Blood unit
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Blood
-Connective tissue
-Composed of cells (rbc, wbc, & platelets) and plasma (water, protein, amino acids)
Blood cells
makes up 45% of blood volume
Plasma
Makes up 55% of blood volume
Erythrocytes
Term for red blood cells
Leukocytes
Term for white blood cells
Thrombocytes
Term for platelets
Red blood cells (RBC)
-made up of proteins called Hemoglobin; contains iron
-transports oxygen
-shaped like concave circular disks
-NO Nuclei
Hematopoiesis
The formation of blood cells; occurs in bone marrow
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Hormone that increases RBC production
Oxyhemoglobin
term to describe when blood has proper amount of oxygen
Deoxyhemoglobin
term to describe blood with lack of oxygen
Veins
What blood travels through to return to the heart
Arteries
What blood travels through to retrieve oxygen from lungs
Capillaries
What blood travels through to deliver oxygen to the tissues
Granulocytes
Type of white blood cell (Leukocyte) that contains granular cytoplasm
Agranulocytes
Type of white blood cell (Leukocyte) that lacks granular cytoplasm
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
Types of granulocytes
monocytes and lymphocytes
Types of Agranulocytes
lymphocytes
Makes up most of the agranular leukocytes (20-25%)
neutrophils
Makes up most of the granular leukocytes (60-70%)
Neutrophils
-nucleus has several lobes
-makes up majority of white blood cells
Eosinophil
-granular leukocytes that attacks parasites in blood
Basophil
-granular leukocytes that produces heparin (a blood thinner)
Monocyte
-agranular leukocyte that has horse-shaped nucleus and can become dendritic cells
Lymphocyte
-agranular leukocyte that produces antibodies to defend the immune system
Platelets
-initiates blood clotting, thickens blood, closes wound
-made up by thrombocytes
transport nutrients, gases, vitamins, and maintain water balance and pH levels
Role of plasma
Albumins
Plasma protein that regulates blood pressure
Globulins
Plasma protein that regulates transport of antibodies
Fibrinogen
Plasma protein that regulates transport of blood clotting
Hemostasis
-process of blood clotting/coagulation
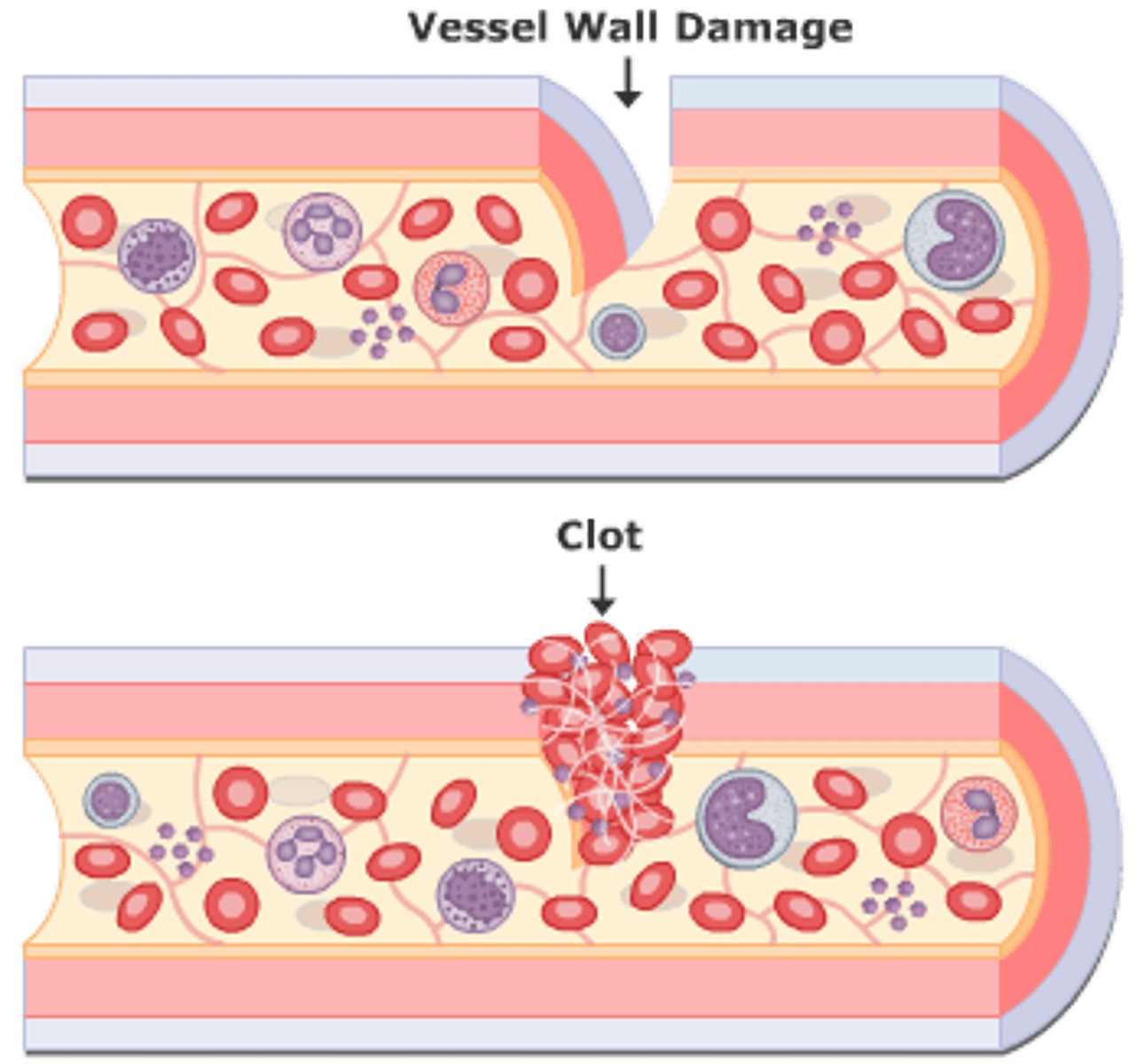
Hemostasis steps
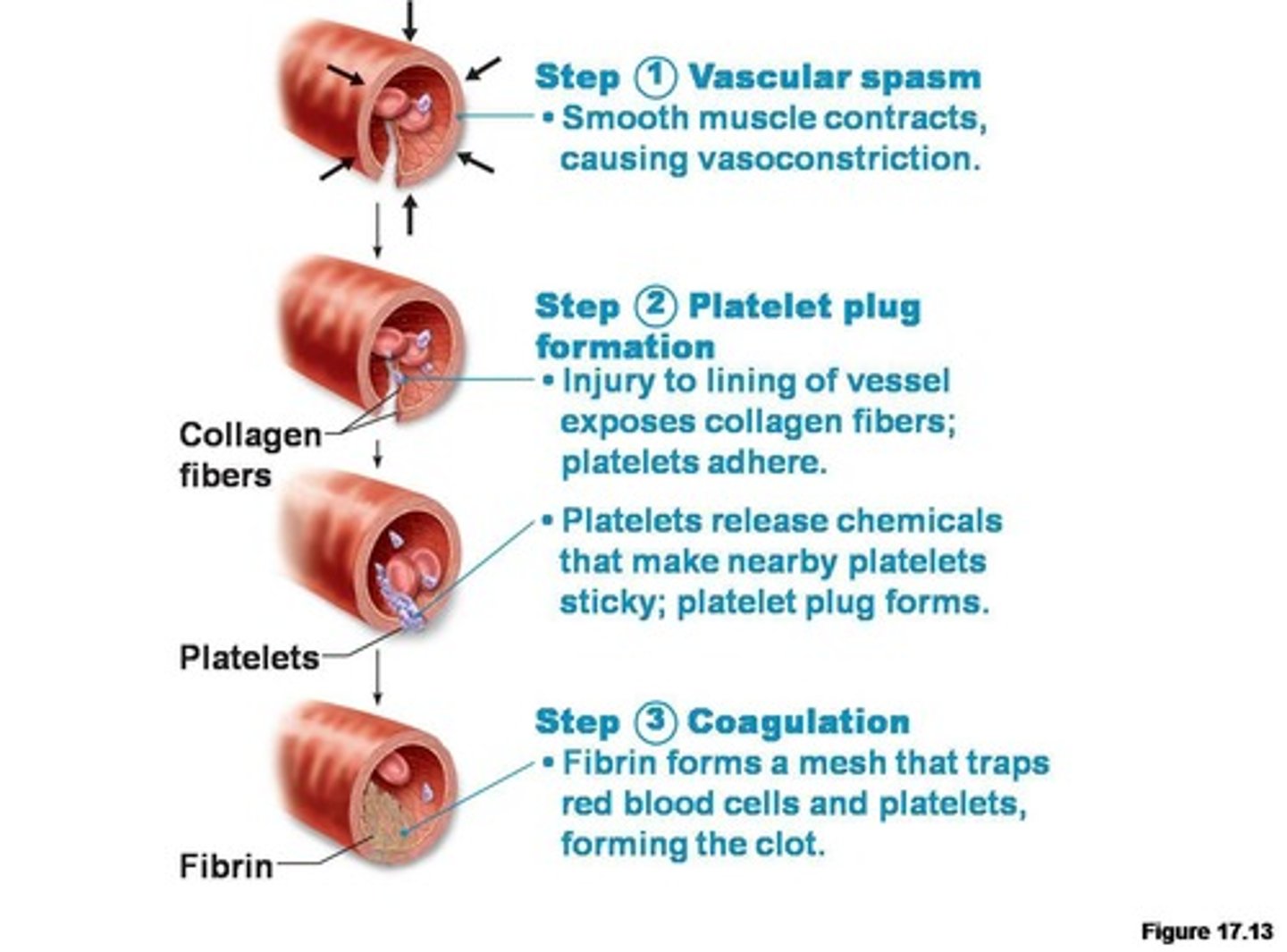
First step in hemostasis
blood vessel spasm serotonin that shrinks the vessel (vessel contracts)
Second step of hemostasis
Platelet plug forms and closes the opening
Third step in hemostasis
Coagulates as fibrin forms over the plug creating a scab
Thrombin
enzyme in blood plasma that causes the clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin
Embolus (emboli)
Occurs when a blood clot moves throughout veins (one place to another)
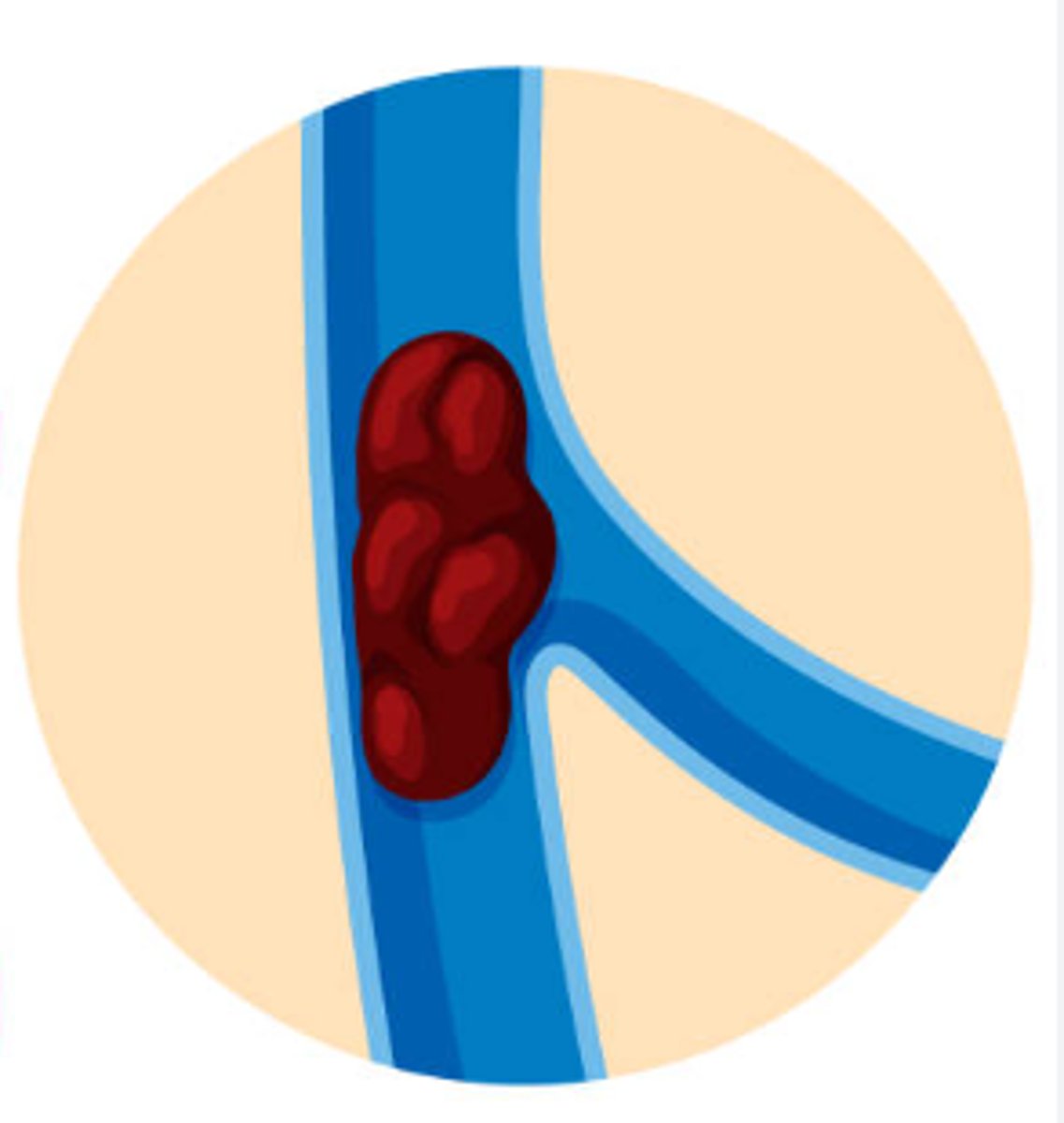
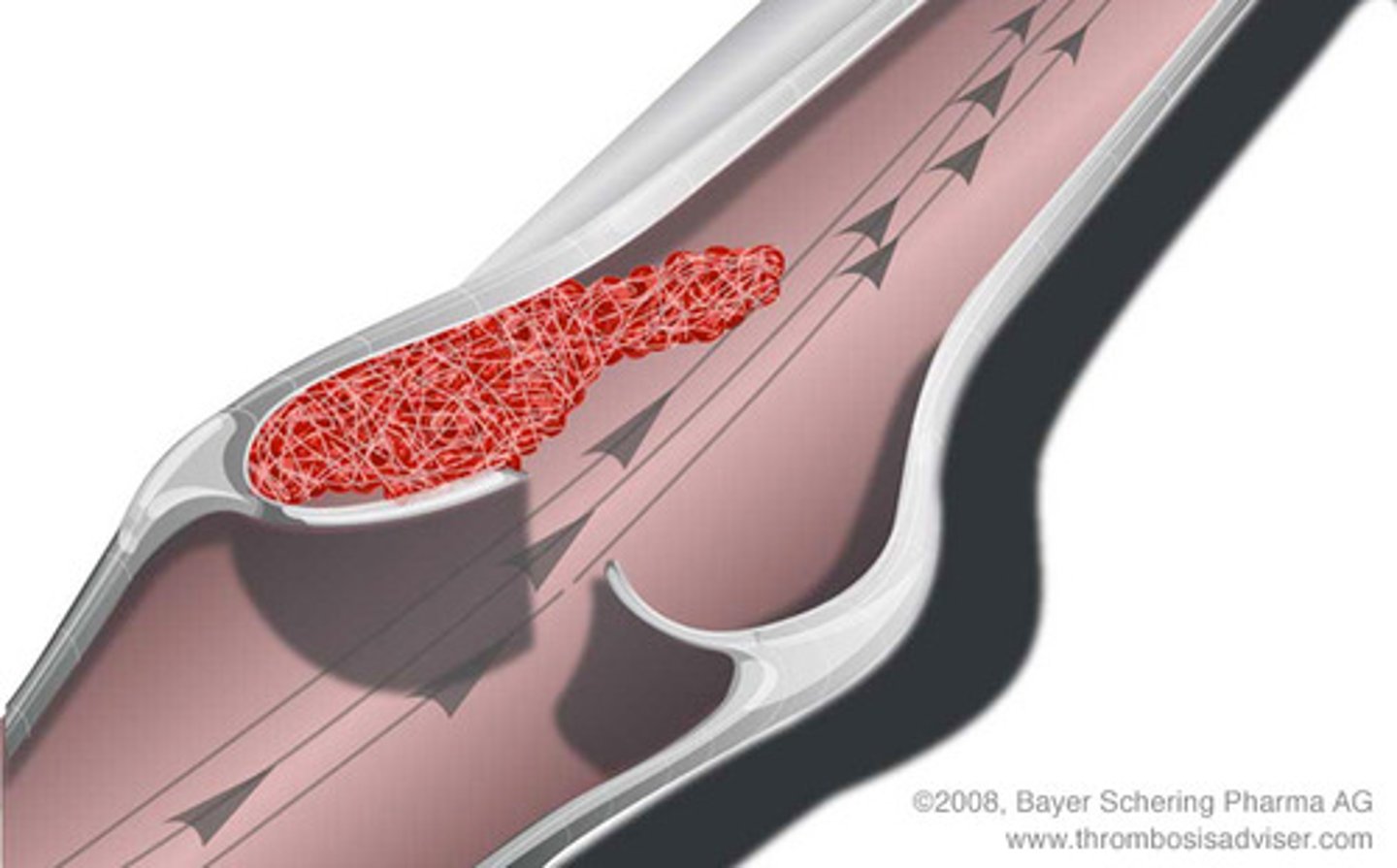
Thrombus
a blood clot attached to the interior wall of an artery or vein
- (abnormal)
splenomegaly
enlargement of the spleen
hypochromia
cells have reduced color (less hemoglobin)
anemia
an inherited disorder that interferes with the blood's ability to carry oxygen
Beta Thalassemia
Blood disorder that reduces the production of hemoglobin
sickle cell anemia
a genetic disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin, resulting in some red blood cells assuming an abnormal sickle shape
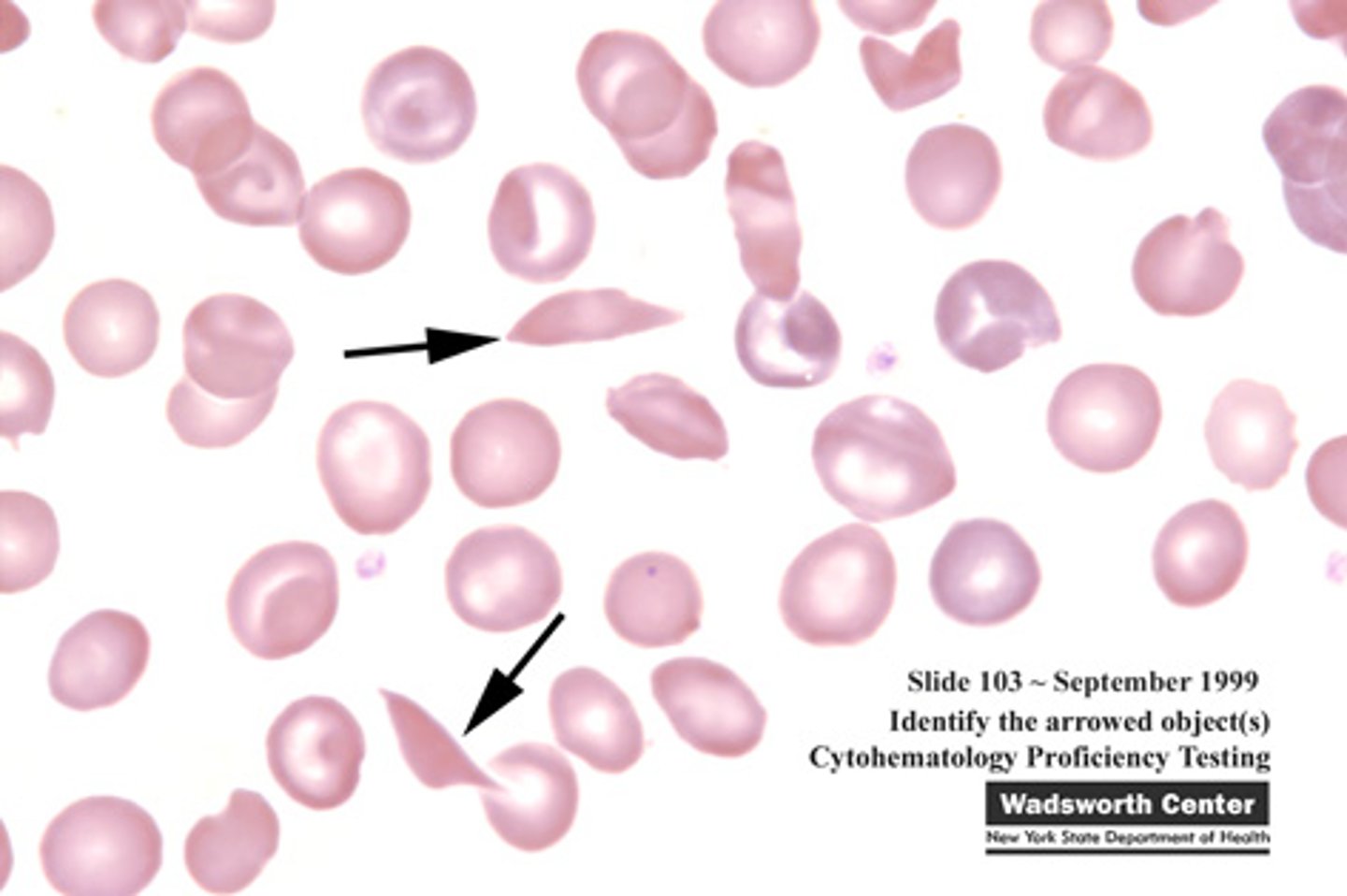
hematocrit
percentage of blood volume occupied by red blood cells
acute
a cancer that progresses quickly
herapin
prevents blood clotting (blood thinner)
Lymphocytic
pertaining to a white cell formed in lymphatic tissue
leukemia
cancer of white blood cells
Dermatographia
immune system releases excess amounts of histamine causing welts to appear when lightly scratched
Cold Urticaria (essentially meaning "cold hives")
is an where hives or large red welts form on the skin after exposure to a cold stimulus
Mononucleosis
refers to an increase in one type of white blood cells (lymphocytes) in the bloodstream
-infection usually caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
the virus that causes AIDS
- Infection occurs from exposure to body fluids, like blood or semen
- weakens the immune system by infecting specific immune cells
AIDS
acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Hemophilia
A hereditary disease where blood does not coagulate to stop bleeding
"bleeder's disease"
erythroblastosis fetalis
antigens produced by the fetus can generate antibodies in the mother. If you are Rh neg, and the father of the baby is Rh pos, then this could be a problem
Blood type AB
"universal acceptor" blood type
Blood type O
(blood type) Can donate to A, B, AB, O (universal donor)
- no antigen