AP Psych Unit 7
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
personality
an individual's consistent characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling and acting (By adulthood, they are consistent)
openness
receptive to new ideas, broad interests, abstract
conscientiousness
responsible, organized, detail-oriented
extraversion
outgoing, fun-loving, assertive, talkative
agreeableness
trusting, helpful, warm, empathetic
neuroticism
insecure, anxious, moody, gets angry, emotionally unstable
factor analysis
statistical technique used to identity clusters of related info
MMPI
the most widely researched and clinically used personality inventory; contains true/false questions that are scores on a scale used to describe a person's mental processes and how they manage stress
evaluating trait theories:
+: gives us terminology to describe behavior
-: overestimates the consistency of behavior from one situation to another
doesn't explain behavior
doesn't create a unique description for everyone
focus of psychodynamic perspective
unconscious drives/impulses drive personality
Id
primitive, instinctual component of our personality (urges)
superego
moral components of personality (values, conscience, right v wrong)
learned from parents and society
ego
operates on the reality principle (delay gratification until id's urges can be satisfied in a socially acceptable way = balancing 2 extremes)
purpose of defense mechanisms
unconscious reactions that protect a person from unpleasant emotions such as anxiety and guilt resulting from unconscious conflict (protect the ego)
denial
refusal to recognize or acknowledge a threatening situation
repression
"pushing" threatening or conflicting events or situations out of conscious memory
rationalization
making up acceptable excuses for unacceptable behavior
projection
placing one's own unacceptable thoughts onto others, as if the thoughts belonged to them and not to oneself
reaction formation
forming an emotional reaction or attitude that is the opposite of one's threatening or unacceptable actual thoughts
displacement
expressing feelings that would be threatening if directed at the real target onto a less threatening substitute target
regression
falling back on child like patterns as a way of coping with stressful situations
sublimation
turning socially unacceptable urges into socially acceptable behavior
TAT
tell the story of a picture
Rorschach inkblot test
shown a series of inkblots; respond to what you see
humanistic perspective
emphasizes the unique qualities in humans, especially the freedom to choose their destiny and potential for personal growth
unconditional positive regard
a caring, accepting, nonjudgmental attitude, which allows individuals to develop self-awareness and self acceptance, leading to personal growth
self-actualizing tendencies
the motivation to fulfill one's potential
social-cognitive perspective
personality and behavior are influenced by the interaction between people's traits (including their thinking) and their social context
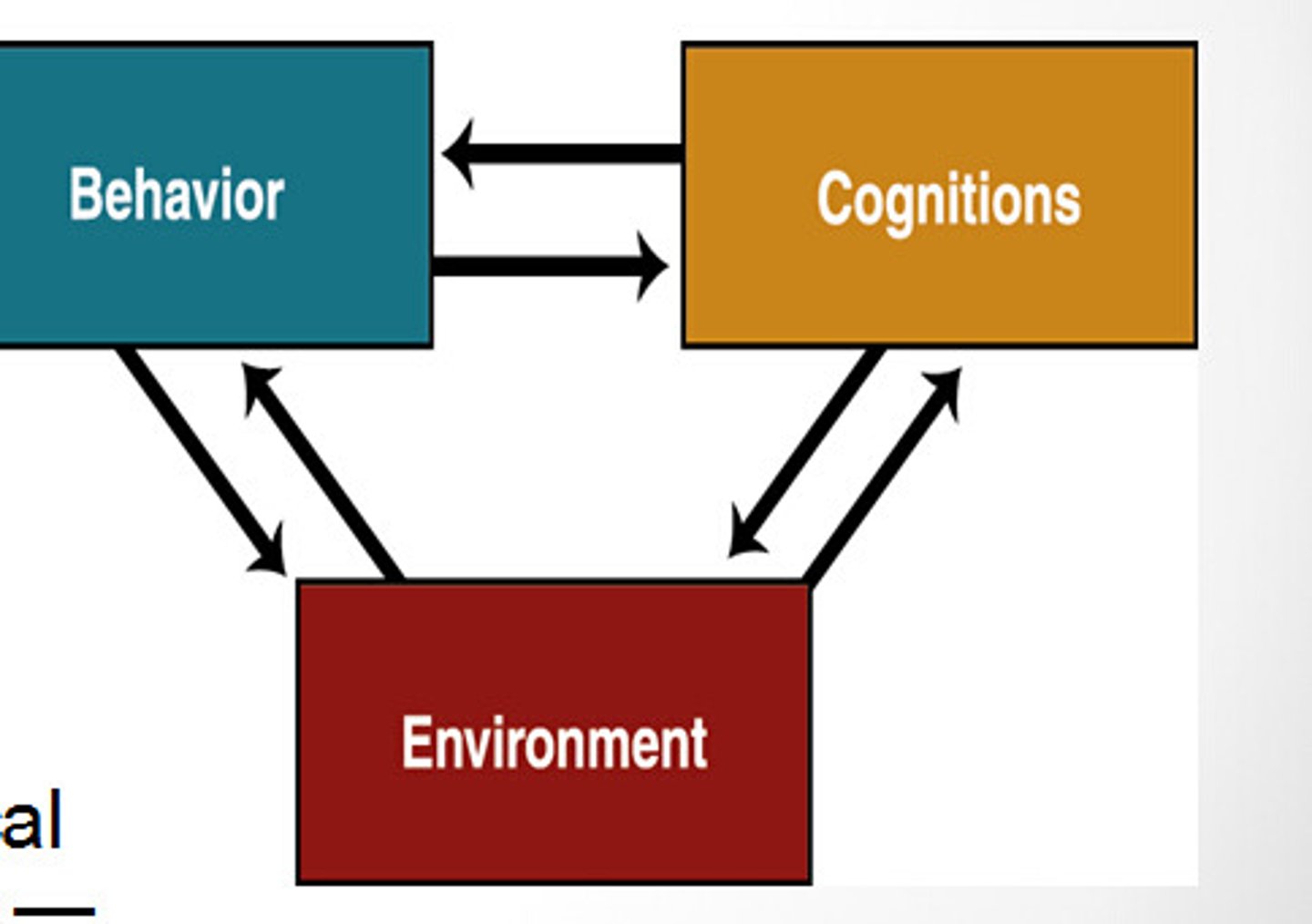
reciprocal determinism
the interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment
self-concept
the collection of beliefs about one's own nature, human qualities, and typical behavior
self-esteem
our overall feelings of self-worth
self-efficacy
one's beliefs about their ability to succeed (produce expected outcomes) in a new/different situation
motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
instinct theory
based on survival, natural selection, reproductive capacity, automatic, involuntary, and unlearned behaviors
Yerkes-dodson theory
the principle that performance increases with arousal only up to a point, beyond which performance decreases
- higher arousal benefits simple tasks, moderate arousal benefits complete tasks
drive-reduction theory
we are motivated to maintain homeostasis, explains physiological needs
homeostasis
state of physiological equilibrium or stability
drive
internal state or tension that motivates an organism to behave in a certain way
self-determination theory
we feel motivated to satisfy our needs for competence, autonomy, and relatedness
intrinsic motivation
desire to engage in a behavior for its own sake
extrinsic motivation
desire to engage in a behavior in order to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishments
incentive theory
incentive= an external goal
we are motivated to obtain desirable stimuli or avoid negative stimuli
arousal theory
people are motivated to maintain their optimal level of arousal (which is different for everyone)
- if over-aroused= motivated to reduce levels of arousal
- if under aroused= motivated to increase arousal
sensation seeking theory
individuals have varying levels of desire for arousa; and new and intense experiences
experience seeking
a preference for new and unconventional experiences like traveling, meeting new people, or trying new foods
thrill/adventure seeking
a desire to engage in impulsive, carefree behavior
boredom susceptibility
a tendency to become easily bored with routine activities and a craving for constant change
maslow's hierarchy
people are motivated to fulfill certain needs that are arranged in a hierarchy; the lower the needs on the hierarchy must be fulfilled before someone can be motivated by the need next on the hierarchy
Ghrelin
stimulates appetite
leptin
sends satiety signals to the brain
what are some of the environmental factors that influence eating behaviors?
presence of food, time of day, social gatherings
james-lange
the physical reactions of the body determine what emotion we experience (each emotion has a specific physical reaction)
cannon-bard
the brain determines what emotion we experience. the physical reaction and emotion occur simultaneously
schater-singer
the physical reactions PLUS our appraisal of the situation determine what emotion we express
broaden-and-build theory
when you experience positive emotions, you tend to broaden awareness and encourage new actions and thoughts. negative emotions reduce this
universal emotions
happiness, sadness, contempt, surprise, fear, disgust, anger
display rules
a social group or culture's information; norms that distinguish how one should express oneself
health psychology
the subfield of psychology that explores the impact of psychological, behavioral, and cultural factors on health and wellness
stress
the process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called stressors, that we appraise as threatening or challenging
eustress
good stress
distress
negative stress
acute stressors
threatening events that have a relatively short duration and a clear endpoint
chronic stressors
threatening events that have a relatively long duration and no readily apparent time limit
catastrophes
unpredictable, large-scale disasters that threaten us
approach-approach conflict
a choice must be made between two attractive options
avoidance-avoidance conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two distasteful alternatives
approach-avoidance conflict
A conflict in which there are both appealing and negative aspects to the decision to be made.
fight-or-flight response
physiological reaction to threats in which the autonomic nervous system mobilizes the organism for attacking (fight) or fleeing (flight) an enemy
general adaptation syndrom (GAS)
theory that describes the body's physiological response to stress. It's a three-stage process that can occur in response to any type of stress.
alarm reaction. (phase 1)
the initial shock of the stressor, short lived and intense
- fight or flight
resistance (phase 2)
provides the energy we need to fight the stressor (prolonged). Sympathetic NS engaged to get us through stressor
exhaustion
continual depletion of energy resources= suppression of immune system = get sick
tend-and-befriend
understress, people (especially women), may nurture themselves and others (tend) and bind with and seek support from others (befriend)
appraisal
the cognitive interpretation of the stressor
type A personality
personality type that describes people who are competitive, driven, hostile, and ambitious
Type B personality
Personality characterized by relatively relaxed, patient, easygoing, amicable behavior.
locus of control
an individuals belief about the extent to which their actions influence the outcomes/environment
internal locus of control
believe that their actions DO have an impact on the outcome/environment
external locus of control
believe that their actions DO NOT have an impact on the outcome/environment
fixed mindset
the idea that we have a set amount of an ability that cannot change
growth mindset
the idea that our abilities are malleable qualities that we can cultivate and grow
problem-focused coping
focuses on reducing stress by addressing the source of the stress
emotion-focused coping
focuses on reducing the response (emotional arousal) to the stressor
positive psychology
The scientific study of optimal human functioning, focusing on what allows humans to thrive
subjective well-being
perceived satisfaction with life/how happy do you think you are
objective well-being
physical health indications, income, living conditions
resilience
The ability to adapt well in the face of challenging life experiences, such as trauma, tragedy, or significant stress
gratitude
involves recognizing and appreciating the positive aspects of life and the kindness of others
wisdom
cognitive strengths that involve acquiring and using knowledge
courage
emotional strengths that involve the exercise of will to accomplish goals in the face of opposition
humanity
interpersonal strengths that involve tending and befriending others
justice
civic strengths that underlife healthy community life
temperance
strengths that protect against excess(self-control/restraint)
transcendence
strengths that forge connections to the larger universe and provide meaning
satisfaction
feeling that one has accomplished a goal during a certain period of time
post-traumatic growth
refers to the positive psychological change experienced as a result of struggling with highly challenging life circumstances