FAM Exam 3
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms

Actinobacillosis
AKA: woody tounge
MOA: Actinobacillus lignieresii (G-)
Sporadic NOT contagious
Entry via Mucosal abrasions
CS: chronic granulomatous inflam of upper resp, drooling, stridor
ID: biopsy, culture, sulfur granules
Tx: Iodine (NaI/KI) until indium, Ceftiofur/penicillins/florfenicol (antibiotics)
good prognosis

Actinomycosis
AKA: lumpy jaw
MOA: A. bovis (G+)
oral abrasions
CS: osteomyelitis of mandible, painless jaw mass(unless tooth involved), draining tracts(w/ sulfur granules), dropping food
ID: rads, biopsy, culture
DDX: tooth root abscess, fracture
Tx: Iodine (NaI or KI), Ceftiofur/penicillins/florfenicol (antibiotics), Sx debulking
poor prognosis
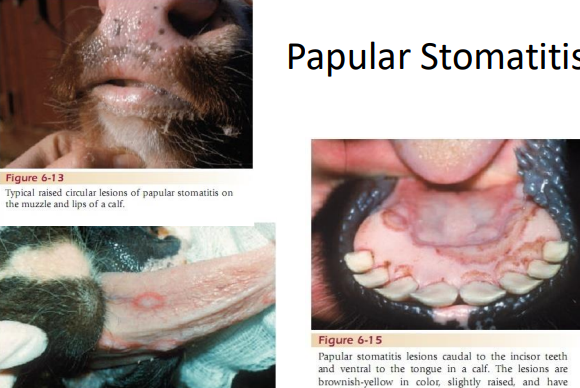
Papular Stomatitis
MOA: parapoxvirus: Related to the contagious ecthyma virus of sheep and goats
zoonotic, young cattle <1y
Direct contact
CS: oral lesions, circular edema
Dx: EM of scab lesions- see virus particles
DDX: BVDV, FMD, VS
Tx: none, no vaccine
Pseudocowpox
MOA: Parapoxvirus
Milking
zoonotic
CS: red titty/utter papules progress to vesicles, pustules, scabs, horse shoe ring scabs that heal in 7-12d, mastitis
ID: EM of scabs
Tx: support
Control: improve milking hygiene- teat dip
• Zoonotic Risk! - milkers pox/ hand pox
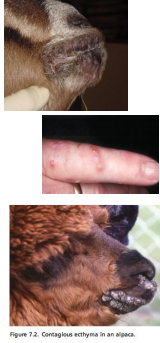
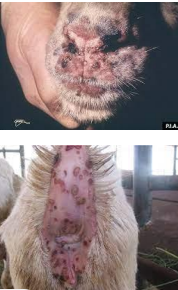
Contagious Ecthyma (Orf)
Sheep, goats, llamas, alpacas
MOA: Parapoxvirus
CS: Scabby lesions on mouth, nostrils, eyes,
udder, vulva
direct contact
ID: EM, PCR, histopathology, virus isolation
DDX: CE, lumpy skin
Tx: support, vax
zoonotic, REPORT
Sheep Pox and Goat Pox
Reportable Foreign Animal Diseases in USA!
Africa, Asia, Europe
Poxviridae
direct contact
CS:Fever, enlarged lymph nodes, nasal/ocular
discharge, Skin lesions (muzzle, eyelids, ears, mammary gland,
etc.)
Complications: Fly strike, secondary pneumonia
Dxs: Virus isolation, PCR, serology
Vaccinate endemic regions
Lumpy Skin Disease
MOA: Poxviridae
biting insects or direct
CS: Raised nodules on head, neck, udder, perineum, and legs
Major economic impact due to loss of production
ID: Virus isolation
DDX: CE, SR pox
Tx: support, vax
Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease
cows
MOA: Orbivirus
White-tailed deer (acute/fatal), cattle (milder), sheep/goats (subclinical)
Culicoides midges
CS: Fever, anorexia, dehydration, muzzle/oral ulcers, teats/udder redness, conjunctival edema, lameness
ID: PCR
DDX: BT, BVD, FMD, IBR, VSV, MCF
Tx: NSAIDS, fluids, fly prevention
Report in most states
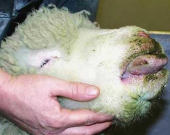
Bluetongue BTV
sheep
MOA: Orbivirus
Culicoides midges
Sheep (severe), deer (severe), cattle (subclinical), goats (subclinical)
CS: Fever, facial/lip edema(swollen head), frothy salivation, oral/nasal ulcers, lameness, hemorrhagic mucous membranes, PI, abortion, fetal reabsorption, hydranencephaly, cerebral hypoplasaia
ID: virus isolation, PCR, cELISA
DDX: Photosensitization, BVDV, MCF, FMD, snakebite
Tx: fluids, NSAIDs, Cull, fly control, vax
report
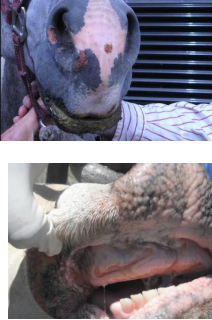
Vesicular Stomatitis
MOA: Rhabdoviridae
Cattle, horses, swine, llamas, ruminants
midge, blackflies, sandflies
CS: Vesicles/erosions on mouth(looks like FMD), teats, coronary bands, drooling, lameness, fever, mastitis
ID: Virus isolation, PCR, ELISA
DDX: Identical to FMD
Tx: fluids, NSAIDs, fly control
Zoonotic: flu like CS in humans
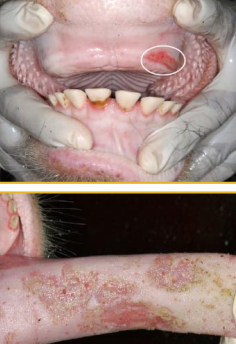
FMD
MOA: Picornaviridae, Aphthovirus
Africa, Asia, South America, Europe
Cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, bison, buffalo, deer
NOT Horses
CS: Vesicles/erosions on mouth, teats, coronary bands, drooling, lameness, fever, mastitis
ID: PCR, ELISA
DDX: VS
Tx: Vax, quarantine, cull
eradicated, REPORT
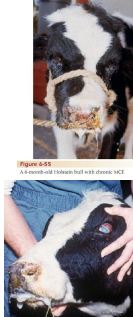
Malignant Catarrhal Fever MCF
MOA: Alcelaphine herpesvirus 1 or Ovine herpesvirus 2
Wildebeest, sheep (resiviours)
Cattle (dead end and fatal)
Sporatic and fatal
CS: fever, lymphadenopathy, KCS, corneal opacity, nasal/ocular discharge, Meningoencephalomyelitis, cracked muzzle, tremors, convulsions, nystagmus, peracute death
ID: PCR, ELISA, serum neutralization, IFA, mononuclear cells in the CSF
DDX: IBR, BVDV, VSV, FMD
Tx: cull
Winter Dysentery
MOA: Bovine Covid
reoccurs 3-15y (cyclical)
100% contagious w/in a week
CS: Explosive dark green, brown, black diarrhea
ID: Fecal- EM, ELISA
DDX: BVDV, Cocc, Salmonella
Tx: self limiting in 3d
no vaccine
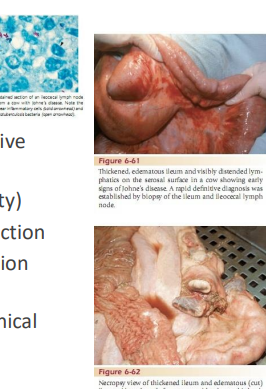
Johne's Disease
MOA: Mycobacterium
soil, feces, milk
zoonotic crohn’s, SR, cattle
CS: Slow progressive PLE, "bottle jaw", no fever till terminal, diarrhea, "Rope-like" thickened intestines
ID: Acid-fast, PCR, ELISA, Ileocecal junction granulomas biopsy/necropsy, AGID
Tx: cull, clean maternity pens, remove @ birth(<2h) w/ heat treated milk replacers, vax in cattle only
Salmonellosis
MOA: S. Typhimurium & S. Newport (non host adapted), S. Dublin (Host-Adapted)
feces, milk, colostrum, fomites, stress
zoonotic
CS: Septicemia(calves), meningitis, pneumonia, abortions(adults), septic tank bloody/foul feces (Ty/Newport), leukopenia (Ty/Newport)
ID: PCR, ELISA, necropsy w/ necrotic enteritis, culture (5x)
Tx: fluids, NSAIDs, Antibiotics, pasteurize, biosecurity(test/cull)
Poor prognosis, isolation
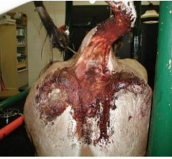
Hemorrhagic Bowel Syndrome
MOA: unknown
Fatal: GIT in high producing dairy cows(early lactation)
CS: sudden, "Blackberry/strawberry jam" feces, Abdominal distension, dehydration, shock, pale MM, tachycardia, hypothermia, death w/in 24h
ID: US of paralyzed Sm I, necropsy of hemorrhagic jejunum w/ clots
DDX: Intussusception, volvulus, Salmonella, enterotoxemia
TX(ER): fluids, antibiotics, NSAIDs, Sx resections, high quality roughage, slow diet changes, ionophores, vax
poor prognosis
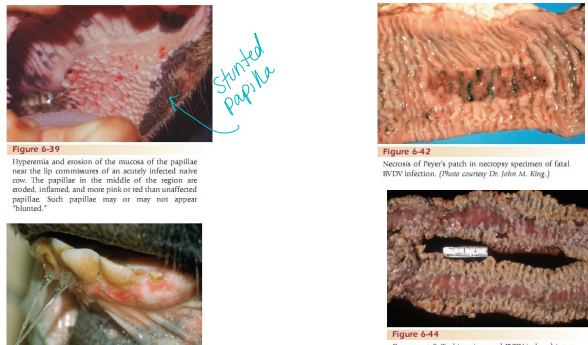
Bovine Virual Diarrhea BVD
MOA: Flaviviridae
BVDV-1(b): subclinical - Noncytopathic (NCP-BVDV) most common
BVDV-2 (NCP): acute/hemorrhagic
Semen: seminal vesicles, prostate and testicular tissue
CS: PI calves (1-4m gestation), early embryonic death (0-40d), Cerebellar hypoplasia(congenital) (125-150 gestation), fever, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, hemorrhage, mucosal disease (oral leasions)
after 125d, normal calves possible
Dummy calves
ID: SN confirms active infection, ELISA (cant tell vax or not), Virus isolation (WBC/Spleen/LN), PCR cold ear notch samples, IHC
Test all calves alive/dead, cows w/ PI calves, new cows
Paired serum samples for active infection in adults
DDX: FMD, BTV, MCF
TX: cull, vax
BVD1 ML Vax (#1): lowers PI, can cause mucosal dx in PI cows, not for preg, give 1m pre breeding
Killed vax: preg cows, less effective, 2 doses
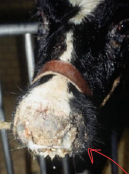
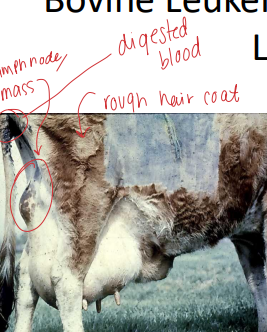
Bovine Leukemia/Enzootic Bovine Leukosis
MOA: BLV
Bld, utero, colostrum/milk, insects
CS: Systemic, malignant neoplasia of the reticuloendothelial system
Asymptomatic (#1)
Persistent Lymphocytosis w/ no tumors
Lymphosarcoma (paralysis, edema, CHF, bloat, infertility)
ID: AGID (#1), ELISA/PCR (herd), test + cull
Tx: none, certified "Leukosis-Free" herds

Sporadic Bovine Leukosis
MOA: unknown, non-viral
Young <3y
No herd spread (isolated cases)
No retrovirus detected
non contagious
CS: acute death, lymph system tumors, skin nodules
Fatal
ID: biopsy
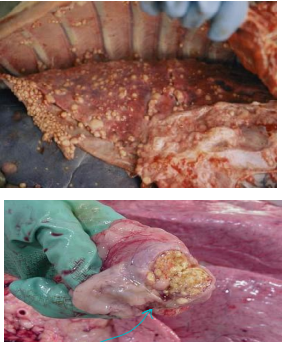
Bovine Tuberculosis
Chronic
MOA: M.bovis
Cattle, SR, SACs, white tailed deer, zoonotic
raw milk, aerosols, direct contact
CS: chronic wasting, lymphadenopathy#1, cough, "Pearl-like" granulomas on pleura/peritoneum, granulomas
ID: acid fast, Tuberculin Skin Testing, Caudal Fold Test, comp cervical test, test + cull
DDX: M. avium (poultry non-zoonotic.), use cervical test
TX: test/cull, quarantine, deer control, pasteurize all milk
Report
#1 Caudal Fold Test: Bovine PPD injected in tail fold; read at 72h for swelling
#2 Comparative Cervical Test:
Pseudorabies
AKA: Mad itch, Aujeszkys dx
MOA: Suid alphaherpesvirus 1
swine is primary host
absent in commercial swine
cattle, SR, SA, horses, rodents are secondary hosts
CS:
Pigs(age/immune status): fevers, tremors(neonatal), resp dx(weaners/growers), repo failure(adults)
Cows Mad itch: intense puritis, salivating, aggression, ataxia, sudden death
SR: Pruritus, neuro dx, resp dx, sudden death
ID: virus isolation
Tx: none
reportable, voluntary national eradication program
Leptospirosis
MOA: cows and SR
life infections of kidneys and repro tract
CS:
Non-Hardjo Serovars- acute
Fever, hemolytic anemia, hemoglobinuria, jaundice, congestion, meningitis, sudden death
Hardjo Serovar- chronic
late term abortions, milk drop, Agalactia, blood-tinged milk, still borns, weak calves, light tan cotyledons, yellowish intercotyledonary areas, plancentitis, icteric aborted calf
ID: Paired serology, PCR/IFA
TX: serovars vax (2doses 6w, booster, 6w pre breeding) & rodent control
Acute: Systemic antibiotics (penicillin, tetracyclines)
Chronic: oxytetracycline, certifiur
Anthrax
MOA: Bacillus
lives in soil for decades
zoonotic
CS: Sudden death, bloody discharges, no rigor mortis, neck edema, fever
ID: Ear bld smear(acid fast), Ascoli test or thermo precipitation
DO NOT OPEN CARCUS
Tx: vax, quarantine, bleach, burry 2m or incinerate
reportable
Caseous lymphadenitis
MOA: Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis.
adult ews
skin wounds (sheering)
CS: lymph abscesses, abscess of organs (liver, kidney)
draining
ID: "Chinese letters" on staining, Culture, PCR, ELISA, synergistic hemolysin inhibition
TX: antibiotics + sodium iodide, sx drainage, vax, pasture rest for 6m, Ca hypochlorite/formalin/cresol disinfectants
Chronic, lifelong infection
Black Disease
AKA: infectious necrotic hepatitis
MOA: Clostridium novyi type B
liver flukes
CS: sudden death, rapid putrefaction of carcass, black SQ tissue
ID: culture, histo, FAT, IHC, PCR
TX: ineffective, vax
Fascioliasis
Liver flukes
MOA: Trematodes
cattle, SR, SACs
Freshwater snails
CS: Anemia, bottle jaw, Bile duct damage,
Acute: black dz to death
Chronic: bottle jaw, weight loss, loose stool
cholangiohepatitis, secondary black dx, sudden death
ID: fecal, ELISA
TX: Albendazole, Clorsulon, clostridia vax, snail control, pasture management

Ostertagiosis or Teladorsagiosis
MOA: Brown Stomach Worm
L3 larvae ingested
invade abomasal gastric glands
parietal cells (HCl) & chief cells disruption
CS: Moroccan leather, poor condition, profuse watery diarrhea
ID: fecal, high serum pepsinogen
TX: deworm whole herd
Beef: pre, 3w, 6w of turnout
Dairy: spring and fall

Haemonchosis
MOA: Barber’s Pole Worm
SR
tropics
bld feeding pathogen
CS: poor condition, anemia #1, bottle jaw, sudden death
ID: fecal, FAMACHA, necropsy
TX: Benzimidazoles, Macrocyclic, Levamisole, pasture management, periparturient ewes

Border disease
AKA: hairy shaker lambs
MOA: Pestivirus
CS: abortion @ any stage, weak kids w/ congenital tremors, abnormal hairy coat, PI
ID: IFA, Serology on the mom
TX: BVD vax can help
Brucellosis
AKA: Bang’s Dx
MOA: Brucella abortus (cow) or ovis (SR)
bison, elk, zoonotic
CS: placentitis, abortion (~7m) or stillbirth, necrotic red cotyledons, fetal bronchopneumonia, contagious epididymitis in SR
ID: IFA, isolation, serology on the mom (paired serum)
TX: calfhood vax
reportable
Campylobacteriosis
AKA: vibrosis
MOA: Campylobacter fetus venerealis.
spread by asymptomatic carrier bulls
zoonotic
CS: 4-8m abortion, infertility, early embryonic death, fibrinous pleuritis, peritonitis, bronchopneumonia, placentitis w/ hemorrhagic cotyledons
ID: Darkfield of abomum, placenta culture
TX: bull streptomycin, AI, vax
Trichomoniasis
MOA:
chronic venereal dx in bulls (for life)
Aborted cows are lifelong carriers
CS: early abortion, infertility, placentitis, hemorrhagic cotyledons, flocculent exudate, petained placenta, pyometra
ID: culture, preputial wash on microscope( bulls)
TX: none, AI, Cull, Vax
Chlamydiosis
MOA: Chlamydophila abortus or pecroum
zoonotic in preg women
CS: last trimester abortion, placentitis, yellow (cow) or red (SR) exudate adhered to the cotyled, fetus w/ enlarged liver w/ white foci, arthritis + conjunctivitis of sheep,
ID: ELISA, PCR, Culture lung/liver/placenta, Elementary bodies on stained smears of placenta or vag
TX: no vax for cows, vax for SR, Tetracycline
Epizootic bovine abortion
AKA: foothill abortion
MOA: ticks
CS: abortion storm in endemic areas, late term abortion w/ no illness, granulomatous inflam of fetal lymphoid tissues
ID: histo, fetal IgG
TX: fine after first storm
Enzootic abortion in sheep
Chlamydophila pecorum- Arthritis and conjunctivitis of sheep
Chlamydophila abortus- Late-term abortions, stillbirths, and weak lambs
Elementary bodies by examination of Giemsa-stained smears of the placenta or vaginal discharge

Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis IBR
Mostly BHV-5, but occasionally BHV-1 (herpes)
MOA: major resp + repo dx
latent infections
CS: Placentitis, 4m abortion, fetal multifocal hepatic necrosis, pneumonia, fever, seizure, depression, most remain visual
ID: Staining, Virus Isolation, Paired Serum Samples
TX: vax
Mycotic abortion
MOA: Aspergillus, Mucor spp.
CS: Sporadic abortion >4m-term, necrotizing placentitis, leathery intercotyledonary area, gray ringworm-like skin lesions over the head and shoulders, liver
ID: fungal hyphae from stomach
TX: Avoid moldy feed
Ureaplasma diversum
CS: late term sporadic fresh abortions, stillbirths, birth of weak calves, retained placenta, placentitis
ID: isolation from placenta, lungs, and/or abomasal
contents
Tx: None, avoid overcrowding, ventilation
Schmallenberg Virus SBV
MOA: Orthobunyavirus
midges, cattle, bison, sheep, goats, vertical
CS: Adult: fever, anorexia, diarrhea. Congenital: stillbirths, arthrogryposis, Hydrocephaly, Brachygnathia, Ankylosis, Torticollis, Scoliosis
TX: none, cull, vax, fly control

Cache Valley Virus
eradicated in most parts of USA
MOA: mosquitoes, sheep, zoonotic
CS: infertility, abortions, stillbirths, congenital abnormalities- hydranencephaly, hydrocephalus, cerebral and cerebellar hypoplasia, arthrogryposis, scoliosis, torticollis.
ID: Serology on the dam (paired serum samples).
TX: None, delay breeding season until after frost kills mosquitoes
Rift Valley Fever Virus
Endemic in Africa
MOA: sheep, goats, cattle, zoonotic, arthropods
CS: fever, abortion, high death rate of newborns
ID: serology
TX: None, vax, bug control
Neosporosis
MOA: Neospora caninum
dogs, coyotes, cows
CS: Abortion >3m: most common (4-6m), not ill moms
most common cause of abortion in dairy and beef cattle
ID: IHC, PCR
TX: none, vax, strict hygiene
Toxoplasmosis
MOA: zoonotic, cats
ingestion of sporulated oocytes
CS: early embryonic death, mummification, abortions, moms not sick, no gross lesions on placenta, distinct sm white foci in cotyledons, focal nonsuppurative inflam on fetal brain
Major cause of abortion in small ruminants
ID: Fetal serology
Prevent cat poop access to feed
Coxiella burnetii
AKA: Q fever
MOA: Goats, sheep, cattle, ticks, zoonotic
CS: Late-term abortions, stillbirths, and weak offspring, gray-brown exudate covering the placenta
ID: stain, PCR< isolation
TX: vax, biosecurity, Oxytetracycline(early), pasteurize milk
Properly dispose of placental tissues, fetal membranes, and aborted fetuses
Humans: miscarriages, flu like symptoms
don’t drink raw milk, PPE
Vaccination program in dairy cows
Neonatal
Day 1- oral rotavirus + corona
Day 3- intranasal IBR, PI-3, BRSV, rep @ 6m, 1y
2-3m caves: MLV, lepto, clostridium then rep @ 1y
Cow 3-4w pre-breeding: IBR, BVD, PI-3, BRSV, lepto, clostridium, RB51
RB51: federal reg, give @ 4-10m and rep @ 12-16m
3-4w Pre-calving: IBR, BVD, PI-3, BRSV, lepto, clostridium, calf hood, RB51
Calf hood: rotavirus, coronavirus, E. coli @ 6 then 3w pre calving
Bulls 60d pre-breeding: breeding exam, IBR, BVD, PI-3, BRSV, lepto, clostridium, BVD test, check feet
Deworming program dairy cattle
Lactating cows: at drying off!!
ONLY Morantel tartrate in lactating cows
Replacement heifers: 1m pre breeding(8-12m), 1m pre calving
Dairy calves: 2x @ warm weather
Bulls: 2m pre breeding season
Vaccination program in beef cattle
Pre-breeding: IBR, BVD, PI-3, BRSV(non-preg), lepto, clostridium, RB51
RB51: federal reg, give @ 4-10m and rep @ 12-16m
45-60d Pre-calving: IBR, BVD, PI-3, BRSV, lepto, clostridium, calf hood, RB51
Killed vaccines
Calf hood: rotavirus, coronavirus, E. coli @ 6 then 3w pre calving
consider pinkeye vax
45d Pre-weaning: IBR, BVD, P13, BRSV, clostridium
Bulls 60d pre-breeding: breeding exam, IBR, BVD, PI-3, BRSV, lepto, clostridium, BVD test, check feet
Deworming program beef cattle
Cows
Deworm 1 month prior to breeding
Deworm 1 month prior to calving
Deworm 1 month prior to turnout to pasture
Feedlot calves
Deworm at entry to feedlot
Deworm again as needed
Bulls
deworm before breeding
Health management in small ruminants
Clostridium CD&T Vax
Lambs and kids
4 + 8w, 1y: Born to immunized dams
2 + 6w, 1y: unknown history
Dams:4w pre birth
Deworming program
FAMACHA or fecal egg count every month
Ewes and does @ 1m pre breeding/birth/thurnout, dip 21d pre/post shearing
Lambs and kids: @ weaning/60d
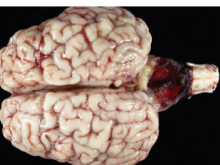
Cerebellar hypoplasia
MOA: congenital
#1 brain malformation
BVDV @ 100-200d gestation
CS: Unable to stand, thrashing, opisthotonos, nystagmus
ID: PCR
TX: dam BVD vax
Poor prognosis

Cerebellar abiotrophy
MOA: hereditary
Progressive cerebellar degen
3-9m holstein, charolais, limousine angus calves
CS: Ataxia, hypermetria, wide base stance, fine head tremors
TX: Poor prognosis
Degenerative myeloencephalopathy
AKA: Weaver syndrome
MOA: hereditary
5-8m brown swiss cattle
Bilateral pelvic limb ataxia and dysmetria
CS: Progressie ataxia to all 4 limbs, paralysis, recumebency
TX: Prognosis is poor
Spastic paresis
AKA: Elso heel
MOA: Hereditary
Affecting sciatic gamma motor neurons
2-10 m calves
CS: Progressive functional spinal cord disorder
TX: Cut tibial nerve
Dont breed
Spastic syndrome
AKA: Crampy
MOA: hereditary
3-7y Holstein and Guernsey cattle
CS: Progressive posterior paralysis, periodic spasticity, progressive hindlimb paralysis, extends its hindlimbs backward
Signs are worse when animal first rises
TX: Culling
Meningitis
MOA: Calves, lambs, kids, crias
Neonate: E.coli sepsis from FPT @ 7-10d baby
Growing: Histophilus somni - feedlot
Adult: Salmonella bacteremia, otitis interna, coliform mastitis, sinus infection
CS: Intermittent tonic clonic seizures, stiffness, hyperreflexia, inducible nystagmus, opisthotonus, head pressing, joint ill, Sudden death (H. somni)
ID: CSF, culture, TTW/blood (H. somni)
TX: Ceftiofur, Florfenicol, Enrofloxacin, ampicillin, tetracycline IV fluids, NSAIDs, colostrum, vax (H. somni)
prognosis poor for H. somni
Otitis Interna/Media
MOA: Histophillus, mycoplasma, mannheimia
calves 1-6m
# 1 vestibular dx
CS: fever, head tilt, dropped ear, dysphagia
ID: rads
TX: Tulathromycin, tetracyclines, enrofloxacin, NSAIDs, fluids

Rabies
MOA: wildlife
No reported cases of Rabies to humans by large animal exposure in North America
Incubation 1-5w
CS: bizarre behavior signs, rapidly progressive (1-3d), hind limb abnormalities, bladder dysfunction, tenesmus, dysphagia, unusual bellowing
no pathognomonic sign!
DI: ANY RUMANAT W/ CNS signs, DONT NECROPSY, CSF, Histopath, Negri bodies, IFA, PCR
DDX: listeria, nervous ketosis
TX: vax @ 3-6m

Listeriosis
AKA: circling disease
MOA: L. monocytogenes
#1 infectious neuro dx of dairy cows
ascends nerves to brainstem causing multiple microabscesses
Cattle fed poor quality silage, after drought
ph<5 to stop listeria growth
ZOONOTIC (contaminates milk!)
CS: unilateral circling, weak tongue, head tilt, nystagmus, strabismus, drool
ID: CSF, mononuclear pleocytosis
more macrophages than lymphocytes which is opposite rabies
TX: Amoxicillin, penicillin, tetracycline, ceftiofur, NSAIDs, fluids, tube feeding, rumen fistula
Tetanus
AKA: Lockjaw, saw horse stance
MOA: Clostridium tetani
wound infection
CS: Muscular spasm, hyperesthesia, hyperexcitability, mastication issues, prolapsed nictitans, High HR/RR, congestion
TX: Penicillin, sedation, IV fluids, Vax
Botulism
MOA: Clostridium botulinum type D exotoxin
decomposing animal tissue
phosphorus deficiency (pica)
CS: Excessive salivation, tongue paralysis, dysphagia, inability to urinate, recumbency, death due to respiratory paralysis
ID: PCR, toxin detection
TX: none, proper disposal of dead animals, remove decaying grass or spoiled silage, Vax
Diagnosis & Clinical Findings: Diagnosis based on clinical signs, PCR, detection of toxin.
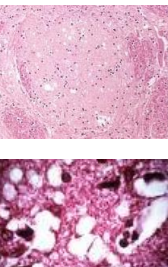
Classical Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy BSE
AKA: mad cow
MOA: prion
ingestion of prion-contaminated feed
Slaughtered scrapie-infected sheep
long incubation
CS: Hyperexcitable, twitching, hypermetric ataxia, progressive ataxia, paresis, death
CJD in humans
ID: no premortem diagnostic, microscopic examination (spongy brain)
SF is normal
TX: none
Report
Scrapie
AKA: mad itch
MOA: prion
vertical transmission at a pre- or postnatal stage
>3y SR
CS: fatal, behavioral changes, excitability, nervousness, or aggressiveness, fine tremors of the head and neck, trot or hop like a rabbit, intense pruritus, dry fleece
ID: Histopath, multiple vacuoles w/ cytoplasmic degeneration, IHC, third-eyelid/rectal lymphoid tissue biopsy
tonsils if subclincal/<1y animals that are incubating
TX: eradication program, cooking does not destroy prions, genetics

Polioencephalomalacia
MOA: Thiamine deficiency
young ruminants on high grain diet- 2-8m old
ruminal acidosis
brakenfern, sulfur
CS: Cerebrocortical edema, stargazing, Cortical blindness w/ ok PLR, Odontopresis
ID: Response to thiamine, CSF, woods lamp
DDX: preg tox, salt/lead toxic, TEME, rabies, listeria
TX: thiamine, dex, feed improve
Lead Poisoning
MOA: motor oil, old paint, batteries
Affect sulfhydryl-containing enzymes and tissues rich in mitochondria
Signs appear within 24-48 hr of exposure
CS: Ataxia, blindness, salivation, spastic twitching of eyelids, jaw champing, bruxism, muscle tremors, and convulsions
ID: blood lead
TX: thiamine, Ca-EDTA, laxities
Salt Poisoning: Hypernatremia
Recent salt exposure or water deprivation
MOA: swelling of brain cells
High sodium milk replacers without free water available
Tubing improperly mixed electrolytes
Frozen water sources
CS: depression and weakness, ataxia, seizure, blindness
ID: serum Na, Azotemia
DDX: PEM, listeria, lead
TX: gradual hydrate, 5% dextrose w/ furosemide, thiamine
ensure: free access to water, proper milk replacer
Water Intoxication
MOA: hyponatremia
Sudden access to water after a period of deprivation.
Excessive or cold water consumption
CS: hyponatremia, cerebral edema, Ataxia, depression, seizures, blindness, head pressing, intravascular Hemolysis
ID: Na <130 mEq/L, low PCV
DDX: PEM, listeria, lead, salt toxicity
TX: Hypertonic saline, Water restriction: Gradual reintroduction
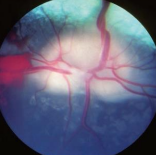
Vitamin A Deficiency
MOA: High CSF
Feedlot cattle or growing dairy replacement heifers
No green forage
CS: seizures, opisthotonus, ataxia, papilledema, abnormal bones, blindness w/o PLR, scruffy hair
Calves born to effected dams may be blind at birth
TX: vitamin A 440 IU/kg BW
Types of blindness in cattle
With an intact PLR: central (most common)
PEM, Lead, Salt, TEME, Listeriosis, Urea toxicity, Meningitis, Pituitary abscess, BHV-1 (IBR)
Blindness with an absent PLR: peripheral
Low Vit A(most common), Orbital tumors
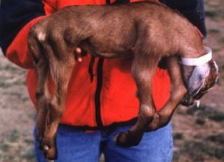
Floppy Kid Syndrome
hand raised
MOA:
metabolic acidosis
Kids 3-21d old
CS: Acute tetraparesis
DDX: diarrhea, pneumonia, white muscle dx
TX: dextrose IV, pepto, Sod bicarb orally, Vit E or Se
Vaccinate the mother, proper nutrition and colostrum
Hypomagnesemic Tetany
AKA: Grass Tetany, Transportation tetany
spring lush grass
MOA: Low blood magnesium
CS: stiffness, tetany, hypertonicity(sound/touch), recumbent, hyperesthesia, sudden death, loud pounding heart is typical , sudden collapse
ID: CSF Mg <1 or vitreous humor <1.8 (24h post mortem)
DDX: tetanus, lead poisoning, toxic plants, Rabies
TX: Magnesium and calcium IV, Mg bullets orally (slow release) IV: dilute and slow
poor prognosis, common relapse
Pasture treatment: most beneficial for whole herd to prevent
Swayback in SR
congenital
MOA: Low Copper, High molybdenum
enzoonotic type 3-4w of age
CS: swayback: lambs born with weakness, ataxia @ birth, ataxiaabnormal wool
Enzootic ataxia: 3-4w after birth
TX: oral administration of copper sulfate, supplement last 3m of preg, ruminal copper oxide capsules
Poor prognosis
Enterotoxemia
MOA:
C. perfringens Type D in intestine
FSE in feedlot lambs
CS: Diarrhea, convulsions, paralysis, sudden death
TX: No treatment, vax
Nervous Coccidiosis
MOA:
Neurotoxin in intestine
Systemic electrolyte derangement
feedlots calves/lambs- overcrowding, poor hygeine, housed on dirt
CS: Seizure, ophisthotonus, death
TX: sulfas or amprolium in water
Nervous Ketosis
Dairy cattle: early lactation, high producers
CS: “Bizarre” acting cows in first 2m of lactation, blindness, weird licking
smell ketones on breath
ID: dip stick
TX: oral propylene glycol, IV dextrose, dexamethasone injection (needs energy)
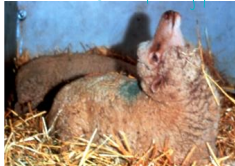
Pregnancy Toxemia
Pregnant ewes and does in late gestation
Negative energy balance
Anorexia, depression, weakness, blindness, teeth grinding
Later recumbency: poor prognosis
Ddx: hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, polio, enterotoxemia, rabies, scrapie, Maedi visna/OPP, lead poisoning, listeriosis
Dx: history, clinical signs, ketouria by urine dip stick
Treatment only successful early- IV dextrose, oral propylene glycol, oral electrolytes, induction of abortion or c-section
Later stages (poorer prognosis if recumbent)- IV dextrose, c-section, euthanasia
Prevention- nutritional management of pregnant animals (provide high energy diet, separate groups of animals according to stage of pregnancy)
Spinal Cord Trauma
Causes
Mounting behavior
Fractures secondary to ankylosing spondylitis in AI bulls
Hypoderma bovis- treatment in winter when larvae in epidural space will cause inflammatory trauma to spinal cord
Clinical signs- dog sitting position (thoracolumber and L/S lesion)
Diagnosis- history, signs, CSF (often increased macrophages), necropsy
Prognosis- poor

Vertebral Body Abscess/Epidural Abscess
Calves- omphalitis, pneumonia
Adults- rumen acidosis, mastitis, metritis, sole abscess
Compression of cord from either abscess and/or acute vertebral fractures
Clinical signs- dog sitting position (thoracolumber and L/S lesion)
Diagnosis- history, signs, CSF @ L/S (often increased macrophages), necropsy
Treatments- antibiotics, surgery
Prognosis- poor
Compressive Neoplasia
Nearly all are lymphoma (BLV+)
Signs depend on site of compression
L/S common
Diagnosis - old age, BLV+, CSF usually normal
Differentials- injury to cord, often from riding injuries
Prognosis-Poor
Key nerves in cattle
Obturator: Calving Paralysis
Recumbency after calving, split hindlegs, not be able to extend fetlock
Radial: Dropped elbow, cant extend carpus and fetlock, drags hoof
prolonged lateral recumbency, trauma
Femoral: Quadriceps atrophy, patella reflex is absent
calves pulled during hip lock dystocia
Sciatic: Dropped hip and hock, cant extend fetlock, analgesia laterally and distal to stifle
glute injection, pelvic fractures, dystocia
Peroneal: Cant flex hock or extend digit
Tibial: Can not extend hock, fetlock doesnt drag and can bear weight
caudal thigh injection, sacral fracture

Treatment of Nerve Injury
SAID
Corticosteroids (contraindicated with pregnancy)
Vit B complex
Hydrotherapy (float tank)
Good footing
Hobbles
Levamisole toxicity
CS: cholinergic signs, PEM, salivation, muscle tremors, ataxia, urination, defecation, collapse, asphyxia due to
respiratory failure
TX: Atropine sulfate
Urea/NPN Poisoning
AKA: bonkers
MOA: Ammoniated feed toxicity
Urea is converted to ammonia by rumen microflora
CS: dead in 2h, tremors, colic, frothy salivation
ID: ammonia smell in rumen, vitreous humor : sample needs to be chilled
TX: vinegar + cold water

Poison Hemlock
CS: Musty odor of urine, trembling, weak, irregular HR, recumbency, coma, death, arthrogryposis
DDX: Charolais cattle, Lupines, Akabane, bluetongue
Nitrate toxicity
MOA: fertilizer, Brassica, pigweed, lambs quarter
nitrite most toxic
CS: methemoglobinemia, Brown cyanotic MM, tremors
Brown/chocolate-colored blood
ID: Diphenylamine test
TX: 1% Methylene Blue IV, oral vinegar and coldwater
Perennial Ryegrass Staggers
MOA: endophytic fungus Neotyphodium lolii
lolitrem B- a tremorgenic neurotoxins (CNS signs)
CS: Head tremors, hypersensitivity(sound/touch), incoordination
TX: none, move animals, good in 2w