pt centered care families exam 3 week 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
mandated reporters
why to report: failure to report is a misdemeanor
how to report: within 24 hours oral and 72 hours written, follow organizational guidelines, involve psychosocial team
what happens next? CPS (if investigation warranted and positive → civil court)
what happens after that? law enforcement (if investigation positive → criminal court)
BC OF SCREEN OUTS, ALWAYS USE THE WORD ABUSE AND EXPLAIN RATIONALE!
who to call?
CPS: immediate safety not a concern, but maltreatment is suspected
law enforcement: when immediate safety is an issue
child abuse specialist: advice on management, reporting, transfer of care
protective holds
can only be done by law enforcement
LE can initiate for safety of the child/children
parents retain decision making
LE not the hospital, decide on terms of visitation
health care workers would not be responsible for supervision
signs of abuse
histories inconsistent with injuries
delay in seeking medical care
changing history
physical signs
bruises on infants
bruises on face, trunk, hands, ears, genitalia, or buttocks
patterned bruises or burns
fx of ribs, sternum, and scapula
shaken baby syndrome
incidence of head trauma?
abusive head injury is a leading cause of serious head injury in small children (shaken baby syndrome)
95% of serious head injury in <1 year
higher in premature infants, twins, children with moms < 18 yrs, children in military families
2/3 perpetrators are male
risk of fatal abuse increases 50x when an unrelated male is living in home/caring for baby
sexual abuse
under age 5 affects boys and girls equally
above age 5 boys rarely report
girls have higher rates of abuse as adolescence progresses
most exams “normal” (report is usually delayed, ano-genital area heals rapidly and often w/o scarring, the perpetrator may take care to not cause injury)
children must be over 3 yrs to be interviewed
STI’s IN CHILDREN OVER 3 LESS THAN 10 IS SUSPICIOUS!
physical forensic exam
pre pubertal
test for STIs, do not treat empirically
never do speculum exam
evidence collection window up to 24 hours
post-pubertal
consider testing for STIs, often treat empirically
may require speculum exam
evidence collection window up to 72 hours
neglect
failure of a caregiver to
provide food, clothing, shelter, medical or mental health care, education, or appropriate supervision
tough to prove, SDOH play a factor
(protect a child from conditions that endanger the child, and take steps to ensure that a child is educated as required by law!)
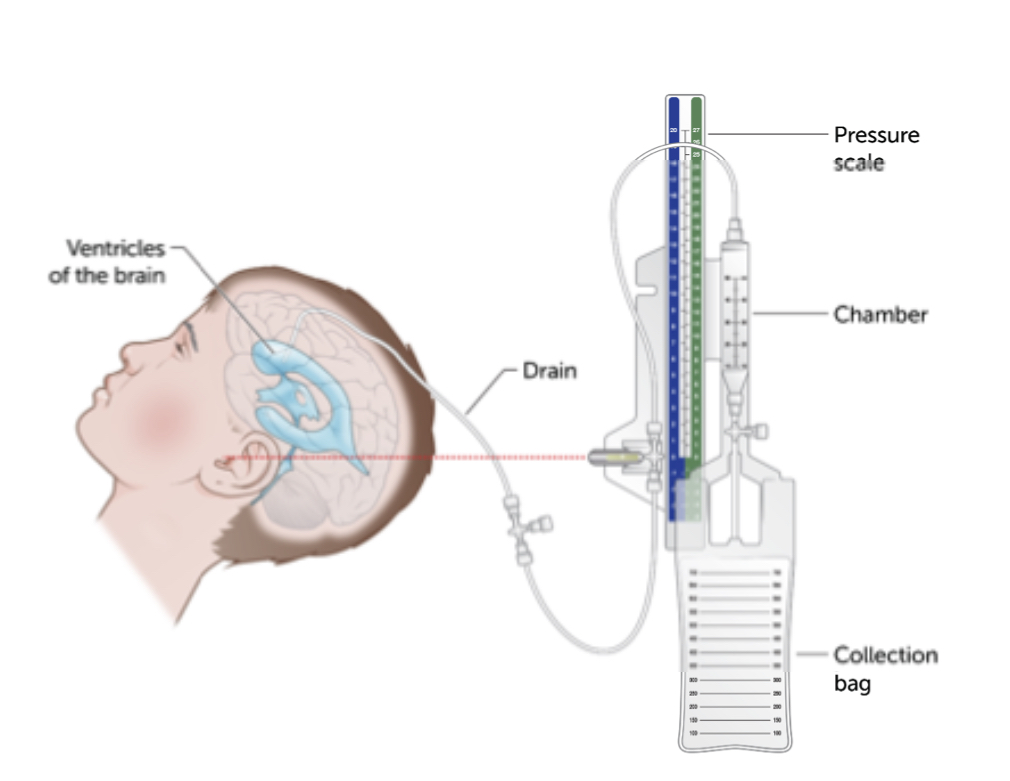
hydrocephalus
excess fluid in the ventricle in the brain
3 types
congenital
acquired (post injury or surgery)
infectious (usually time limited)
management: meds, external ventricular drain, shunts
nursing considerations: infection, monitor for signs of increased ICP, malfunction, education/when to call
signs of increased ICP (intracranial pressure) in infants?
bulging fontanels
increased head circumference
high pitched cry
distended scalp veins
bradycardia
respiratory changes
signs of increased ICP (intracranial pressure) in children?
irritability
headache
vomiting
diplopia
seizures
bradycardia
respiratory changes
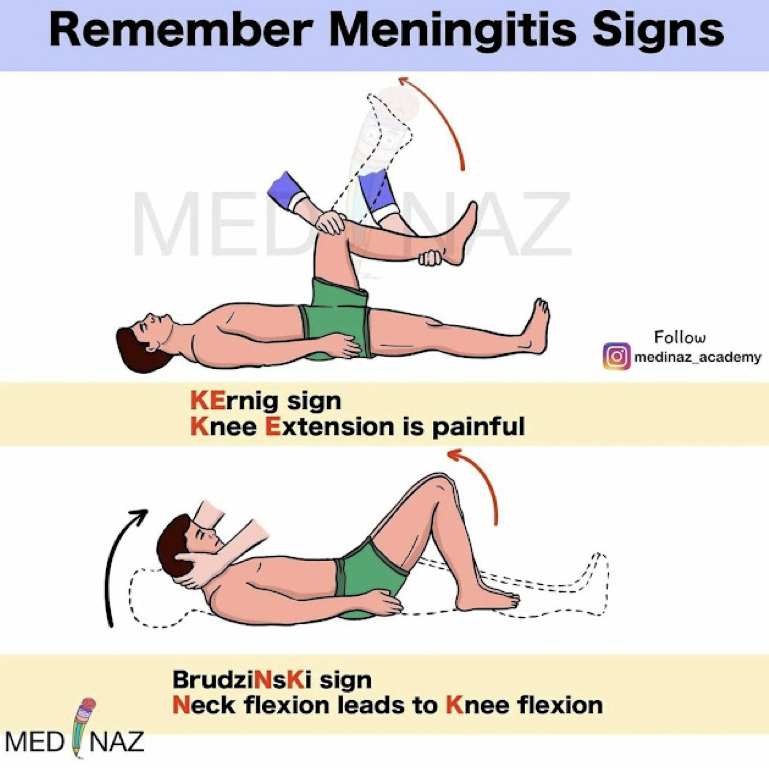
meningitis diagnosis
diagnosis is brudizinski’s sign and kernig’s sign (extension), LP (viral is clear, normal glucose and protein, bacterial is cloudy, elevated glucose, and gram stain…)
meningitis nursing considerations
monitor for signs of increased ICP
spinal headache (post LP)
seizure precautions
comfort measures
calm, quiet, cool, dark room
fluids and supportive cares
meds for bacterial (antibiotics, steroids)
head injury
concerning if…
loss of consciousness or confusion
bleeding does not stop
under 2 yrs
vomiting
seizures
slurred speech or blurred vision
inconsistent report
treatment: ice, rest, stitches…
concussion
common causes in children are
sports (53%)
school PE
bike/recreation
motor vehicle
home accidents
other
treatment: rest, low light, brain rest no screens, gradual return to school, no activities until symptom free
headaches
types: headache, migraine, cluster
acute onset: vision check, sleep, stress measures
reasons for concern: unusually severe, vomiting (without nausea), weakness/balance issues
seizure disorders
classified by type and etiology and location
focal: one area of the brain
generalized: entire brain
risk factors
fever
tumors
infection
toxins, drugs
head injury
epilepsy
2 unprovoked seizures at least 24 hours apart
followed by 1 seizure within 10 years
clonic (grand mal) seizures
most prevalent, 3 phases
tonic: loss of consciousness, eye roll, arch (10-30 sec)
clonic: violent jerking (30-50 sec)
post ictal: sleepy, confused (30-60 minutes)
absence (petit mal) seizures
onset between 4-12
generally gone by adolescence
brief LOC
staring
motionless
myoclonic seizures
brief contractions of one or more muscle groups
no LOC
no postictal
atonic (drop attacks) seizures
2-5 years at onset
lose muscle tone
fall, then confusion
partial seizures
focalized
may just be tingling, eye aversion
infantile spasms (west syndrome)
4-8 months onset
rarely after 2 years
tx is ACTH
seizure disorder treatment
surgical procedures, vagal nerve stimulator, meds
meds
immediate rescue: diazepam or lorazepam (often rectal)
most rescue meds given rectally
side effects of meds are sleepiness, mental fog, and stevens johnson-lamotrigine
spina bifida
location of lesion determines impact
HIGHER LESION = GREATER IMPAIRMENT
T12: neurogenic bowel and bladder, impaired sensation and mobility of lower extremities (not able to walk)
L1-L3: hip flexion and feet issues
L2-L4: hip adduction
L3-S2: hip adduction and knee and hip flexion
S3: no motor impairment
spina bifida nursing considerations
elimination issues (mitrofanoff and ace stoma!)
risk for infection
immobility
nutrition
risk for impaired skin integrity
education
cerebral palsy
unknown causes
in utero, during birth, neonatal period
infection, insufficient oxygen, genetics
more common in LBW babies
may include…
seizures
visual, hearing, or speech impairments
cognitive impairments
motor impairment
spasticity, weakness
what are the 3 types of cerebral palsy?
spastic: high tone
dyskinetic: jerking or twisting movements
ataxic: wide gait, lack of coordination
(wide variation in presentation, not progresive)
risk for: immobility, pressure injuries, pain, respiratory issues, GI issues (nutrition and elim)
duchenne muscular dystrophy
neurodegenerative disease
inherited genetic disorder
early symptoms: frequent falls, waddling gait, muscle weakness
progresses to: trouble swallowing, trouble breathing, heart problems, scoliosis
most may pass in their 20’s
nursing considerations include early involvement w/palliative care and psychosocial support, respiratory support, mobility devices, advanced care planning…
musculoskeletal conditions
soft tissue injury
fracture
infection
congenital
fractures
common injury in children
methods of treatment differ for children and adults
RARE IN INFANTS, WARRANTS INVESTIGATION!
distal forearm is most common fx site
school age most common
neurovasculature assessment (CMS)
used for musculoskeletal conditions involving tissue injury or immobilization (ex: fractures)
skin color
capillary refill time
temp
sensation
movement of digits
pulse distal to the site
assessment of fractures?
5 P’s
pain
pallor
pulseless
poikilothermia
paresthesia
paralysis
IF ALL 5 PRESENT AFTER IMMOBILIZATION, CONSIDER COMPARTMENT SYNDROME!
compartment syndrome
medical emergency, typically seen in first 24-48 hours
bleeding and swelling into the tissue
signs and symptoms
5 p’s! pain, pallor, poikilothermia (coolness)
paresthesia (numbness, tingling)
pulselessness (faint or diminished at early stages)
paralysis (late finding)
cast needs to come off (often times just to check and be safe)
fasciotomy…
muscle; acute viral myositis
often a post viral syndrome
muscles become…
inflamed, achey
release myoglobin
causes short term mobility issues
can cause renal damage
nursing considerations
admin fluids
monitor renal status
treat pain and inflammation
encourage mobility
muscle rhabdomyolysis
rare in children BUT a medical emergancy
typically after an injury, over use, or burns
muscle breaks down and dies
massive release of myoglobin and other toxins which damage the kidneys
LIFE THREATENING
signs and symptoms
muscle weakness
swelling, tenderness
dark urine, tea colored or red
nursing considerations
monitor electrocytes and renal function
fluids, rest
may require dialysis or CRRT
osteomyelitis
infectious process in the bone
may be caused by exogenous or hematogenous sources
staphylococcus aureus: the most common causative organism
osteomyelitis diagnosis
signs and symptoms begin abruptly
resemble symptoms of arthritis and leukemia (fatigue, achiness)
marked leukocytosis
bone cultures obtained from biopsy or aspirate
radiographs (X rays: may appear normal at first)
bone scans for diagnosis
osteomyelitis management
long term IV antibiotics (PICC line!)
presentation may be subacute, with walled-off abscess rather than spreading infection
prompt, vigorous intravenous antibiotics for extended period (3-4 weeks or even months)
monitor hematologic, renal, hepatic responses to treatment
osteomyelitis nursing care
promote bed rest and immobility of limb
pain management
long term IV access for antibiotics (PICC line)
nutritional considerations
long term hospitalization or therapy
watch for DVT
provide routine/activities
psychosocial needs
monitor labs
club feet
about 50% will have bilateral deformities
may be corrected w/exercises or stretching, or splinting or serial casting
may need surgery
treatment starts at 1-2 weeks after birth
GOAL IS FOR CORRECTION BEFORE CHILD STARTS TO WALK!
osteogensis imperfecta
less common, brittle bone disease
genetic disorder
results in frequent fractures and limb deformities
severity varies by type and subtype
most often wheel chair bound
affects eyes, ears, and heart as well
achondroplasia
dwarfism
increased risk of: obesity, hydrocephalus, skeletal issues, bowed legs (varus)
multiple surgical corrections are often needed
limited life expectancy but NOT terminal prognosis…