key figures 4
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
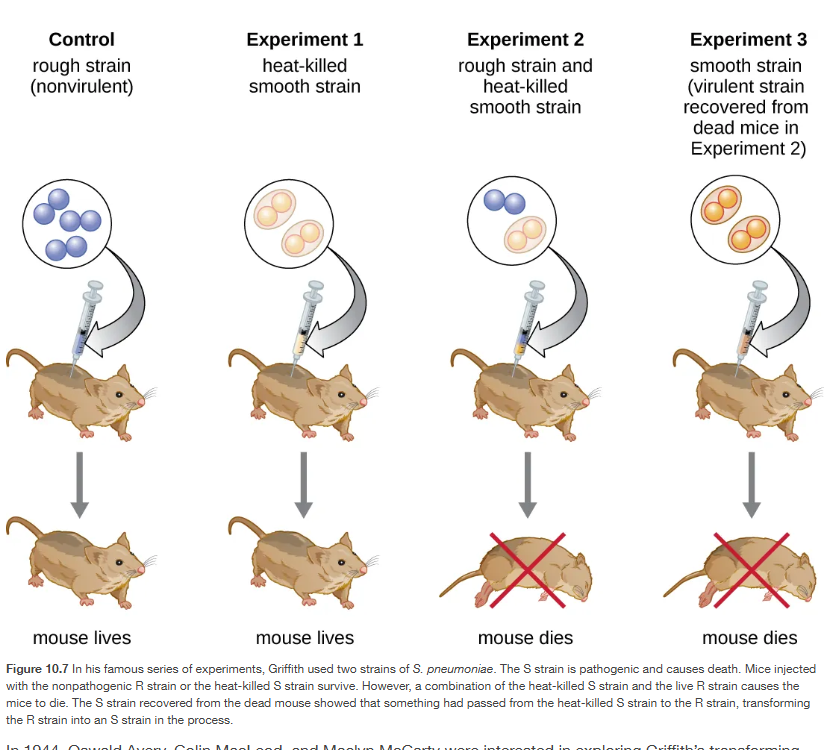
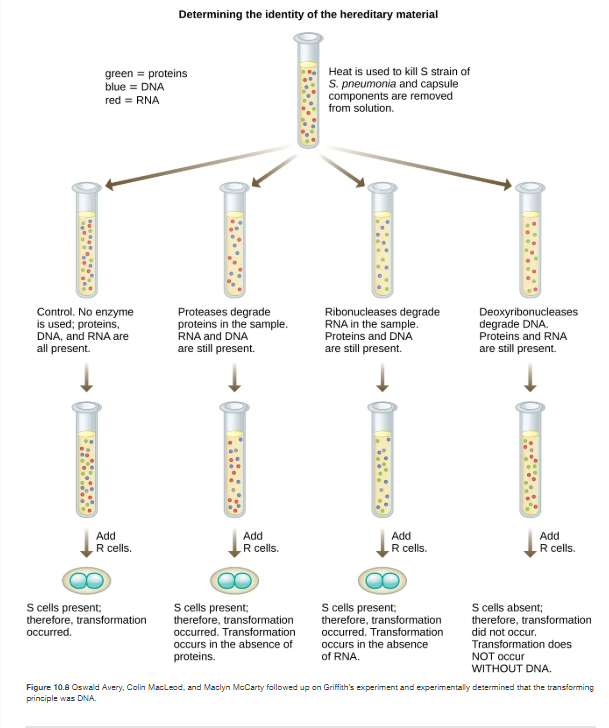
Avery–MacLeod–McCarty experiment
setup:
They took heat-killed virulent S strain bacteria (which by themselves can’t cause infection).
Then they treated these extracts with different enzymes:
Protease → destroys proteins.
Ribonuclease (RNase) → destroys RNA.
Deoxyribonuclease (DNase) → destroys DNA.
Control → nothing destroyed.
After treatment, they added live R cells (non-virulent) to see if they would transform into S cells.
results:
Control (no enzyme): Transformation occurred → S cells appeared.
Protease (no proteins): Transformation still occurred → proteins not required.
RNase (no RNA): Transformation still occurred → RNA not required.
DNase (no DNA): No transformation → without DNA, R cells stayed R.
DNA was the “transforming principle.
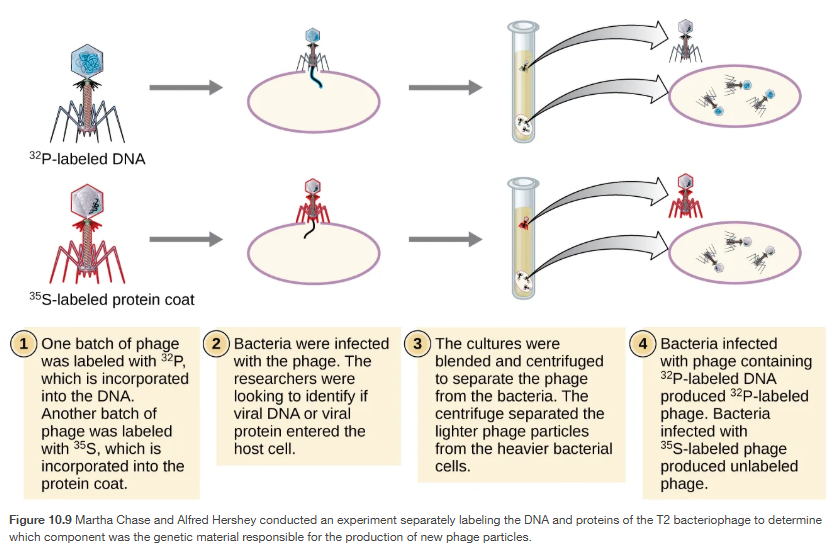
Hershey–Chase experiment
setup: They used a bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria).
to track what part of the virus entered the host cell, they labeled:
DNA with radioactive phosphorus (³²P) → DNA contains phosphorus.
Protein coat with radioactive sulfur (³⁵S) → proteins contain sulfur (DNA does not).
experiment
Phages with ³²P-DNA infected bacteria.
Phages with ³⁵S-protein coat infected bacteria.
After infection, they blended and centrifuged the mixture to separate the empty viral coats (outside) from the bacteria (inside)
results
³²P (DNA) → Found inside the bacteria → DNA entered the host cell.
³⁵S (protein) → Found outside, in the phage “ghosts” → protein did not enter.
Only DNA was passed on to the next generation of phages.
DNA, not protein, is the hereditary material that directs viral replication.
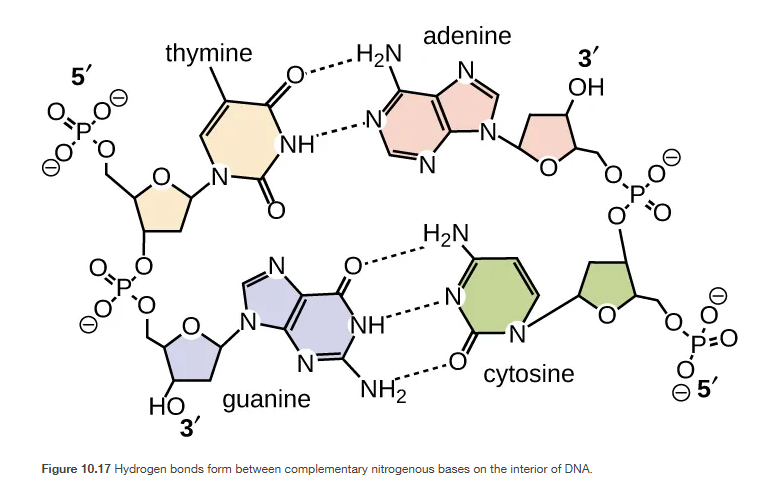
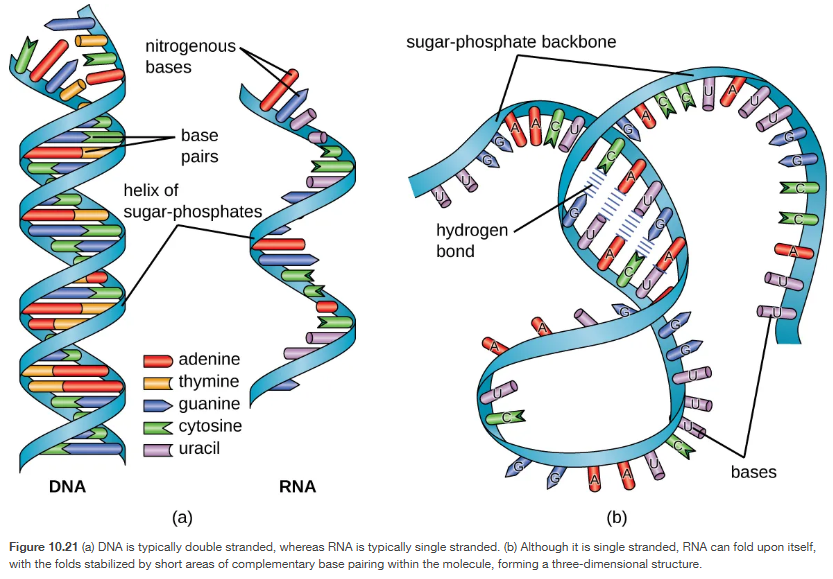
DNA and RNA
DNA: double stranded
C,A,T,G
A - T
C - G
RNA: single stranded, can unfold it self
sugar = ribose
A - U
G,C,A,U
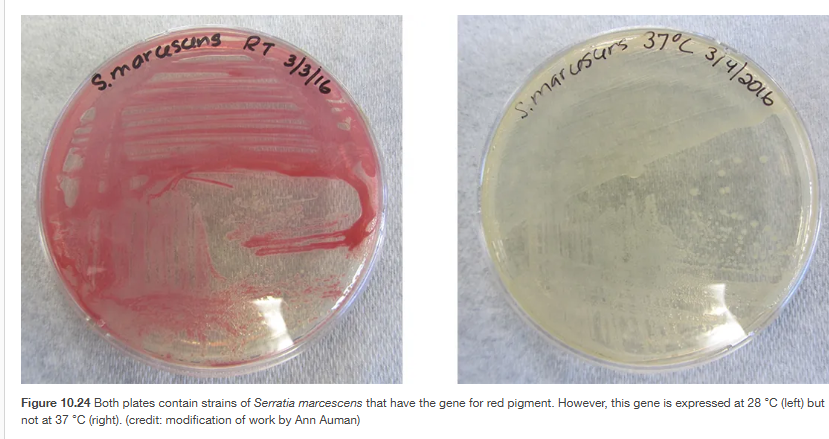
genotype vs phenotype
genotype
In this case, S. marcescens has the gene for producing a red pigment.
The genotype does not change.
phenotype: Even though both plates contain bacteria with the same genotype, the phenotype changes depending on the environment.
Left plate (28°C): Bacteria express the red pigment gene → colonies look red.
Right plate (37°C): The gene is not expressed at this temperature → colonies look white/clear.
So, the genotype is the same, but the phenotype differs due to environmental influence (temperature).
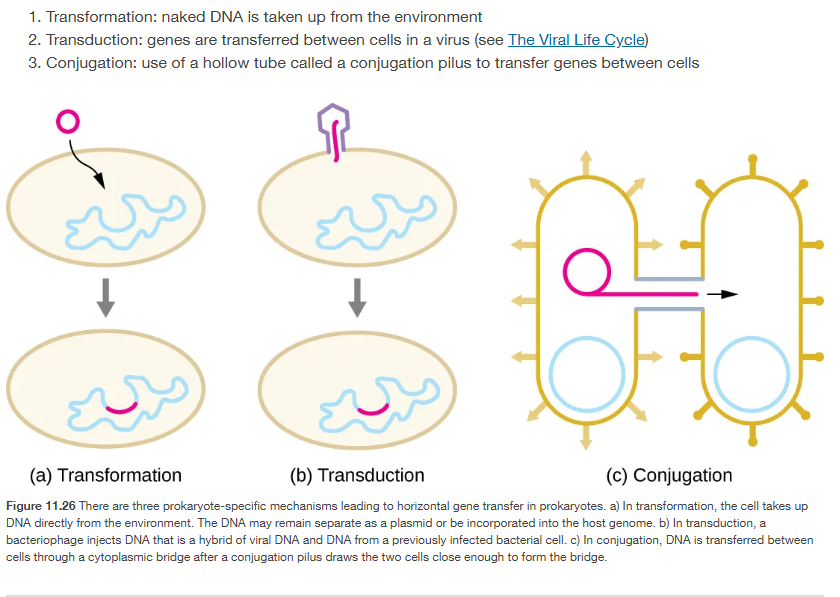
Transformation. transduction, and conjugation
Transformation: naked DNA is taken up from the environment
blocked by DNase (because it depends on free DNA floating around).
Transduction: genes are transferred between cells in a virus (see The Viral Life Cycle)
works with cell-free extracts and resists DNase (DNA is protected inside phage particles).
Conjugation: use of a hollow tube called a conjugation pilus to transfer genes between cells
requires live, direct cell-to-cell contact (pilus), so cell-free extract won’t work.