Lecture 5: Severe Weather
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
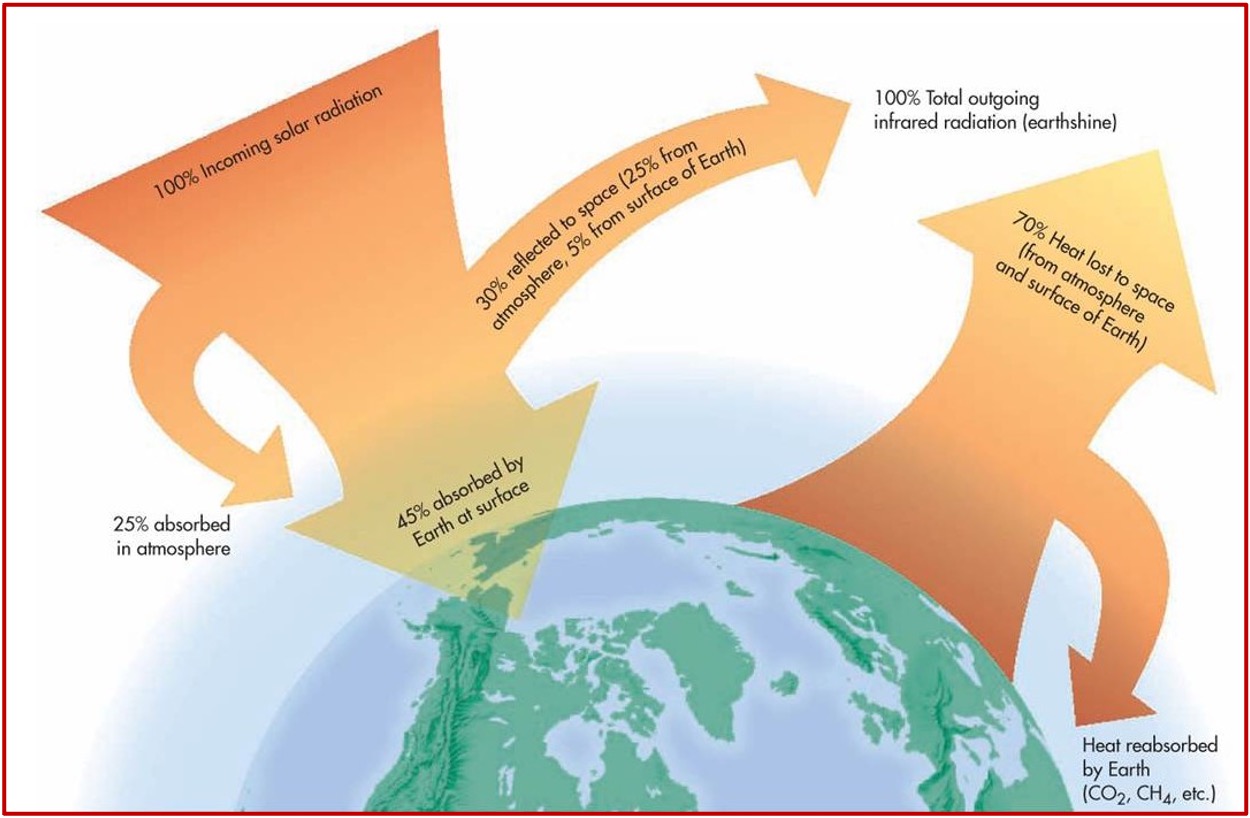
What is the Energy Balance on Earth?
There is an equilibrium between incoming radiation and outgoing radiation
Earth intercepts only a small portion of the Sun’s total radiation
It is this energy from the Sun that drives the hydrologic cycle and all the weather phenomena on Earth
The atmosphere is composed of what? (%s)
78% Nitrogen
21% oxygen
1% water vapour, carbon dioxide, ‘trace gases’
What in the atmosphere leads to cloud development and precipitation?
Water vapour
What causes water vapour?
evaporation from large bodies of water
Structure of the atmosphere
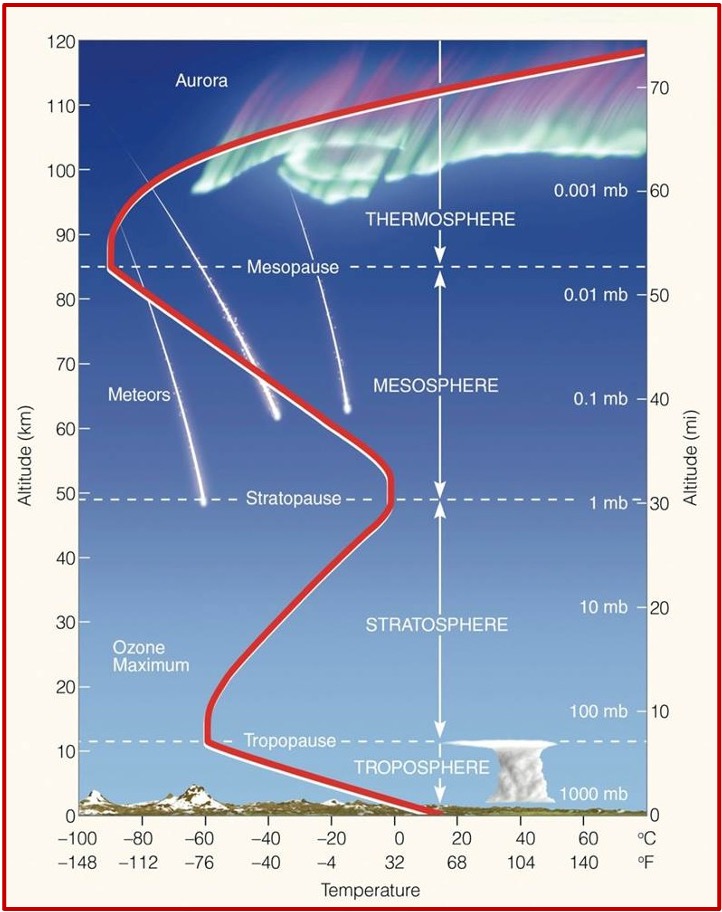
Clouds are in what layer of the atmosphere?
Troposphere
Where is the ozone layer found?
Stratosphere
What does the prefix of a cloud describe?
Height
What does the suffix of a cloud describe?
Appearance
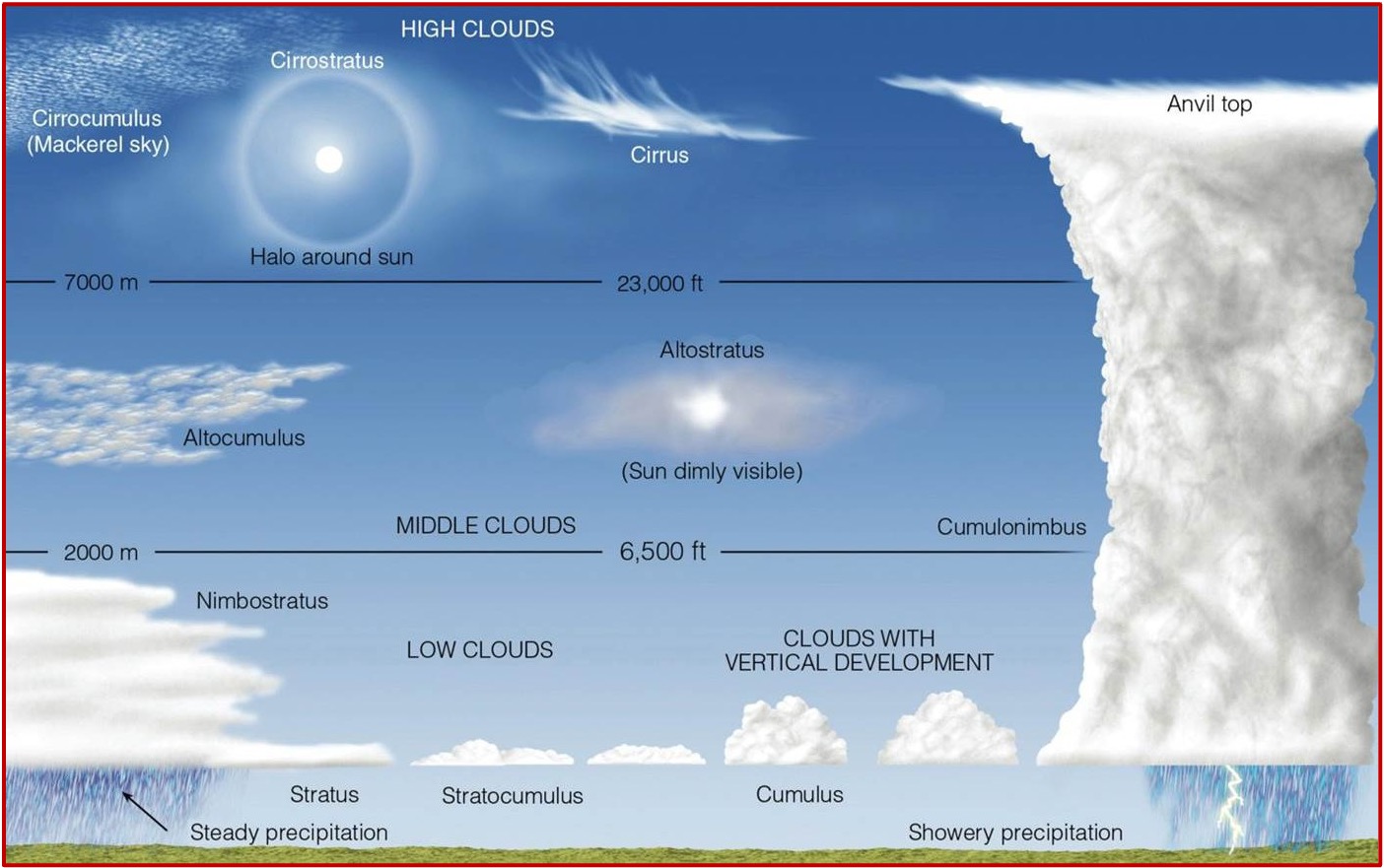
Prefixes & Suffixes
Prefixes: Suffixes:
High cloud: cirro- Puffy: -cumulus
Mid-level cloud: alto- Flat: -stratus
Low cloud: strato-
Clouds that produce precipitation contain what is their name?
“nimb”
What is a cumulonimbus cloud?
A cloud that produces lightening, thunder, and heavy rain
What is a nimbostratus cloud?
A cloud that produces prolonged light to moderate precipitation
Clouds diagram
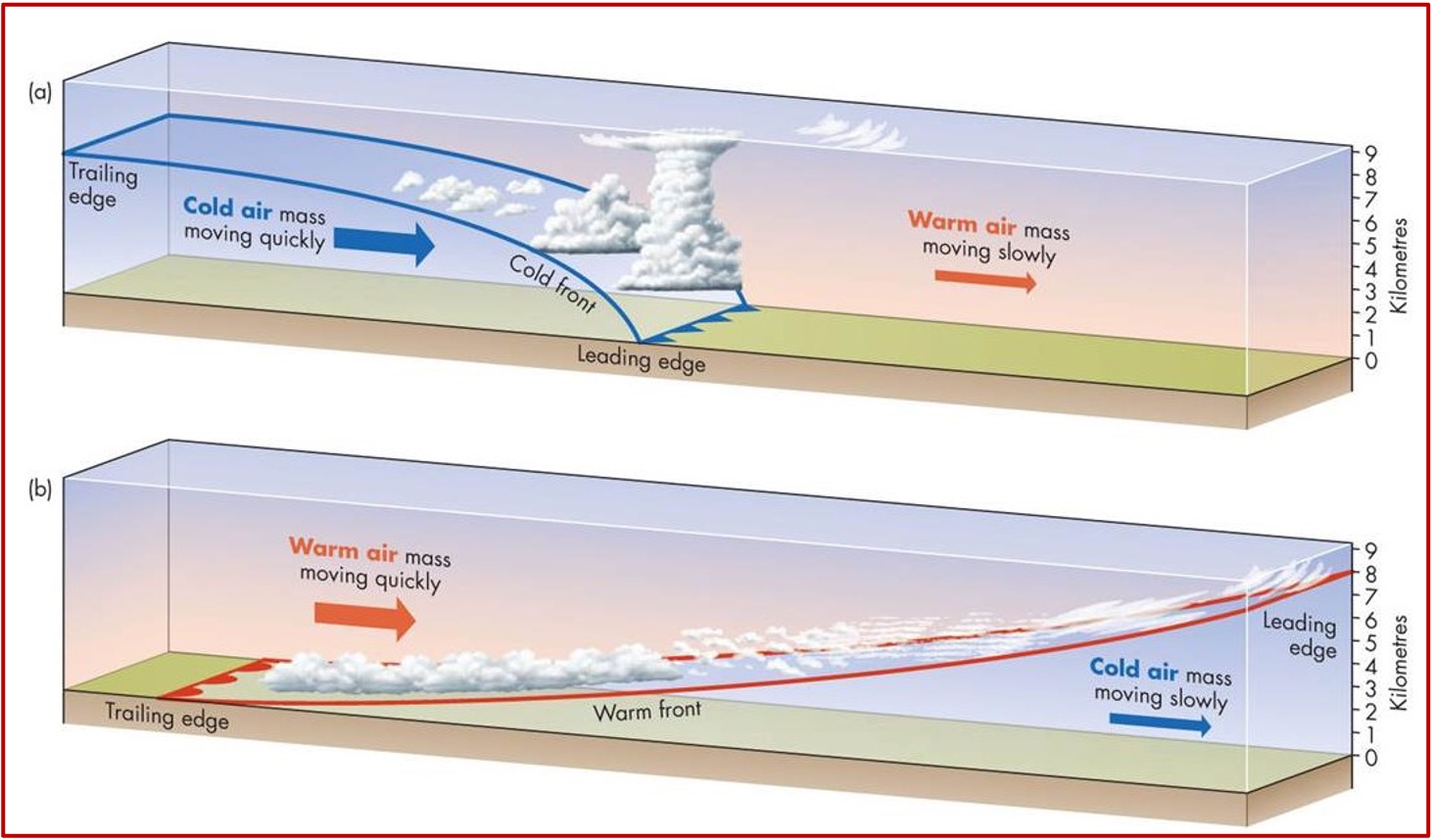
What is a front?
A boundary between two air masses
The name of the front describes the air behind it
Fronts generally move from west to east
At a cold front, dense cold air undercuts warm air
At a warm front, the less dense warm air overrides cold air
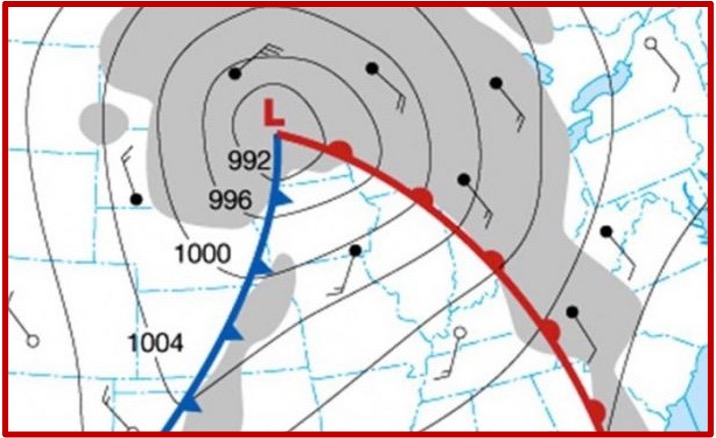
Is this image a cold front or a warm front?
Clod front
the air behind it is cold
arrows point to direction of movement (west-east)
Colf front vs Warm front (diagram)
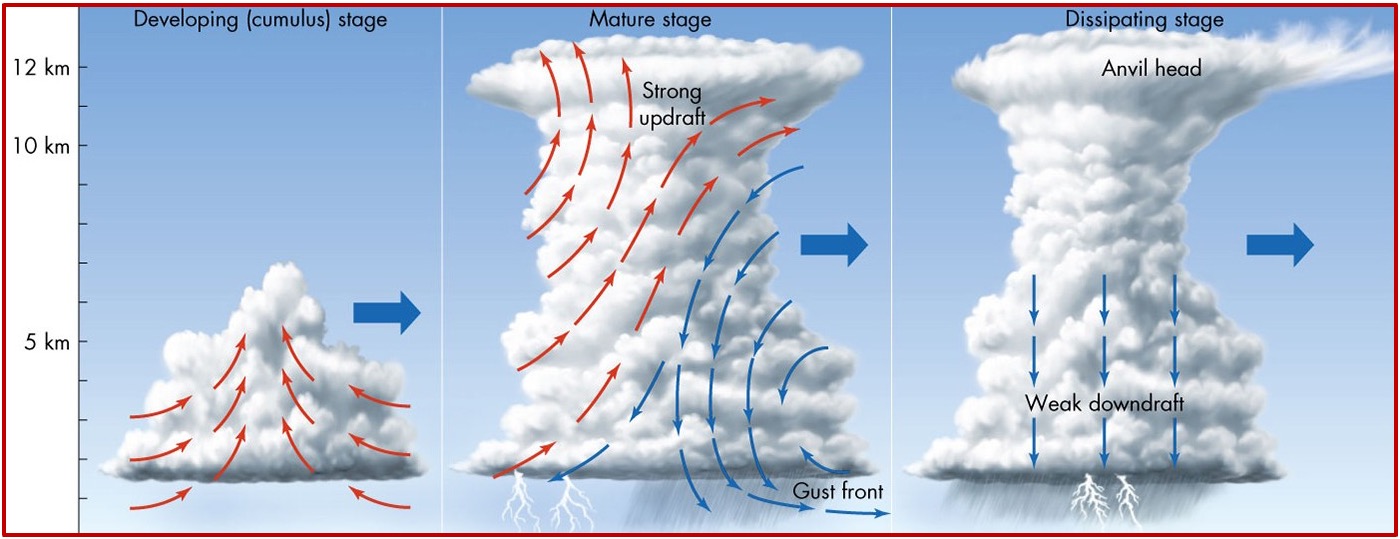
Thunderstorm development requires what 3 things?
water vapour
a large difference in temp between air at the ground and air aloft
rising air (or a lifting mechanism, i.e. a front)
What are the 3 stages of thunderstorm development?
Cumulus
Mature
Dissipative
Most pass through all 3 stages in 1 hr
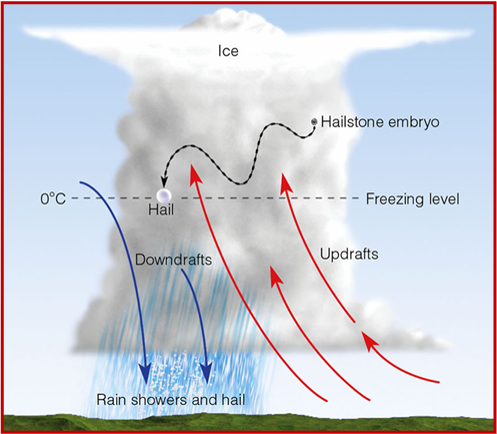
What is the only cloud that can produce hail?
Cumulonimbus
How is hail produced?
Updrafts in the cloud repeatedly force a water droplet upward
The droplet develops a ring of ice around it each time it enters the cold part of the cloud
the ball of ice eventually becomes heavy enough to fall to the ground
What is lightening?
A spark of electricity occurring in a cloud
What causes thunder?
Lightning heats the air causing the air to expand thus creating a shockwave (thunder)
Sometimes the atmosphere refracts thunder making it inaudible
What is the main requirement for lightening?
A cumulonimbus cloud containing a region of opposite charges
The interaction of ice crystals, hailstones, and water droplets result in a separate distribution of charges in the cloud
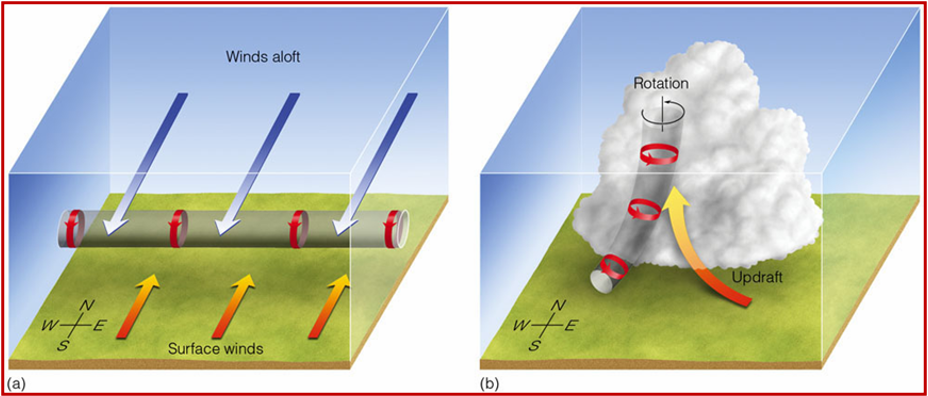
What is a tornado?
A rotating column of low-pressure air touching the ground that forms within a supercell thunderstorm
different from a ‘funnel cloud” (rotating column that doesn’t touch ground)
What are the 4 characteristics of tornadoes?
Most range between 100 and 200 metres wide
They travel from the southwest toward the northeast at an average speed of 50 km/h
They tend to exist for <20 mins with a defined life cycle
The most common season for tornadoes is summer in Canada and Spring in the U.S.
What are the 3 stages tornadoes exist in?
Organizational stage
Mature stage
Rope stage
What occurs in the organizational stage of a tornadoes life cycle?
Wind shear causes rotation to develop
A funnel cloud protrudes from above
Dust and debris rotate beneath
What occurs in the mature stage of a tornadoes life cycle?
Most severe damage occurs
What occurs in the rope stage of a tornadoes life cycle?
The tornado stretches out and weakens
Tornado formation diagram
How do we classify tornadoes?
Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF)
Tornadoes are classified on a scale of EF0 to EF5, based on the damage produced
What classifies as an EF5 tornado?
complete devastation
Wind speed over 322 km/h
Less than 1% of tornadoes
What 2 places experience the most tornadoes on Earth? (tornado alleys)
U.S.
Canada
Where is the U.S. tornado alley?
Kansas & Oklahoma
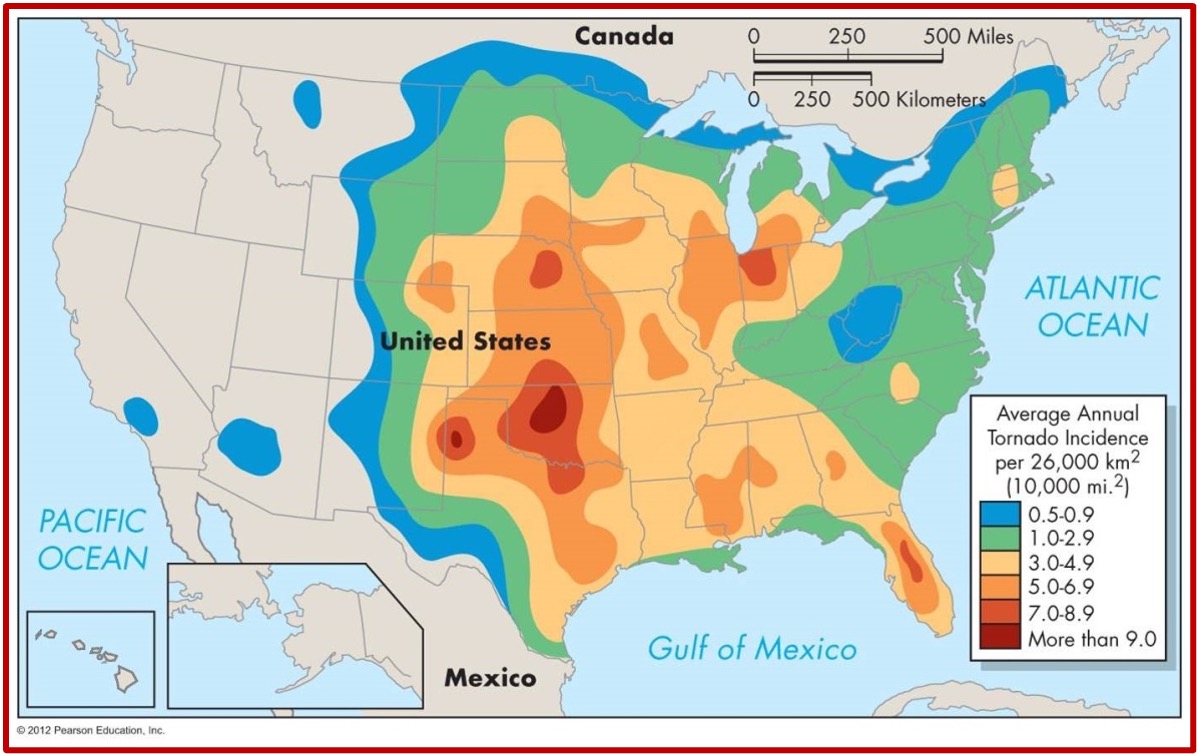
Where is Canada’s tornado alley?
Southwestern Ontario
Why do tornado alleys exist?
They are areas where air asses commonly collide
They are areas of relatively flat land (this allows for undisturbed rotation)
Why does Canada’s tornodo alley exist?
Tornadoes in Ontario occur when a southwesterly wind brings warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico
The warm air may interact with cooler lake breezes
Notable tornadoes: Super outbreak
April 3, 1974
On this day 148 tornadoes touched down between Ontario and Alabama
one of the strongest tornadoes in the outbreak killed 23 people
Largest tornado outbreak in history:
2011, April 25th - 28th
In the southeast U.S., 358 tornadoes touched down
324 people were killed (mainly in Alabama)
Overall, there were more deaths from tornadoes in 2011 than any other year since 1925
Notable tornadoes: Joplin tornado
May 22, 2011 - An EF5 tornado caused 161 deaths in Joplin, Missouri
This tornado was the costliest in U.S. history ($2.8 B) and the deadliest in the U.S. since 1947
Notable tornadoes - Goderich tornado
Killed 1 person and destroyed much of the town core on Aug. 21, 2011
It was the first EF3 tornado to touch down in Ontario in 15 years
The tornado was spotted over Lake Huron on RADAR and a warning was issued 12 minutes before it reached the town
Notable tornadoes - Moore tornado
On May 20, 2013, an EF4 tornado in Moore, Oklahoma caused 24 deaths
A tornado warning was issued for the area 16 minutes in advance
Advances in weather technology have greatly improved warning time
What are the 2 types of cyclones?
Tropical cyclones
Extratropical cyclones
Tropical cyclones:
These only form over warm water, usually at latitudes 5-30°
They include hurricanes and typhoons
They contain high winds, heavy rain, and storm surges
Extratropical cyclones:
These form over land or water in temperate regions at latitudes 30-70°
They are associated with fronts and are also called mid-latitude cyclones
They contain rain, snow, freezing rain, etc.
What are the 4 stages of Tropical cyclone development?
tropical disturbance
tropical depression
tropical storm
hurricane
Tropical disturbance:
A large low-pressure area with unsettled weather
Tropical depression:
An unorganized area of thunderstorms
Tropical storm:
An organized area of storms with wind of 65-119 km/h
Hurricane:
A circle-shaped low-pressure area with winds of at least 120 km/h
Tropical cyclones require what?
A water temperature of at least 26 oC
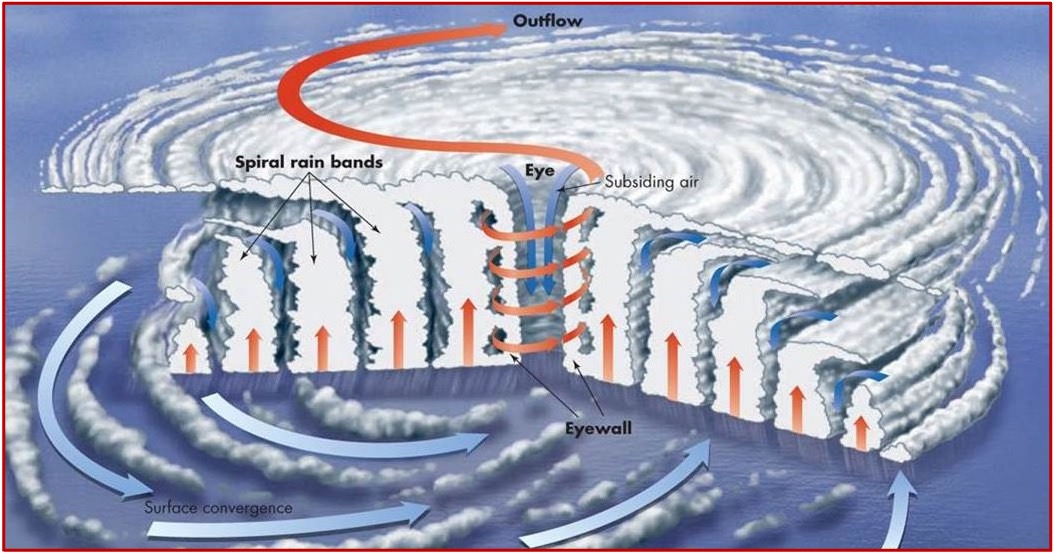
What are the 3 components of a hurricane?
eye
eyewall
spiral rain bands
What is the eye?
A region in the center with light winds and clear to partly cloudy skies
What is the eyewall?
A ring of intense thunderstorms that whirl directly around the aye
Most destructive component
What are spiral rain bands?
Rings of tall clouds and heavy rain that exist throughout the hurricane
Anatomy of a hurricane diagram
How do we name Atlantic Ocean Hurricanes?
Alternating male and female names are used in alphabetical order (5 letters are skipped)
When the list of names is exhausted, the remaining storms are named after the letters of the Greek alphabet (in order)
some names are retired if they produce notable damage (Ex. Andrew, Katrina)
How fast do hurricanes typically travel?
Very slowly → <20 km/h
What direction does wind rotate in a hurricane?
counter-clockwise
If a hurricane is moving northwest, where will its highest winds be located?
The northeast
What is the most devastating effect of hurricanes?
Storm surges
What causes storm surges?
powerful winds that create a rapid rise in sea level
How do we classify hurricanes?
Hurricanes are classified by the Saffir-Simpson Scale
The classification is based on wind speed
Where in North America are the regions most at risk?
Atlantic coast
Gulf of Mexico
What is the hurricane season?
The official hurricane season ranged from June 1st to November 30th
Many hurricanes occur in August and early September because this is when the water is warmest
Hurricanes in Canada: Hurricane Fiona
September 24, 2022
It caused 2 deaths and was a Category 2 hurricane when it made landfall in Nova Scotia
Hurricanes in Canada: Hurricane Hazel
October 15, 1954
It killed 81 people when intense flash floods in Toronto swept away homes
No other natural disaster has caused that many deaths in Canada to this day
What is fog?
a cloud with its base at the Earth’s surface
How does fog occur?
It occurs at night when the air cools to the dew point (at which point water vapor condenses into droplets)
Fog can also form when warm air moves over a cold body of water
In the Great Lakes region, what hazard has caused the most deaths?
Snowstorms
What causes most deaths from snowstorms?
Heart attacks from shovelling snow
What are the very specific conditions for blizzards?
Wind of at least 40 km/h
Snow falling or blowing snow occurring
Visibility less than 400 m
All of these must occur for at least 4 hours
“the rule of 4’s”
What is lake-effect snow?
Snow caused by cold air moving over relatively warm water.
Heavy snow falls downwind of lakes
Snow belts are found downwind of the lakes (in Winter, the wind is often from the northwest)
Where in Southern Ontario typically receive lake effect snow?
London & Kitchener - Lake huron
Windsor - Lake Michigan
why these places have high annual snowfall
When do lake effect clouds diminish?
When ice appears on lakes
What is a haboob?
A sandstorm that occurs in arid and semi-arid regions
What causes a haboob to form?
Downdrafts on the leading edge of a thunderstorm
What is a dust devil?
a small spinning vortex of air formed over hot, dry land
Goes from ground up (opposite of tornado)
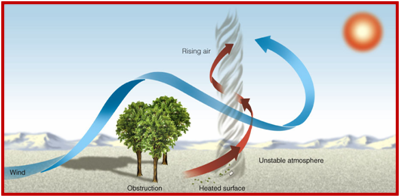
What causes a dust devil to form?
As hot air rises, the wind direction may change due to an obstacle
This may result in a spinning column of air
What causes ice storms?
Mainly caused by freezing rain
The weight of the ice can pull down trees and power lines
Freezing rain is rain that freezes as soon as it lands on a surface
What are droughts?
an extended period of unusually low precipitation
What hazard effects more people in North America than any other? How?
Droughts
They cause water shortages that can lead to crop failure
In developing countries, this may lead to malnutrition and famine.
What is wind chill?
a correction factor to an air temperature caused by the presence of wind making the air feel cooler than the temperature suggests
What is humidex?
a correction factor to a temperature reading caused by high humidity making the air feel warmer than the temperature suggests
Alerts are broken into 3 categpries:
Watch
Warning
Advisory
What is a watch?
An alert covering a wide area
Conditions favour the development of hazardous weather, but has not been reported
Ex: tornado watch, winter storm watch
What is a warning?
An alert that usually covers smaller areas
It indicates that hazardous weather is currently occurring in the area
More severe → actually happening
Ex: severe thunderstorm warning
What is an advisory?
It is issued to alert the public of less hazardous weather conditions
Ex: dense fog advisory