IB Biology Topic 2.1 & 2.2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:21 PM on 5/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
Vitalism
the theory that the origin and phenomena of life are dependent on a force distinct from chemical or physical forces.
2
New cards
Urea
byproduct of human metabolism, created in a lab by Friedrich Wöhler, which disproved vitalism.
3
New cards
hydroxyl
-OH
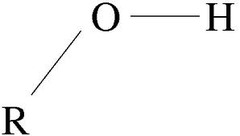
4
New cards
amine
-NH2
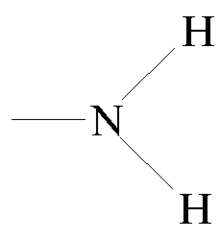
5
New cards
carboxyl
-COOH
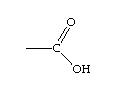
6
New cards
methyl
-CH3
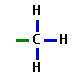
7
New cards
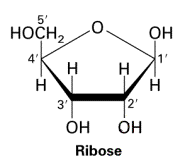
Ribose
5 carbon monosaccharide. Hydroxyl groups point up, down, down.
8
New cards
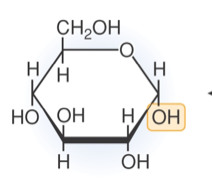
alpha glucose
6 carbon monosaccharide. Hydroxyl groups point down, down, up, down.
9
New cards
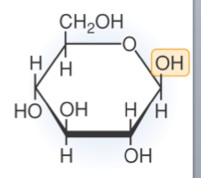
beta glucose
6 carbon monosaccharide. Hydroxyl groups point up, down, up, down.
10
New cards
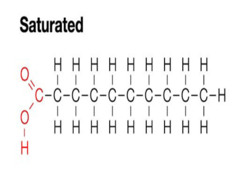
saturated fatty acids
unbranched C chains saturated with H, connected by single bonds
11
New cards
CHONS
Protein acronym
12
New cards
CHO
Carbohydrates acronym
13
New cards
CHOP
Lipids acronym
14
New cards
CHONP
Nucleic acids acronym
15
New cards
1:2:1
ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen in carbohydrates
16
New cards
less
Lipids contain (less/more) Oxygen than Carbohydrates
17
New cards
metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
18
New cards
anabolism
Monomers → Polymers. Requires energy
19
New cards
catabolism
Polymers → Monomers. Releases energy
20
New cards
hydrogen electronegativity
low, has partial positive charge
21
New cards
oxygen electronegativity
high, has partial negative charge
22
New cards
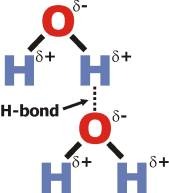
water molecule
each hydrogen atom is joined to the water's lone oxygen atom by a single covalent bond; each hydrogen atom shares an electron with the oxygen atom (not equally)
23
New cards
cohesion of water
water molecules stick together via hydrogen bond
24
New cards
adhesion of water
binding of water molecules with other polar molecules, causing water to stick to them via hydrogen bond
25
New cards
High specific heat capacity
high amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1 g of water by 1°C
26
New cards
High latent heat of vaporization
high amount of energy required for 1 g of water to be converted from the liquid to the vapor phase
27
New cards
high boiling point
Water has a boiling point of 100°C at atmospheric pressure
28
New cards
High Latent Heat of Fusion
amount of energy required for 1 g of water to be
converted from the solid to the liquid phase
converted from the solid to the liquid phase
29
New cards
water and methane
Water has higher thermal properties since water forms hydrogen bonds (polar) whereas methane can not (non-polar).
30
New cards
solvent property of water
Water is commonly referred to as the universal solvent, Medium for metabolic reactions.
31
New cards
hydrophobic interaction
weak chemical interaction caused when molecules that do not mix with water combine to exclude water
32
New cards
Water transparency
Creates suitable habitat for underwater organisms
33
New cards
Sweat
Cools body through water's high latent heat of vaporization. Heat needed for evaporation of water in sweat is taken from skin tissue, reducing temperature.
34
New cards
Sodium chloride solubility
freely soluble. Dissolves into Na and Cl ions which are carried in blood plasma.
35
New cards
Amino acid solubility
Soluble in water, but solubility varies depending on R group. All soluble enough to be carried through blood plasma.
36
New cards
Glucose solubility
Freely soluble in water, then carried by blood plasma.
37
New cards
Oxygen solubility
Non-polar, sparingly dissolved, water becomes saturated w/ oxygen. Binds to hemoglobin and increases capacity of blood for oxygen transport.
38
New cards
Fats molecules solubility
Non-polar and insoluble. Carried in blood by lipoprotein complexes made from phospholipids.
39
New cards
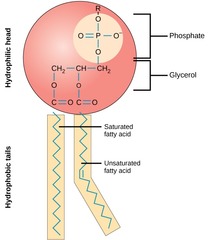
Phospholipid
Hydrophilic phosphate heads, hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails.
40
New cards
Cholesterol solubility
Hydrophobic, transported with fats in lipoprotein complexes.