IB Exams
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
342 Terms
axial skeleton
central points that the body rotates around
cranium, sternum, ribs, vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
appendicular skeleton
attaches to support
clavicle, scapula, humerus, radius, ulna, pelvis, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges, femur, patella, fibula, tibia, tarsals, metatarsals
four types of bones
flat bones, long bones, short bones, irregular bones
structure of a long bone
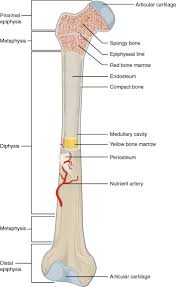
superior
abovein
inferior
below
lateral
towards the outside
medial
towards the middle
proximal
close to joint
distal
farther from joint
anterior
to the front
posterior
to the back
cartilage
acts as a shock absorber and prevents friction where bones articulate
tendons
attach muscle to bone
ligaments
hold bone to bone, secure articulating bones to a stable joint
joint
where two or more bones articulate
fibrous joints
allow no movement
cartilaginous joints
allow little movement
synovial joints
freely moveable
structure of a synovial joint
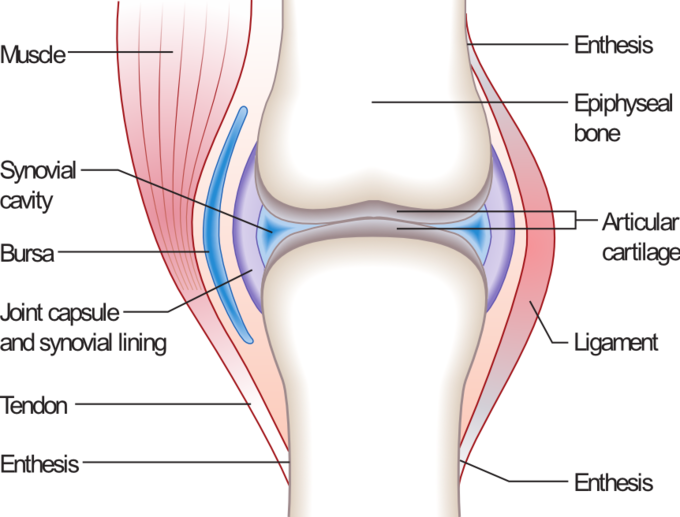
types of synovial joints
hinge, ball and socket, gliding, saddle, pivot, condyloid
contractility
ability to contract
elasticity
ability to return to resting length after contracting
extensibility
ability to extend beyond normal length
hypertrophy
ability to build muscle and increase in size due to training
atrophy
ability to lose mass, size, and strength due to lack of training
how muscles are fed
capillaries provide nutrients like oxygen and glucose and remove carbon dioxide
how muscles are controlled
based on stimulation from the CNS, controlled by nerve stimuli
smooth muscle
involuntary muscles located on the walls of arteries and organs
narrow, non-striated, uninucleated fibers
cardiac muscle
involuntary muscle located on the walls of the heart
striated, branched, nucleated fibers
skeletal muscle
voluntary muscle attached to skeleton via tendons
striated, multi-nucleated fibers
structure of skeletal muscle
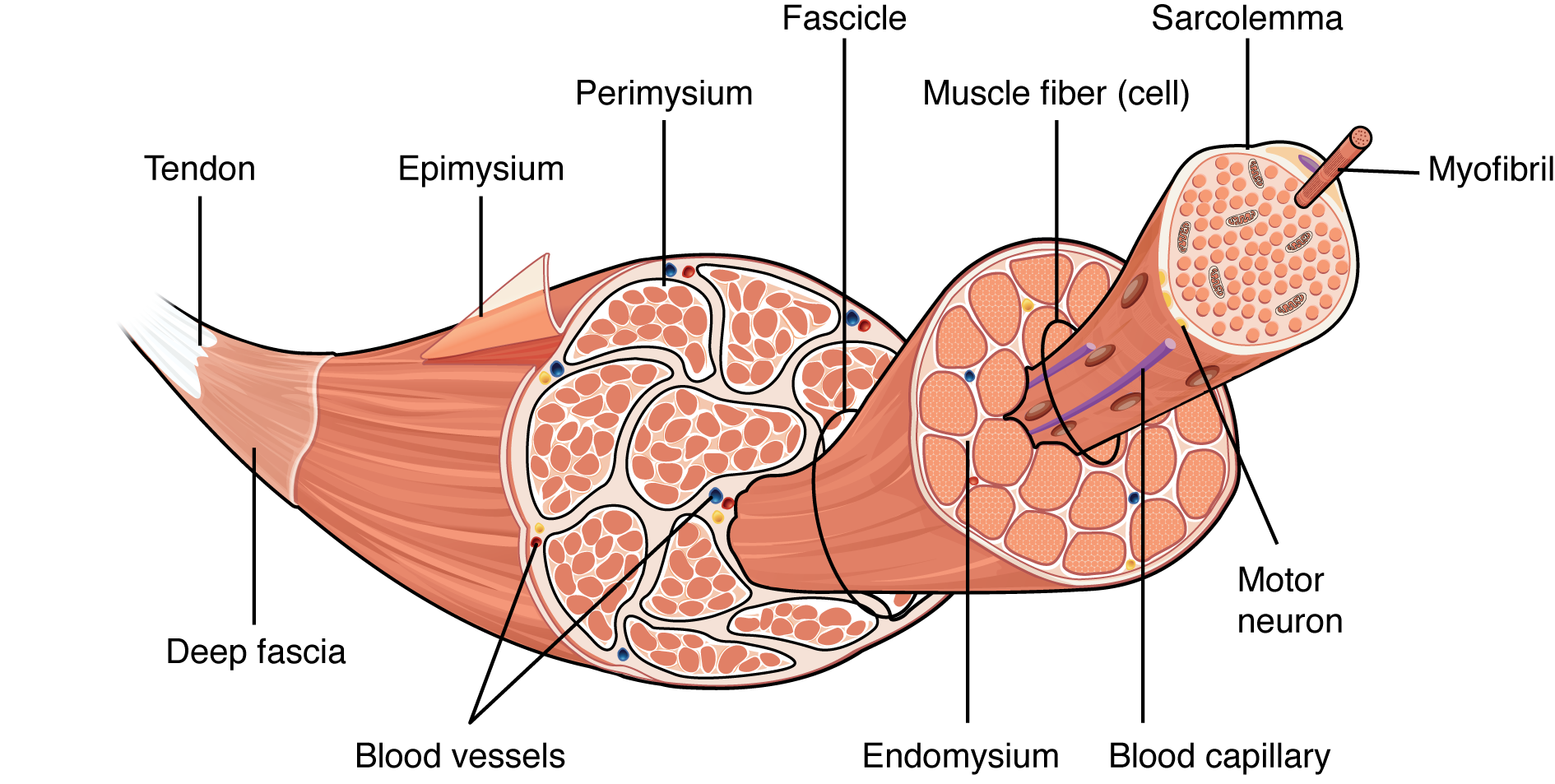
origin of muscle
stabilizes the movement, where the muscle attaches to the stationary bone
insertion of muscle
where the muscle attaches to the moving bone
structure of a motor unit
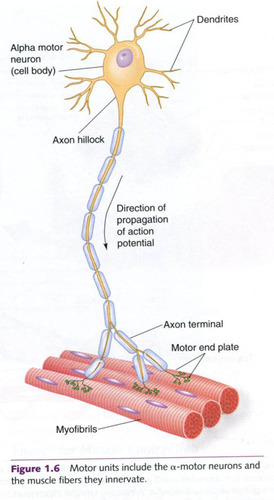
role of acetylcholine in muscle contraction
stimulates muscle contraction by binding to nicotinic receptors on the skeletal muscle
role of acetylcholinesterase in muscle contraction
consumes the excess ACh, leading to muscle relaxation
type 1 slow twitch fibers
high response to fatigue, low force production
type 2a fast twitch fibers
medium resistance to fatigue, high force production
type 2b fast twitch fibers
low resistance to fatigue, very high force production
abduction
movement away from the midline of the body
adduction
movement toward the midline of the body
flexion
bending movement that decreases the angle between the bones of the limb at the joint
extension
straightening movement that returns the body part to the zero position
supination
rotation of the hands and forearms so the palm faces up
pronation
movement of the forearm so the palm is turned down
elevation
movement that raises a body part vertically in the front plane
depression
movement that lowers a body part vertically in the front plane
dorsi flexion
bending the foot in the direction of the upper surface (flexing)
plantar flexion
bending the foot in the direction of the sole (pointing)
circumduction
distal end of the bone moves in a circle while the proximal end remains relatively stable
rotation
moving a bone around its longitudinal axis
inversion
tips the soles medially to face each other
eversion
tips the soles laterally away from each other
isotonic
result in a change in muscle length
isometric
involve no change in muscle length
isokinetic
occur at a constant velocity, typically with specialized machines
concentric
shorten the muscle
eccentric
lengthen the muscle
agonist
muscle that contracts concentrically
antagonist
muscle that contracts eccentrically
delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS)
most often caused by eccentric exercises, large forces and breaking actin-myosin bonds result in lactic acid build up and microtears in muscles
results in pain, restricted movement, stiffness, and reduced muscle force capacity
principal structures of ventilatory system
nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, lungs, and alveoli
functions of the conducting airways
low resistance pathway to airflow, defense against chemicals and other harmful substances that are inhaled, and warming/moistening air
pulmonary ventilation
inflow and outflow of air between atmosphere and lungs
total lung capacity
vital capacity + residual volume
vital capacity
tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume + expiratory reserve volume
tidal volume
normal volume of air breathed
expiratory reserve volume
air in excess of tidal volume that can be forcibly exhaled
inspiratory reserve volume
additional inspired air over tidal volume
residual volume
air still in lungs after a maximum exhale
mechanics of inhalation
diaphragm contracts, external intercostals contract, internal intercostals relax, thoric cavity volume increases and pressure decreases
mechanics of exhalation
diaphragm and external intercostals relax, internal intercostals contract, thoracic cavity volume decreases and pressure increases
chemoreceptors
detect chemical changes in blood (pH)
more CO2 = increased breathing rate/depth
proprioceptors
detect angle movement at joints
increased movement = increased breathing rate/depth
stretch receptors
inhibit inspiration and stimulate expiration after a large inhalation to prevent over-stretching in the lungs
hemoglobin in O2 transport
O2 enters red blood cells and binds with the heme group, O2 disassociates into body cells where the partical pressure is lower
gas exchange at th ealveoli
passive diffusion between alveoli and capillaries with O2 and CO2
composition of blood
erythrocytes, leucocytes, platelets, and plasma
erythrocytes
red blood cells, transport O2 and CO2
leucocytes
white blood cells, identify and eliminate pathogens
thrombocytes
platelets, form clots to prevent bleeding
structure of the heart
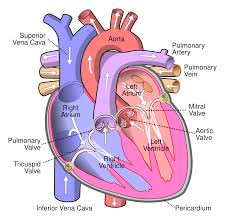
pulmonary circulation
blood that circulates to the lungs
systemic circulation
blood that circulates to the body systems
regulation of heart rate
SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → purkinje fibers
how the sympathetic nervous system regulates heart rate
secretes adrenaline to increase alertness
how the parasympathetic nervous system regulates heart rate
releases ACh to decrease alertness and calm the body
heart rate
the number of times your heart beats per minute
stroke volume
the amount of blood ejected from the heart per beat
cardiac output
heart rate * stroke volume
stroke volume, heart rate, and cardiac output in males vs females
SV: slightly higher for men
HR: slightly higher for women
CQ: slightly higher for men
stroke volume, heart rate, and cardiac output in trained vs untrained
SV: significantly higher in trained
HR: significantly higher in untrained
CQ: higher in trained
stroke volume, heart rate, and cardiac output in young vs old
resting HR: slightly higher in old
exercise HR: slightly higher in young
SV: higher in young
CQ: slightly higher in young
cardiovascular drift
an increase of body temperature results in lower venous return to the heart and a small decrease in blood volume from sweating → a reduction in stroke volume causes the HR to increase to maintain CQ
systolic
force exerted on the arterial walls as blood is ejected from the ventricles (contracted)
diastolic
force exerted on arterial walls as blood fills the ventricles (relaxation)
systolic BP vs diastolic BP during exercise
systolic BP increases and diastolic BP stays the same or slightly decreases
dynamic - systolic BP increases and diastolic BP decreases
static - systolic BP increases and diastolic BP decreases
distribution of blood at rest
most blood goes to digestive organs, kidneys, muscles, and the brain
distribution of blood during exercise
most blood goes to the muscles