LUKE ENTO 201
1/394
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
395 Terms
How many main tagmata does the insect body have and what are they called?
3 - head, thorax, abdomen
How many fused segments make up an insect's head?
6
What can be found on the head on an insect?
compound eyes, ocelli (light receptive organ), antennae, mouthparts
What is the head used for?
Sight, eating, tasting, brain, feeling/touching (antennae, tiny hairs)
How do insects smell?
On the antennae, there are lots of tiny little hairs that have gaps in the cuticle. The water insoluble odorant binds with the water soluble odorant binding protein and enters through those tiny gaps to reach the receptors inside the hair and make its way to the olfactory nerve which then sends a signal to the brain.
How are insect mouthparts modified?
according to diet
What kind of mouthpart is this?
chewing
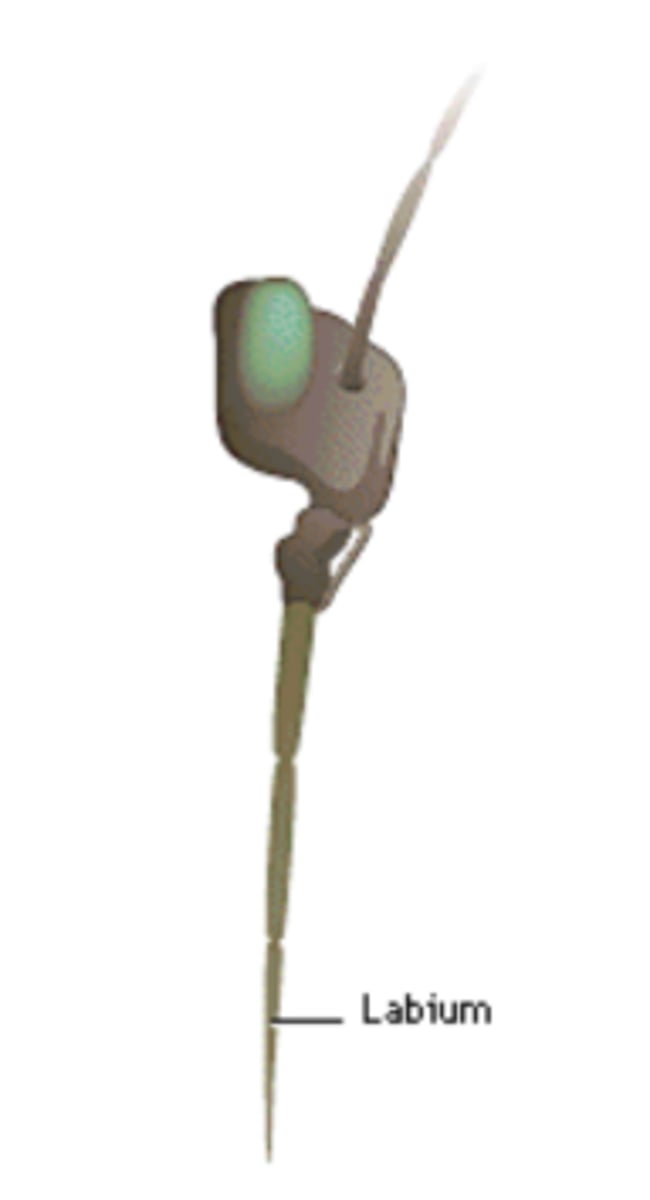
What kind of mouthpart is this?
sponging
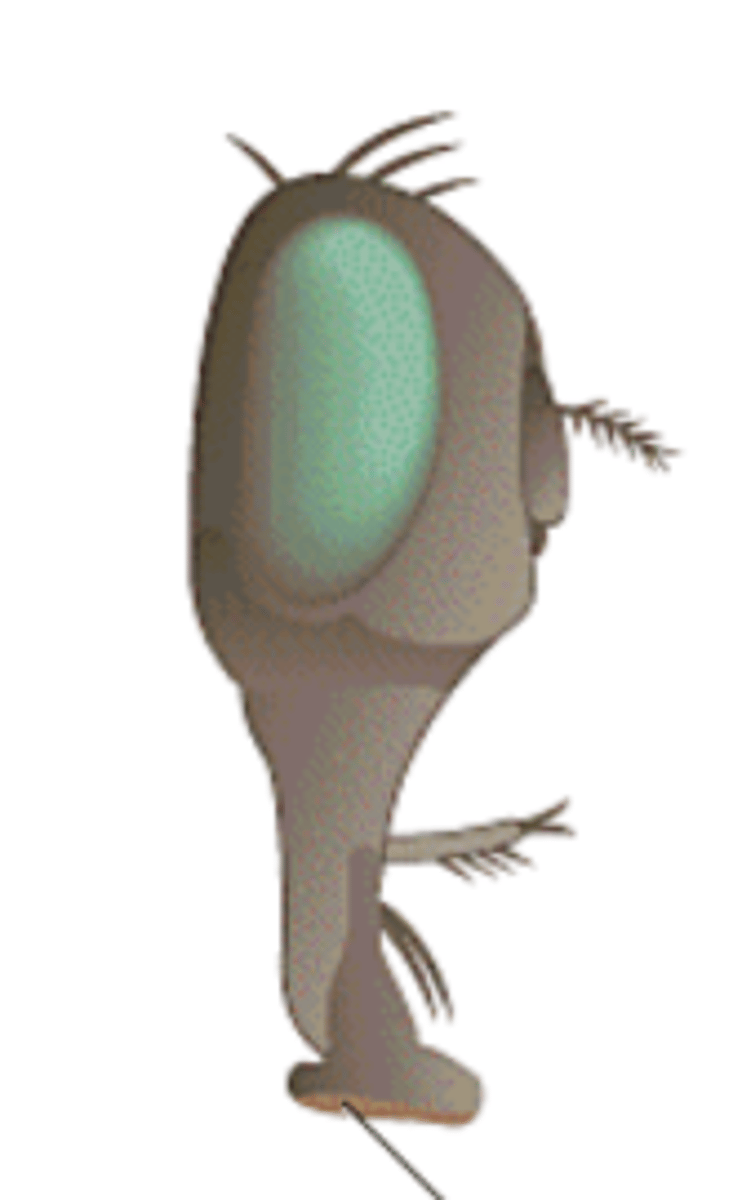
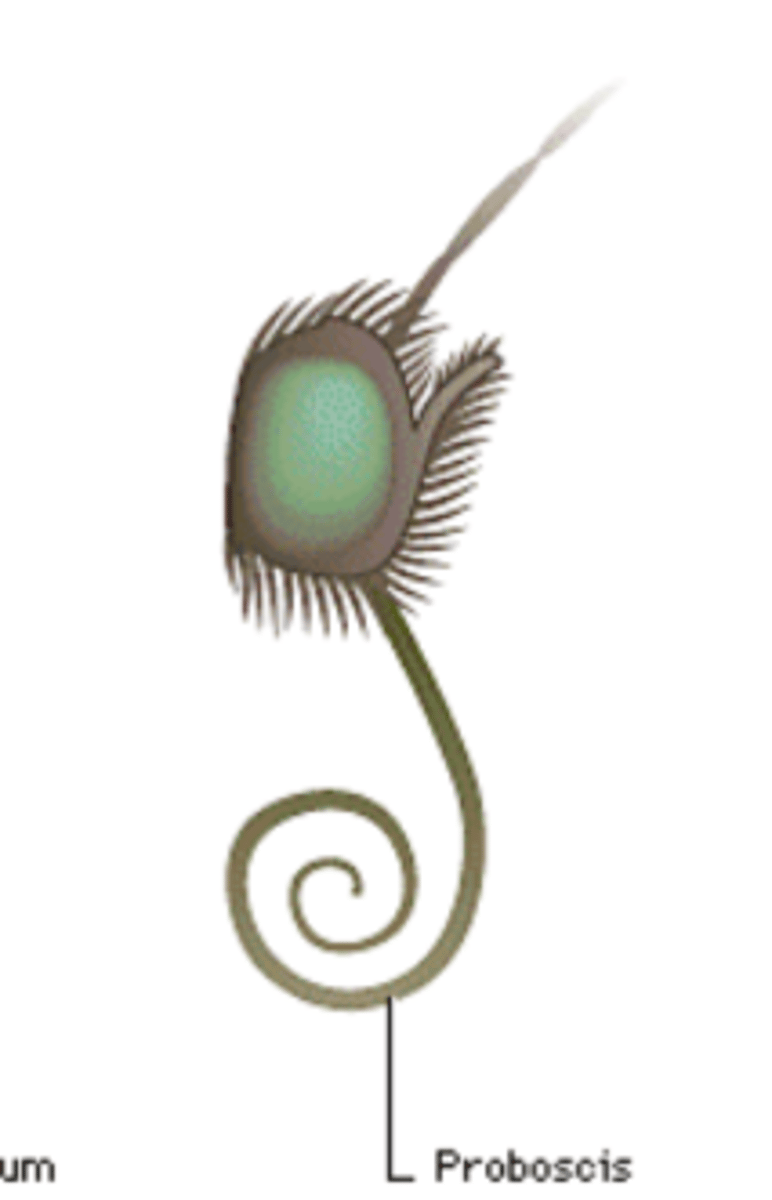
What kind of mouthpart is this?
sucking

What kind of mouthpart is this?
piercing-sucking

How many segments make up the insect thorax?
3
How many pairs of leg are found on each segment of the thorax?
1 pair per segment
Where can an insect's wings be found?
On the posterior (back) two segments of the thorax
Do all insects have the same kind of legs?
no, they can be greatly modified
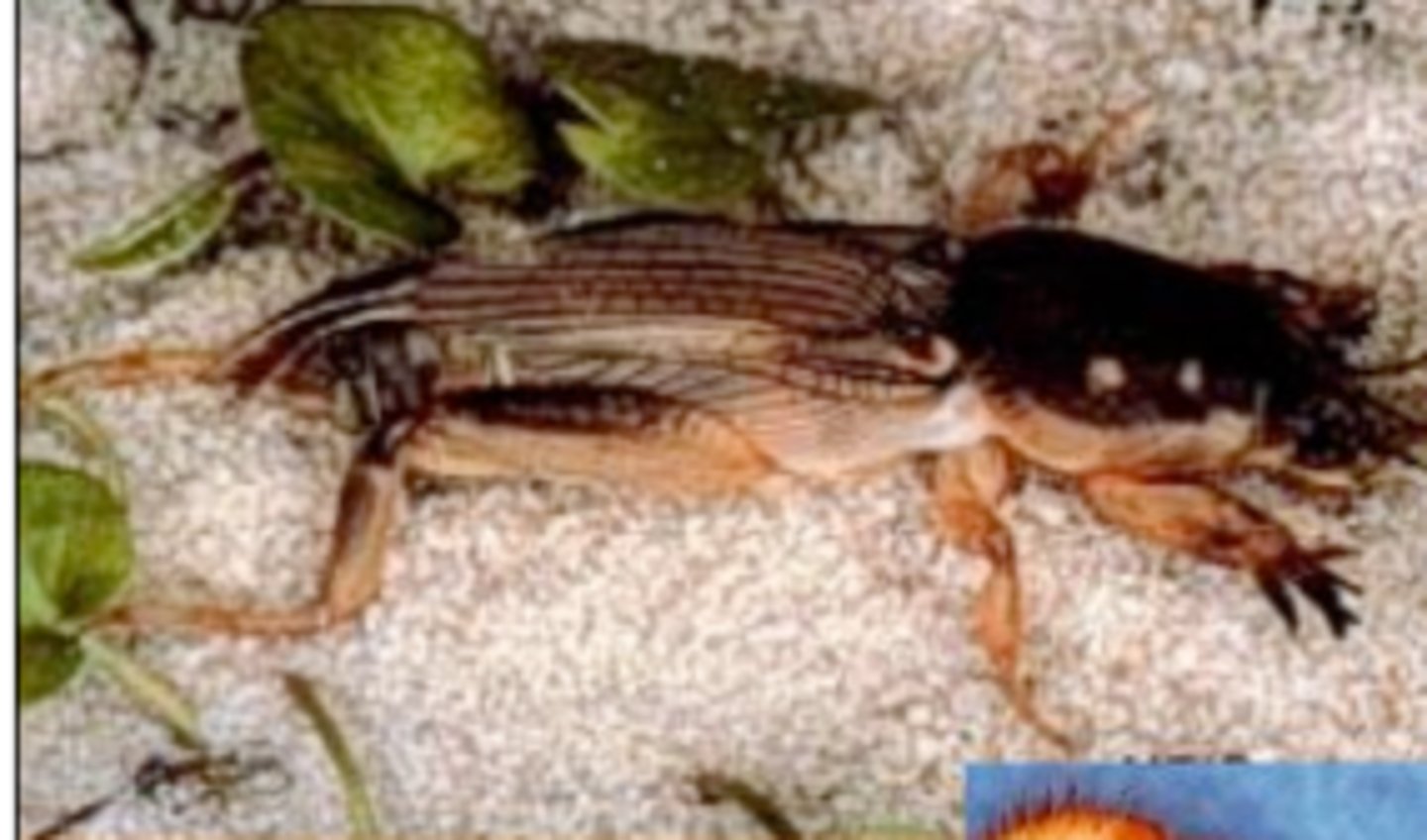
What kind of legs can be found on this insect?
fossorial front legs on a mole cricket (Orthoptera)

What kind of legs can be found on this insect?
saltatorial hind legs on grasshoppers (Orthoptera)
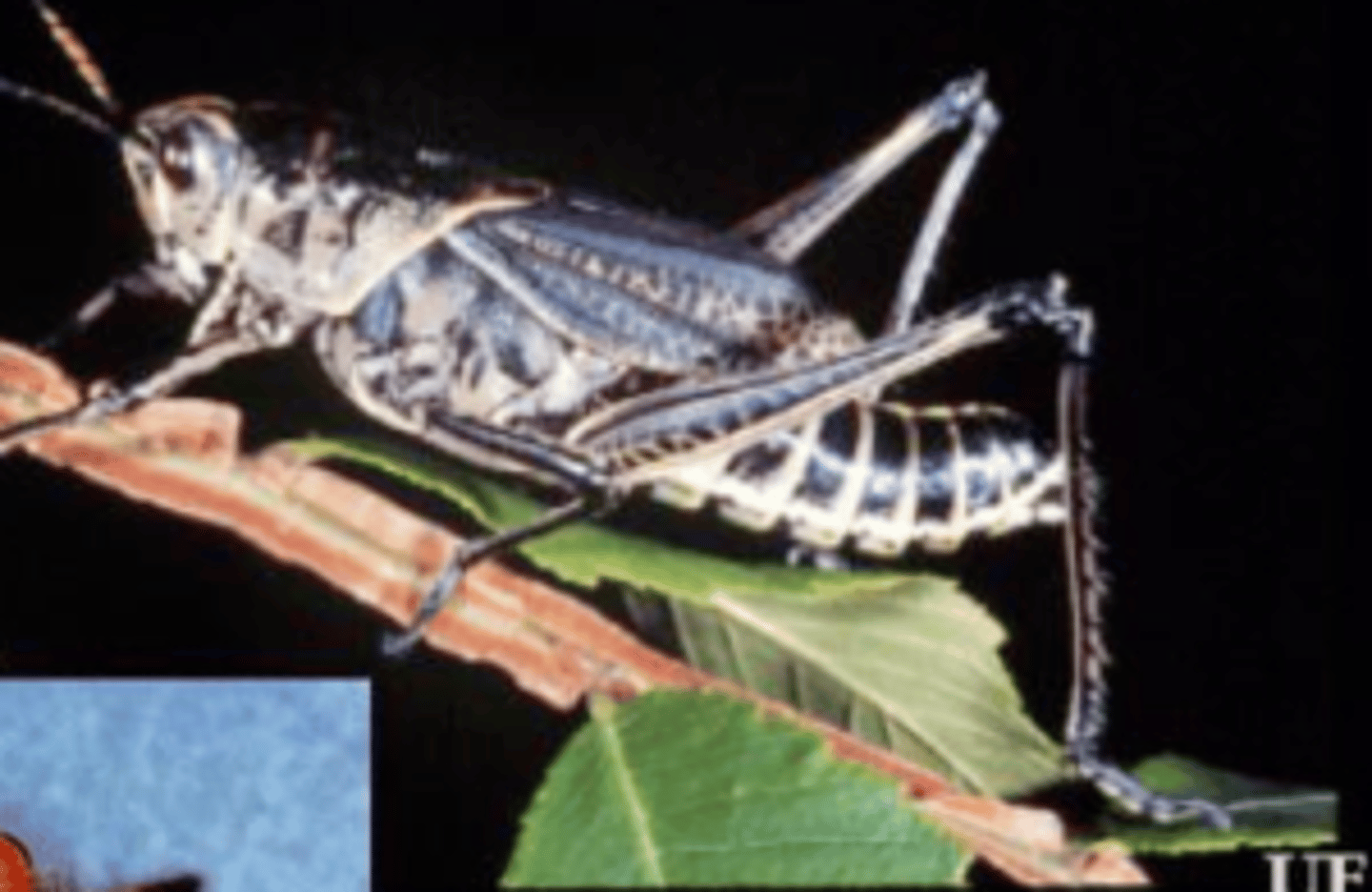

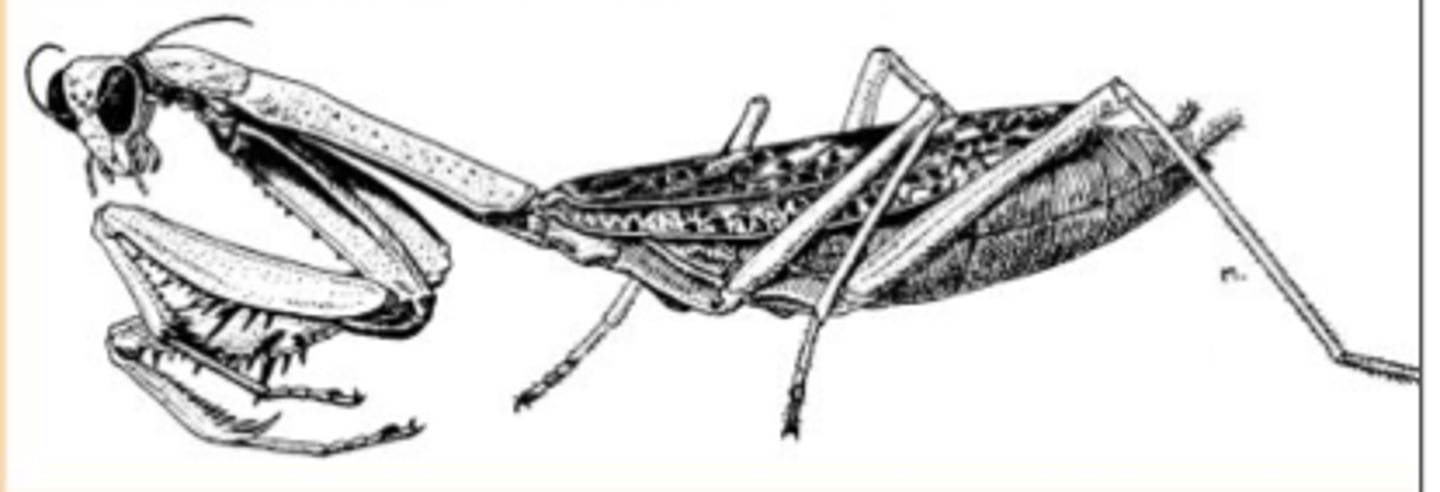
What kind of legs can be found on this insect?
raptorial front legs on mantids (Mantodea)
How many segments can be found on an insect abdomen?
usually 11
What does the abdomen contain?
digestive & reproductive organs, and it carries internal & external genitalia
Which tagmata does not have chemoreceptors?
thorax
What are the internal systems of insects?
peripheral nervous system, circulatory system, digestive system, respiratory system, & reproductive system
What is the peripheral nervous system?
sensory nerves moving information from receptors to the central nervous system; motor nerves that control muscles; and has stomatogastric nervous system that innervates the gut. (provides nerves to the digestive system inside the gut)
What are ommatidia and how many are there?
they are individual eyes inside a compound eye and can have up to 10,000 per eye.
What are tympanal organs used for?
hearing
Where can tympanal organs be found?
legs, wings, abdomen, and antennae
true or false: there are chemoreceptors found on the mouthparts
true
true or false: there are olfactory receptors on the antennae
true
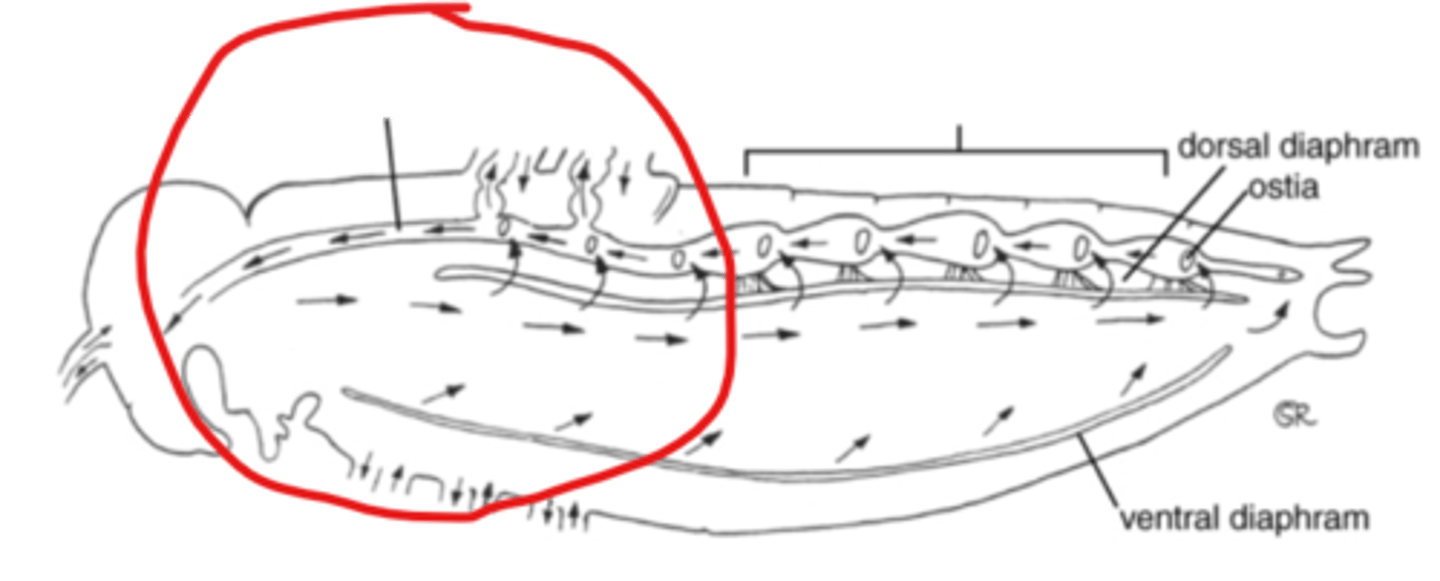
What portion of the dorsal vessel is shown?
aorta

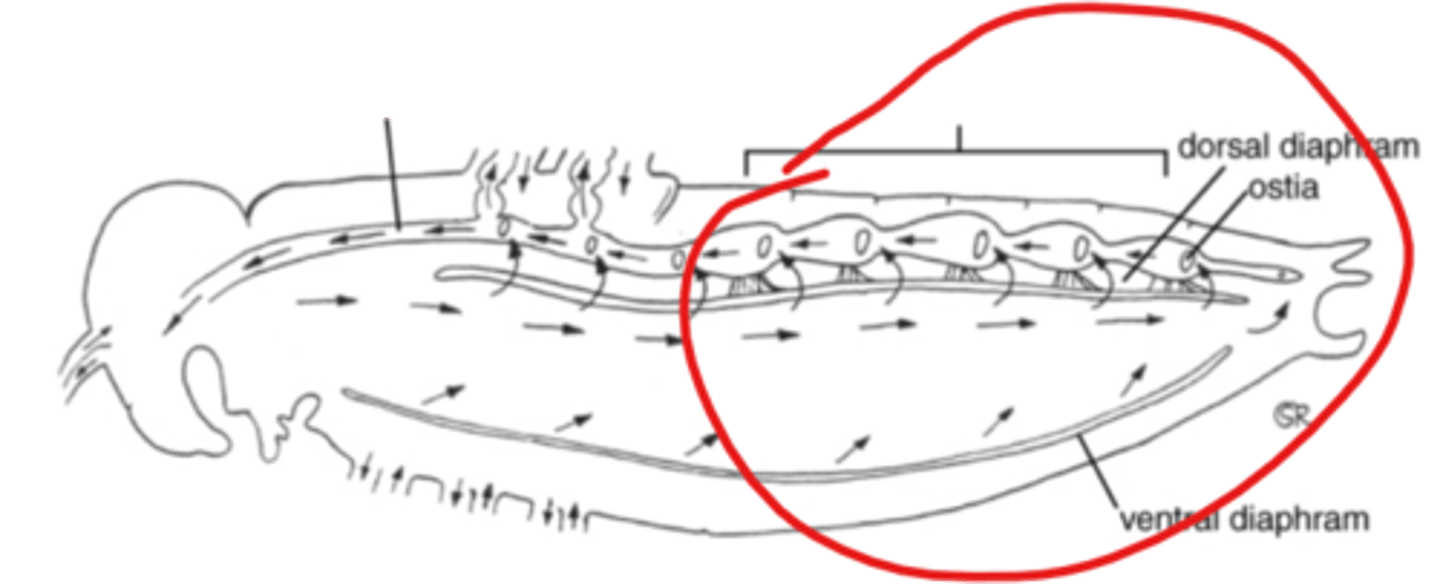
What portion of the dorsal vessel is shown?
heart

What are the internal organs of an insect bathed in?
haemolymph
How is haemolymph moved around the body?
by a dorsal combined heart and aorta
Which sections of the digestive system is lined with cuticle?
stomodeum (foregut) & proctodeum (hindgut)
What is the foregut called?
stomodeum
What is the midgut called?
mesenteron
What is the hindgut called?
proctodeum
Which section of the digestive system is unlined and is home to enzyme production & nutrient absorption?
mesenteron (midgut)
What is produced in the midgut?
peritrophic envelope to help protect the midgut since it is so thin
How does gaseous exchange occur?
Through a system of internal tubes called the tracheal system
Does blood play a role in the transport of oxygen?
no, oxygen is carried directly to its sites of utilization
How does oxygen enter the body?
through the spiracles
How many spiracles do insects have?
10 or fewer per insect
true or false: spiracles can be closed to prevent water loss
true
What are air sacs?
swollen trachae that can be pumped by body movement
How long do tracheae branch?
tracheae branch until they become intracellular tracheoles and are the site of gas diffusion
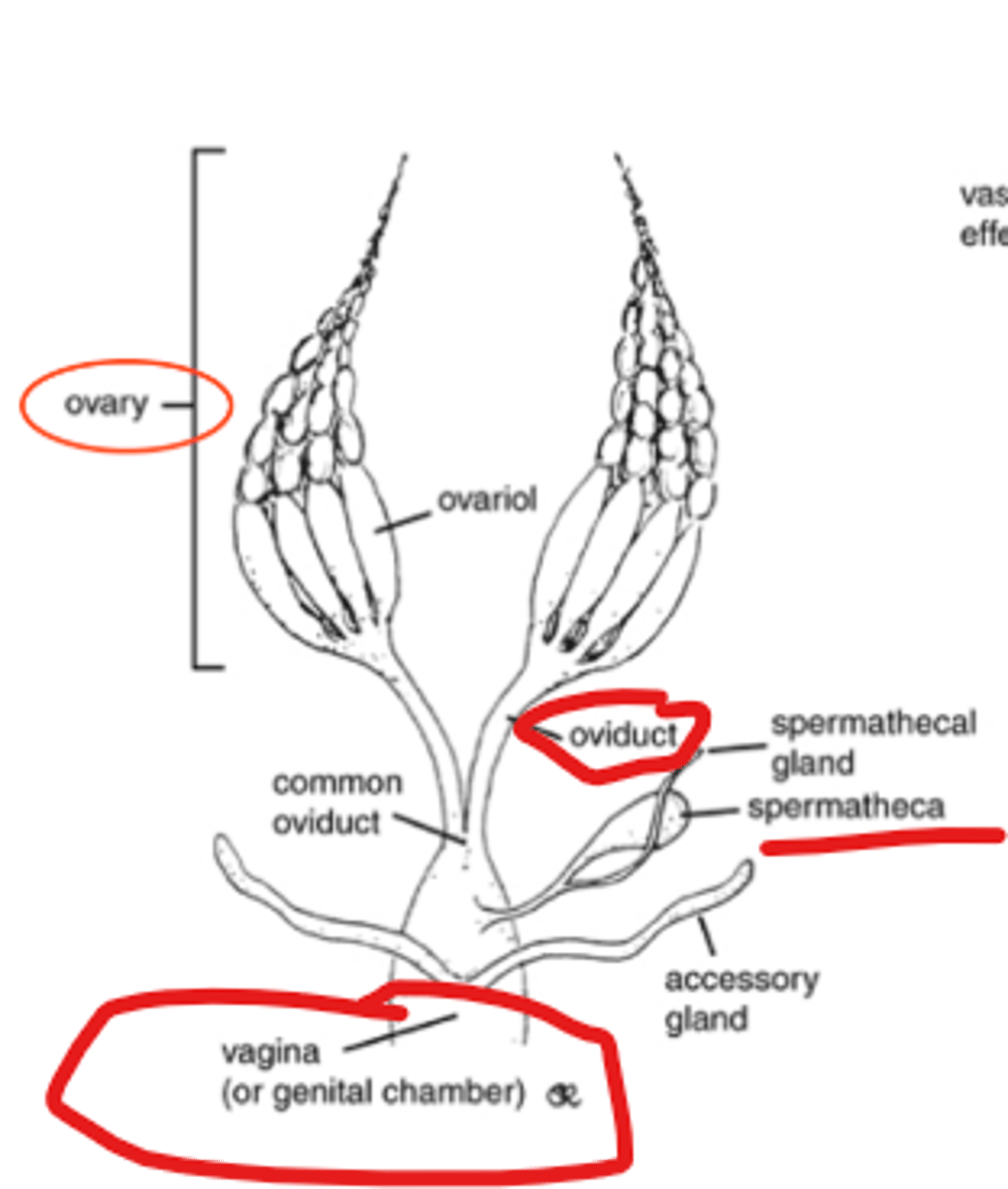
Is this the male or female reproductive system?
female
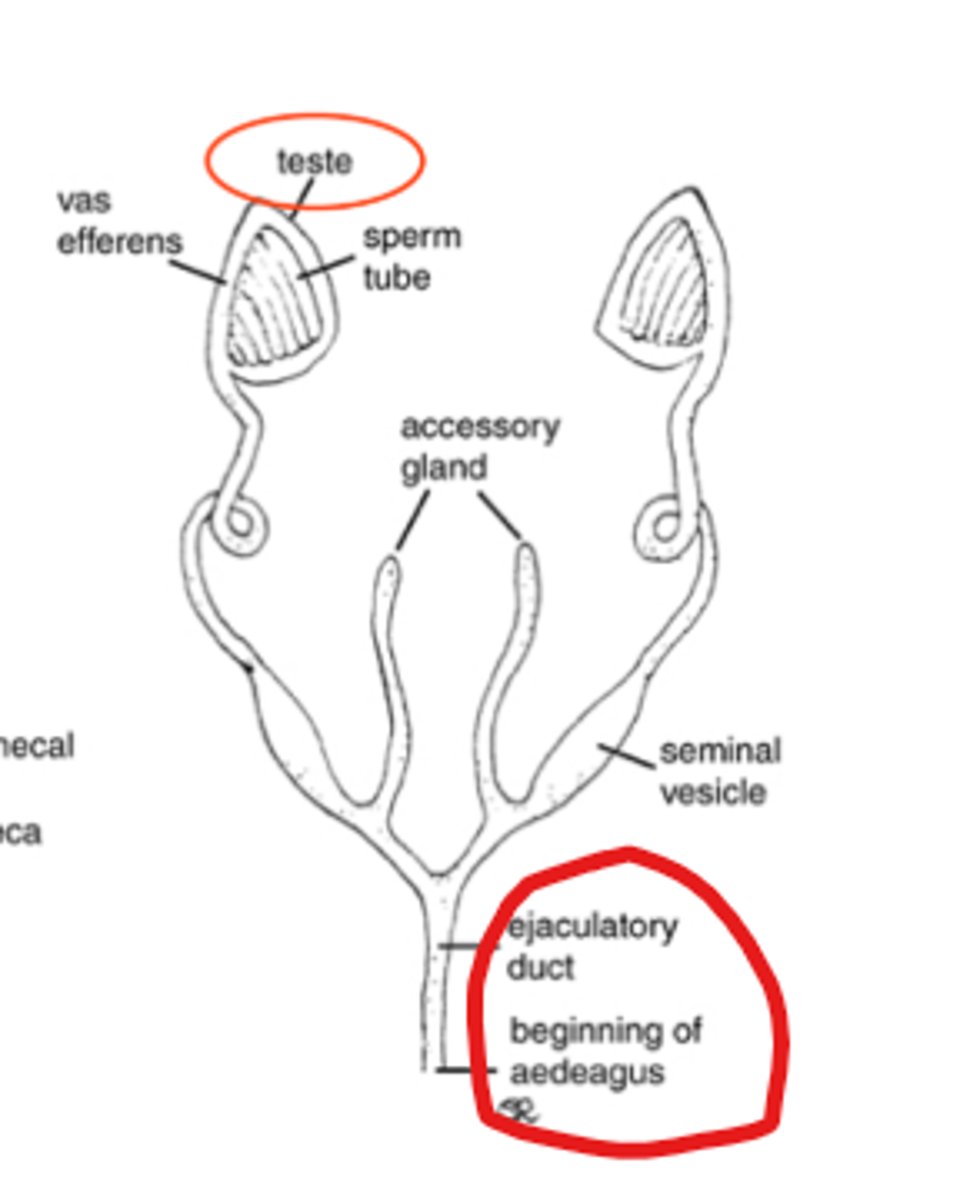
Is this the male or female reproductive system?
male
What is taxonomy?
the science of classification according to a pre-determined system, with the resulting catalog used to provide a conceptual framework for discussion, analysis, or information retrieval.
What does the Greek word "taxis" mean?
arrangement or division
What does the Greek word "nomos" mean?
law
What does a good taxonomy take into account when being developed?
the importance of separating elements if a group (taxon) into subgroups (taxa) that are mutually exclusive, unambiguous, and taken together, include all possibilities.
What does the pre-determined system use to classify insects into monophyletic groups?
homologies
What do all eukaryotes share in common?
cells have a nucleus
true or false: insects are ecdysozoans which are a type of protostomes
true
true or false: insects are most closely related to crustaceans
true
What clade are insects in?
Pancrustacea
What are the common ancestors of arthropods (including crustaceans & insects)?
trilobites (now extinct)
true or false: insects and crustaceans share the same body plan
true
What is Hexapoda classified as?
subphylum
How many orders of insects are there?
27
What does apterygota mean?
wingless insects
What does pterygota mean?
winged insects
How much of the total insect biodiversity does the apterygota (primitively wingless) make up?
less than 1%
What is the difference between the Dicondylia & Archaeognatha subclasses?
divergence in jaw structure. Archaeognatha has one point of attachment in the jaw and is monocondylic while the Dicondylia has two points of attachment in the jaw and is dicondylic
What does hemipterans (once considered 2 suborders) mean?
true bugs with sucking mouthparts
What is the standard tool for separating taxa?
dichotomous key
Hexapoda
six legs
Insecta
three-part body plan
Dicondylia
jaw attached at two points
Pterygota
with wings
Neoptera
wings can fold
Endopterygota
holometabolous development (AKA holometabola)
Orthopteroid orders
an older classification - grasshoppers, katydids, stick insects, praying mantids, cockroaches, mantophasmatodea
Hemipteroid orders
true bugs
Neuropteroid orders
Megaloptera & Neuroptera
What does "archaeos" mean?
ancient
What does "gnatha" mean?
jaw
What are the defining characteristics of Archaeognatha?
thorax humped, pair of cerci, and longer, central filament
What are the defining characteristics of Zygentoma?
abdomen with three roughly equal filaments
What does the Greek word "thusanos" mean?
tail
What does "ephemeros" mean?
short-lived
Ephemeroptera meaning
short-lived winged insect
Archaeognathta
bristletails
Zygentoma
silverfish
Ephemeroptera
mayflies
What are the defining characteristics of Ephemeroptera?
two pairs of wings, long cerci, and central filament. They also have aquatic nymphs.
Odonata
damselflies & dragonflies
What does "odont" mean?
tooth
What are the defining characteristics of Odonata?
short antennae, two pairs of richly veined wings, and aquatic nymphs
What does "pleiken" mean?
braided
Plecoptera meaning
braided wing
Plecoptera
stoneflies
Blattodea/blatta
cockroach
What does "iso" mean?
similar
Isoptera meaning
similar wing
Blattodea
cockroaches & termites
True or false: termites are just fancy cockroaches and have been reclassified scientifically but will keep their common name of termites
true
What does "grylli" mean?
cricket
What does "blatta" mean?
cockroach
Grylloblattodea
rock crawlers or ice crawlers
What does "mantis" mean?
prophet