macro chapter 1
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
what is macroeconomics
the study of the forces that affect the economy as a whole
the science of macroeconomic processes
looks into prosperity variation, value of money, inflation rates, recessions, etc
macroeconomic variables
real GDP (gross domestic product): reflects the price-adjusted total income of all economic actors in an economy
nominal GDP: not price adjusted (measured at current prices)
inflation rate: describes how quickly prices are rising
unemployment rate: tells you what portion of labour force in an economy is out of work
measures: investments, inequality, satisfaction
what does an increased GDP mean
economy grew
income has risen, more trade, more products produced
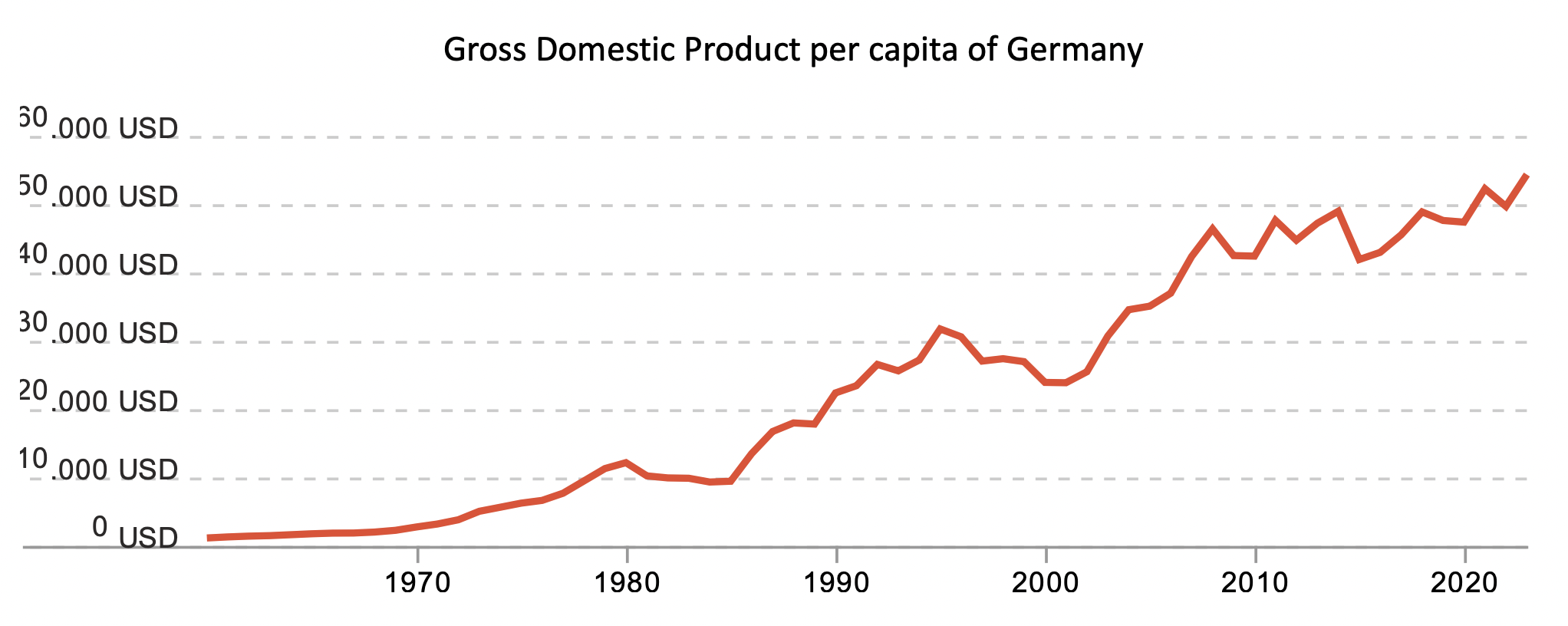
GDP per capita (per person)
measures economic activity/income per person
can tell you if the size of the economy per individual is larger than before
graph is not price adjusted
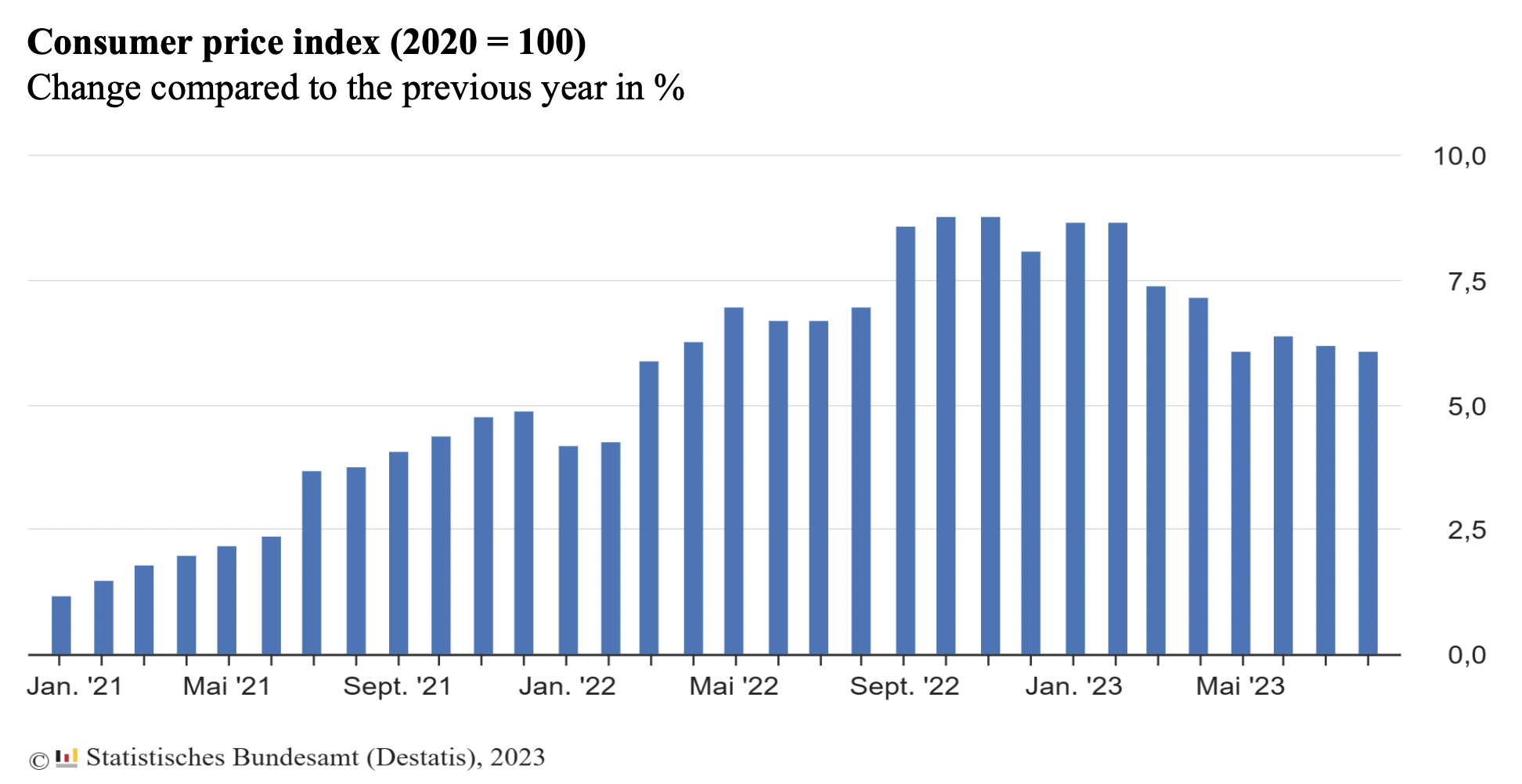
what is inflation
a monthly statistic
a sustained increase in the general price level of goods/services in an economy over a period of time, which reduces the purchasing power of currency
measured as change compared to previous year in %
Macroeconomic instruments
Simplified representations of reality in models
We concentrate on the central variables (try to abstract irrelevant details)
Models are constructed using very restrictive assumptions.
exogenous vs endogenous variables
Exogenous variables are determined outside the model. They are introduced into the model or are fixed
Endogenous variables are determined within the model itself.
how economic models work
simplified theories and show the essential relationships between economic variables
exogenous variables are variables that are determined outside the model
endogenous variables are explained by the model
model shows how a change in an exogenous variable affects all endogenous variables
supply and demand model

problems of simplifying assumptions
not all varieties of the same product are sold at the same price
not all place selling similar products are located in the same place (some may be easier/harder to get to)
flexible vs fixed prices
economists assume that price of goods adjusts quickly → market clearing
at this price, consumers can demand desired quantity, which is offered by producers at this price
flexible: adapt to changes in supply and demand without delay → suitable for describing the long-term (fully adjusted) equilibrium
wage + price rigidity justify a slow/delayed adjustment to changes in supply or demand
Short-term (cyclical) fluctuations are often associated with fixed prices
what is market clearing?
economic process where quantity of a good or service supplied exactly matches the quantity demanded, establishing an equilibrium price
no shortages or surpluses