Dental Anomalies
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
Anomaly
a deviation from normal
-usually an absence, excess, or deformity
More anomalies occur in _________________ teeth
Permanent
More anomalies occur in the _____________ arch
maxillary
Anodontia
absence of teeth
True anodontia
no teeth
Commonly missing teeth
maxillary 3rd molars
mandibular 3rd molars
maxillary lateral incisors
mandibular premolars
Tooth agenesis
the tooth did not form
Edentulous
no teeth because lost them from disease
Anodontia vs edentulous
anodontia is the congenital absence of teeth
edentulous means you lost the teeth and therefore don't have them
Is anodontia rare or common?
rare
What is anodontia associated with usually?
other ectodermal (skin/hair) disorders
Supernumerary teeth
extra teeth
Mesiodens
a supernumerary tooth between 8 and 9
Distomolar
an additional tooth in the 3rd molar area
Another name for distomolar
paramolar
Where is a common location for supernumerary teeth in the mandibular arch?
2nd premolars *does not have a specific name
Supernumerary teeth are often
malformed
Malposition
deviations in the position of teeth
Malposition teeth are typically
unerupted or impatcted
Common malpositioned teeth
3rd molars
What is the last anterior permanent tooth to erupt?
canine
What tooth is typically "blocked out" if there is not enough space?
maxillary canine
Transposition
in the wrong place
Example of transposition
a canine and premolar are in each other's place
What is the tooth that is most often rotated?
Maxillary 2nd premolar
Microdontia
Abnormally small teeth
Macrodontia
abnormally large teeth
What teeth are the most variable in shape?
3rd molars
__________ 3rd molars vary more than _____________ 3rd molars
Maxillary, mandibular
What teeth are the 2nd most variable tooth in shape?
Maxillary lateral incisors
Example of malformed maxillary lateral
peg lateral
Peg lateral
A maxillary lateral incisor developed from only one lobe
Gemination
Incomplete division of one tooth during development. Usually share a common root
"Twinning"
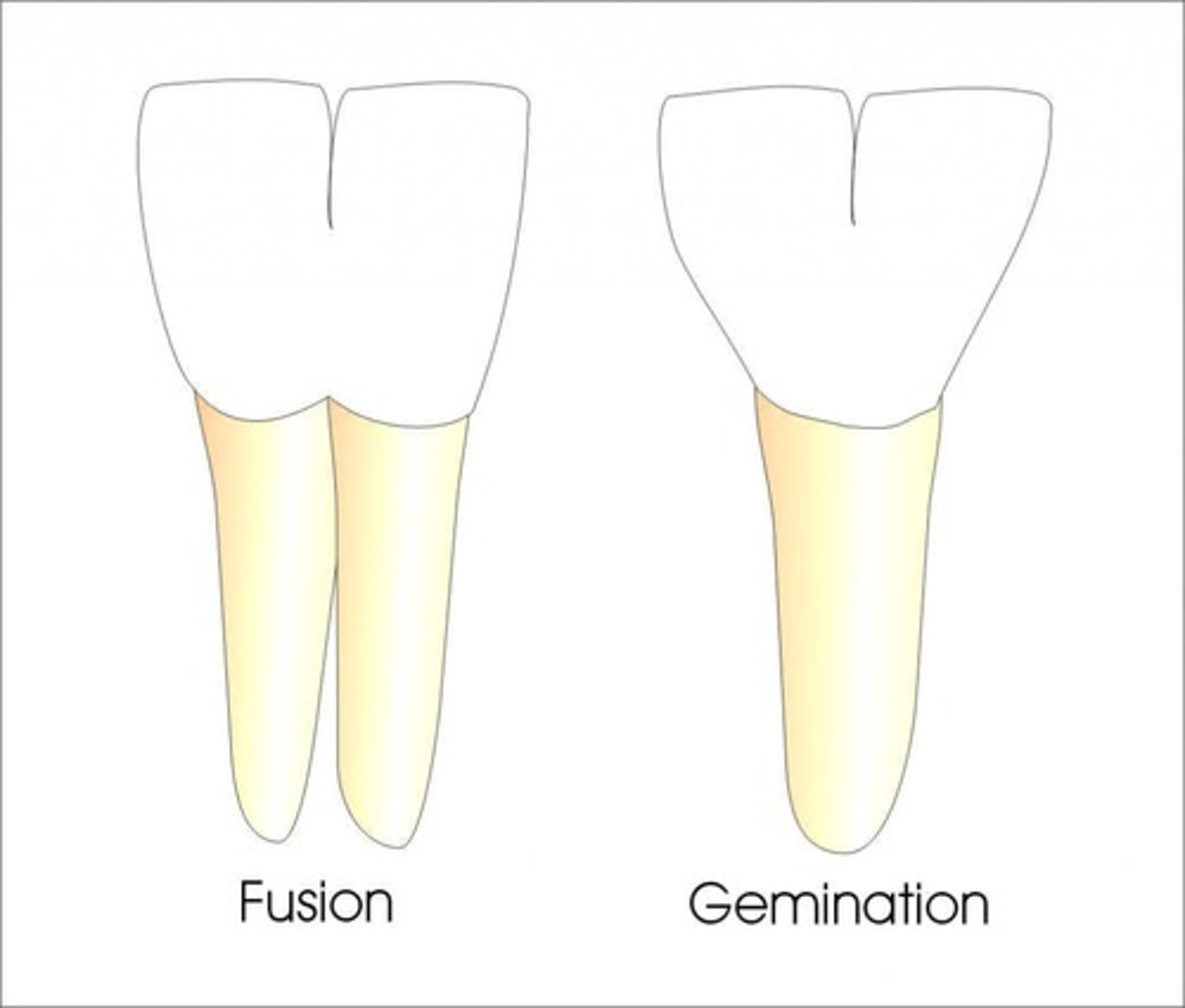
Gemination occurs when...
a single bud splits, forming 2 teeth (1 root)
Where is Gemination more common?
Primary dentition
In gemination, are there one or two roots?
1
What is shared in gemination?
a common pulp canal and a root
If you are counting the teeth and you count the normal number (counting the malformed crown as one tooth) what type of malformation is it?
gemination
Fusion appears like you are ______________ one tooth
missing
Fusion
union of two independently developing primary or secondary teeth
Fusion involves...
dentin
Fusion is more common in _____________ dentition
primary
Common location for fusion?
mandibular incisor
Congenital syphillis can lead to
Hutchinson's incisors and Mulberry molars
Hutchinson's incisors
notched incisal edges
Mulberry molars
Molars with multiple cusps that are caused by congenital syphilis
Talon cusp
A Cingulum like "claw"
Projection on the lingual surface of an anterior tooth
Talon cusps usually have a
Pulp horn
Tubercles
small extra enamel projections
Where are tubercles common?
mesial marginal ridges
Where is a shovel shaped maxillary incisor common?
Asian, Arctic, and Native American dentitions
Enamel pearls
Small spherical enamel projections on tooth surface
Where are enamel pearls often found?
near furcation
What can enamel pearls lead to?
periodontal problem
Taurodantia
Elongated pulp chambers
Taurodantia is due to
developmental problems or genetics
Dens in dente
Tooth within a tooth
Dens in dente leads to what in the cingulum area?
deep crevice
Dilaceration
severe bend of the root on the crown (90 degrees or more)
Flexion
Bend of the root only less than 90 degrees
Concrescence
Joining of roots
What part of the tooth is joined in concrescence?
cementum
Dwarfed roots
Short roots
Hypercementosis
Excess thickness of the cementum
When does hypercementosis occur?
After eruption, may be in response to trauma
Accessory roots
extra roots
Common areas of accessory roots
third molars
mandibular canines
mandibular premolars
Dysplasia
Abnormal development
Forms of enamel dysplasia
amelogenesis imperfecta
fluorosis
focal enamel hypoplasia (turner's tooth)
enamel hypoplasia
Amelogenesis imperfecta
incomplete or improper development of the enamel tissue
Amelogenesis imperfecta affects what dentitions?
both
Fluorosis
Too much fluoride during tooth development
-white to yellow or brown enamel, pitting, resistant to decay
Focal Enamel Hypoplasia name
Turner's Tooth
Turner's Tooth
Primary tooth with an abscess (infection at root apex)
A primary tooth with an abscess can lead to
permanent tooth enamel malformation
Hypoplasia
incomplete development
Enamel hypoplasia
incomplete development of tooth enamel
Examples of dentinal dysplasias
dentinogenesis imperfects
tetracycline staining
Dentinogenesis imperfecta
Faulty dentin formation
Dentinogenesis imperfecta is
Hereditary
Dentinogenesis imperfect affects what dentitions?
both
What is more common- Dentinogenesis imperfecta or enamel dysplasia?
Dentinogenesis imperfecta is 2x more common
Dentinogenesis imperfecta results in...
Opalescent blue color and brittle enamel due to lack of dentinal support
Dentinogenesis imperfecta affects what dentitions?
Both
Tetracycline staining
Bands of grey-brown dentin corresponds to areas forming while taking tetracycline
Attrition
Tooth wear from tooth to tooth contact
Abrasion
Tooth wear from contact with a foreign object
-Abrasive toothpastes
-Brushing with too much force
-Pipe smoking
Erosion
Enamel and dentin loss from acids and not associated with bacteria
Abfraction
Loss of tooth structure from a fracture of enamel rods
Changes to a tooth after eruption:
Attrition
Abrasion
Erosion
Abfraction
3 shapes of mandibular 2nd premolar grooves
Y, H, U
Focal hypomaturation
chalky white opaque appearance, prone to dental caries