Alt to Incarceration Midterm Review
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What effects can crime have on life? (PG 1)
It can affect where we live, where we shop, where out children go to school, how much we pay for our car/insurance/taxes and how safe we feel
What effect do politics/elected officals have on crime? (PG 1)
What is corrections? What does it mean? (Pgs 2&3)
post adjudication processing of convicted criminal offenders
Understand the effects that police discretion might have on alternatives to incarceration (pg 4)
Understand the history of Correctional institutions (pg 7)
Understand what, if any benefits there are to probation (pg 10)
understand what our prision populations are doing (increasing/decreasing) and why (pg 11)
Prison populations are decreasing
Understand what pretrial services are (pg 18)
Programs are alternatives to adjudication or convictions. There are no nationwide standards, but there are common characteristics. SIversion programs are in lieu of a conversation. Participants are offered the proetial intervention in place of a formal charge or conviction, and the criminal jusitve system can reduce its burden of a trial an dincarceration. If the person completes the program, the charges are usually dropped. Most ficersion prograsm target first-time offenders, or specialied populations.
types of bond or releases for awaiting trial - understand differences between bonds (pg 19)
Money bail - arrested puts up a determined amount of money to ensure his/her return to court. If they do not return to court, they risk forfeiting the money.
Own Recognizance - those released on monetary bail
21 - different ways to measure risk - know definitions of each - NA, AA, Actuarial, and no made risk
Criminal history (number of priors, seriousness of priors), current offense (level of charges, level of offense), history of appearances in court (number of prior failures to appear)
Employment (employment at time of arrest), housing (stable housing at time of arrest), stability in the community (friends/family in the local community), Substance use (problems with substance use)
Which state has a specific bail bond system? (pg 26)
Kentucky
Standard and specific (subjective) conditions of release (pg 26
Standard - conditions everyone has to follow
Specific/Subjective - tailored to the person
understand post conviction diversion means - which one is an example of post-conviction diversion (pg 28)
Starts with a conviction and them work backwards. In exchange for completing a formal tratment program (eg specialty court), the final convictions is vacated and the individuals record iss sealed. Post-conviction diversion prograsm are generalt offered to individuals with usbstance abuse issues.
Understand what sentencing is and what form it comes from - punishment, preparation for release, etc. (pg 32)
Plea bargains, understand how they are used, the limitations, overall (34)
Exchange of prosecutorial and/or judicial concessions, commonly a lesser charge, the dismissal of other pending charges, a recommendation by the prosecutor for a reduced sentence, or a combination thereof, in return a lesser plea of guilty
Tourniquet sentencing - 36
tightening or increasing the conditions of probation to encourage the client to conform to legal and supervisory expectations
What dis Alexander Macanochie do? - 37
Developed the mark system, a system of parole and rehabilitation for prisoners that allowed them to earn marks for good behavior, leading to potential early release
What did Sir Walter Crofton do - 38
Developed the “Irish” system - Stages of confinement, “tickets of leave”, focus on rehab, impact on parole
Understand what powers a parole boards has - 39
Correctional person, authority, or board that has the authority to release on parole those adults (or juveniles) committed to confinement facilities, to set conditions for behavior, to revoke from parole, and to discharge from parole. Also, recommend executive clemency through pardon or sentence commutation (shortening), as well as setting policies for supervision.
3 strikes laws/policy - understand what their purpose is and their intended purpose - 41
long-term punishment (25+ years) for those people convicted of a serious or violent third felony. In addition, retribution as a foal becomes attractive, inasmuch as it would impose deserved punishment.
mandatory minimum sentences - who gets them, and for what crimes - 42
What gives judges guidance for sentencing - 43
Sentencing Guidelines - structuring the penalty decision of judges work by providing decision-makers with criteria and weights on which the sanctions decision should be based on
47 - understand reasons behind alts to incarceration - what are we trying to accomplish
Rising cost of incarceration
54 - definition - know the definition of parole, probation, and sentencing guidelines
Probation - conditional senetnece that divers the offender from jail/prison and allows them to remain in the community in exchange for thefollowing a set of conditions
Parole - Correctional person, authority, or board that has the authority to release on parole those adults (or juveniles) committed to confinement facilities, to set conditions for behavior, to revoke from parole, and to discharge from parole. Also, recommend executive clemency through pardon or sentence commutation (shortening), as well as setting policies for supervision.
Sentencing guidlelines - structuring the penalty decision of judges work by providing decision-makers with criteria and weights on which the sanctions decision should be based on
55 - know stats on community supervision - 2005
4,162,300 probation population
8.4% change
56 - John Augustus - what is he know for
Most often credited for the establishment of probation
57 - early US harsh punishment - what did we change how we do punishment - who influenced this
French Philosophers. We moved from harsh punished due to lack of public support. System began to restructure penalties to balance the level of the offense with the offender’s
58&59 - guardian ad lidem - know definition
an individual, usually not associated with the justice system, who acts in the best interest of the child. Are often the voice of youth - ensuring that their interests is heard and taken into consideration
59 - state one - where probation originated in the US
Ohio
61 - concerns about federal probation from DOJ - what are the concerns the DOJ had
reduce the benefit of prison
wouls allow for offenders to remain in society freely
would afford criminals rights that they did not desereve
64 - understand the objectives of probation
reduce offending
protect the community from further criminal behavior
provide probation conditions (and services) necessary to change offenders and to achieve the aforementioned objectives
65 - understand eh cost of jail/prison -chart
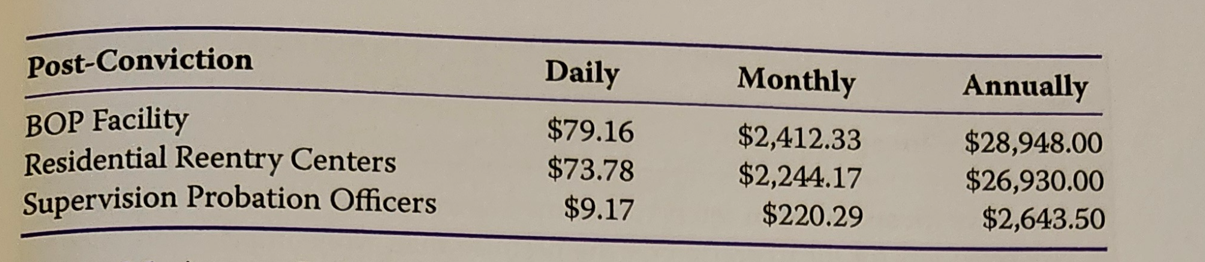
66 - understand what is involved in a presentence investigation
Gathering information about the current offense, victims statement(s), previous probation and technical violations, employment history, information on family and friends.
67 - what is the purpose of a PSI (presentence investigation)
gather comprehensive information about the defendant and the current offense to assist the court in making informed sentencing decisions.
74 - know the difference between general and specific conditions of probation
General - Required of all probationer
Specific 0 Required to an individual probatione
82 - know the US Supreme Gagnon v Scarpelli from 1973 - what did the case decide
Due process procedures in probation. Probation cannot be withdrawn unless certain basic elements of due process are observed
96 - Know what definition of parole, probation, and sentencing guidelines
100 - 4 names listed, choose appropriate name - Mark system?
alexander macanochie
102 &111 - earning a reduction in someone's sentence - what is the term
Good time Credits - earned by a formula established within correctional settinfs, sometimes set into law but usually decided by institutionalansw admin in collaboration with the parole board decided
112 - parole guideline, what are they and there intended purpose
Restricted the discretionary powers of the parole boards. The operation of parole, obviously, is not all uniform
114 - understand the US Supreme court ruling/stance on someone seeking parole
The US Supreme Court has taken a stance that individuals seeking parole are entitled to certain due process protections. This means that parole cannot be denied or revoked without adhering to specific legal procedures that ensure a fair hearing.
127 - effects of long vs short-term sentencing - what is more effective and why
Early research that examined the effects of the amount of time served in prison on parole has generally concluded that the shorter the amount of time served, the greater the likelihood of successful parole
most researchers have concluded that longer prison terms hurt aparolle’s chances of success, implying that the negative aspects of presentation seem to intensify with time.
143 - understand goals of offender assessment
The goals of offender assessment are primarily to evaluate the risk and needs of offenders to inform sentencing, supervision, and rehabilitation decisions. The assessments help identify appropriate interventions, enhance public safety by minimizing the risk of re-offending, and facilitate effective resource allocation in correctional settings.
144/145 - 4 main principles of offender classification (Bolded)
Risk - who should we target
Need - What should we target
Responsivity - How we should target problem behaviors
Professional Discretion - having considered risk, need, and responsivity, decisions are makde as approproate under present conditions.
148 - know the major risk factors, which is not a major risk factors
antisocial/pro-criminal attitudes, values, beliefs, and cognitive-emotional statesre
pro-criminal assocaites and isolation from anti-criminal others
Tempermental and personality factors conductive to criminal activity
a history of anti social behavior
Family factors that include criminality and a variety of psychological problems in the family of origin
low levels of personal, educational, vocational, or financial achievement
low levels of involvement in prosocial leisure activities
Abuse of alcohol/drugs
46. 154 - whether judges typically agree with offender assessment - if they disagree which way do they lean
When a judge review Offender Assessment do they agree or disagree? Do they go harsher or lighter on sentencing
Upward - Harsher
164 - understand the criticisms that come with assessment tool
Staff may resist use of a toll that totally supplants professional judgement and experience
Practical reason, such as political considerations that require certain offenses (serious felonies) to be treated as higher risk
Gaps in assessment information
166 - how when completing offender assessment how they are statistically most successful
169 - Risk management
Involves determining the eisk level of the offender and providing approprite sanctions and supervision
169 - risk reduction
invoices determining the risk level and crime-producing needs and reducing risk factors through effective interventions and appropriate supervision