1.7 Proteins
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exclusion statement: the molecular structure of amino acids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Protein
molecule consisting of polypeptides folded into a 3D shape
Carbon,hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur
The shape determines the function
the functions can include
antibodies- help protect body from disease
enzyme- carry out chemical reactions or assist in creating new molecules
messenger- transmit signals (ex hormones)
structural- provide structure and support
transport/storage- bind to and carry small atoms and molecules through the body
the formation is amino acid—>peptide—>polypeptide—>protein
Amino acid
molecules that have an amino group and a carboxyl group
monomers of proteins
20 different amino acids
each amino acid has a unique side chain
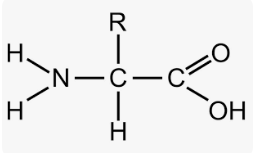
Unique side chain
each AA has a unique side chain
“R”
unique aspects of the AA are based on the side chain’s physical and chemical properties
can be grouped as non polar(hydrophobic), polar (hydrophilic), or charged/ionic (hydrophilic)
side chains interact, which determine the shape and function of the protein
to locate, look between the n terminus (amino group) and c terminus(carboxyl group) and opposite the side the H is on, below/above the C is the side chain
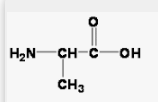
Polar side chains
tons of oxygen in these side chains
hydrophilic
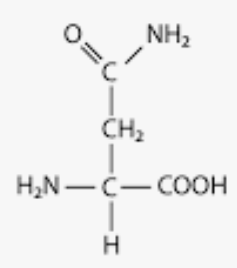
Nonpolar side chains
tons of carbon and hydrogen
3 special exceptions which are:
cysteine(contains sulfur), methionine(contains sulfur), and tryptophan(contains nitrogen)
hydrophobic
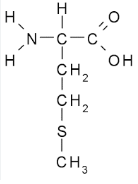
Charged/ionic side chains
have a charge in their side chain indicating if it is positively charged or negatively charged
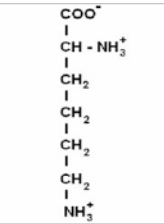
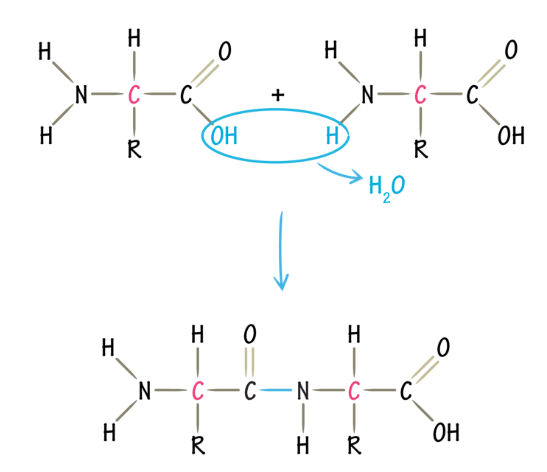
Peptide bond
link AA
to form a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one AA must be positioned next to the amino acid group of another AA
they go through a dehydration reaction and form a peptide bond (covalent)
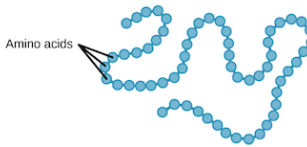
Polypeptides
many AA linked by peptide bonds
each polypeptides has a unique sequence of AAs and directionality (the terminus)
one end is a free amino group (N-terminus)
one end is a free carboxyl group (C-terminus)
the sequence of AAs determines the 3D shape(shape determines function)
when a polypeptide twists and folds(because of R group interaction) it forms a protein
the unique sequence of AAs is determined by genes
Primary structure
linear chain of amino acids
determined by genes
dictates the secondary and tertiary forms
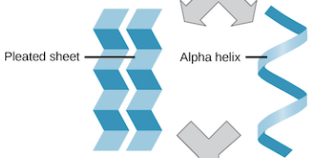
Secondary structure
coils and folds due to hydrogen bonding within the polypeptide backbone
B(beta) pleated sheet-hydrogen bonds between polypeptide chains lying side by side
A(alpha) helix- hydrogen bonding between every 4th AA
Teritiary structure
3D folding due to interactions between the side chains of the AAs
reinforced by hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and disulfide bridges of the side chains
disulfide bridges are the covalent bond formed between sulfer atoms of 2 cysteine monomers
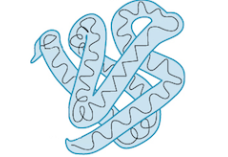
Quaternary structure
association of 2 or more polypeptides, found only in some proteins
some proteins don’t get to this level
all 4 levels of a protein’s structure determine the protein’s function
