1.2 - the refracting telescope
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is the equation for magnification?
magnification = image height / object height
what is the unit for magnification?
there is no unit as it’s a ratio
what is magnification?
the image appears larger than the object
magnification = image height / object height. what units should image and object height be in?
any, providing they are in the same units as each other
what are the 2 types of telescope?
reflective
refractive
what are some features of a refractive telescope?
there are 2 converging lenses of different sizes; the large one is the objective lens and the smaller one is the eyepiece
i.e., 2 lenses in a tube in which the distance can be adjusted to focus the image
image is inverted, real, diminished
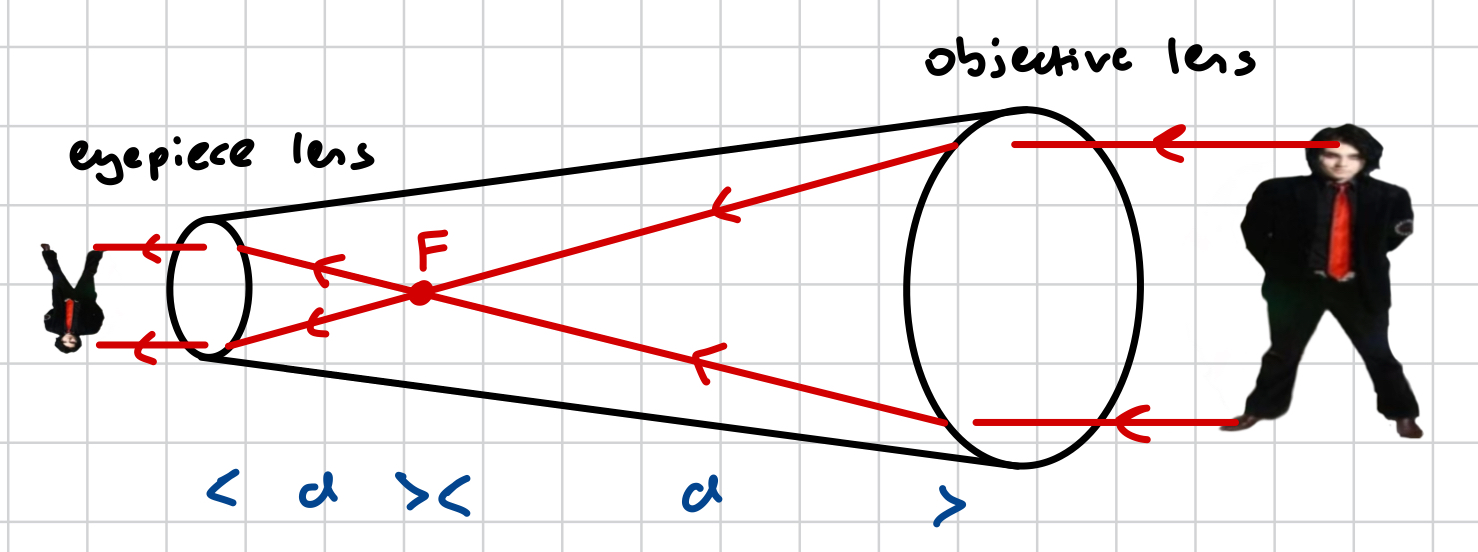
is the distance between the lenses in a refractive telescope fixed or can it be moved?
the distance between the lenses can be adjusted
how do we focus the image in a refractive telescope?
by adjusting the distance between the 2 lenses in the tube
are the lenses inside a refractive telescope converging or diverging?
converging
what is the objective lens?
ANSWER LATER
what is the eyepiece lens?
ANSWER LATER
how many lenses are in a refractive telescope?
2 converging ones - an objective lens and an eyepiece
what image does a refractive telescope produce?
an inverted one
how does a refractive telescope work?
parallel light rays passing through an object are refracted when passing through the objective lens
the light rays converge in the within the tube (between the 2 lenses), inverted the image
the light rays refract at the eyepiece into parallel rays
a real, diminished, inverted image is produced
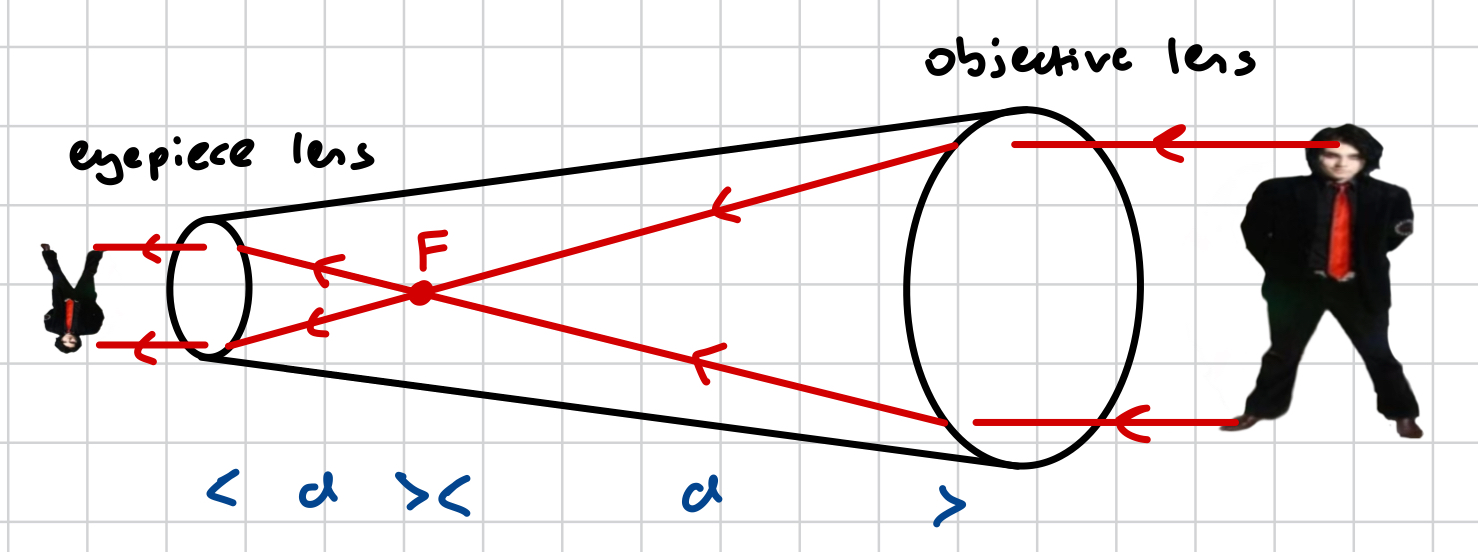
why does the image in a refractive telescope come out inverted?
because the light rays of the object converges within the tube, inverting the image, before coming out at the eye piece as an inverted image
why is the image in a refractive telescope real?
because it is on the opposite side of the lens
why does the image in a refractive telescope come out diminished?
because the objective lens (which the rays enter from) is larger than the eyepiece lens (which the rays exist from)
ray diagram for a refractive telescope
DIAGRAM HERE
do some questions on the ray diagram for the refractive telescope !
what is normal adjustment?
when the refractive telescope is adjusted so the virtual image is at infinity
what is it called when the refractive telescope is adjusted so the virtual image is at infinity?
normal adjustment
where is the normal adjustment?
where the principal focus of both lenses overlap
where distance between 2 lenses = sum of focal lengths
what happens when the principal focus of both lenses overlap and the distance between the 2 lenses equals the sum of the focal lengths?
normal adjustment
for normal adjustment, what is needed from the distance between the 2 lenses?
to equal the sum of the focal lengths
for normal adjustment, what is needed from the principal focus of both lenses?
they overlap
real image is inverted and diminished ? of the normal adjustment or of the refracting diagram? are they the same thing?
what are all angles in astrophysics measured in?
radians
what is angular size?
θ = h/d
θ - angle (in radians) subtended by an object
h - height of object
d - distance (distance subtended?)
what does subtended mean?
area swept out
what is angular size used for?
used to understand sizes of huge objects
what is angular magnification?
M = β / α
M - angular magnification (magnifying power)
β - angle (in radians) subtended by final image at infinity to viewer
α - angle (in radians) subtended by distant object to unaided eye
M = f0 / fe
M - angular magnification of telescope in normal adjustment
f0 - focal length of object lens (m)
fe - focal length of eyepiece lens (m)
kinda confused about this..
DIAGRAM
what does angular magnification mean?
the magnifying power of a telescope
radians → degrees
x 180 / π
degrees → radians
x π / 180
when can angular size be used?
it can only be used when β or α are < 10°
DIAGRAM
how does length change the angular magnification?
the bigger the length, the higher the angular magnification
why do industrial places have huge telescopes?
because the bigger the length, the higher the angular magnification