Topic 4-Biodiversity and Natural Resources
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Why do individuals of the same species vary?
Due to different alleles
What is genetic diversity?
Variety of alleles in the gene pool of a species or population.
What is the gene pool?
The complete set of alleles in a species.
What are two things you can look at to measure genetic diversity?
Phenotype and genotype
What do different alleles codes for?
Slightly different versions of the same characteristics
The larger number of phenotypes…
The greater the genetic diversity
How can the genotype be tested?
Samples of an organisms DNA can be taken and the sequence of base pairs analysed
What can you tell by sequencing the DNA of individuals of the same species?
You can see similarities and differences in the alleles within a species
What can you measure using the genotype of see genetic diversity?
The number of different alleles a species has for one characteristic
What does the heterozygosity index measure?
Genetic diversity
What does a higher heterozygosity index mean in a population?
There’s is greater genetic diversity
What is the equation for the heterozygosity index?
H=number of heterozygotes/number of individuals in the population
What is the equation for the index of diversity?
N=Total number of organisms of all species
n=Total number of organisms of one species
Sum of
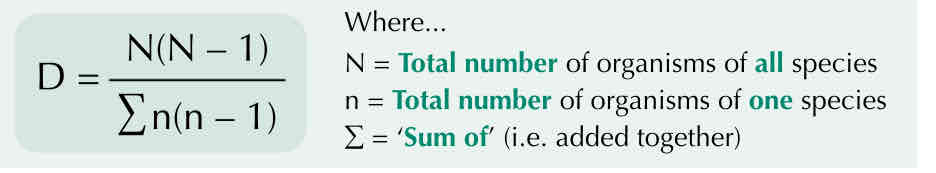
What does biodiversity mean?
The variety of living organisms in an area
What is species diversity?
The number of different species and the abundance of each species in an area
What does genetic diversity mean?
The variation of alleles within a species or a population of a species
What does endemism mean?
When a species is unique to a single place
What 3 things has natural selection lead to?
-adaptation
-evolution
-increased biodiversity
What reduces species diversity?
Human activity
What helps maintain biodiversity?
Conservation
What does habitat mean?
The place an organism lives
Describe how to measure species diversity in terms of counting the number of different species in an area.
Count the number of different species in an area
This is the species richness
The higher the number of species the greater the species richness
What does species richness not show?
Abundance of each species
Describe how to measure species diversity in terms of also counting the number of individuals in each species.
Count the number of different species and the number of individuals in each species
Use an index of diversity to calculate species diversity
Describe the method for sampling species diversity.
Choose a small area within the species to sample
The sample should be random to avoid bias-you can use a random number generator to get coordinates for a box in the grid
Count the number of individuals of each species in the sample area
-Plants= quadrat
-Flying insects=sweepnet
-Ground insects=pitfall trap
-Aquatic animals=net
Repeat
Use the results to estimate the total number of individuals or the species richness in the habitat
When comparing habitats use the same sampling technique
What does niche mean?
The role of a species which in its habitat
What 2 groups does a niche interact with?
-living organisms
-non living environment
How many species can occupy the same niche?
1
What may happen if 2 species have the same niche?
One will always outcompete the other
What are adaptations?
Features that increase an organisms chance of survival
What are behavioural adaptations and what is one example?
-ways an organism acts that increases its chance of survival
-possums play dead to escape attack
What are physiological adaptations And what is an example of this?
-processes inside and organisms body that increase its chance of survival
-some bacteria produce antibiotics to kill other bacteria and reduce competition
What are anatomical adaptations and what is an example for this?
-structural features of an organism that increases its chance of survival
-otters have a streamlines shape making it easy to glide through the water and catch prey
Describe how evolution occurs by natural selection.
Every population has variation due to random mutations
Some variations make individuals more likely to survive
Selection pressures (predators, disease, competition, climate change)
The better adapted individuals have a selective advantage and are more likely to survive, reproduce and pass on their beneficial alleles
Over many generations the proportion of individuals with the advantageous allele increases and the species has evolved to adapt to its surroundings
How does evolution occur?
By natural selection
What does allele frequency mean?
How often an allele occurs in a population
What are new alleles generated by?
Mutations
What does the hardy-Weinberg principle predict?
That allele frequencies won’t change
What are the conditions needed to calculate the hardy-Weinberg principle?
-large population
-no immigration
-no emigration
-no mutations
-no natural selection
-random mating
What is the hardy-Weinberg equation that predicts allele frequency and what does each letter represent?
p+q=1
-p=frequency of the dominant allele
-q=frequency of the recessive allele
What is the hardy-Weinberg equation that predicts genotype and phenotype and what does such part mean?
p²+2pq+q²=1
-p²=frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype
-2pq=frequency of the heterozygous genotype
-q²=frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype
When does geographical isolation happen?
When a physical barrier divides a population of a species.
What may cause geographical isolation?
-Floods
-volcanic eruptions
-earthquakes
What may happen because the environment is different on each side of the barrier?
Different characteristics become more common due to natural selection because there are different selection pressures
Describe how the phenotype changes due to geographical isolation?
-different characteristics will be more advantageous on each side, allele frequency will change in each population
-mutations will take place independently in each population, also changing allele frequencies
-leading to changes in phenotype frequencies
What will each of the geographically isolated groups not be able to do as they become more genetically distinct?
They won’t be able to breed to produce fertile offspring-they’re reproductively isolated
What is taxonomy?
Science of classification
What does taxonomy involve?
Naming organisms and organising them into groups based on similarities and differences
How many taxonomic groups are there?
8
What are the groups organisms are put into?
-Domain
-Kingdom
-Phylum
-Class
-Order
-Family
-Genus
-Species
How are species named?
By using their genus and species in a binomial wording system
Why are species given a specific name?
-to minimise confusion
What is the classification of organisms based on?
Phenotypes and genotypes
-looking at DNA sequence
Describe the features of the prokaryotae kingdom and an example for it
-bacteria
-prokayotes, unicellular, no nucleus
Describe the features of the protoctista kingdom and an example for it
-algae
-eukaryotic cells, live in water, single celled/simple organisms
Describe the features of the fungi kingdom and give an example for it
-Yeasts
-eukaryotic, chitin cell wall, saprotrophic
Describe the features of the plantae kingdom and give an example for it
-moss
-eukaryotic, multicellular, cellulose cell walls, photosynthesise
Describe the features of the animalia kingdom and give an example for this
-mammals
-eukaryotic, multicellular, no cell wall
What is phylogeny?
The study of the evolutionary history of groups of organisms
What does phylogeny tell you?
Which species are related to which and how closely related they are
What does molecular phylogeny look at?
DNA and proteins to see how closely related organisms are
What are the 3 domains?
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukaryota
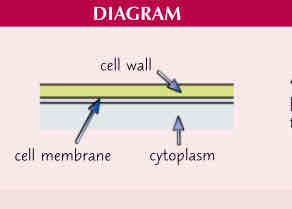
Describe the cell wall and its function
-rigid structure that surrounds plant cells
-made of cellulose
-supports plant cells
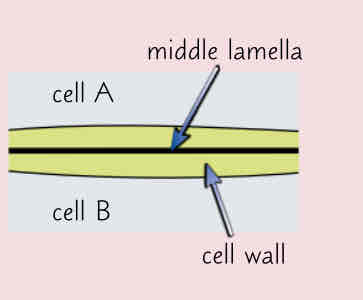
Describe the middle lamella and its function
-outermost layer of the cell
-acts as an adhesive p, sticks adjacent plant cells together
-provides stability
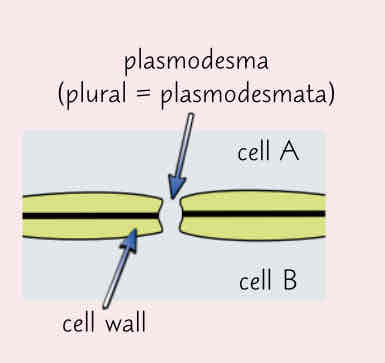
Describe the plasmodesmata and its function
-channels in the cell walls that link adjacent cells together
-allows transport of substances and communication between cells
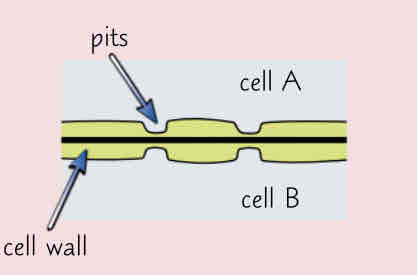
Describe the pits and its function
-wall is very thin
-they’re arranged in pairs
-allows transport of substances between cells
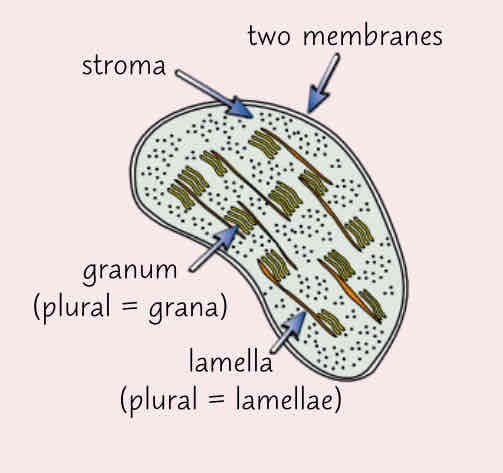
Describe the chloroplast and its function
-small, flattened structure
-surrounded by a double membrane
-contains thylakoid membranes which are stacked to form grana
-grana are linked together by lamella- thin flat pieces of thylakoid membrane
-site of photosynthesis
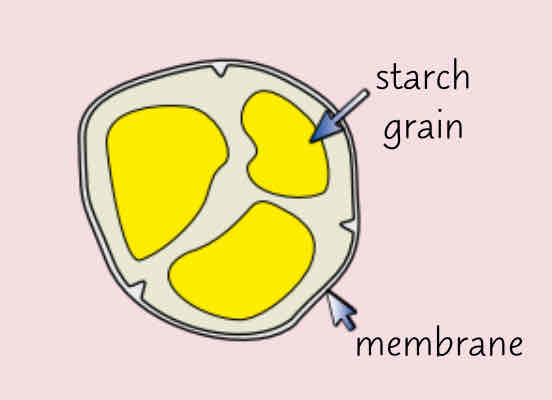
Describe the amyloplast and its function
-small organelle enclosed by a membrane
-contain starch granules
-store starch grains and convert starch back to glucose
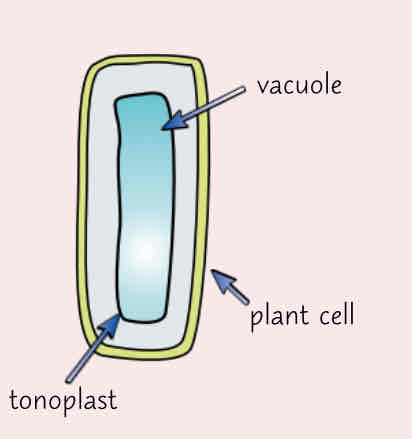
Describe the vacuole and tonoplast and its function
-vacuole is a compartment surrounded by a membrane called the tonoplast
-vacuole contains cell sap which keeps the cells turgid
-involved in the break down and isolation of unwanted chemicals in the cell
-tonoplast controls what enters and leaves the vacuole
How do plants store excess glucose?
As starch
What two polysaccharides of alpha glucose does starch contain?
-amylose and amylopectin
Describe amylose
-long unbranched chain of alpha glucose
-glycosidic bonds give it a coiled structure
-compact so it’s good for storage
Describe amylopectin
-long branched chain of alpha glucose
-side chains allow easy breakdown of glycosidic bonds
-glucose can be released quickly
Why doesn’t Starchaffect osmosis?
It’s insoluble
Describe the structure and formation of cellulose
-long unbranched chains of beta glucose
-joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds where one cellulose monosaccharide is rotated by 180 degrees
-straight chain
-condensation reaction
What do the string threads in cellulose provide?
Structural support
Why are cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall strong?
-contains cellulose in a net like arrangement
-strength of microfibrils and their arrangement in the cell wall gives plant fibres strength
-cellulose embedded in a matrix
-hydrogen bonds hold cellulose chains together
-which prevents cellulose from sliding over each other.
What is the function of xylem cells?
Transports water and minerals up the plant and provides support
Describe the structure of xylem cells
Long, tube like structures made of dead cells
Found in bundles
Cells are longer and they have a hollow lumen with no cytoplasm and end walls
Walls are thickened with lumen to support the plant
Water and mineral ions move into and out of the vessels through pits in the walls where there is no lignin
What is the function of the scleremchyma?
Provide support
Describe the structure of the sclerenchyma
-made of bundles of dead cells that run vertically
-cells are longer and have hollow lumen and have end walls
-walls thickness by lignin but dont contain pits
-have more cellulose than other plants
What is the function of the phoenix tissue?
Transports organic solutes like sugars from where they’re made in the plant to where they’re needed.
Translocation
What diffrent types of cells does phloem tissue include?
Sieve tube elements and companion cells
What are sieve tube elements?
Living cells and are joined end to end to form sieve tubes
What do the sieve tubes allow?
For solutes to pass through
What is unusual about sieve tube elements?
They have no nucleas, a very thin layer of cytoplasm and few organelles.
Cytoplasm of adjacent cells is connected through the holes in the sieve plates.
What does the lack of nucleas and other organelles in sieve tube elements mean?
They can’t survive on their own, so it has a companion cell
What do companion cells do?
Carty out the living functions fir both themselves and their sieve cells.
What do xylem vessels and phloem tissue group together to form?
Vascular bundles
What does sustainability mean?
Using resources in a way that meets the needs of the present generation without messing it up for future generations
What are renewable resources?
Resources that can be used indefinitely without running out
How is making products from plant fibres more sustainable?
Less fossil fuel is used up and crops can be regrown to maintain the supply for future generations
Other than being sustainable what are products made from plant fibres also?
They’re biodegradable-they can be broken down by microbes
What is easier to do to plants than oils?
Easier to grow and process, making them cheaper and is easier to do in developing countries as less technology and expertise is used
Where is starch found?
All plants
What are plastics made from plant based materials called?
Bioplastics
Why is making plastics from starch more sustainable?
Less fossil fuel is used up and the crops which the starch came from can be regrown
What can vehicle fuel also be made from?
Starch-bioethanol
How are water and inorganic ions absorbed by plants?
Through the roots and travel through the plant in the xylem
Why do plants need water?
-photosynthesis
-to transport minerals
-to maintain structural rigidity
-to regulate temperature