N236: Bacterial Infections of Humans
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Acne Vulgaris
Pathogen: Propionibacterium acnes
S+S: Clogging of skin pores with sebum and dead cells --> formation of papules and pustules on face, forehead, chest, upper back and shoulders
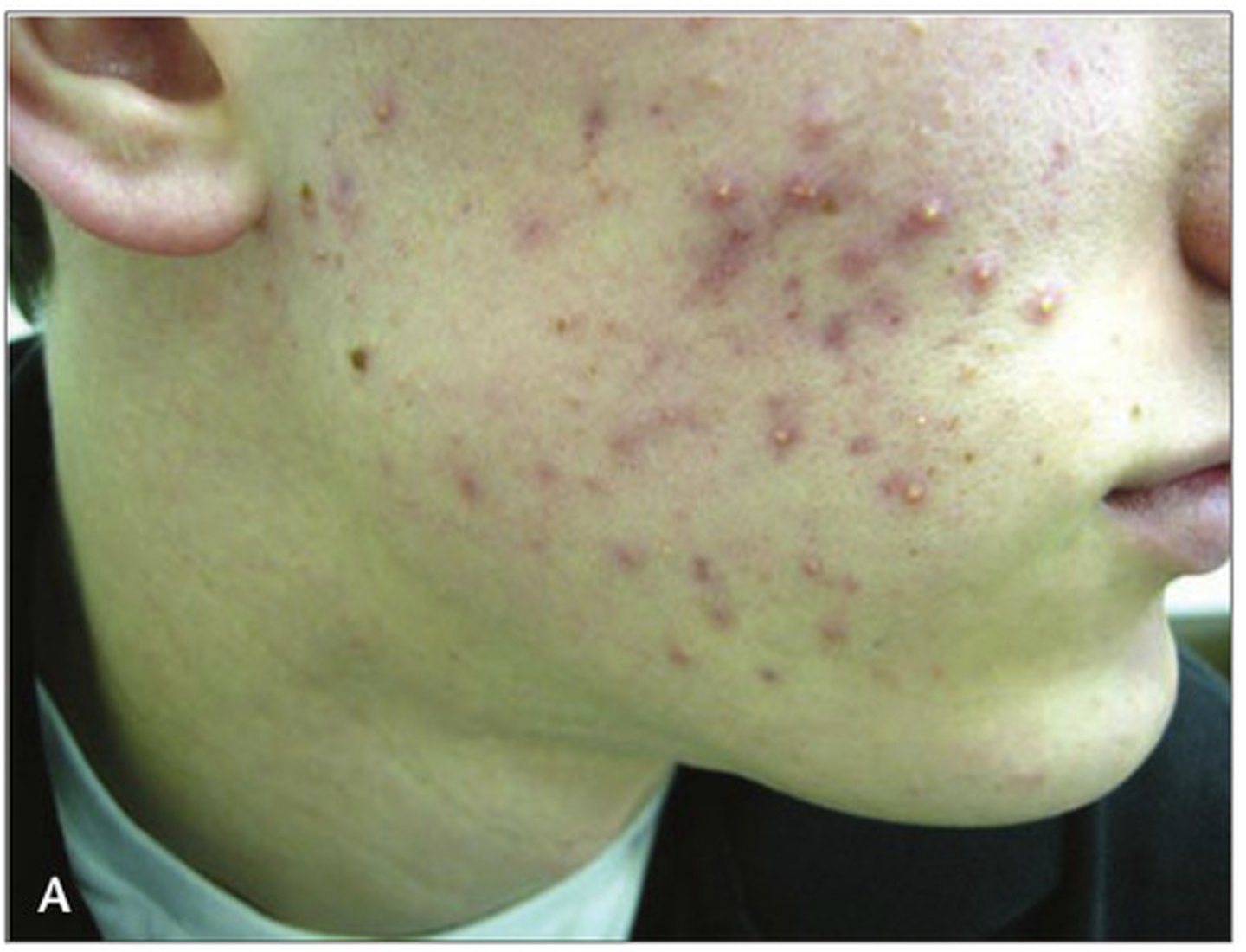
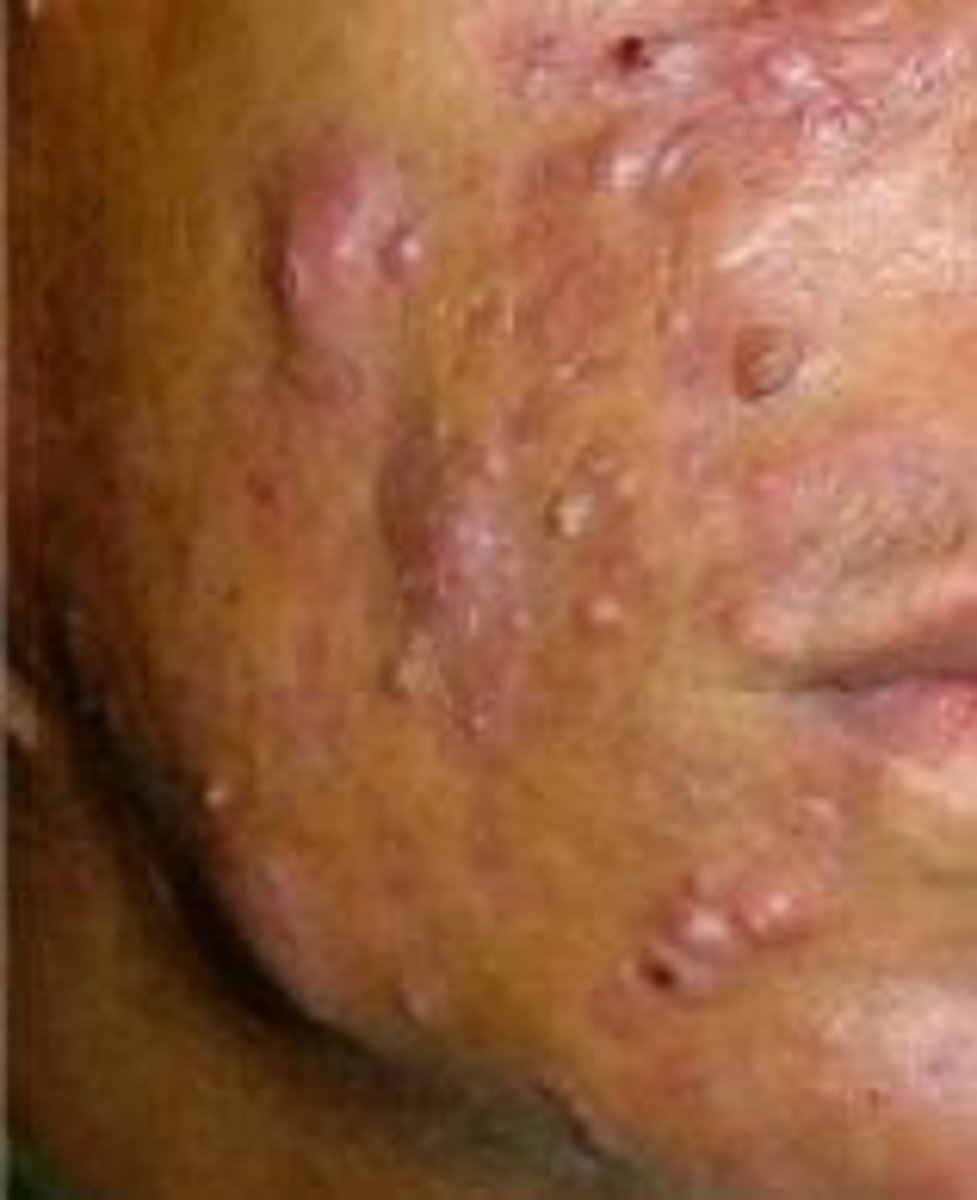
Cystic acne
Uncommon, severe form of acne with painful pustules
Gas gangrene (clostridial myonecrosis)
Pathogen: Clostridium perfringens
S+S: Rapid destruction of muscle and soft tissues by necrotizing exotoxins
Reservoir: Soil
Treatment: Amputation
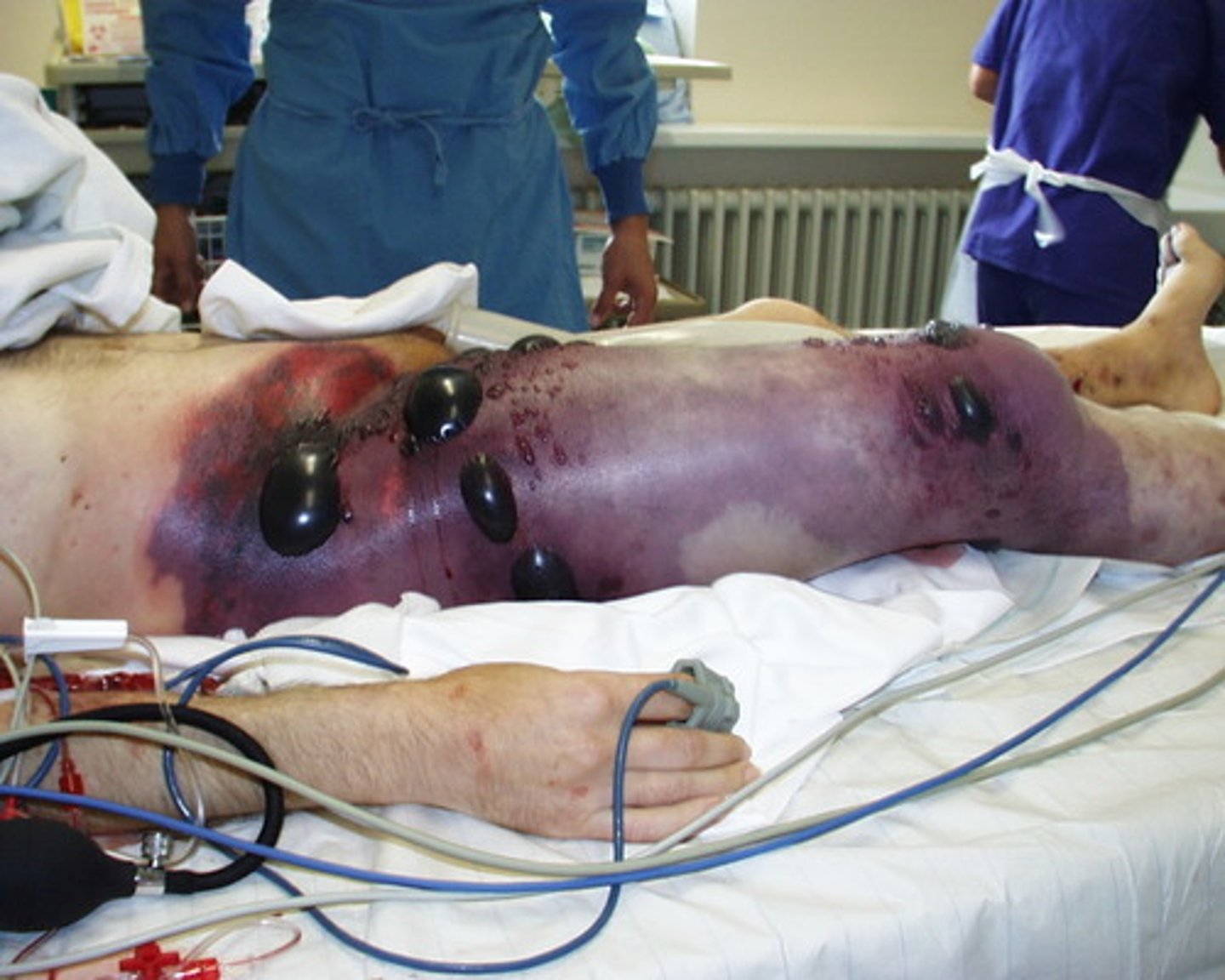
Palpable crepitus
Crackling sensation or popping sound during palpation due to the presence of gas in the subcutaneous tissue
Hansen's Disease (Leprosy)
Pathogen: Mycobacterium leprae
S+S:
skin: Flat, discolored patches on skin, ulcers on the feet, nodules on the face, loss of eyebrows/eyelashes,
mucous membranes: stuffy nose, epistaxis,
peripheral nerves: numbness, paralysis
limbs: shortening of fingers and toes
Reservoir: Armadillos
Transmission: Long term inhalation of respiratory secretions; touching/handling infected armadillos
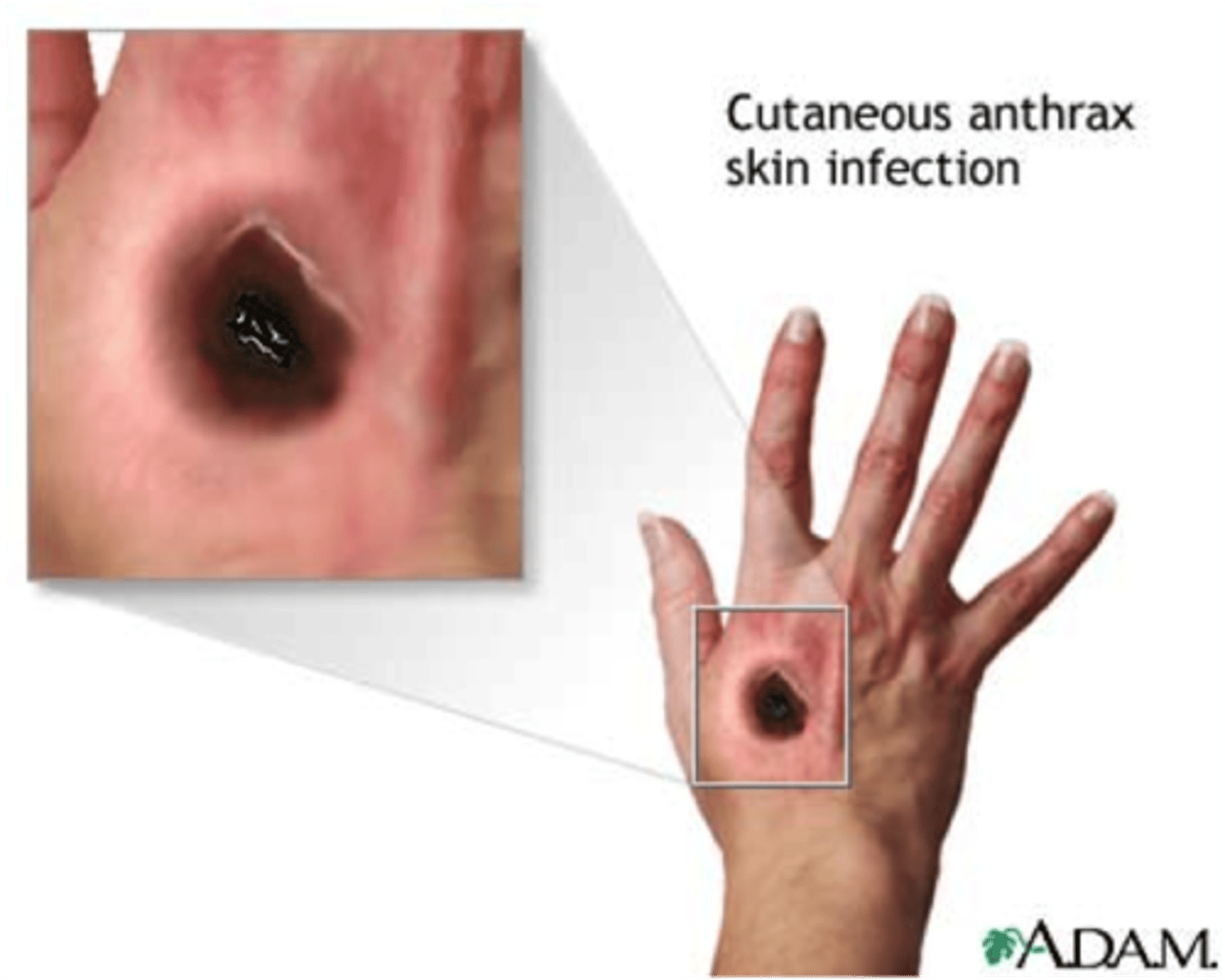
Anthrax
Bacillus anthracis
S+S: Cutaneous anthrax --> depressed black lesions (eschars) on the skin of the head, neck, forearms, and hands as a result of damage by exotoxins
Reservoirs: Animals (wool)
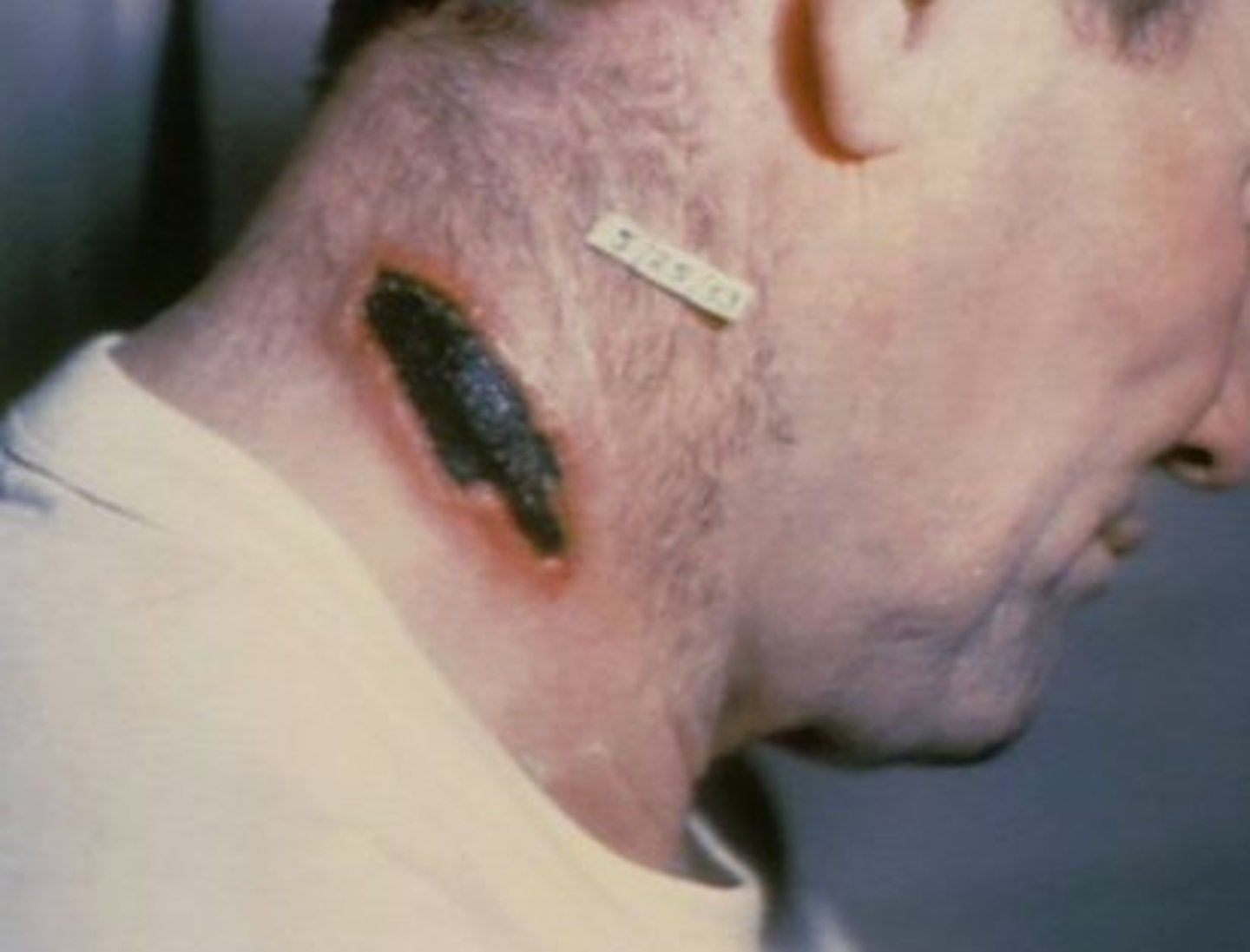
Anthrax used to be called...
Woolsorters' disease
Other forms of anthrax
Inhalation --> Flu-like symptoms, SOB, hemoptysis, death
GI --> Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, followed by diarrhea/dysentery, and death
Injection --> Redness and swelling at the site of injection, no eschars, multiple organ failure
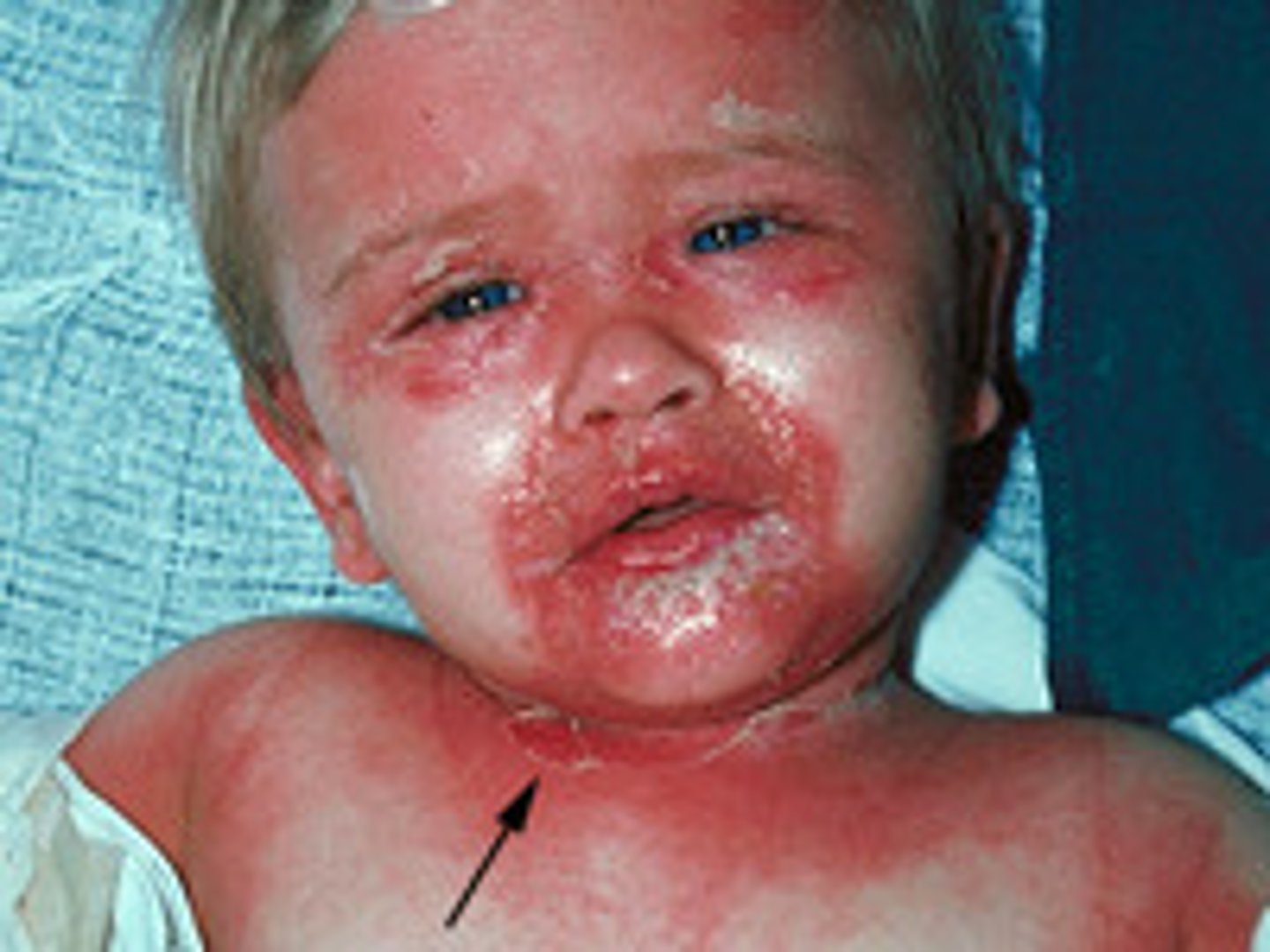
Staphylococcal Skin Infections
Pathogen: Staphylococcus aureus
Infections: Folliculitis, hordeolum (sty), furuncle (boils), carbuncle
Scalded skin syndrome
Rare infection caused by certain toxin-producing strains of Staphylococcus aureus
S+S: Peeling of the epidermis --> looks like the skin has been burned over large parts of the body
higher risks to immunocompromised and children <5 years
treatment: burn units or ICUs
MRSA
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
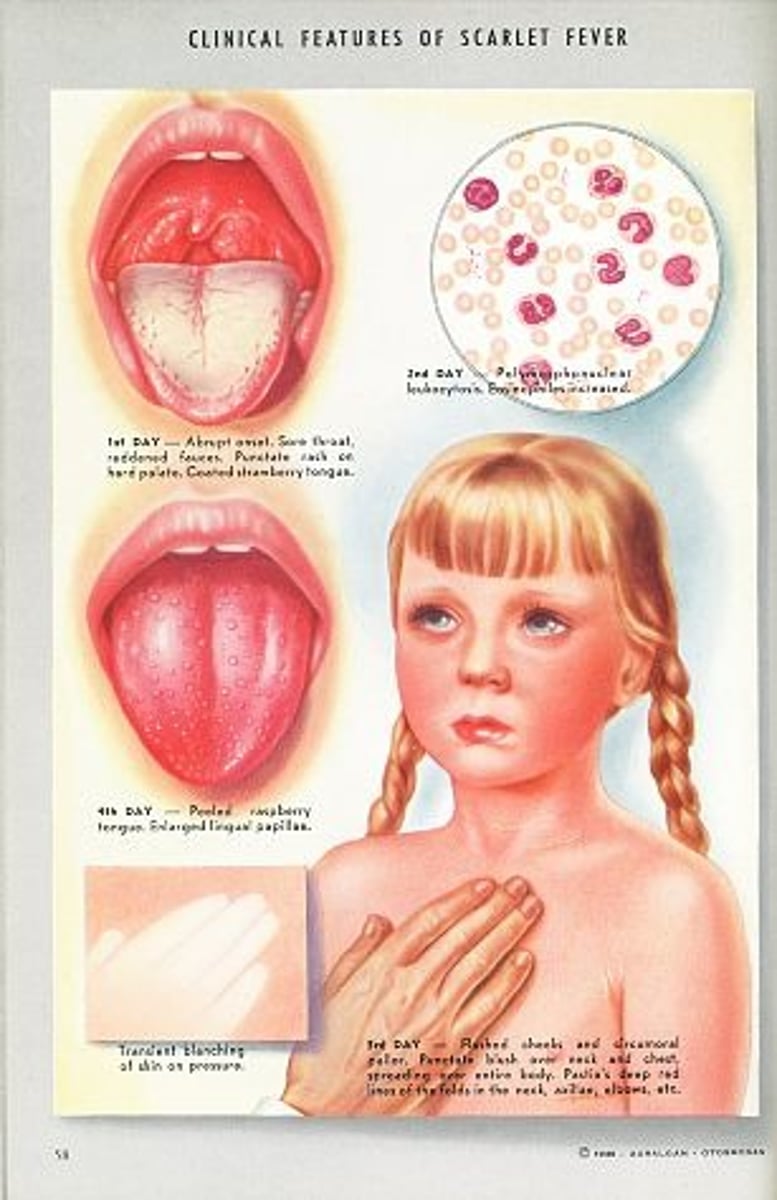
Scarlet fever
Pathogen: Streptococcus pyogenes
S+S: High fever, sore throat, bright red colored skin rash progressing from macular > papular, resolving within a week
Transmission: Inhalation of infected oropharyngeal secretions, contact with articles freshly soiled with infected oropharyngeal secretions
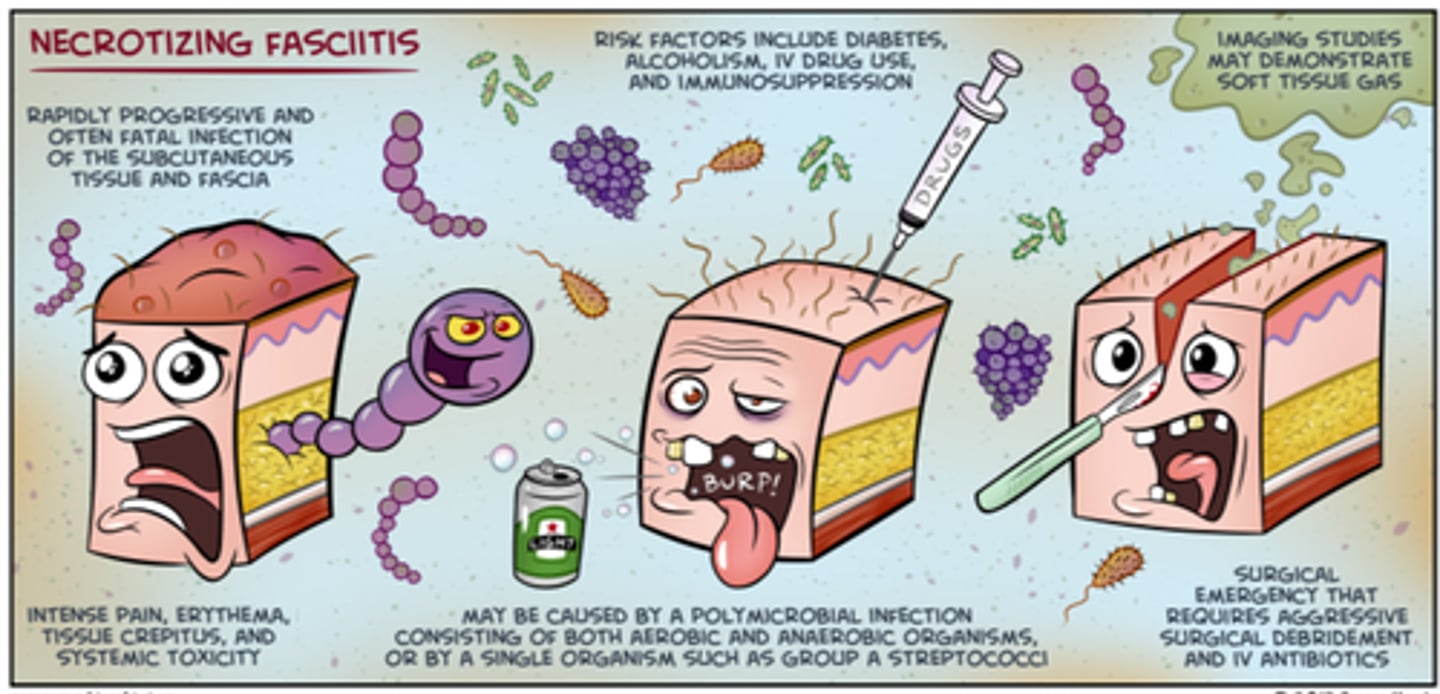
Necrotising fasciitis
Pathogen: Streptococcus pyogenes (“flesh-eating” strain)
S+S: Red, warm, blistered skin, swelling, severe pain
Transmission: Bacteria enter through skin cuts
treatment: requiring surgery removing dead, damaged tissue (debridement)
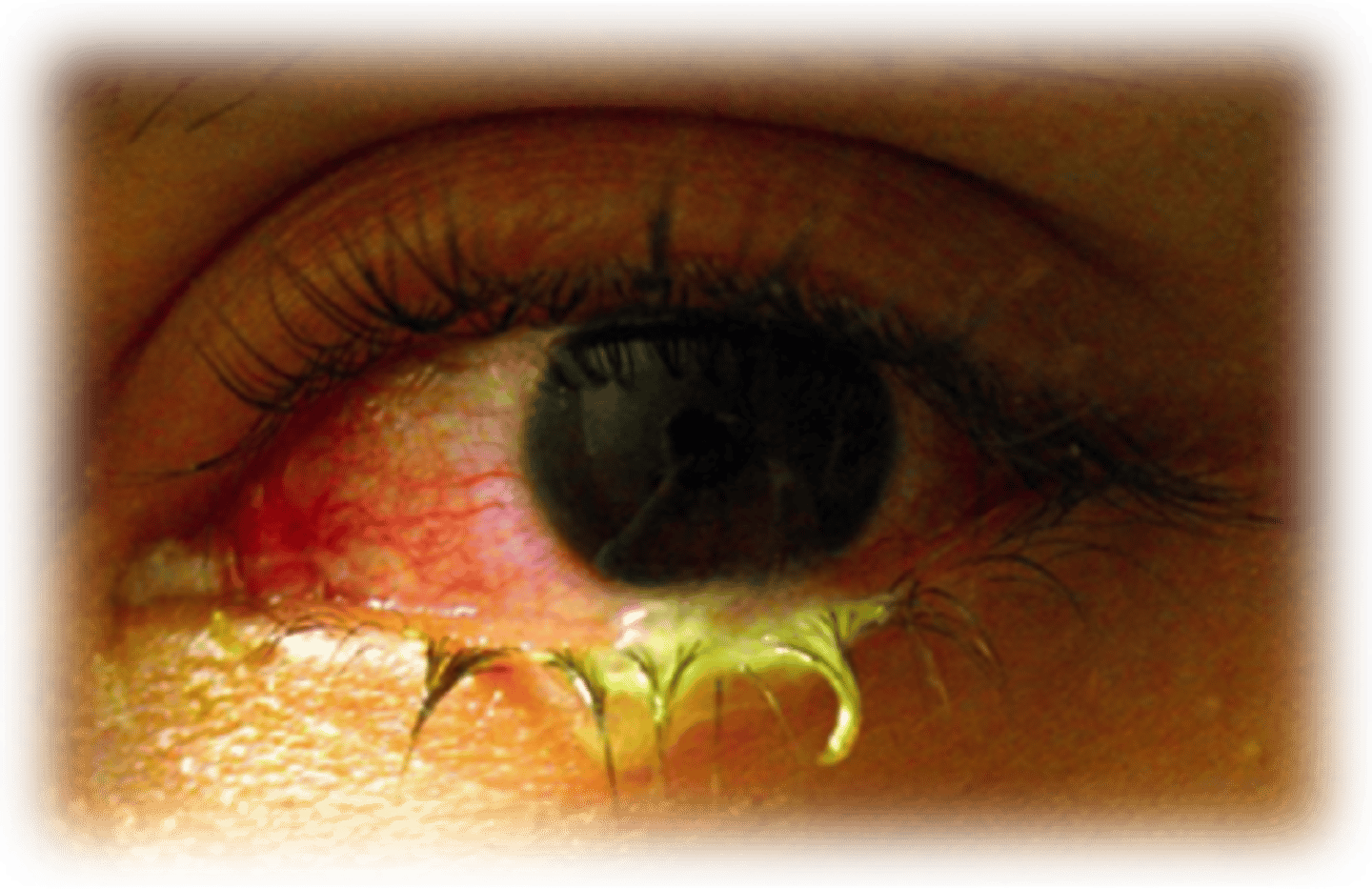
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Pathogen: Neisseria gonorrhoeae
S+S: Inflammation of the conjunctiva, redness, purulent discharge; scarring if untreated
Transmission: Direct contact with an infected birth canal during delivery, finger-to-eye contact with infected genital secretions
Another name for Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Gonococcal Ophthalmia Neonatorum, occurs within 2 days after birth
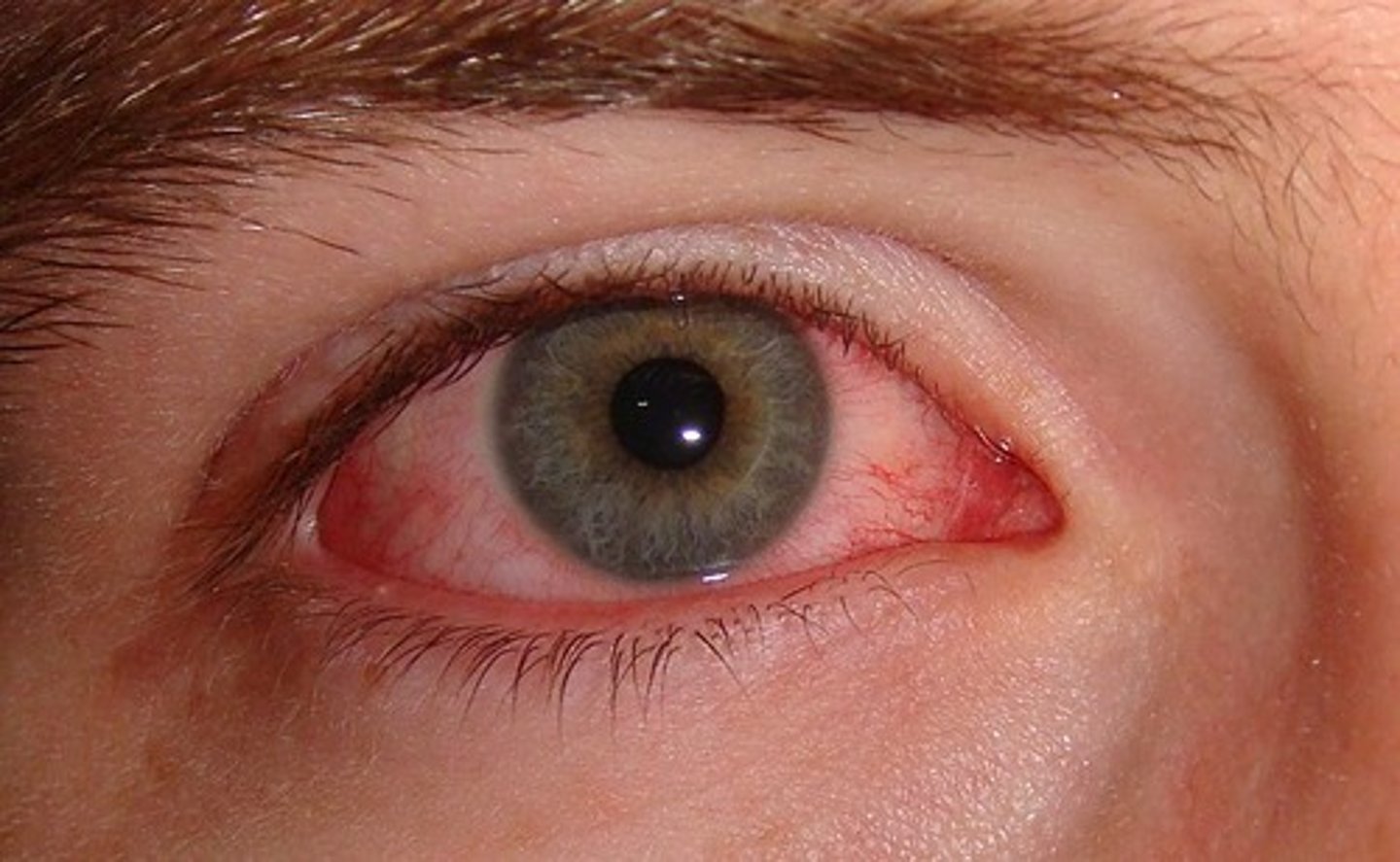
Chlamydial Conjunctivitis
Pathogen: Chlamydia trachomatis
S+S: Inflammation of the conjunctiva, redness, purulent discharge; scarring if untreated
Transmission: Direct contact with an infected birth canal during delivery, finger-to-eye contact with infected genital secretions
Another name for Chlamydial Conjunctivitis
Chlamydial Ophthalmia Neonatorum, occurs within weeks after birth
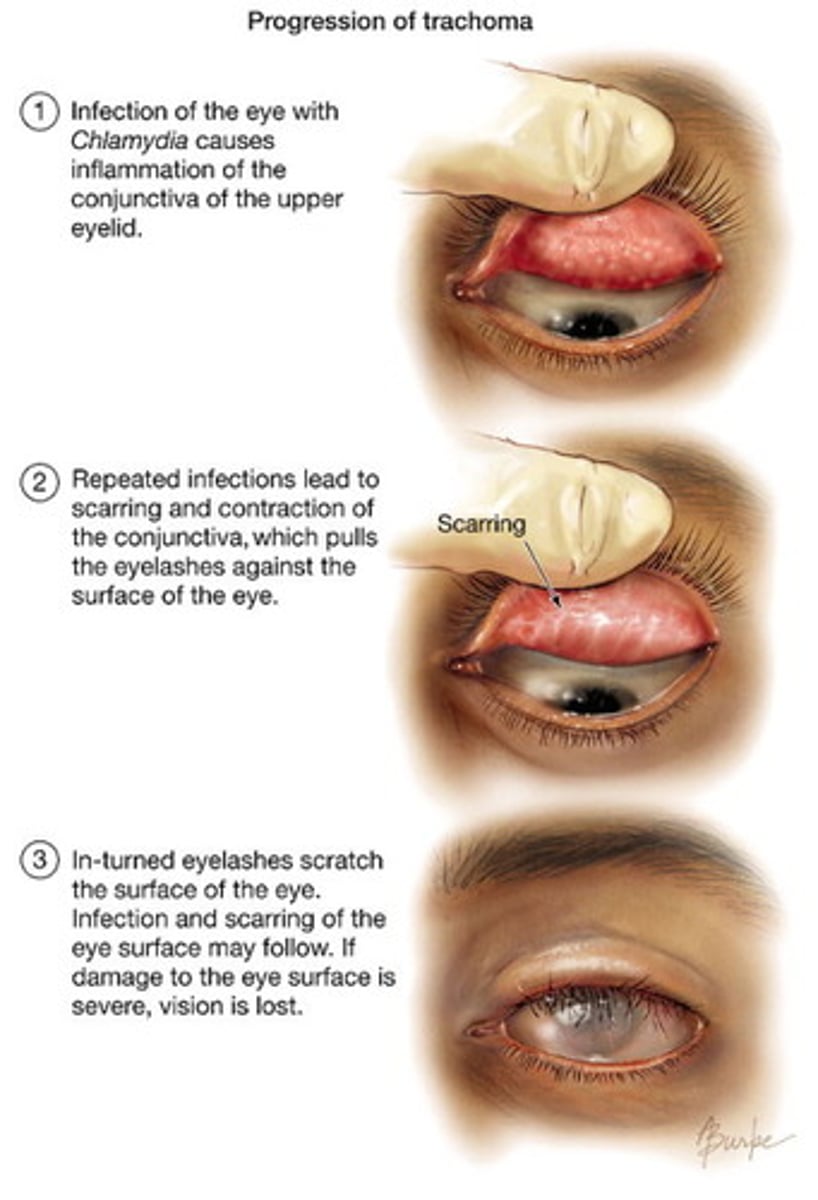
Trachoma
Chlamydia trachomatis
Inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea --> eyelid swelling, pain, photophobia, blindness
Transmission: Direct contact with infected ocular secretions, fomites, flies that have touched infected ocular secretions
Musca sorbens
Bazaar fly, eye seeking fly --> causes trachoma

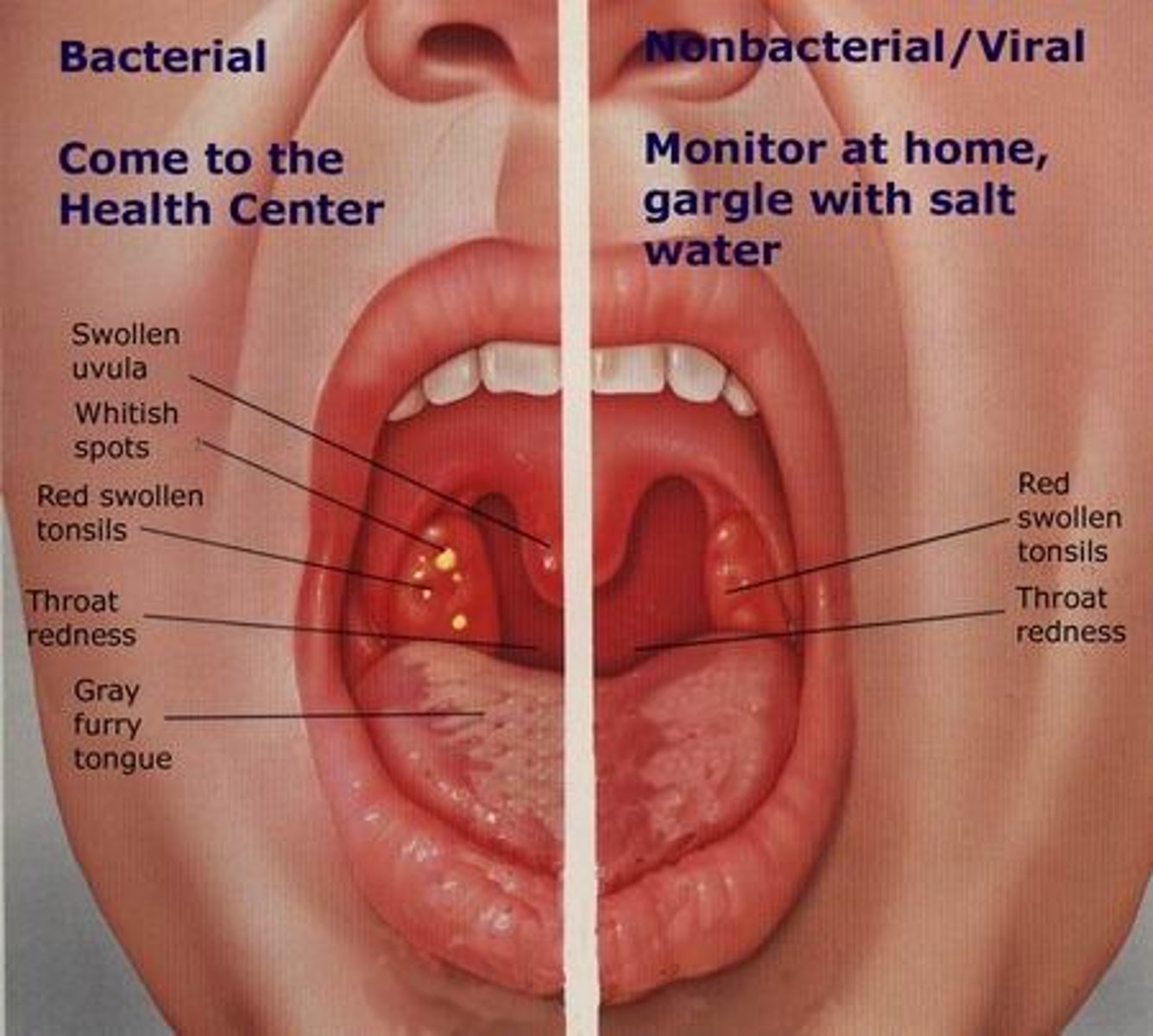
Streptococcal Pharyngitis
Streptococcus pyogenes
S+S: Inflammation of the pharynx, throat pain, dysphagia, fever, headache, enlarged tonsils, enlarged cervical lymph nodes
Transmission: Inhalation of or contact with infected oropharyngeal secretions
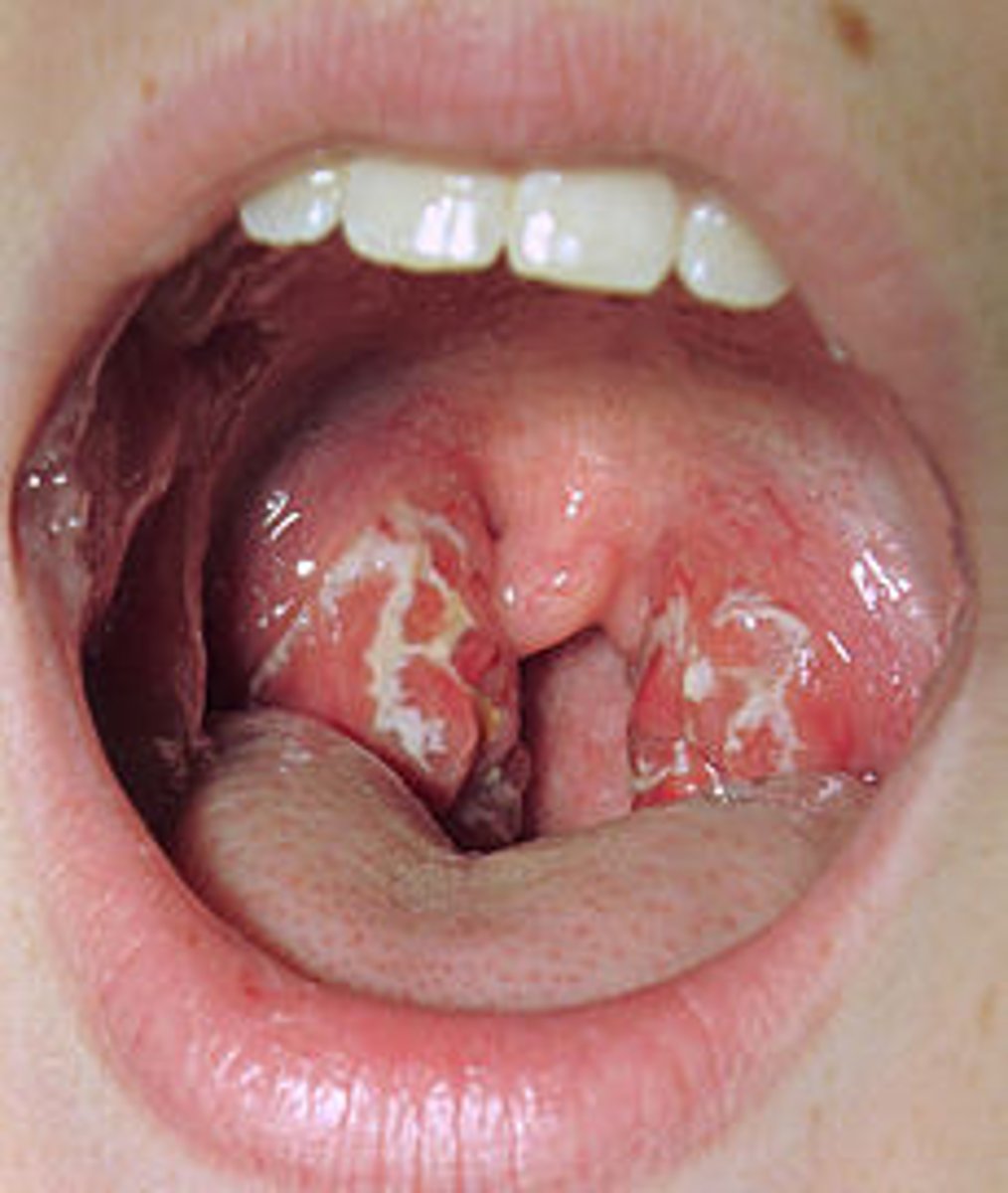
Diagnosis of strep throat
Rapid strep test where they swab the back of ur throat and you literally fight for your life trying not to gag and throw up all over the nurse lmao
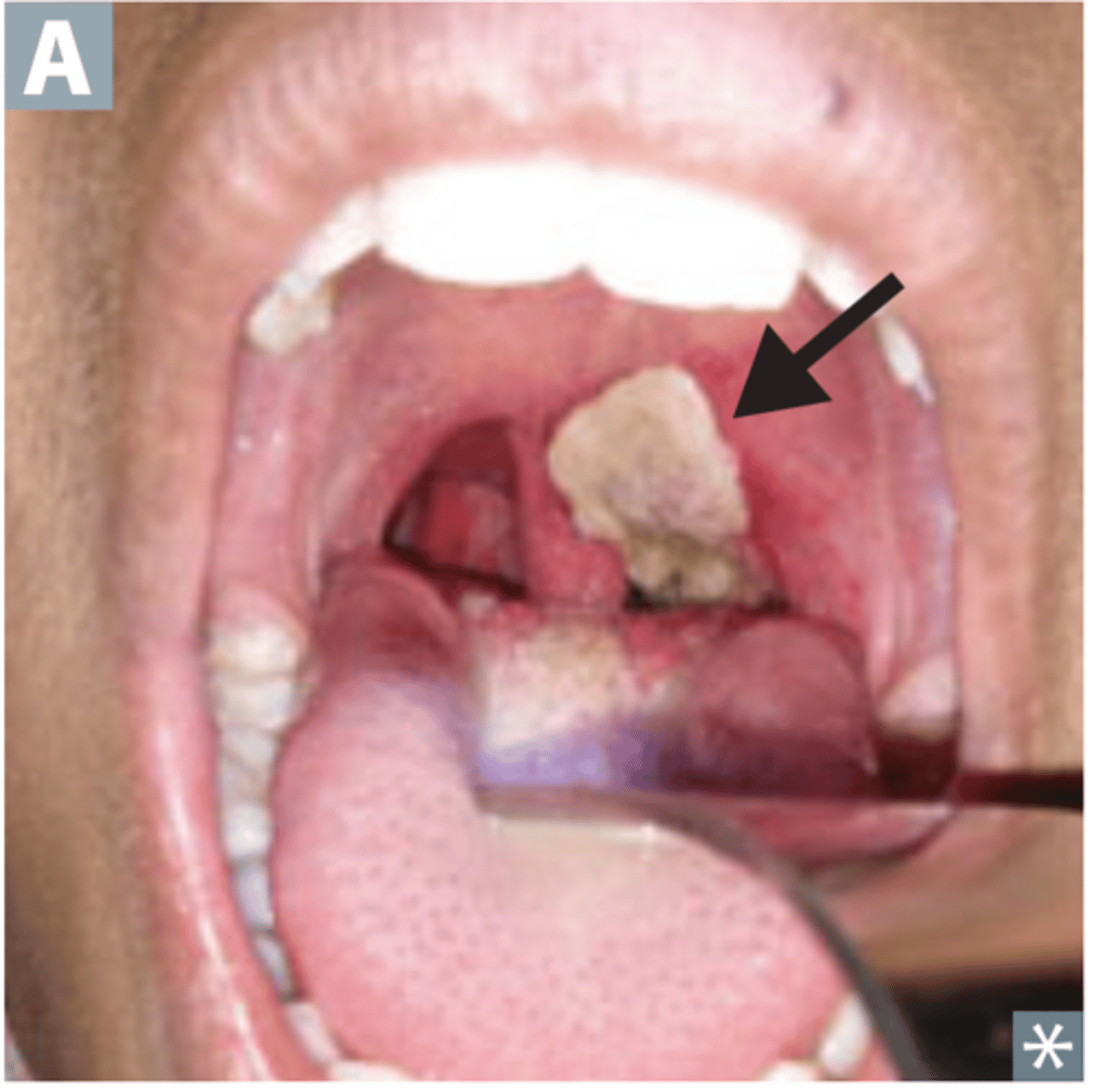
Diphtheria
Corynebacterium diphtheriae
S+S: Inflammation of the pharynx and larynx --> throat pain, dysphagia, fever, headache, enlarged tonsils, enlarged cervical lymph nodes, tough adherent grayish-white pseudomembrane in throat
Transmission: Inhalation of or contact with infected oropharyngeal secretions
Vaccine: DTaP or Tdap
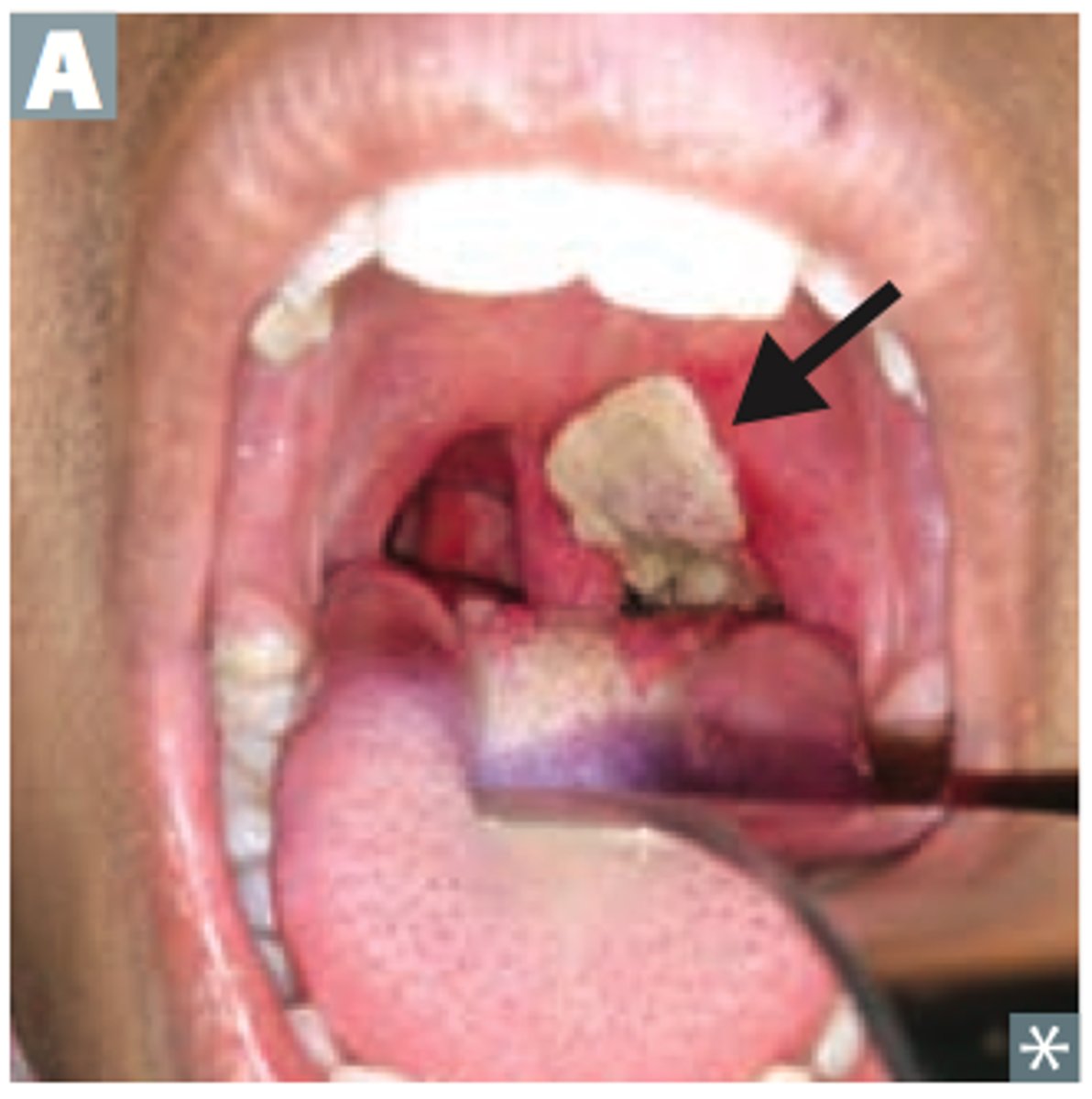
Pseudomembrane
A layer of exudate resembling a membrane, made of dead cells and bacteria --> causes severe airway obstruction, death
DTap/Tdap
Vaccine that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
Bordetella pertussis
SS+: Inflammation of the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tubes --> whooping cough
Prevention: DTap or Tdap vaccine
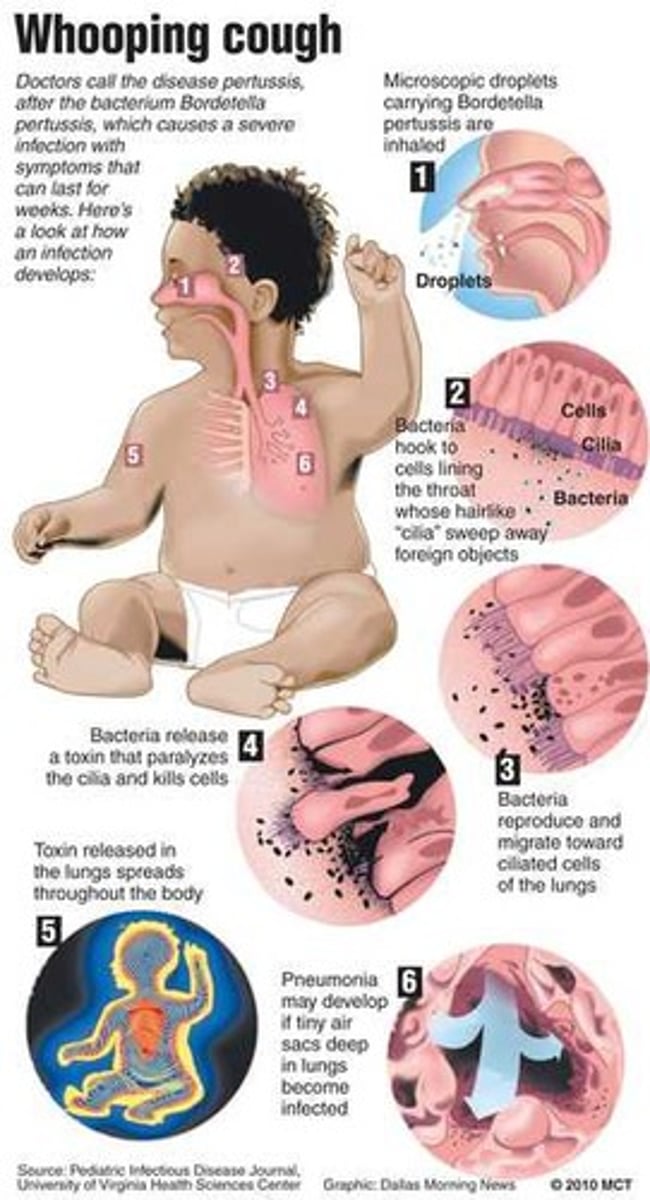
Prodromal stage of pertussis
Mild, cold-like symptoms
Paroxysmal stage of pertussis
Bouts of severe coughing (paroxysm) + "whooping" sound on inspiration

Convalescent stage of pertussis
Gradual cessation of the coughing
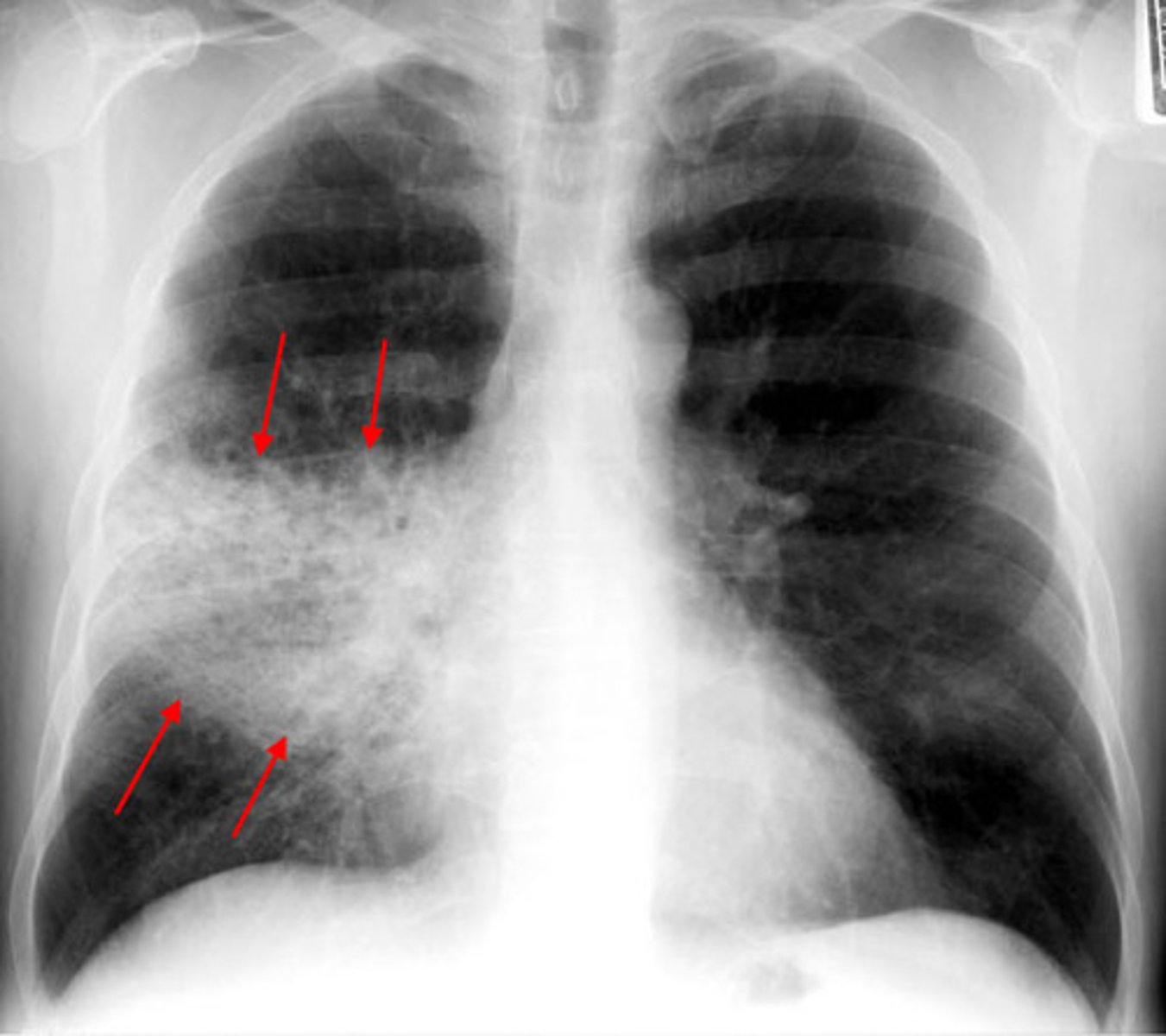
Typical Pneumonia
Pathogen: Streptococcus pneumoniae
S+S: Inflammation of the alveoli in one or both lungs --> Rapid onset of chest pain, dyspnea, high fever, productive cough
X-Ray: Looks equal to S+S severity - lobar involvement
Transmission: Inhalation of or contact with infected oropharyngeal secretions
Legionnaires' Disease (Pontiac fever)
Pathogen: Legionella pneumophila
S+S: Inflammation of the alveoli in one or both lungs --> Rapid onset of chest pain, dyspnea, high fever, productive cough
Transmission: Inhalation of contaminated mist and dust particles
Reservoirs: Hot water, humidifiers, shower heads
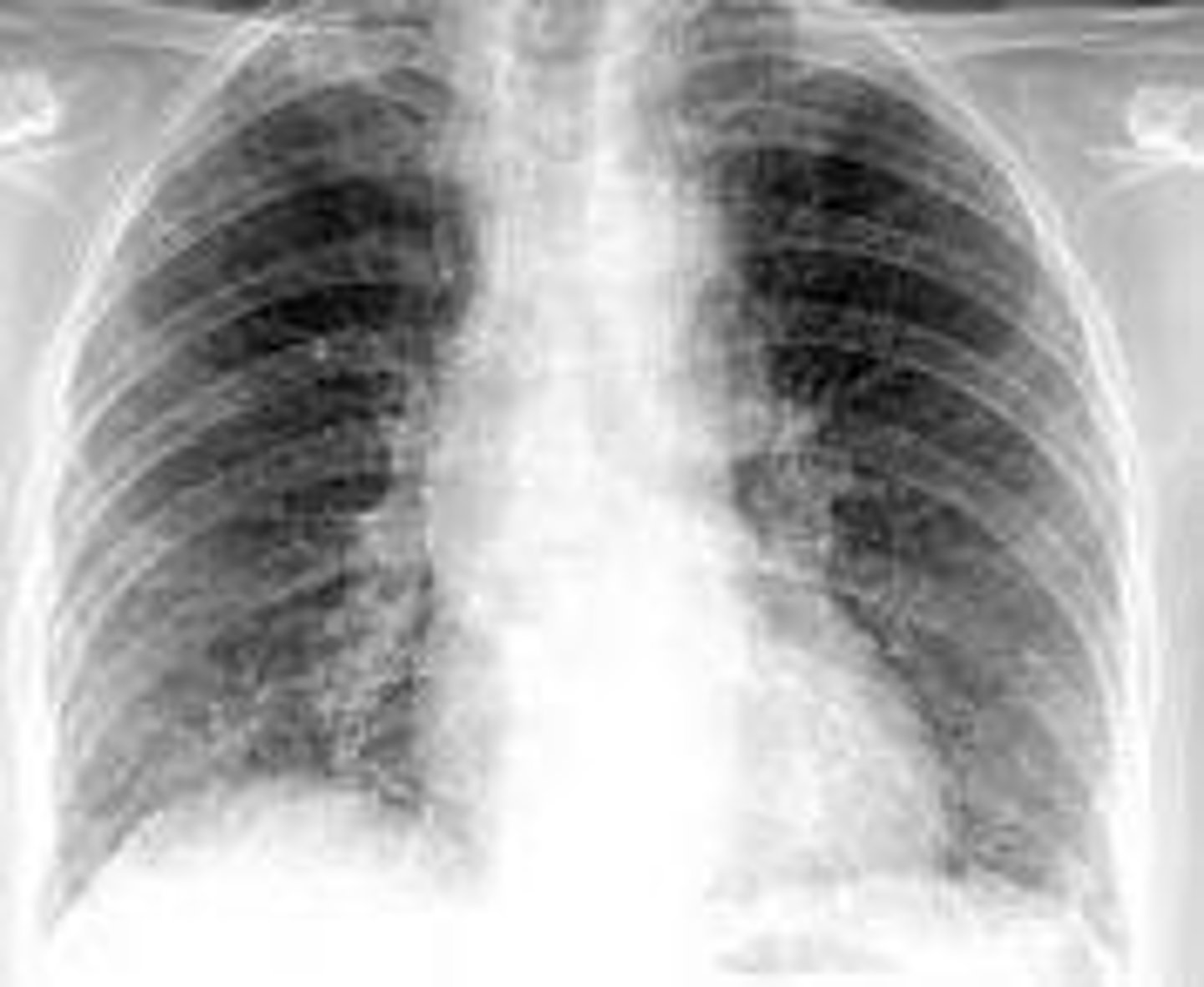
Atypical (walking) Pneumonia
Pathogen: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
S+S: Inflammation of the alveoli in one or both lungs --> Slow onset of dry cough and mild fever, NO chest pain/dyspnea
X-Ray: Look worse than symptoms - interstitial involvement
Transmission: Inhalation of/contact with infected oropharyngeal secretions
Psittacosis/Ornithosis/Parrot Fever
Pathogen: Chlamydophila psittaci
S+S: Inflammation of the alveoli in one or both lungs --> Slow onset of dry cough and mild fever, NO chest pain/dyspnea, Horder spots
Transmission: Inhalation of respiratory secretions of birds
Reservoirs: Birds

Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB)
Pathogen: Mycobacterium tuberculosis
S+S: Inflammation of the alveoli
Transmission: Inhalation of infected respiratory/oropharyngeal secretions (coughing, sneezing)

How to test for TB?
Skin test or blood test --> if positive, sputum smear and x-ray to confirm
Latent TB infection
TB bacteria is present in the body, but there is no evidence that the bacterium is growing/causing disease --> TB skin/blood test is positive, but no other S+S, NOT contagious
TB disease
TB bacteria is causing disease --> fever, weight loss, cough, dyspnea, hemoptysis, positive TB test/abnormal x-ray, CONTAGIOUS
https://www.sciencehistory.org/distillations/podcast/vampire-panic
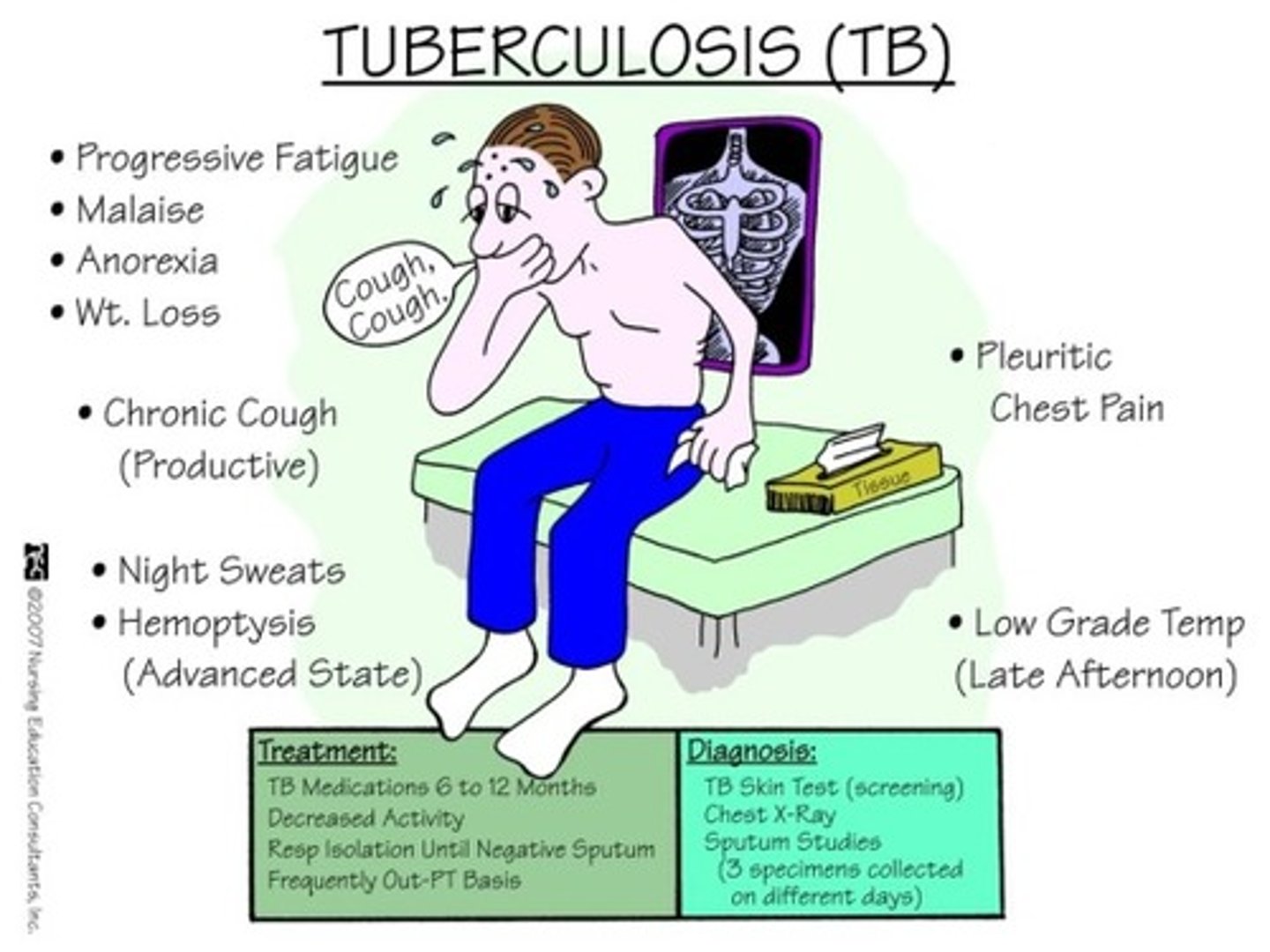
prevention of pulmonary tuberculosis
preventing exposure when traveling abroad, trating LTBI, Bacille Calmette-Guerin BCG vaccine - single dose is recommended soon after birth in countries w/ high burden of TB disease
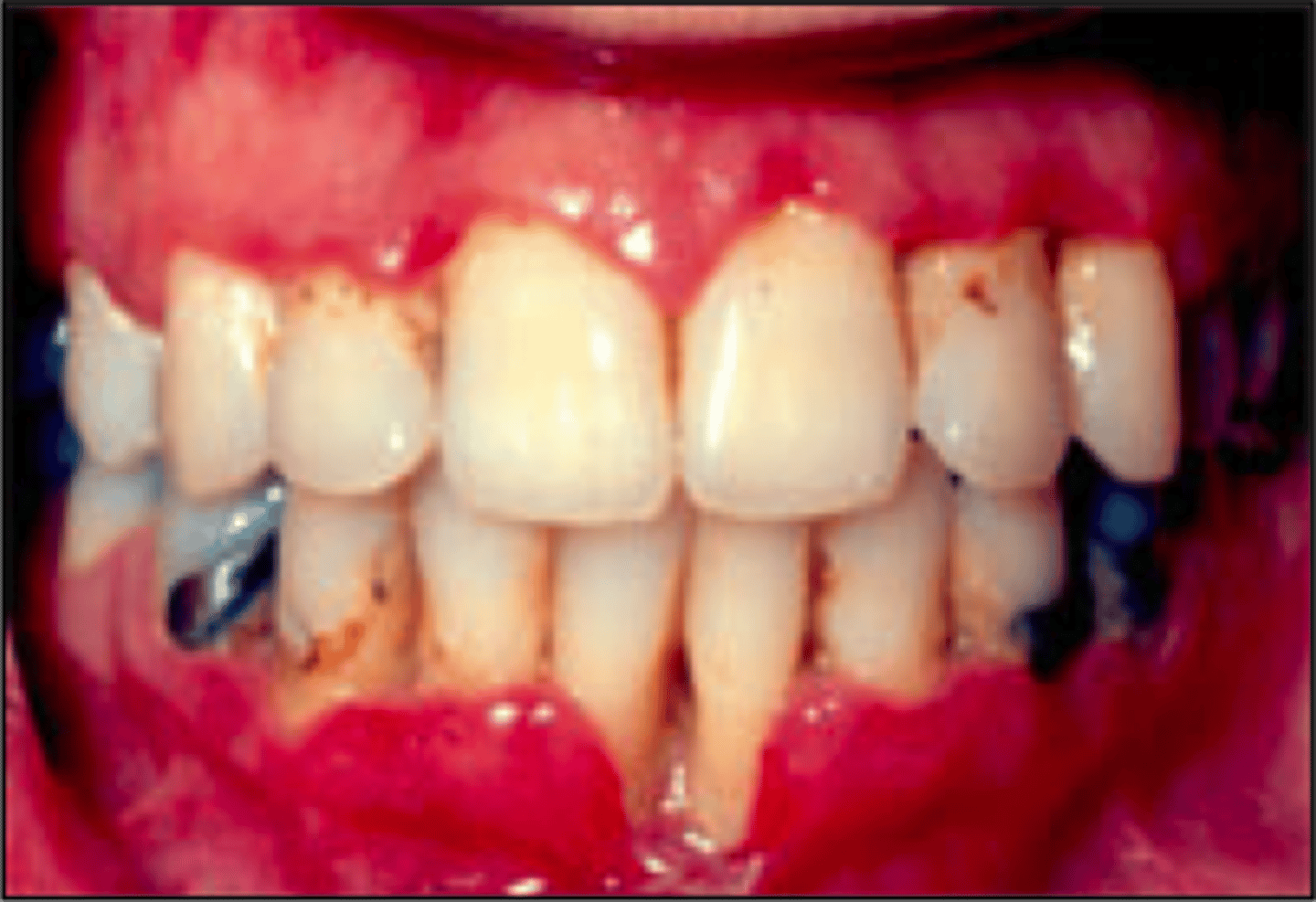
Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis/Trench Mouth
Pathogen: 2 or more species of anaerobic bacteria
S+S: Painful bleeding of the gingivae, fever, swollen cervical lymph nodes, extreme halitosis
Prevention: Maintain good oral hygiene (not contagious)
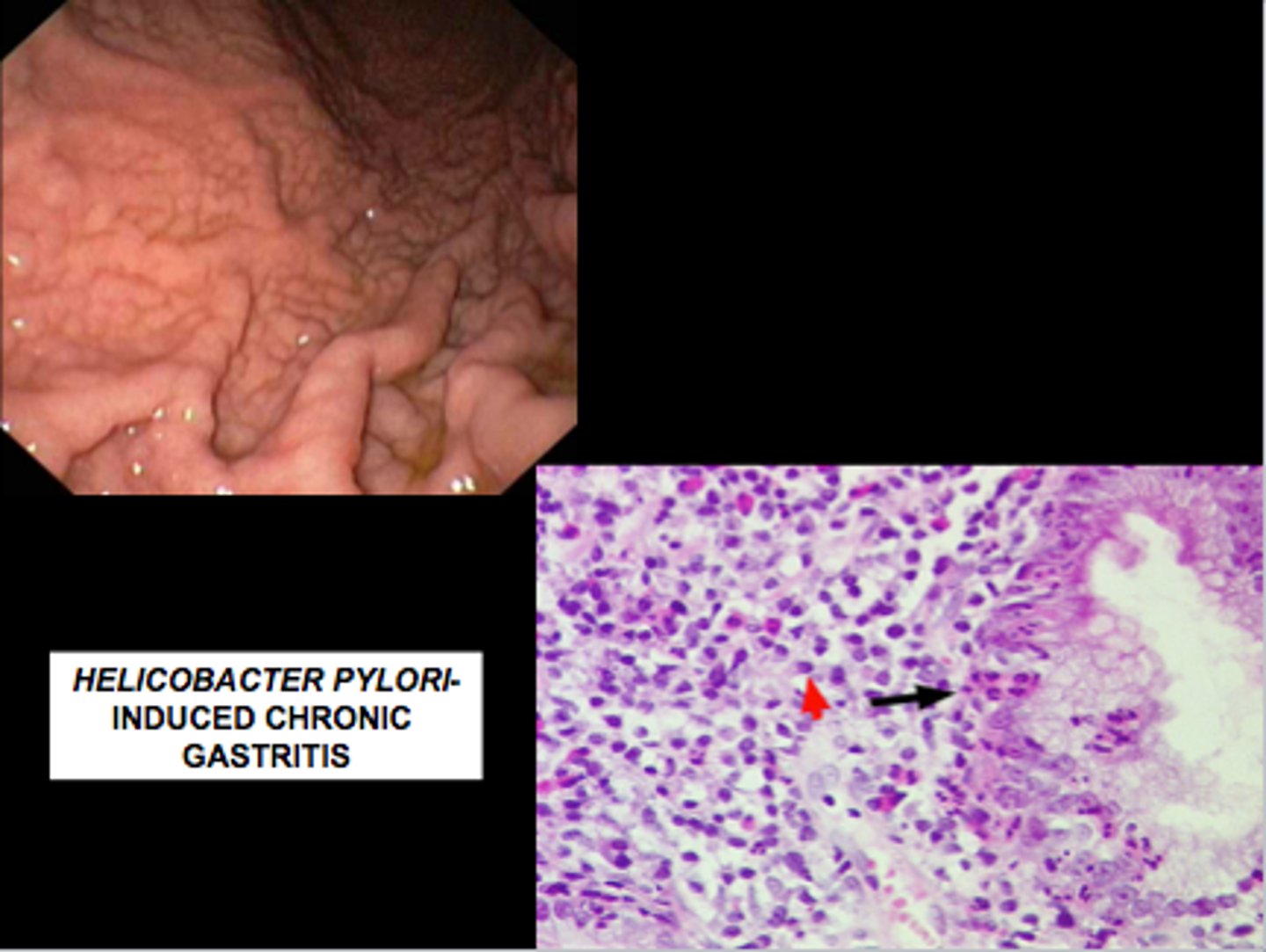
Chronic Bacterial Gastritis
Pathogen: Helicobacter pylori
S+S: Chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa --> early satiety, indigestion, nausea, vomiting, ulcer formation, pyrosis when the stomach is empty, epigastric pain
Transmission: Saliva, fecal-oral route
Typhoid Fever
Salmonella typhi, Salmonella paratyphi
S+S: Fever, malaise, severe headache, dry cough, loss of appetite, rose spots
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, ingestion of contaminated food or water, vectors (houseflies)

Rose spots
Red macular rash on the chest/abdomen caused by typhoid infection
Campylobacter Enteritis
Pathogen: Campylobacter jejuni
S+S: Acute inflammation of the small intestine --> nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, diarrhea --> lasts 2-5 days
Reservoirs: Pigs, cattle, chicken
Transmission: ingestion of infected chicken, beef, pork, or food prepared on contaminated cutting boards

Cholera
Pathogen: Vibrio cholerae
S+S: Profuse watery diarrhea, vomiting, rapid dehydration --> death in 50% of untreated cases
Reservoirs: Shellfish
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, ingestion of contaminated food or water, vectors (houseflies)

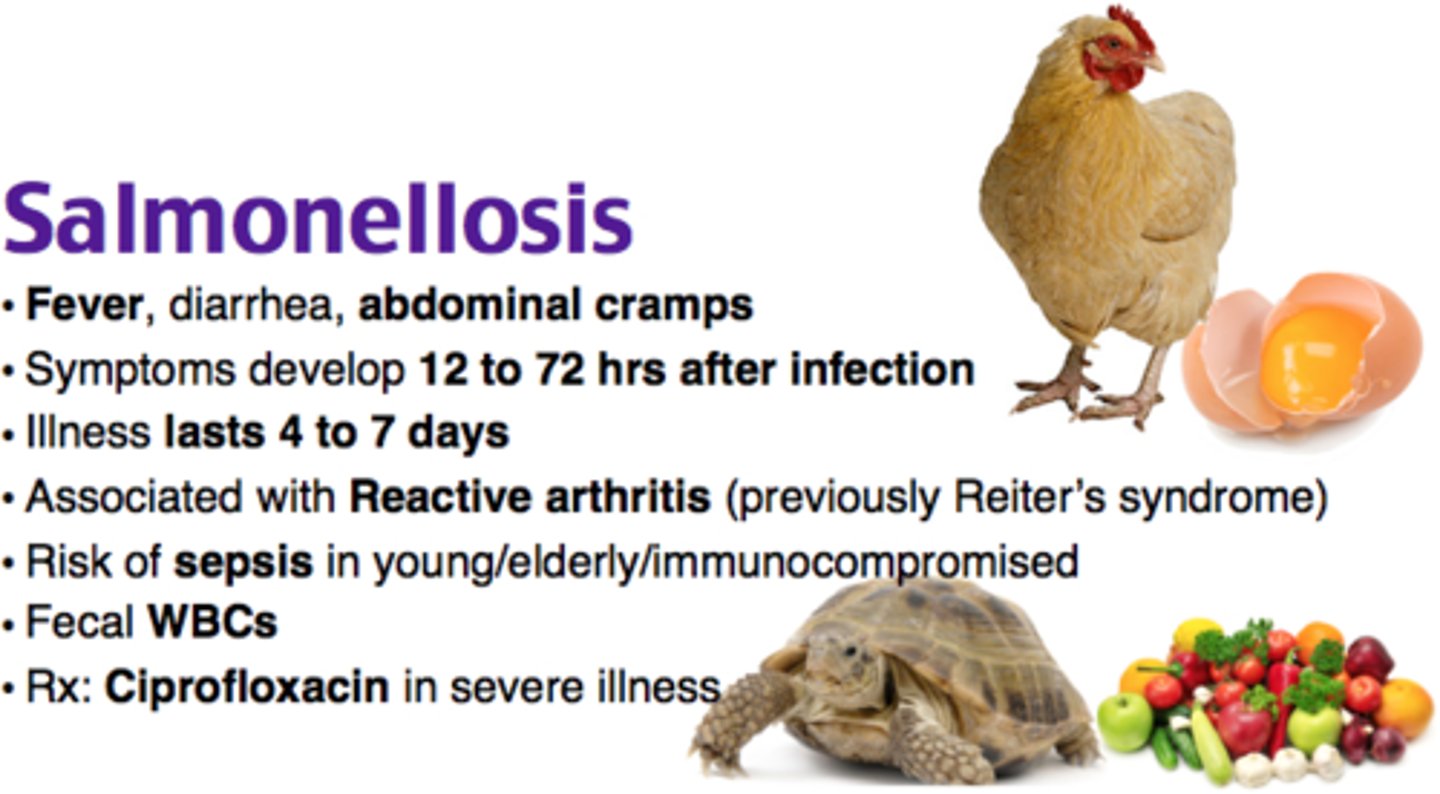
Salmonellosis
Pathogen: Salmonella enterica
S+S: Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Reservoirs: Pigs, chicken, cattle
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, ingestion of infected chicken, beef, pork, incompletely cooked eggs
Shigellosis
Pathogen: Shigella dysenteriae
S+S: Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, dysentery
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, ingestion of contaminated food or water

Clostridium difficile Colitis
Pathogen: Clostridium difficile
S+S: Inflammation of the colon --> bloody diarrhea 1-2 weeks after starting oral antibiotic therapy
Transmission: Fecal-oral route (spores persist on surfaces for weeks)
EHEC Enterocolitis
Pathogen: Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (common strain is O157:H7)
S+S Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, dysentery
Reservoirs: Humans, cattle
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, ingestion of infected beef, contaminated fruits, green leafy vegetables, or fluids

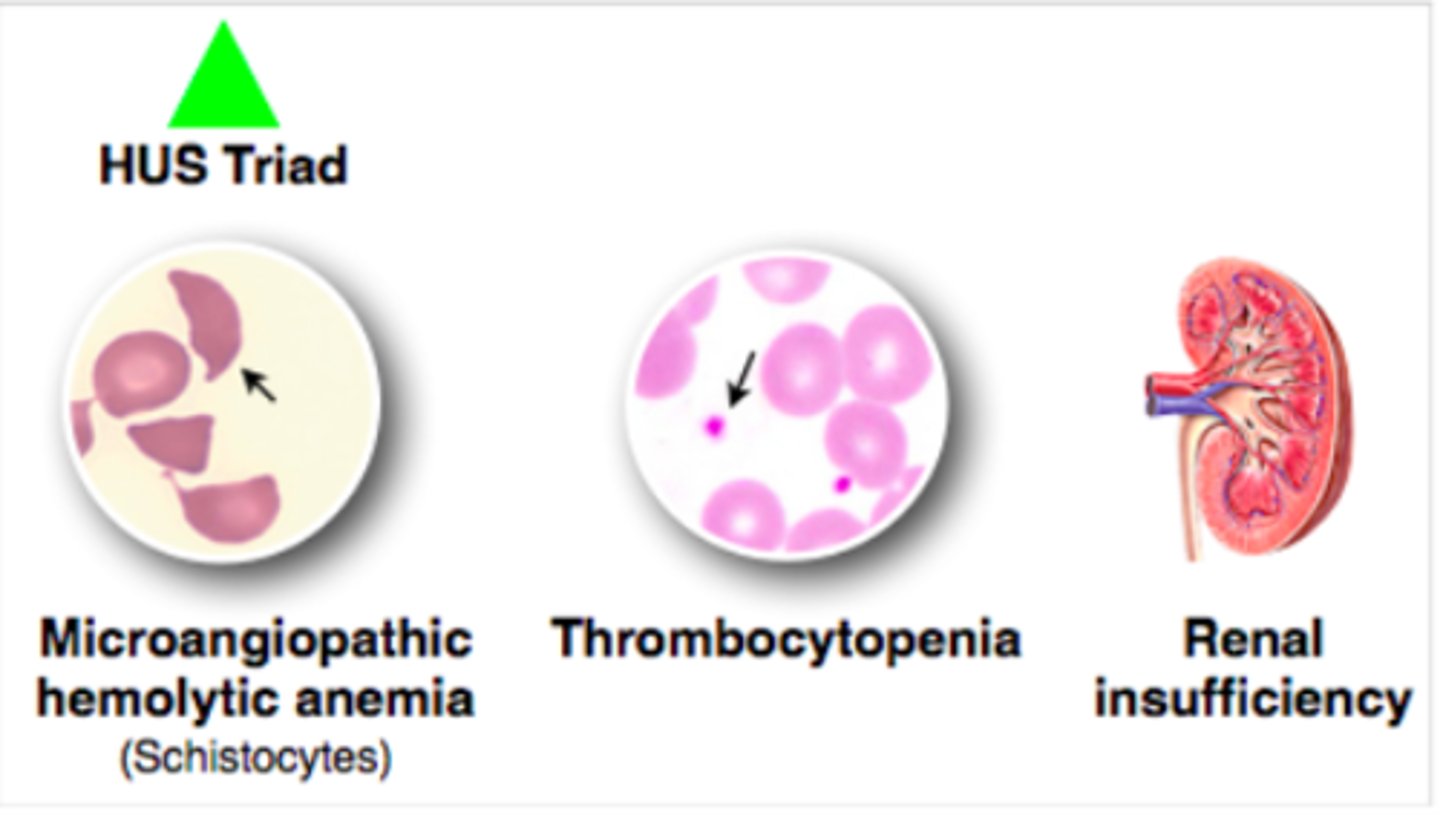
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Complication of EHEC Enterocolitis, destruction of RBCs and platelets by shiga toxin --> acute kidney failure
ETEC Enterocolitis
Pathogen: Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
LT strain produces a heat labile toxin
ST strain produces a heat stable toxin
S+S: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea
Reservoirs: Humans, cattle
Transmission: Fecal-oral route, ingestion of infected beef, contaminated fruits, green leafy vegetables, or fluids
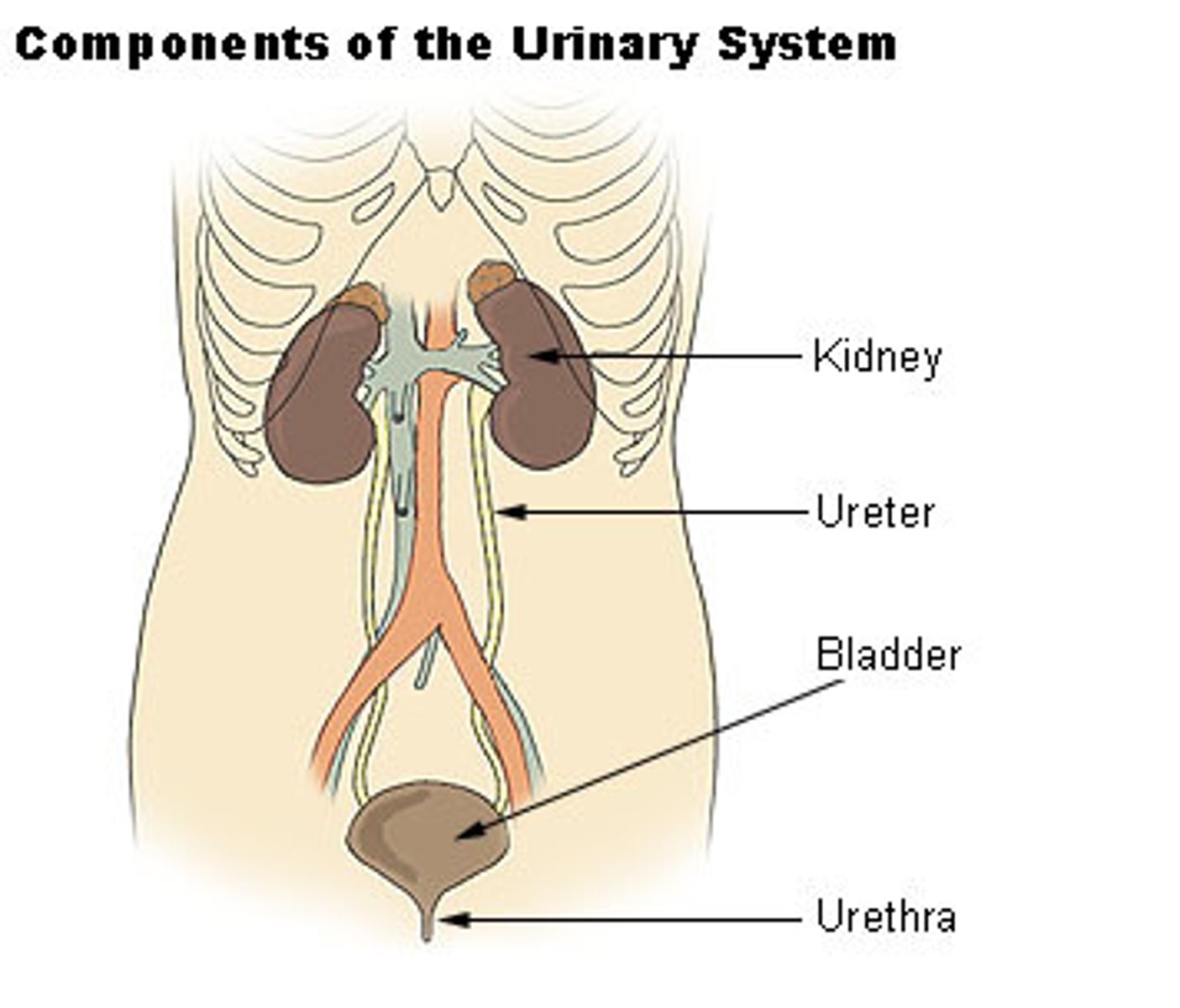
Urinary Tract Infections
Pathogen: Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydia trachomatis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escheria coli
S+S: upper UTI’s - fever, chills, lumbar pain; lower UTI’s - fever, pelvic, pelvic discomfort, a persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, hematuria, redness around the opening of the urethra
Transmission: Urinary catheterization, person to person by sexual contact
Gonorrhea
Pathogen: Neisseria gonorrhoeae
S+S: Urethral --> dysuria, purulent discharge from penis or vagina within one week after infection, pain
Rectal --> anal itching, purulent discharge/bleeding from rectum
Oropharyngeal --> sore throat, dysphagia, swollen cervical lymph nodes
Transmission: Person to person by sexual contact
Chlamydia
Pathogen: Chlamydia trachomatis
S+S: Urethral --> dysuria, purulent discharge from the penis or vagina within 2 weeks after infection, pain
Rectal --> Anal itching, purulent discharge/bleeding from the rectum
Oropharyngeal --> Sore throat, dysphagia, swollen cervical lymph nodes
Transmission: Person to person by sexual contact
Syphilis
Pathogen: Treponema pallidum
S+S: Vary depending upon the stage
Transmission: Person-to-person by sexual contact
Primary Syphilis
Hardened, painless chancre develops 3 weeks after exposure
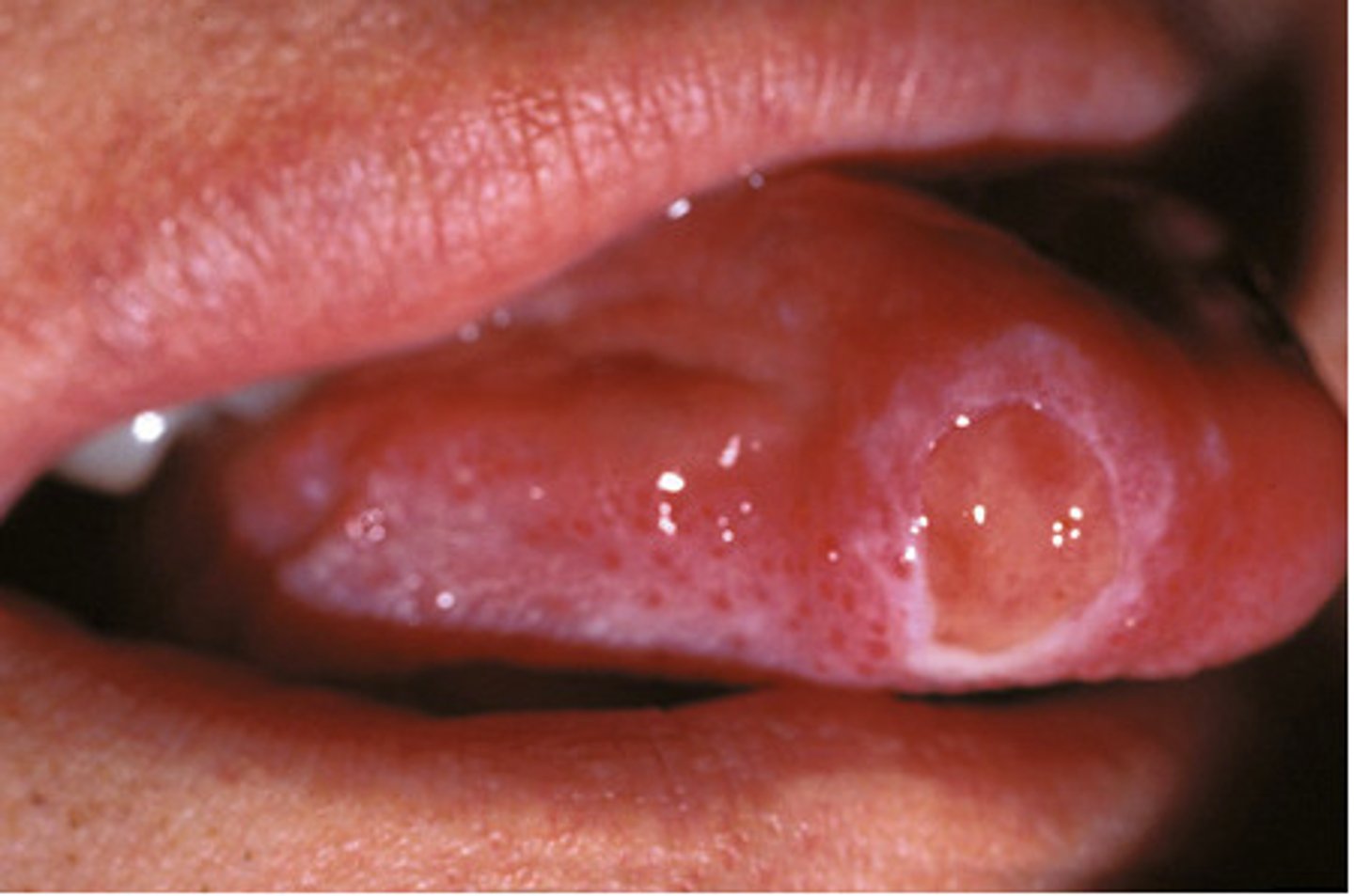
Secondary Syphilis
Chancre curls inward and a rash develops about 4 to 6 weeks after exposure; rash resolves within weeks to 12 months
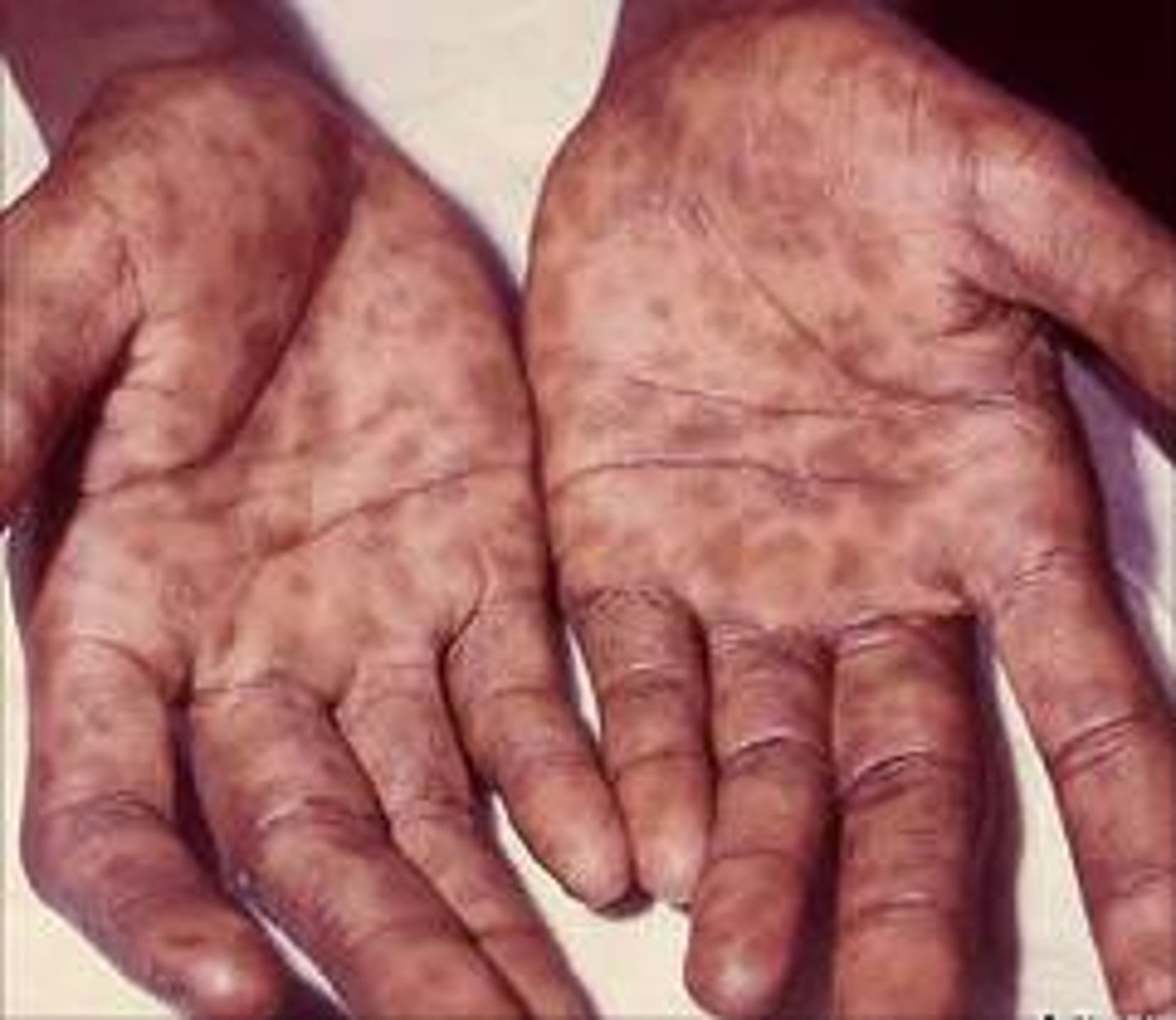
Latent Syphilis
No symptoms; may last for weeks to years; sometimes continues throughout life
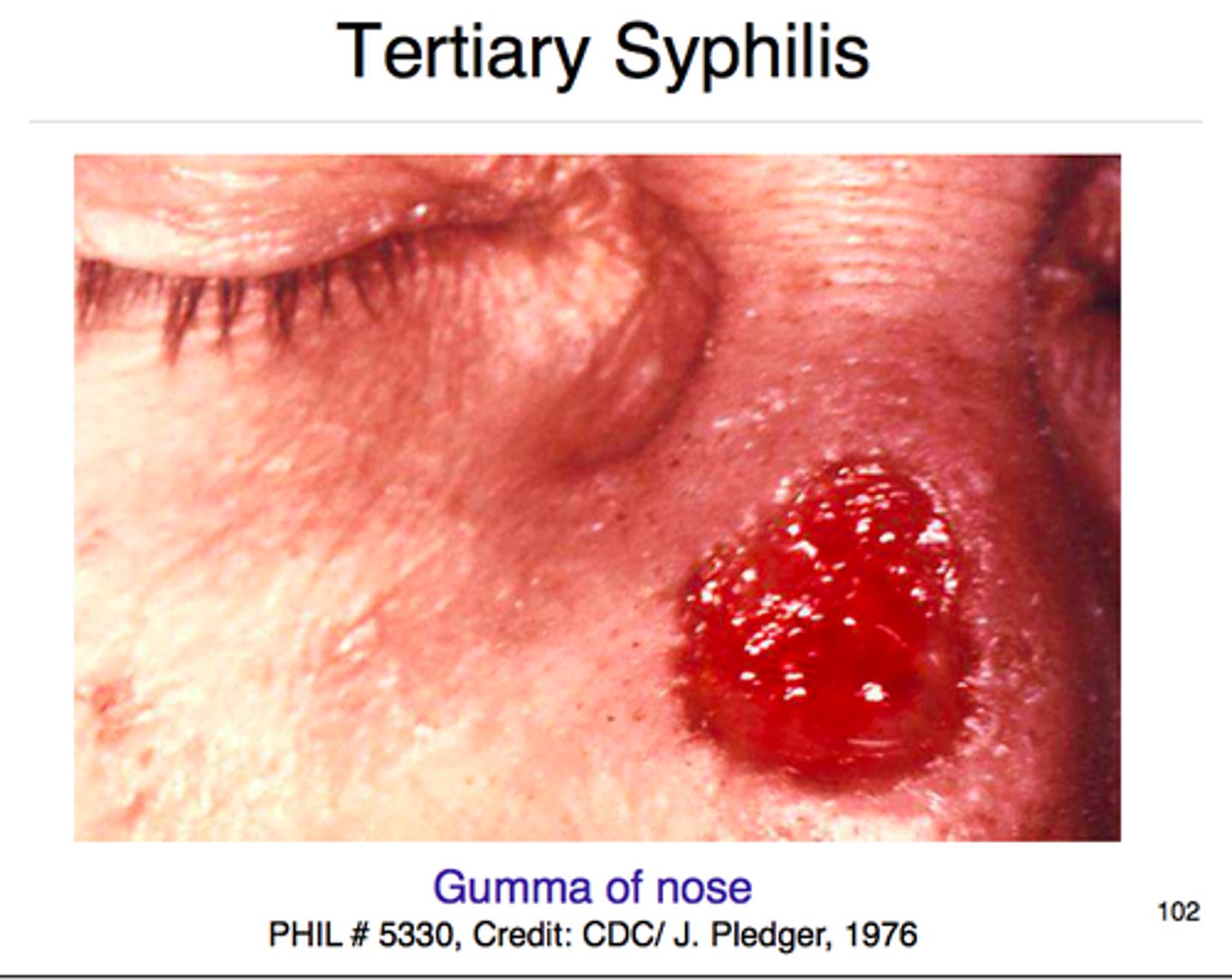
Tertiary Syphilis
CNS, cardiovascular, and other symptoms (sometimes death) occur 5 to 20 years after exposure, gummas
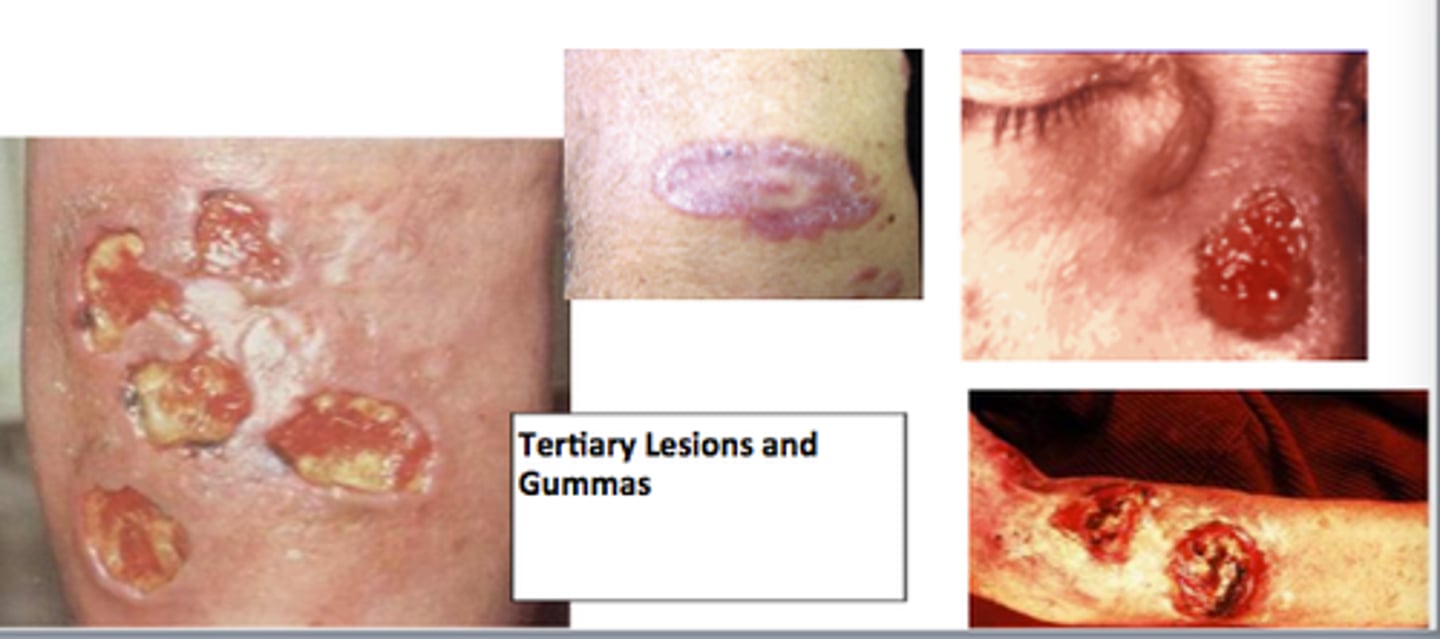
Gummas
Soft, rubbery tumors seen in tertiary syphilis
Congenital syphilis
S+S: Failure to gain weight, loss of hearing, loss of vision, skeletal abnormalities, scarring of the skin around the genitals, teeth abnormalities
Transmission: Mother to baby via placenta
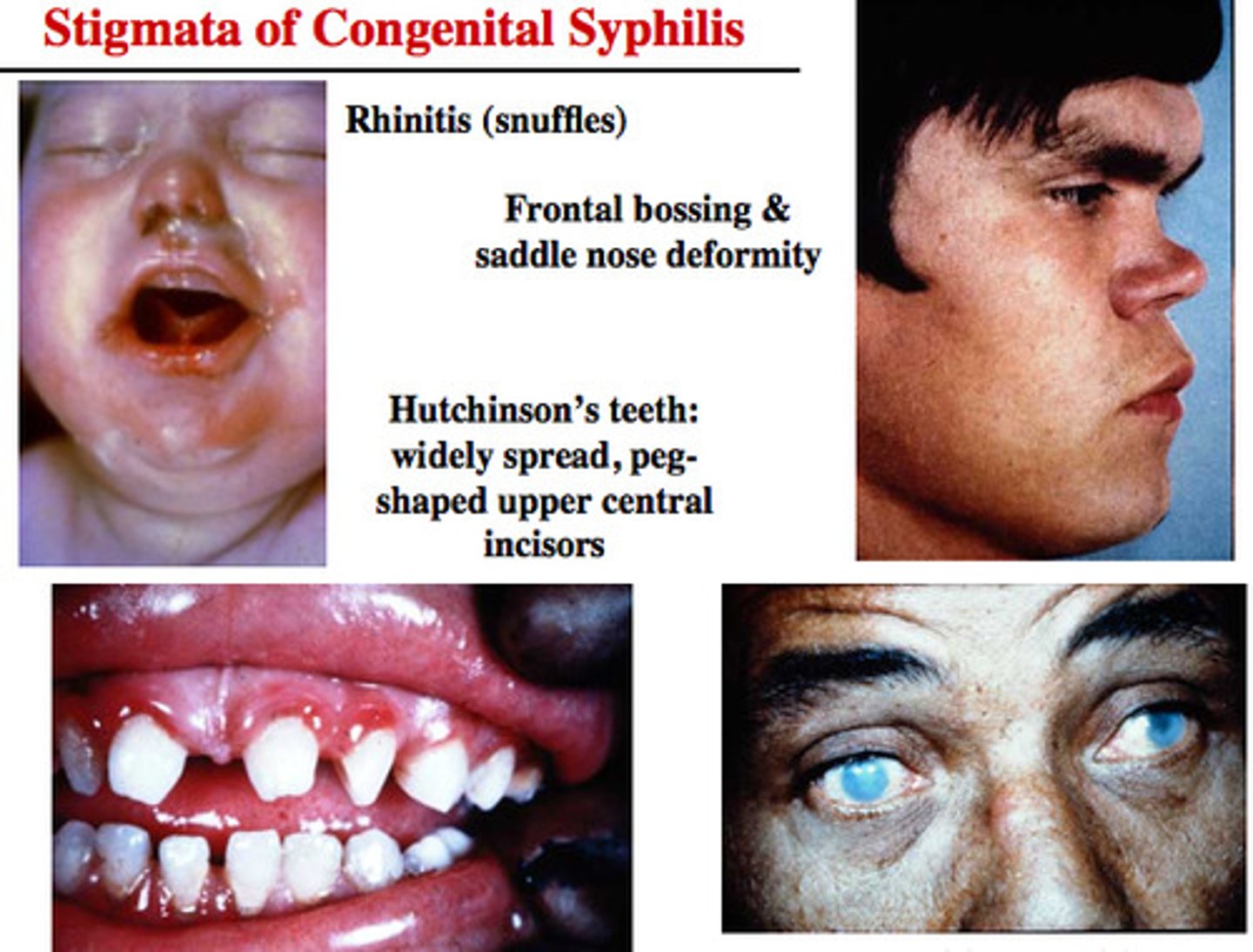
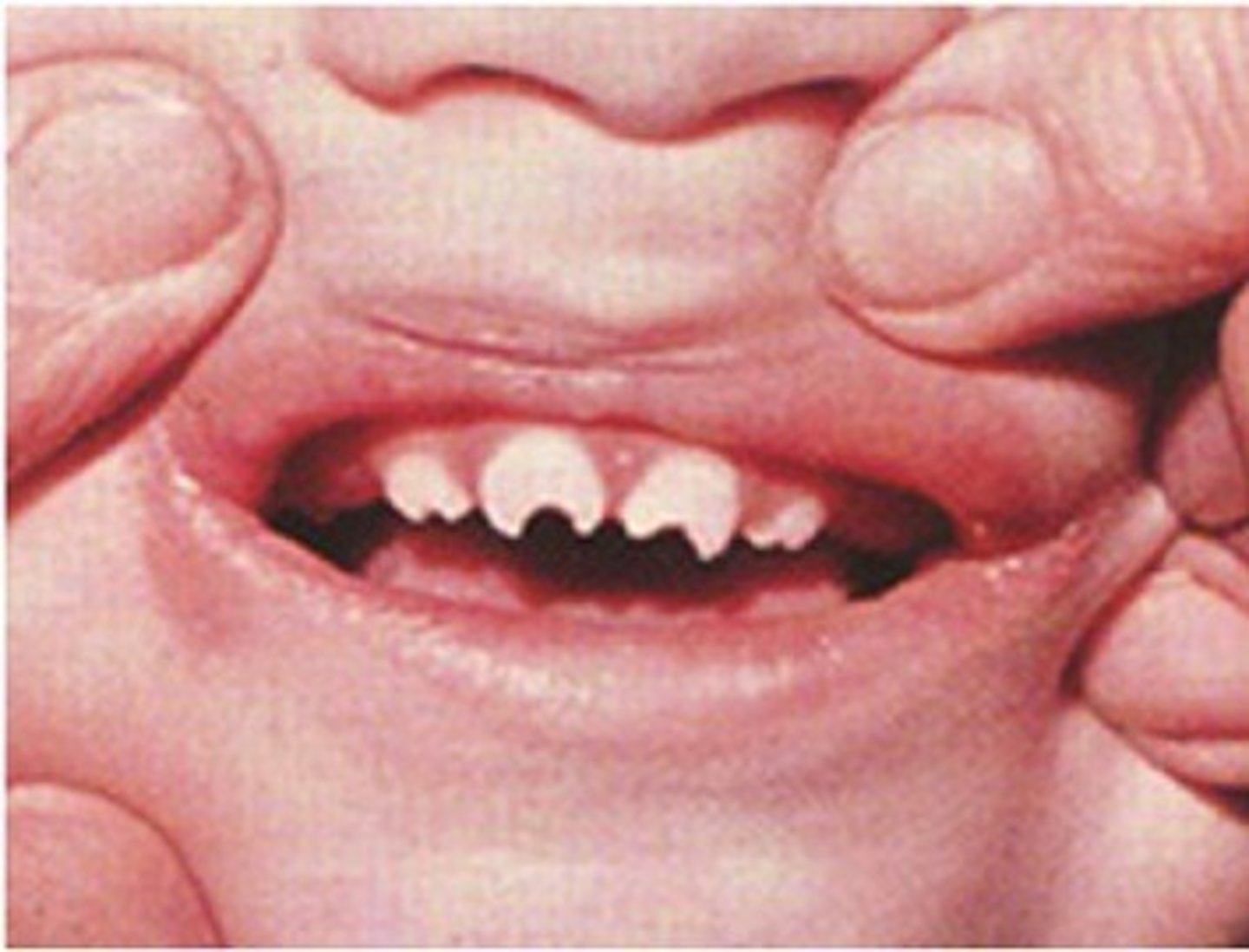
Hutchinson teeth
Peg-shaped teeth; seen in congenital syphilis
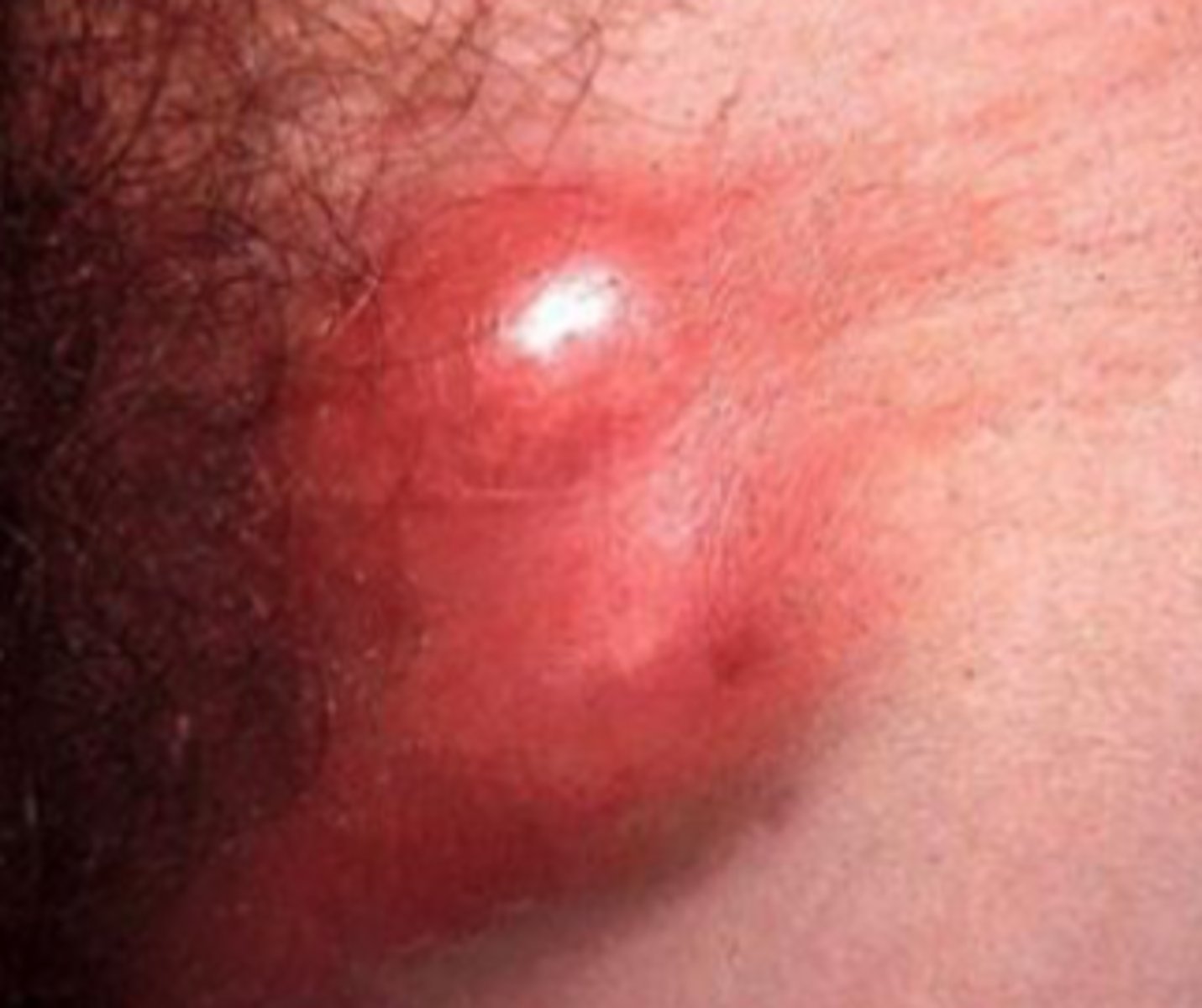
Chancroid
Pathogen: Haemophilus ducreyi
S+S: Small, painful papules appear within 1 week of infection --> break down into shallow, painful ulcers w/ elevated erythematous edges, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes
Transmission: Person-to-person by sexual contact
Lymphogranuloma Venereum
Pathogen: Chlamydia trachomatis
S+S: Small, painless, ulcer on the genitals --> chronic inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes --> buboes
Transmission: Person-to-person by sexual contact
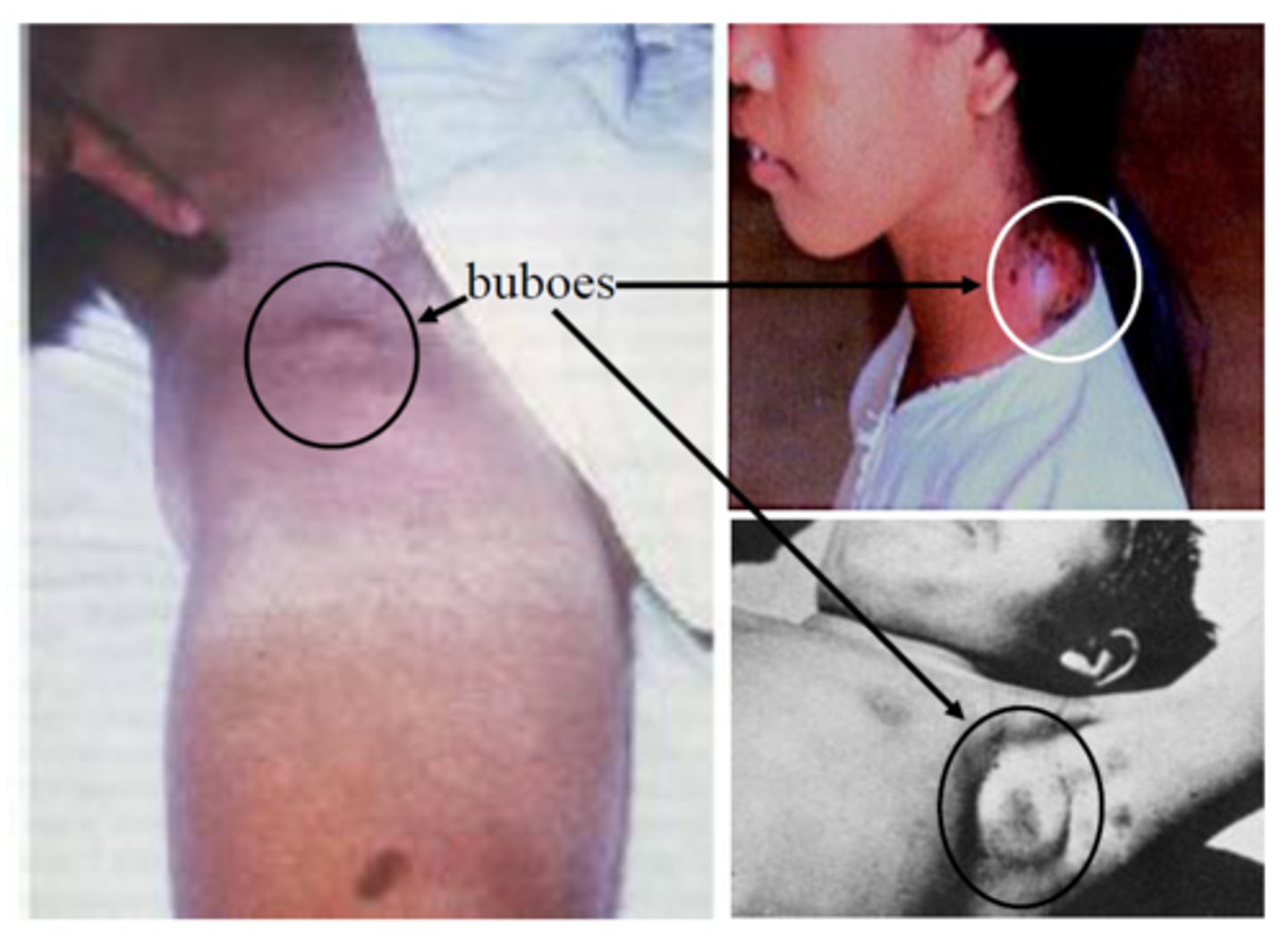
Buboes
A swollen, inflamed lymph node in the armpit or groin
Bacterial Vaginosis
Pathogen: Several anaerobic bacteria
S+S: Inflammation of the vagina --> grayish-white discharge --> itchin' and burnin', stanky and fishy
Transmission: unknown, sexual contact??
Risk factors: Douching, multiple sex partners

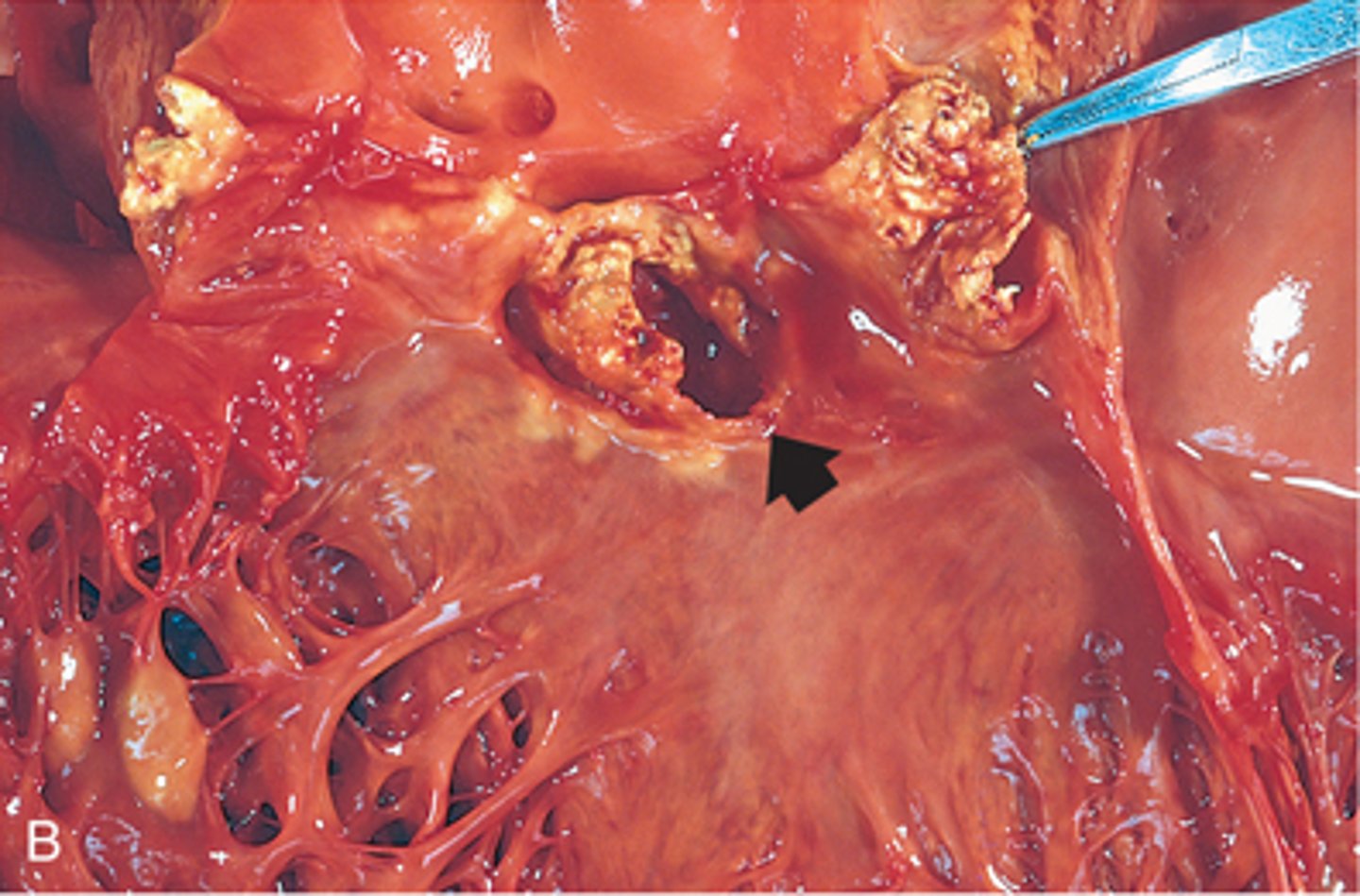
Infective Endocarditis
Pathogen: Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes
S+S: "Vegetations" on the endocardium, fever, heart murmurs, myalgia, Osler's nodes, Janeway's lesions
Transmission: Entry of bacteria into the bloodstream following tooth brushing, oral surgery, phlebotomy, IV, injections
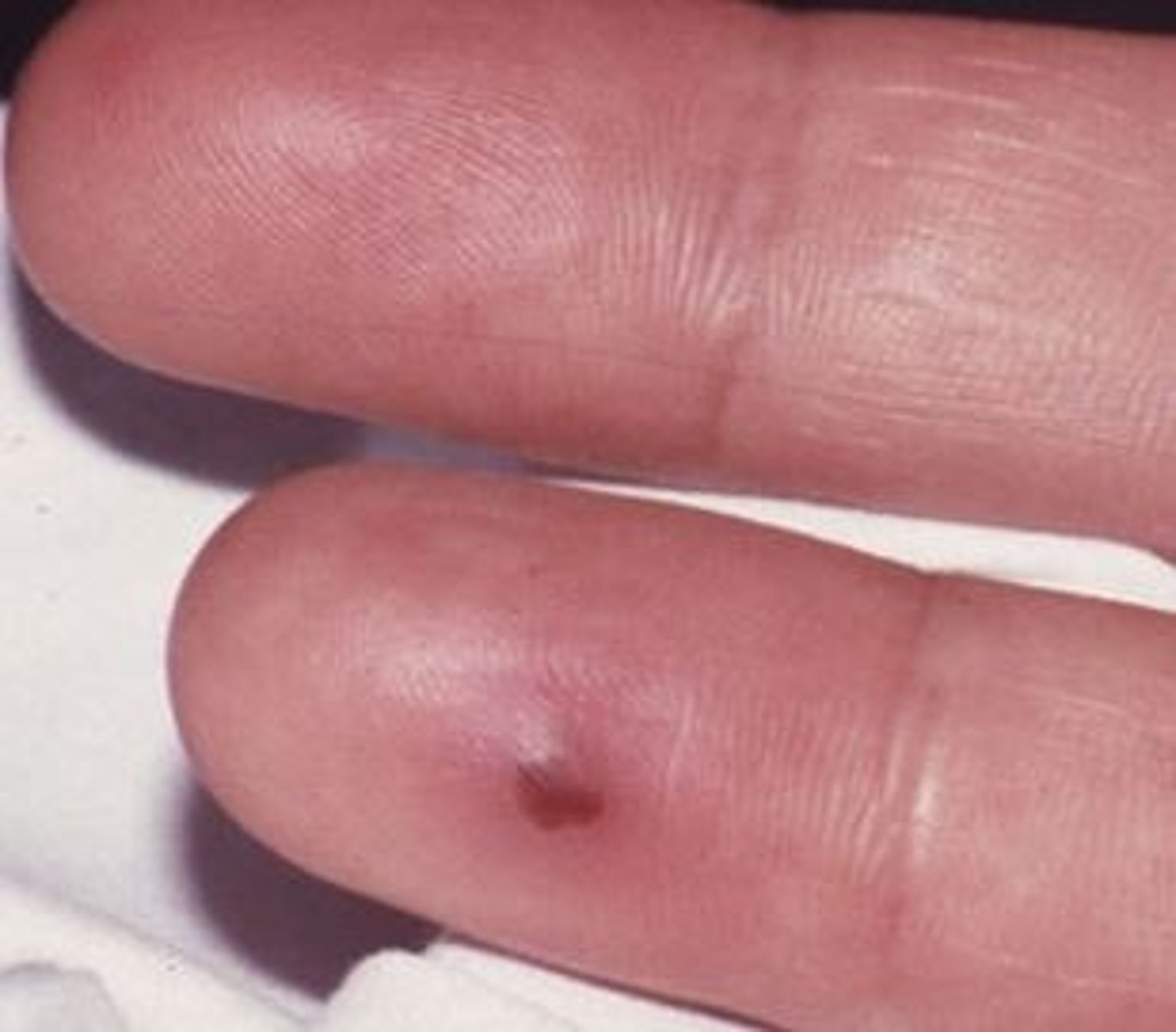
Osler's nodes
Painful erythematous nodules on fingers and toes
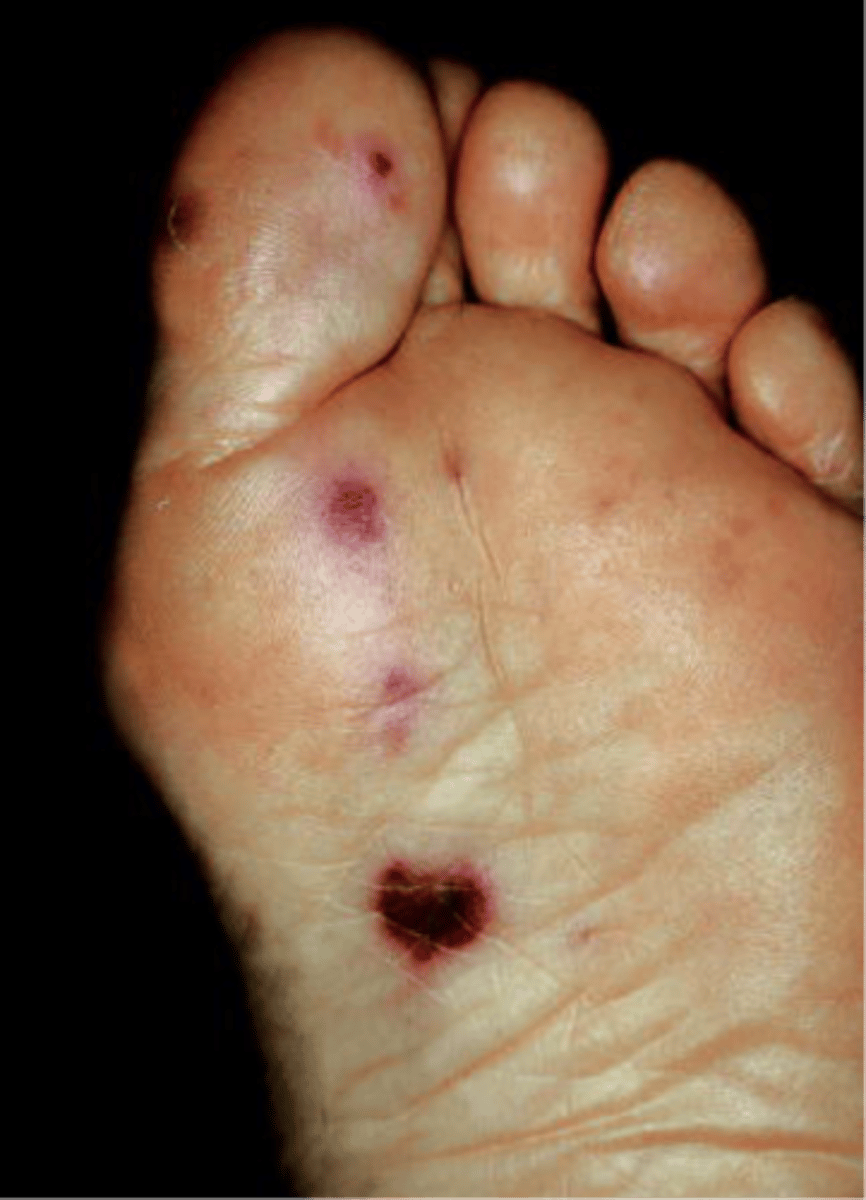
Janeway's lesions
Painless erythematous nodules on palms and soles of feet
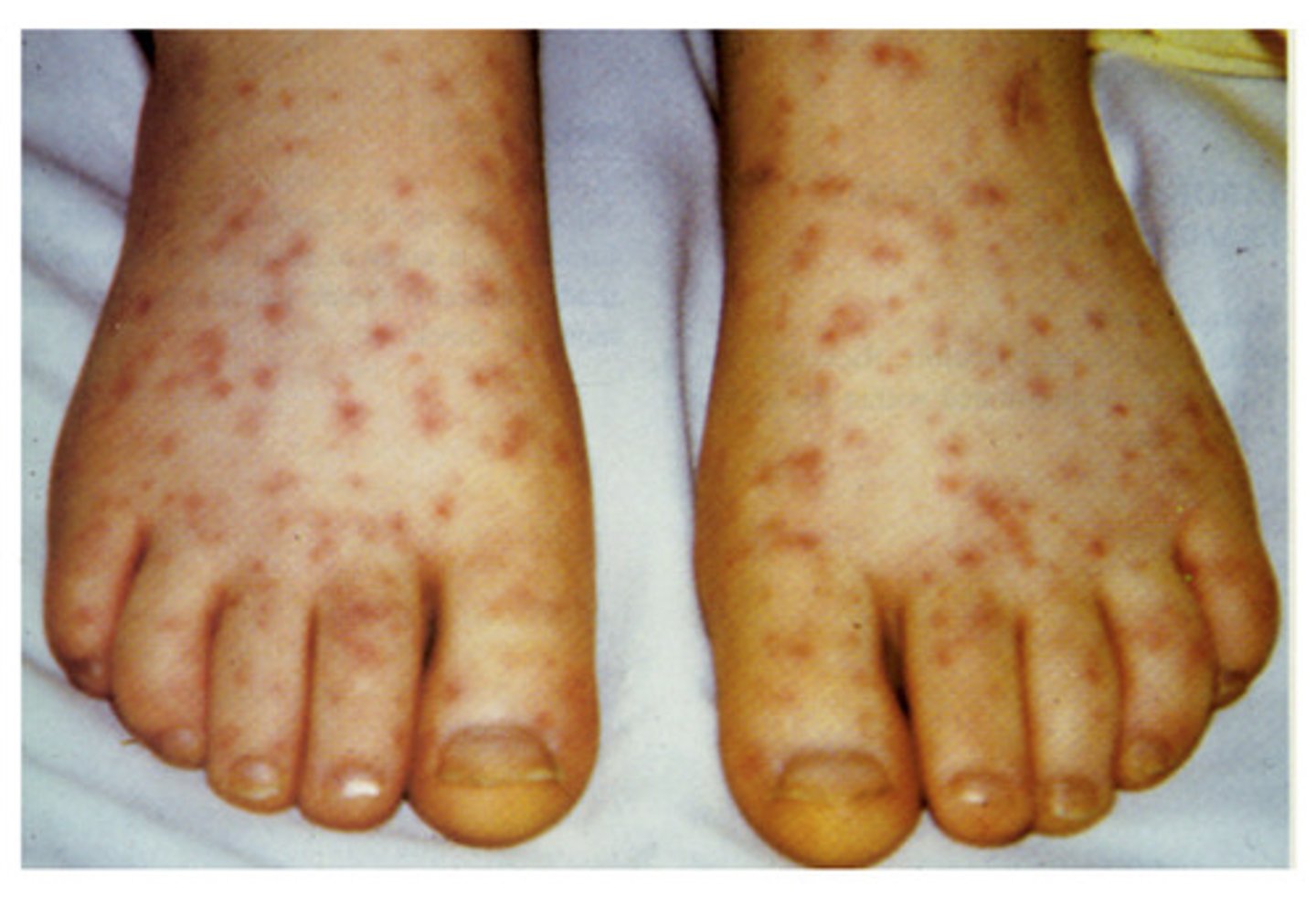
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Pathogen: Rickettsia rickettsii
S+S: Infected capillaries --> Fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, Red, non-itchy rash on wrists and ankles --> then spreads to the rest of the body
Reservoirs: Dogs, deer, rodents
Transmission: American dog tick bite
Ehrlichiosis
Pathogen: Ehrlichia bacteria
S+S: Infected leukocytes --> fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, myalgia, rash
Reservoirs: Dogs, deer, rodents
Transmission: Lone star tick bite
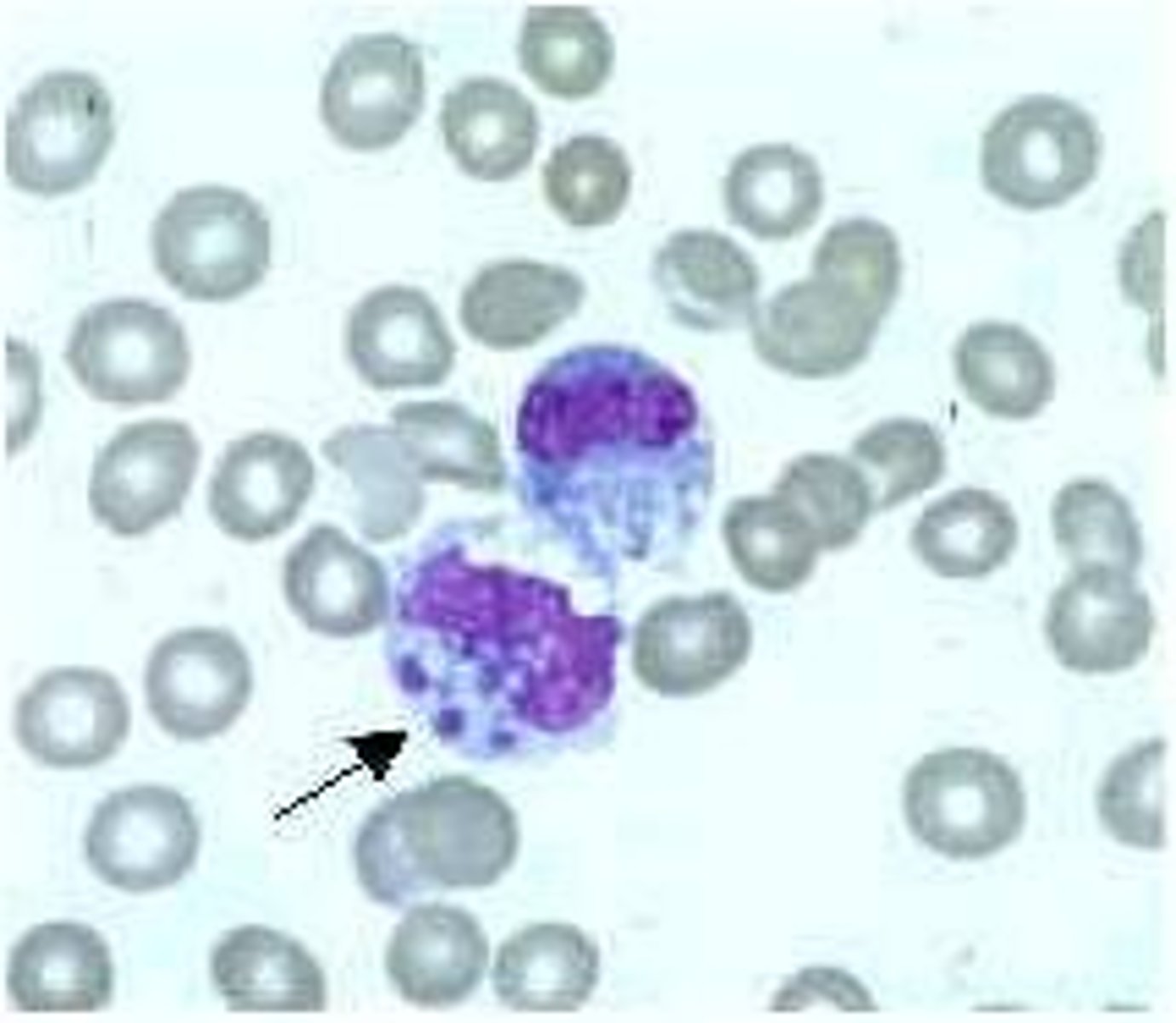
Bubonic Plague (Black Death)
Pathogen:Yersinia pestis
S+S: Fever, headache, weakness, chills --> infected lymph nodes --> buboes
Reservoirs: Infected rodents (rats, mice, squirrels)
Transmission: Infected flea bite
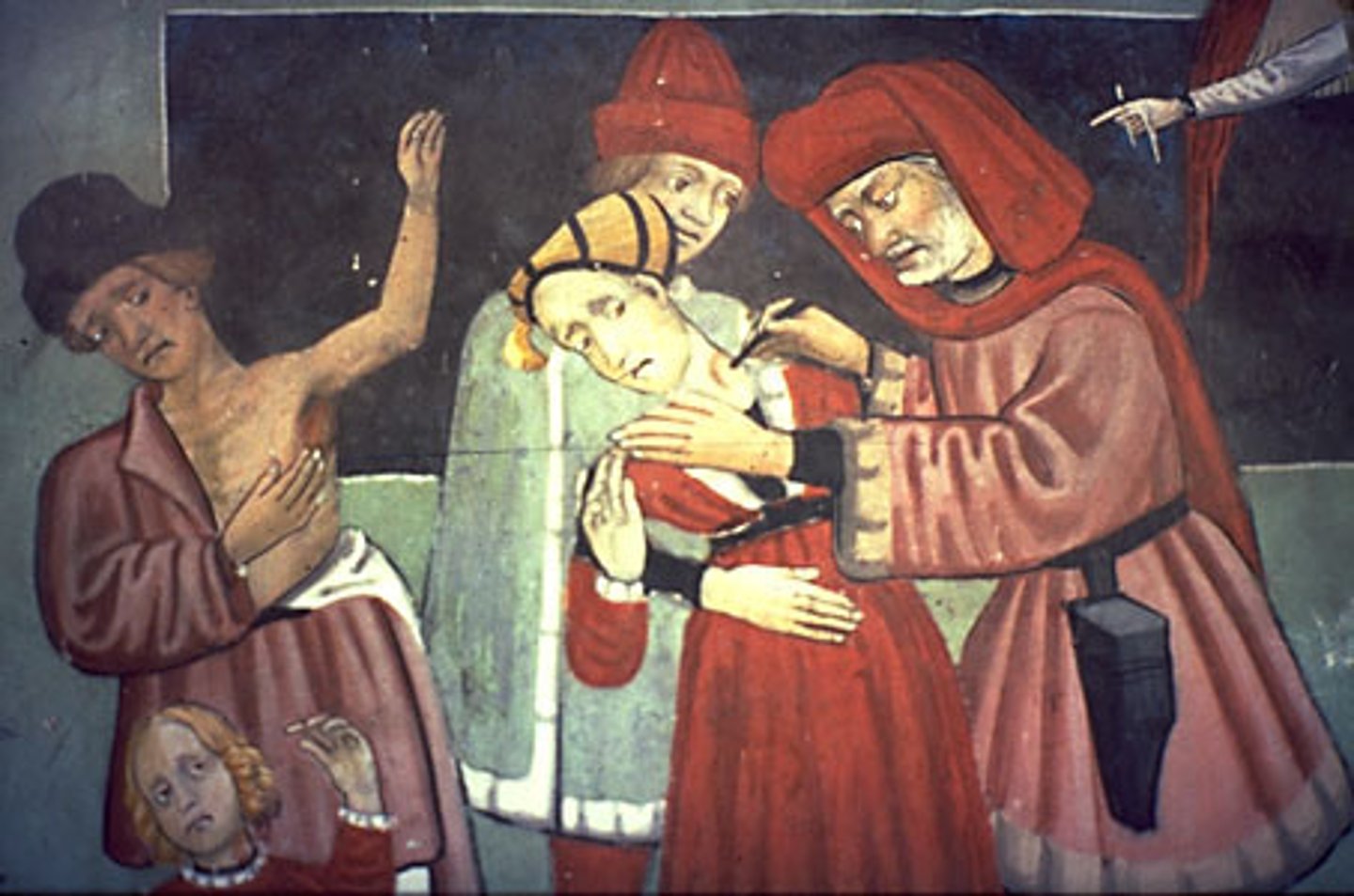
Septicemic Plague
Pathogen: Yersinia pestis
S+S: Fever, headache, weakness, chills --> infected bloodstream --> blackening/necrosis of fingers and toes
Reservoirs: Infected rodents (rats, mice, squirrels)
Transmission: Infected flea bite
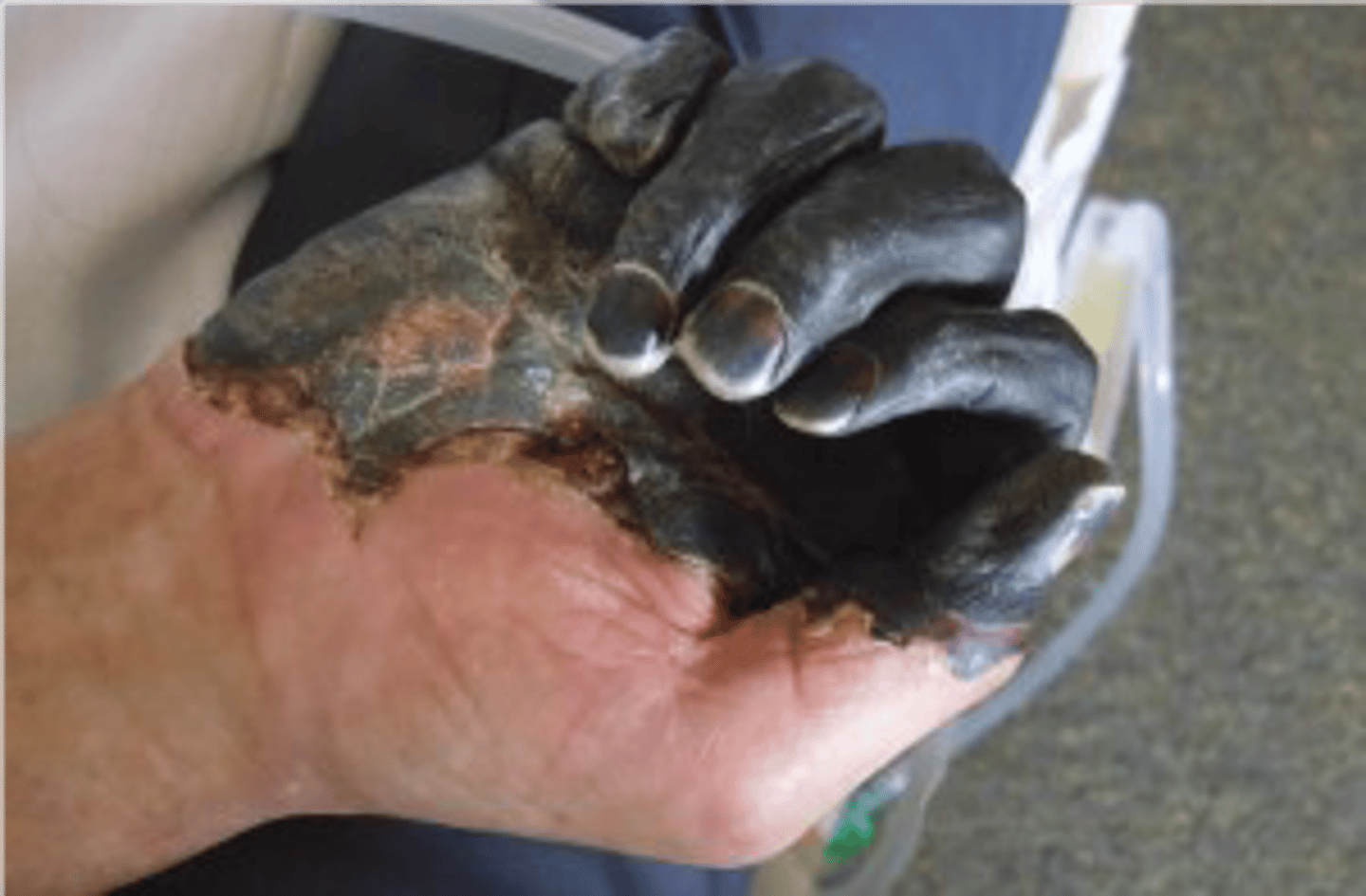

Pneumonic Plague
Pathogen: Yersinia pestis
S+S: Fever, headache, weakness, chills --> infected alveoli --> dyspnea, hemoptysis
Reservoirs: Infected rodents (rats, mice, squirrels)
Transmission: Inhalation of infected respiratory secretions

Lyme Disease
Pathogen: Borrelia burgdorferi
S+S: Fever, headache, chills, myalgia, arthralgia, fatigue, bull's-eye rash (erythema migrans)
Reservoirs: Infected deer and rodents
Transmission: Bite of infected deer tick
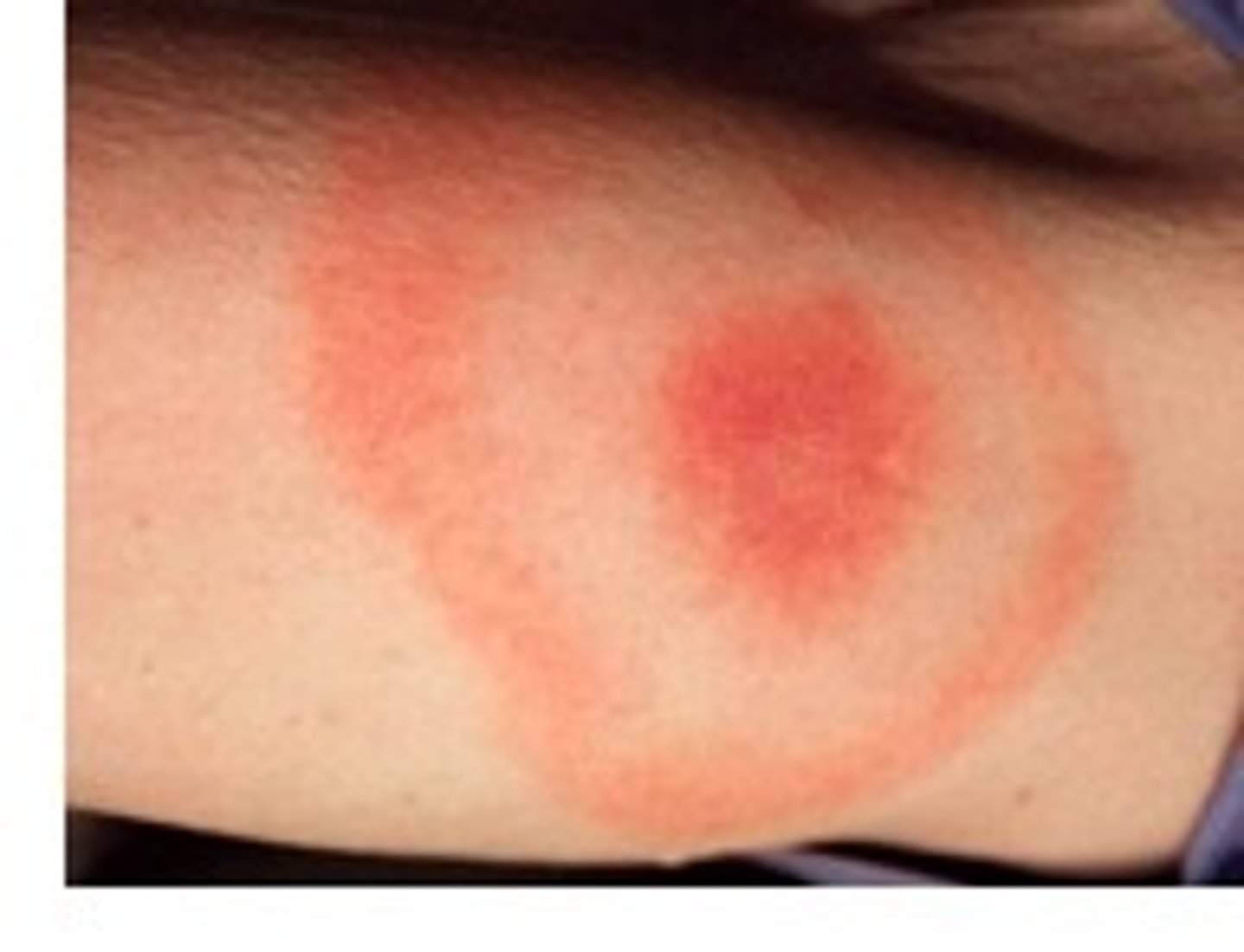
Bacterial (purulent) Meningitis
Pathogen: Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae
S+S: Fever, headache, nuchal rigidity
Transmission: Respiratory or oropharyngeal secretions
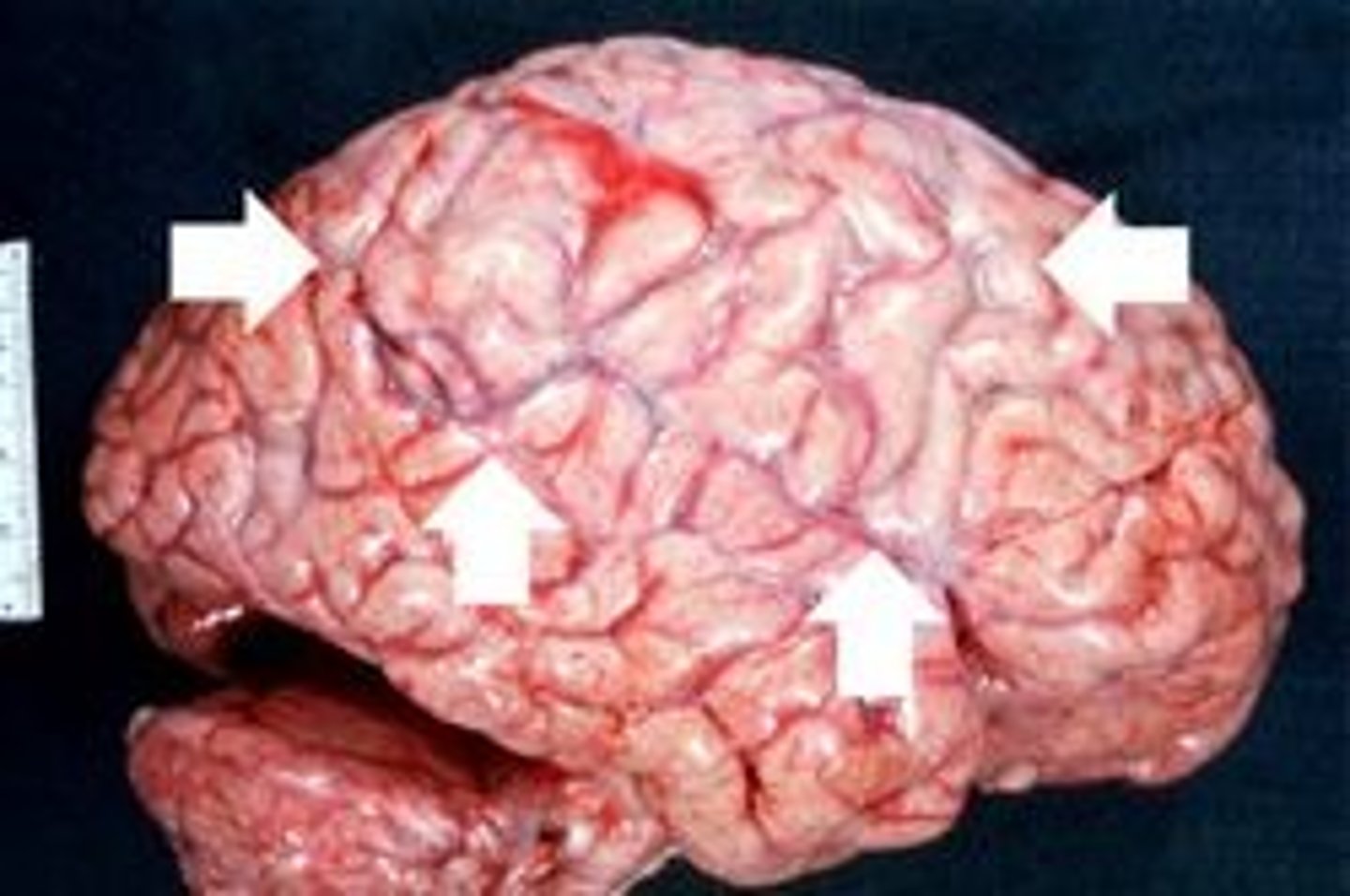
Listeriosis
Pathogen: Listeria monocytogenes
S+S: Mild illness to meningoencephalitis --> fever, headache, nuchal rigidity
Reservoirs: Soil and water
Transmission: Contaminated foods

Botulism
Pathogen: Clostridium botulinum
S+S: Ptosis, diplopia, dysphagia, muscle paralysis
Transmission: Can be from infected food, wounds, or environmental
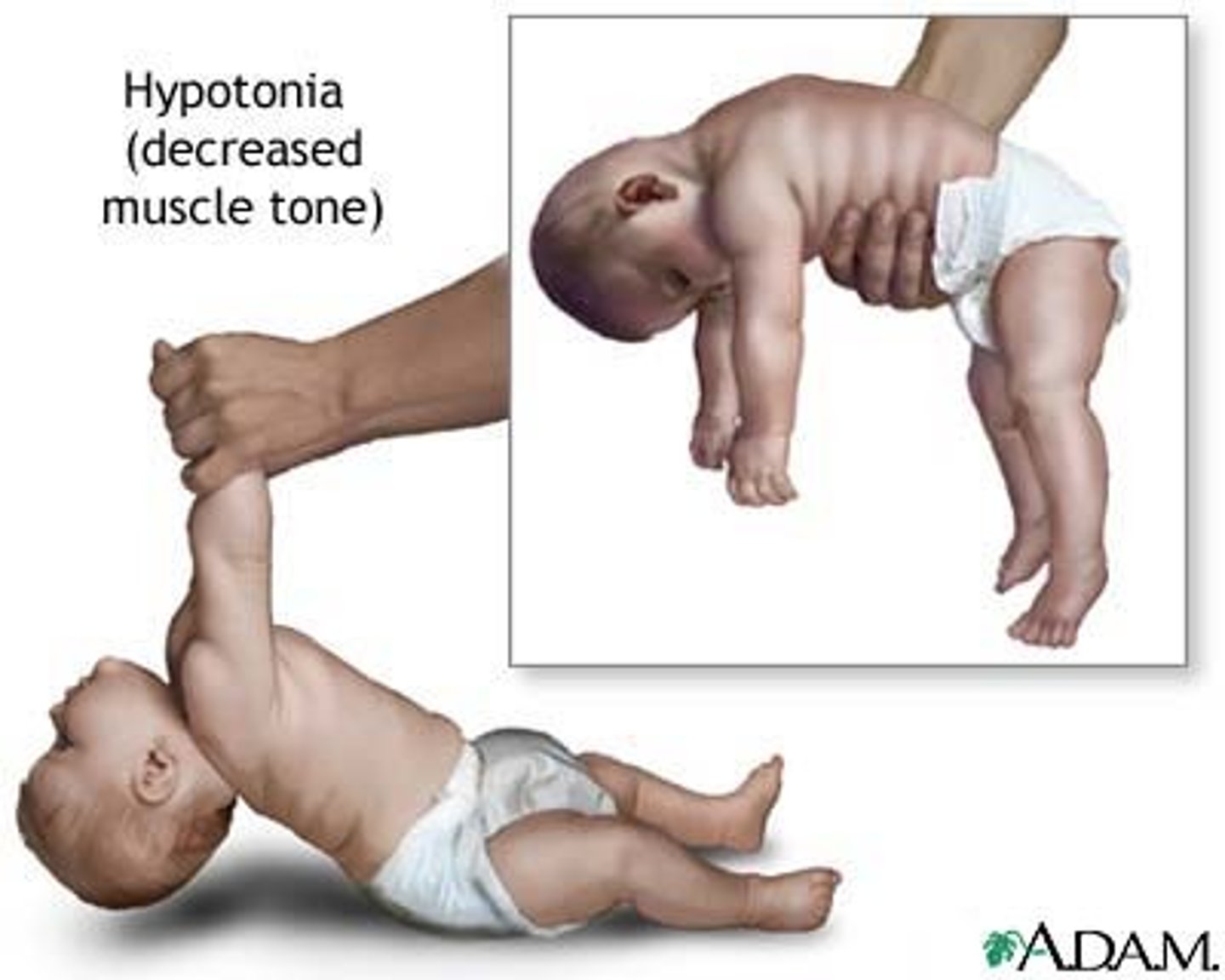
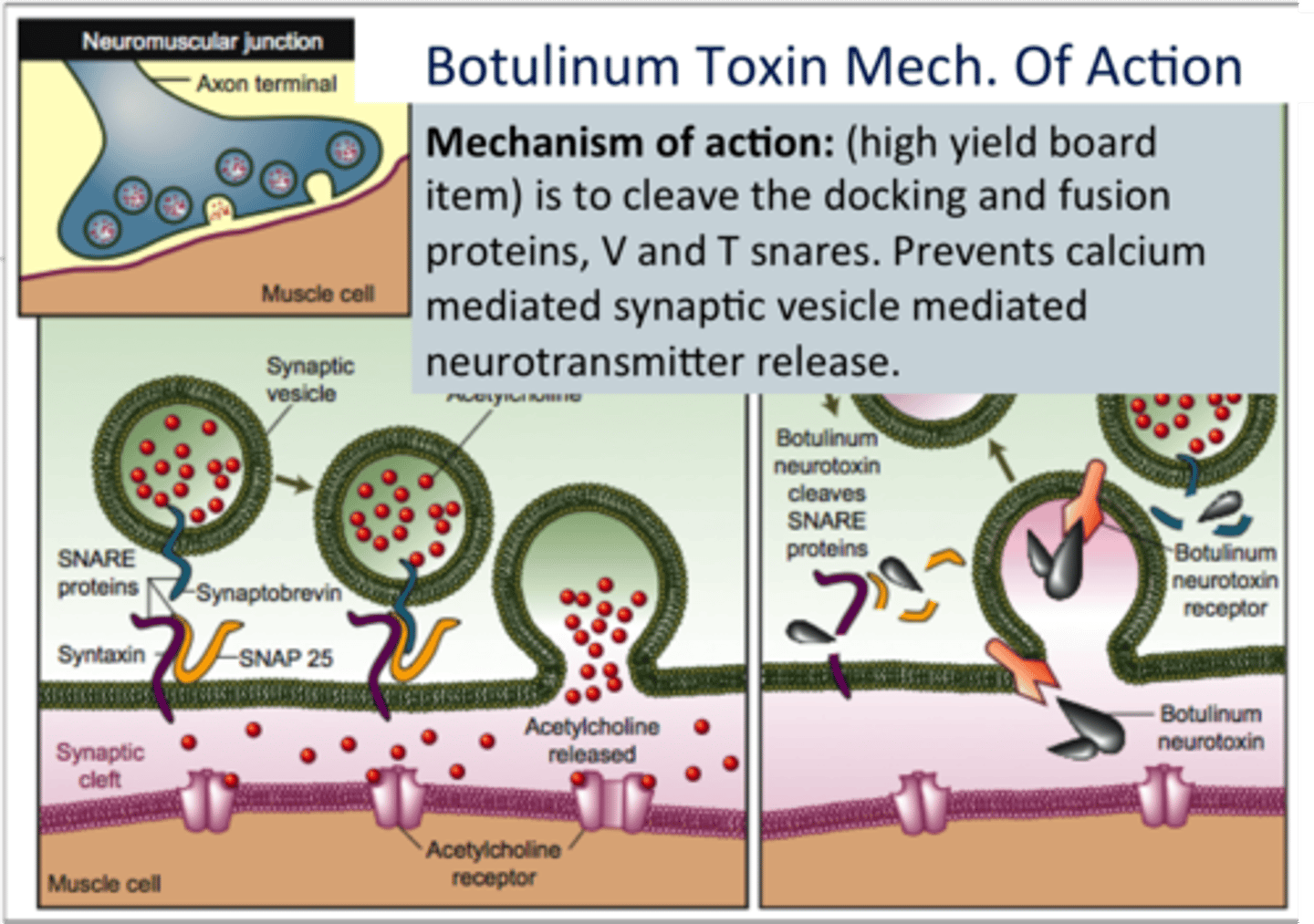
Botulinum
A neurotoxin produced by bacteria --> prevents the release of Acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction --> depressed motor response
Used in BOTOX !!
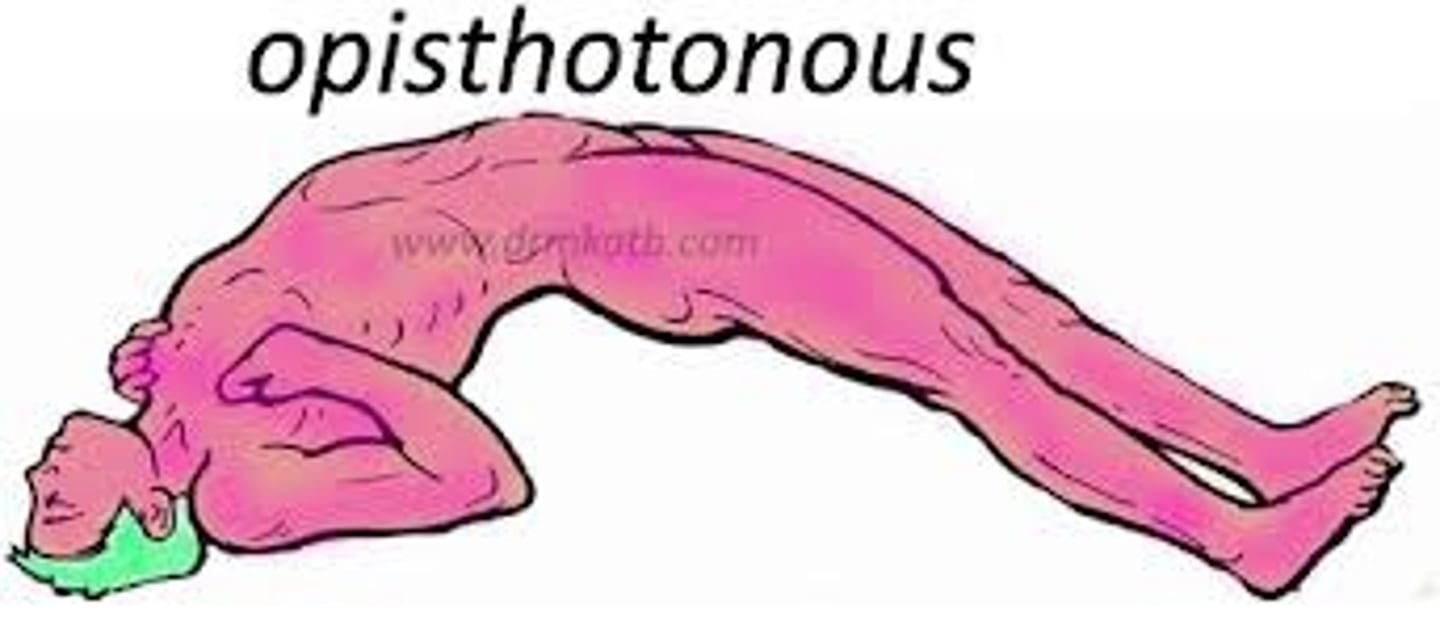
Tetanus (lockjaw)
Pathogen: Clostridium tetani
S+S: Spasms of the masseter, neck and respiratory muscles, opisthotonus
Reservoirs: Soil contaminated with animal or human feces
Transmission: Bacteria enter an open wound from soil

Tetanospasmin
Bacteria secrete a toxin --> toxin inhibits the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the motor neurons --> muscles cannot relax --> involuntary muscular contractions
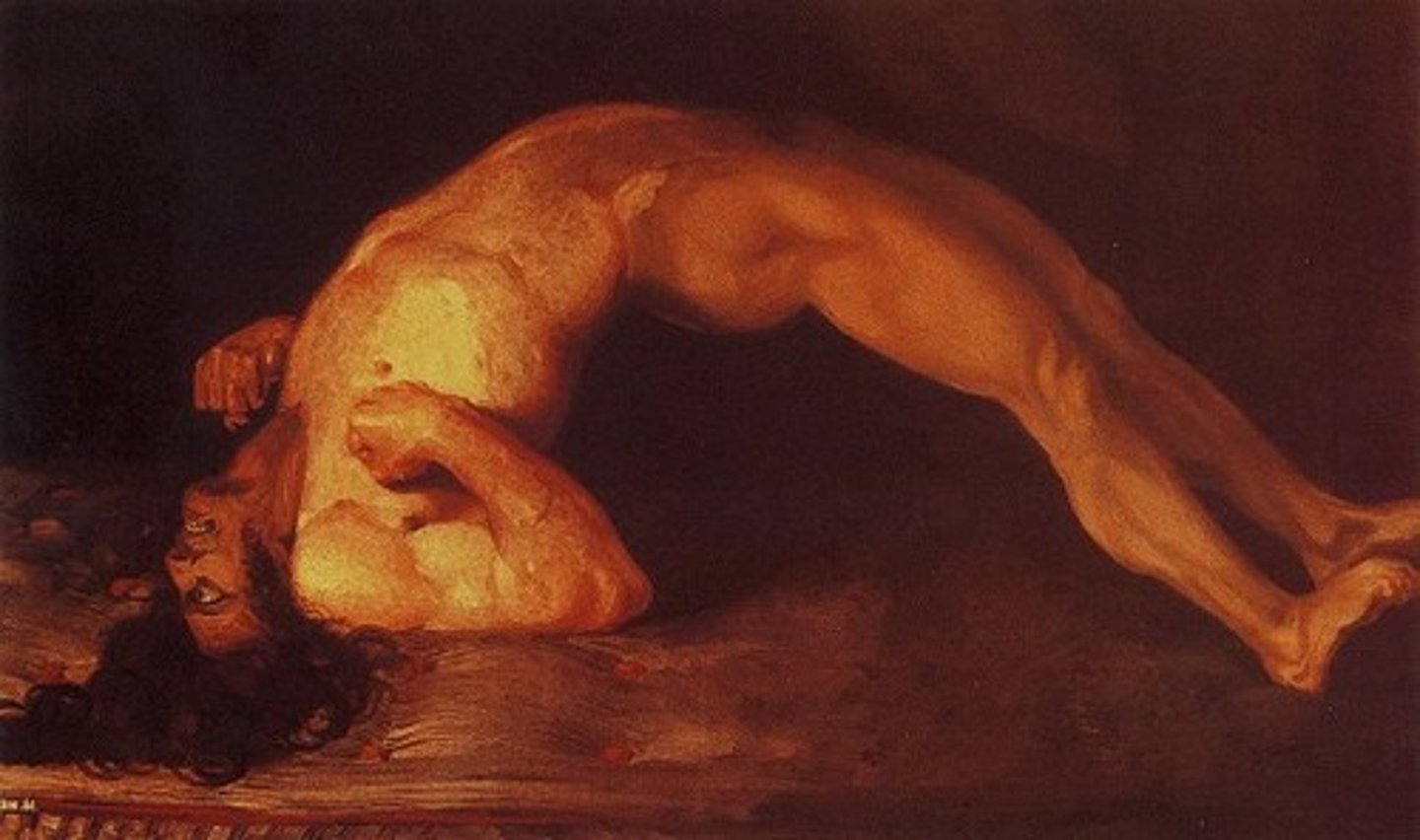

Opisthotonus
Abnormal posture seen in severe tetanus --> the back becomes extremely arched due to muscle spasms
Sensitivity
Probability of testing positive when you have a disease
P (T+ / D+)
Specificity
Probability of testing negative when you do not have a disease
P (T- / D-)
Positive predictive value
Probability of having a disease if you test positive
P (D+ / T+)
Negative predictive value
Probability of not having a disease if you test negative
P (D- / T-)
pyelonephritis
upper UTI involving inflammation of one or both kidneys
ureteritis
upper UTI involving inflammation of one or both ureters
cystitis
lower UTI inflammation of the urinary bladder
urethritis
inflammation of the urethra
ascending UTI (more common)
bacteria migrating up the urethra to the urinary bladder, then the ureters, and finally the kidneys
descending UTI (less common)
bacteria from an infection elsewhere in the body can spread to the kidneys via the bloodstream
prevention of UTI
maintaining adequate fluid intake, wiping from front-to-back after defecation, emptying the bladder after sex, avoiding delaying urination
complications of gonorrhea
septic arthritis - spread via bloodstream to one or more joints
pelvic inflammatory disease - spread to uterus and fallopian tubes
epididymitis - spread to the epididymides
risk factor for bacterial vaginosis
multiple sex partners, condomless sex, low levels of lactobacilli in the vagina,
douching - rinsing out vagina with water or other cleansing agents, which can upset the natural balance of resident bacteria and alter its acidic environment