BIOCHEM: Hemoglobin
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
myoglobin
- oxygen storage protein
- single polypeptide
hemoglobin
- Oxygen transport protein
- tetrameric protein
- 4 myoglobin is what it basically consists of

Fe(II)
- This is a strong tendency to bind oxygen
- chelated to tetrapyrrole ring system
protoporhyrin IX
What is the name of the tetrapyrrole ring system?

Heme
- Deals with Fe being non covalently bound in a hydrophobic pocket
proximal histidine
- This is the histidine that is in direct contact with Fe
distal histidine
This is the histidine that is not in direct contact with Fe
- this one holds the oxygen in place
Picture of proximal and distal histidine

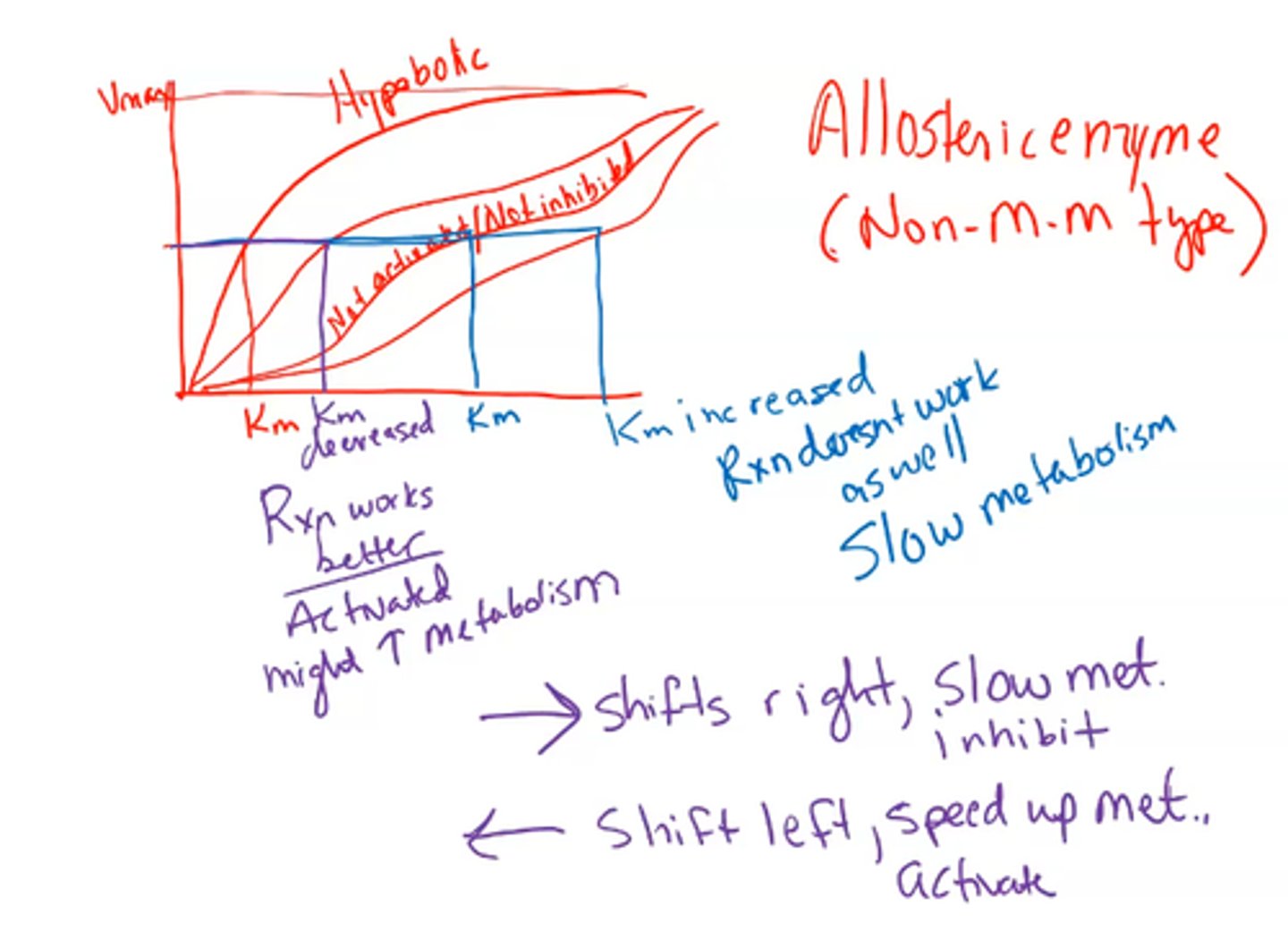
hyperbolic
The binding curve for myoglobin binding to oxygen is ______________
means 1 P50 only
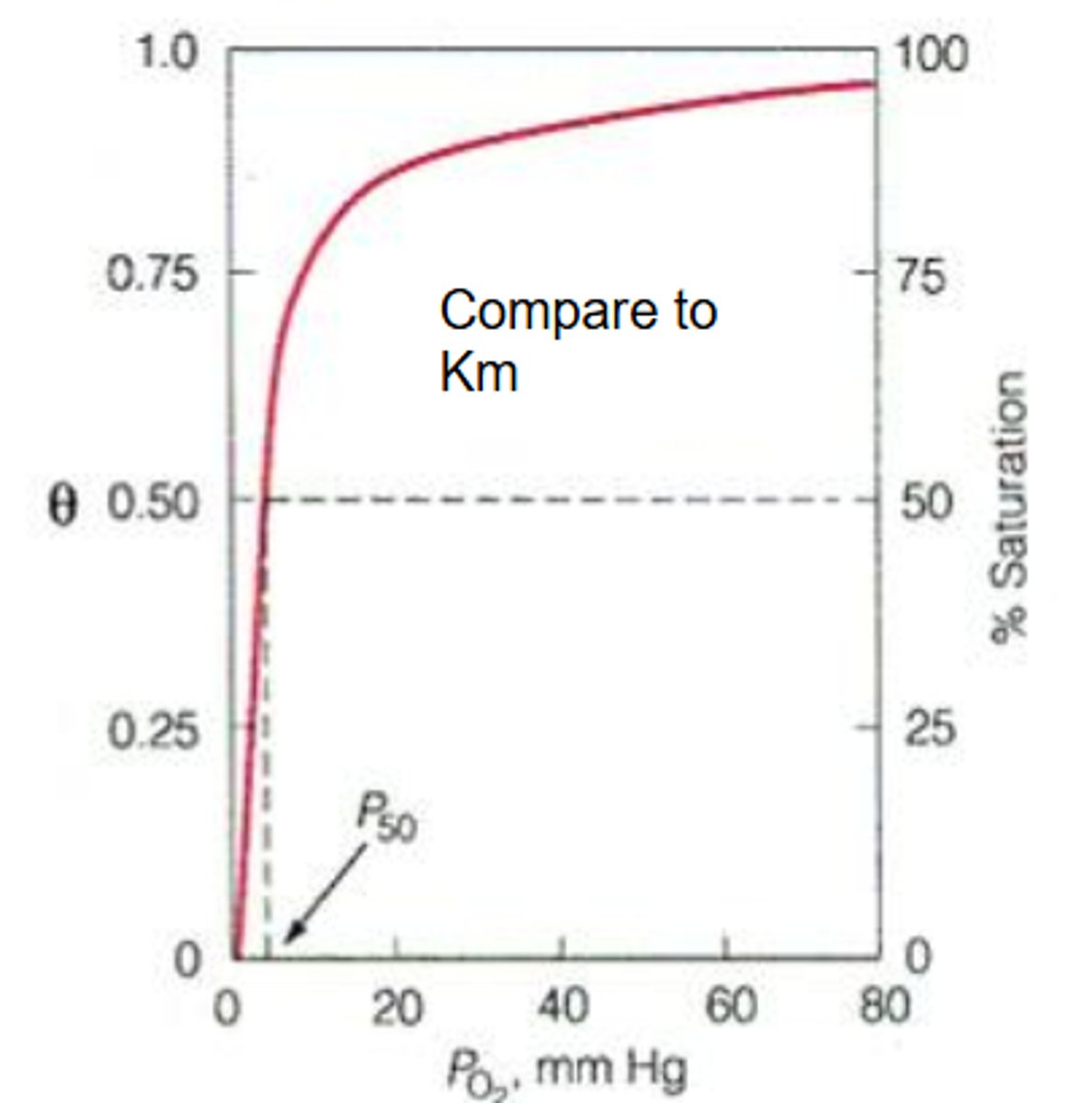
P50
This is the partial pressure of oxygen where half of the binding sites are bound
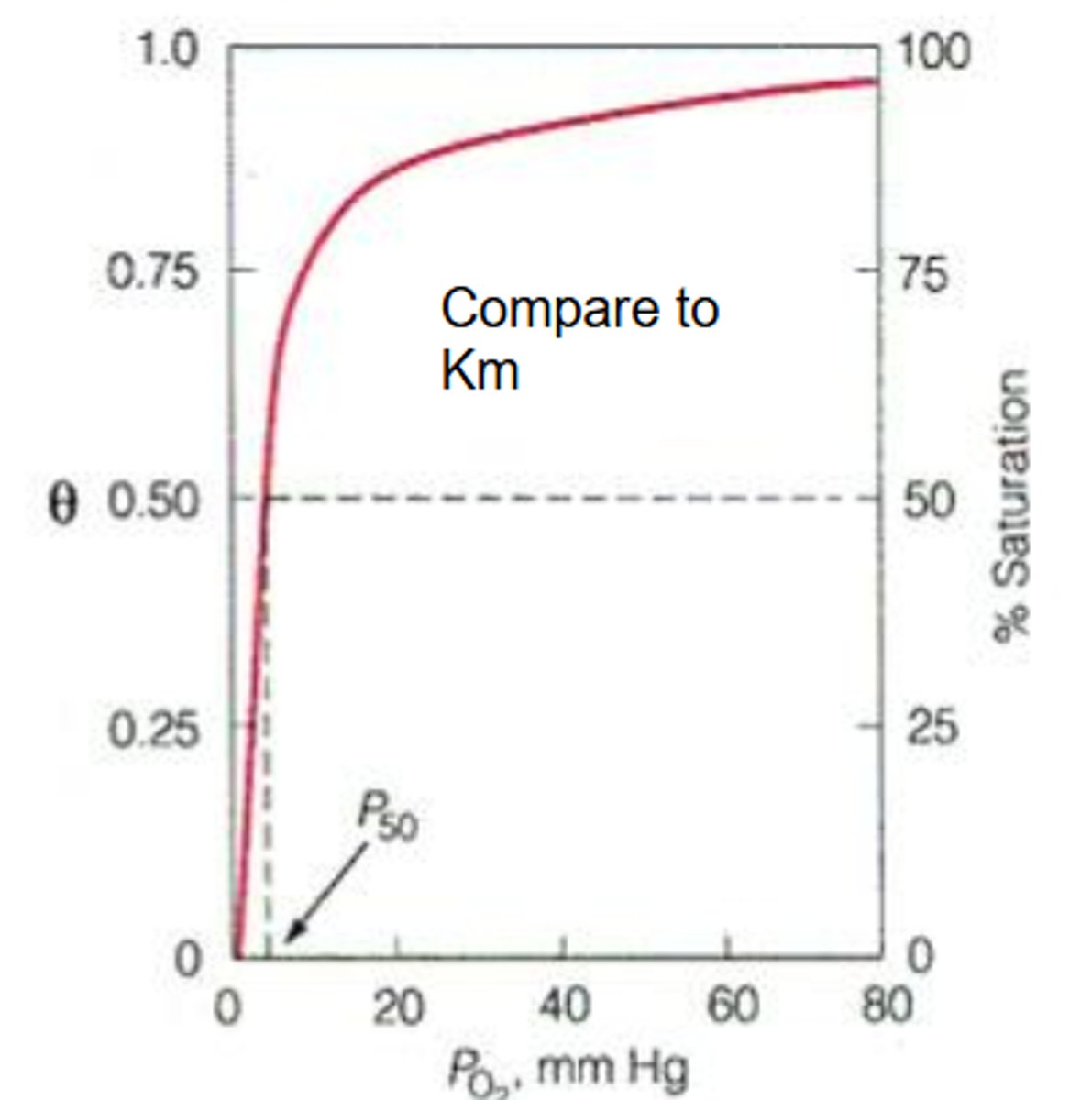
You do not need very much oxygen pressure in order to bind 50% of the sites
What does having a low P50 mean?
HIGH binding affinity
If you don't need a lot of oxygen pressure in order to bind to sites then what does that mean?
high
If you have a low P50 then you have a ___________ affinity.
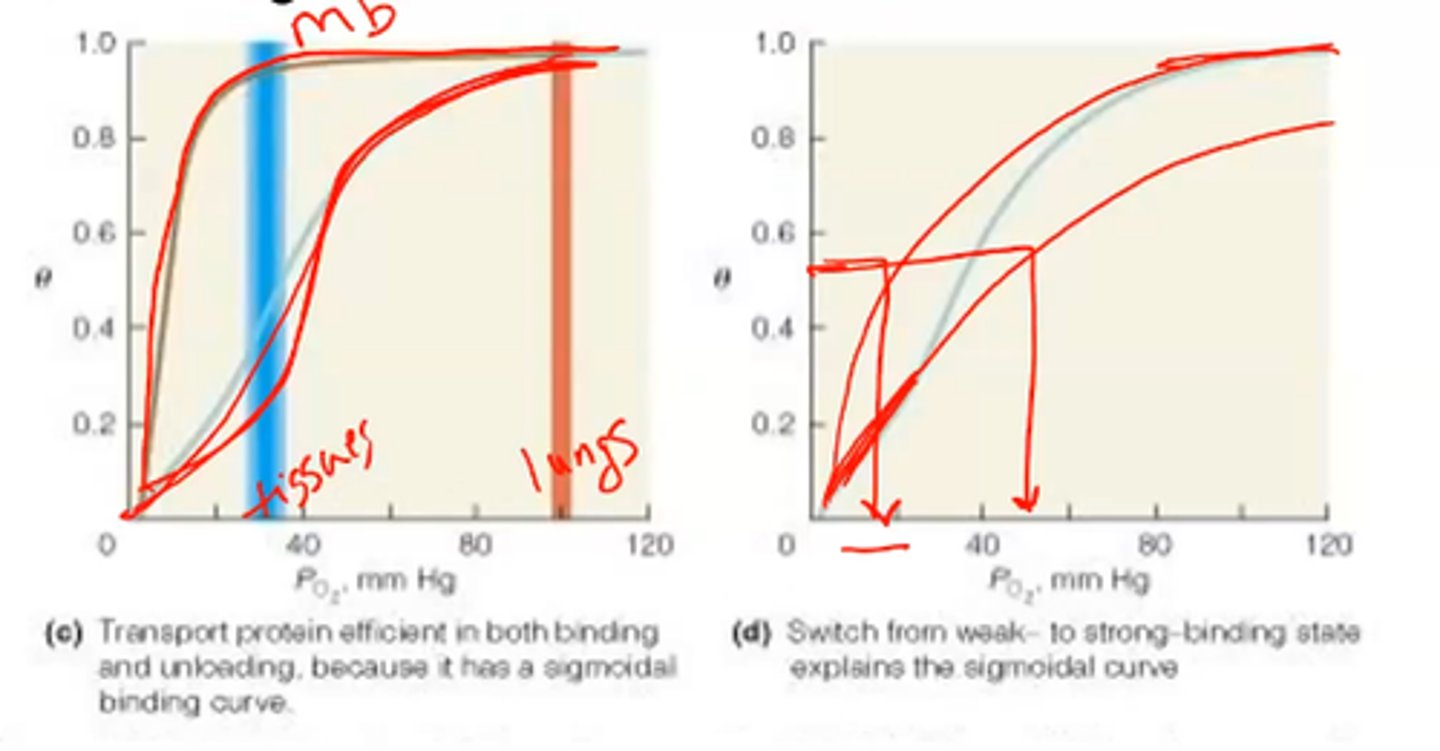
Requirements of oxygen transfer
1. Accept oxygen efficiently at partial pressure found in the lungs (100 mm Hg)
2. Upload a fraction of O2 to tissues (30 mm Hg)
- Cannot be hyperbolic binding
- Must be sigmoidal - this means it is allosteric
True
True or False: Oxygen transport by hemoglobin is allosteric meaning the P50 can change
sigmoidal curve

Cooperative binding
a type of allostery
known as the allosteric switch
deals with the binding of multiple things
conformational change
Cooperative binding results from ____________ in the protein causing the affinity of the binding site to increase.
photo of oxygen transfer being allosteric
binding
There is an increase of O2 affinity with O2 ___________.
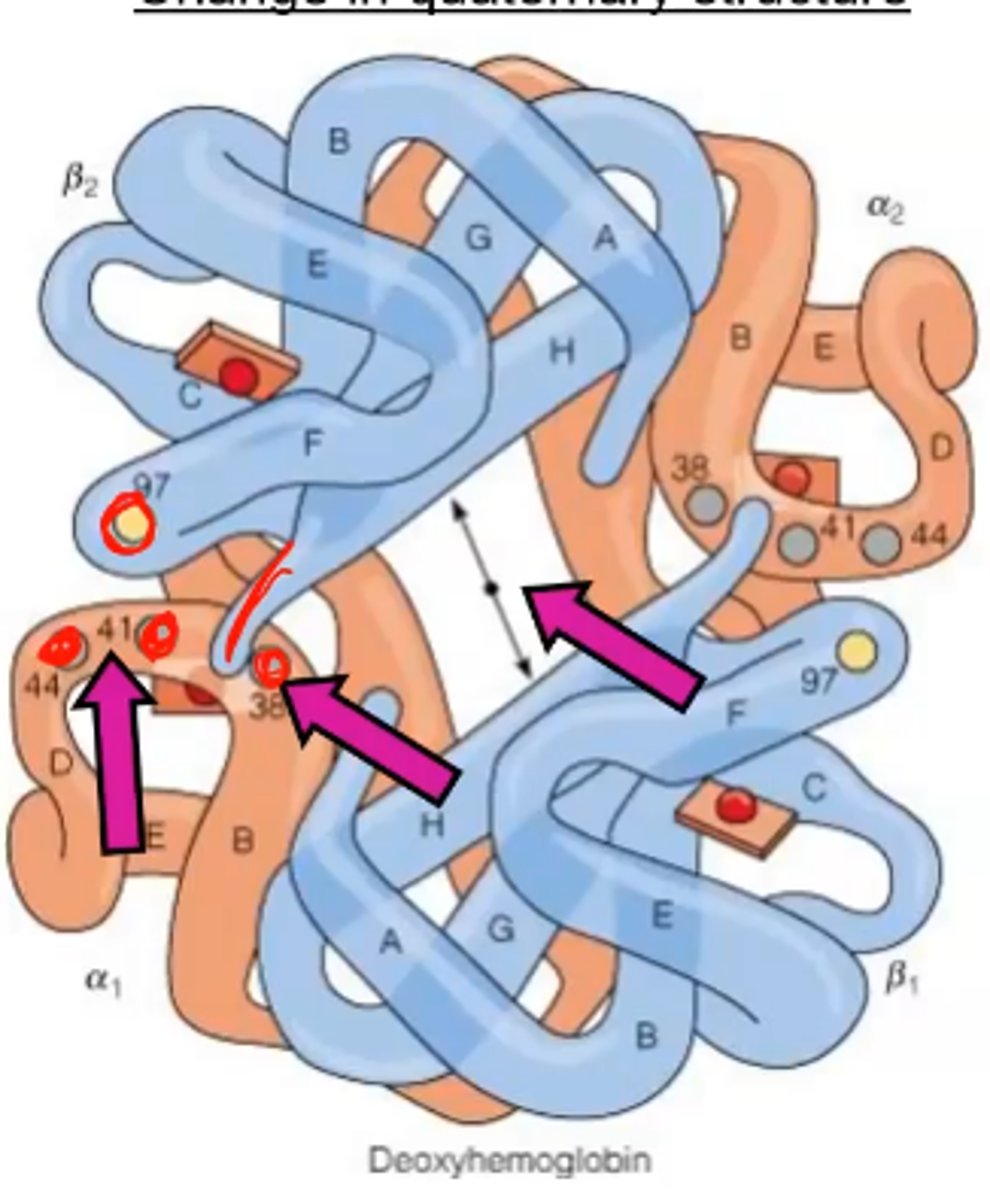
Deoxy (T) Hemoglobin
- shows a change in quaternary structure (TENSE)
- this structure deals w/ low affinity for O2 and salt bridges forming (high P50)
Oxy (R) Hemoglobin
- this structure deals w/ high affinity for O2 and salt bridges NOT forming
- O2 is bound to it
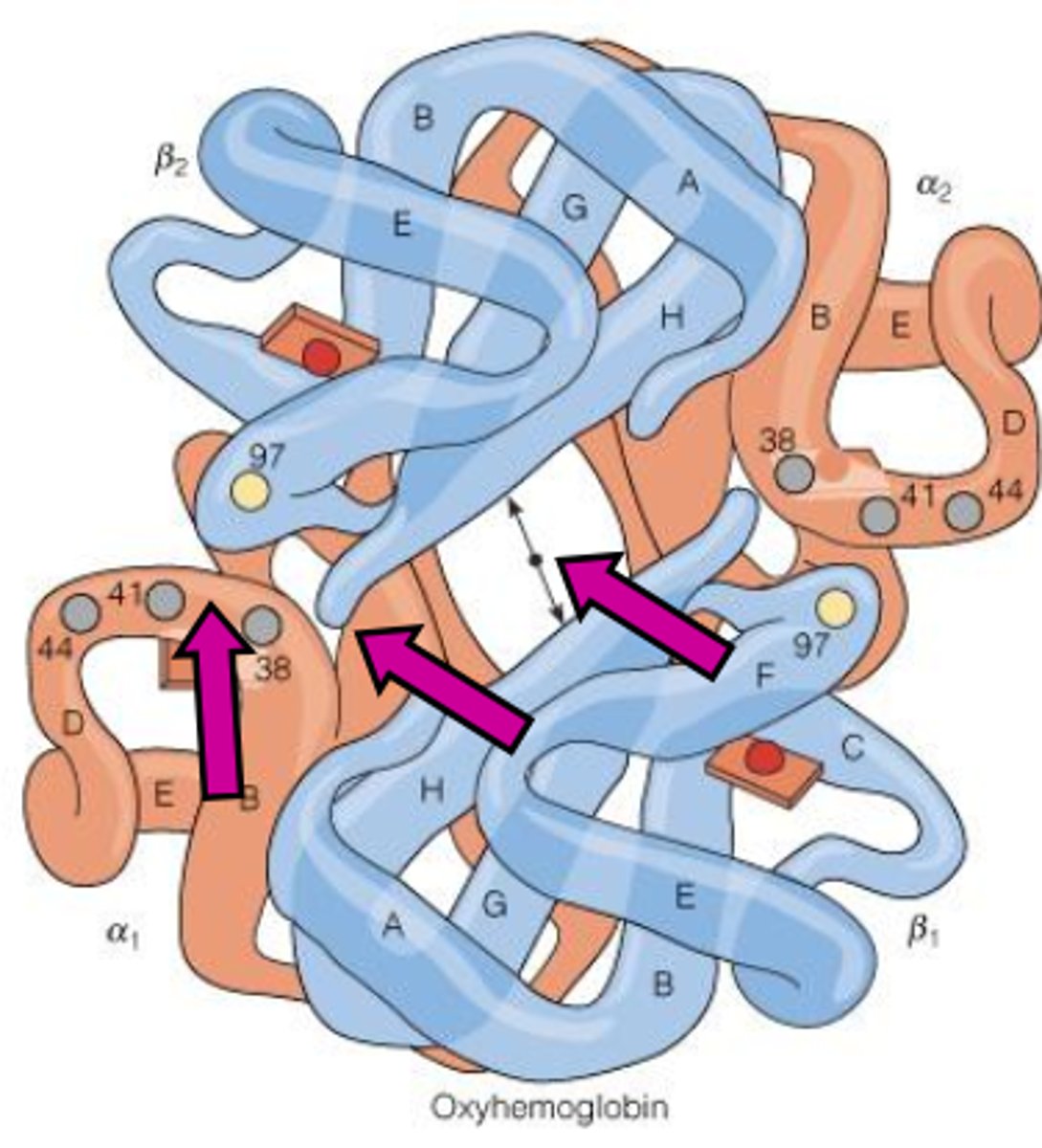
Deoxy overlaps compared to Oxy
Deoxy has a bigger hole in the middle (allosteric site)
From the photo what is difference between Deoxy and oxy hemoglobin?

communication between hemoglobin sites
Relationship of His F8 and neighboring Val to heme in deoxyhemoglobin demonstrate the change in conformation associated with the T to R transition – change in secondary structure causes a change in tertiary
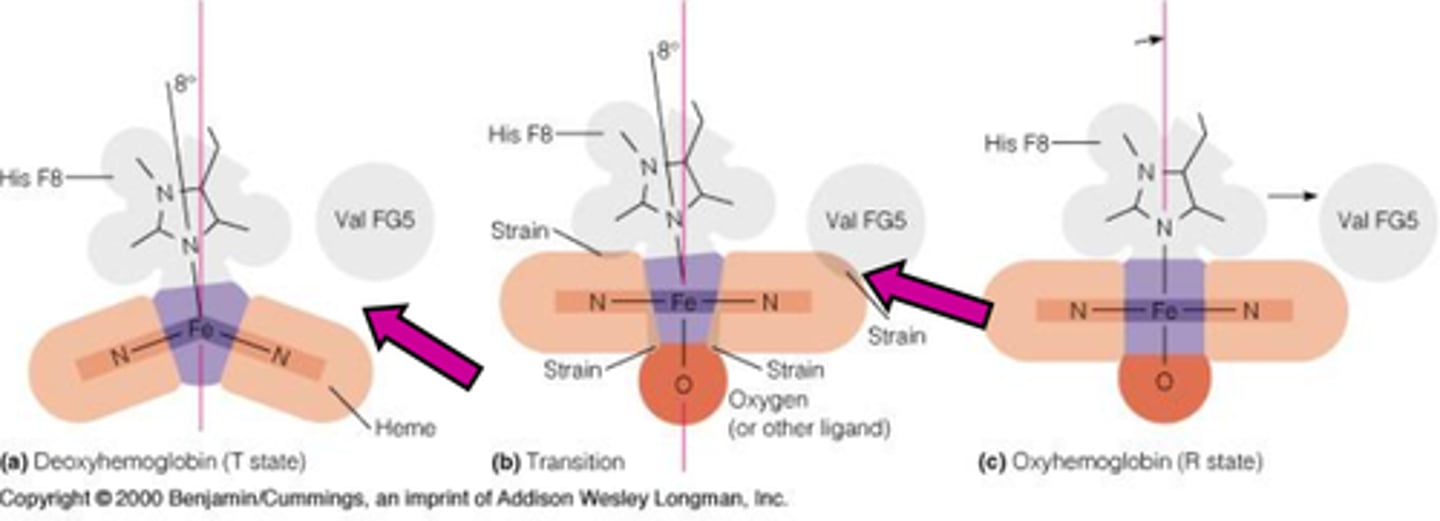
strain
_________drives conformational change in the communication between hemoglobin sites when oxygen binds to it.
C02
- another allosteric ligand of hemoglobin (oxygen is the other one)
- This accumulates in erythrocytes and lowers the PH
increase
As PH low we see the efficiency of oxygen unloading _____________
- His forms salt bridge with Asp in the deoxy form which increases the pKa of the His by stabilizing the protonated (positive) form
- Salt bridge does not form in the oxy form, lowering the pKa
When the PH lowers why does the efficiency of oxygen unloading increase? ITSCALLED THE BOHR EFFECT
KNOW THESE PROPORTIONS
increase of CO2 binding
decrease of pH
increase of P50
increase of oxygen unloading (will not bind with as much affinity)
know this photo
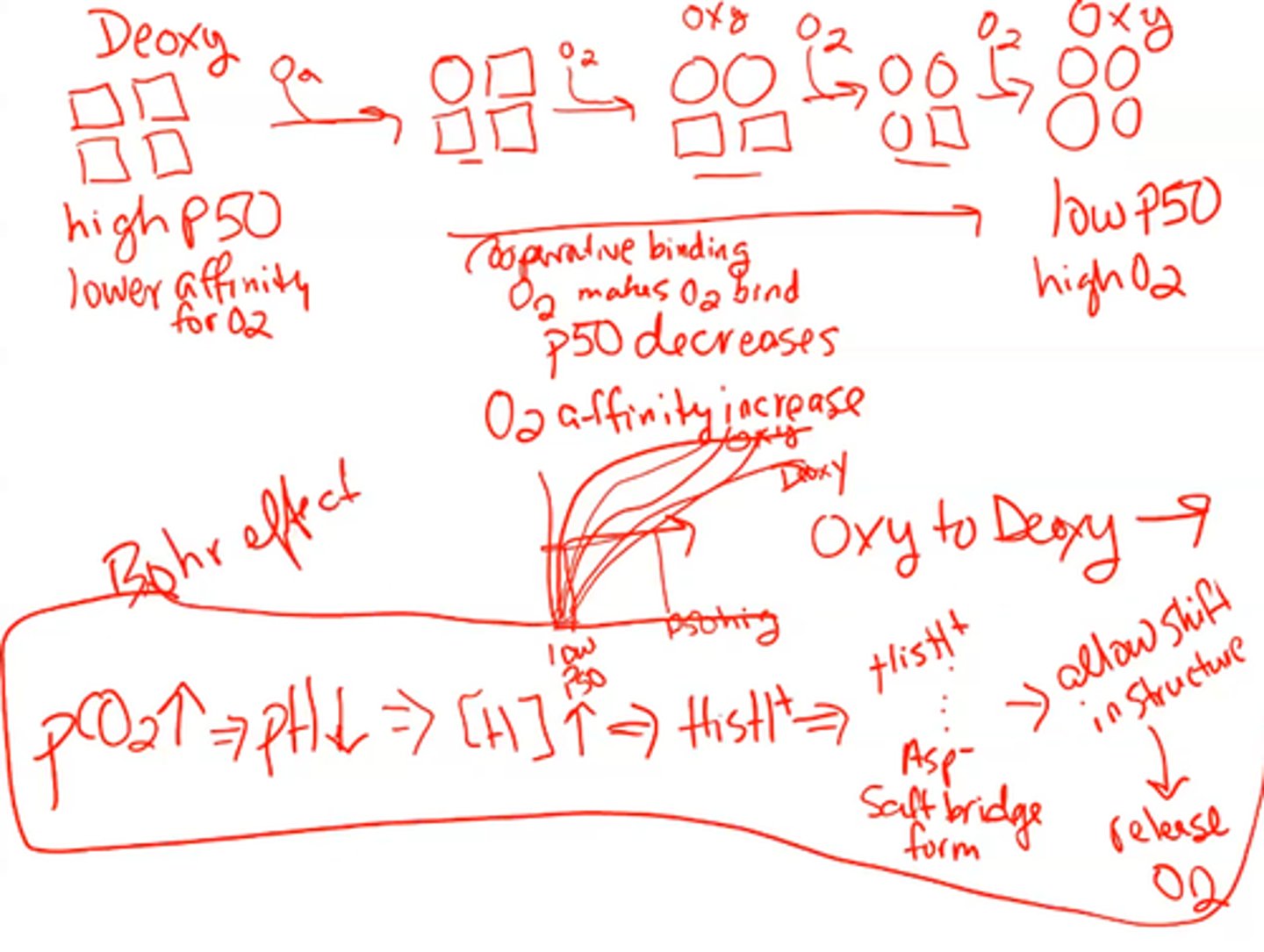
know this photo
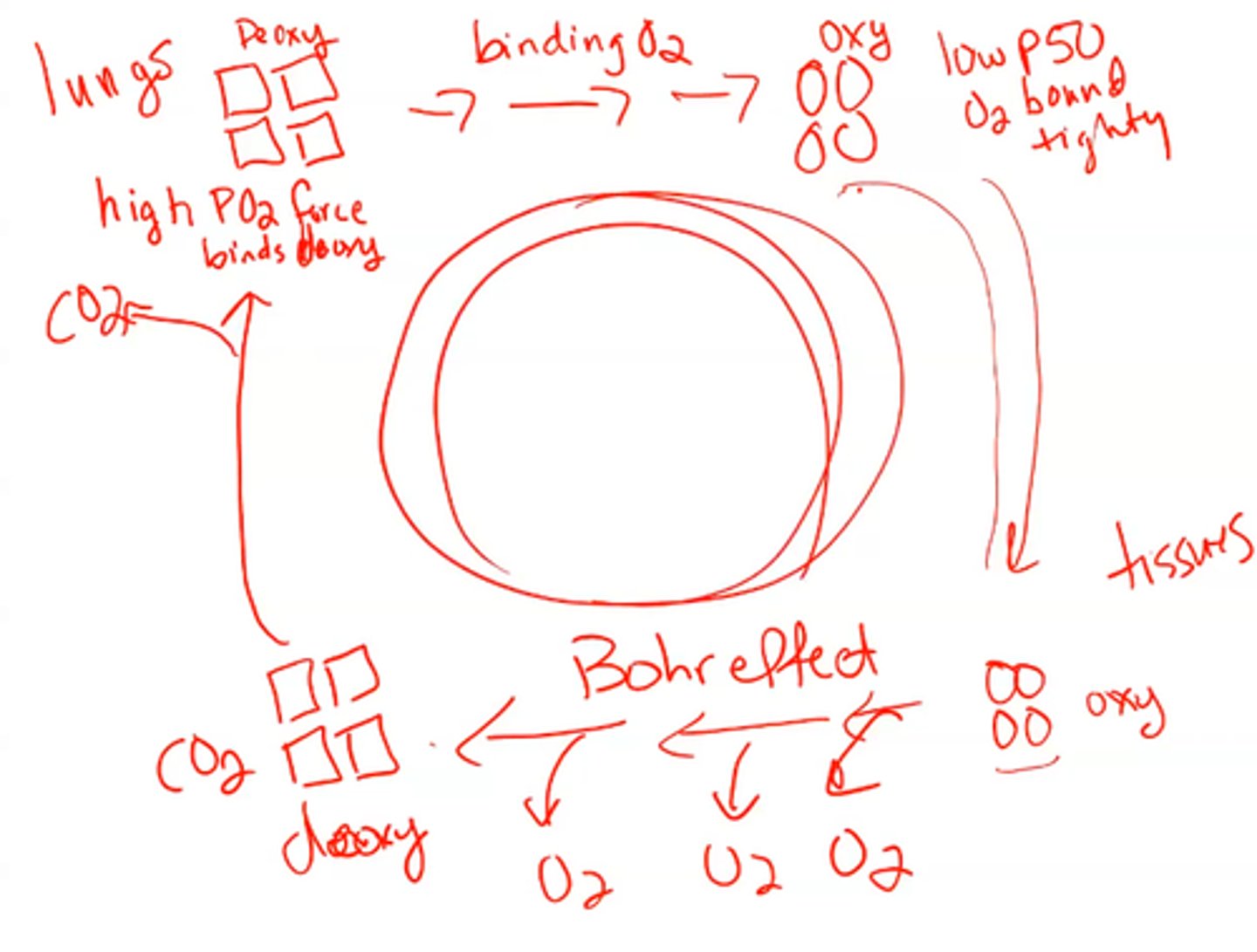
Diphosphoglycerate (BPG)
- Acclamation (adjustment)of lower oxygen pressure of high altitude over time due to increases of production of hemoglobin and changes in amount of BPG
- has a more efficient unloading of O2
- stabilizes deoxy form
lowers
The binding of BPG ___________ O2 affinity of Hb.
True
True or False: BPG cannot bind to the oxy form of hemoglobin.
True
True or False: Both CO2 and O2 and BPG are all allosteric effectors.
photo of BPG

BPG and how it deals w/ fetuses
A fetus obtains oxygen from mother's blood; must have higher O2 affinity
- Adult hemoglobin (HbA) is α2β2
- Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) is α2γ2
- Lower affinity for BPG
- Replacement of His 143 with Serine
HbA
Does BPG bind better to HbA or HbF?
Sickle Cell Hemoglobin
- This is caused by the aggregation of deoxyhemoglobin and the blockage of capillaries
Mutation that deals with the cause of sickle cell hemoglobin
Glutamic acid to valine (hydrophobic amino acid which fits into a hydrophobic pocket causing hemoglobin molecules to "lock" together
metabolism
If you have a higher Km (shifted to the right) then reaction won't work as well and slows __________ (INHIBITION)
QUESTION WILL BE ON FINAL FOR THIS