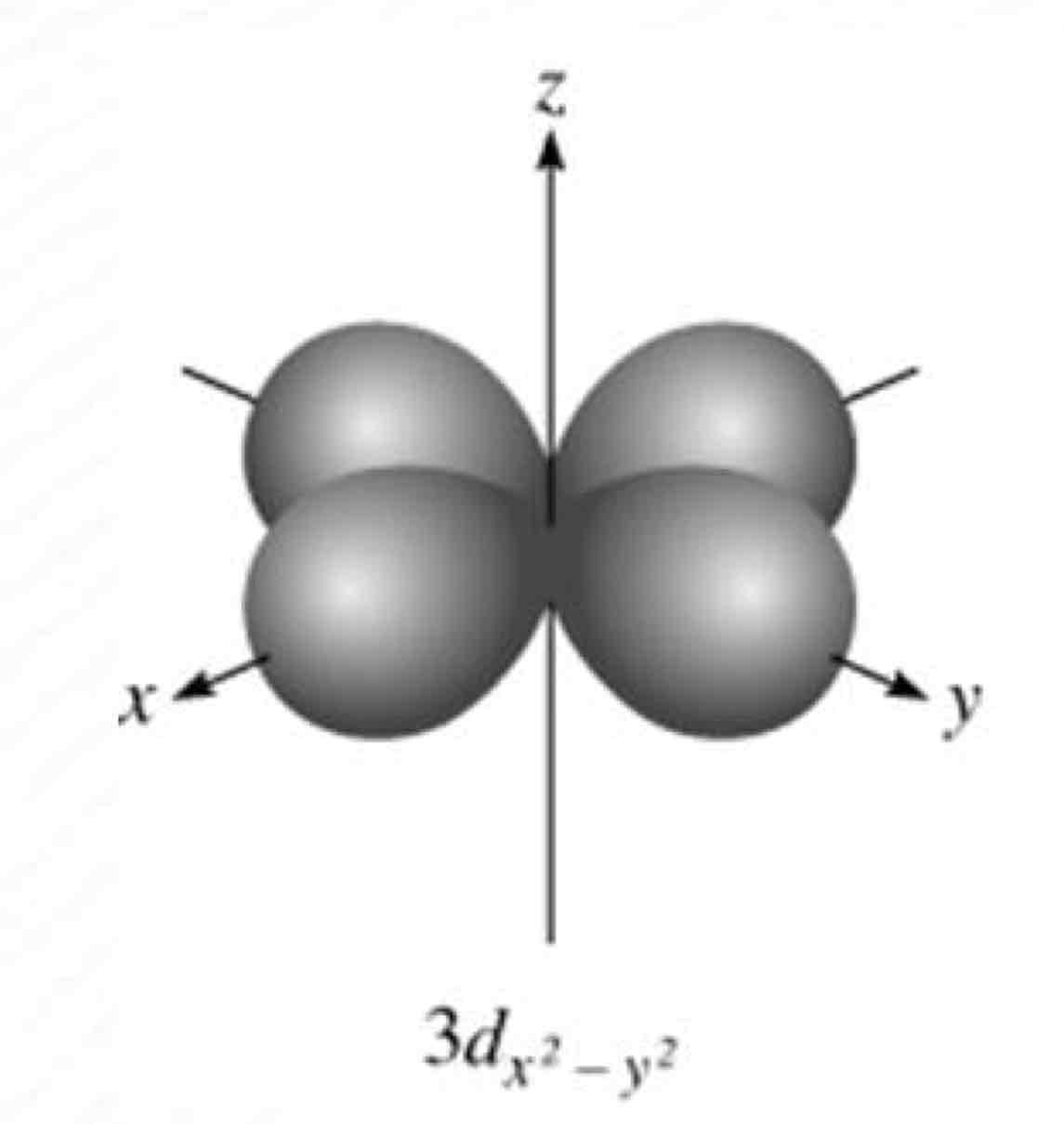
dx²-y²
What atomic orbital is being shown?
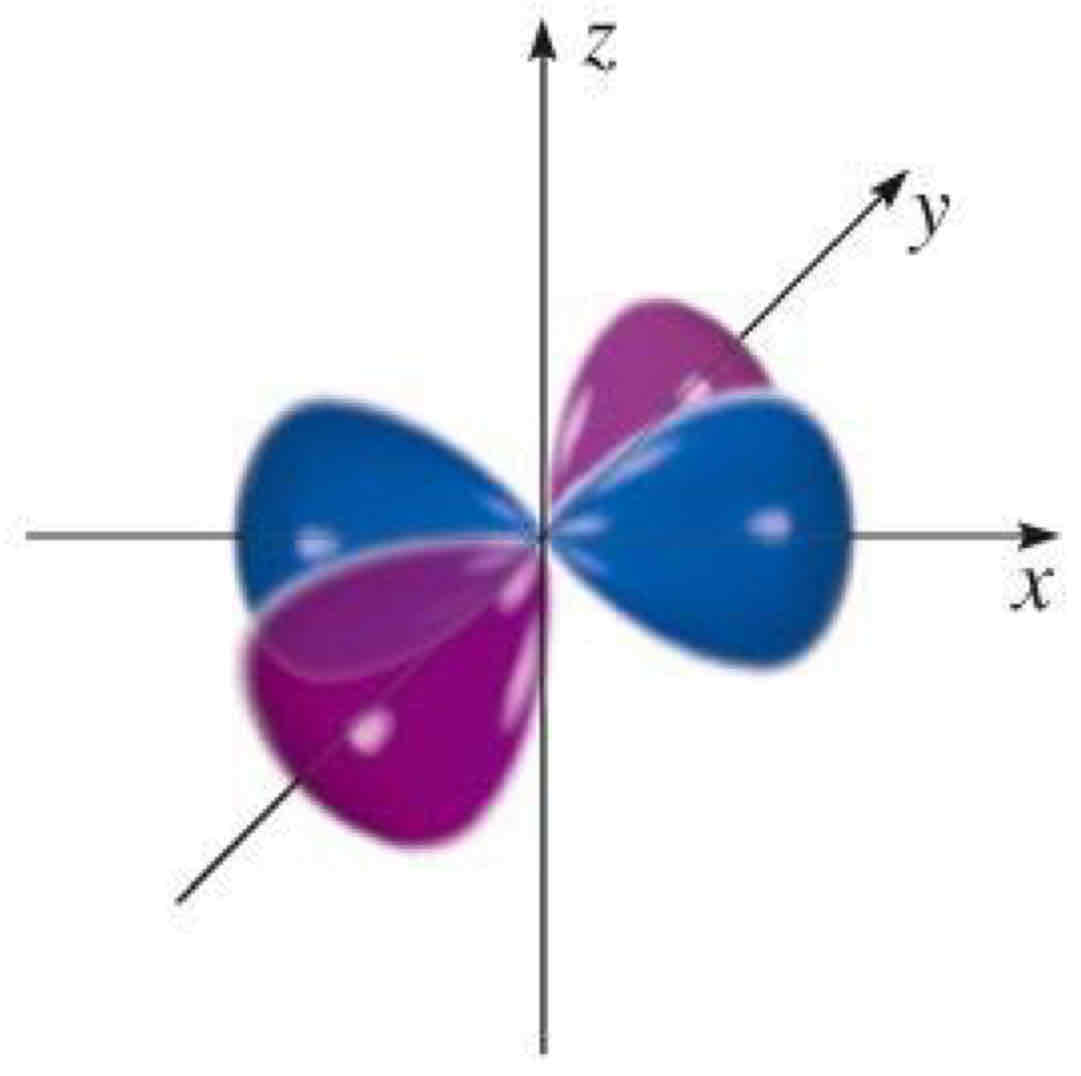
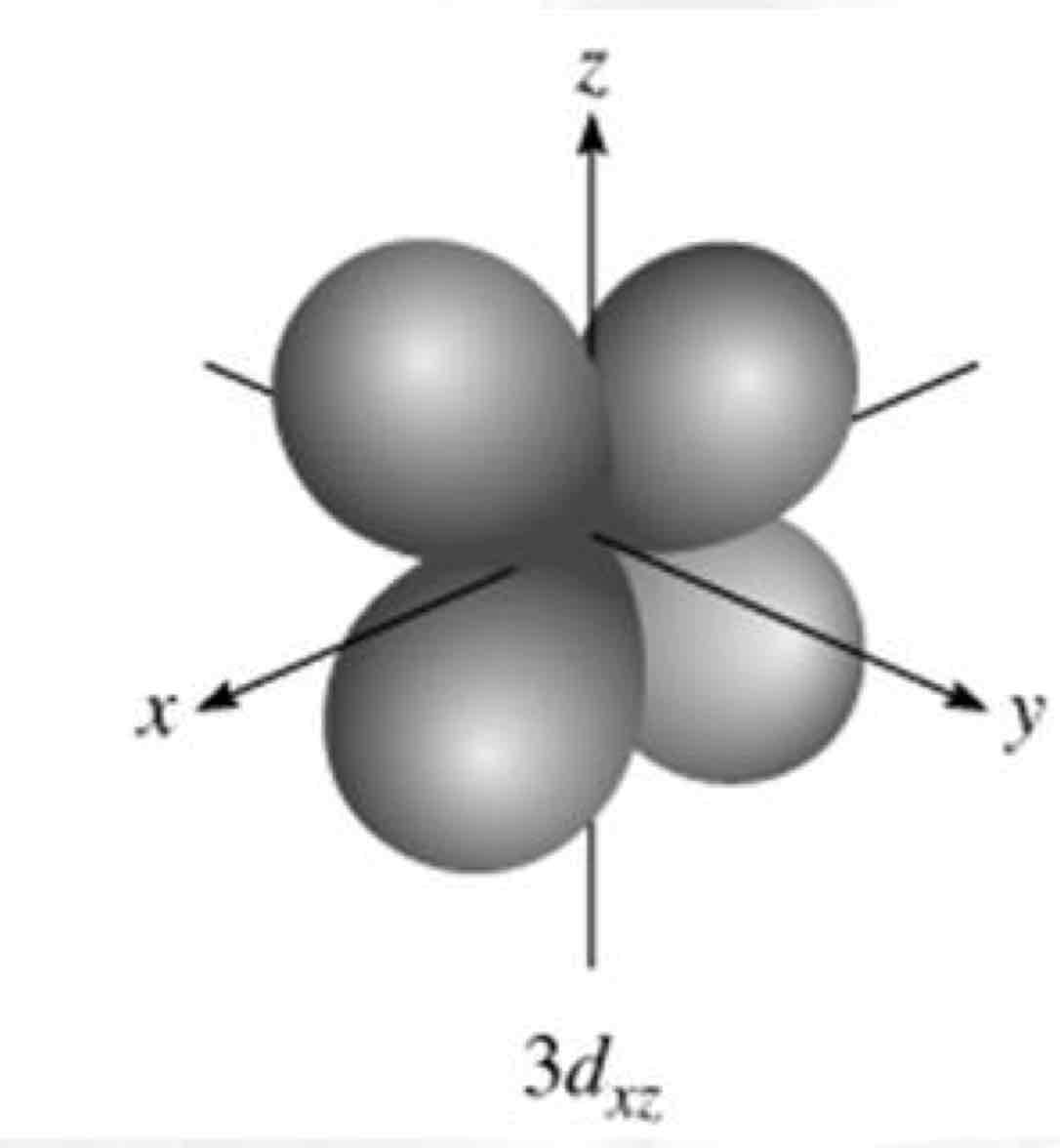
dxz
What atomic orbital is being shown?
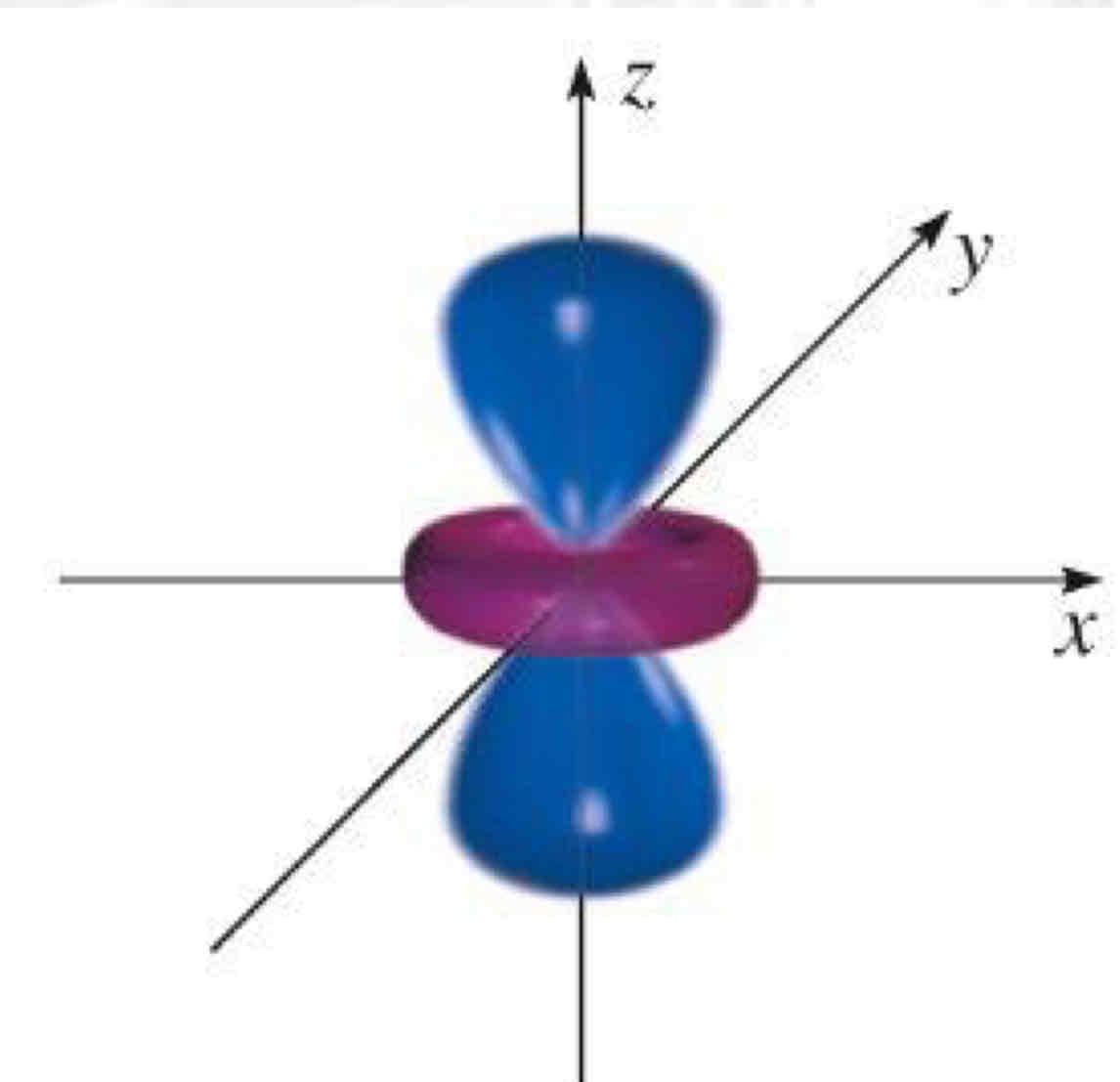
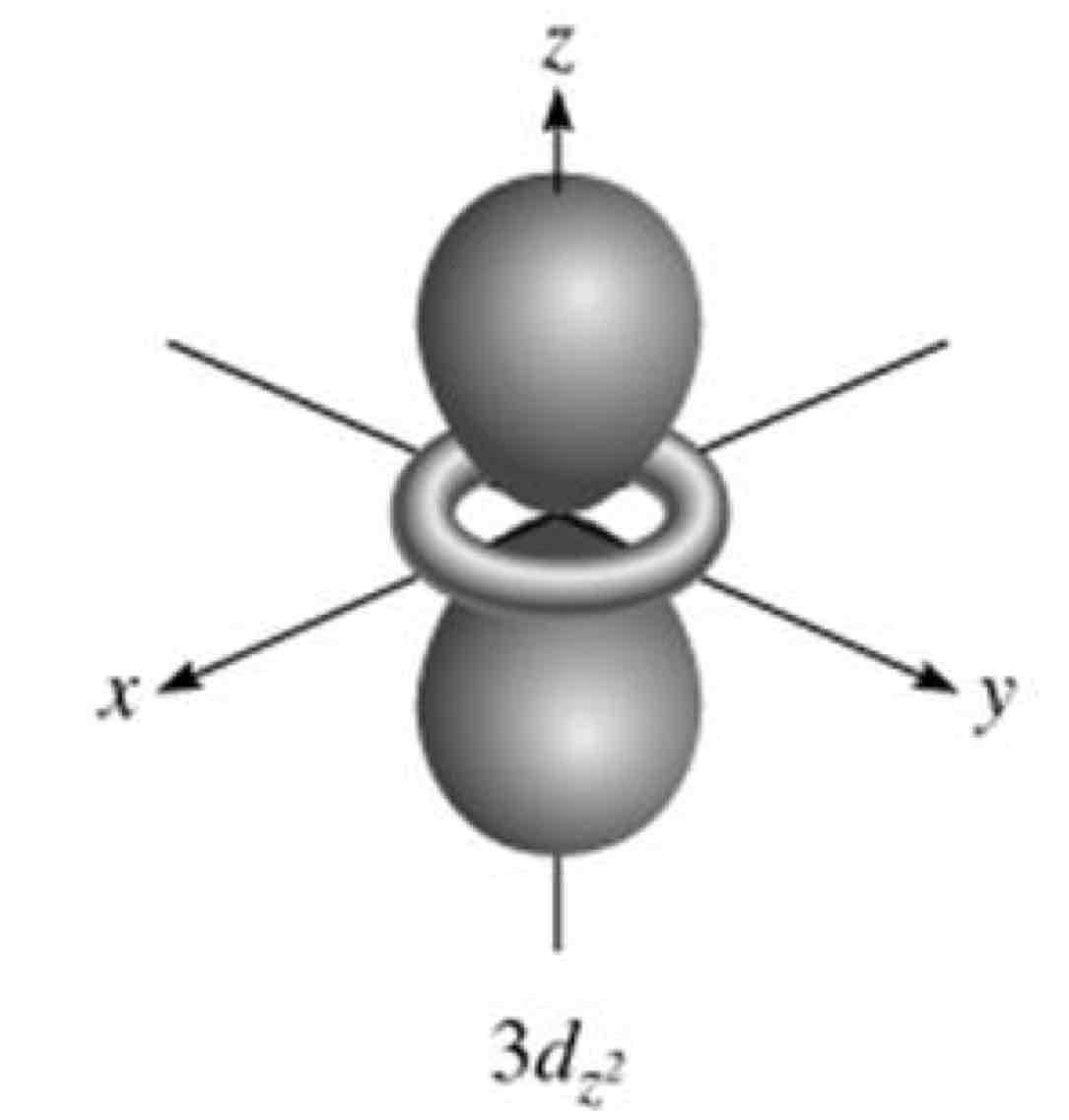
dz²
What atomic orbital is being shown?
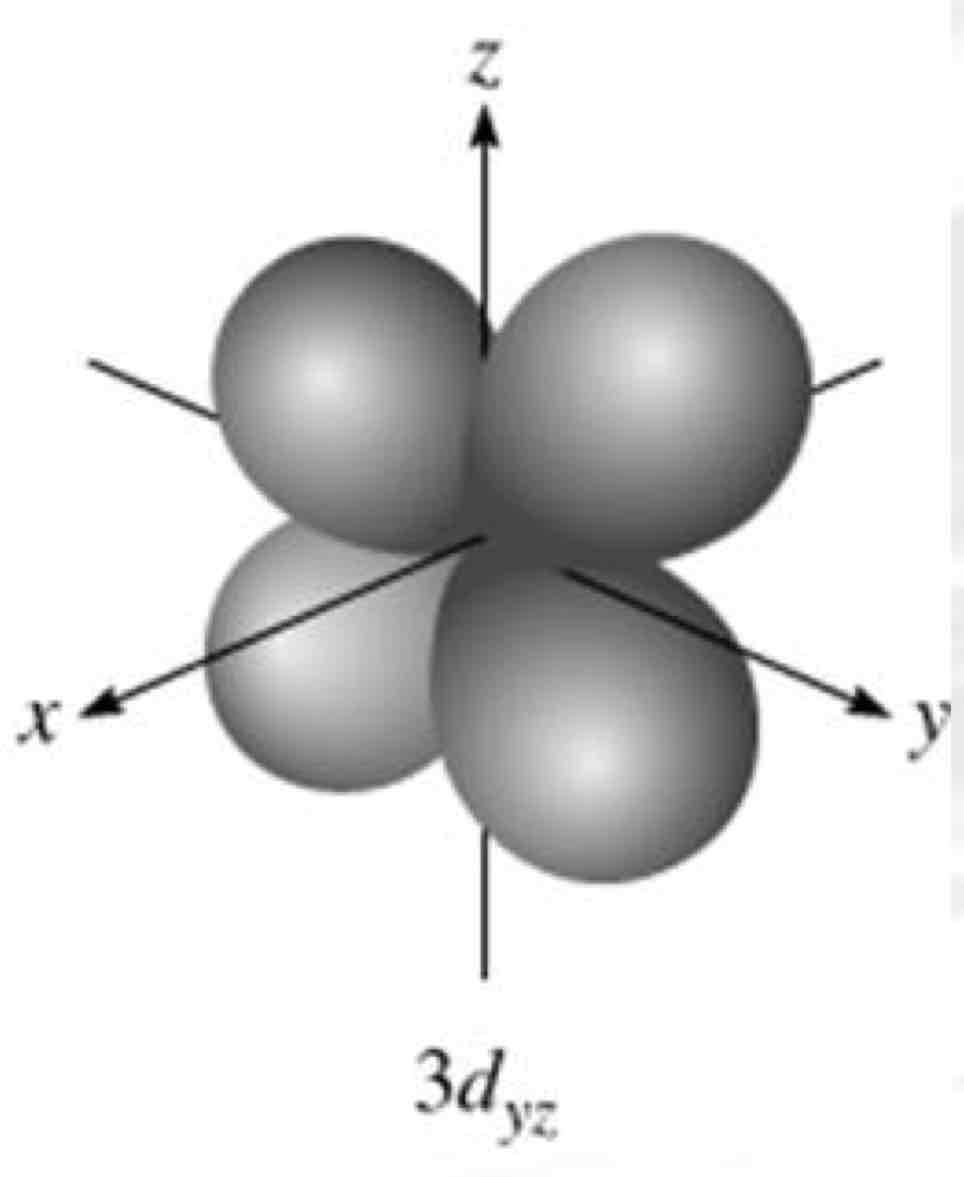
dyz
What atomic orbital is being shown?
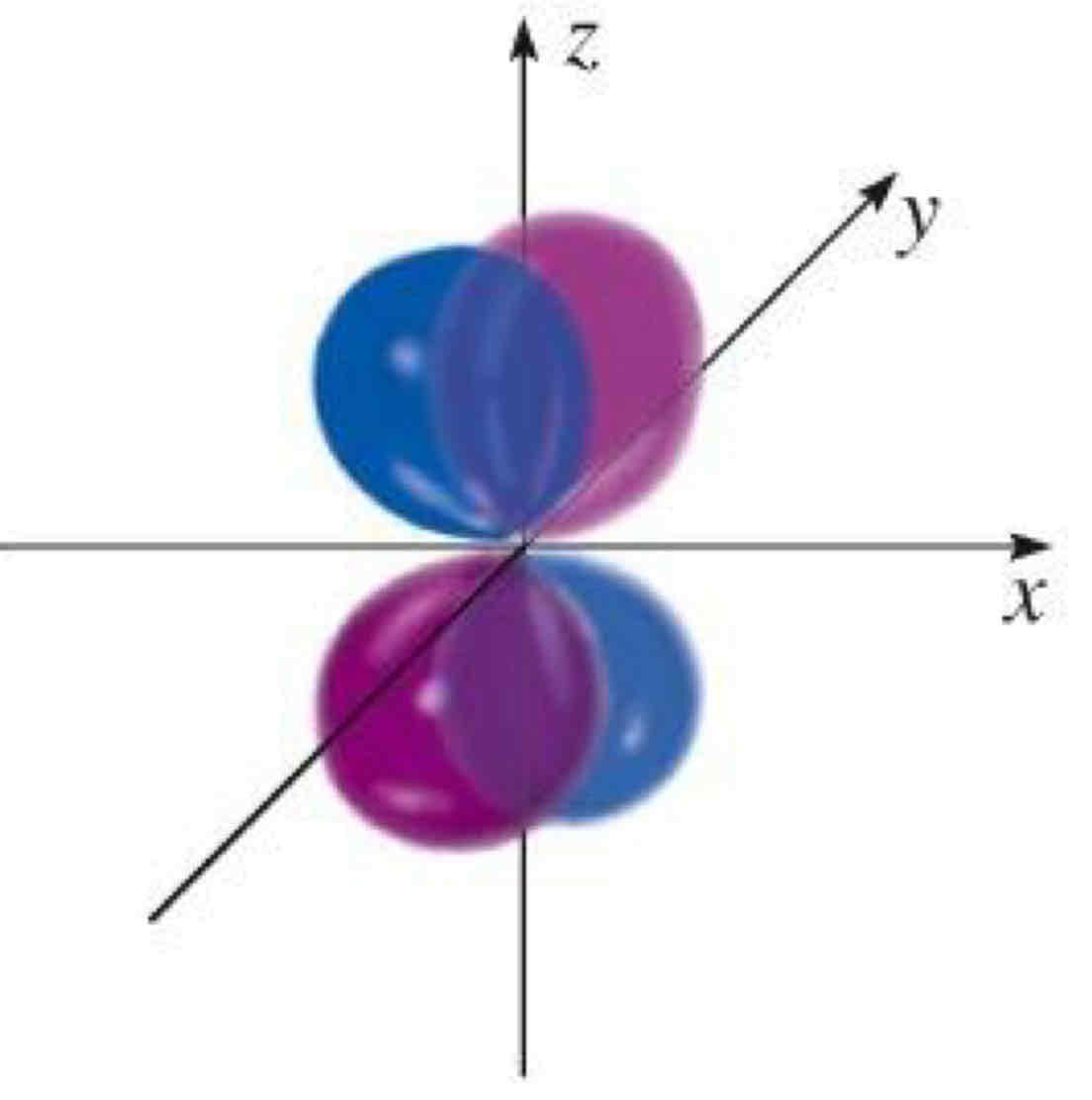
ml=-1
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=0
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=1
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=-2
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=-1
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=0
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=1
What quantum number is being shown?
ml=2
What quantum number is being shown?
Electron spin quantum number (ms)
_____________- quantum number that can be +½ or -½.
Pauli exclusion principle
___________________- in a given atom no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers.
False. An orbital can hold only two electrons, and they must
have opposite spins.
(T/F) An orbital can hold three electrons, and they can have same spins.
spherically symmetric
The potential energy of an electron in the field of a nucleus is __________________(it is proportional to Z/r and independent of orientation relative to the nucleus).

spherical polar coordinates
Since the potential energy of an electron in the field of a nucleus is spherically symmetric, orbitals are best expressed in terms of the ____________________.
angular functions
The ____________ θ and ϕ determine how the probability changes from point to point at a given distance from the center of the atom; in other words, they give the shape of the orbitals and their orientation in space.
radial function R
The _______________ describes electron density at different distances from the nucleus.
radial distribution function, 4πr2R(r)2
The ______________, allows us to imagine the region of space in which the electron can be found.
nodes
The positions where either component of the wavefunction passes through zero are called ________.
Radial nodes
A type of node where they occur where the radial component of the wavefunction passes through zero.
Angular nodes
A type of node where they occur where the angular component of the wavefunction passes through zero
distance from the nucleus increases
In all the radial probability plots, the electron density, or probability of finding the electron, falls off rapidly beyond its maximum as the ______________________.
large distances
At ________ from the nucleus, the electron density, or probability of finding the electron, falls off rapidly.
nodal plane
An electron will not be found anywhere on a ________.
nodal surface; zero
The 2s orbital also has a __________, a surface with zero electron density, in this case a sphere with r = 2a0 where the probability is __________
52.9 pm
The Bohr radius, a0 = _______
nodal plane
Each boundary surfaces of the three p orbitals possesses a __________ passing through the nucleus
two perpendicular;
One representation of the boundary surfaces of the d orbitals. Four of the orbitals have _______________ nodal planes that intersect in a line passing through the nucleus.
two cones
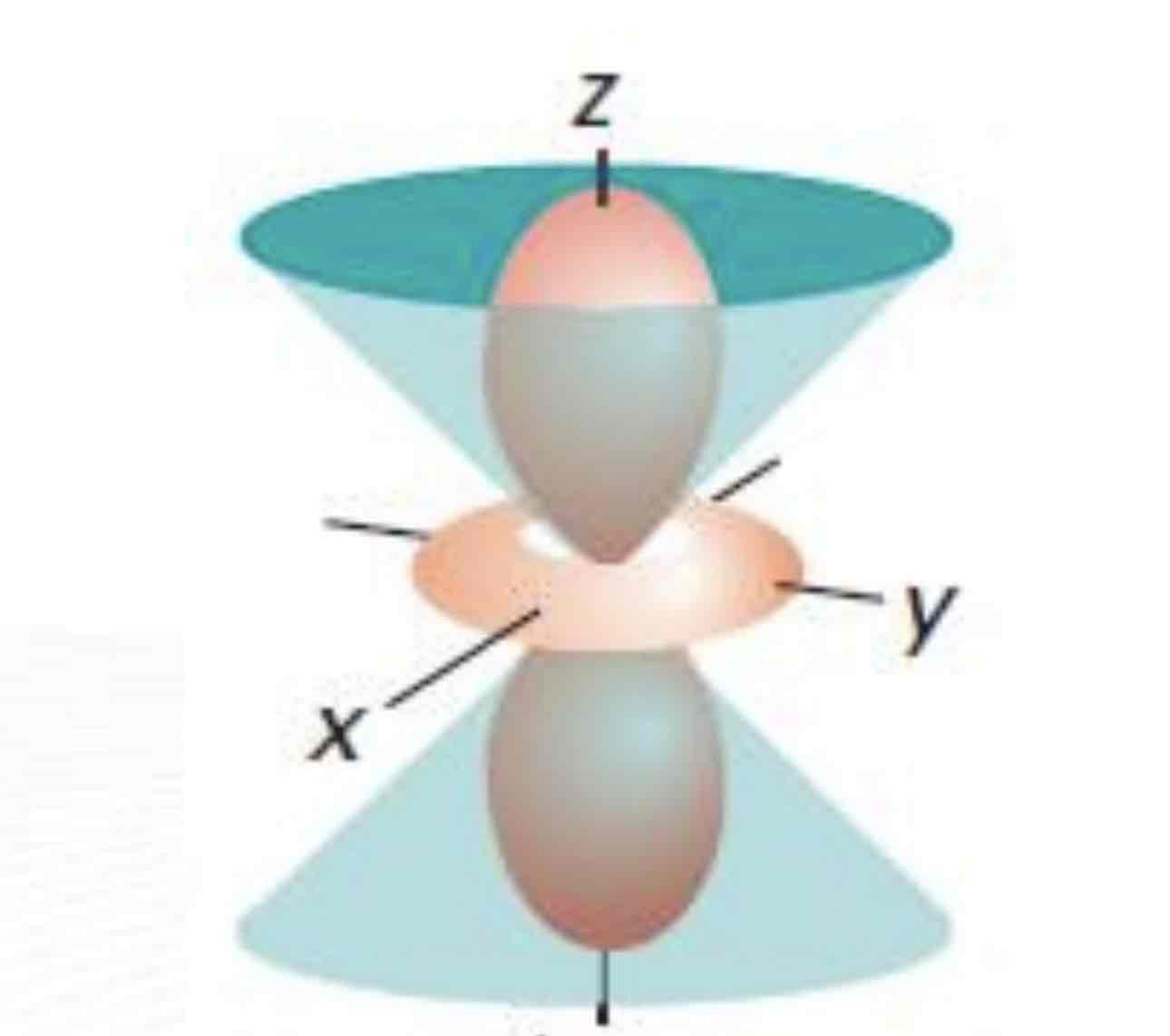
In the dz2 orbital, the nodal surface forms __________that meet at the nucleus.
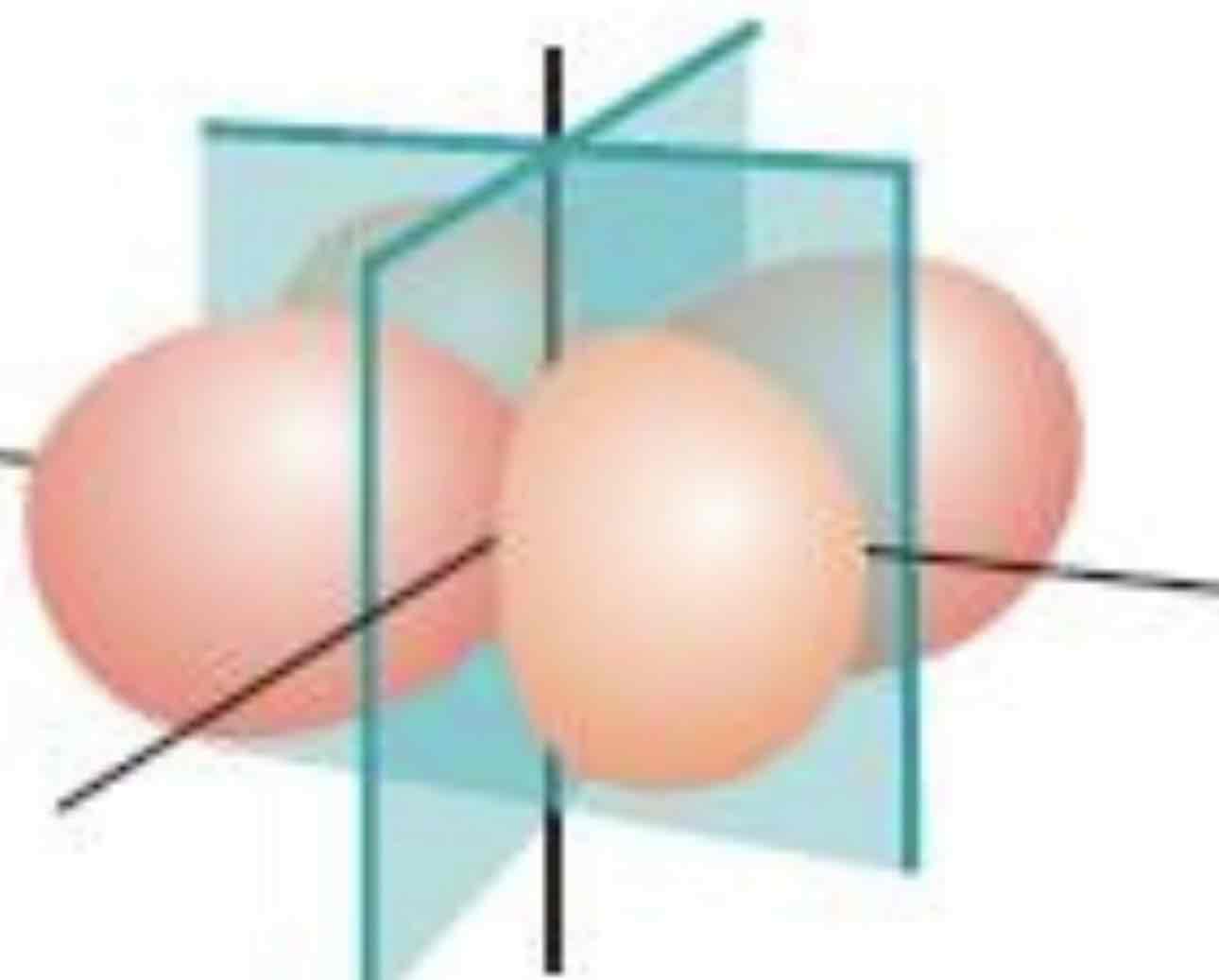
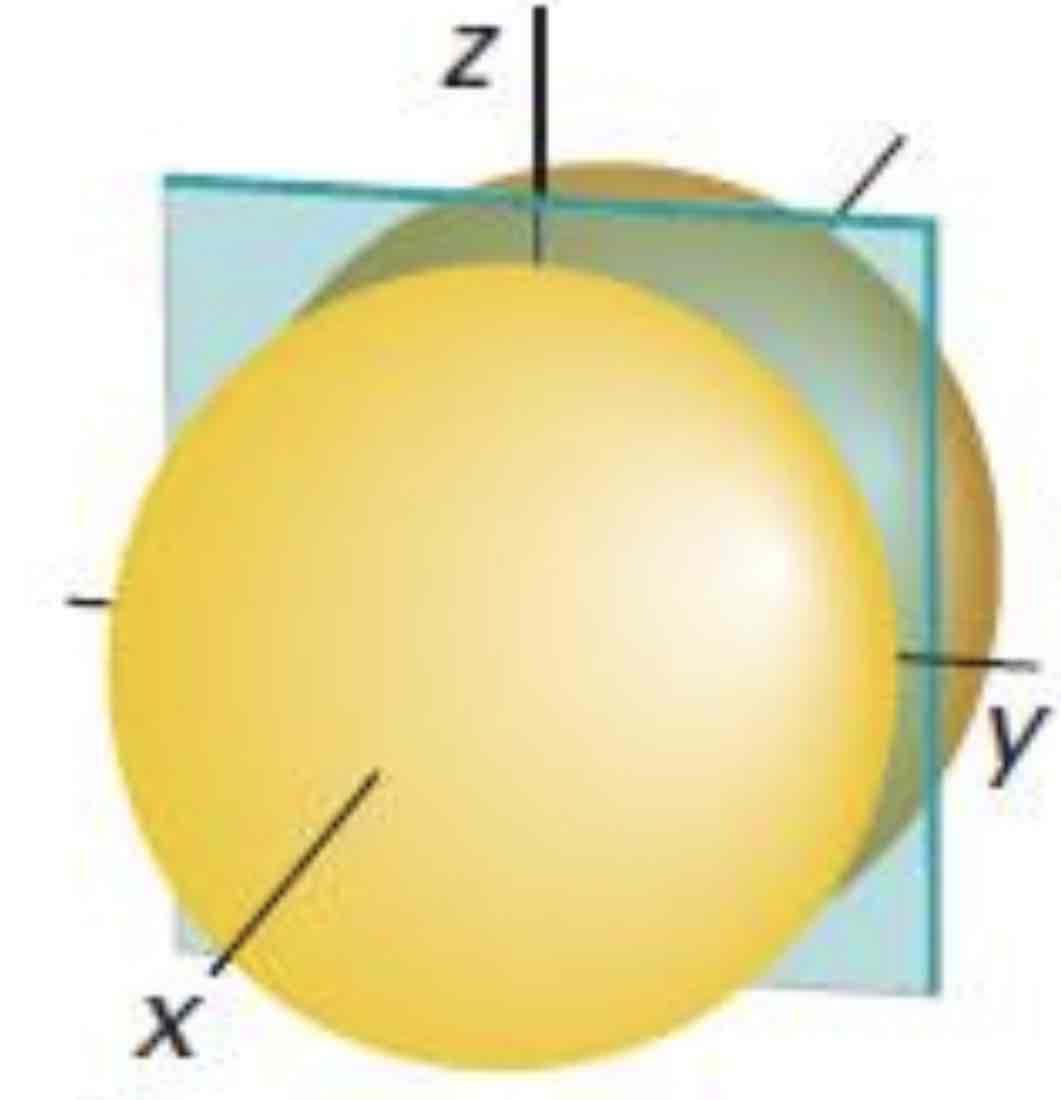
px
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
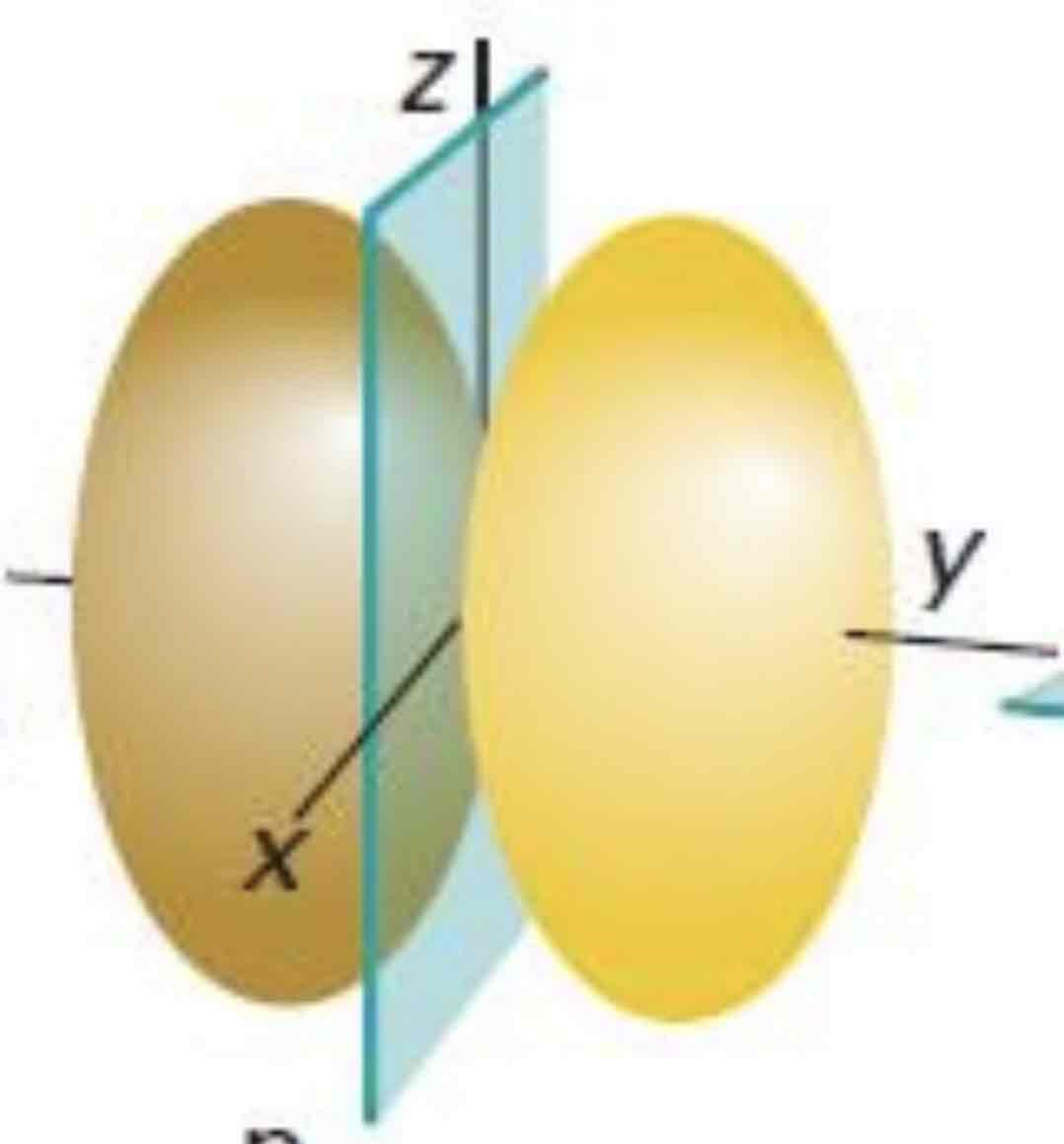
Py
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
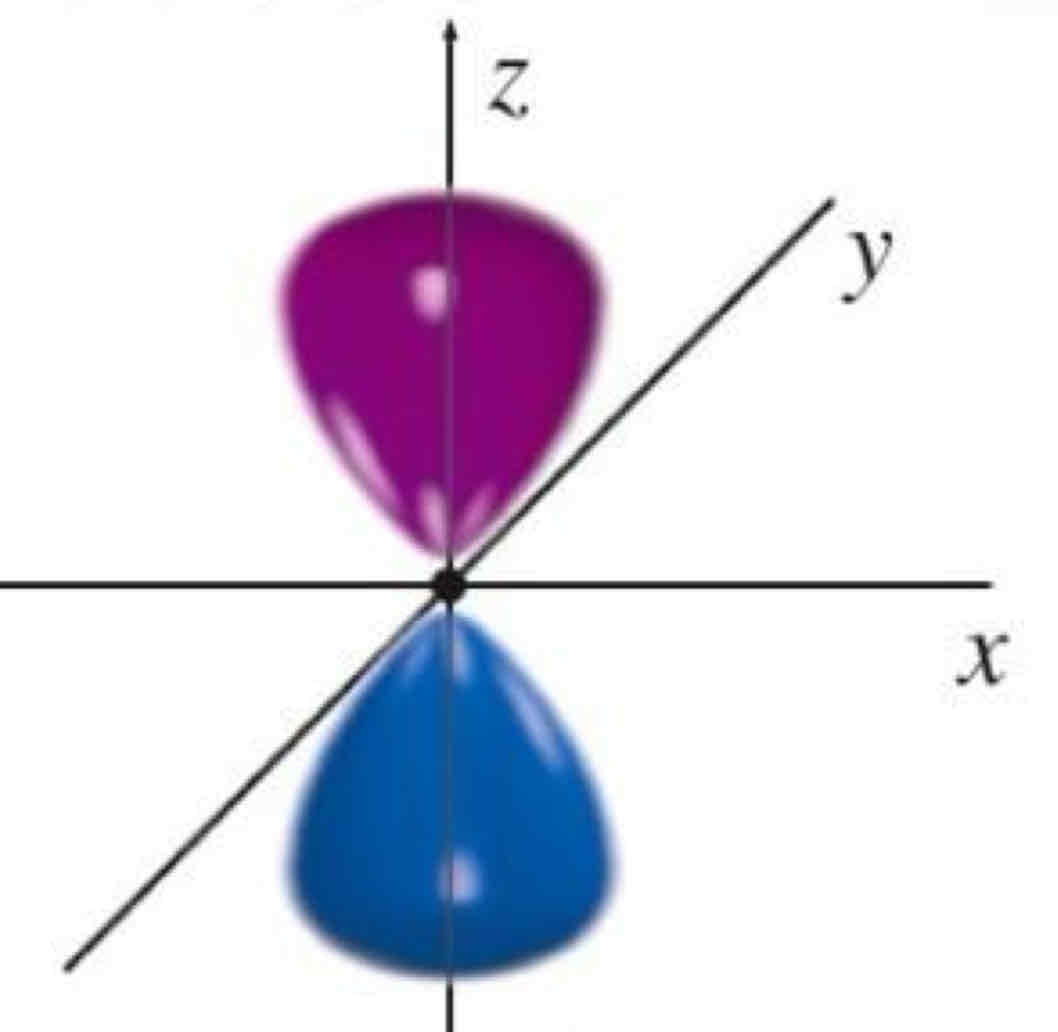
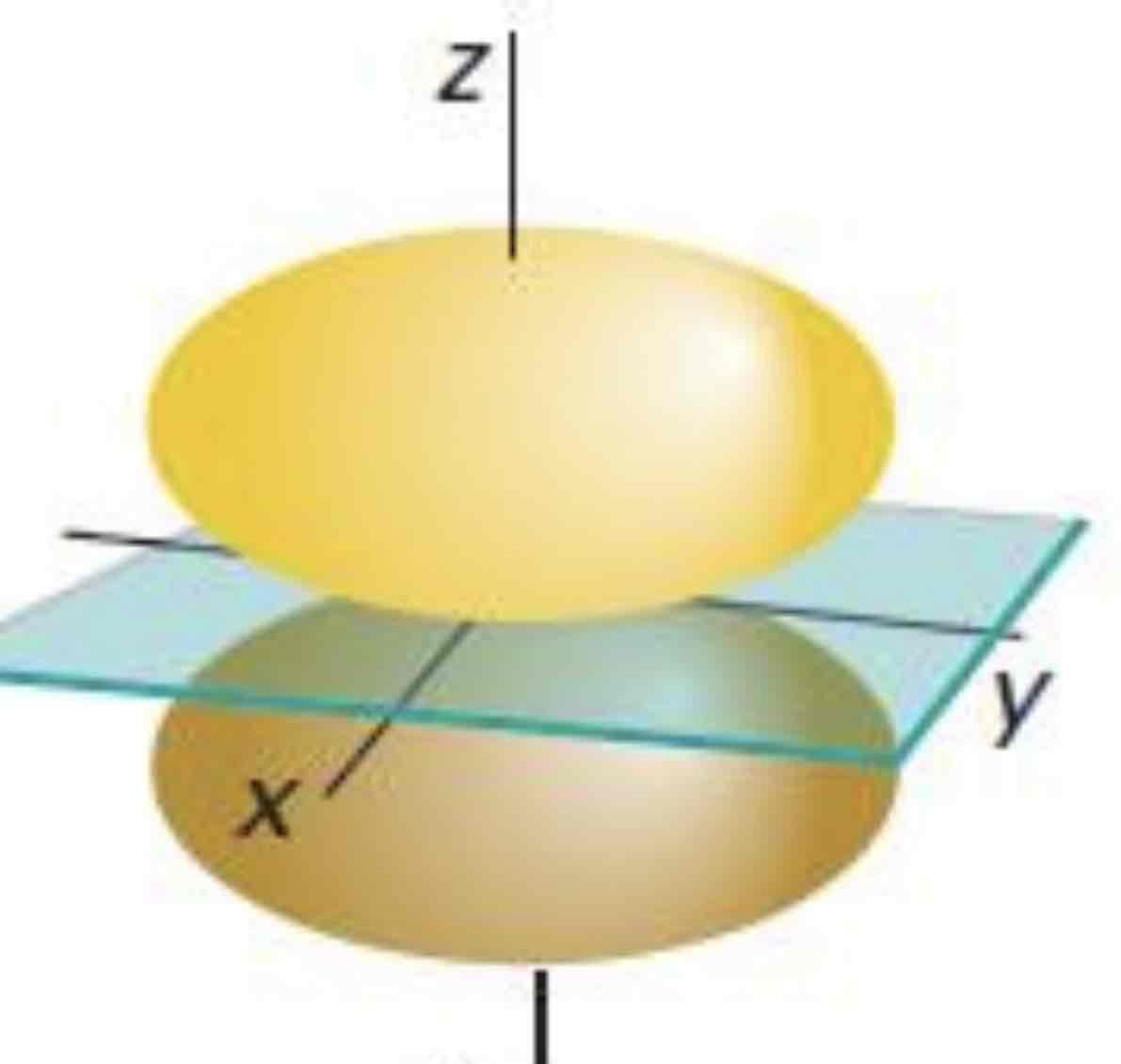
Pz
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
dz²
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
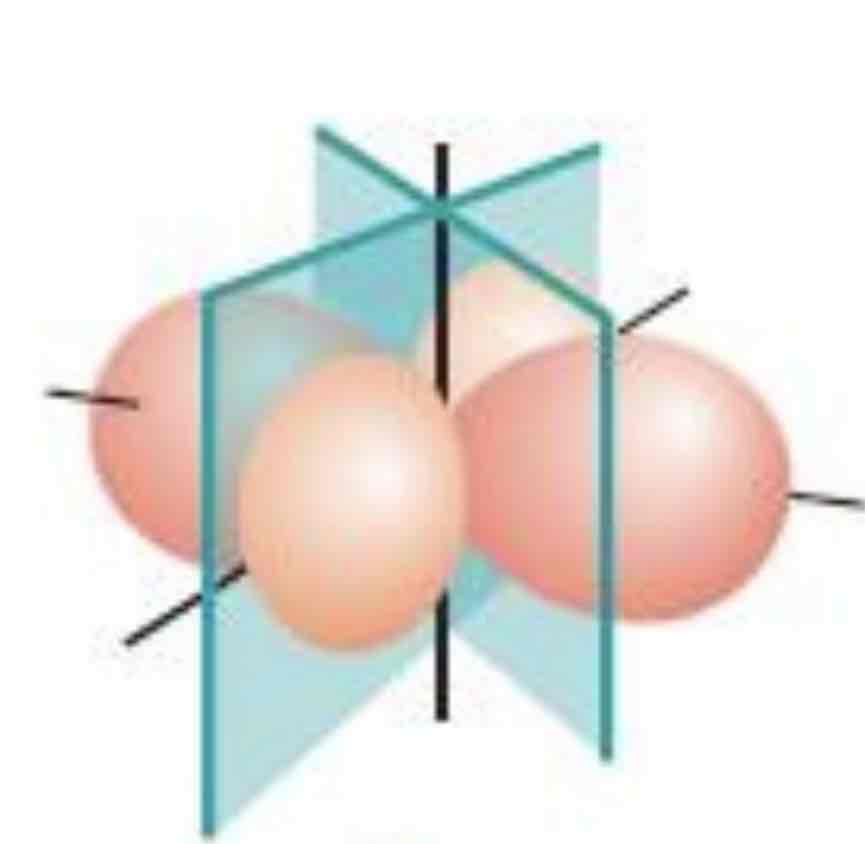
dx² -y²
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
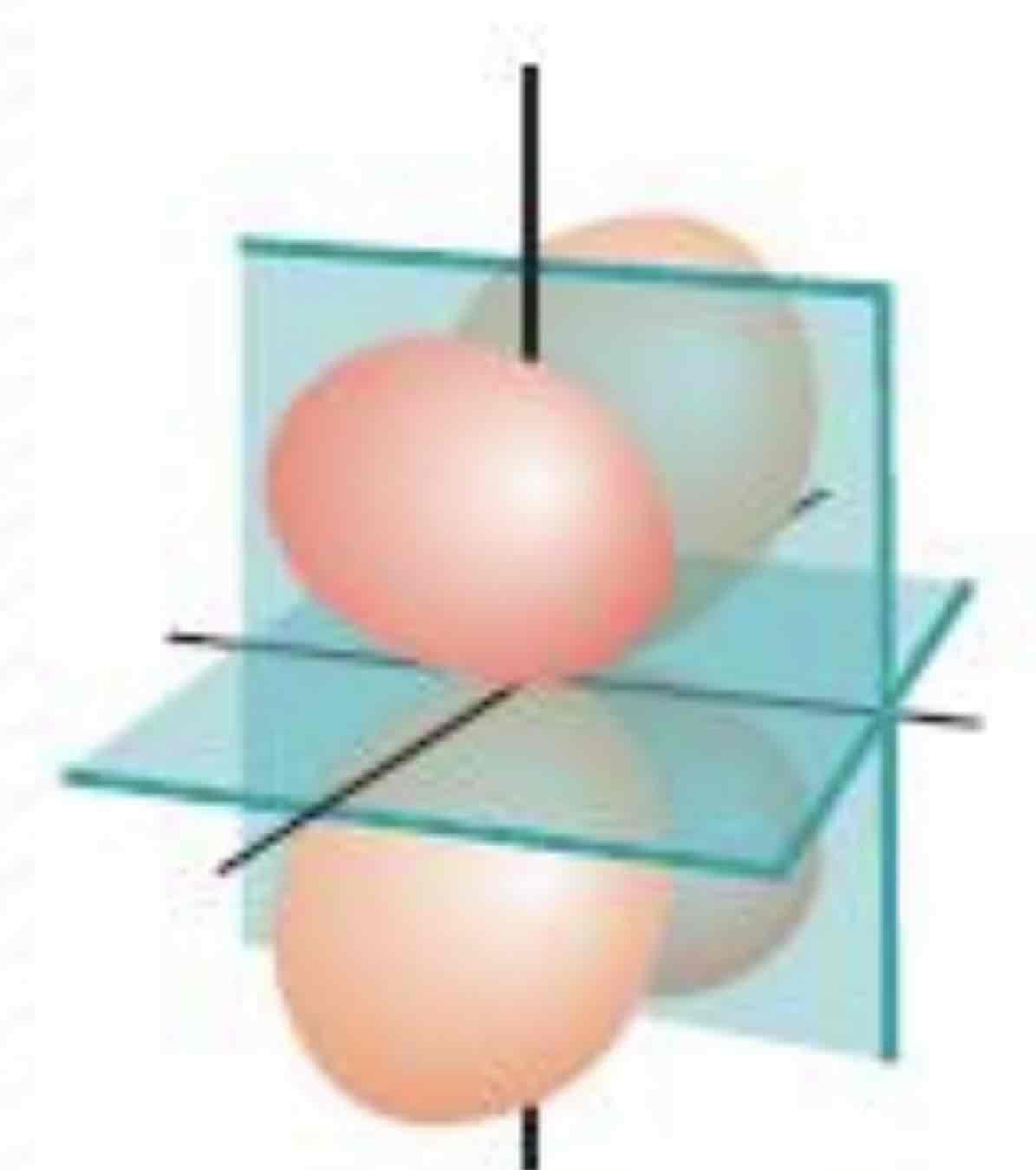
dzx
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
dyz
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?
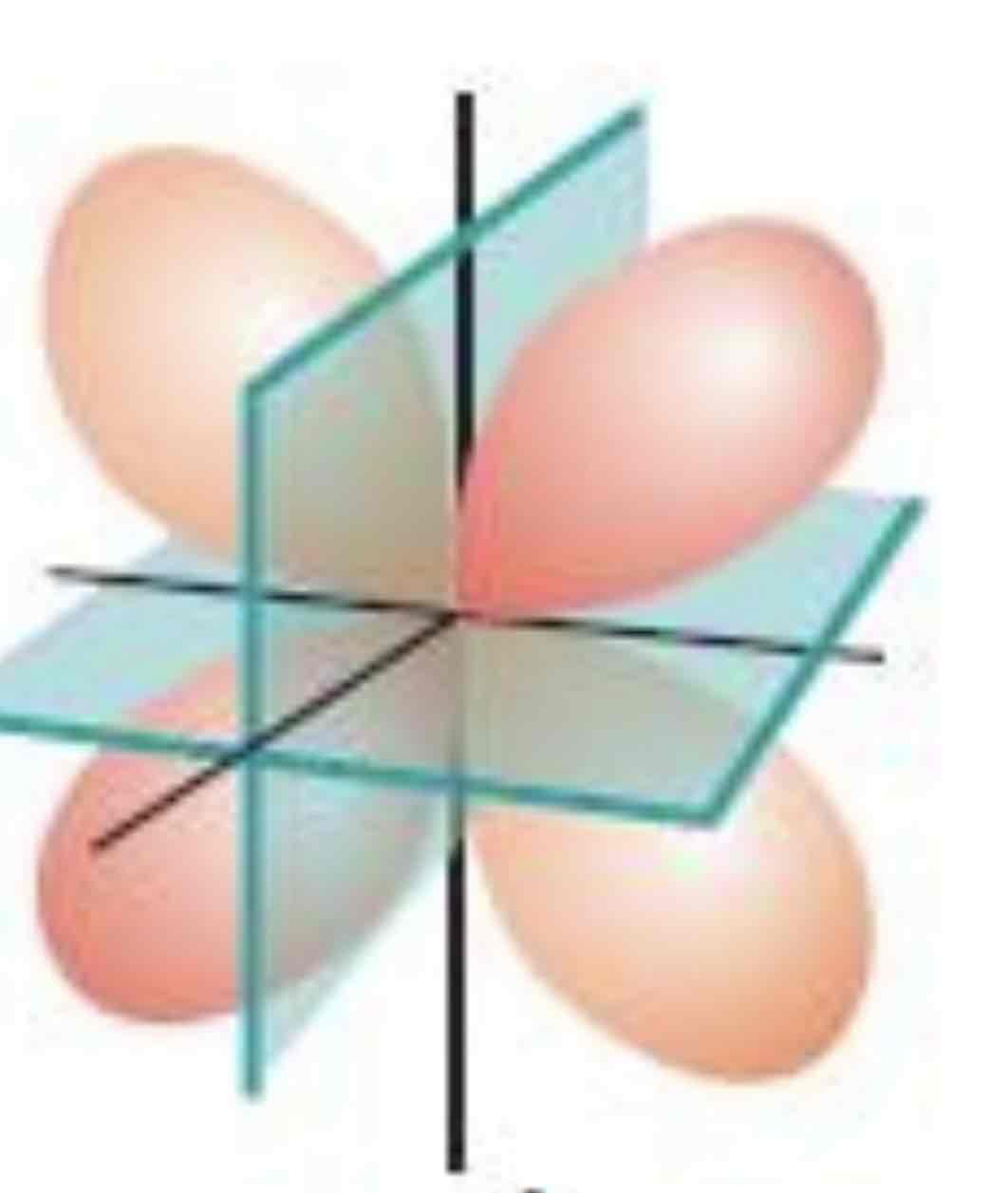
dxy
What atomic orbital is being shown (w/ nodal plane)?