Section 1 and 2 (The basic economic problem and Allocation of Resources
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is economics?
Economics is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
What is scarcity?
Scarcity is the lack of sufficient resources to satisfy unlimited human wants.
Why does the basic economic problem exist?
Because resources are finite and wants are infinite, leading to scarcity.
What are economic goods?
Goods that are limited in supply and have an opportunity cost.
What are free goods?
Goods that are unlimited in supply and have no opportunity cost, like air and sunshine.
What are the four factors of production?
Land, Labour, Capital, and Enterprise.
What is land in economics?
All natural resources used in the production of goods and services.
What is the reward for land?
Rent.
What is labour?
Human effort (mental and physical) used in production.
What is the reward for labour?
Wages or salaries.
What is capital?
Man-made goods used to produce other goods and services.
What is the reward for capital?
Interest.
What is enterprise?
The ability to organize the other factors of production and take risks in business.
What is the reward for enterprise?
Profit.
What is opportunity cost?
The next best alternative forgone when making an economic decision.
Give an example of opportunity cost.
If the government builds a hospital instead of a school, the school is the opportunity cost.
What is a production possibility curve (PPC)?
A diagram showing the maximum combination of two goods that can be produced using all available resources.
What does a point on the PPC represent?
Efficient use of resources.
What does a point inside the PPC represent?
Inefficient use of resources.
What does a point outside the PPC represent?
An unattainable level of production with current resources.
What causes an outward shift in the PPC?
Technological improvement, more resources, increased labour force.
What causes an inward shift in the PPC?
Natural disasters, resource depletion, low investment.
How is opportunity cost shown on a PPC?
As more of one good is produced, the quantity of the other good forgone shows the opportunity cost.
What is an economy?
An area where people and firms produce, trade, and consume goods and services.
What is microeconomics?
The study of individual markets and economic units like consumers and firms.
What is macroeconomics?
The study of the economy as a whole, including issues like unemployment and inflation.
What is resource allocation?
Deciding what to produce, how to produce it, and for whom to produce.
What is a market?
A place where buyers and sellers interact to exchange goods and services.
What is the price mechanism?
The process where prices adjust due to changes in supply and demand to allocate resources.
What is demand?
The willingness and ability of consumers to buy a good at a given price.
What is effective demand?
Demand backed by the ability to pay.
What is the law of demand?
As price increases, quantity demanded decreases, and vice versa.
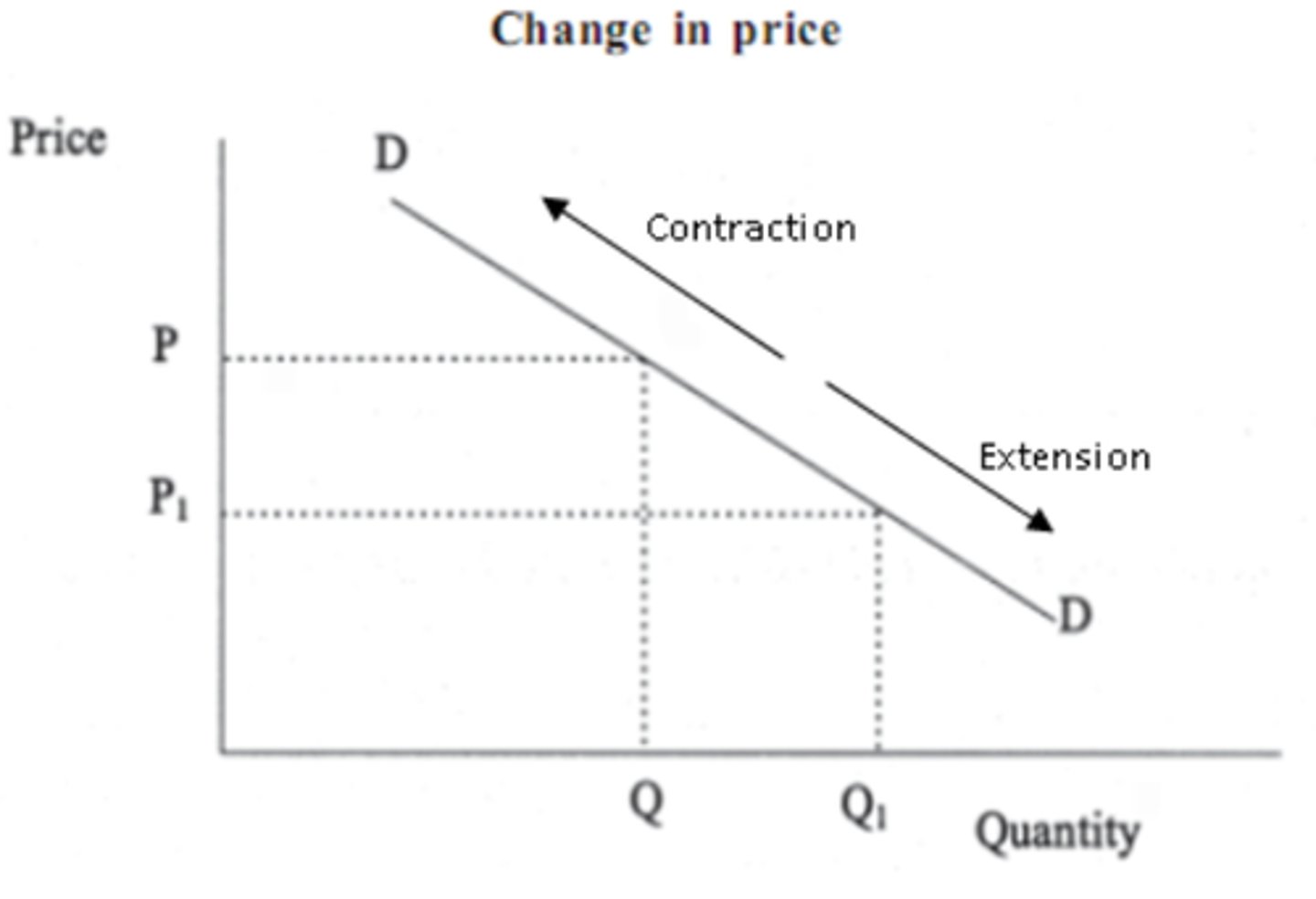
What causes a movement along the demand curve?
A change in the price of the good itself.
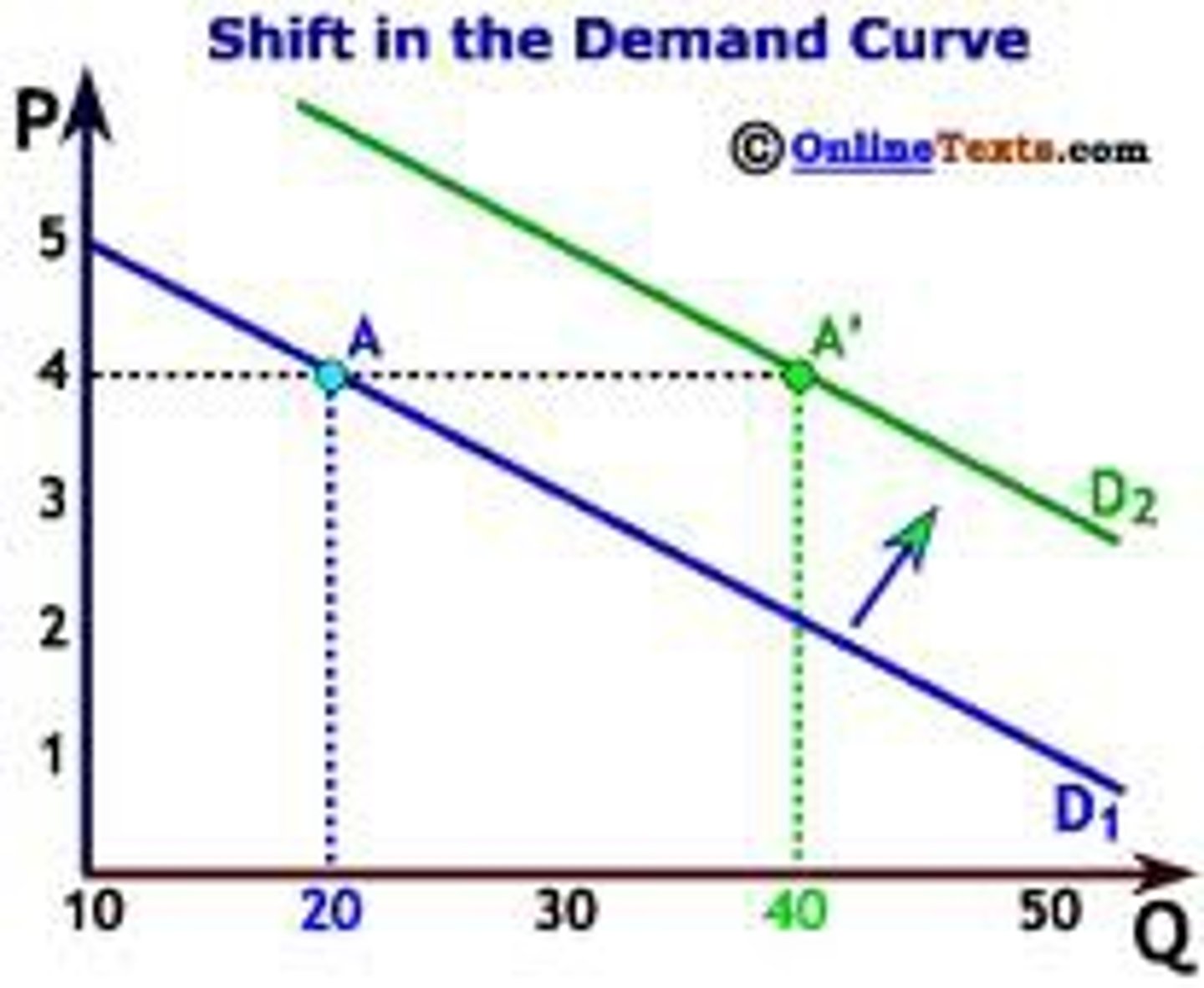
What causes a shift in the demand curve?
Changes in income, taxes, substitutes, complements, tastes, advertising, population.
What is supply?
The willingness and ability of producers to offer goods for sale at a given price.
What is the law of supply?
As price increases, quantity supplied increases, and vice versa.
What causes a movement along the supply curve?
A change in the price of the good itself.
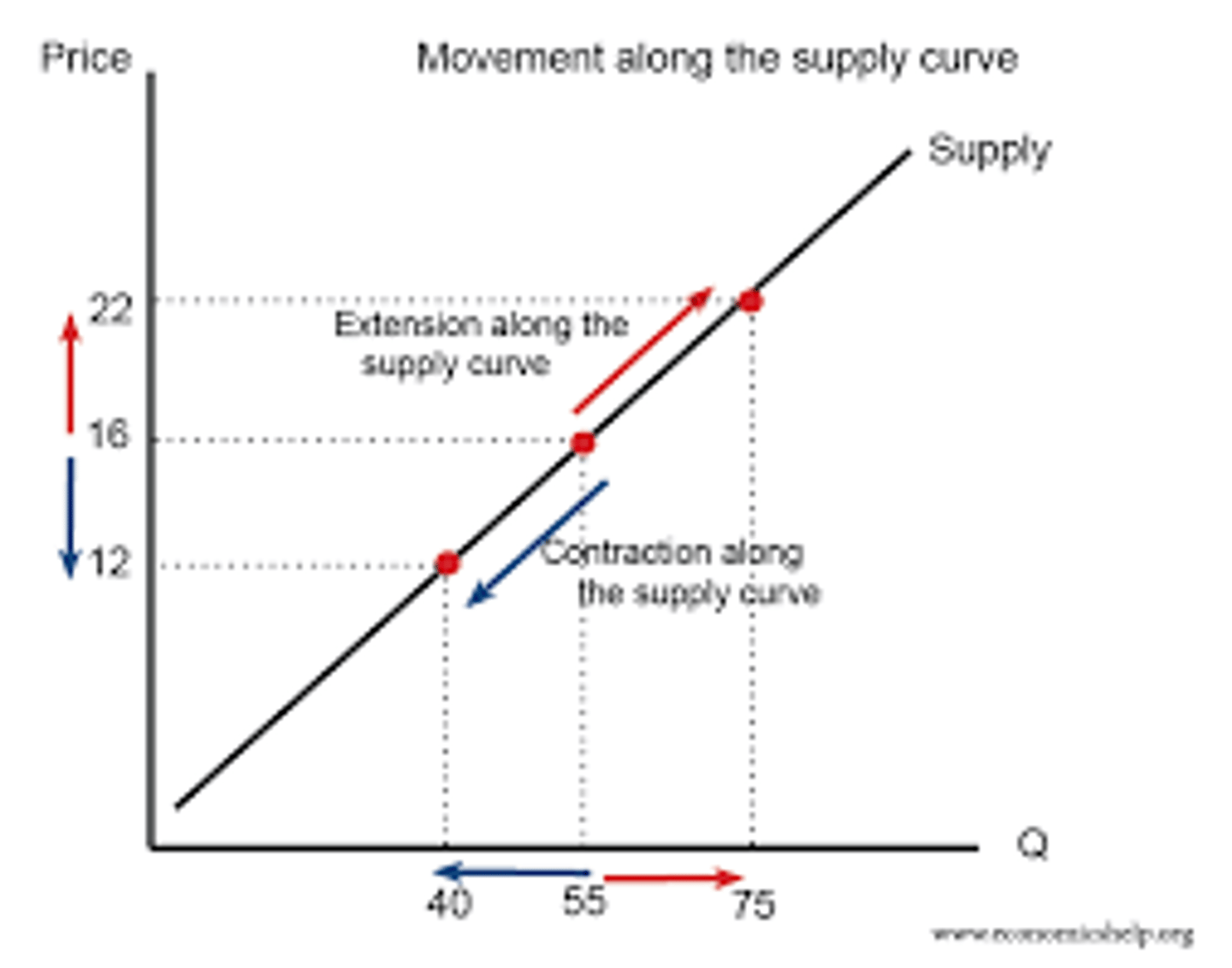
What causes a shift in the supply curve?
Changes in cost of production, resources, technology, profitability of other goods.
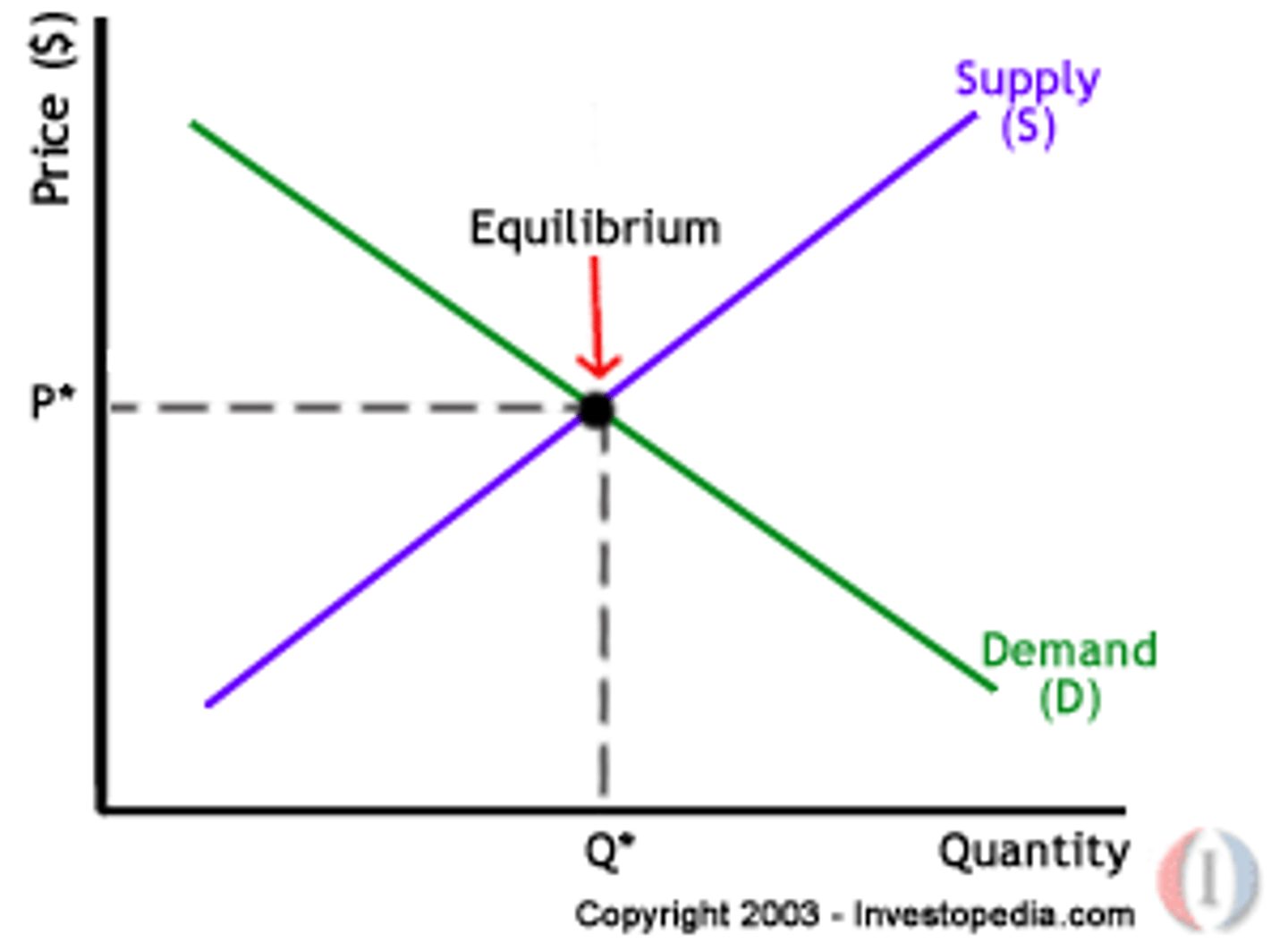
What is equilibrium price?
The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
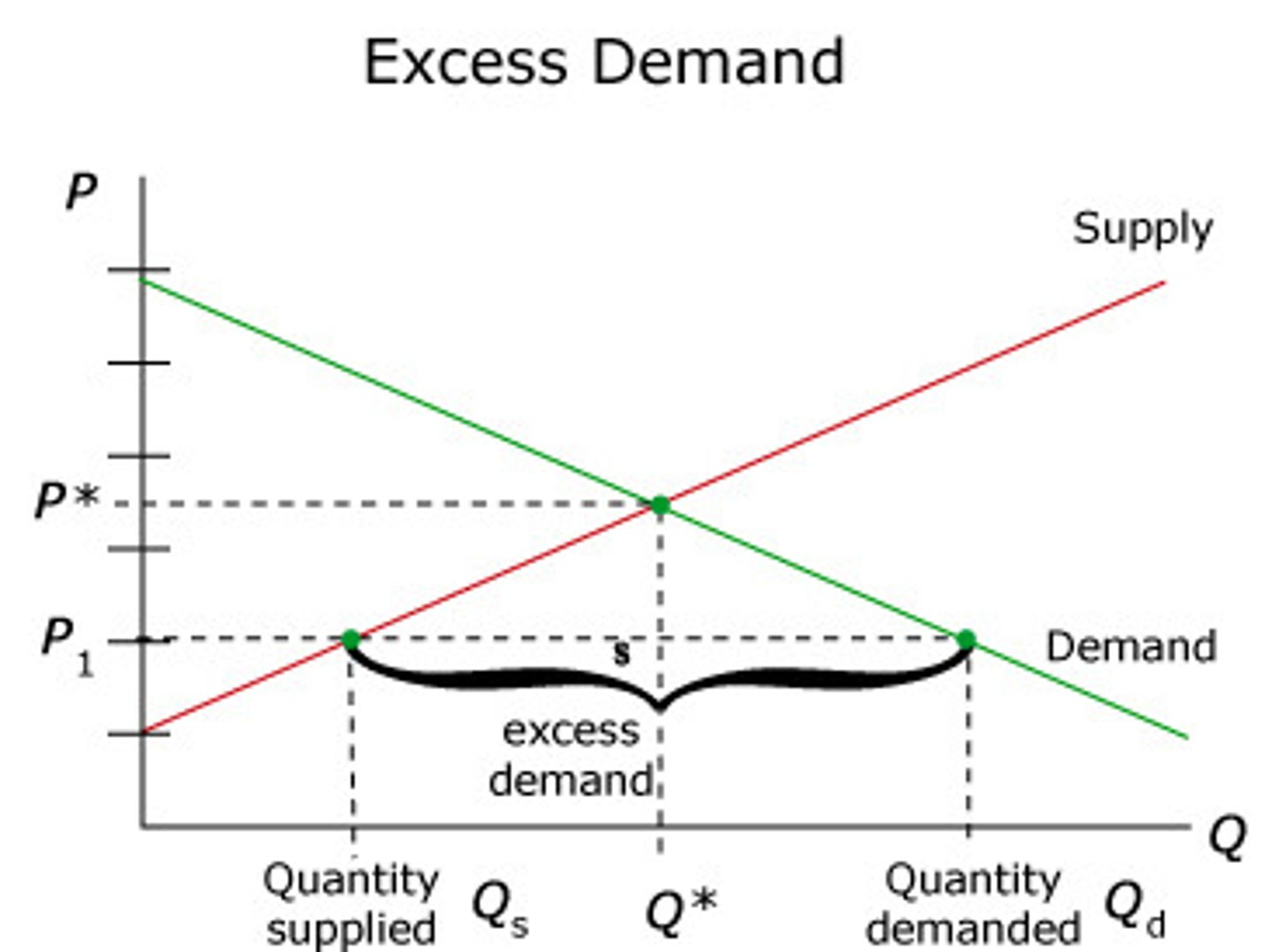
What is excess demand?
When quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied at a given price.
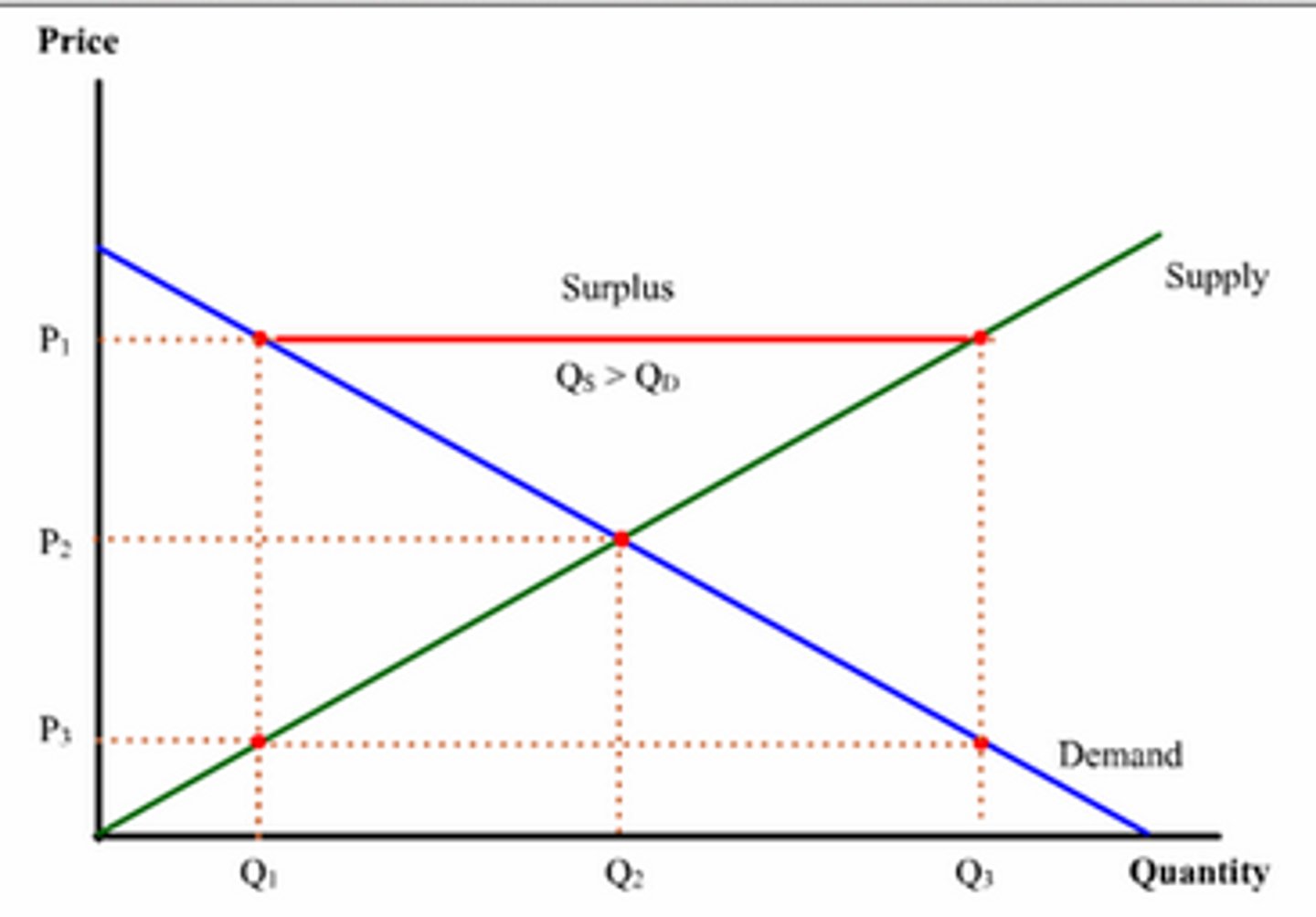
What is excess supply?
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded at a given price.
What is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
The responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
What is the PED formula?
% change in quantity demanded ÷ % change in price
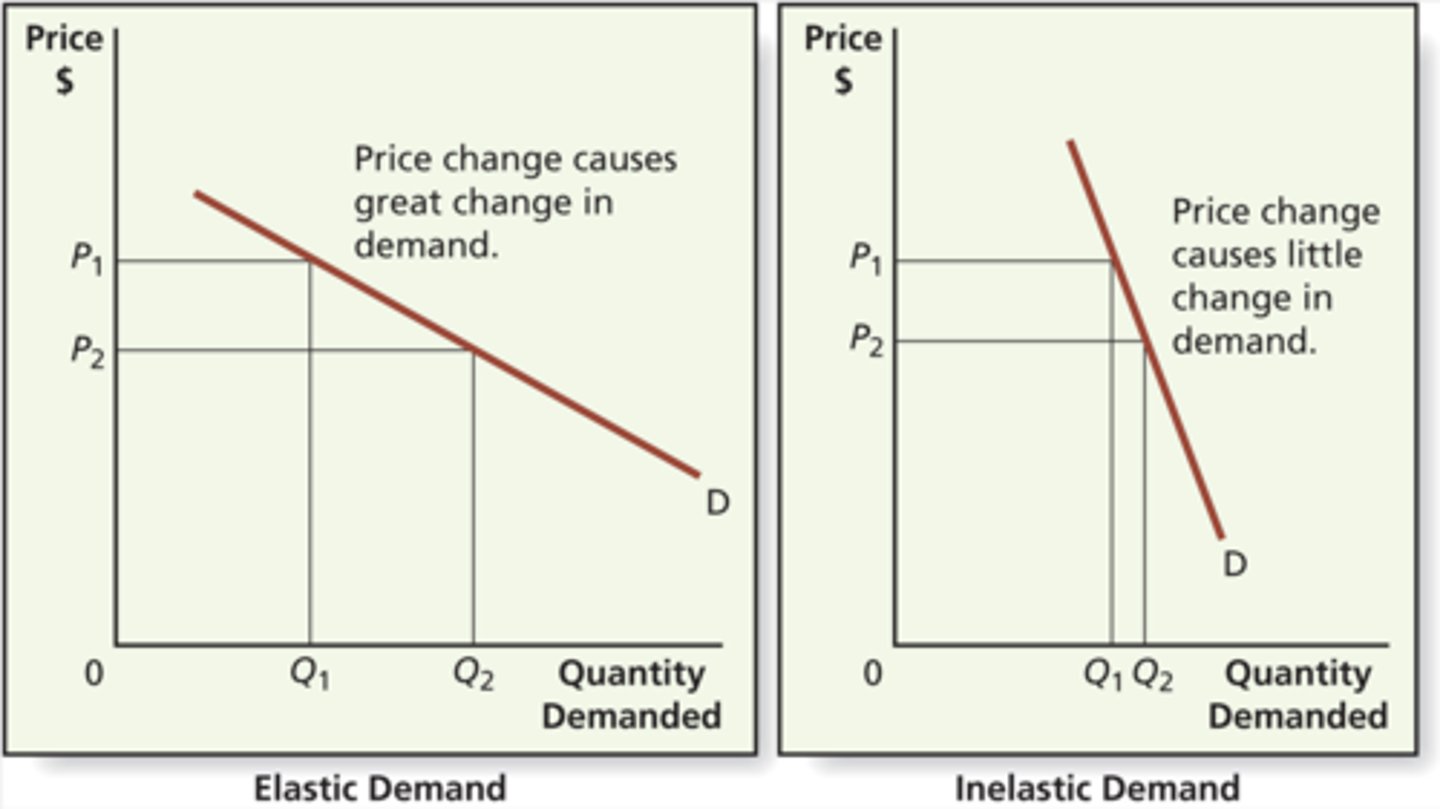
What does it mean if PED > 1?
Demand is price elastic.
What does it mean if PED < 1?
Demand is price inelastic.
What does it mean if PED = 1?
Demand is unit elastic.
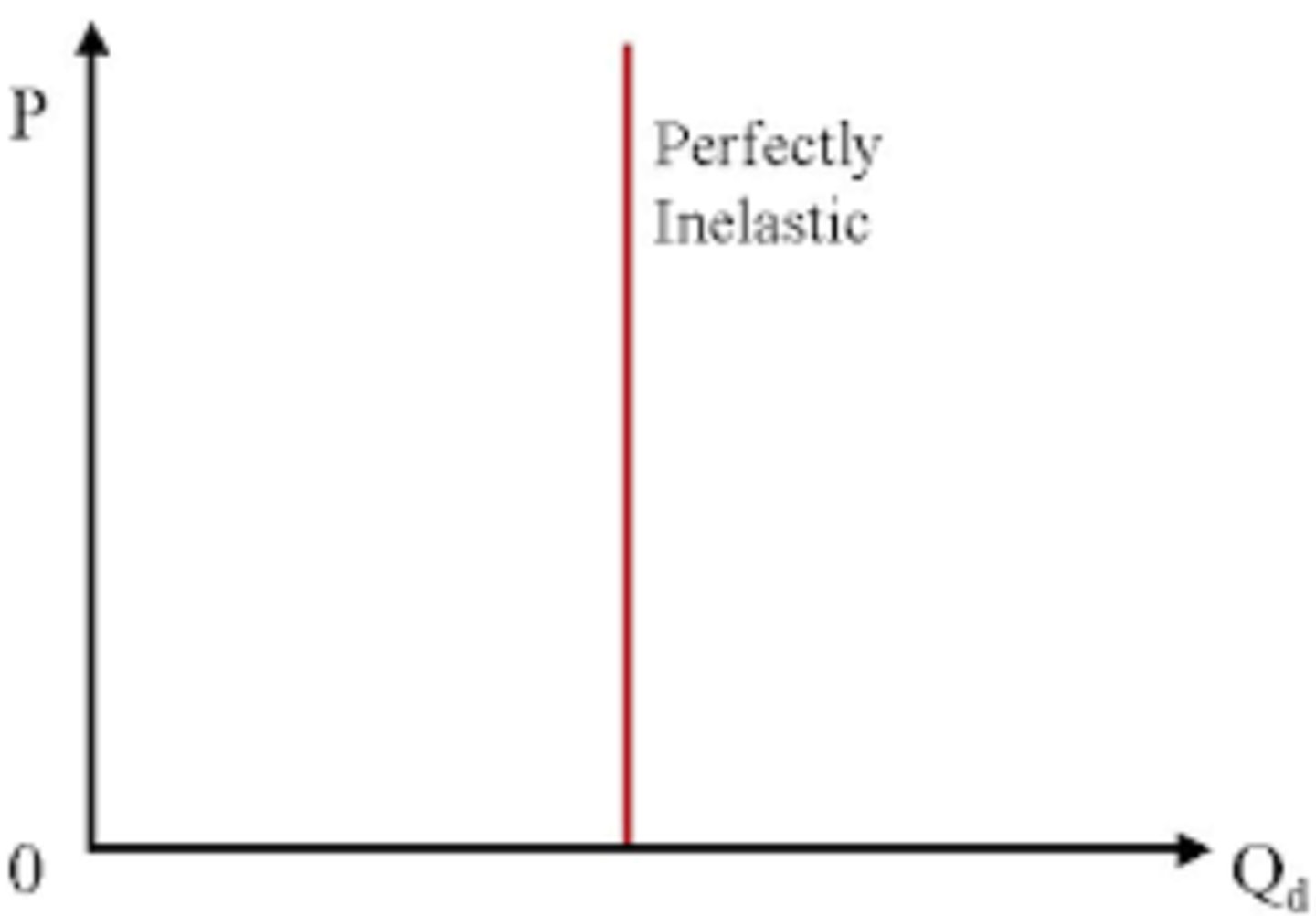
What does it mean if PED = 0?
Perfectly inelastic demand.
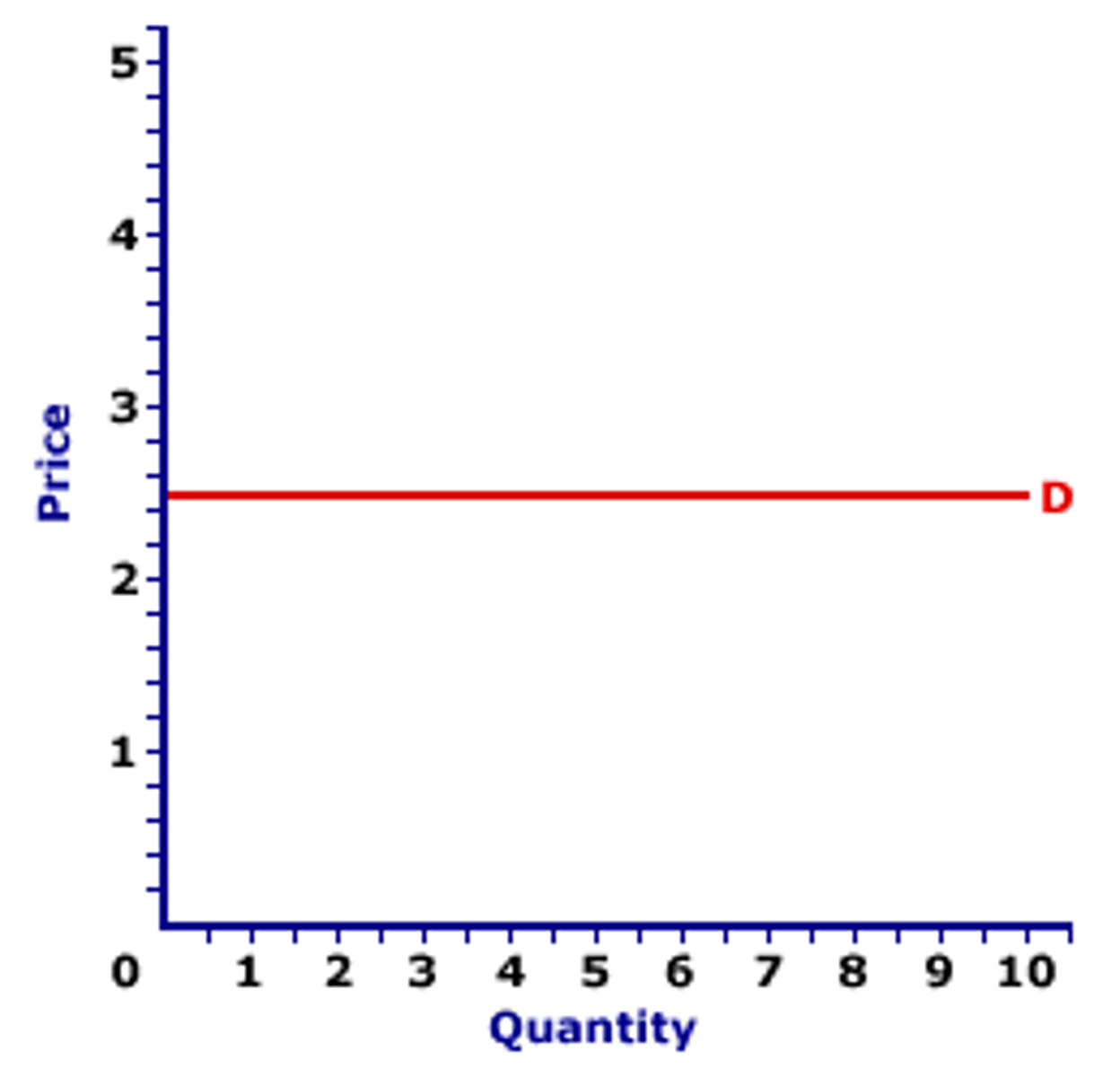
What does it mean if PED = ∞?
Perfectly elastic demand.
What factors affect PED?
Availability of substitutes, time period, proportion of income spent.
How does PED affect revenue?
If demand is elastic, lowering price increases revenue; if inelastic, raising price increases revenue.
What is price elasticity of supply (PES)?
The responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price.
What is the PES formula?
% change in quantity supplied ÷ % change in price
What factors affect PES?
Time, availability of resources, and production speed.
What is a market economic system?
An economy where resources are allocated by private individuals with no government involvement.
What are advantages of a market economy?
Efficient resource use, consumer choice, profit incentive, fast response to demand.
What are disadvantages of a market economy?
Inequality, market failure, harmful goods, environmental damage, monopoly risk.
What is market failure?
When the price mechanism fails to allocate resources efficiently.
What causes market failure?
Externalities, public goods, merit/demerit goods, monopoly, information failure.
What are external costs?
Negative side-effects of economic activity on third parties (e.g., pollution).
What are external benefits?
Positive side-effects of economic activity on third parties (e.g., education).
What are private costs?
Costs borne by the producer or consumer directly involved in the activity.
What are social costs?
Private costs + external costs.
What are private benefits?
Benefits received by the producer or consumer.
What are social benefits?
Private benefits + external benefits.
What is a mixed economic system?
An economy that combines market forces with government intervention.
How can governments correct market failure?
Through regulation, taxes, subsidies, direct provision, price controls, and tradeable permits.
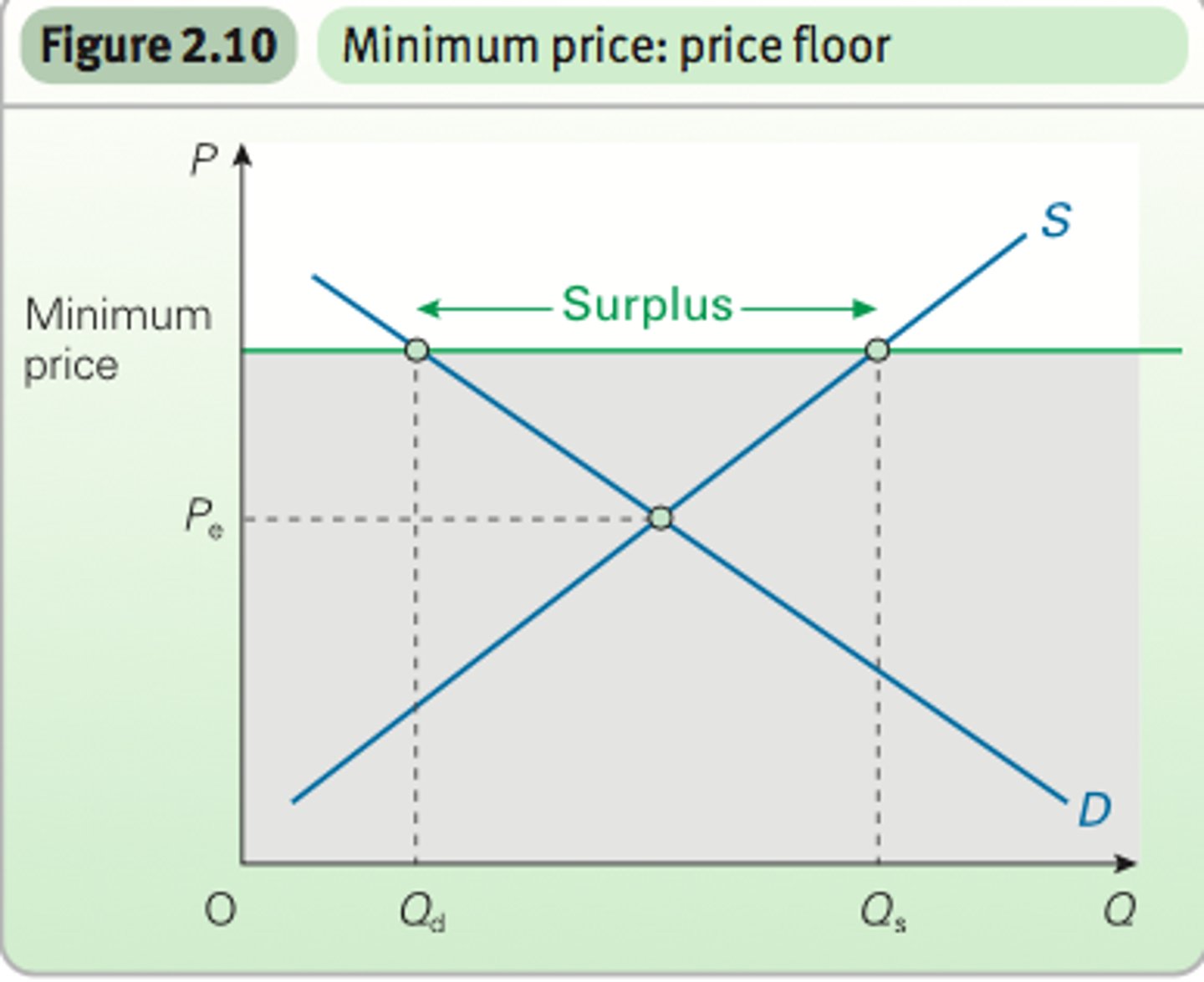
What is a minimum price?
A price floor set above equilibrium to ensure producers receive a minimum reward.
What is a maximum price?
A price ceiling set below equilibrium to protect consumers.
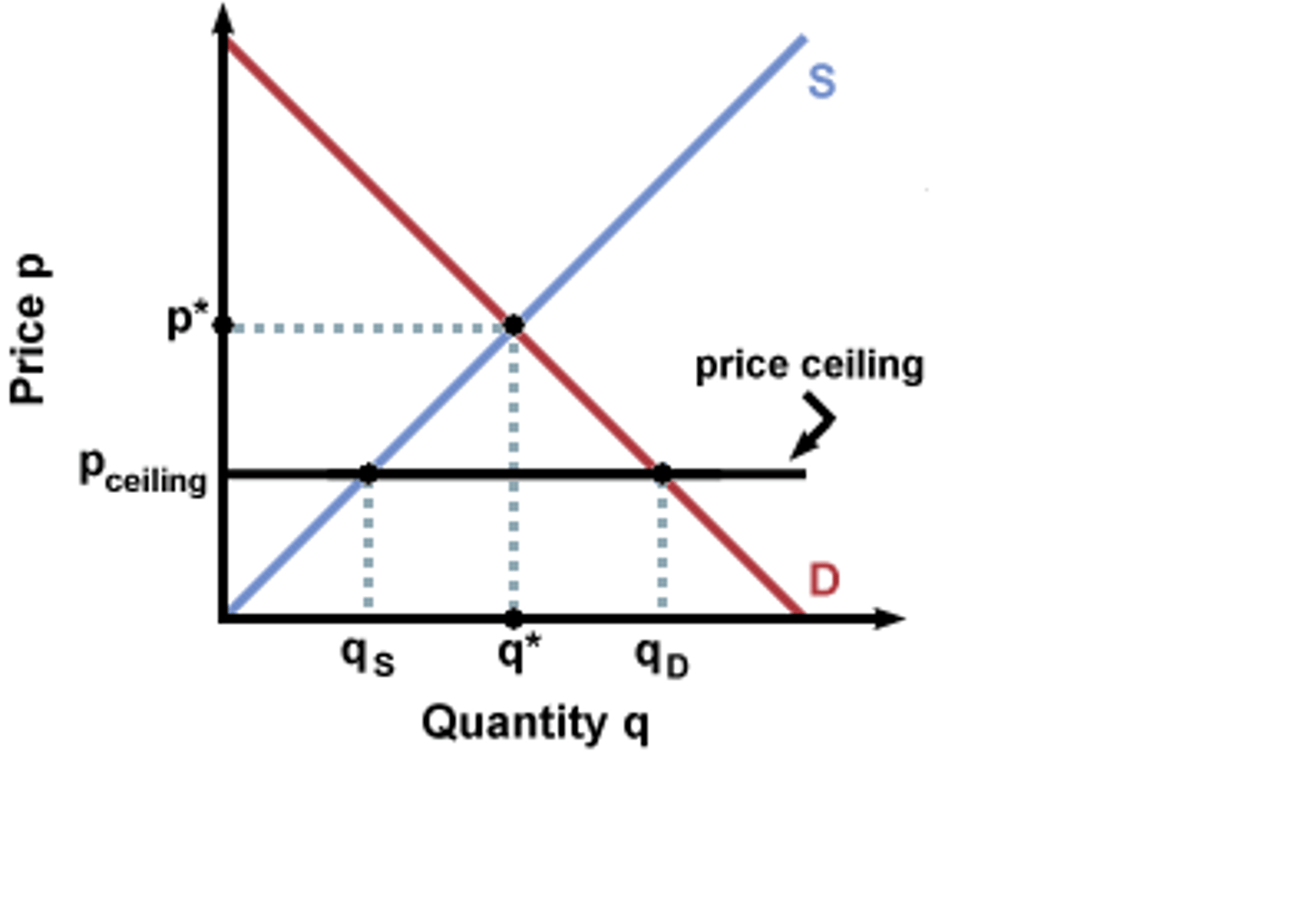
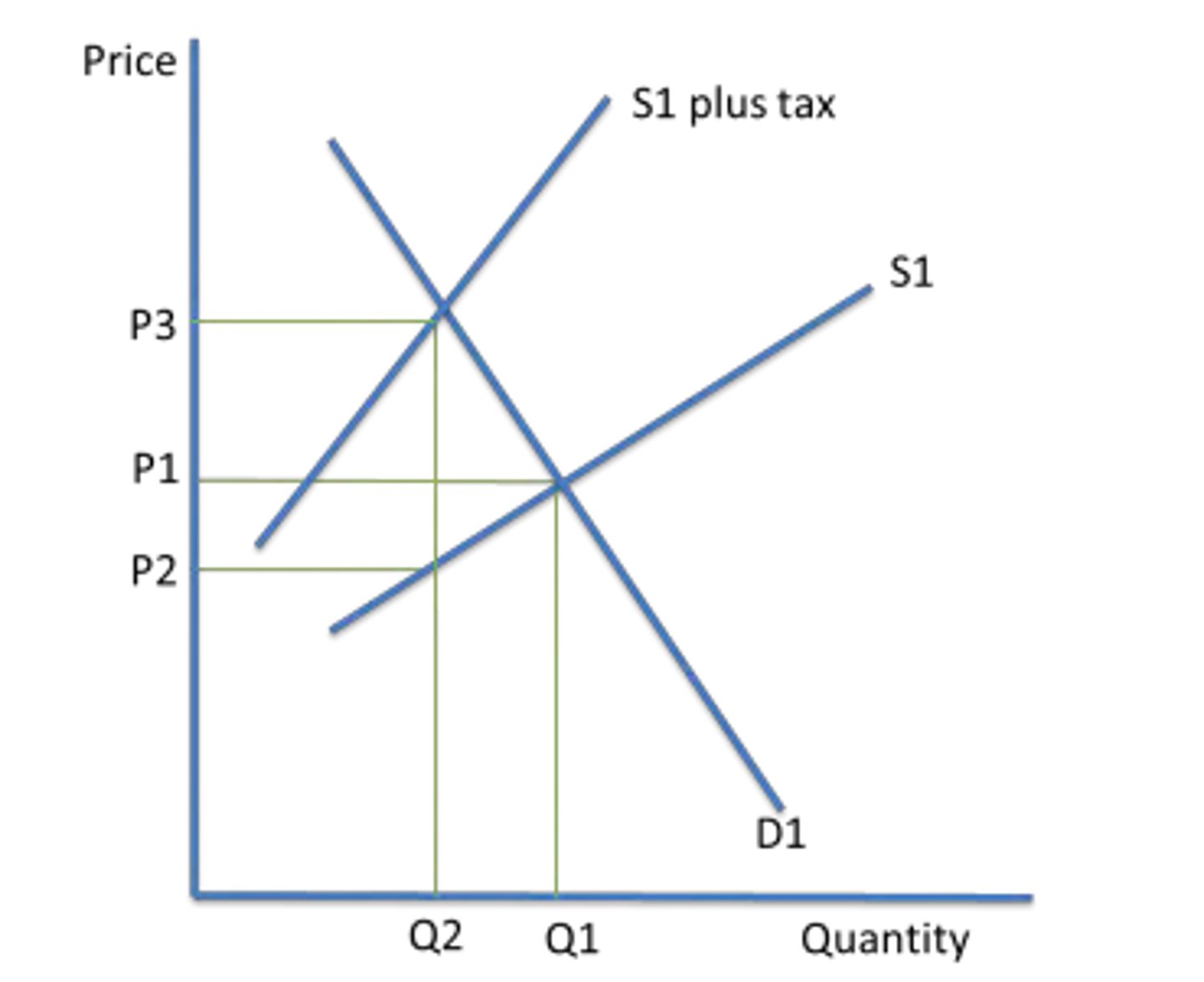
What does a tax on a product do?
Shifts the supply curve left, increases price, and reduces quantity traded.
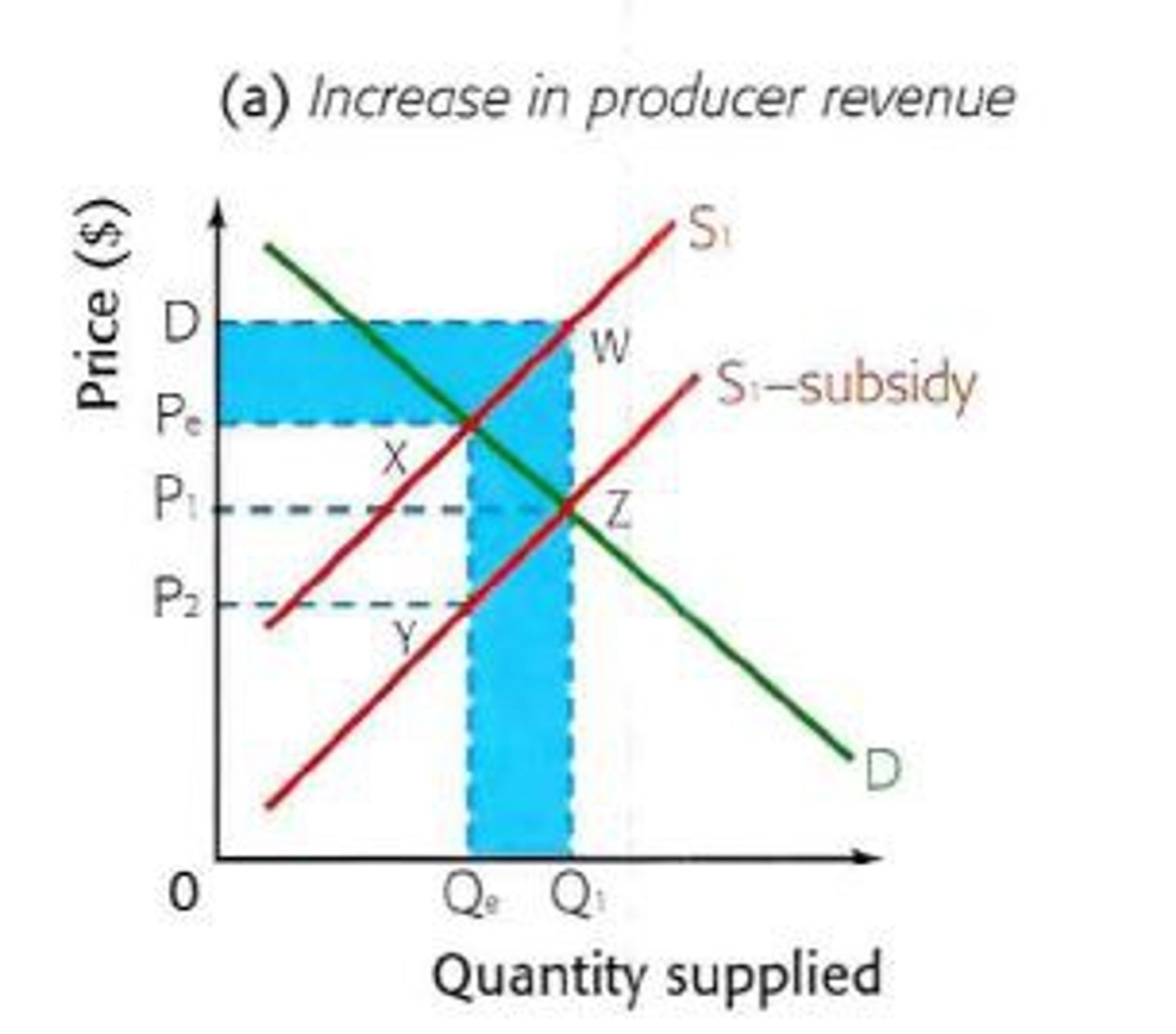
What does a subsidy on a product do?
Shifts the supply curve right, decreases price, and increases quantity traded.