L1: Water: the "universal" solvent
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what makes water the “universal” solvent
nearly all biological molecules assume their shapes and functional properties based on their interactions w water
the “solvent” for most biochemical reactions is water, and metabolites depend on water for their transport in vivo
water is catalytically involved in many biochemical reactions
OH- acts as electron -
donor
H+ acts as an electron -
acceptor
in most biochemical reactions
when water is a reactant, the reaction is called -
when water is product, the reaction is called -
hydrolysis, dehydration/condensation
angular geometry results from - nature of H2O
polar
four hybrid sp3 electron orbitals of oxygen form a -
two orbitals represent the - electrons of of oxygen
other two orbitals represent the - electrons between O and H
tetrahedron, unshared, shared
oxygen, with its 2 pairs of -, is electronegative and the H atoms carry a net - charge
this creates an -
unshared electrons, positive, electrical dipole
water molecules orient themselves according to their - and hydrogen bonds form between a - H and - O in adjacent water molecules
electric dipole, donor, acceptor
H bonds between adjacent molecules give water its strong - and unique properties (ex. - melting, boiling, vaporizing temperatures)
internal cohesion, high
in ice, each water molecule H bonds with - other water molecules, forming -
this is the reason why water - upon freezing
four, hexagonal lattices, expands
liquid water does not possess the static hexagonal structure of ice but it is still -
strongly cohesive
theoretical and spectroscopic data suggests that liquid water forms between - membered H bonded rings
3-7
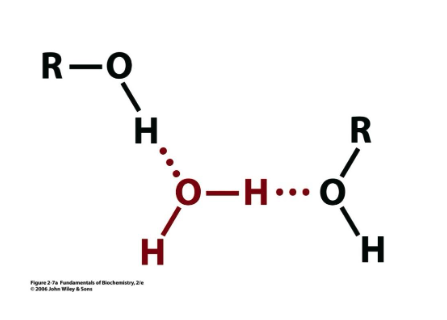
water H-bonded to what?
hydroxyl functional groups
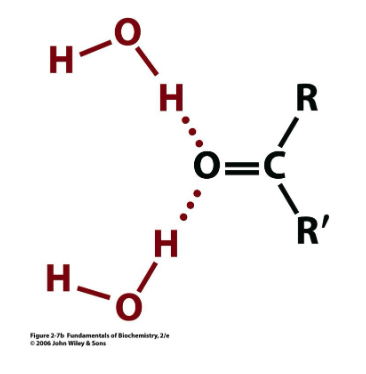
water H-bonded to what?
carbonyl functional groups
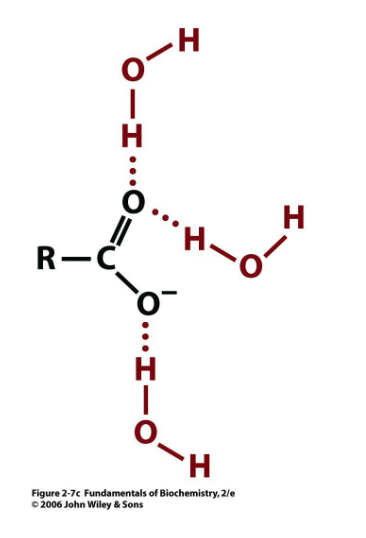
water H-bonded to what?
carboxylate functional groups
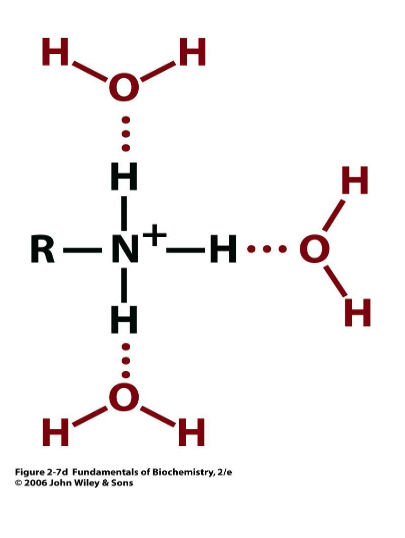
water H-bonded to what?
amino functional group
water dipole is able to interact with both - and -
anions, cations
when water molecules surround an ion, they - the attractive forces between opposite ions and keep them -, which is why - dissolve readily in water
weaken, apart, salts
the strength of multiple water:ion bonds compensates for the energy used to break - between water molecules
hydrogen bonds
like water, carbon dioxide bonds also form dipoles and can orient themselves via weak - interactions called -
electrostatic, permanent dipoles
dipole of a polar molecule can induce a dipole in an, otherwise, neutral molecule by attracting electrons toward the dipole
higher negative exponent, the higher affinity
weakest VDW form when complementary dipole moments occur in - molecules
non-polar
strength of chemical bonds
covalent » ionic > h bond > polar VDW > non-polar VDW
non-polar/hydrophobic molecules added to water do not -
this is because they are unable to form - or - bonds with water
instead, water molecules form - bonds between themselves around the non-polar solute
dissolve
ionic, hydrogen
hydrogen
clustering of non-polar solutes is driven by the thermodynamic properties of water = -
hydrophobic effect
delta G = -
if delta G is negative, reaction/interaction can occur -
negative delta G means reaction or interaction is energetically -
free energy change
spontaneously
favourable
delta H = - change in making or breaking bonds
generally forming bonds yields - delta H and breaking bonds - delta H
negative delta H favours reaction or interaction by making delta G more -
enthalpy
negative, positive
negative
delta S = change in relative order of reactants and products = -
increase in disorder = - delta S, favours reaction or interaction
- delta S decreases delta G
entropy
positive
positive
increase in - increases delta S, lowers delta G
temperature
it is always unfavourable to have - solutes in water
non-polar
water becomes more - around the non-polar solute → - in entropy
despite reduction in entropy, clustering of non-polar solutes occurs because the same volume of solutes can be “caged” by a - surface area of water
ordered, decrease
smaller
structure of macromolecules is driven by the -
hydrophobic effect