Economics unit 10-12
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
microeconomics - rational consumer behaviour, market power (perfect competition, monopolistic competition, monopoly, oligopoly
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
short run
a period where at least one of the factors of production is fixed and cannot quickly change the quantity output. e.g. building size
long run
a period where all factors of production are variable. - however, the state of technology is fixed. e.g. firm may move to new building or build a completely new building (in the long run)
total product (TP)
total output that the firm produces using its fixed and variable factors, in a given period of time.
average product (AP)
output that is produced on average. by each unit of the variable production factor (V)
AP calculation
=TP/V
Marginal product
extra output that is produced by using one more unit of the variable factor. e.g. when one more unit of labour (V) is used, 3 more bags (Q) can be produced.
MP calculation
= (new TP - old TP)/(new V - old V)
law of diminishing returns
as more of the variable factor is added, there is a point where TP only rises at a diminishing rate.
intersection points of MP and AP
MP>AP: average product is increasing
MP=AP: average product is at its maximum
MP<AP: average product is decreasing
total cost (TC)
the complete costs of producing output
marginal cost (MC)
the increase in total cost (C) when producing one more unit of output (Q), marginal cost is equal to the slope of the TC curve
MC calculation
=(new TC - old TC)/(new Q - old Q)
Average Total Cost (ATC)
cost per unit of output
ATC calculation
= TC/Q
fixed cost (FC)
cost of fixed assets such as rent for the company space. these costs will be constant and will not change in the short run.
variable cost (VC)
costs of variable assets. these costs increase when production is increased. e.g. raw materials, wages - more workers or overtime pay
AFC calculation
= TFC/Q
AVC calculation
TVC/Q
opportunity cost
the next best alternative that is foregone when a choice is made
explicit costs
the opportunity cost of the money spent on resources not currently owned by the company. e.g. wages, rent, utilities
implicit costs
the opportunity cost of the usage of resources currently owned by the company. e.g. personal savings to start a business
LRAC increasing returns to scale
(Economies to scale): average cost is decreasing when production is increased
LRAC constant returns to scale
average cost is constant when production is increased
LRAC decreasing returns to scale
(diseconomies to scale): average cost is increasing when production is increased.
total revenue (TR)
total amount of money a firm receives from selling goods and services in a given time period
average revenue (AR)
the revenue a firm receives per unit of sales
AR calculation
= TR/Q = (P x Q)/ Q = P
marginal revenue (MR)
the extra revenue that a firm gains by selling one more unit of the product in a given time period.
MR calculation
= (new TR - old TR)/(new Q - old Q)
revenue maximisation at
MR = 0
economic profit (abnormal profit)
total revenue exceeds total cost (TR>TC)
normal profit
total revenue is equal to total cost (TR=TC)
Loss
negative economic profit, total cost exceeds total revenue (TR<TC)
profit maximisation
MC = MR
MC>MR vs MC<MR
when MC>MR, selling one more unit of the product would lead to a loss
when MC<MR, selling one more unit of the product would lead to more profit
possible goals of the firm
profit maximisation, revenue maximisation, satisficing, corporate social responsibility (CSR)
satisficing
the firm tries to perform satisfactorily rather than maximising profit or revenue
corporate social responsibility (CSR)
the business includes public interest in its decision making. e.g. company wants to produce as environmentally friendly as possible, provide g/s for consumers, employ workers under favourable conditions etc.
4 factors giving rise to economies of scale
specialisation, efficiency, marketing, invisibilities —> all lead to lower average cost
invisibilities
some production factors cant be divided into small pieces such as large machines. small firms will still have these large costs, even if production is low. when production is increased, these invisible costs can be divided by more units of output, lowering average cost (AC)
2 factors giving rise to diseconomies of scale
problems of coordination and problems of communication
5 perfect competition characteristics
freedom to enter and exit the market
there is perfect resource mobility. resources can move from location to location at zero costs.
the product is homogeneous
there is perfect information
there are a lot of firms
price taker
firms in perfect competition are price takers. they cannot influence the price in the industry.
profit for firms in perfect competition and monopolistic firms (calculation)
= (AR-AC) x Q
shutdown price (when P=)
when P = AVC
breakeven price (when P = )
when P = ATC
allocative efficiency
suppliers are producing the optimal mix of goods and services required by consumers. it occurs when the company produces at the point where MC=AR (cost to producers = value to consumers)
Productive efficiency
suppliers produce the product at the lowest possible unit cost (average cost AC). it occurs when production takes place at minimum point of ATC
MC = AR
allocative efficiency
3 characteristics of a monopolist firm (monopoly)
there is a single or dominant firm
there are no close substitutes to the good on the market
there are significant barriers to enter the market
4 examples of barriers to enter a monopolistic market
economies of scale
branding/brand loyalty
legal barriers
natural monopoly
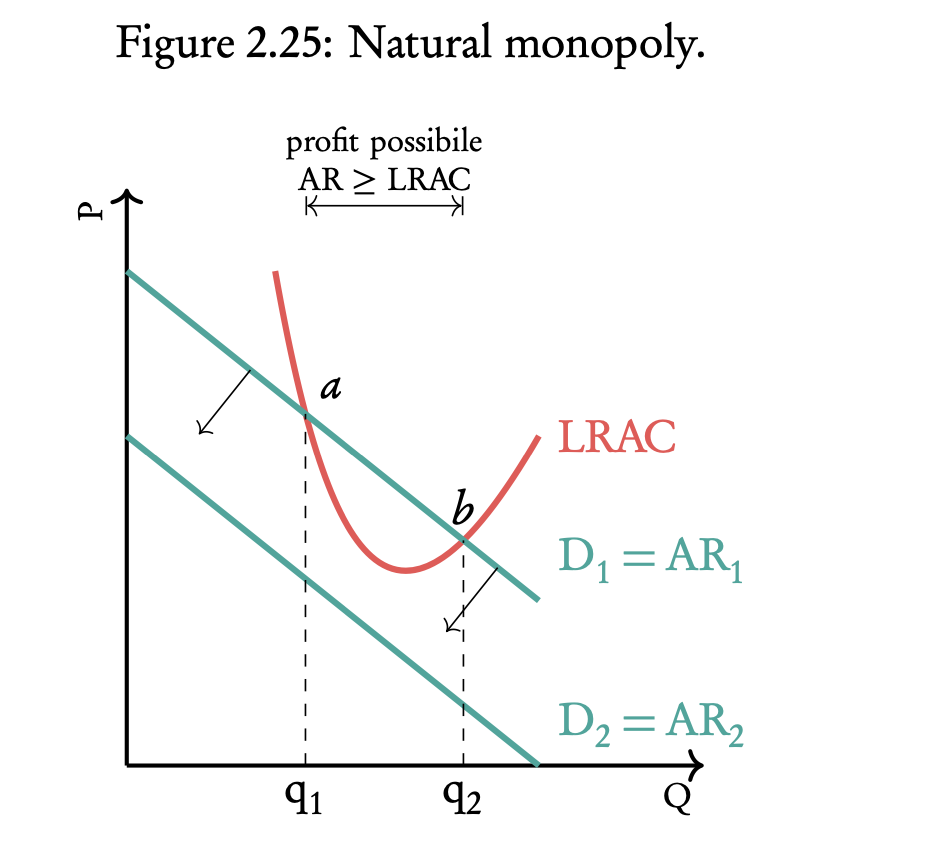
explain natural monopoly using the diagram
one firm on the LRAC and D1=AR1 curve. this firm can make abnormal profit when the production lies in between Q1 and Q2 (as in this range, the Average Revenue will exceed Average Cost).
if another firm enters the market the demand curve for the goods of the existing firm will shift left (to D2=AR2). the existing firm cannot make a profit anymore at D2=AR2 because there are no points where average revenue exceeds average cost.
price maker
the firm determines the price all on itself.
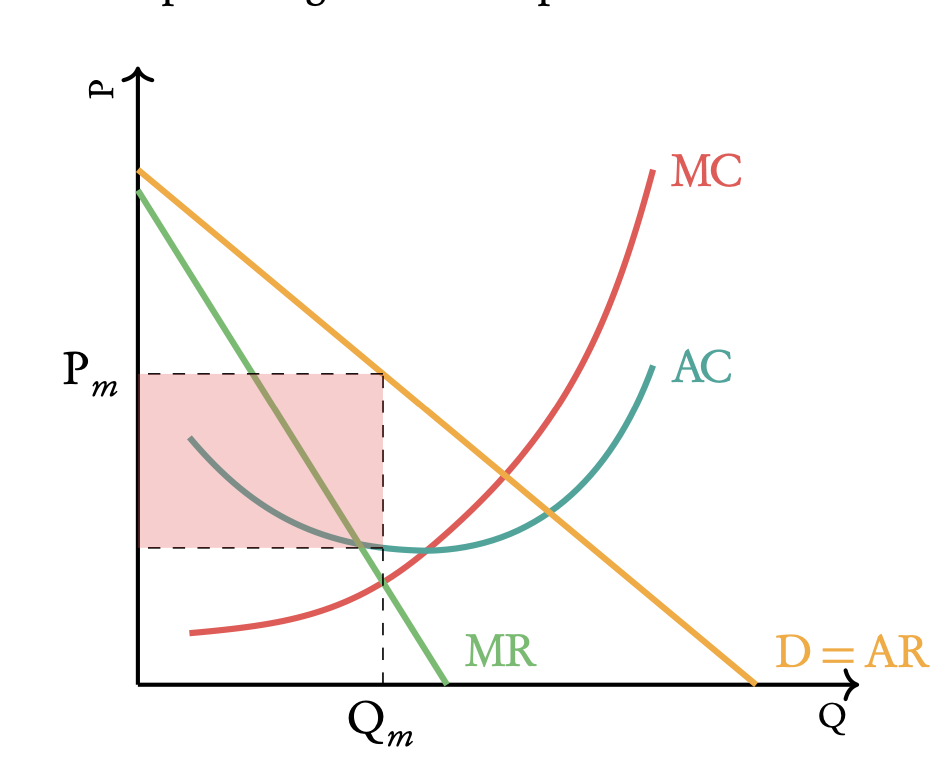
what does this show?
Profit for a monopolist when pursuing maximum profit.
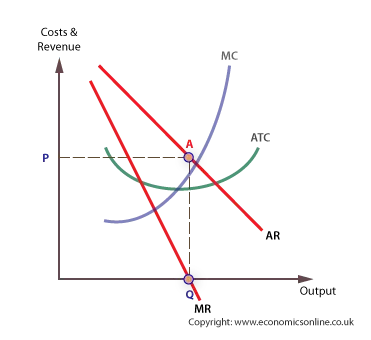

revenue maximisation
3 advantages of monopoly compared to perfect competition
higher levels of research and development from abnormal profits
need to innovate to maintain abnormal profit
may benefit consumers in the long- run
possibilities of economies of scale:
pushes MC curve down
may produce at a higher output and lower price than in perfect competition
2 disadvantages of monopoly compared to perfect competition
high profits of monopolists are unfair:
depends on size and power of the monopoly
if significant economies of scale do not exist: may restrict output and charge higher price than under perfect competition
can exercise anti-competitive behaviour to maintain monopoly power
3 ways of government intervention in response to abuse of significant market power
legislation and regulation
government ownership
fines
3 characteristics of monopolistic competition
there are a large number of firms
the products sold are differentiated
there are no barriers to enter/exit
price competition
rivalry between suppliers solely based on price
non-price competition
rivalry between suppliers based on the other aspects than price e.g. quality of service, packaging, advertising and product development
why isn’t there allocative or productive efficiency in the short & long run of monopolistic competition?
because MR =/= MC at the production level + the production level is not at the minimum of AC.
why do monopolist firms make normal profit in the long run?
due to the absence of barriers to enter/exit.
EITHER: if the companies made a profit in the short run, companies will enter the market in the long run. these new firms take away business from the existing firms, shifting the demand curve to the left.
OR: if the companies made a loss in the short run, then in the long run, firms will leave the market. the firms that left will leave their business for the old firms, shifting demand to the right, generating more revenue for the firms in the market → creating a normal profit in the end.
4 characteristics of an oligopoly
dominance by a small number of firms (dominance ratio (DR))
differentiated or homogenous goods - in an oligopoly, either can be the case.
high barriers to enter - like the monopoly
interdependence: decisions by one firm influence the other firms. e.g. deciding on a price: higher price of firm A generates more revenue for firm B etc.
what is a collusion?
the collaboration of firms to charge the same price; the firms will act together as one monopoly
what is a cartel?
a collusive monopoly - group of firms making price arrangements
2 forms of collusion?
formal collusion and Tacit collusion
what is a formal collusion?
firms agree on a price, all firms participating in the collusion know that they are participating and know the negotiated price. → often done in secrecy and not openly communicated with the general public or the government
what is a tacit collusion?
firms charge the same price by looking at each other. there is no formal agreement involved.
why are collusions difficult to maintain?
due to fear of government penalties as it is illegal.